Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Increase bit density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
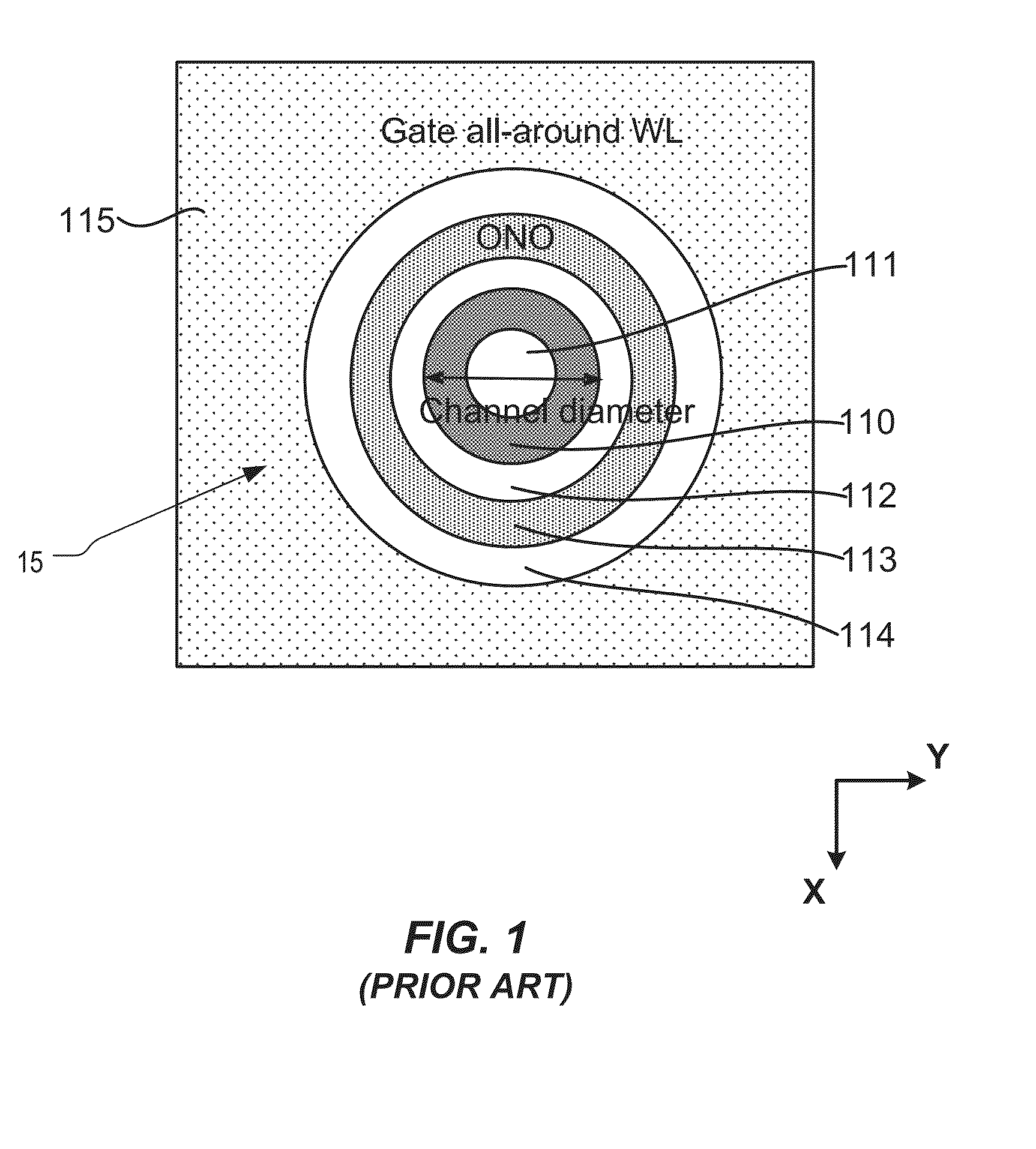
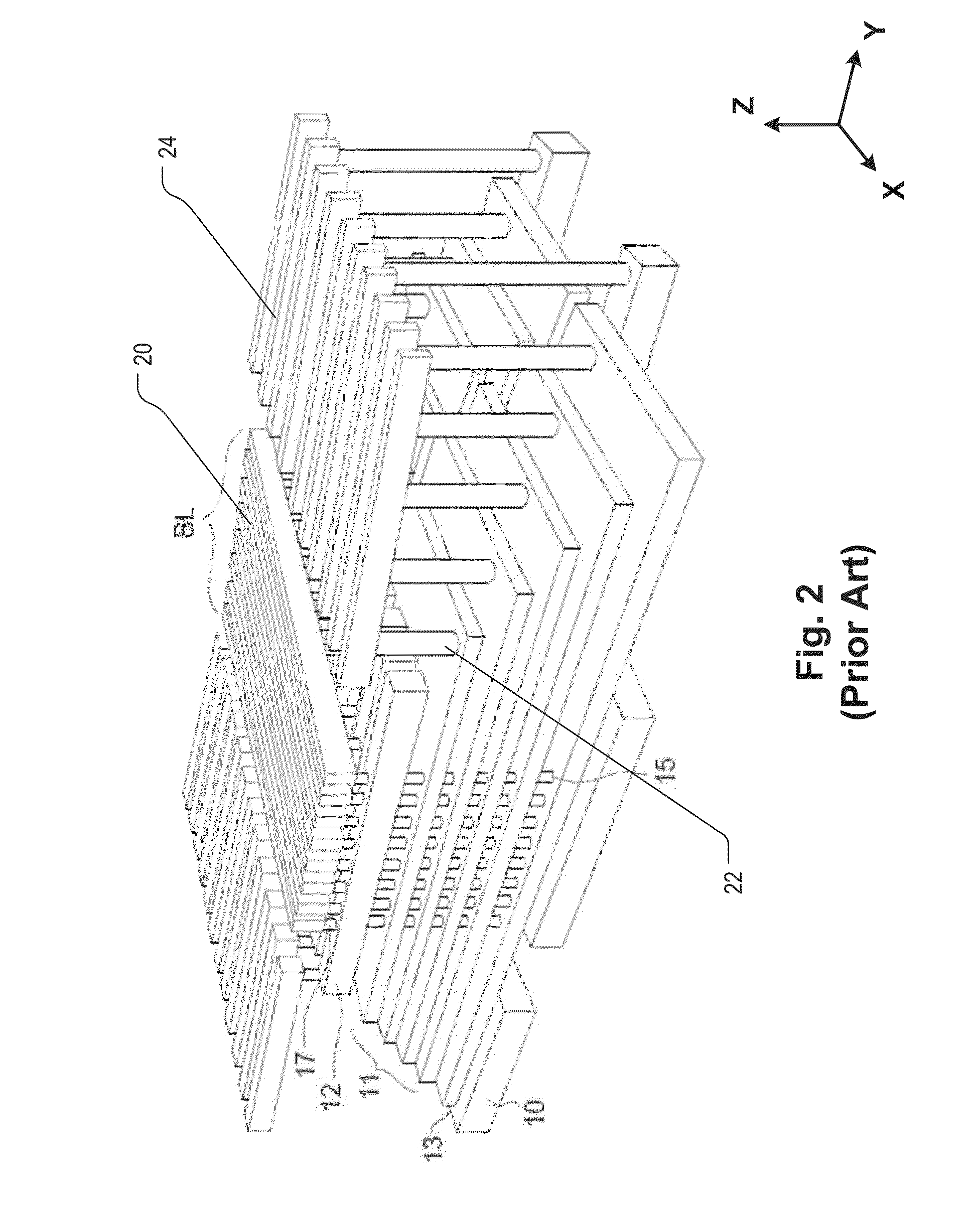
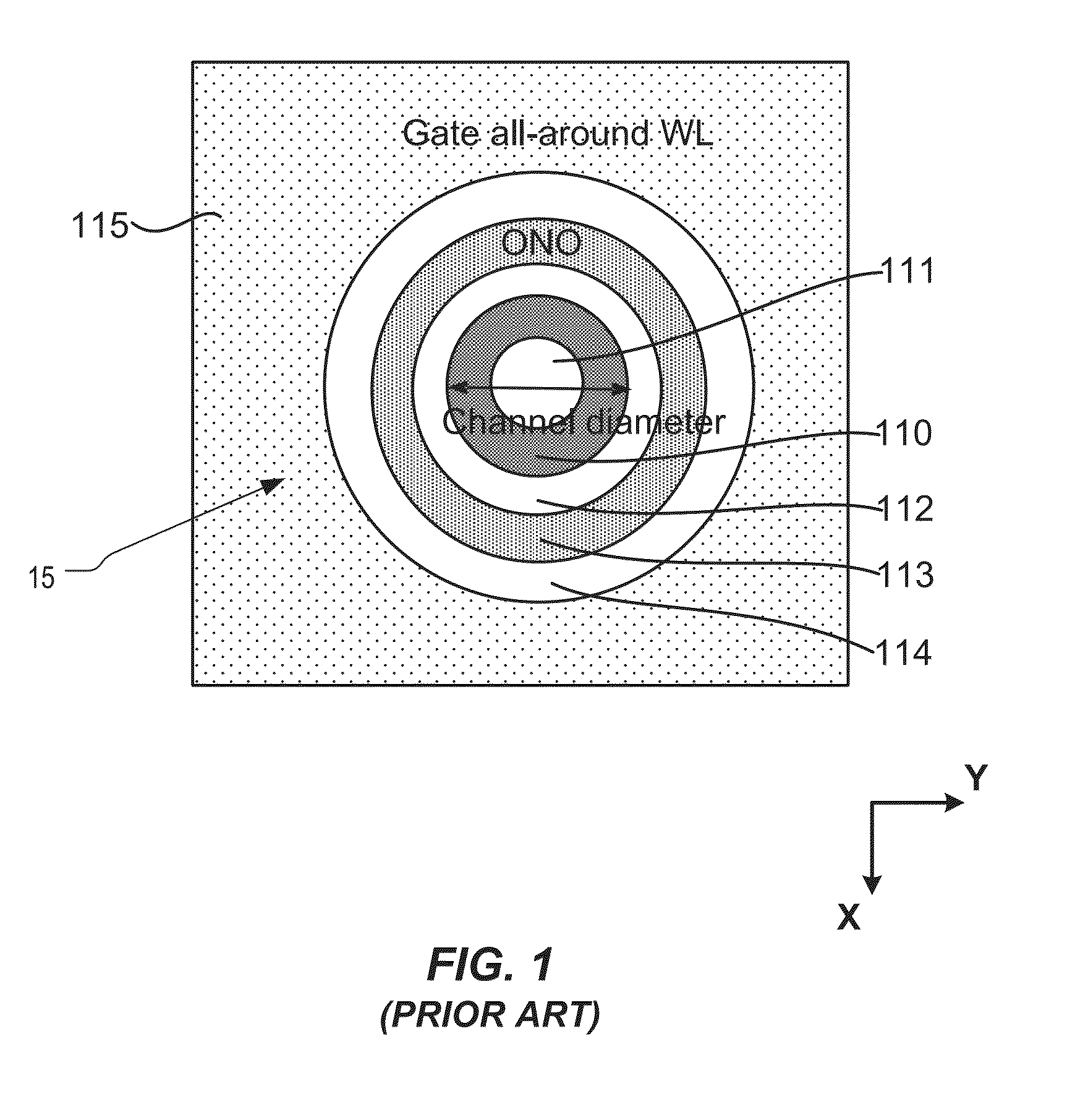
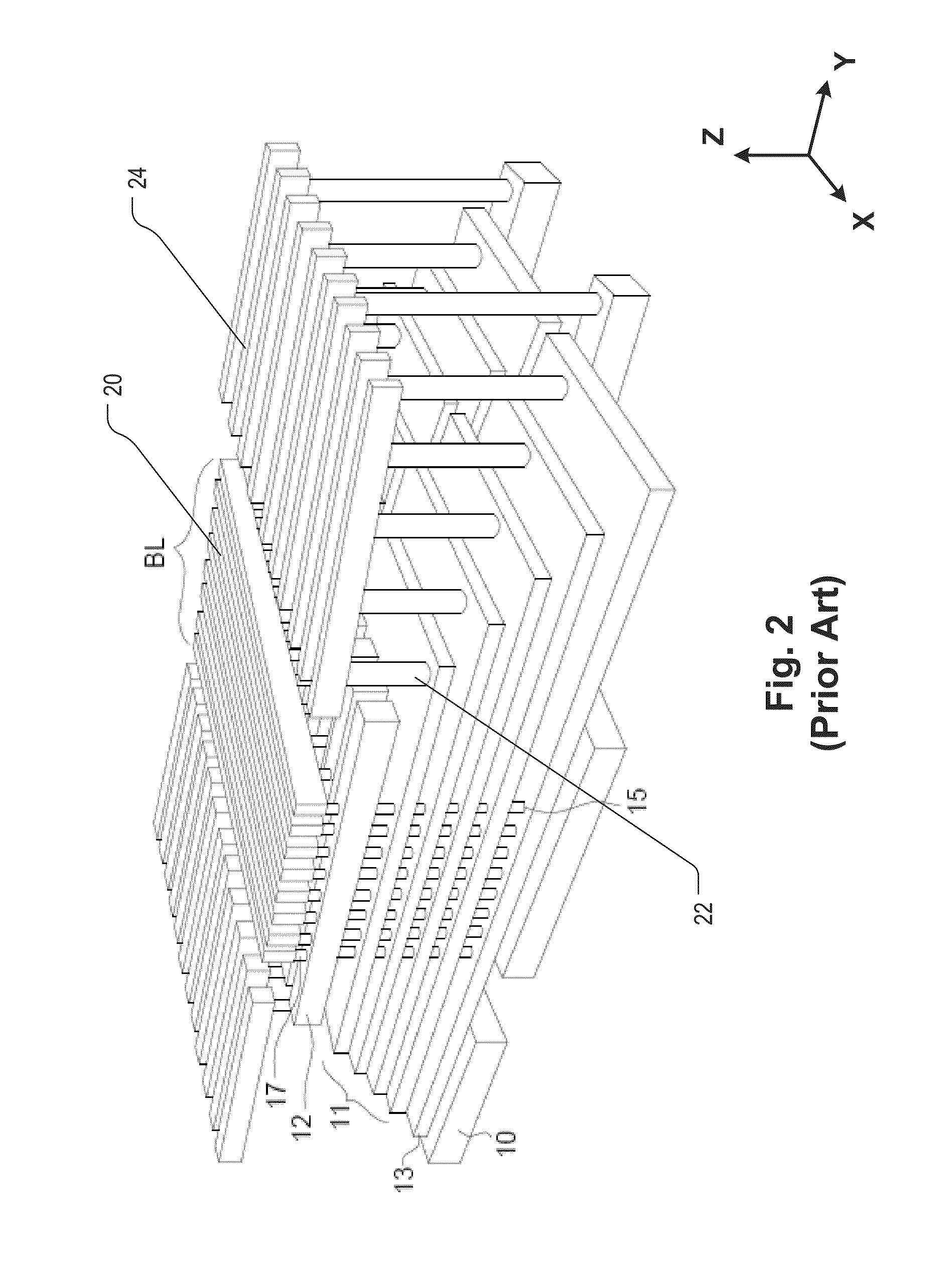
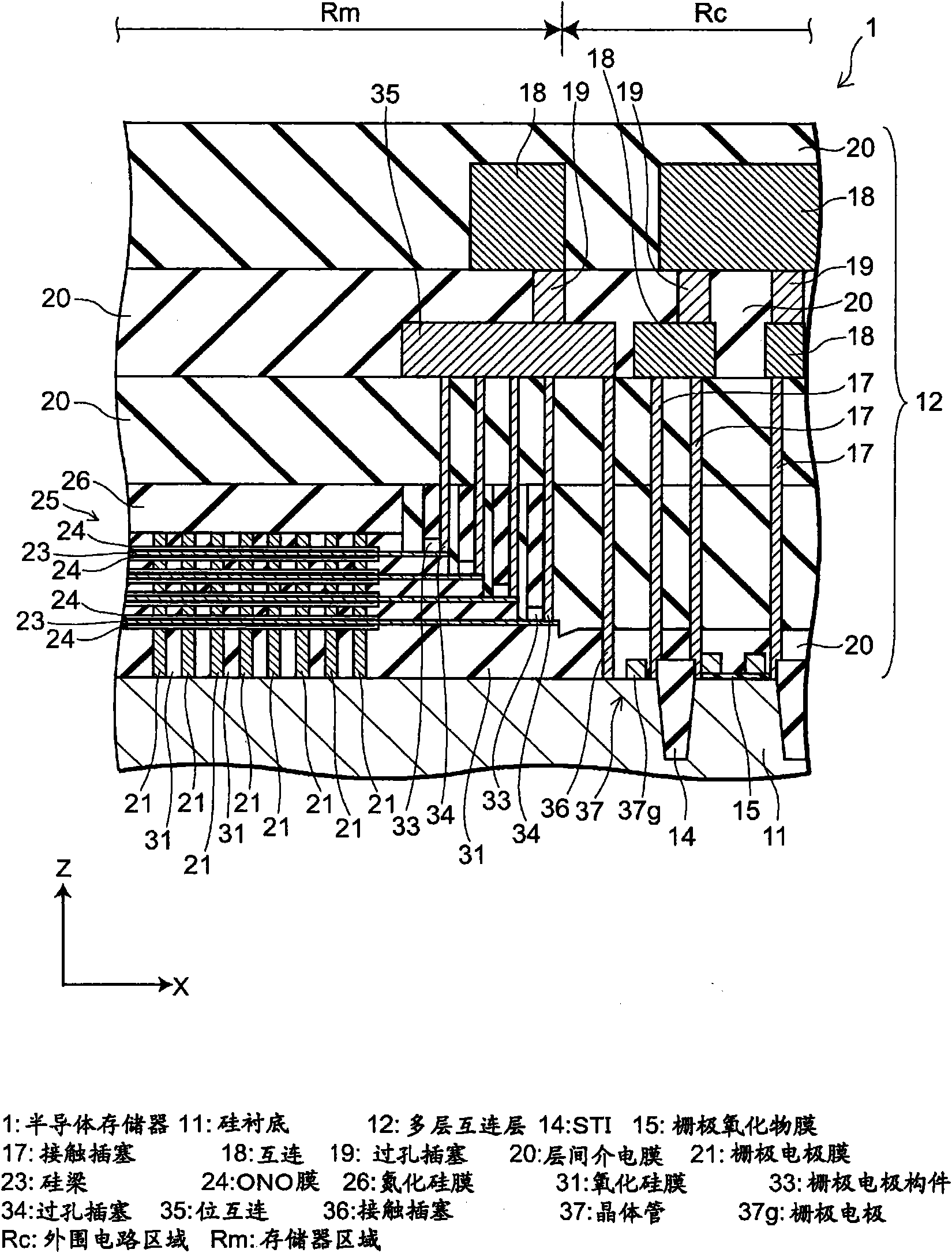
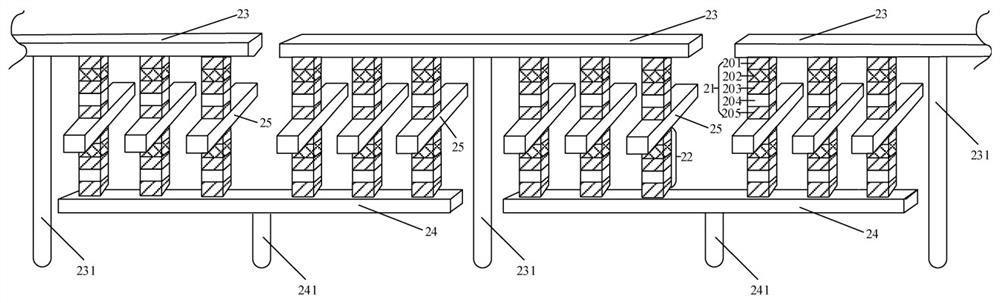
Semiconductor memory and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20110284946A1Increase bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSilicon
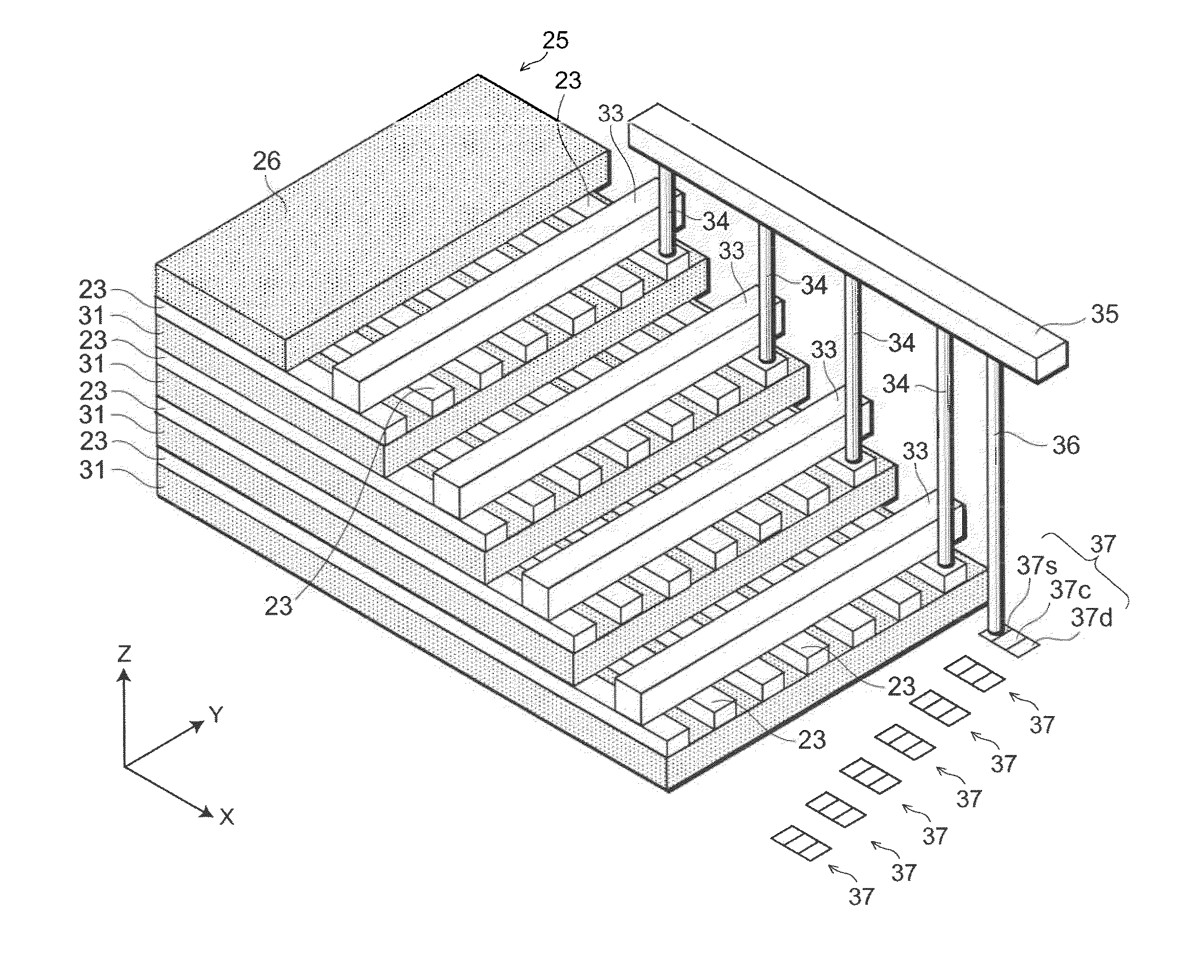
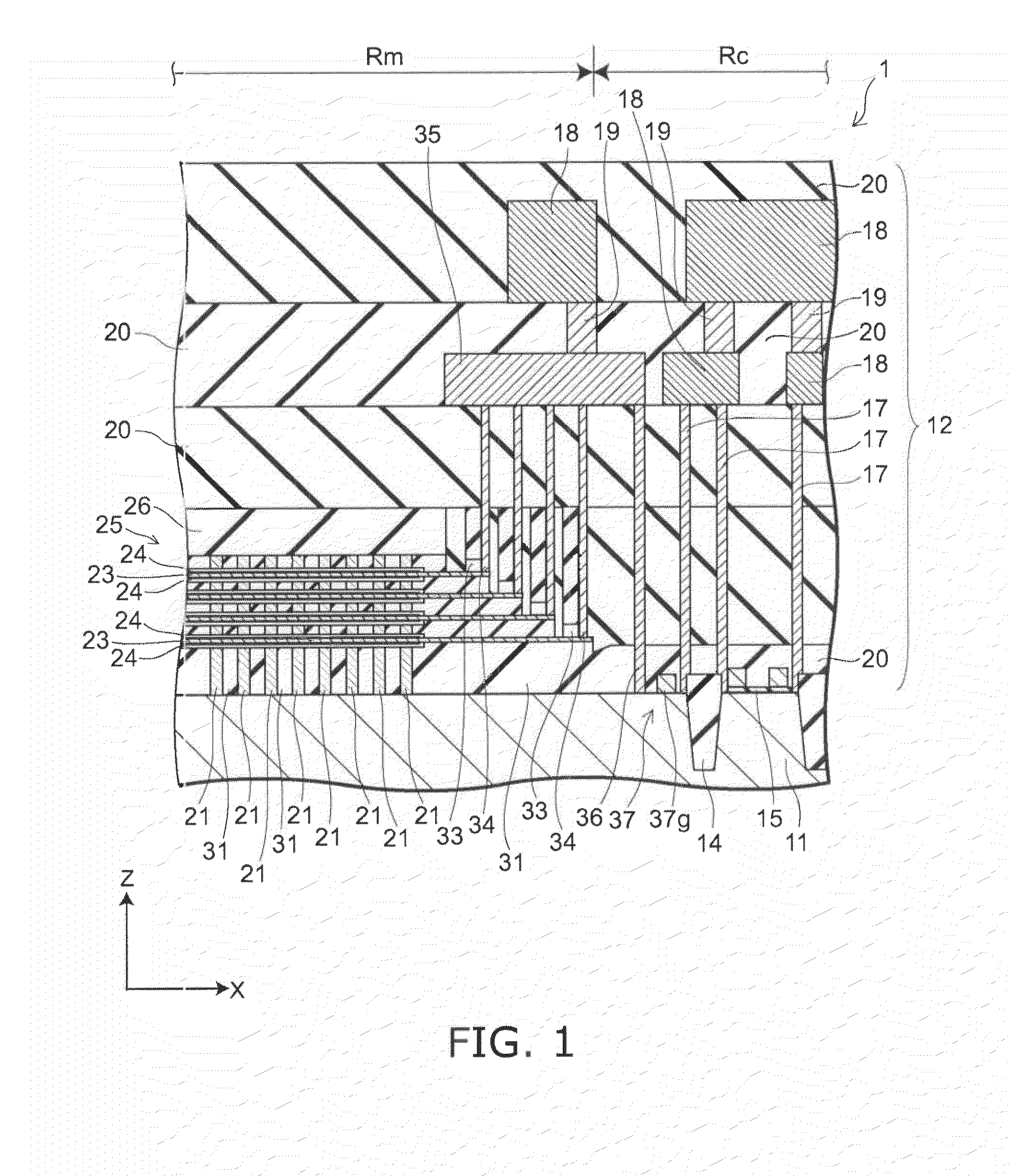
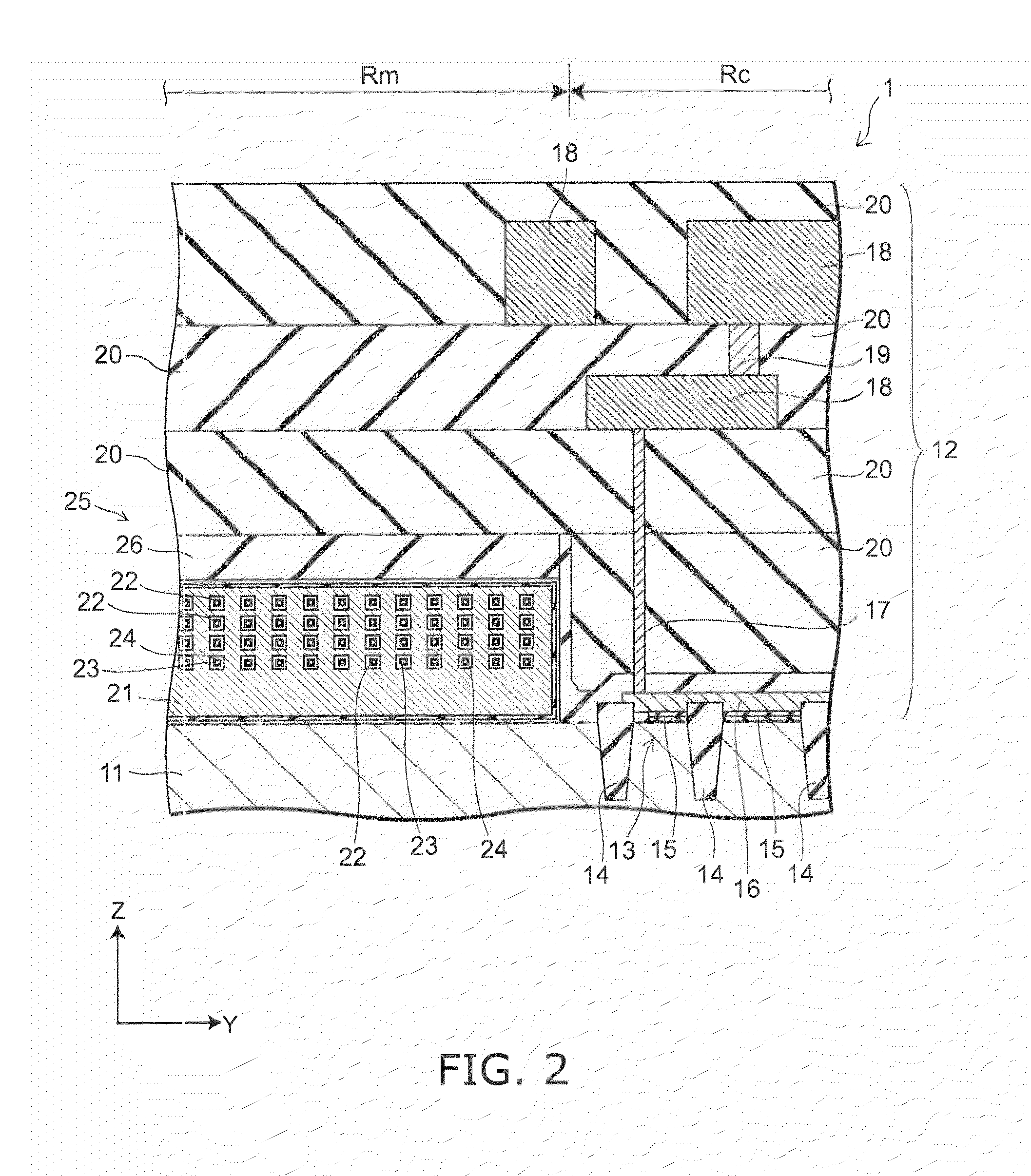
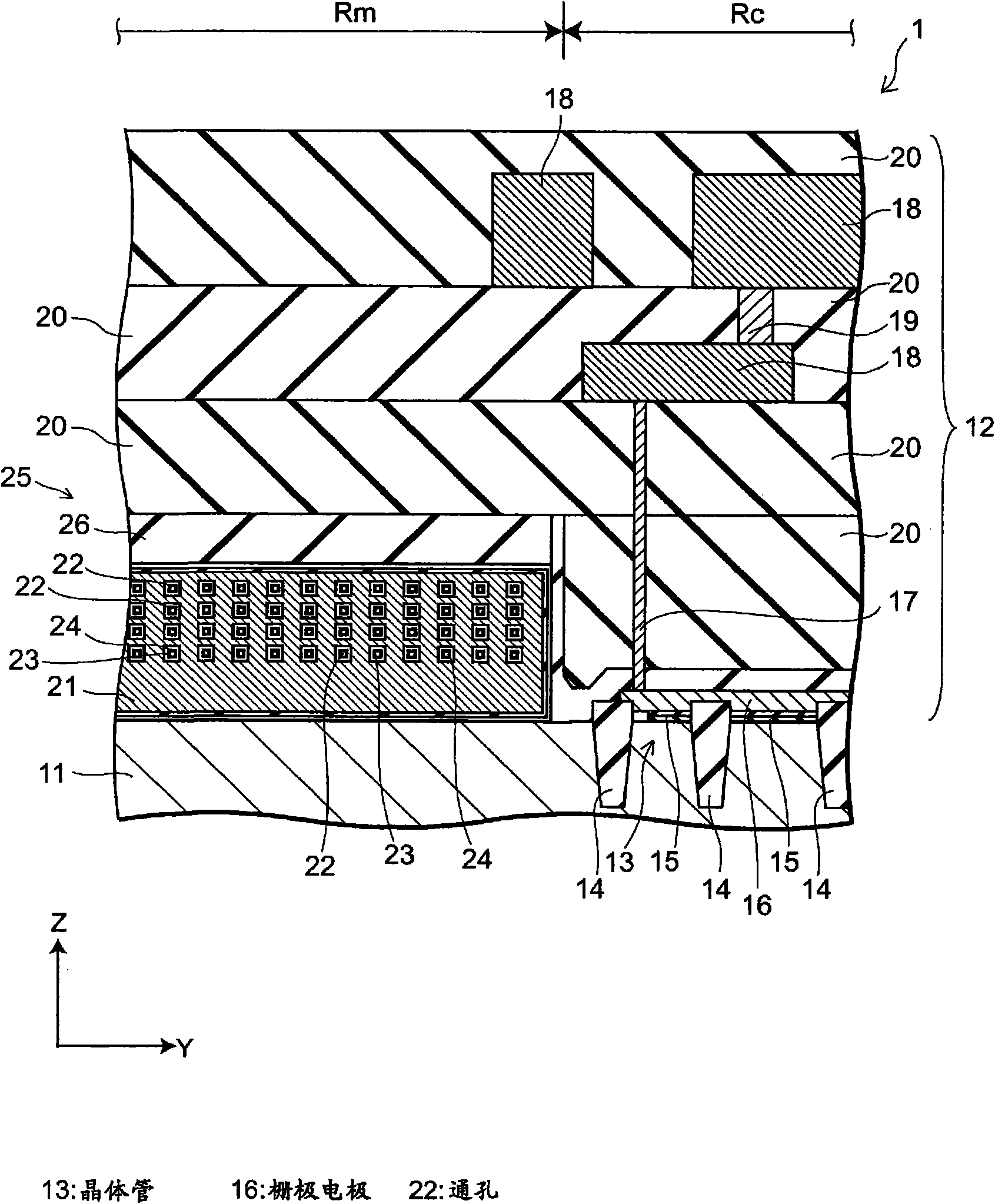
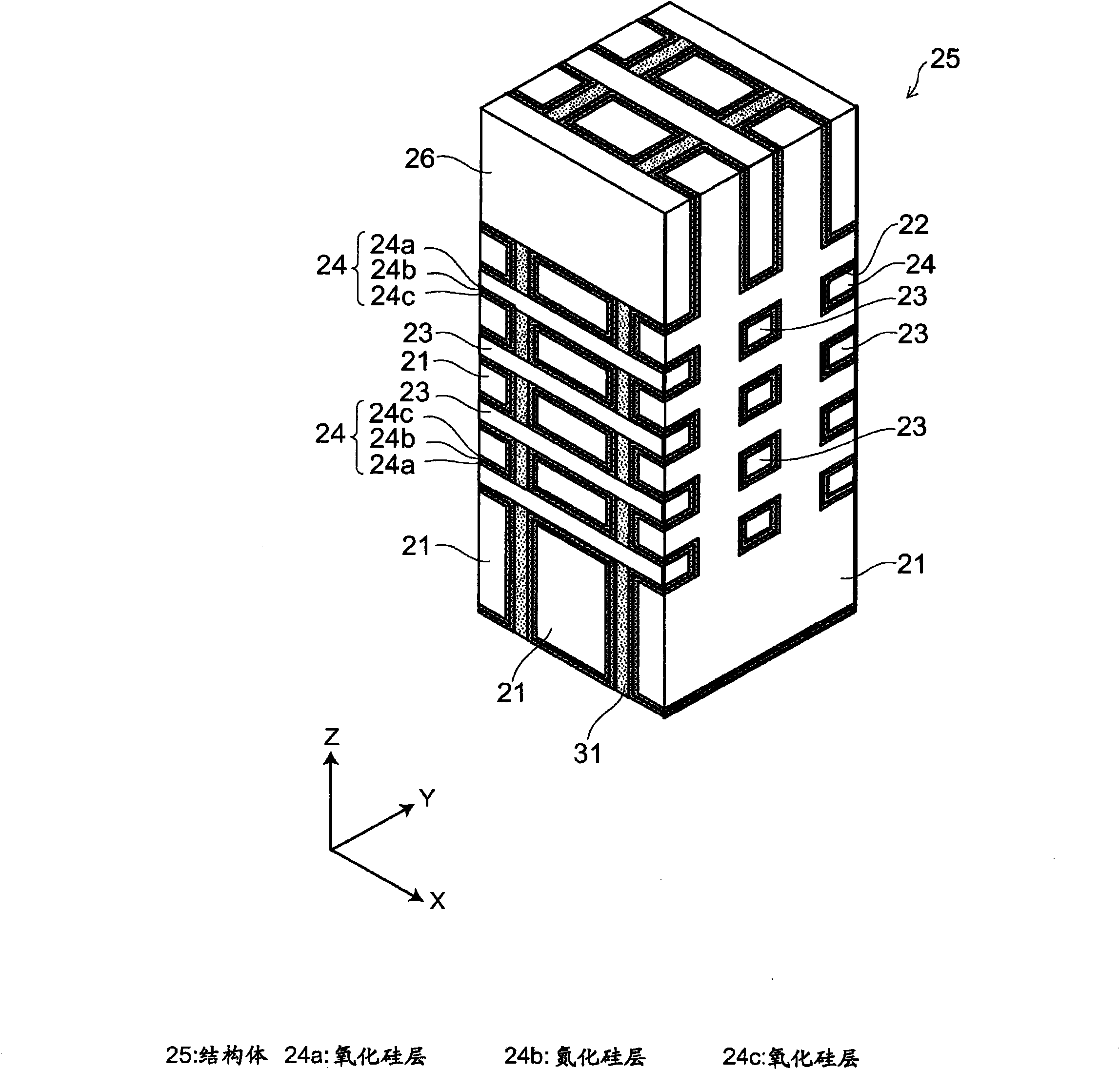
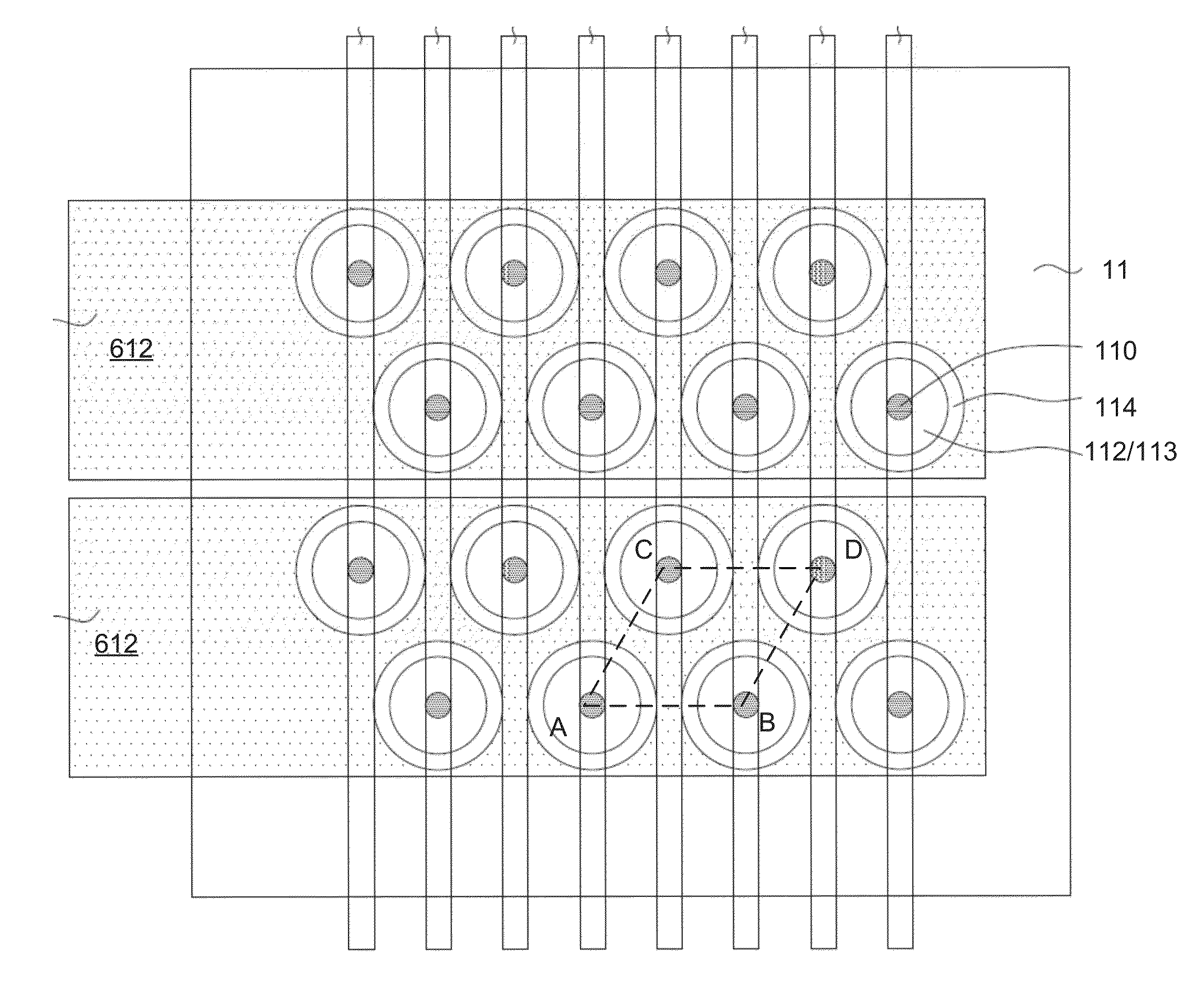
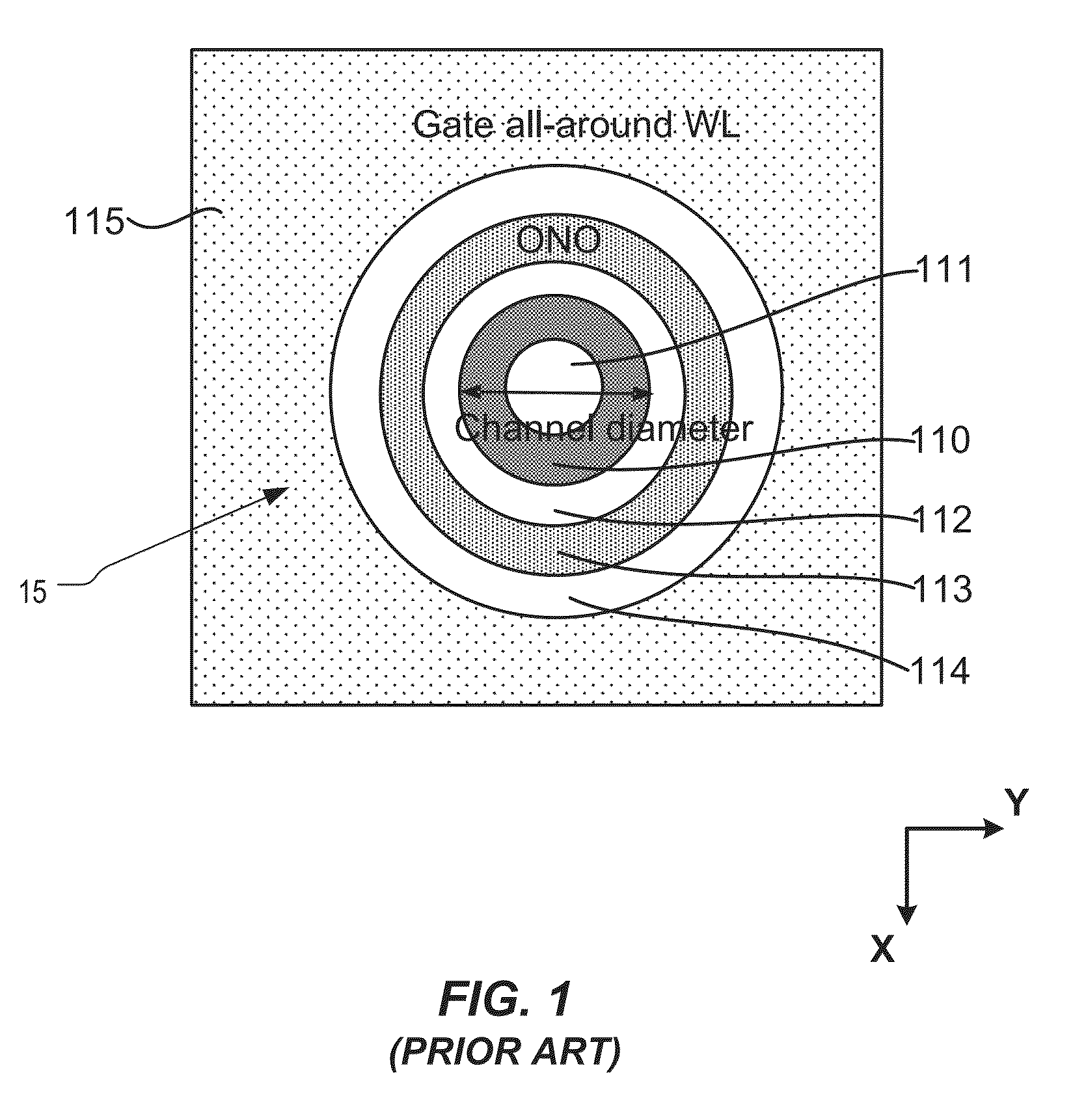
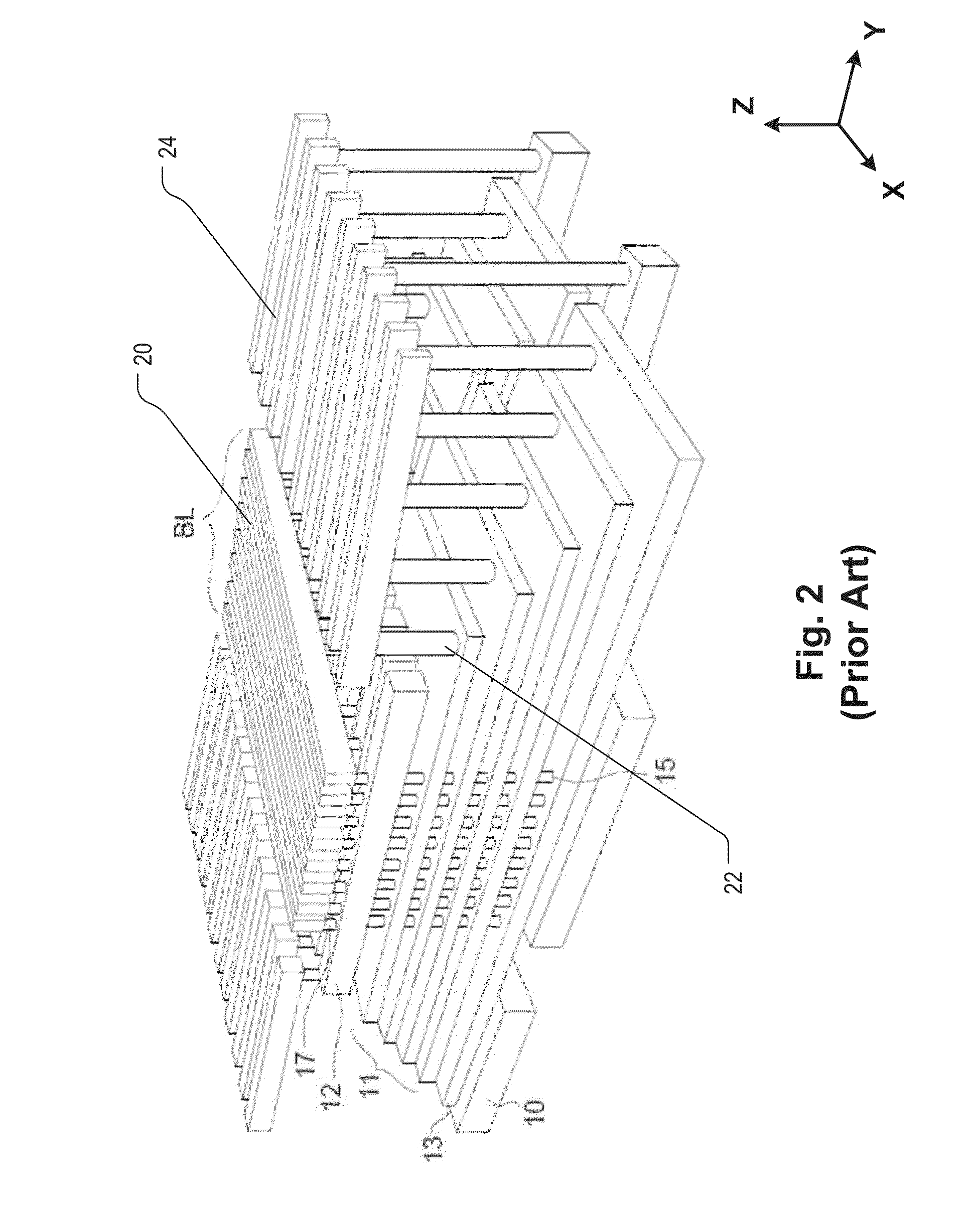
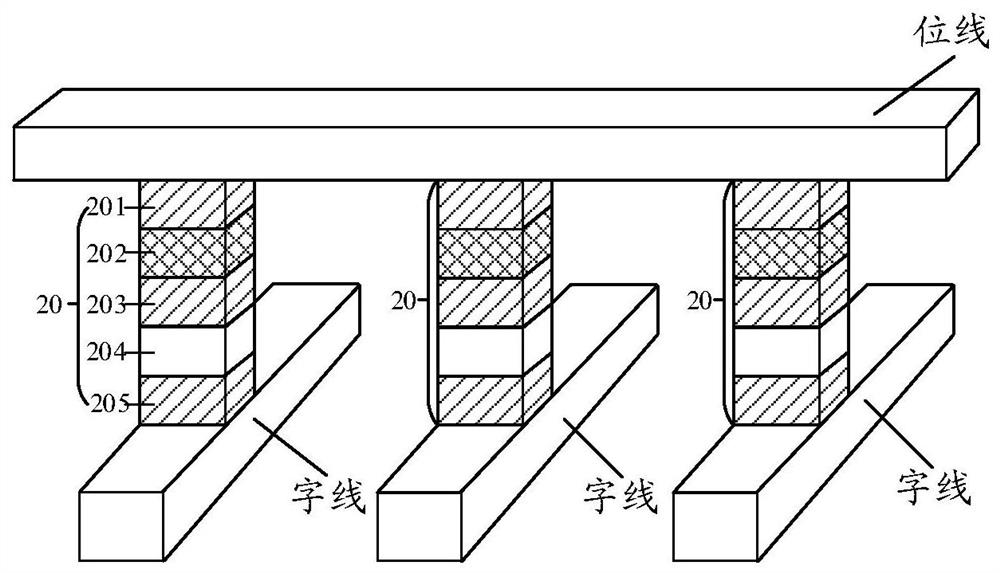
A semiconductor memory capable of increasing bit density by three-dimensional arrangement of cells and a method for manufacturing the same are provided.In a semiconductor memory 1, gate electrode films 21 are provided on a silicon substrate 11. The gate electrode films 21 are arranged in one direction parallel to the upper surface of the silicon substrate 11 (X direction). Each gate electrode film 21 has a lattice plate-like shape, having through holes 22 in a matrix form as viewed in the X direction. Silicon beams 23 are provided passing through the through holes 22 of the gate electrode films 21 and extending in the X direction. Further, an ONO film 24 including a charge storage layer is provided between the gate electrode film 21 and the silicon beam 23.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
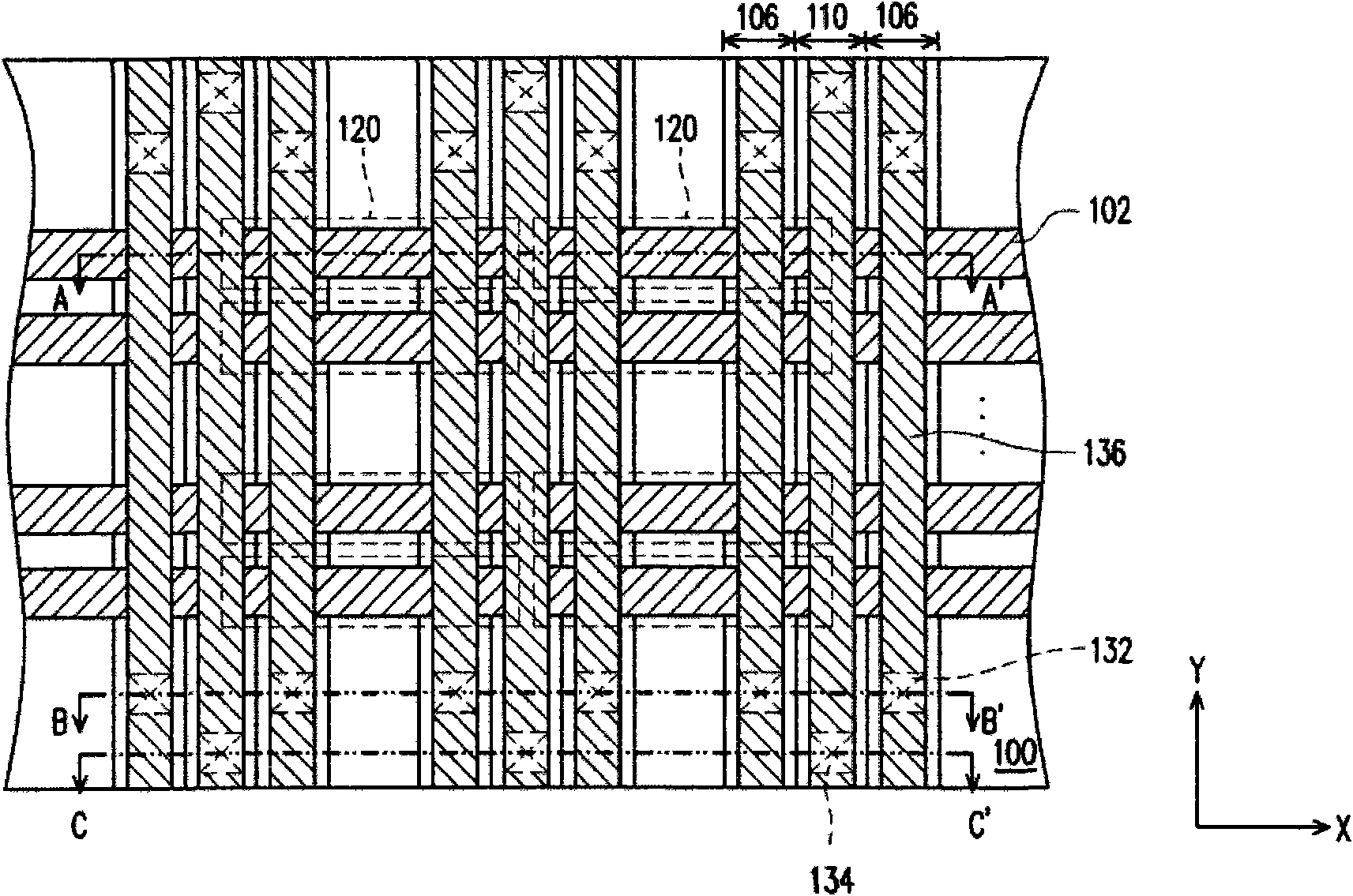
Parallelogram cell design for high speed vertical channel 3D NAND memory
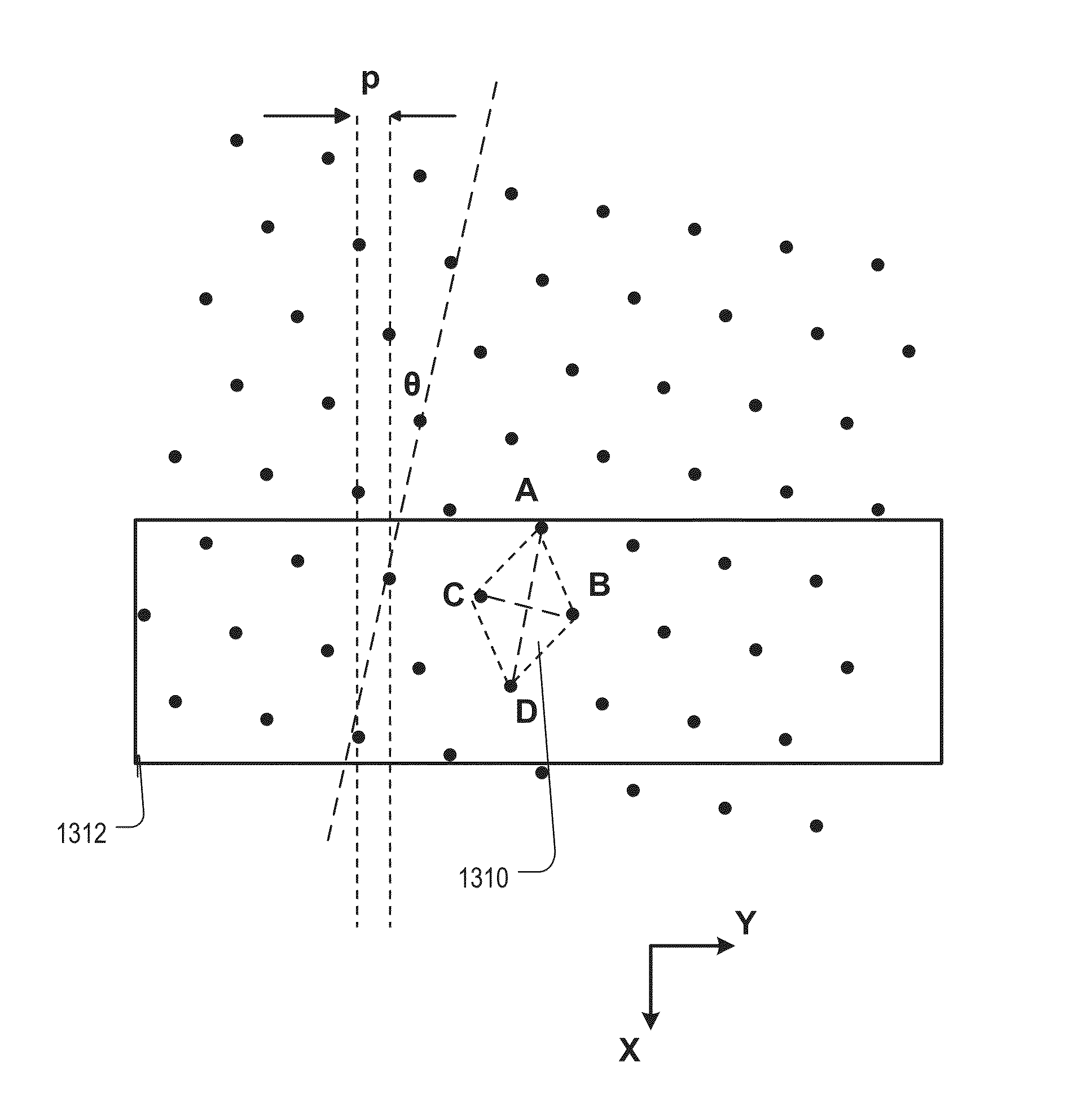
ActiveUS20150206898A1Increase bit densityReduce distractionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceBit line
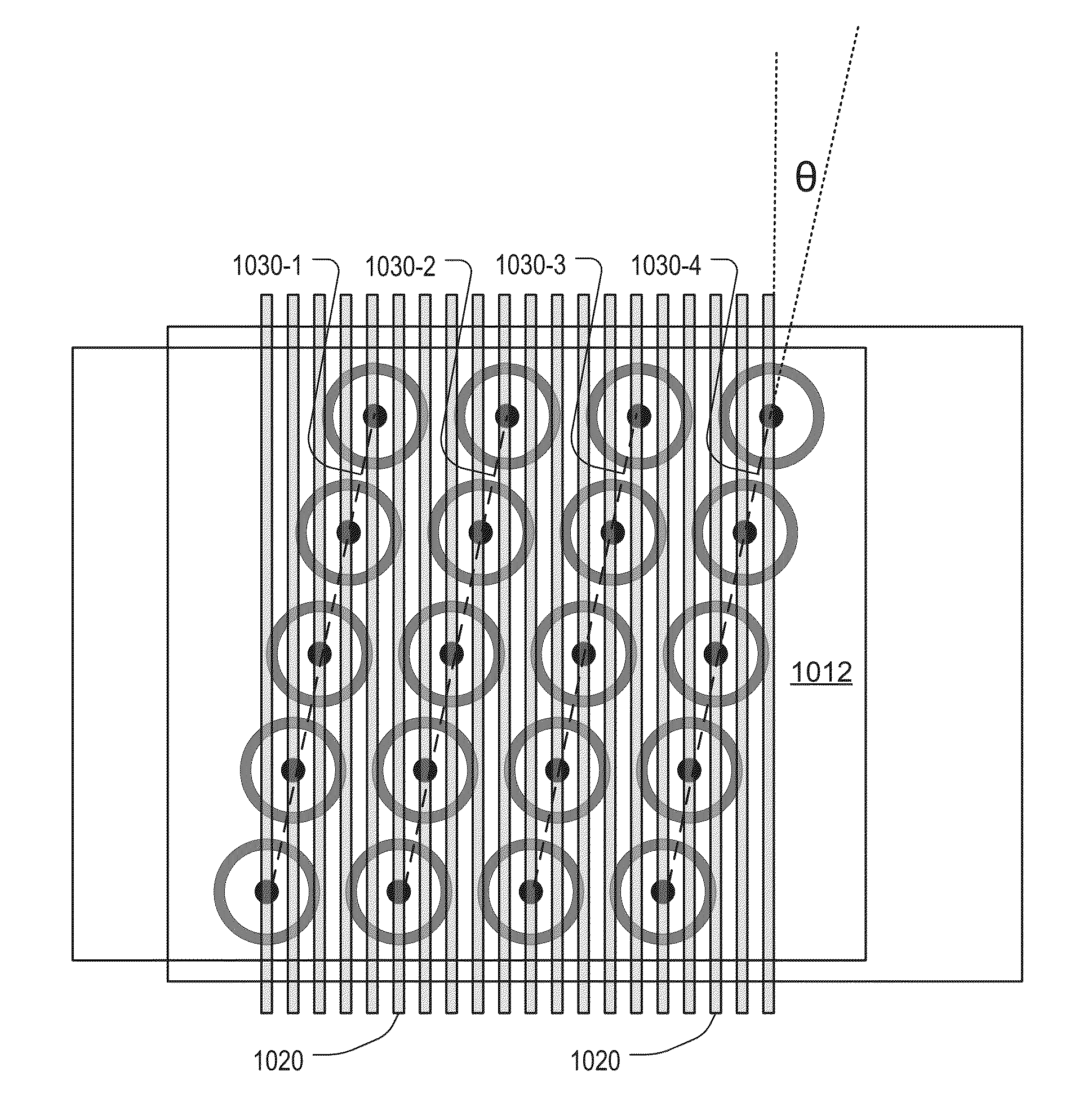
Roughly described, a memory device has a multilevel stack of conductive layers. Pillars oriented orthogonally to the substrate each include series-connected memory cells at cross-points between the pillars and the conductive layers. String select lines (SSLs) are disposed above the conductive layers, and bit lines are disposed above the SSLs. The pillars are arranged on a regular grid having a unit cell which is a non-rectangular parallelogram. The pillars may be arranged so as to define a number of parallel pillar lines, each having an acute angle θ>° relative to the bit line conductors, each line of pillars having n>1 pillars intersecting a common one of the SSL. The arrangement permits higher bit line density, a higher data rate due to increased parallelism, and a smaller number of SSLs, thereby reducing disturbance, reducing power consumption and reducing unit cell capacitance.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
System and method for dynamic perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
InactiveUS7162096B1Increasing bandwidth required to carry videoImprove video qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Perceptual coding
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Twisted array design for high speed vertical channel 3D NAND memory
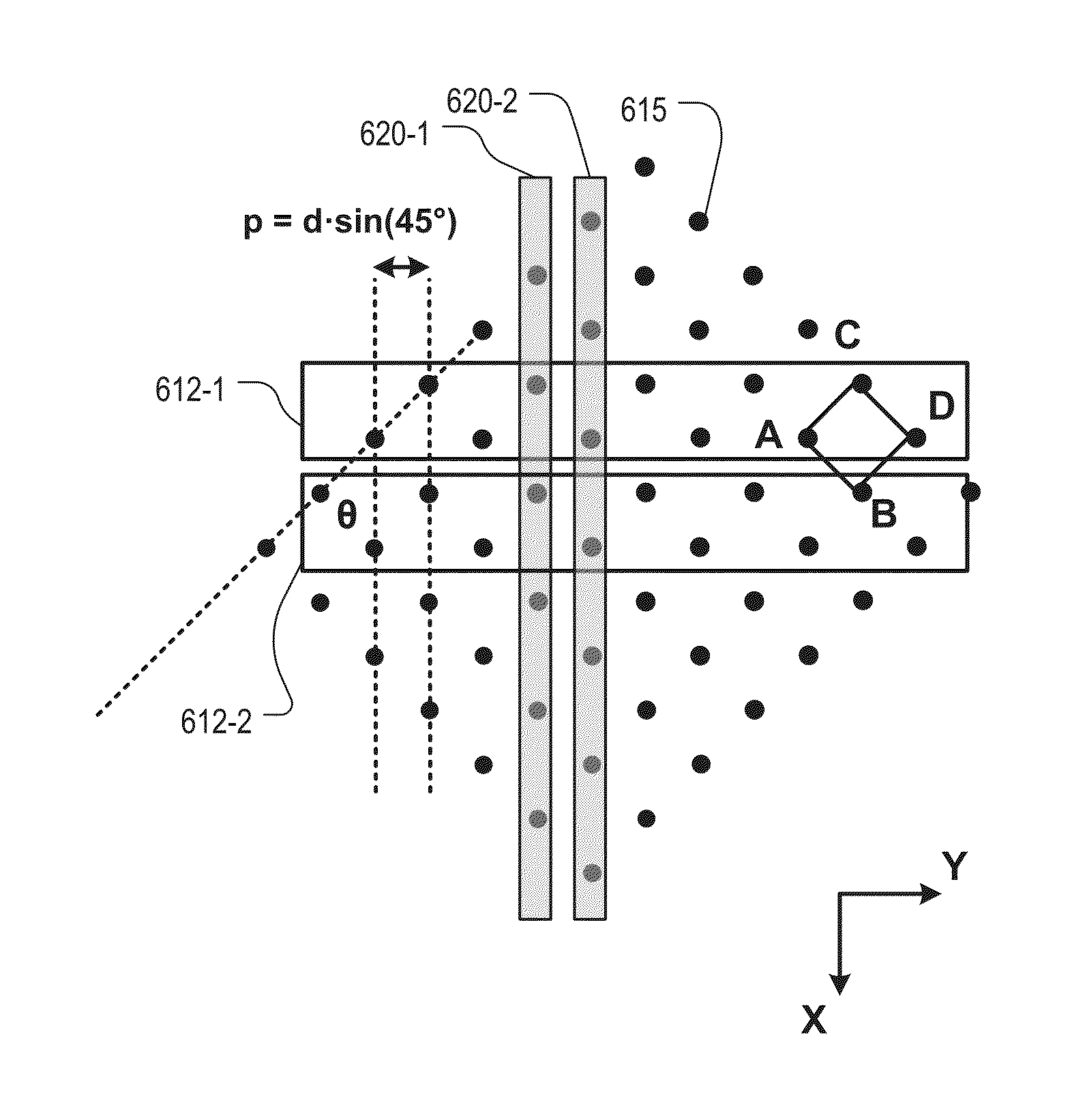
ActiveUS20150206899A1High bit densityHigh data rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhysicsElectrically conductive
Roughly described, a memory device has a multilevel stack of conductive layers. Vertically oriented pillars each include series-connected memory cells at cross-points between the pillars and the conductive layers. SSLs run above the conductive layers, each intersection of a pillar and an SSL defining a respective select gate of the pillar. Bit lines run above the SSLs. The pillars are arranged on a regular grid which is rotated relative to the bit lines. The grid may have a square, rectangle or diamond-shaped unit cell, and may be rotated relative to the bit lines by an angle θ where tan(θ)=±X / Y, where X and Y are co-prime integers. The SSLs may be made wide enough so as to intersect two pillars on one side of the unit cell, or all pillars of the cell, or sufficiently wide as to intersect pillars in two or more non-adjacent cells.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Semiconductor memory and method for manufacturing the same
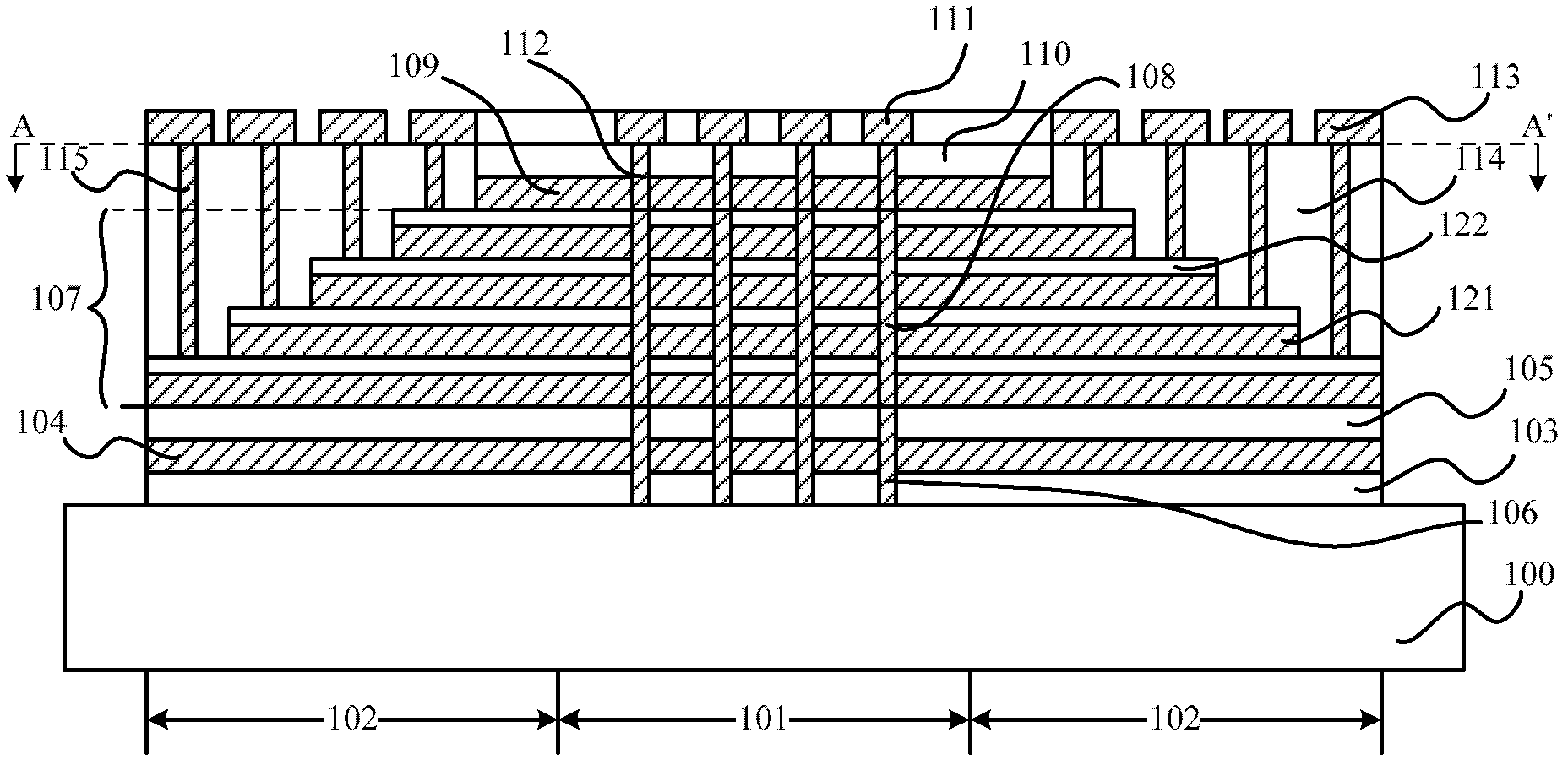
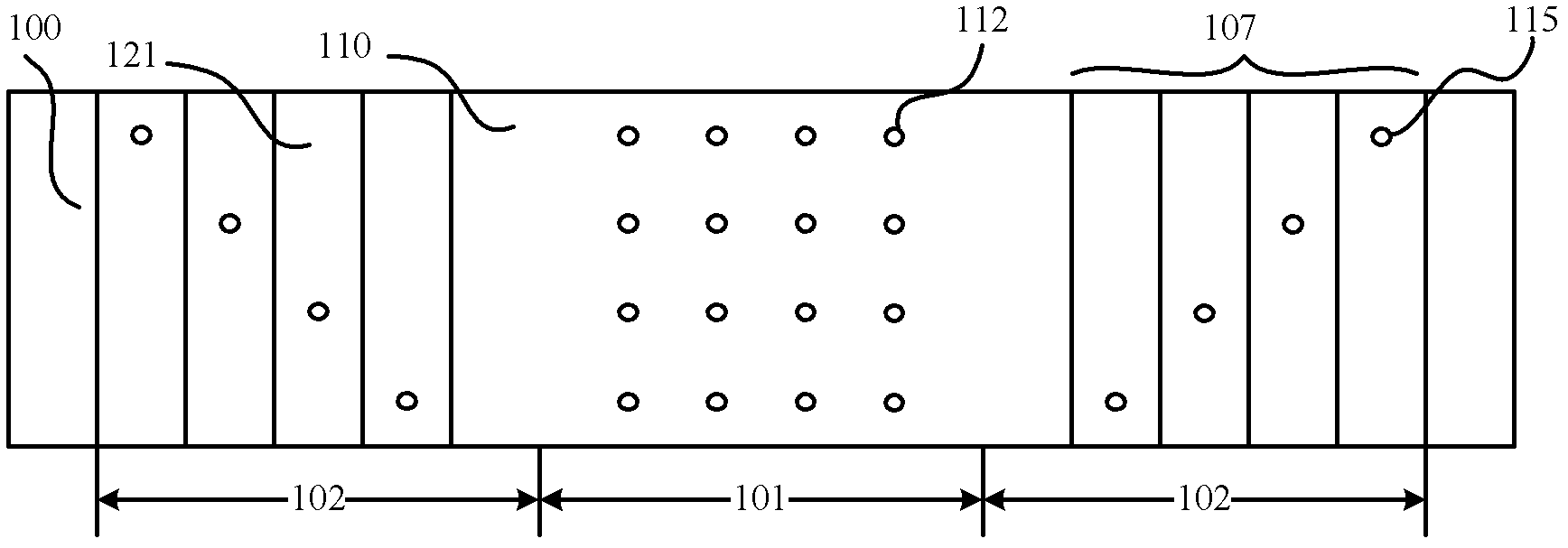
Provided are a semiconductor memory wherein bit density is improved by three-dimensionally arranging cells, and a method for manufacturing such semiconductor memory. In a semiconductor memory (1), a plurality of gate electrode films (21) are arranged on a silicon substrate (11). Gate electrode films (21) are arranged along one direction (X direction) parallel to the upper surface of the silicon substrate (11). Each gate electrode film (21) has a shape of a grid-like board, and a plurality of through holes (22) are formed in matrix when viewed from the X direction. Furthermore, a plurality of silicon beams (23) are arranged such that the beams penetrate the through holes (22) on the gate electrode films (21) and extend in the X direction. Furthermore, an ONO film (24), including a charge accumulating layer, is arranged between the gate electrode film (21) and the silicon beam (23).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Systems and methods for extended life multi-bit memory cells
ActiveUS8289768B2Extend the life cycleIncrease bit densityRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectronic systemsComputer science
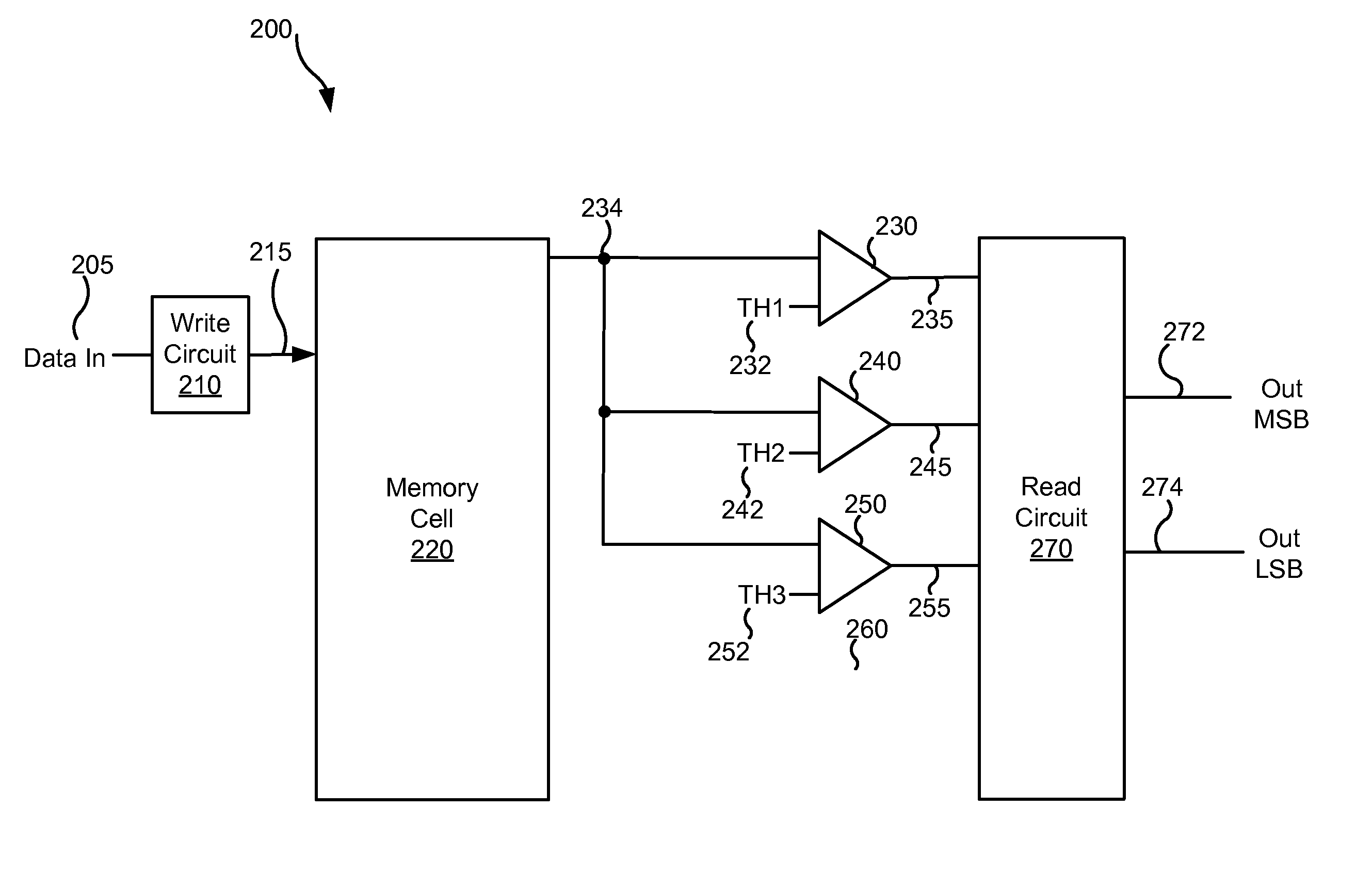
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for extended life operation of multi-bit memory cells. As an example, some embodiments of the present invention provide electronic systems that include a plurality of multi-bit memory cells, an encoding circuit and a decoding circuit. Each of the plurality of multi-bit memory cells is operable to hold at least two bits. The encoding circuit is operable to receive a data input including at least two data bits, and to encode the two data bits as an encoded output to the plurality of multi-bit memory cells. The encoded output may be selected to be either a single two bit output representing the two bits, or a series of two two bit outputs representing the two bits. The decoding circuit is operable to reverse the encoding applied by the encoding circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Divisible true dual port memory system supporting simple dual port memory subsystems
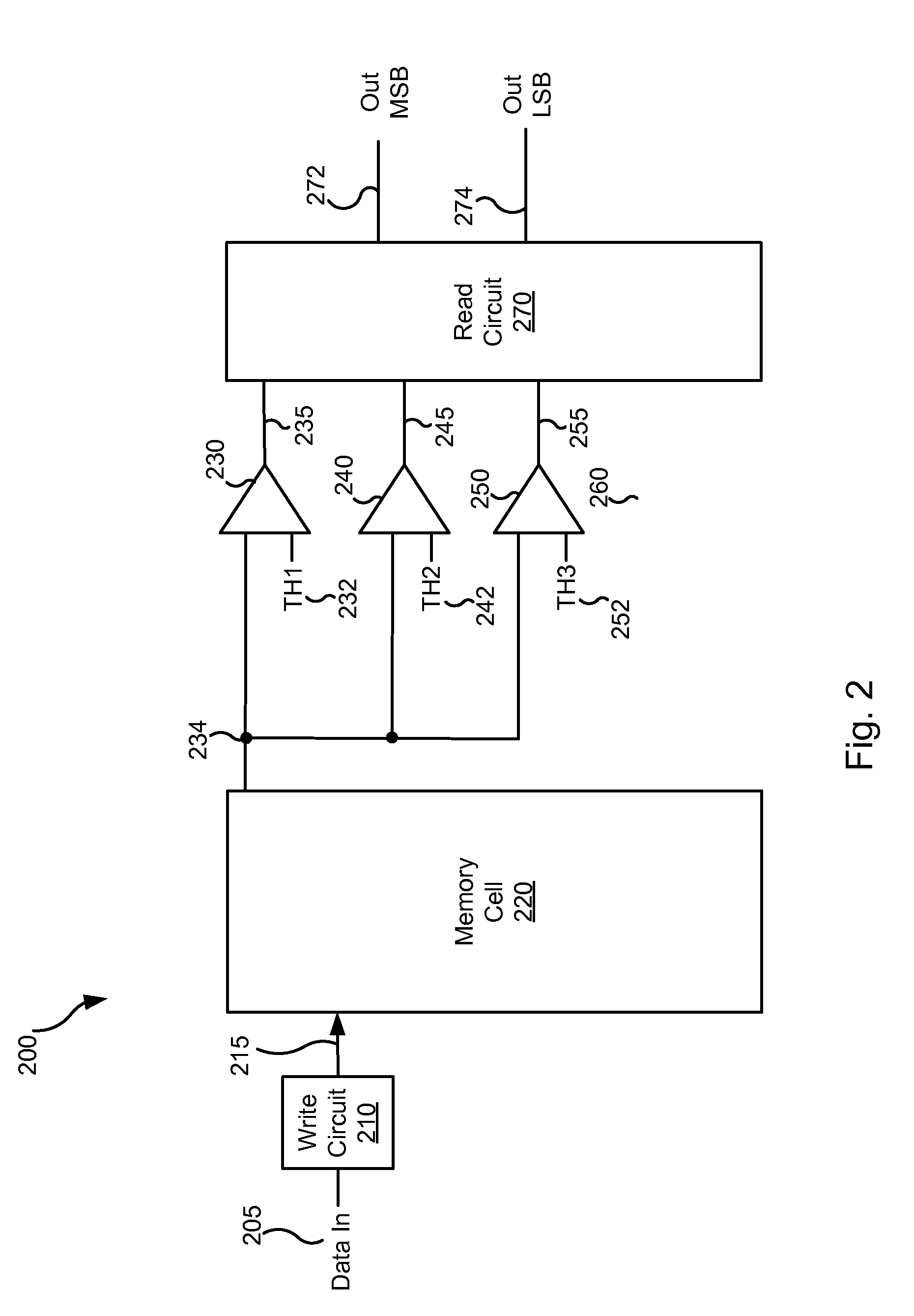
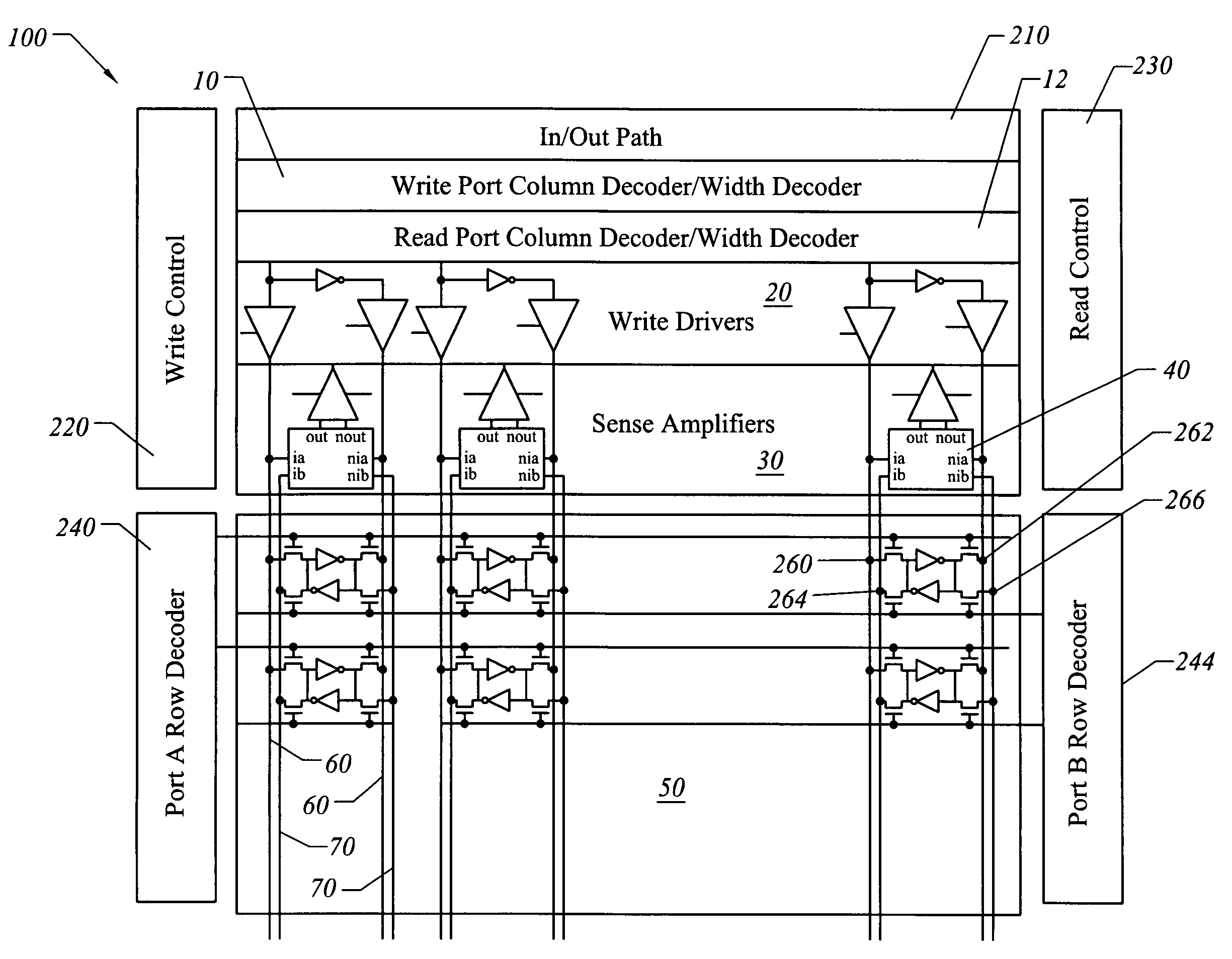
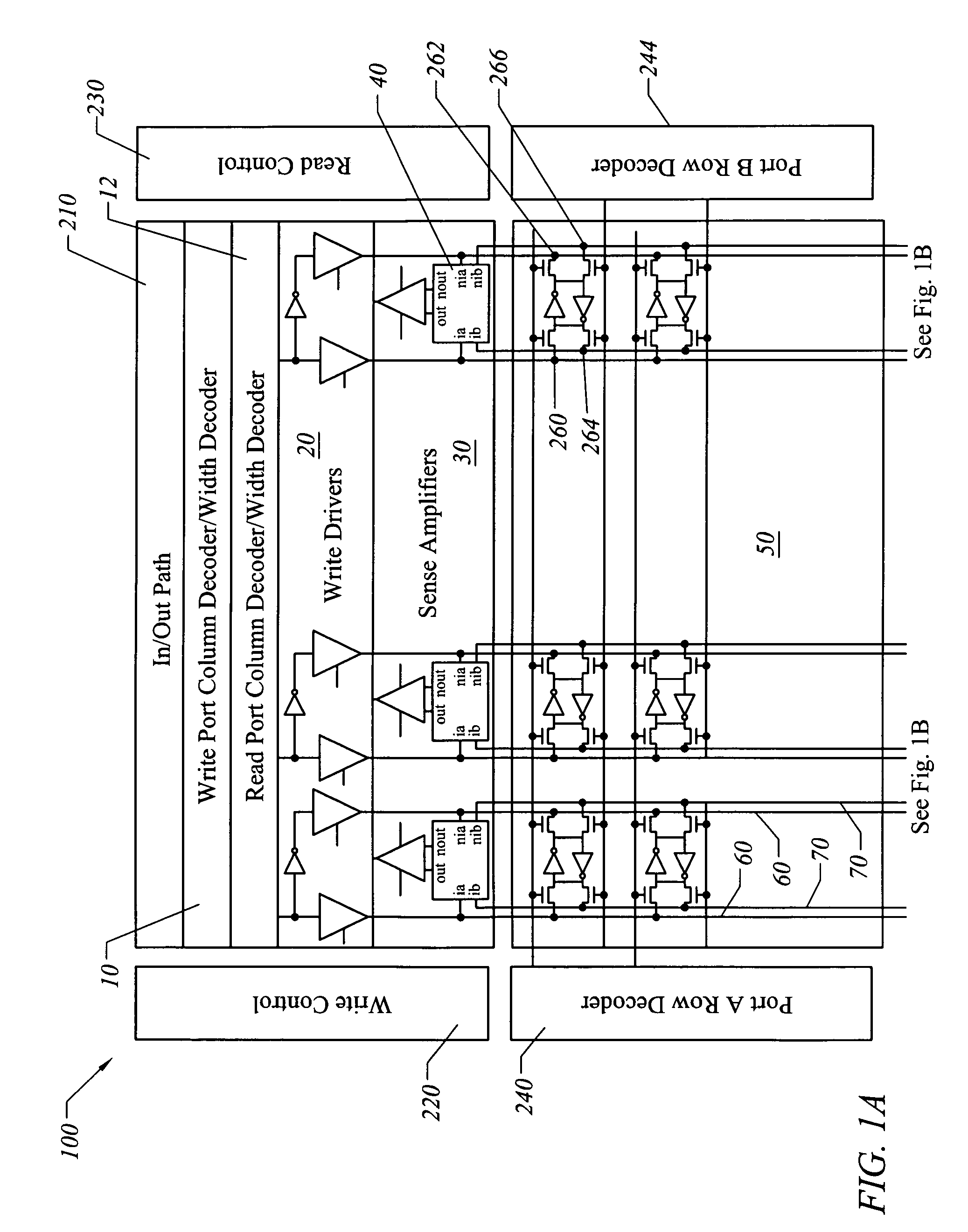
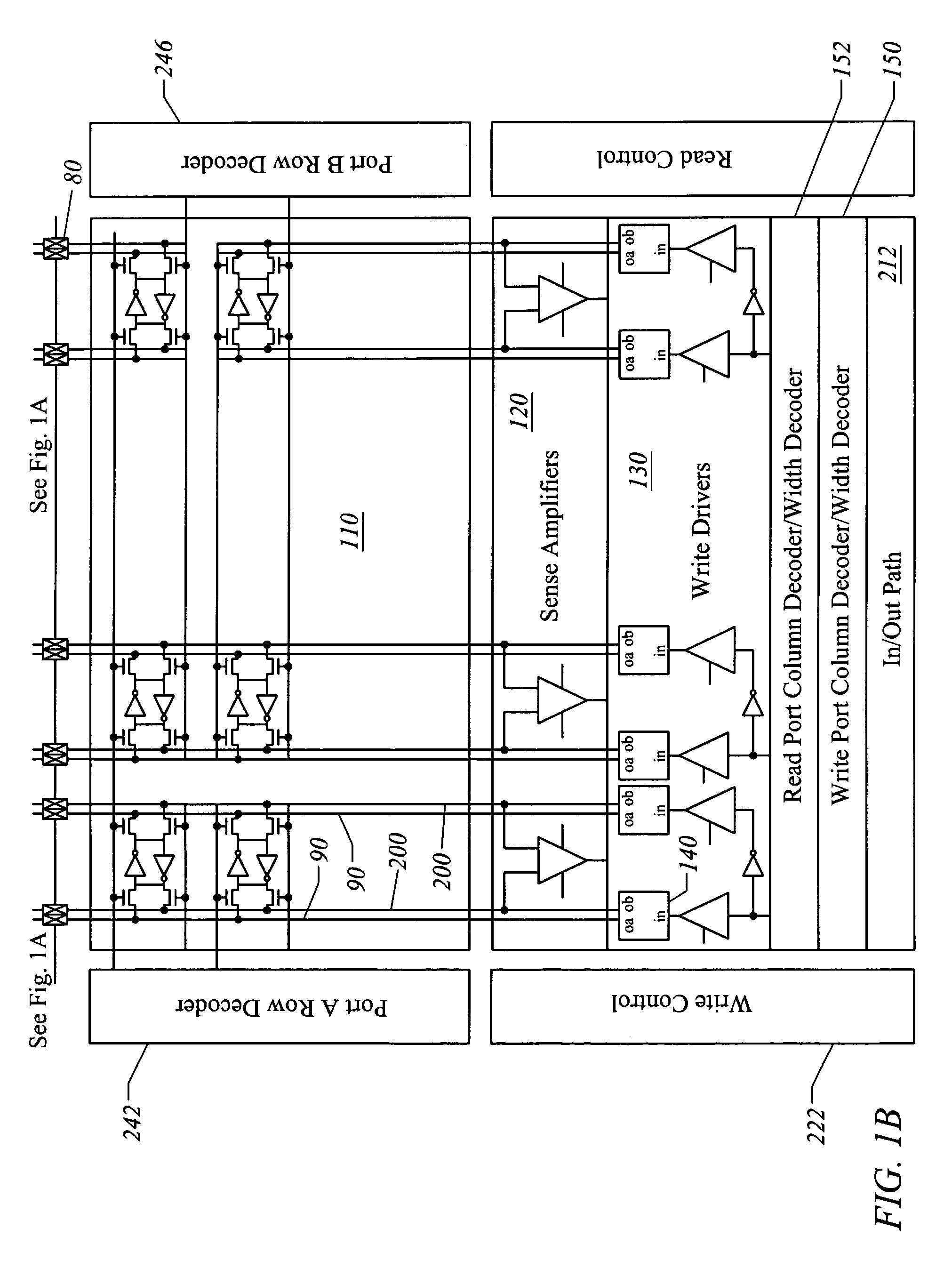
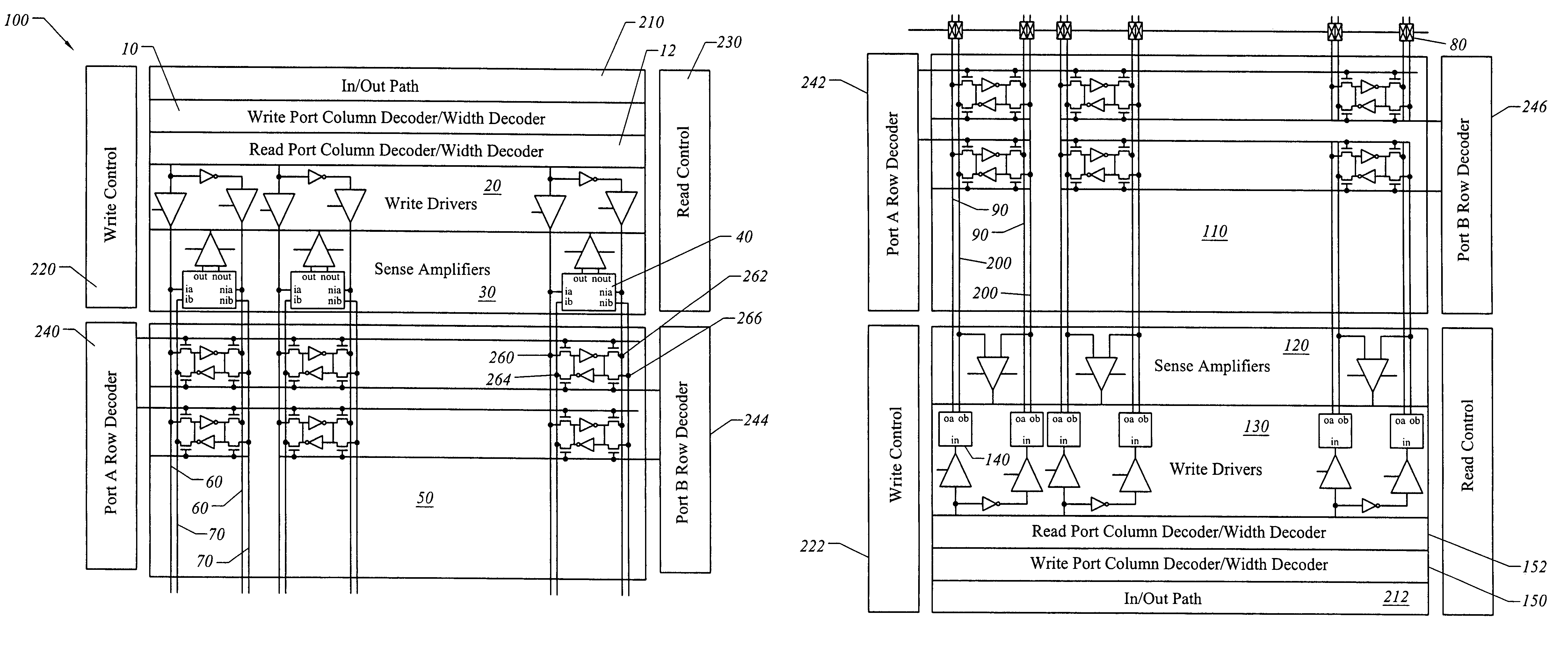
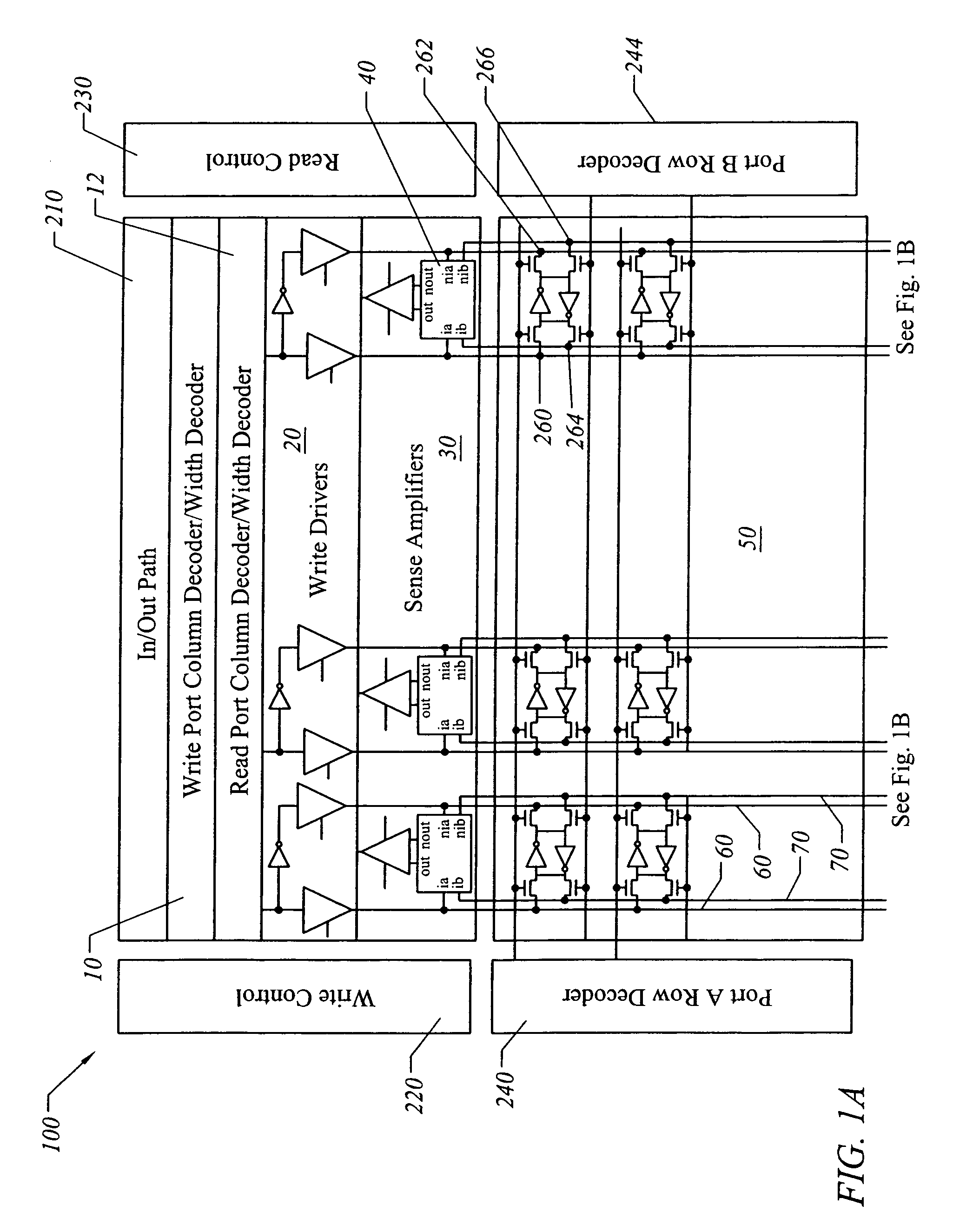
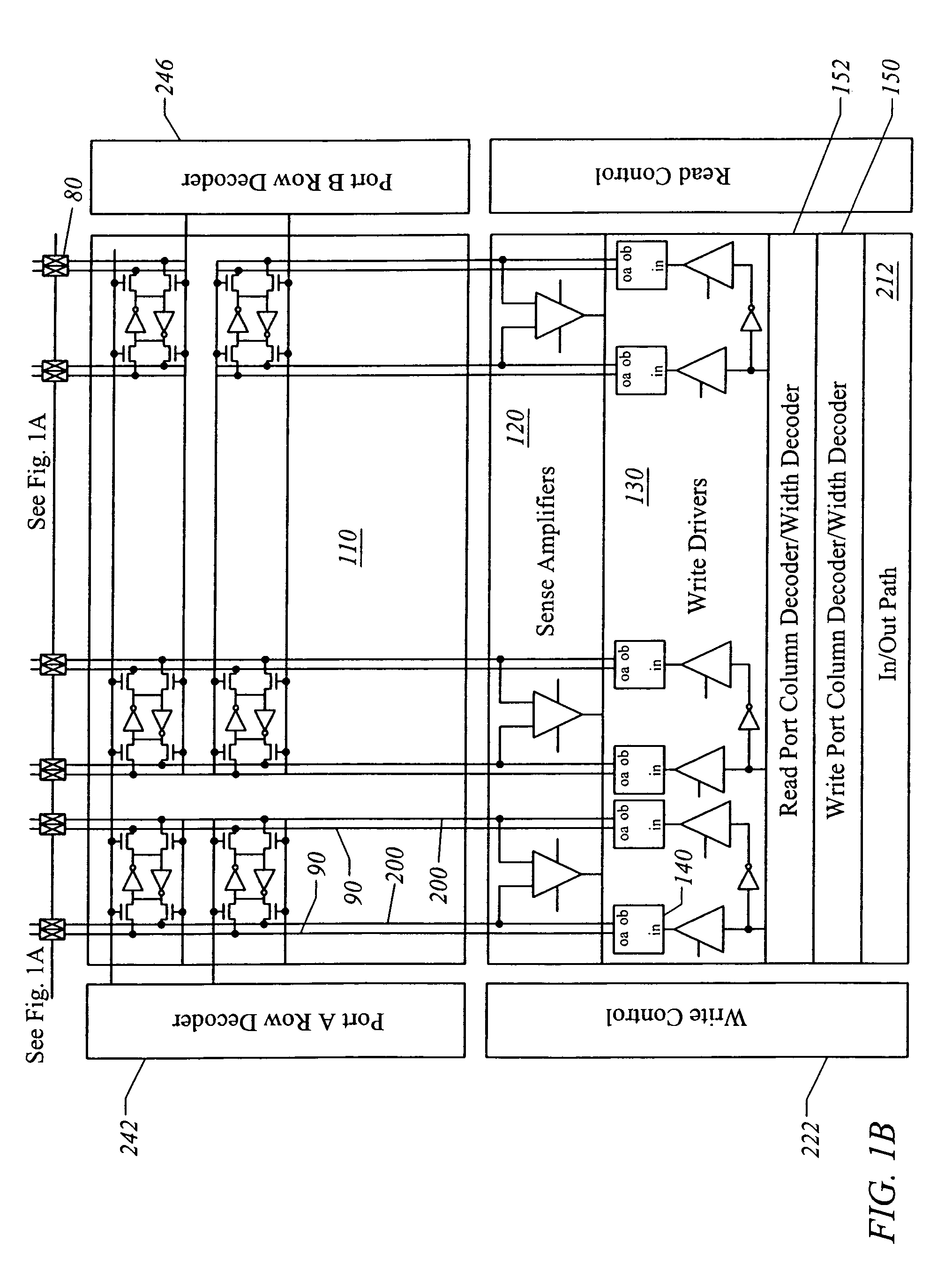
InactiveUS7130238B1Increase bit densityAvoid countingDigital storageLogic circuitsAudio power amplifierRandom access memory
A random access memory circuit and a method for configuring the same. The circuit includes a first array of memory cells including a first plurality of ports and a second plurality of ports, and a second array of memory cells including a third plurality of ports and a fourth plurality of ports. Additionally, the circuit includes a plurality of switches connected to the first plurality of ports and the third plurality of ports respectively or connected to the second plurality of ports and the fourth plurality of ports respectively. Moreover, the circuit includes a plurality of sense amplifiers and a plurality of write drivers.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Parallelogram cell design for high speed vertical channel 3D NAND memory
ActiveUS9219073B2Increase bit densityIncrease data rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
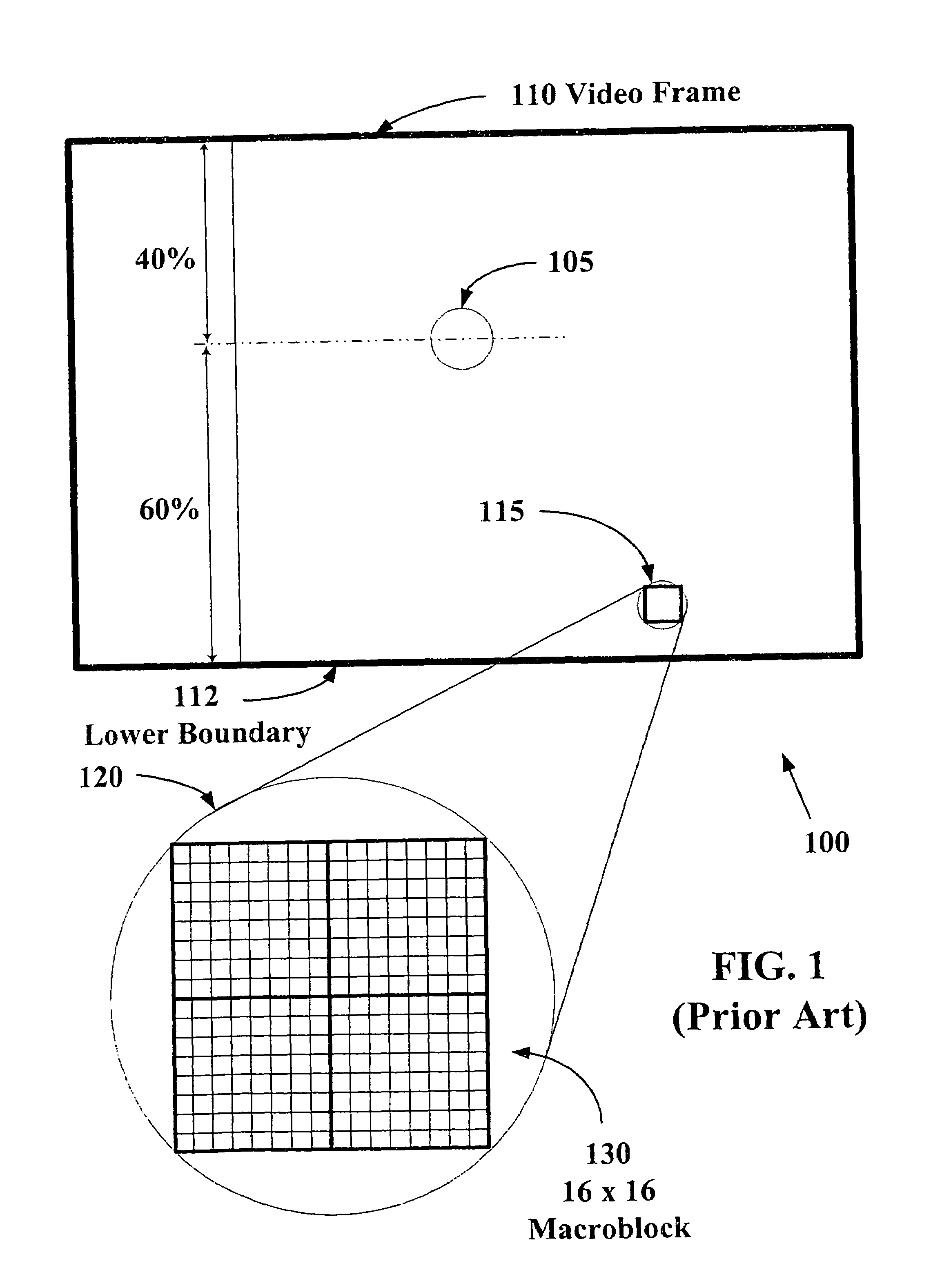
System and method for static perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
InactiveUS6864909B1Increased subjective video qualityIncreasing bandwidth required to carry videoTwo-way working systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Video quality
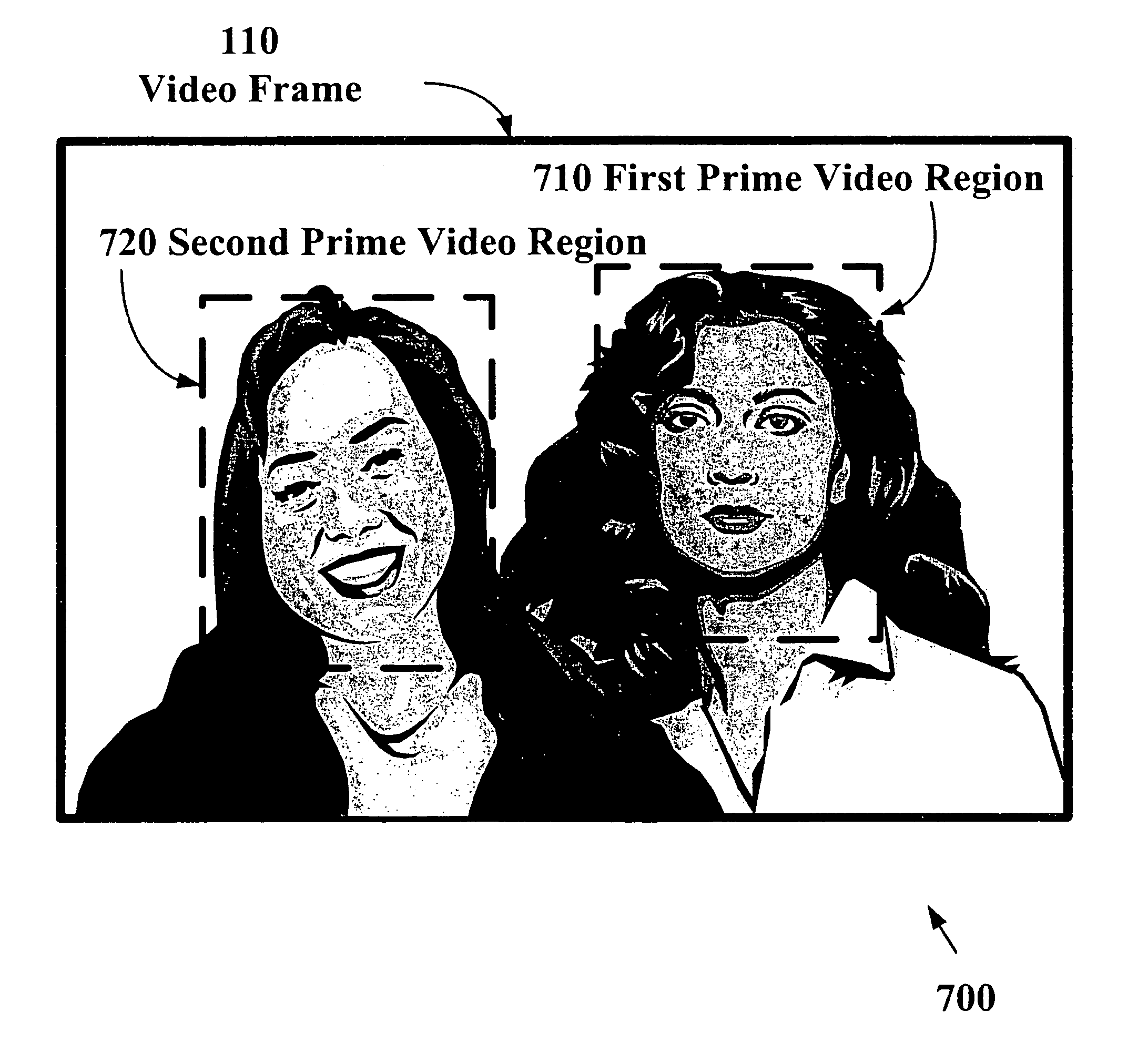
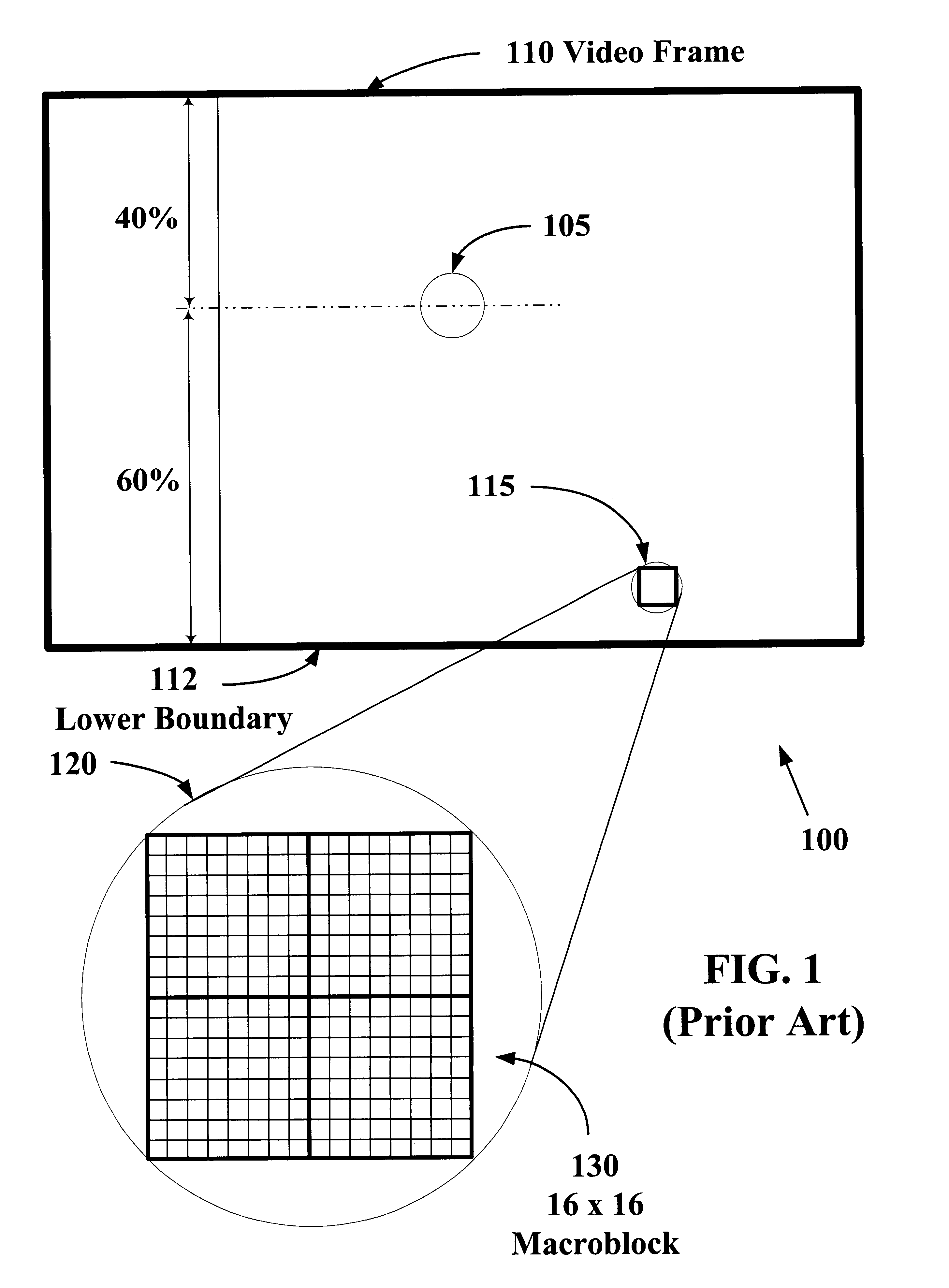
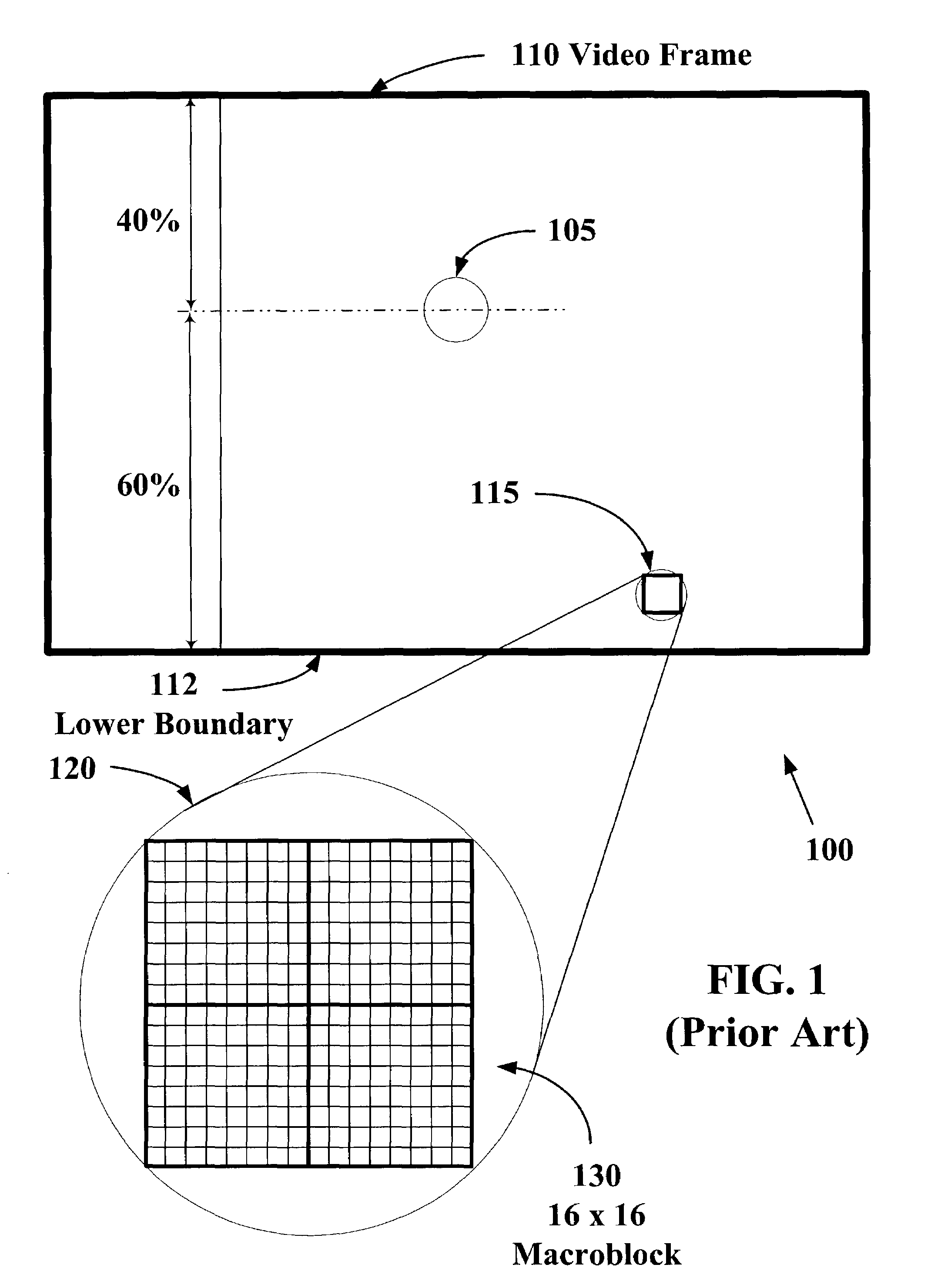
The present invention allows video images with improved subjective quality to be transmitted without a concomitant increase in a total number of bits transmitted per frame. Quantization parameters are applied to coefficients of macroblocks within a given video frame. A lower value of quantization parameter is applied near a central region of a video frame. This central region is referred to as a prime video region. Applying a lower quantization parameter to the prime video region has the effect of increasing the bit density within that area thereby improving the video quality. Outside of the prime video region, the bit density is progressively decreased on a macroblock-by-macroblock basis so as to have a zero or near-zero net-gain in bit density over the entire video frame.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System and method for dynamic perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
ActiveUS6987889B1Improves perceived video qualityIncreasing bandwidth required to carry videoCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Perceptual coding
The present invention allows higher quality video images to be transmitted without a concomitant increase in a total number of video data bits transmitted per frame. Quantization parameters are applied to coefficients of macroblocks within a given video frame. A lower value of the quantization parameter is applied near a central region of a video frame. This central region is referred to as a prime video region. Applying the lower quantization parameter to the prime video region has the effect of increasing the video data bit density within that area. Outside of the prime video region, the video data bit density per macroblock is decreased so as to have a zero net-gain in bit density over the entire video frame. Furthermore, there may be a plurality of prime video regions where quantization parameters are dynamically coded. In this case, the value of the quantization parameter will increase or decrease within a given prime video region based on a relative importance of a particular prime video region. Consequently, a quantization parameter matrix may vary depending on the video scene.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Twisted array design for high speed vertical channel 3D NAND memory
ActiveUS9373632B2Increase bit densityIncrease data rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBit lineRegular grid
Roughly described, a memory device has a multilevel stack of conductive layers. Vertically oriented pillars each include series-connected memory cells at cross-points between the pillars and the conductive layers. SSLs run above the conductive layers, each intersection of a pillar and an SSL defining a respective select gate of the pillar. Bit lines run above the SSLs. The pillars are arranged on a regular grid which is rotated relative to the bit lines. The grid may have a square, rectangle or diamond-shaped unit cell, and may be rotated relative to the bit lines by an angle θ where tan(θ)=±X / Y, where X and Y are co-prime integers. The SSLs may be made wide enough so as to intersect two pillars on one side of the unit cell, or all pillars of the cell, or sufficiently wide as to intersect pillars in two or more non-adjacent cells.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Memory cell of flash memory and forming method
ActiveCN103258824AIncrease bit densityLower bit costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceDielectric layer
The invention discloses a memory cell of a flash memory and a forming method. The memory cell of the flash memory comprises a semiconductor substrate, an isolating layer, a base layer selecting grid, a base layer dielectric layer, control grid layers, a memory plugging array and a plurality of polycrystalline silicon layers. The semiconductor substrate comprises an array area and step areas and the step areas are arranged at two sides of the array area. The isolating layer, the base layer selecting grid and the base layer dielectric layer are sequentially arranged on the surface of the semiconductor substrate. The control grid layers are arranged on the surface of the base layer dielectric layer. The control grid layers further comprises a plurality of polycrystalline silicon layers and a plurality of interlayer dielectric layers arranged on the surfaces of the polycrystalline silicon layers. The memory plugging array penetrates through the control grid layers of the array area in a thickness direction. The polycrystalline silicon layers are arranged in the control grid layers of the step areas and form a ladder layer by layer from the lowermost layer to the topmost layer in a decreasing mode. Projections of steps of all levels of the ladder on the semiconductor substrate are arranged in the shape of a line, and the line is parallel to the boundaries of the array area and the step areas. According to the memory cell of the flash memory, bit density of the flash memory is improved, and cost is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Medical system comprising a detection device for detecting an object and comprising a storage device and method thereof
InactiveUS20080177176A1Increase bit densityImprove overall utilizationCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringX-rayComputer science
The invention relates to a medical system comprising a detection device for detecting an object in at least two dimensions by x-rays. The detection device is constructed to detect the object and to produce data comprising a 2D data record or a sequence of 2D data records over time representing the object in a projection through the object in two dimensions and to output the data. The medical system comprises at least one storage device with a data input actively connected to the detection device and which is constructed to receive the data at the input side and to write on a storage medium, in particular a portable storage medium, in such a way that the storage medium represents the data so it can be read out again. The medical system is constructed to digitally transmit the data from the detection device through to the storage device.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
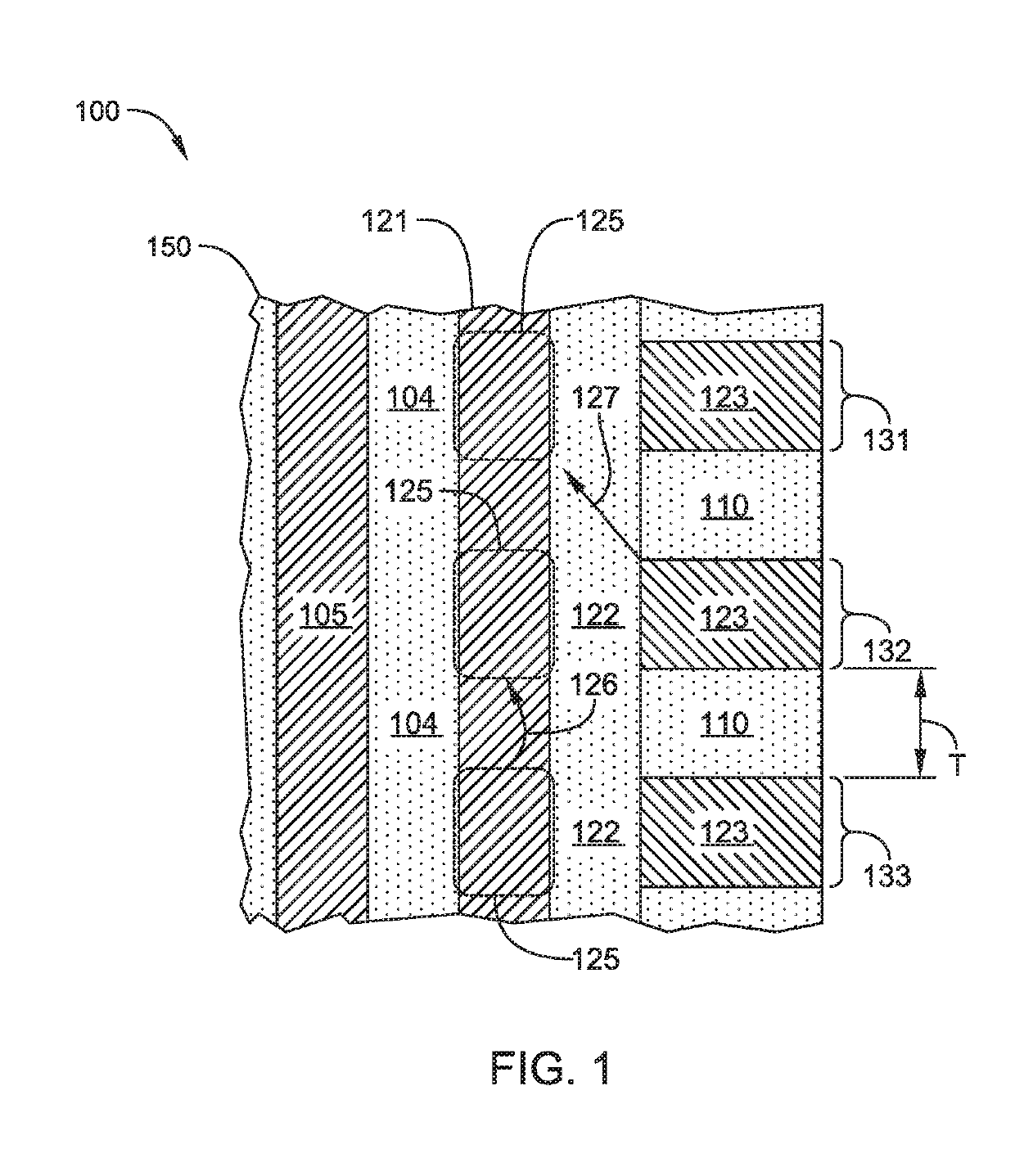
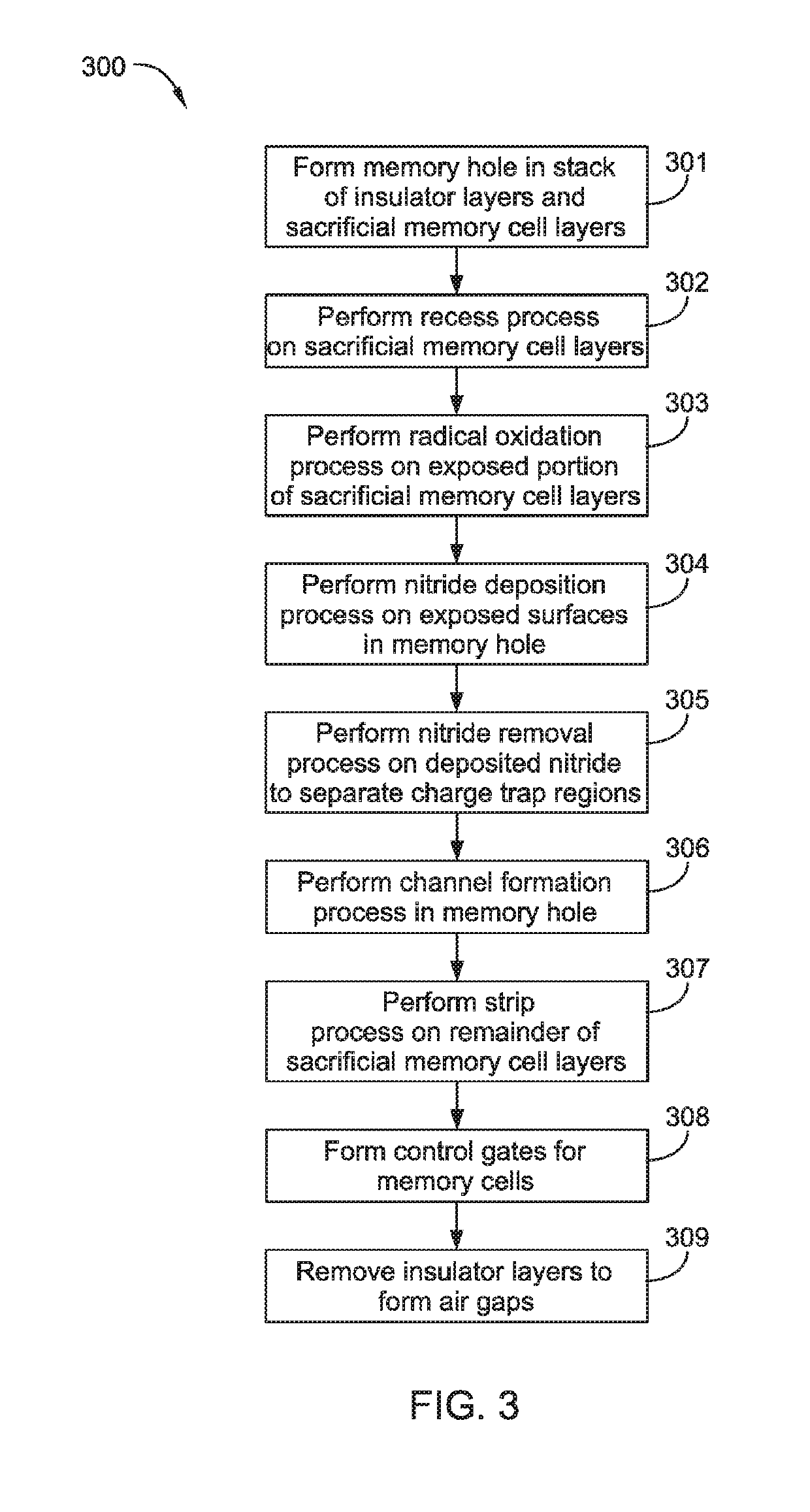
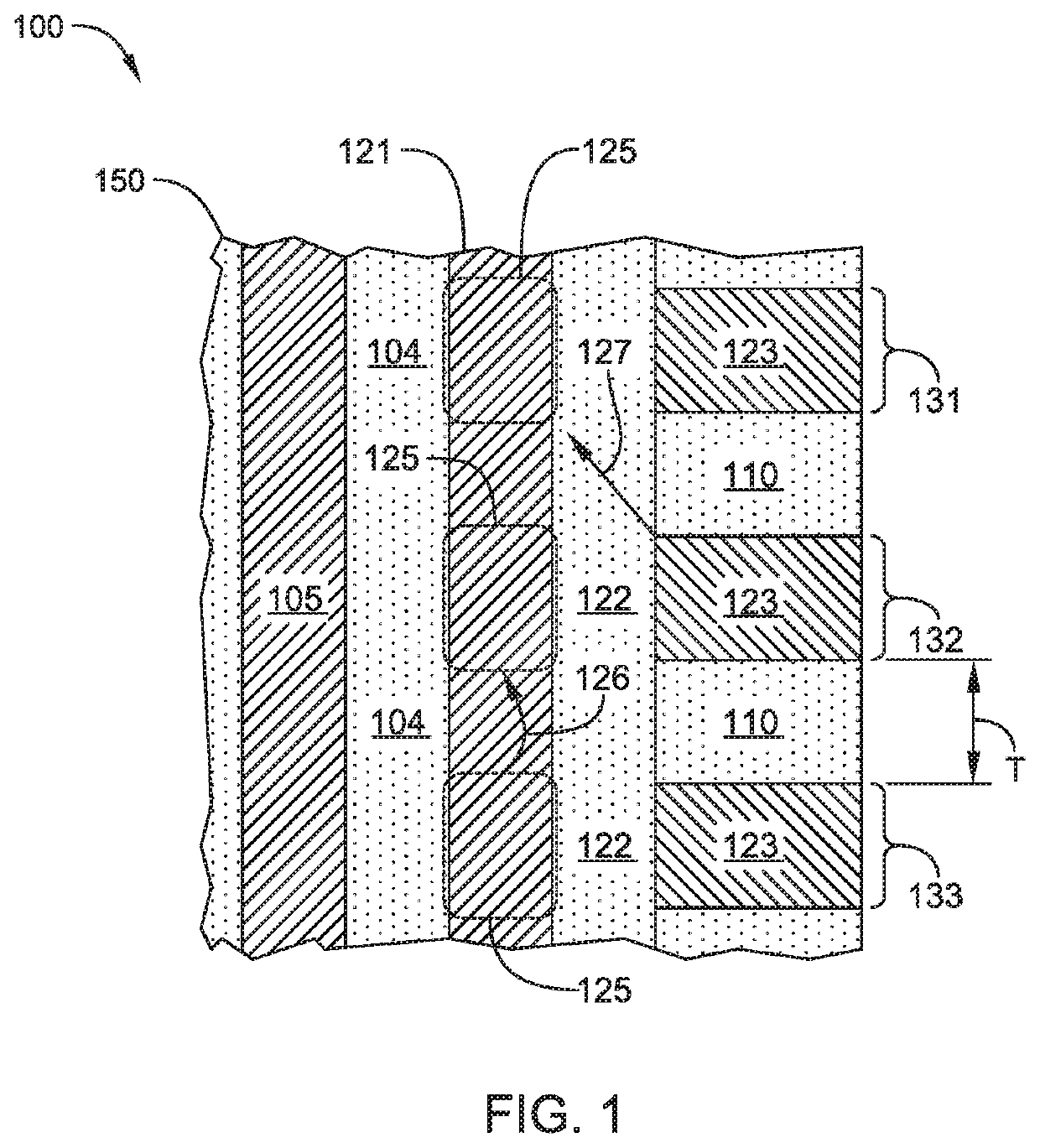
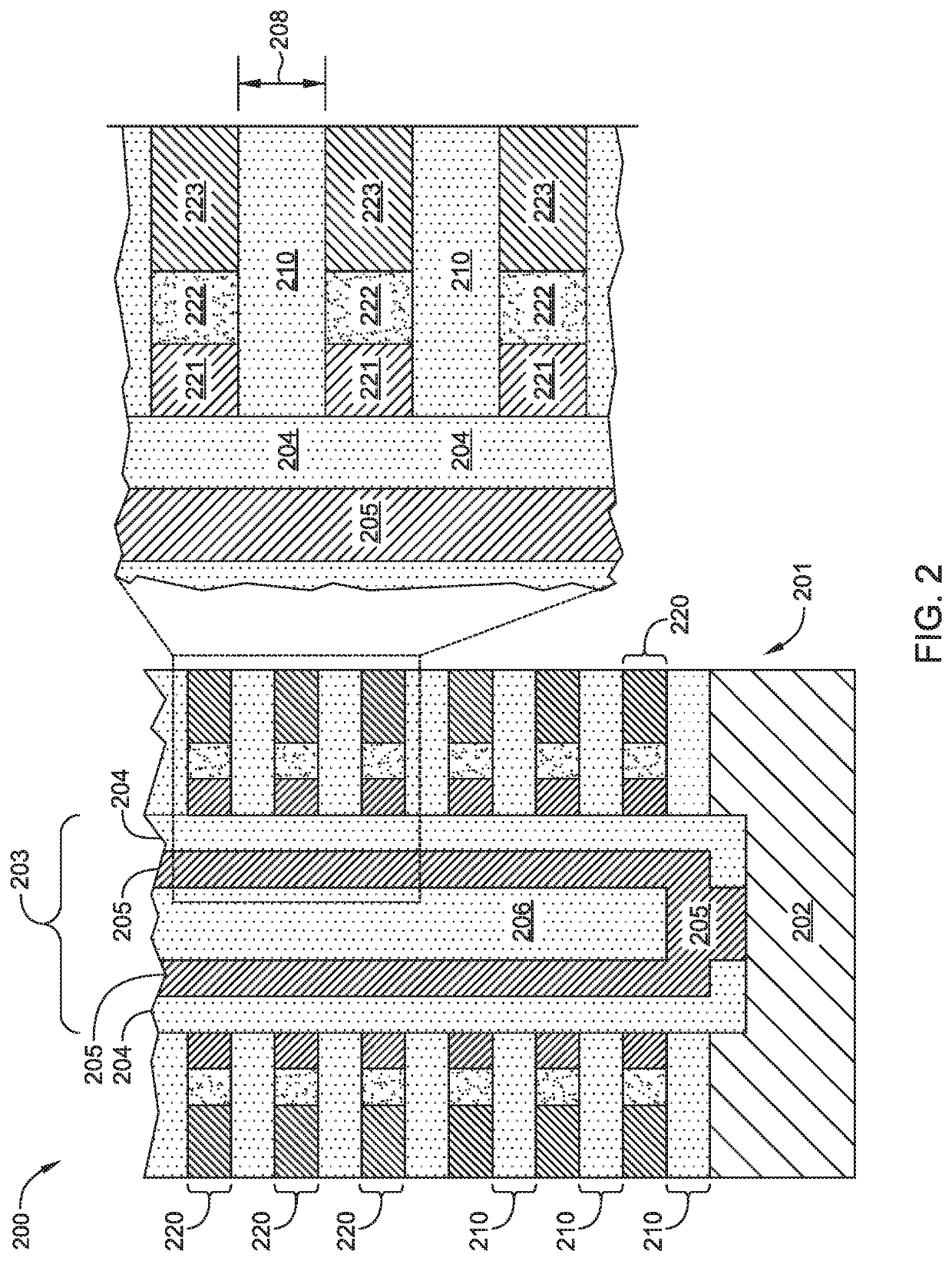
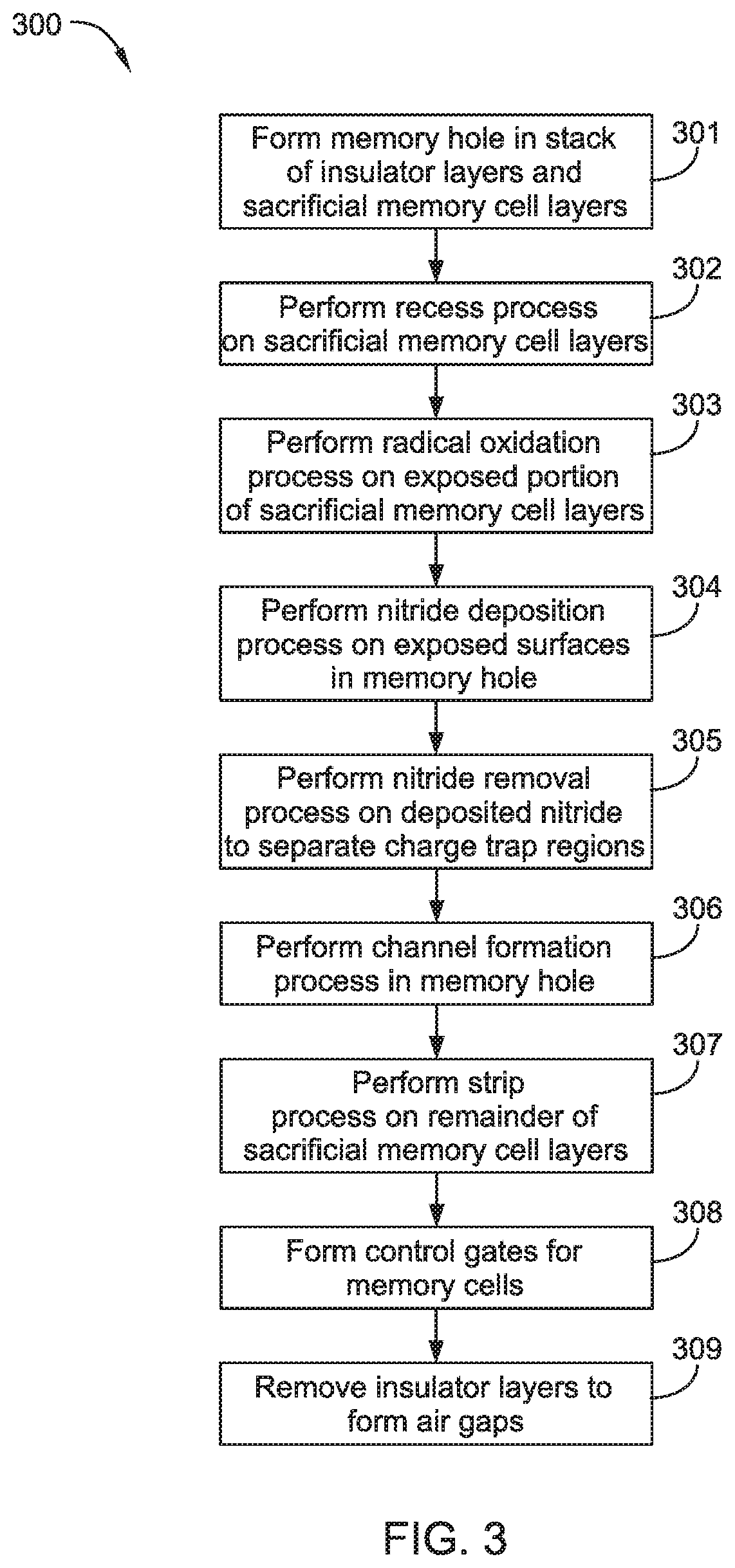
Multi-layer stacks for 3D NAND extendability
ActiveUS20190115365A1Easy to eraseIncrease bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
Embodiments described herein relate to methods and materials for fabricating semiconductor devices, such as memory devices and the like. In one embodiment, a memory layer stack includes materials having differing etch rates in which one material is selectively removed to form an airgap in the device structure. In another embodiment, silicon containing materials of a memory layer stack are doped or fabricated as a silicide material. In another embodiment, a silicon nitride material is utilized as an interfacial layer between oxide containing and silicon containing layers of a memory layer stack.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
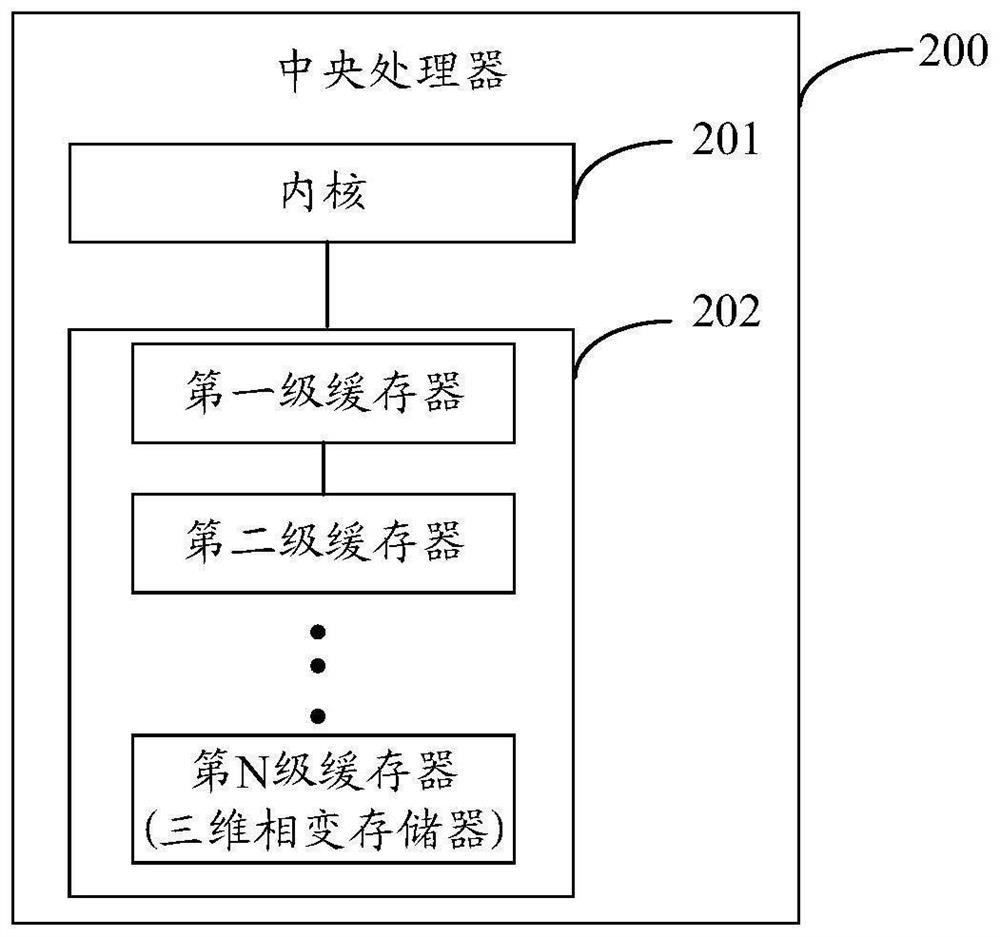
Central processing unit and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112928136AIncrease bit densityIncrease capacitySolid-state devicesDigital storagePhase-change memorySemiconductor structure
The embodiment of the invention provides a central processing unit (CPU) and a manufacturing method thereof. The CPU comprises a first semiconductor structure, and the first semiconductor structure comprises at least one core, first to (N-1) th levels of buffers in signal connection with the core, and a first bonding layer comprising a first conductive contact; wherein N is equal to three or four; The CPU also comprises a second semiconductor structure which comprises an Nth level buffer and a second bonding layer comprising a second conductive contact; the Nth level of buffer comprises a three-dimensional phase change memory; the three-dimensional phase change memory comprises a plurality of storage units; each storage unit comprises a first electrode layer, a gating layer, a second electrode layer, a phase change storage layer and a third electrode layer which are sequentially arranged in a stacked mode. The CPU also comprises a bonding combination layer which is located between the first semiconductor structure and the second semiconductor structure; wherein the first conductive contact is electrically connected with the second conductive contact at the bonding combination layer.
Owner:YANGTZE ADVANCED MEMORY INDUSTRIAL INNOVATION CENTER CO LTD
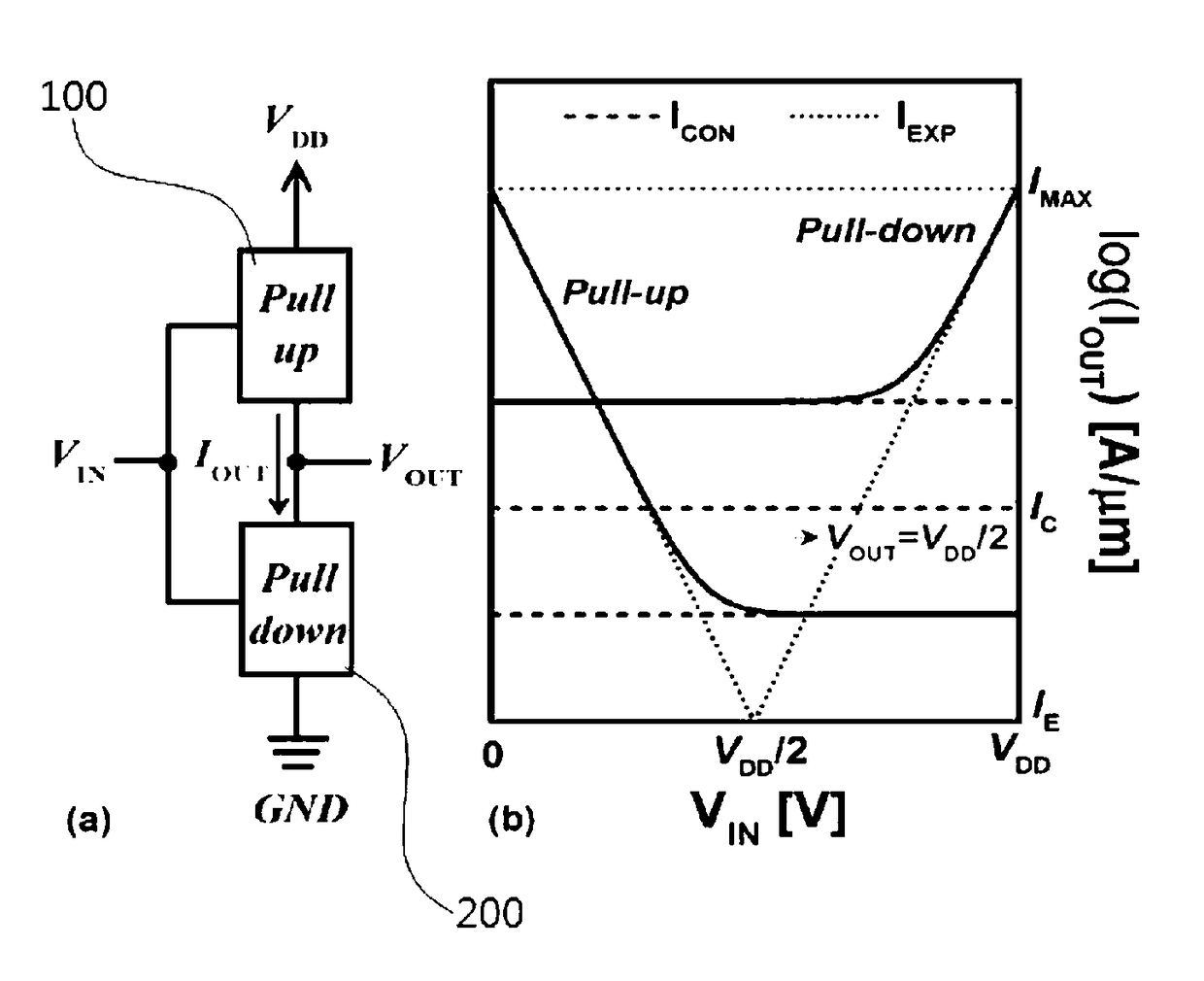
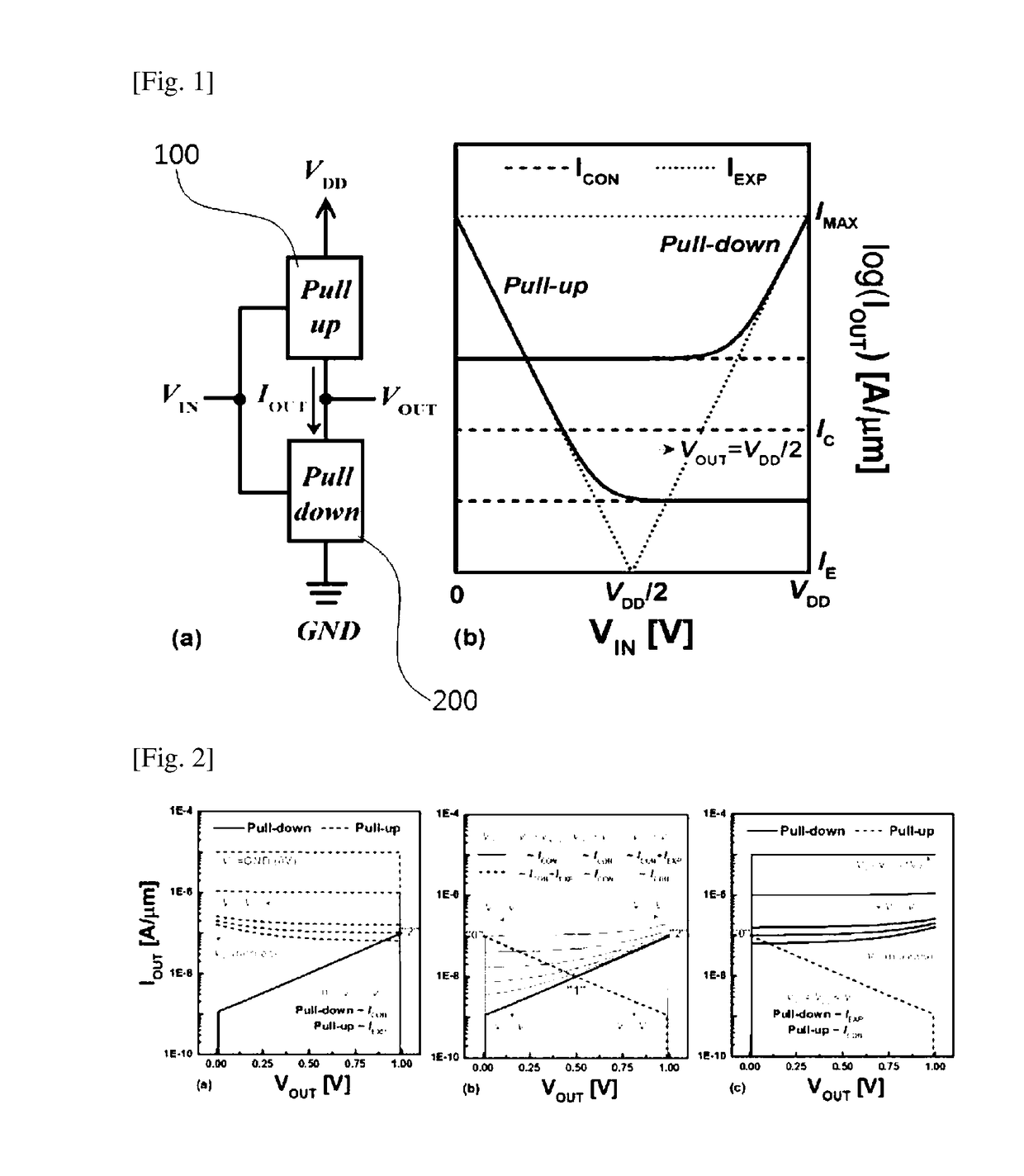
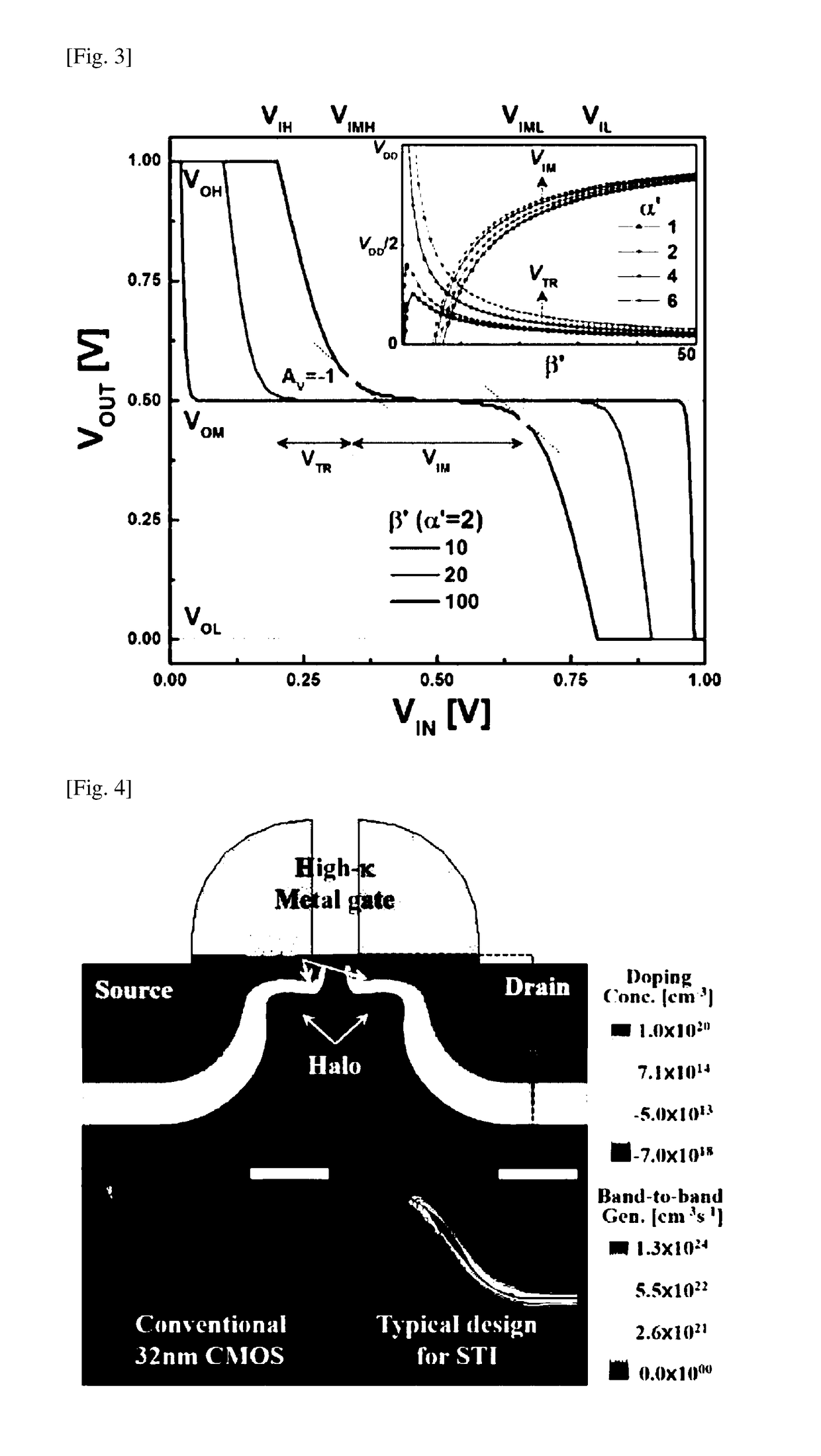
Ternary digit logic circuit
ActiveUS20180074788A1Increase bit densityReduce power densityPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringVoltage source
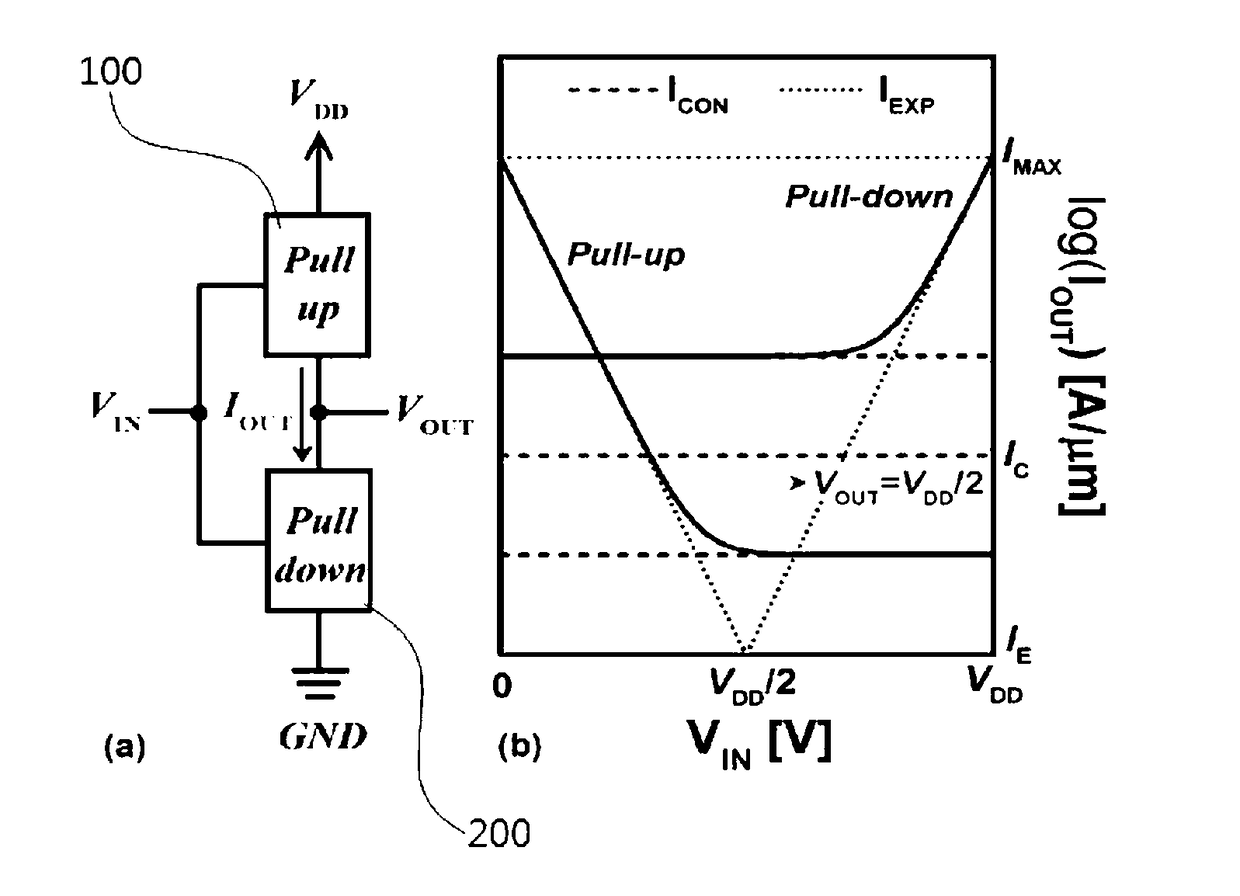
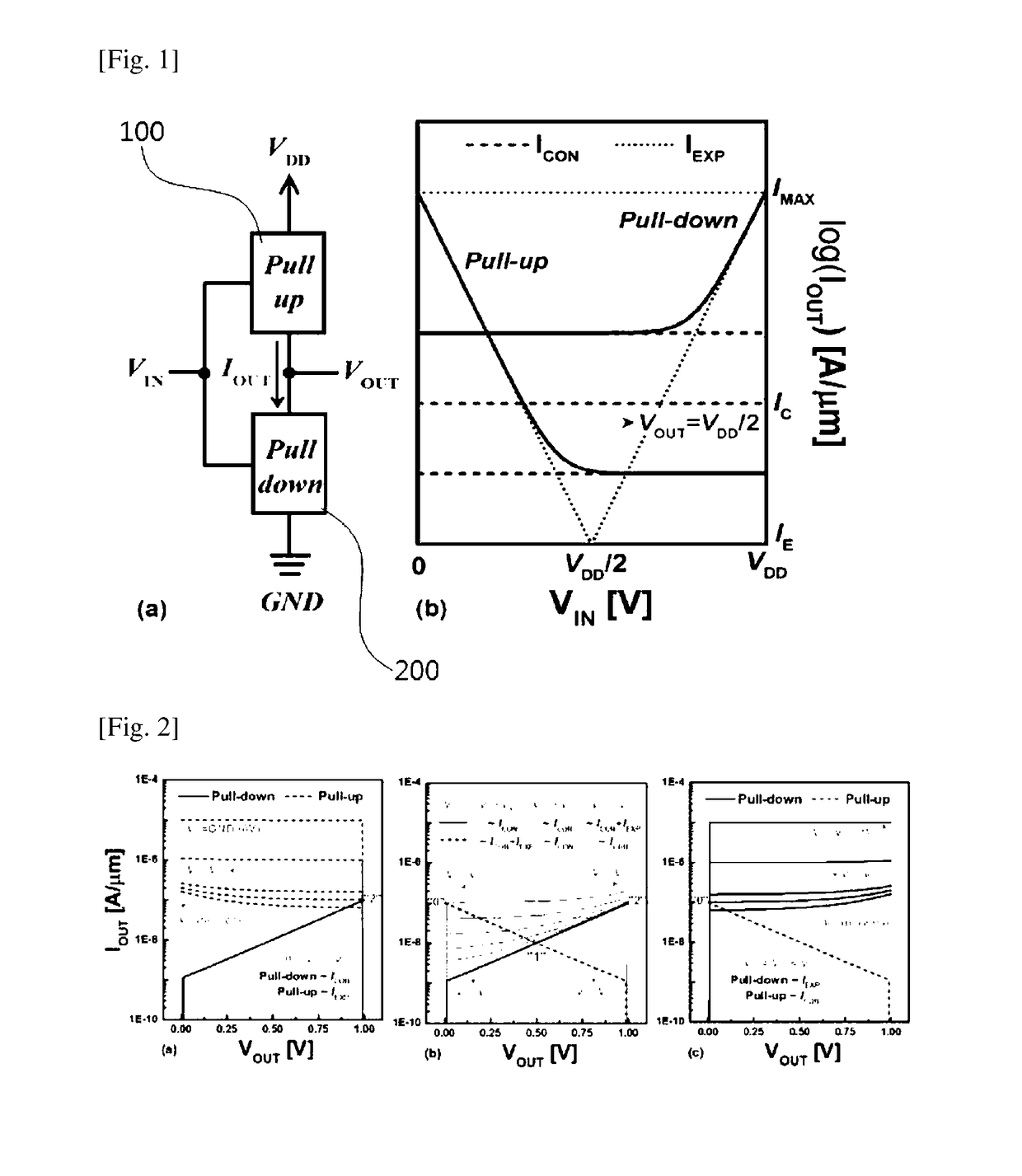
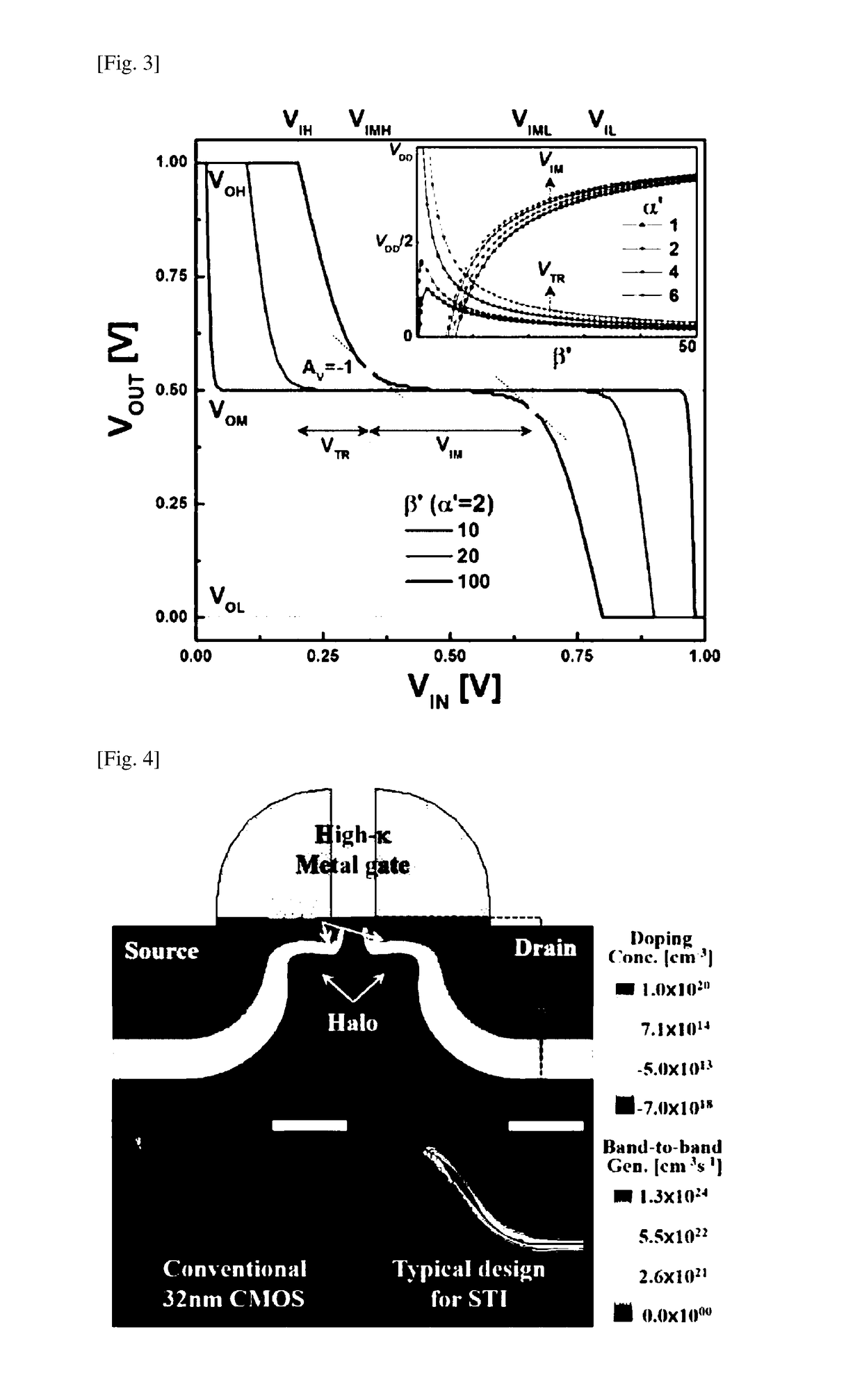
A ternary logic circuit according to the present invention includes a pull-up device (100) and a pull-down device (200) connected in series between power voltage sources (VDD and GND), and an input voltage (VIN) source and output voltage (VOUT) source. When both the pull-up device (100) and the pull-down device (200) are turned off by an input voltage (VIN), both the pull-up device (100) and the pull-down device (200) operate as simple resistors which are affected only by an output voltage (VOUT) and form a ternary digit (“1” state) through voltage division. When only one of the pull-up device (100) or the pull-down device (200) is turned on to allow a current to flow therethrough, VDD (“2” state) or GND (“0” state) is output as the output voltage (VOUT). Accordingly, a bit density can be remarkably increased.
Owner:UNIST ULSAN NAT INST OF SCI & TECH
Manufacturing method of three-dimensional memory
ActiveCN112018238AIncrease bit densityElectrical apparatusSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a manufacturing method of a three-dimensional memory. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps forming a three-dimensional memory with four layers of stacked memory unit modules, wherein the manufacturing method of each layer of memory unit module comprises the following steps forming a first address line material layer, forming a plurality ofmemory units on the first address line material layer, and forming a second address line material layer above the plurality of memory units, wherein the projection of the address line of the first address line material layer on a first plane is perpendicular to the projection of the address line of the second address line material layer on the first plane, the projections of the address lines ofthe first address line material layers in different memory unit modules on the first plane are partially overlapped, and the projections of the address lines of the second address line material layersin different memory unit modules on the first plane are partially overlapped.
Owner:YANGTZE ADVANCED MEMORY INDUSTRIAL INNOVATION CENTER CO LTD
Memory device and methods for fabricating and operating the same
ActiveCN101901810AIncrease bit densityDoes not affect layout sizeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical conductorEngineering
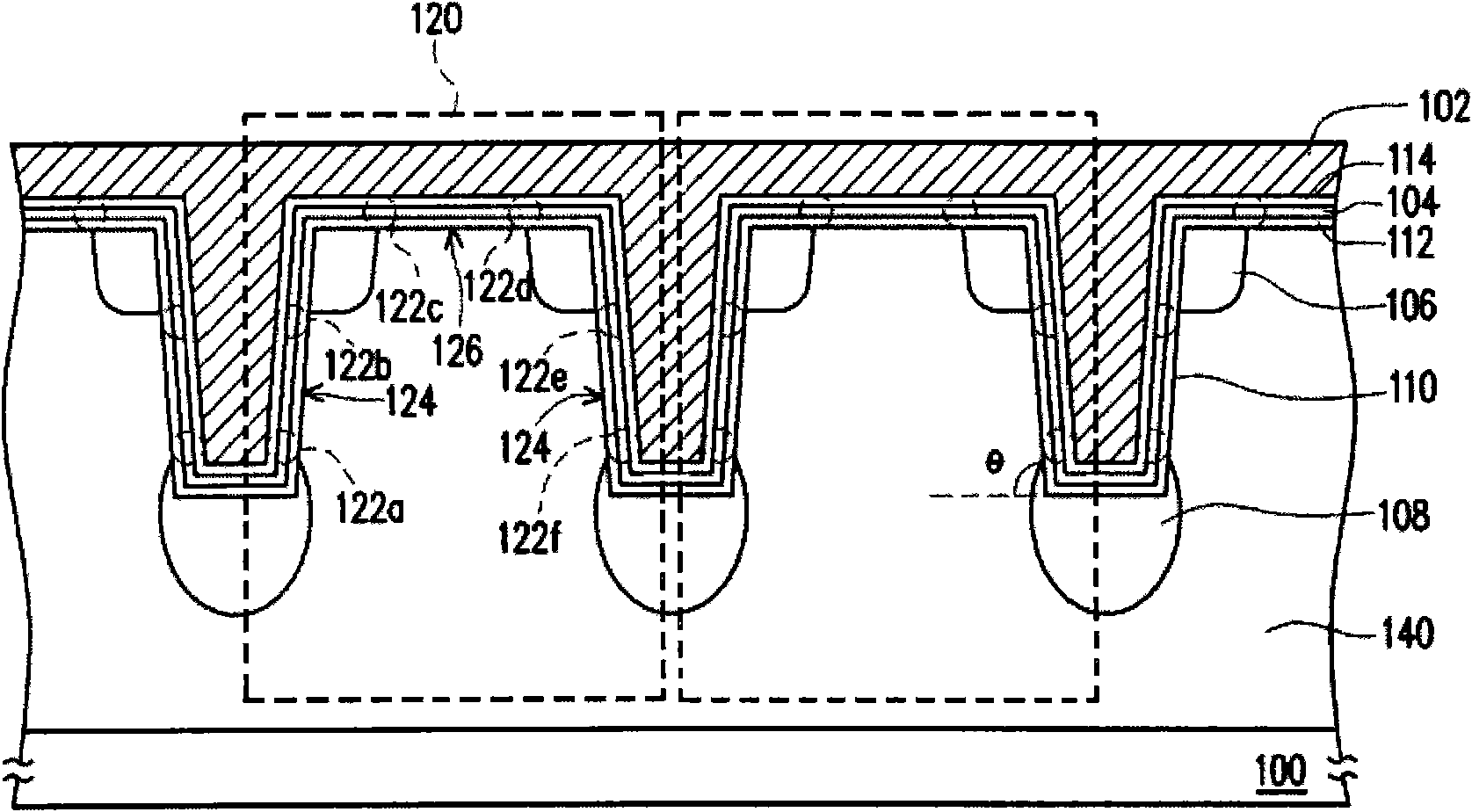
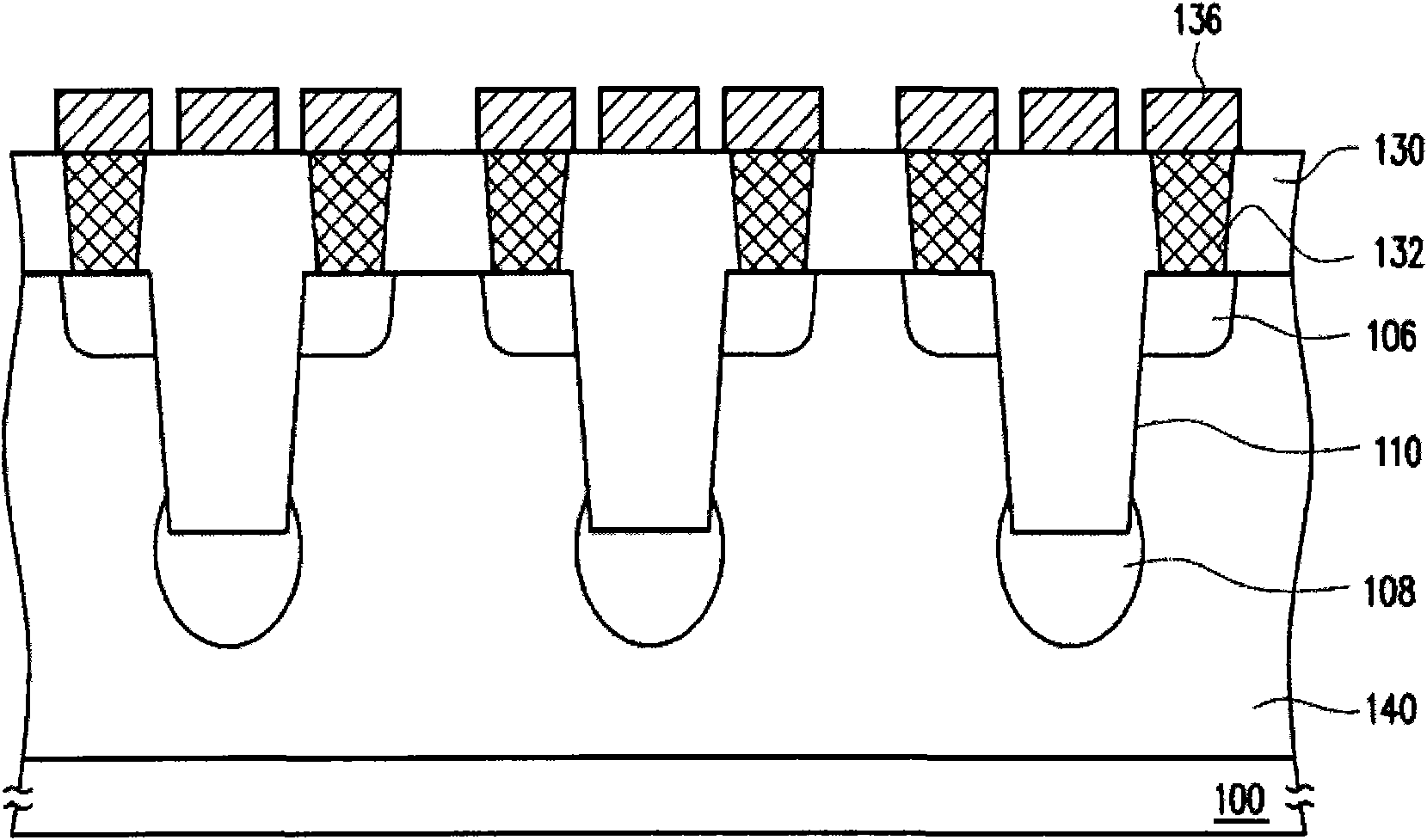
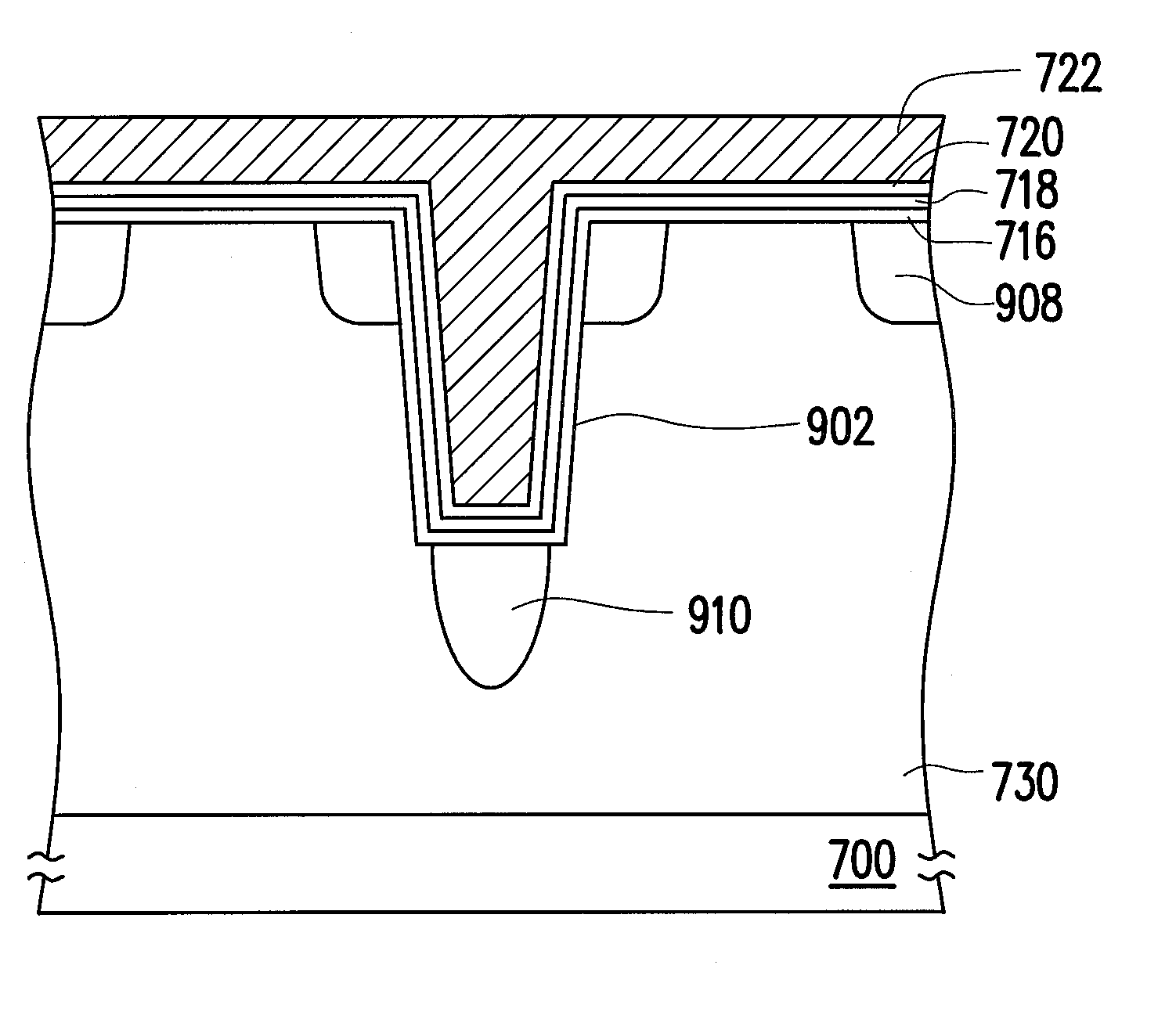
The invention relates to a memory device and method for fabricating and operating the same. The memory device is described, which includes a substrate, a conductive layer, a charge storage layer, a plurality of first doped regions and a plurality of second doped regions. The substrate has a plurality of trenches formed therein. The conductive layer is disposed on the substrate and fills the trenches. The charge storage layer is disposed between the substrate and the conductive layer. The first doped regions are configured in the substrate adjacent to both sides of an upper portion of each trench, respectively. The first doped regions between the neighbouring trenches are separated from each other. The second doped regions are configured in the substrate under bottoms of the trenches, respectively. The second doped regions and the first doped regions are separated from each other, such that each memory cell includes six physical bits. The the bit density is increased and the storage density is increased without effecting the layout size.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Ternary digit logic circuit
ActiveUS10133550B2Increase bit densityReduce power densityPulse generation by bipolar transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringVoltage source
A ternary logic circuit according to the present invention includes a pull-up device (100) and a pull-down device (200) connected in series between power voltage sources (VDD and GND), and an input voltage (VIN) source and output voltage (VOUT) source. When both the pull-up device (100) and the pull-down device (200) are turned off by an input voltage (VIN), both the pull-up device (100) and the pull-down device (200) operate as simple resistors which are affected only by an output voltage (VOUT) and form a ternary digit (“1” state) through voltage division. When only one of the pull-up device (100) or the pull-down device (200) is turned on to allow a current to flow therethrough, VDD (“2” state) or GND (“0” state) is output as the output voltage (VOUT). Accordingly, a bit density can be remarkably increased.
Owner:UNIST ULSAN NAT INST OF SCI & TECH
Memory device and methods for fabricating and operating the same
ActiveUS20100302845A1Increase the number of digitsIncrease bit densitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineering
The memory device is described, which includes a substrate, a conductive layer, a charge storage layer, a plurality of first doped regions and a plurality of second doped regions. The substrate has a plurality of trenches formed therein. The conductive layer is disposed on the substrate and fills the trenches. The charge storage layer is disposed between the substrate and the conductive layer. The first doped regions are configured in the substrate adjacent to both sides of an upper portion of each trench, respectively. The first doped regions between the neighbouring trenches are separated from each other. The second doped regions are configured in the substrate under bottoms of the trenches, respectively. The second doped regions and the first doped regions are separated from each other, such that each memory cell includes six physical bits.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Multi-layer stacks for 3D NAND extendibility
ActiveUS10700087B2Easy to eraseIncrease bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
Embodiments described herein relate to methods and materials for fabricating semiconductor devices, such as memory devices and the like. In one embodiment, a memory layer stack includes materials having differing etch rates in which one material is selectively removed to form an airgap in the device structure. In another embodiment, silicon containing materials of a memory layer stack are doped or fabricated as a silicide material. In another embodiment, a silicon nitride material is utilized as an interfacial layer between oxide containing and silicon containing layers of a memory layer stack.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Non-volatile transistor element including a buried ferroelectric material based storage mechanism
ActiveUS10176859B2Good flexibilityEffective approachRead-only memoriesDigital storageInformation densityTransistor
The present disclosure provides storage elements, such as storage transistors, wherein at least one storage mechanism is provided on the basis of a ferroelectric material formed in the buried insulating layer of an SOI transistor architecture. In further illustrative embodiments, one further storage mechanism is implemented in the gate electrode structure, thereby providing increased overall information density. In some illustrative embodiments, the storage mechanism in the gate electrode structure is provided in the form of a ferroelectric material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Divisible true dual port memory system supporting simple dual port memory subsystems
InactiveUS7269089B1Increase bit densityAvoid countingDigital storageLogic circuitsAudio power amplifierRandom access memory
A random access memory circuit and a method for configuring the same. The circuit includes a first array of memory cells including a first plurality of ports and a second plurality of ports, and a second array of memory cells including a third plurality of ports and a fourth plurality of ports. Additionally, the circuit includes a plurality of switches connected to the first plurality of ports and the third plurality of ports respectively or connected to the second plurality of ports and the fourth plurality of ports respectively. Moreover, the circuit includes a plurality of sense amplifiers and a plurality of write drivers.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Non-volatile transistor element including a buried ferroelectric material based storage mechanism
ActiveUS20180322912A1Good flexibilityEffective approachRead-only memoriesDigital storageEngineeringInformation density
The present disclosure provides storage elements, such as storage transistors, wherein at least one storage mechanism is provided on the basis of a ferroelectric material formed in the buried insulating layer of an SOI transistor architecture. In further illustrative embodiments, one further storage mechanism is implemented in the gate electrode structure, thereby providing increased overall information density. In some illustrative embodiments, the storage mechanism in the gate electrode structure is provided in the form of a ferroelectric material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and Structure for Integrated High Density Memory Device
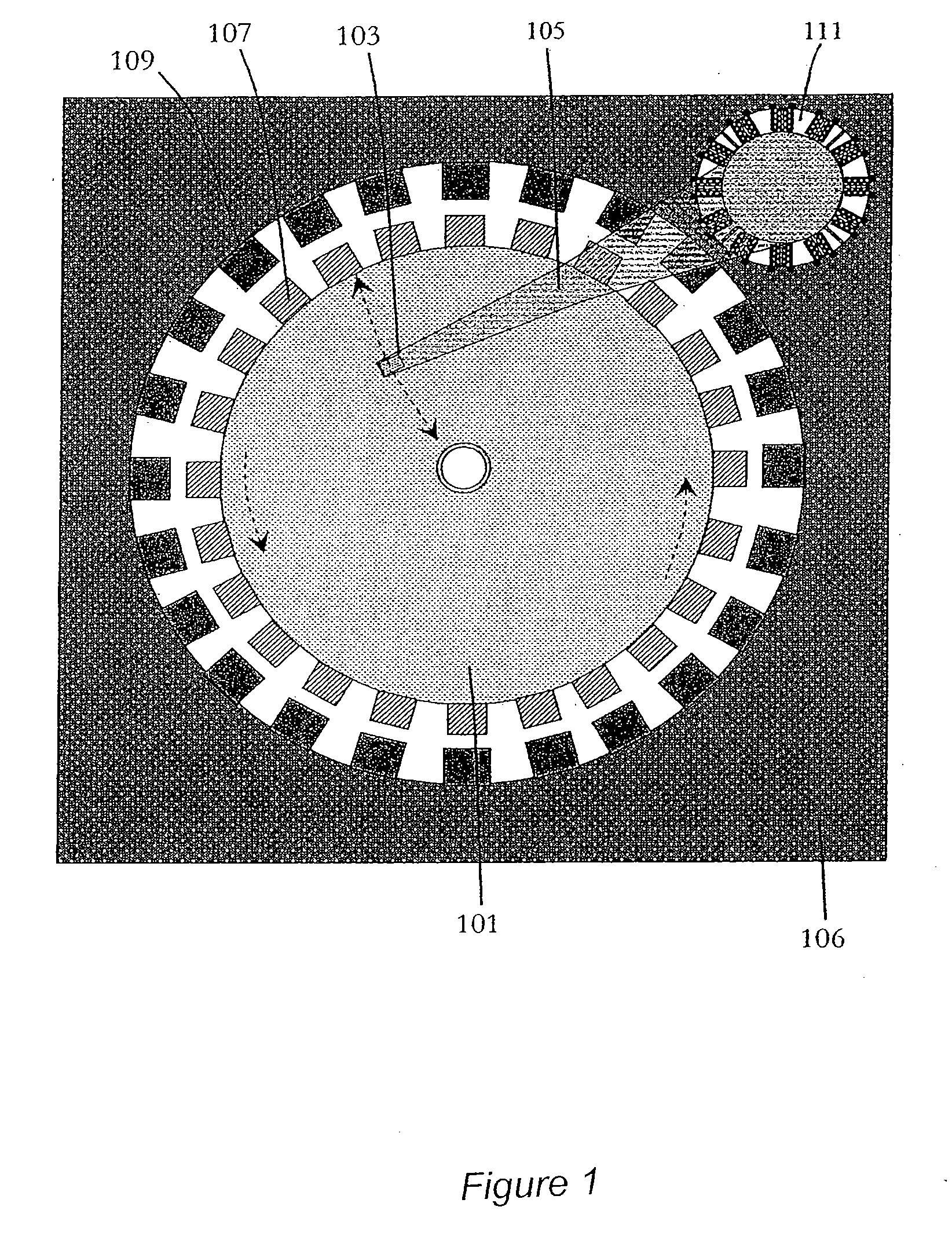
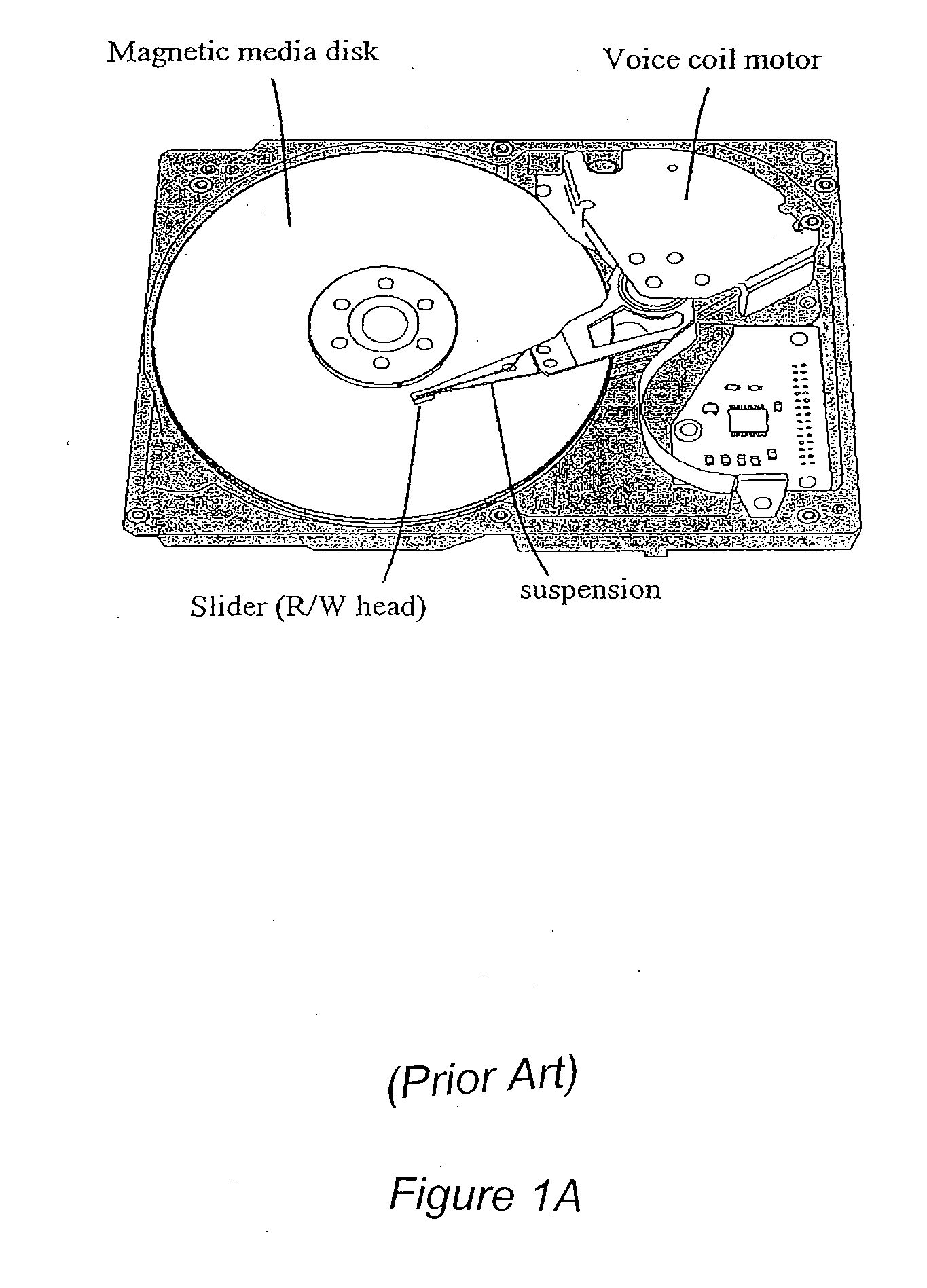
InactiveUS20070097551A1Easy to useHigh mechanical bandwidthNanoinformaticsRecord information storageHard disc driveHigh density
The present invention provides a method and device for fabricating high density memory device. Similar to a Hard Disk Drive (HDD), the integrated memory device is consisted with a rotating media plate and a Read / Write (R / W) head on a movable suspension. Unlike HDD where the media plate is coupled to a motor, the media plate is micro fabricated on a semiconductor substrate and is also a motor which is actuated and rotated by electrostatic forces. The head suspension is also micro fabricated and anchored to an electrostatic comb drive micro actuator. Control IC can also be integrated on-chip with the integrated memory device as well as acceleration sensing devices such as MEMS accelerator for anti-shock measures. The integrated disk storage device is fabricated by conventional semiconductor and MEMS fabrication process technology.
Owner:YANG XIAO
Optical recording material and optical recording medium
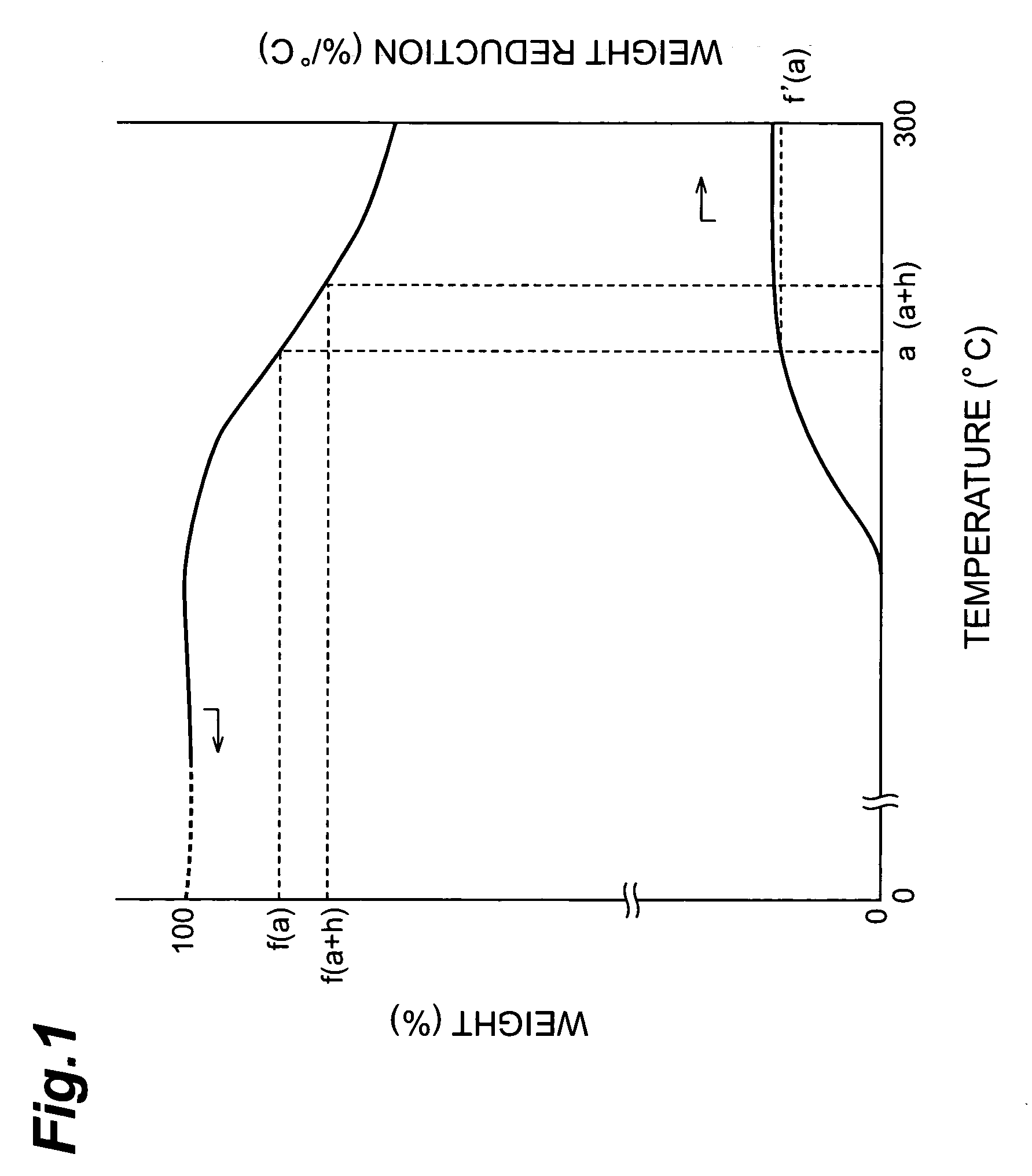
InactiveUS20060141203A1Shortening recording timeHigh bit densityMonoazo dyesMethine/polymethine dyesPhotochemistryMetal
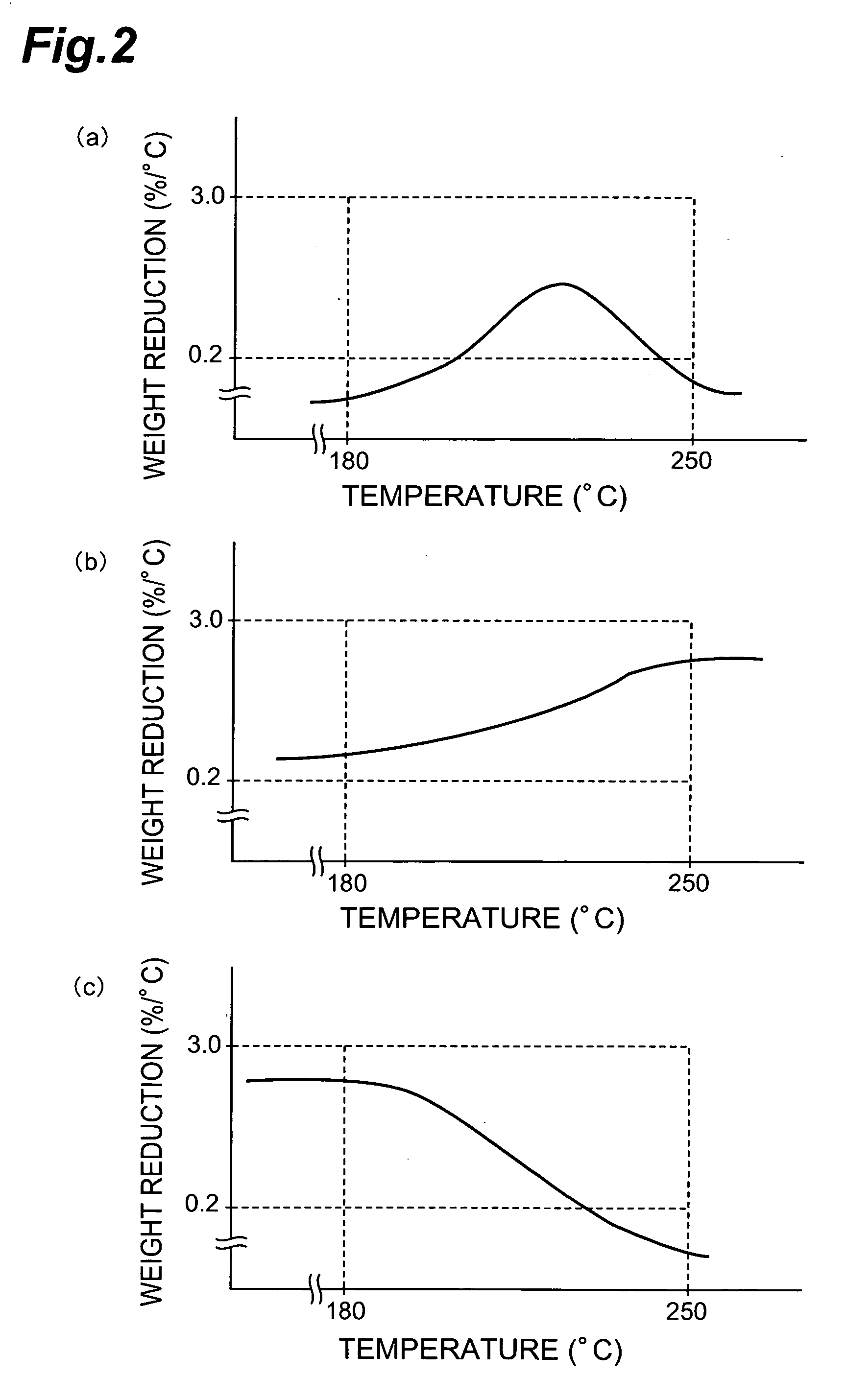
The optical recording material of the invention is an optical recording material used for an optical recording medium capable of recording information by irradiation of light, the optical recording medium being an optical recording medium which records information at a linear speed of at least 14 m / sec, wherein the dye component in the optical recording material comprises at least one type of chelate compound of an azo compound and a metal, and when the dye component is used as a sample for thermogravimetry in an inert gas atmosphere, the dye component sample exhibits a maximum weight reduction of 0.2-3.0% / ° C. at 180-250° C.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
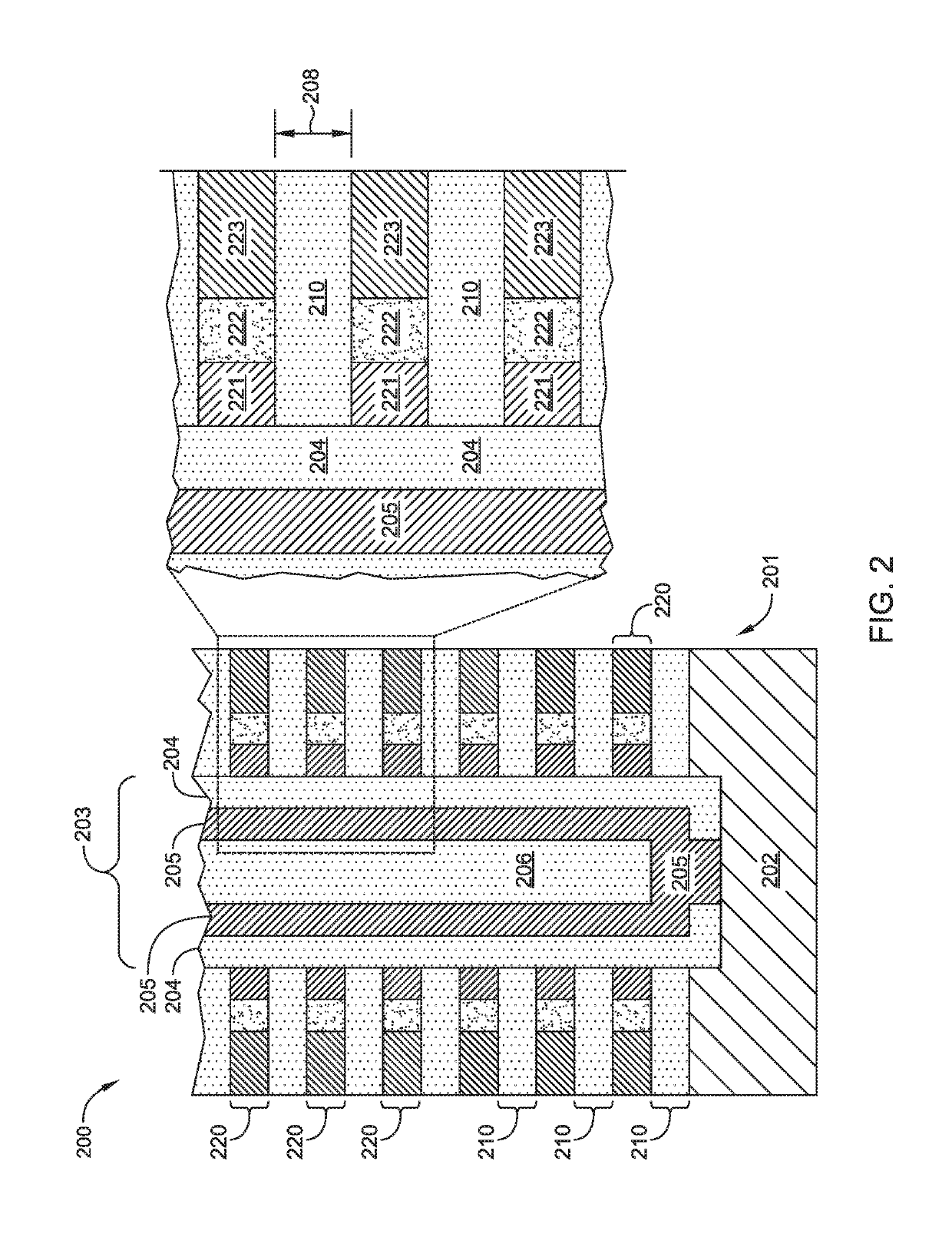
Formation method of memory device
ActiveCN105762115AReduce space areaIncrease bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOccupancy rateDevice form
The invention relates to a formation method of a memory device. The method includes the following steps that: a multi-layer overlapped composite layer is formed on the surface of a substrate, the surface of the composite layer is provided with a mask layer, the composite layers include insulating layers and device layers arranged on the surfaces of the insulating layers; a strengthened layer is formed on a part of the side wall surface of the mask layer, and the strengthened layer exposes the top surface and a part of the side wall surface of the mask layer; with the strengthened layer adopted as a mask, the exposed side wall surface of the mask layer is etched, so that a part of the surface of the composite layer at the top is exposed; with the mask layer and the strengthened layer adopted as a mask, the exposed composite layer is etched, the etching thickness of the composite layer is greater than or equal to the thickness of a single device layer; the steps in which the side wall of the mask layer and the composite layer are etched are repeated for once or by a plurality of times until the size of the projection pattern of the plurality of device layers is gradually decreased from the bottom layer to the top layer along at least one direction, so that the plurality of device layers can form a steeped structure which is shrunk gradually from the bottom layer to the top layer. The memory device formed by the method of the invention has the advantages of low space occupancy rate, high bit density and low bit cost.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Central processing unit and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN113096706AImprove performanceIncrease bit densityElectrical apparatusDigital storagePhase-change memoryEmbedded system
The embodiment of the invention provides a central processing unit (CPU) and a manufacturing method thereof. The CPU comprises at least one kernel, a multi-stage buffer in signal connection with the kernel; wherein the buffers of different levels in the multi-level buffer comprise storage unit layers of different layers in the phase change memory; the phase change memory comprises a plurality of stacked memory unit layers; the storage unit layer comprises a plurality of storage units. Different levels of caches in the multi-level caches in the CPU adopt different layers of storage unit layers in the same phase change memory; wherein the final size of the CPU can be obviously reduced due to the smaller size of the phase change memory, so that the delay between a CPU kernel and each level of buffer is reduced, and more data can be exchanged through the multi-level buffer due to the higher capacity of the phase change memory, so that the use amount of the cached data is increased. The CPU provided by the embodiment of the invention has better performance.
Owner:YANGTZE ADVANCED MEMORY INDUSTRIAL INNOVATION CENTER CO LTD
Method and apparatus for joint adaptation of two-/multi- dimensional equalizer and partial response target
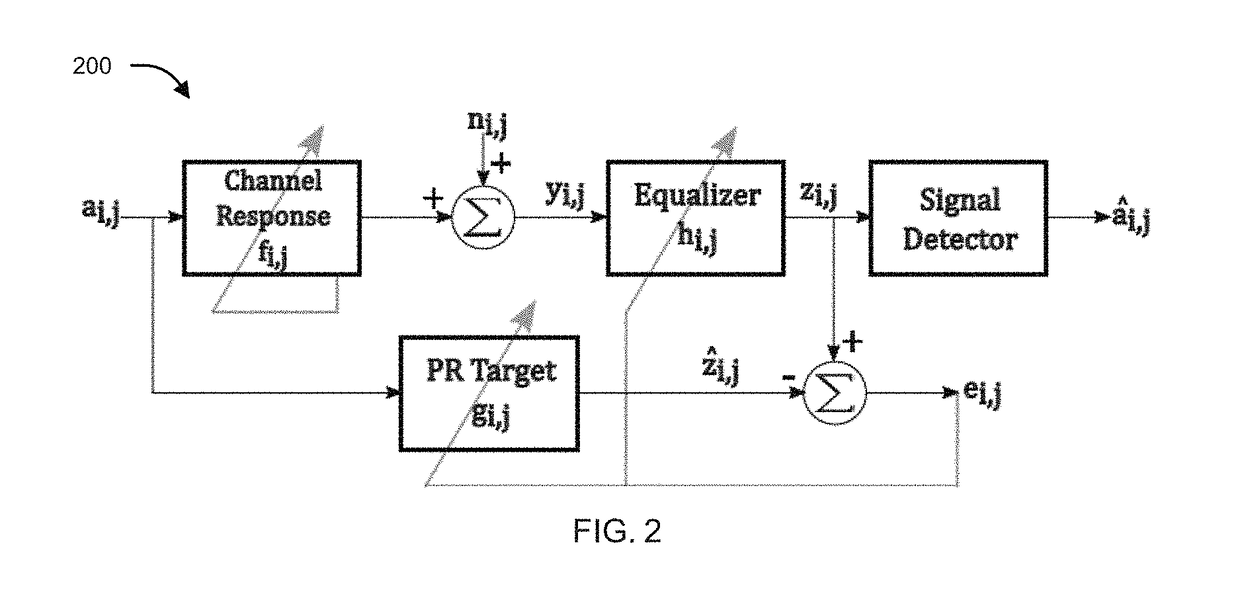
ActiveUS20180018997A1Increase bit densitySimple designModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageAlgorithmData recording
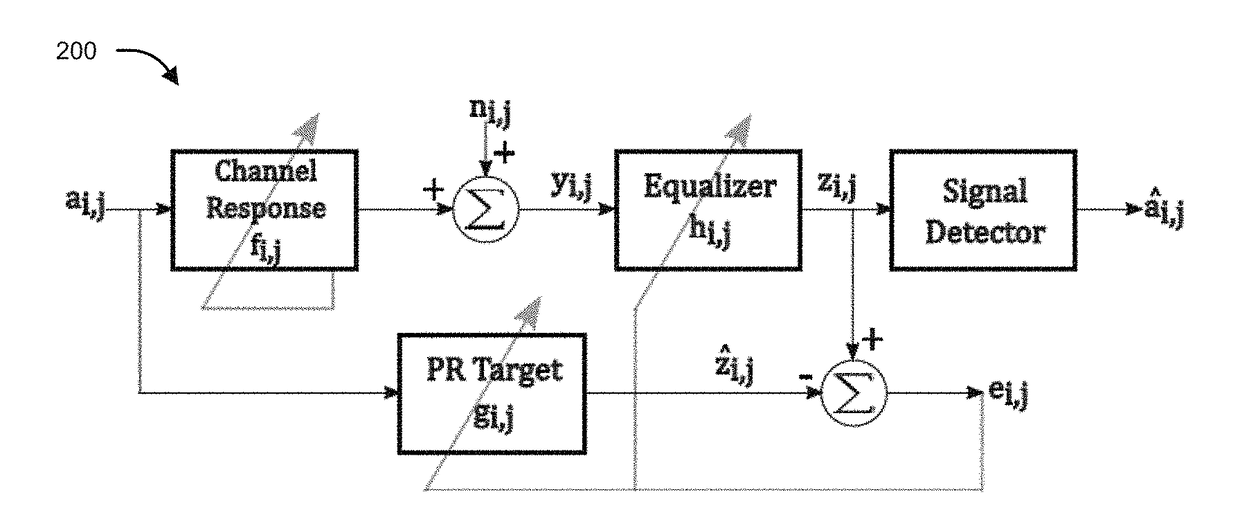
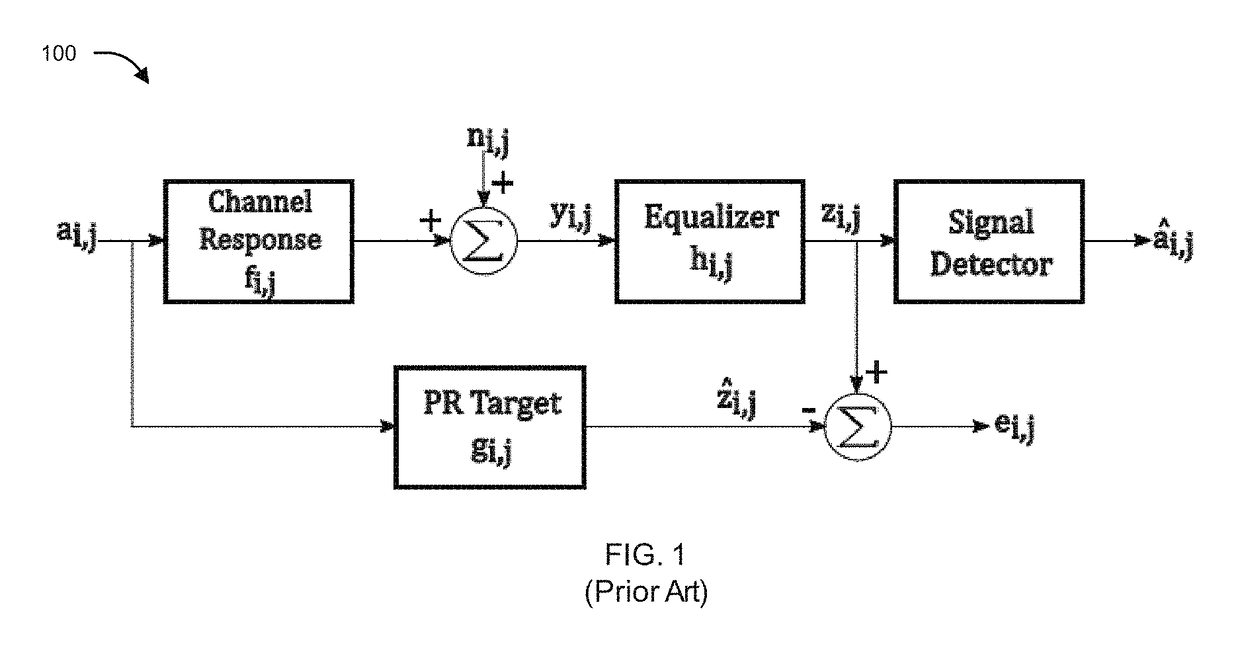
The present disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for processing of multi-dimensional readback signal from magnetic recording or optical, physical data recording so as to reduce / control Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) and noise within acceptable limits. The method is based on Partial Response Maximum Likelihood (PRML) detection and takes care of time varying channel conditions. In an embodiment, the filter coefficients of both the equalizer and the partial response (PR) target are jointly adapted to account for the channel condition for both separable and non-separable targets thus reducing signal detection complexity. In an aspect, the disclosure provides an apparatus that incorporates an adaptation engine along with the equalizer and the PR target that updates filter coefficients of both the equalizer and the PR target following the formulated mathematical equations.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE
Three-dimensional memory having four stacked layers
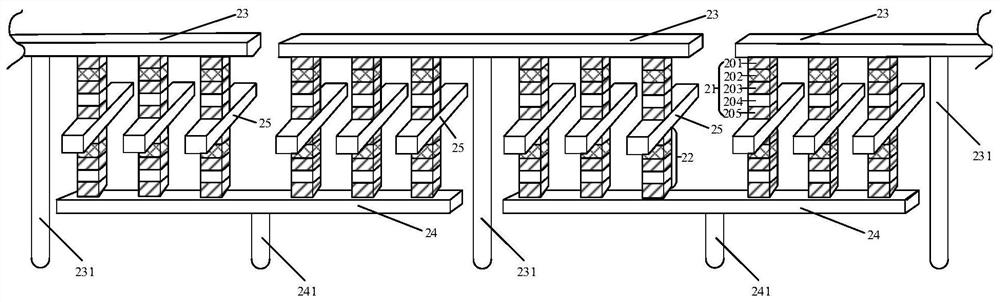
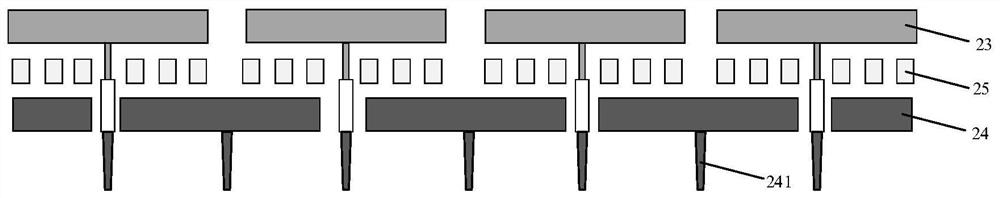
The embodiment of the invention provides a three-dimensional memory with four stacked layers. The three-dimensional memory comprises at least one memory cell array block; wherein the memory cell arrayblock comprises a first bit line layer, a second bit line layer and a third bit line layer which are sequentially arranged from top to bottom and are parallel to one another, and the bit lines of thebit line layers are parallel to each other, and the projections of the bit lines of the bit line layers on the first plane are partially overlapped; a first word line layer between the first bit linelayer and the second bit line layer; a second word line layer between the second bit line layer and the third bit line layer; wherein the word lines of each word line layer are parallel to each other, and the projection of the word line of each word line layer on the first plane is vertical to the projection of the bit line of the first bit line layer on the first plane; and four memory cell layers which are respectively positioned between two adjacent bit line layers and word line layers.
Owner:YANGTZE ADVANCED MEMORY INDUSTRIAL INNOVATION CENTER CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com