Artificial carrier system with site-specific mutagenesiss and site-specific mutagenesis method
A technology of artificial systems and regulatory elements, applied in botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve the problem of low editing efficiency of GC and AC at target sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] 1. Construction of vectors
[0048] Through the routine operation of DNA cloning, the constitutive promoter Ubi-p (SEQ ID No.17), SEQ ID No.8, and Nos terminator (SEQ ID No.20) of maize were cloned in order from 5' to 3' onto the pUbi-ccdB vector, named pUbi:rBE5, and used for transgenic rice plant research.
[0049] The OsU6-p promoter (SEQ ID No.18), two BsaI restriction sites (SEQ ID No.14), sgRNA sequence (SEQ ID No.13), (T)8 terminator (SEQ ID No. 21), japonica rice U6 snRNA promoter (SEQ ID No.19), two BtgZI restriction sites (SEQ ID No.15), sgRNA sequence (SEQ ID No.13), (T)8 terminator (SEQ ID No. .21) Cloning into the multiple cloning site of the pENTR4 vector in the order from 5' to 3', named pENTR4:sgRNA. The two BtgZI or two BsaI restriction sites can be used to clone the target sequence of the specific gene in the following example 2 respectively.
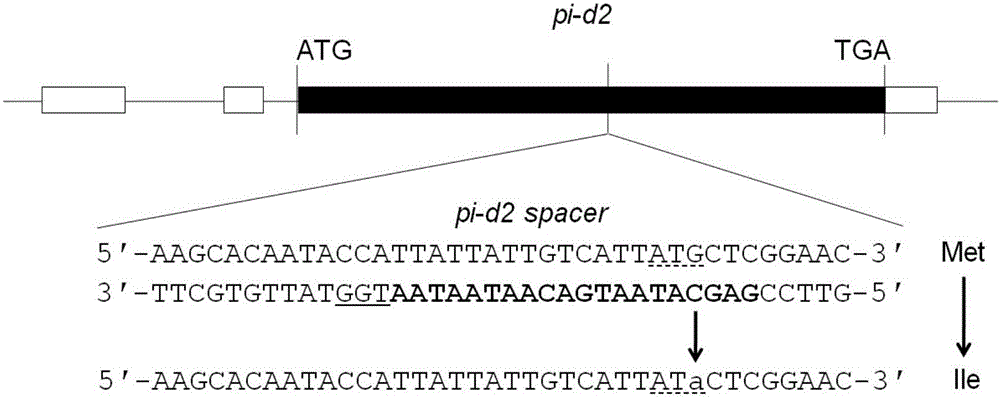
[0050] 2. Design and cloning of recognition sequence for Pi-d2 gene.
[0051] Transcript sequences and ge...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Through the routine operation of DNA cloning, the constitutive promoter Ubi-p (SEQ ID No.17), SEQ ID No.28 and Nos terminator (SEQ ID No.20) of maize were cloned in order from 5' to 3' onto the pUbi-ccdB vector, named pUbi:rBE3. Linearize pENTR4:gPi-d2 with AatII enzyme digestion, and then transfer the targeting sequence transcription element into pUbi:rBE3 through Gateway reaction, and obtain the final vector pUbi:rBE3-gPi-d2, which is used for transgenic rice plant research . Its genome target site sequence for Pi-d2 is the same as that in Example 1, which is 5'-TTATTATTGTCATTATGCTC-3' (SEQ ID No. 24). The nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.28 encodes the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.29.
[0068] Other operations are the same as in Example 1.
[0069] The edited plants that obtained Pi-d2 were not screened in the transgenic plant population.
[0070] The present application obtained transgenic rice containing rBE3 (pUbi:rBE3-gPi-d2) and rRE5 (pUbi:rB...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com