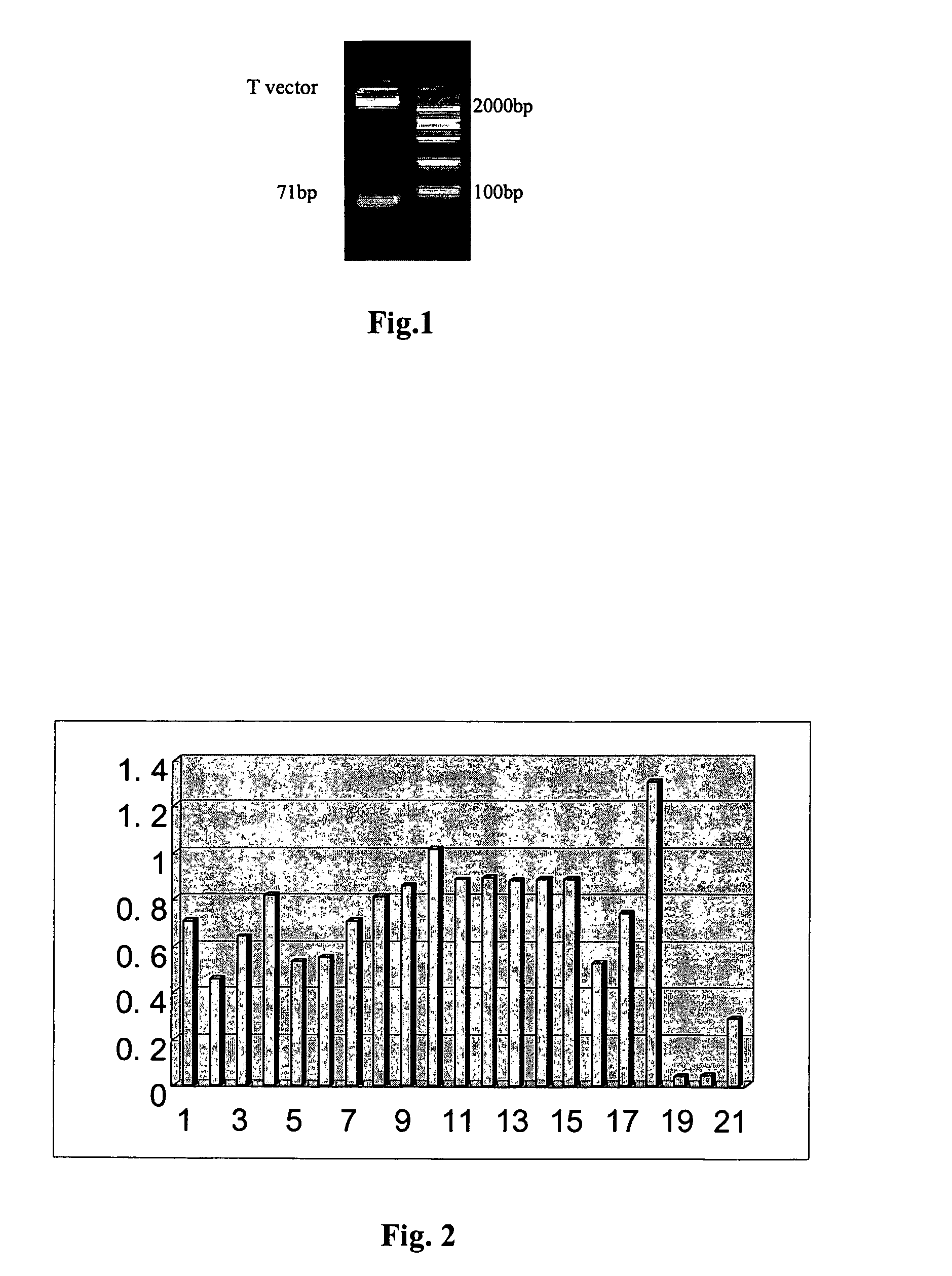
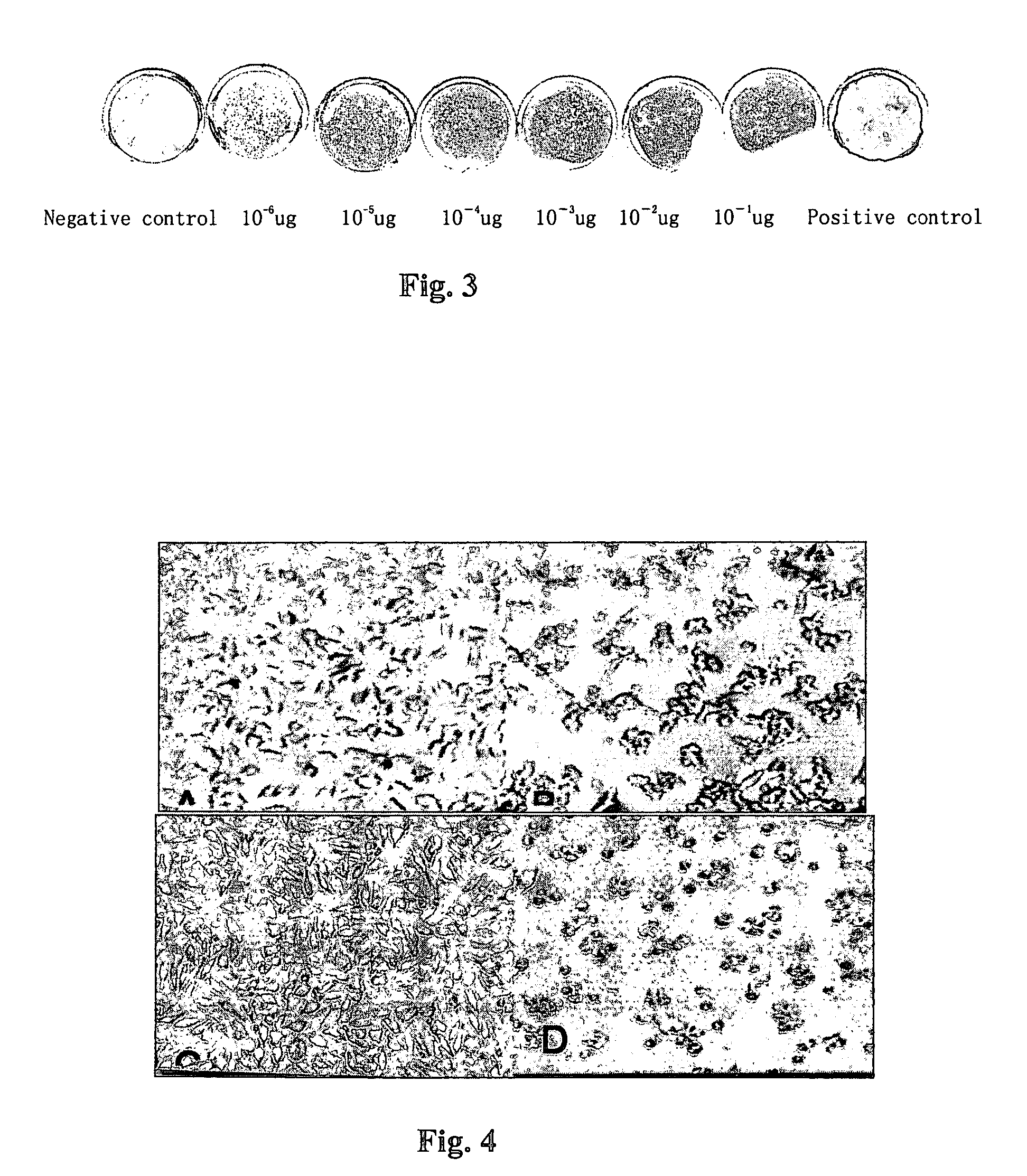
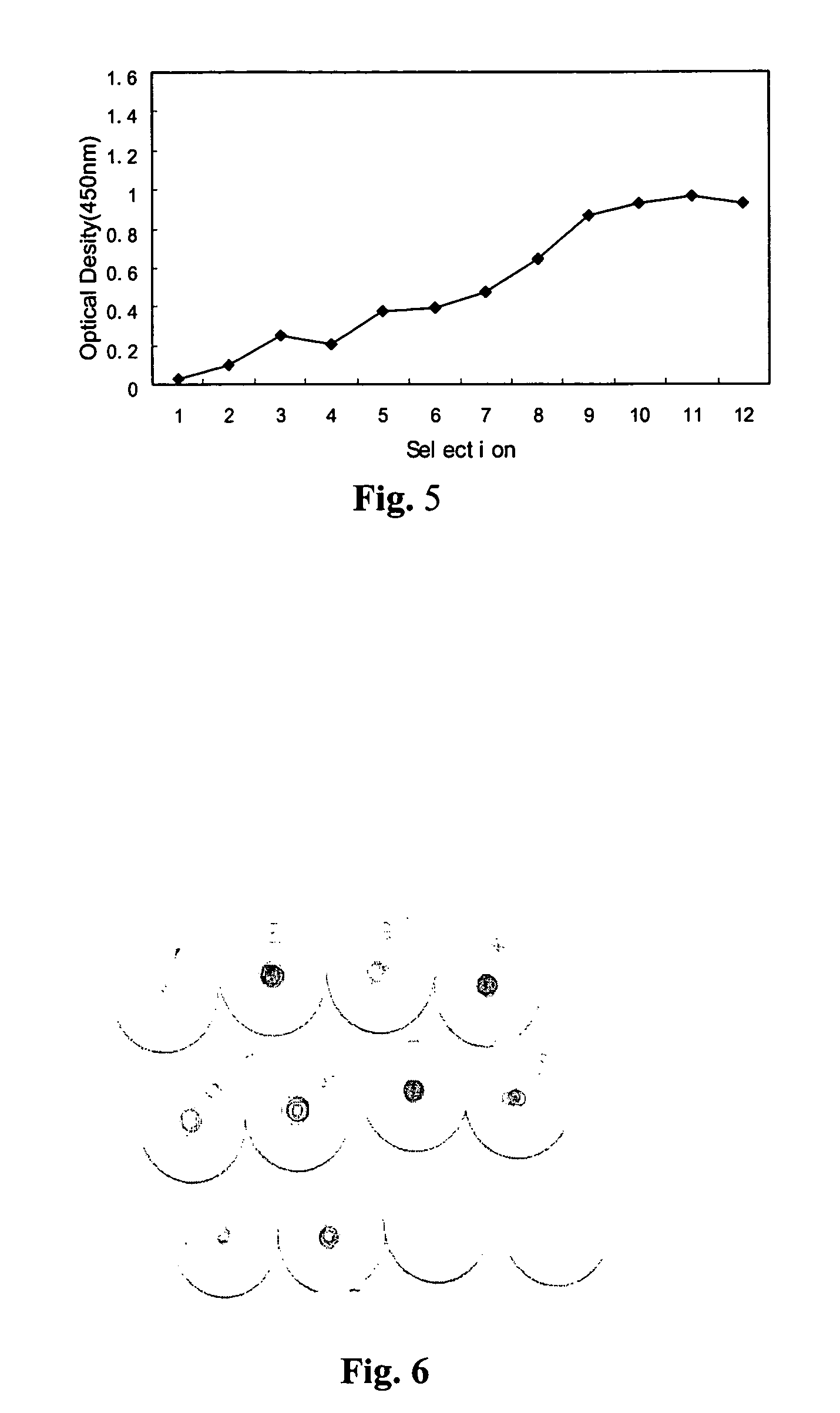
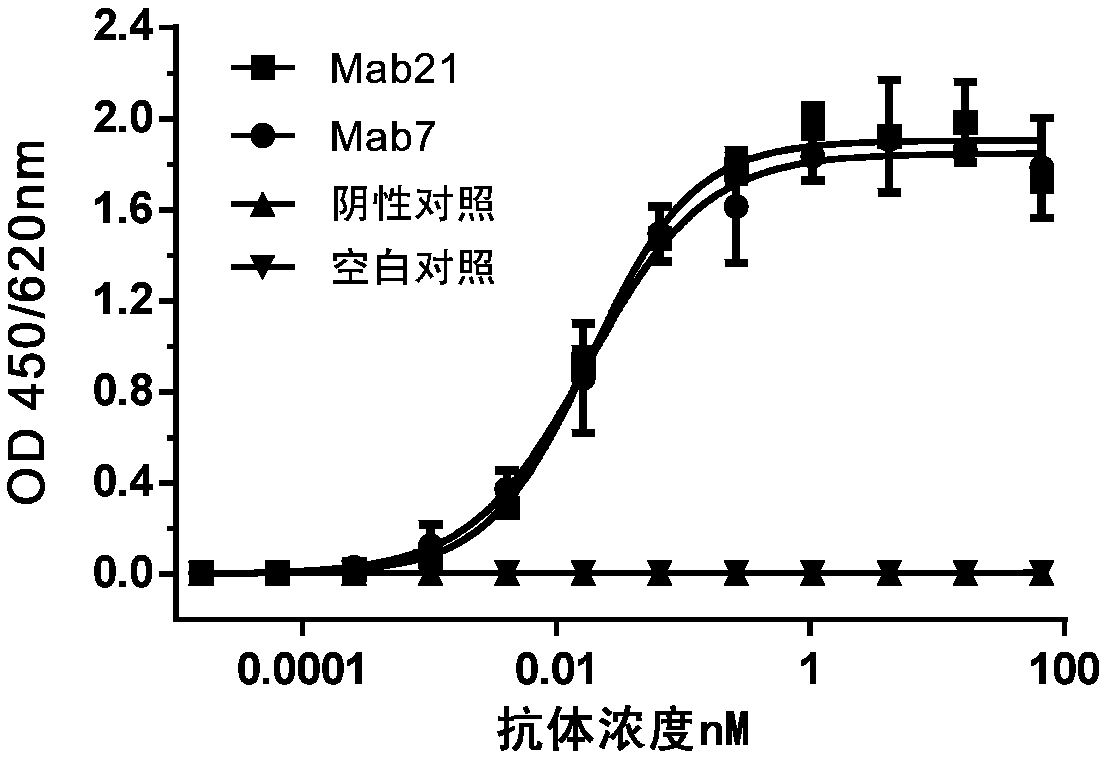
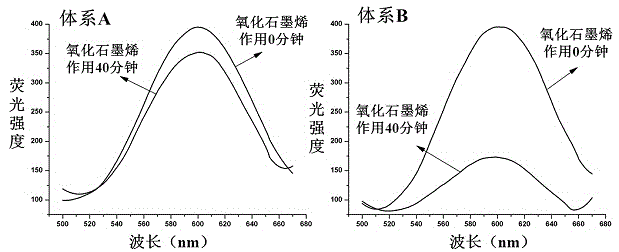
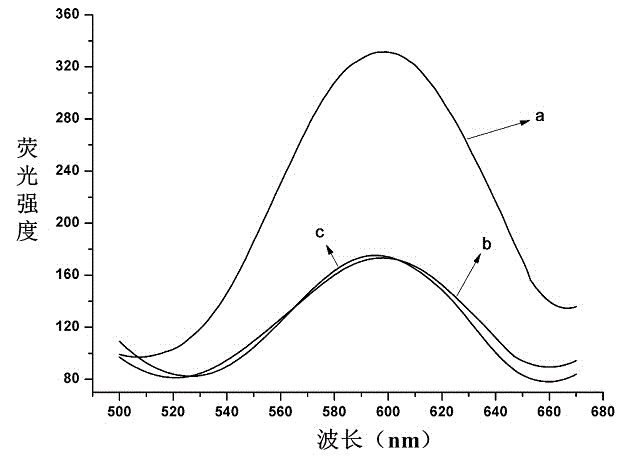
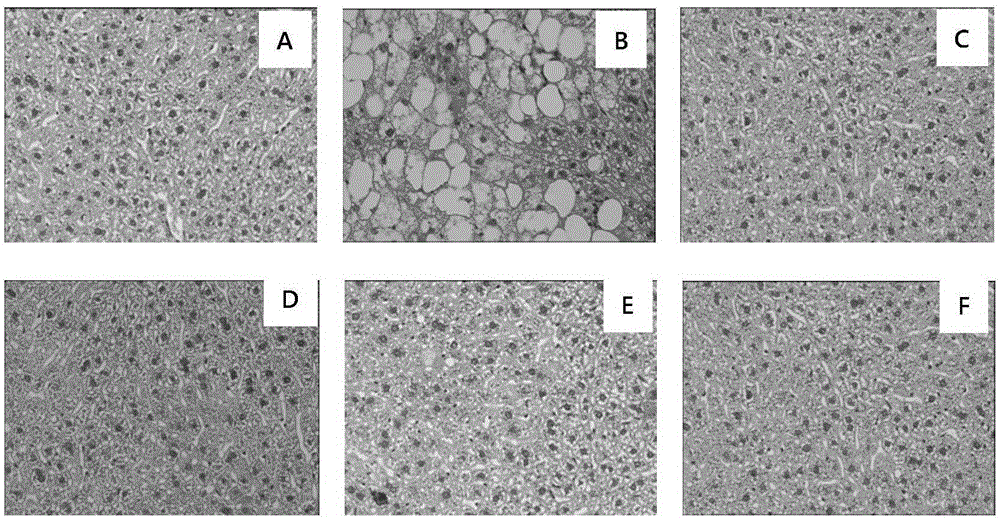
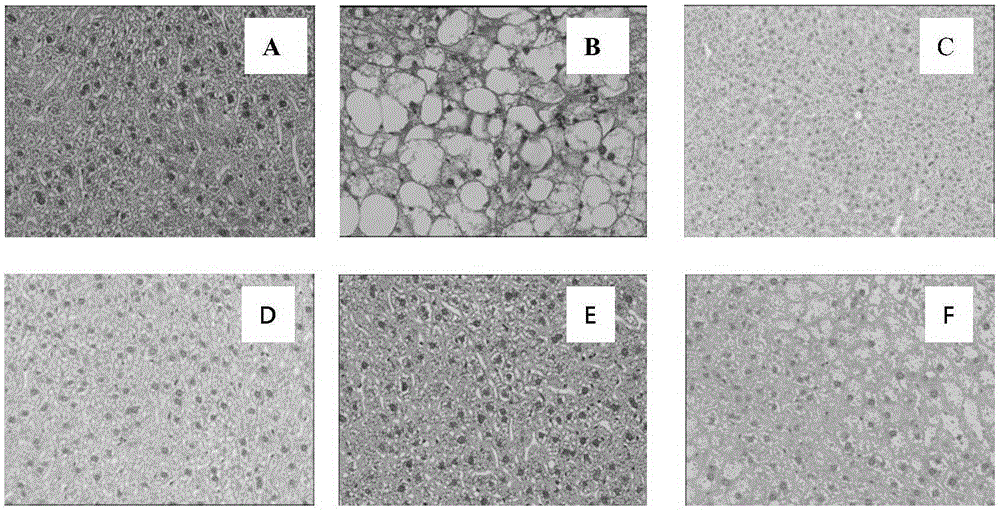
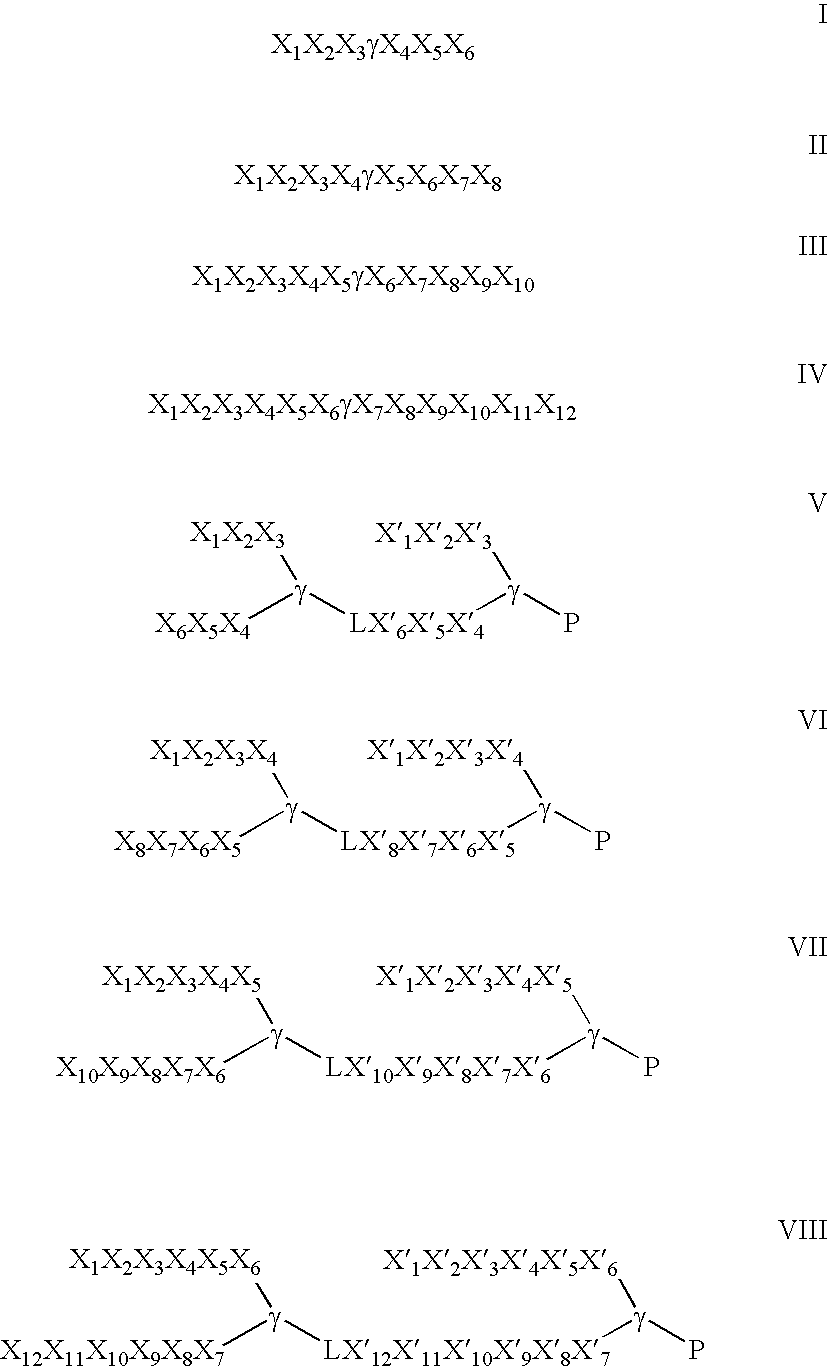
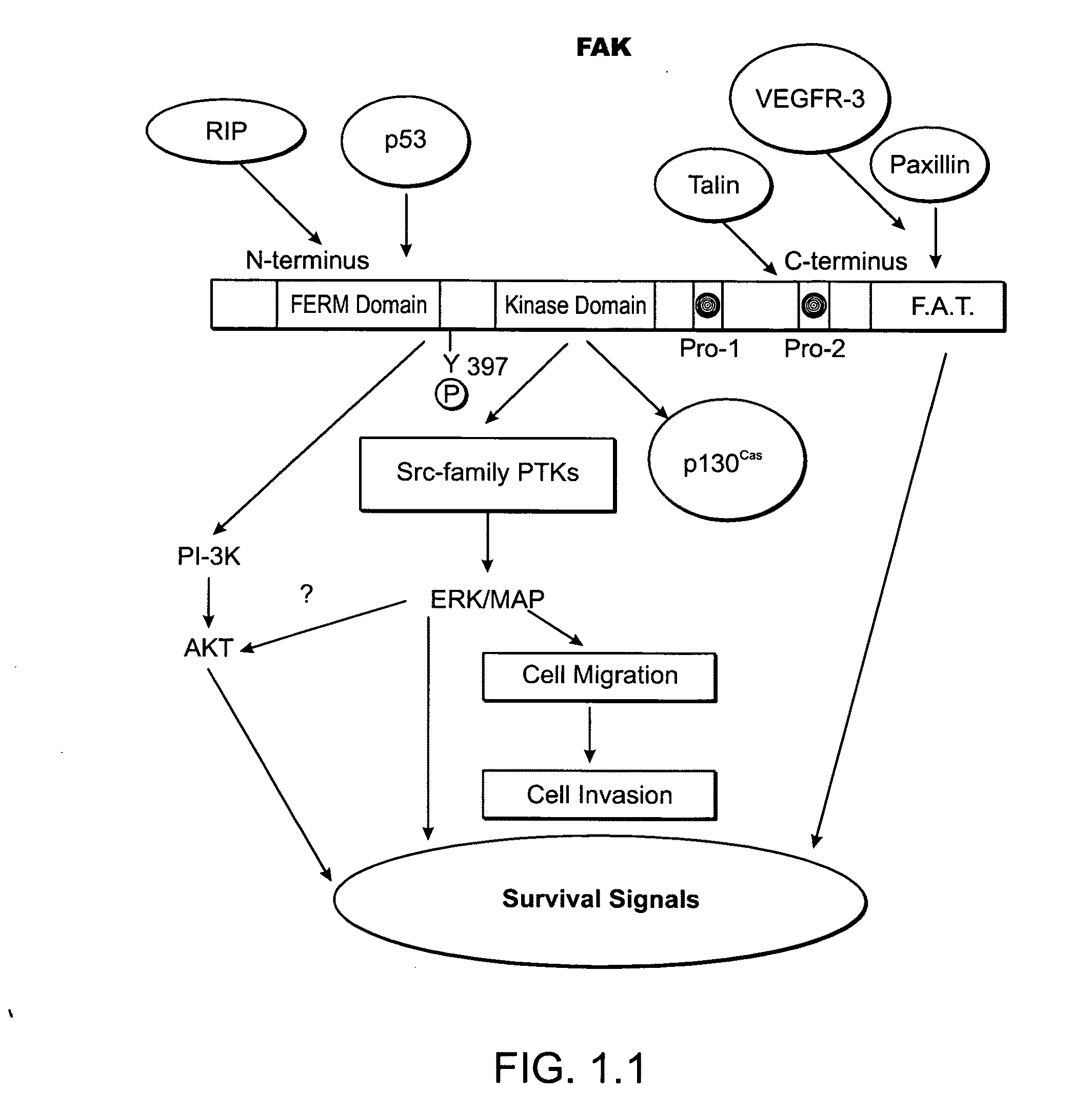
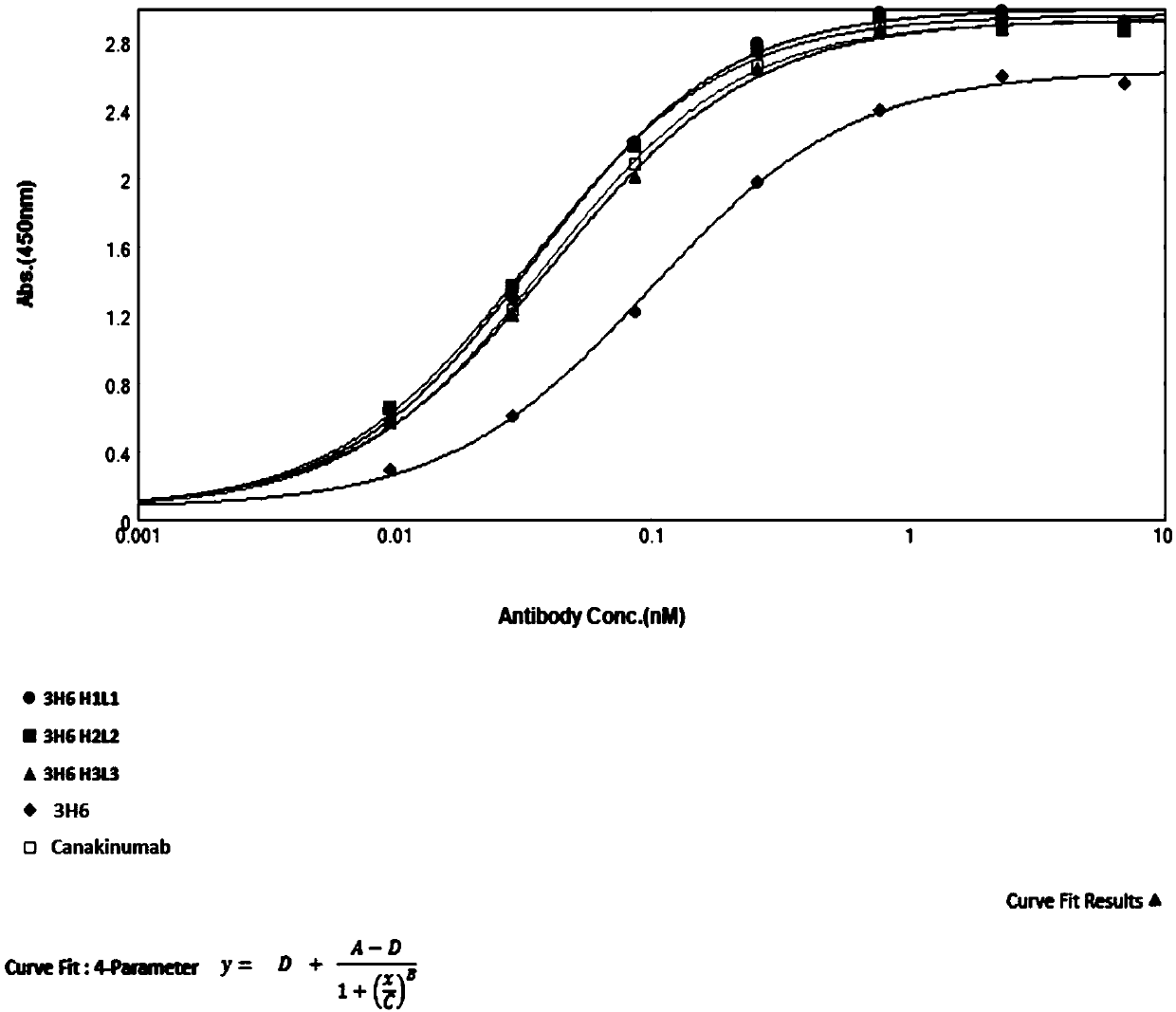
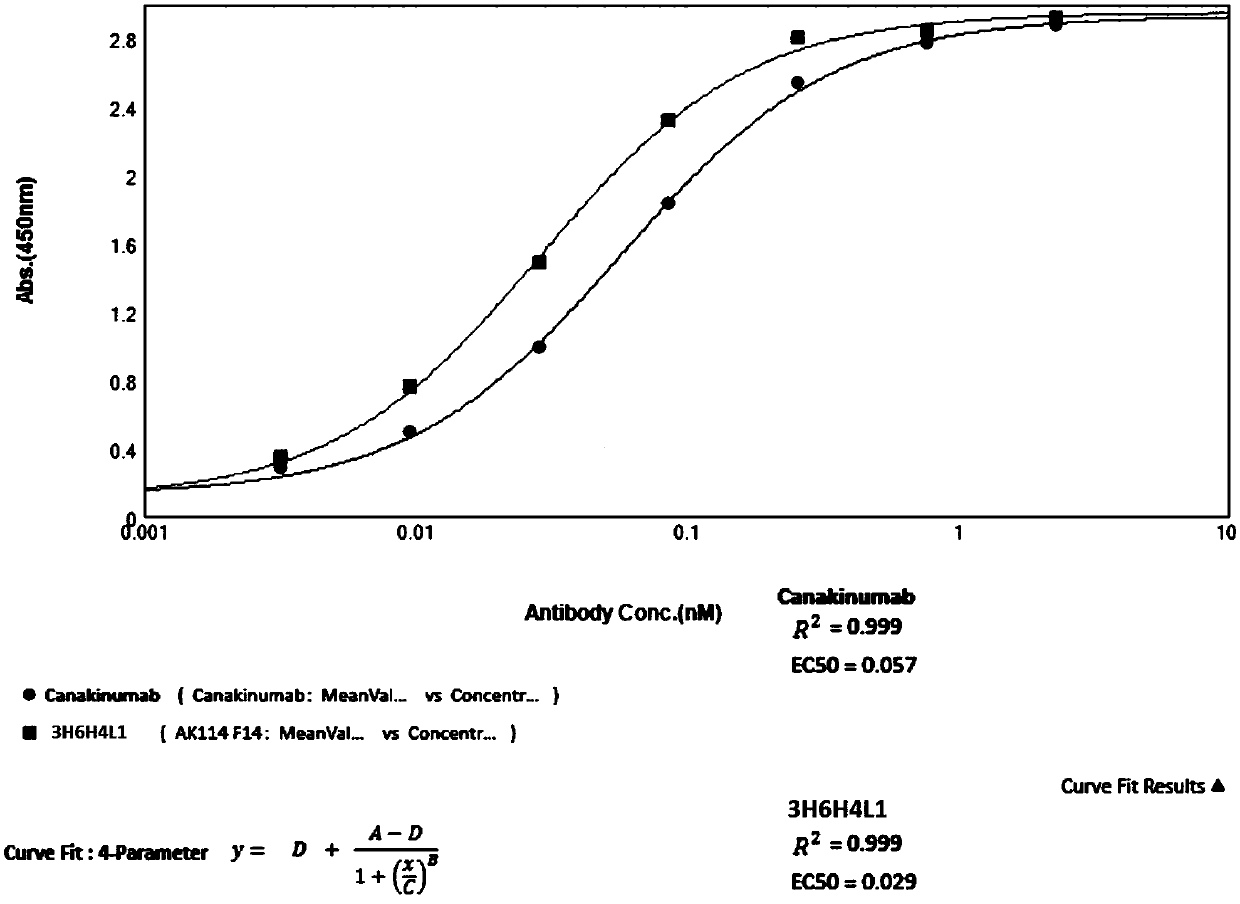
Patents
Literature
153 results about "Binding inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This article examines the enzymatic class. In competitive inhibition of enzyme catalysis, binding of an inhibitor prevents binding of the target molecule of the enzyme, also known as the substrate. This is accomplished by blocking the binding site of the substrate – the active site – by some means.
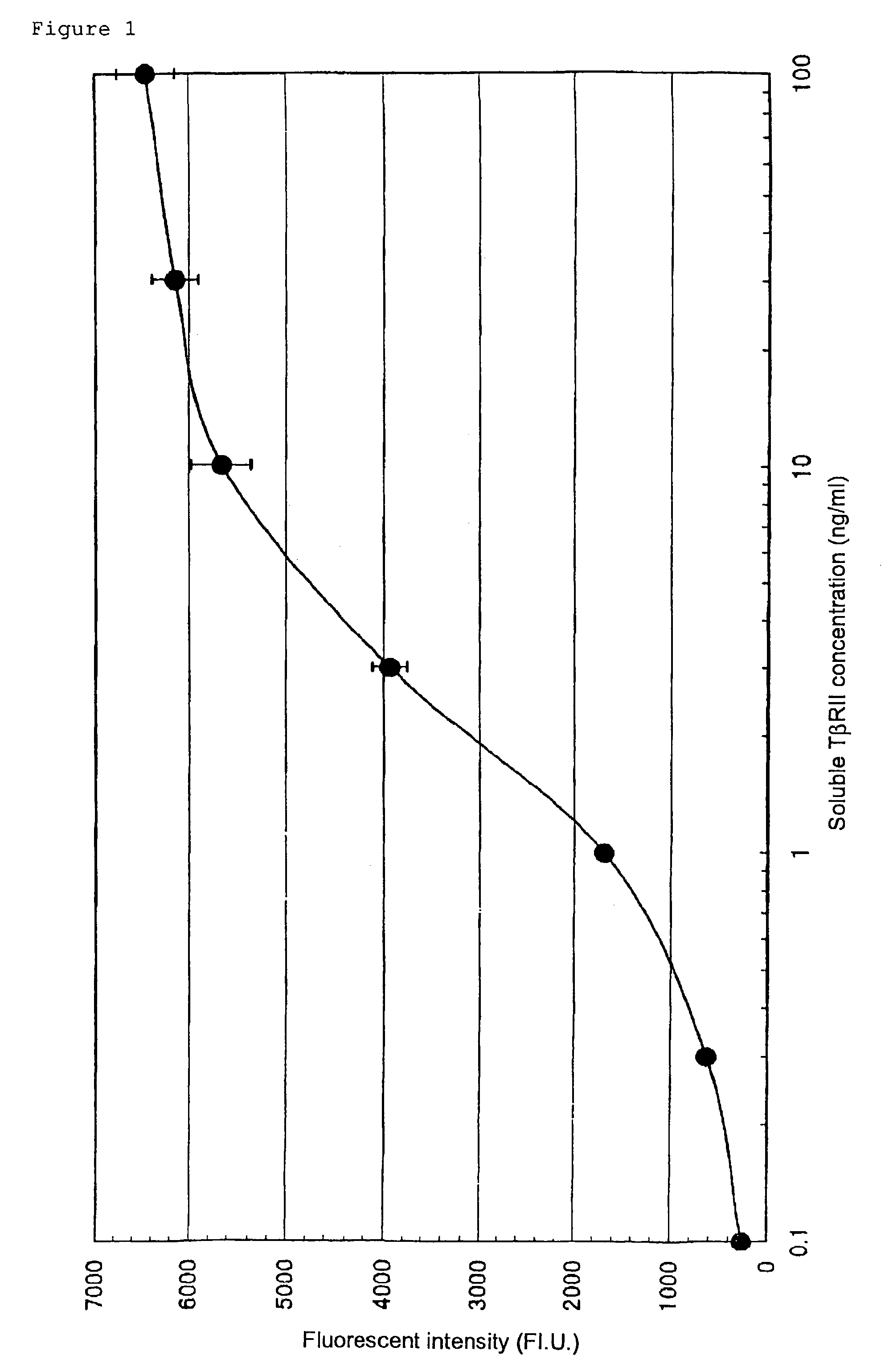
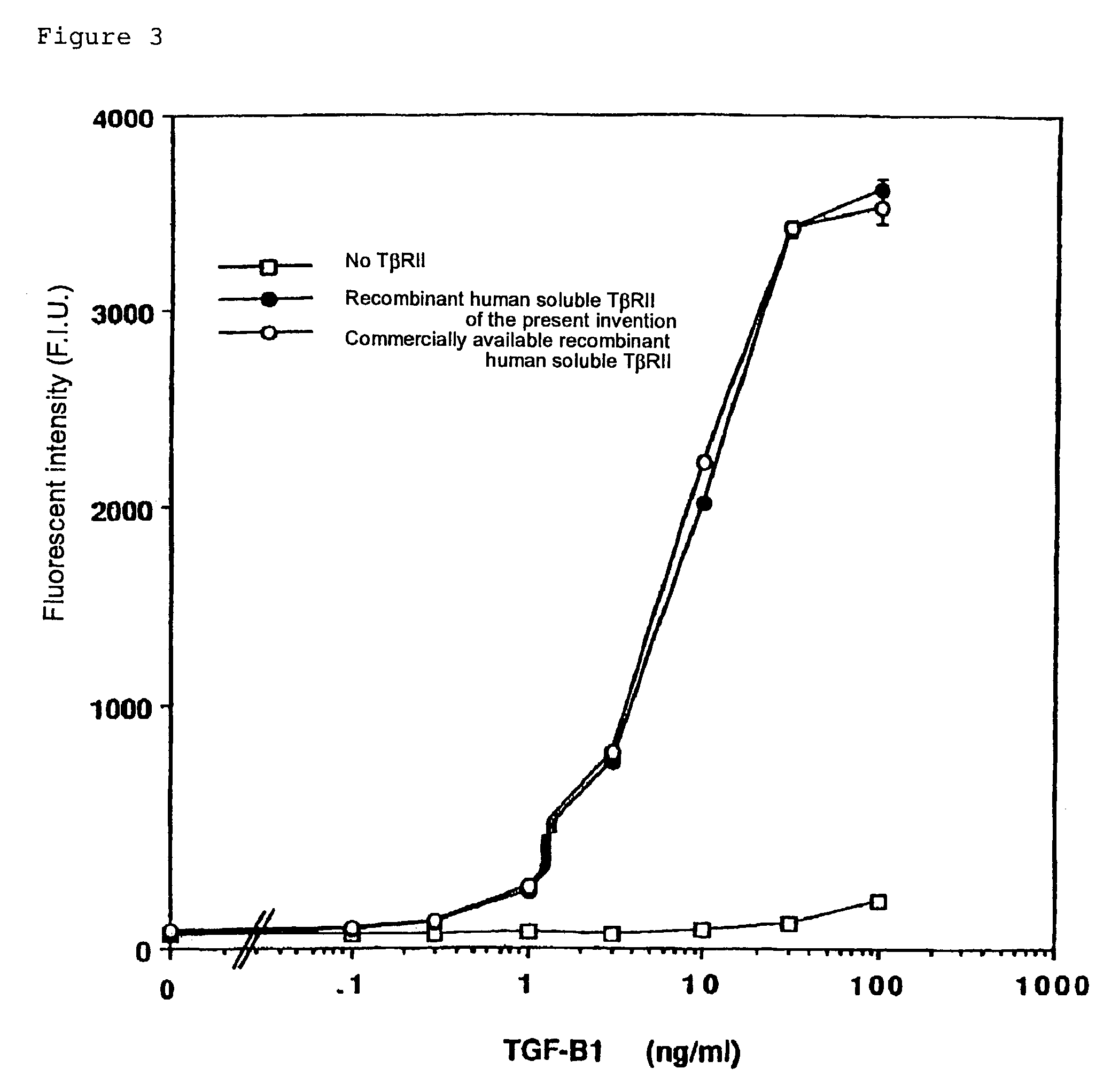
Human monoclonal antibody against TGF-beta type II receptor and medicinal use thereof
InactiveUS7579186B1Inhibits signal transductionIncrease valueAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseMonoclonal antibody
Various human monoclonal antibodies that bind to human TGF-β type II receptor to inhibit the signal transduction of human TGF-β signal into cells are produced by immunizing human antibody-producing transgenic mice generated by genetic engineering techniques with the soluble human TGF-β type II receptor. Further, these human monoclonal antibodies were demonstrated to be effective for preventing and treating various diseases induced by human TGF-β in various organs (for example, tissue fibrosis).
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
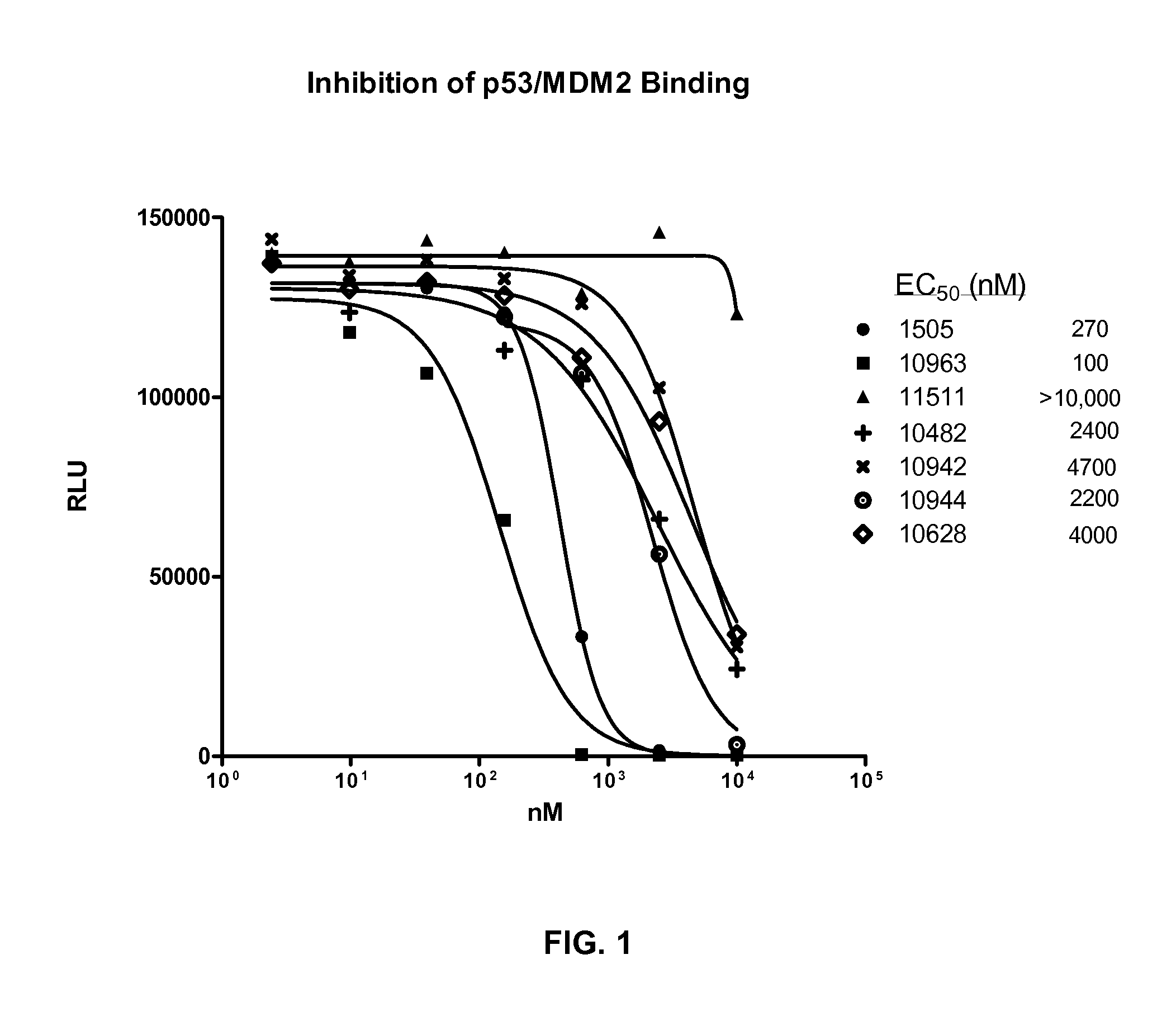
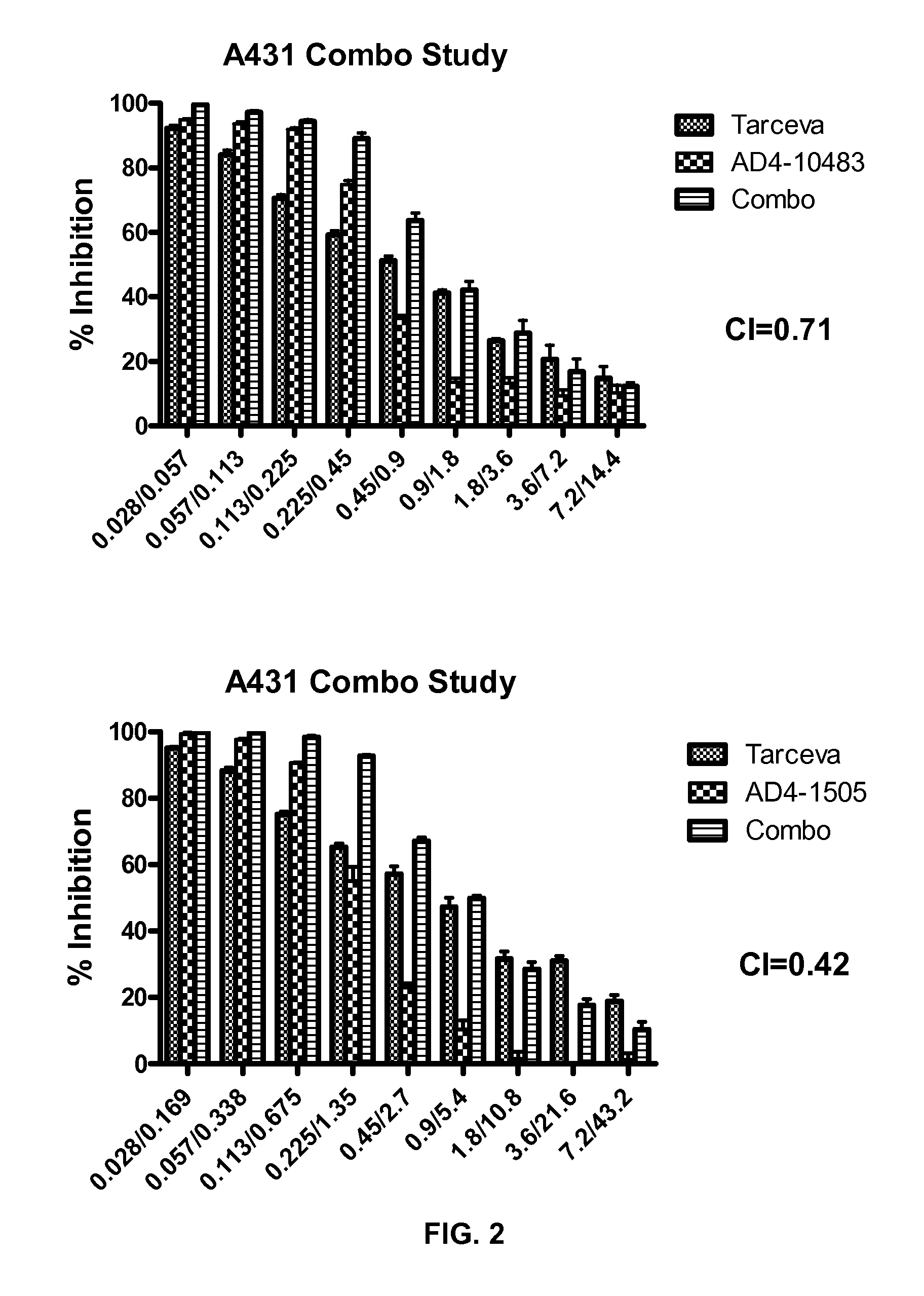
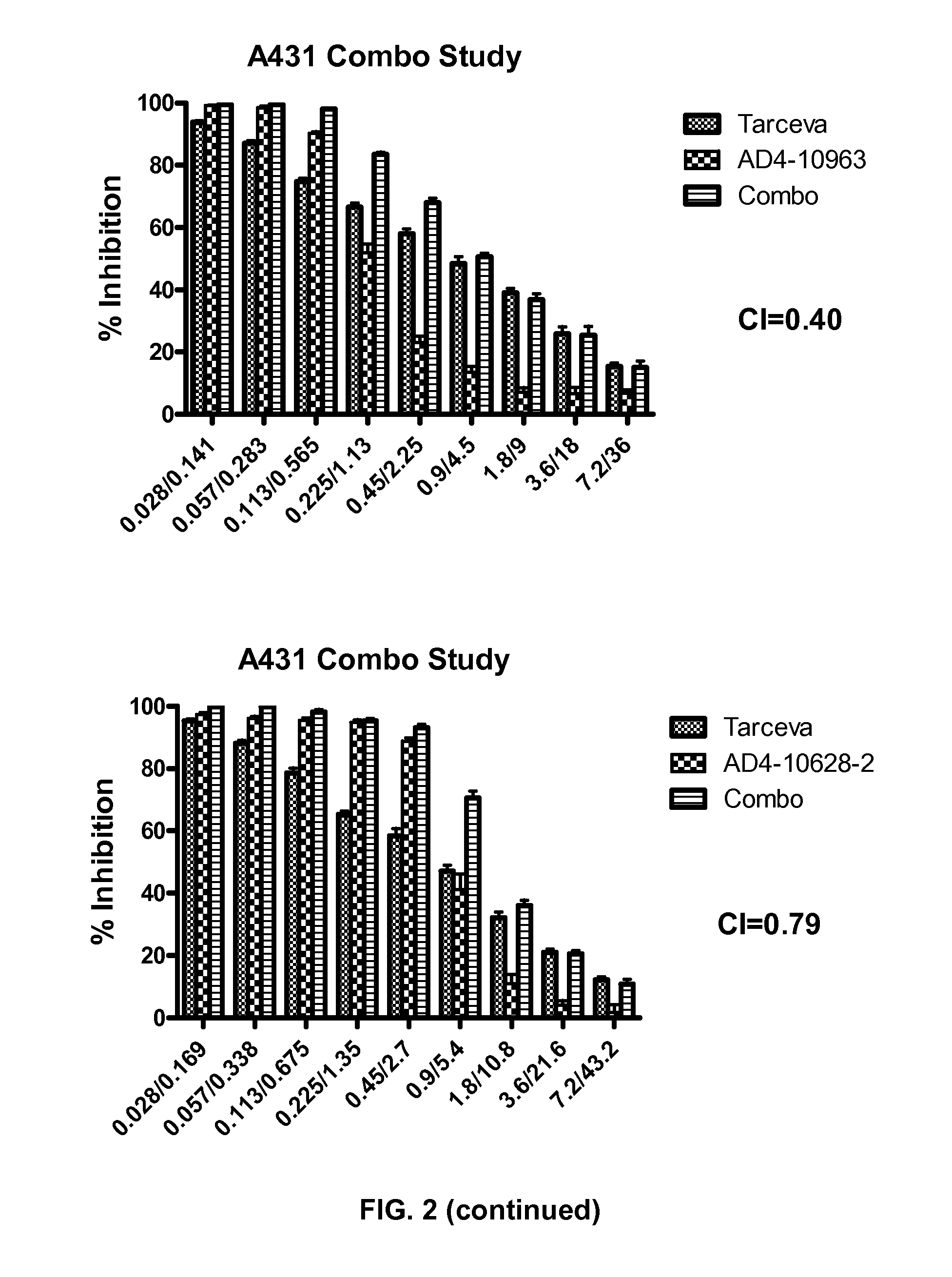
Combination therapy with mdm2 and efgr inhibitors
Provided is a method of treating a proliferative disease, condition, or disorder in a subject by administering a combination of an inhibitor of p53 and MDM2 binding and an EGFR inhibitor. Various embodiments of the disclosed methods provide a synergistic anti-proliferative or anti-apoptotic effect compared to administration of one agent alone.
Owner:ERRICO JOSEPH P
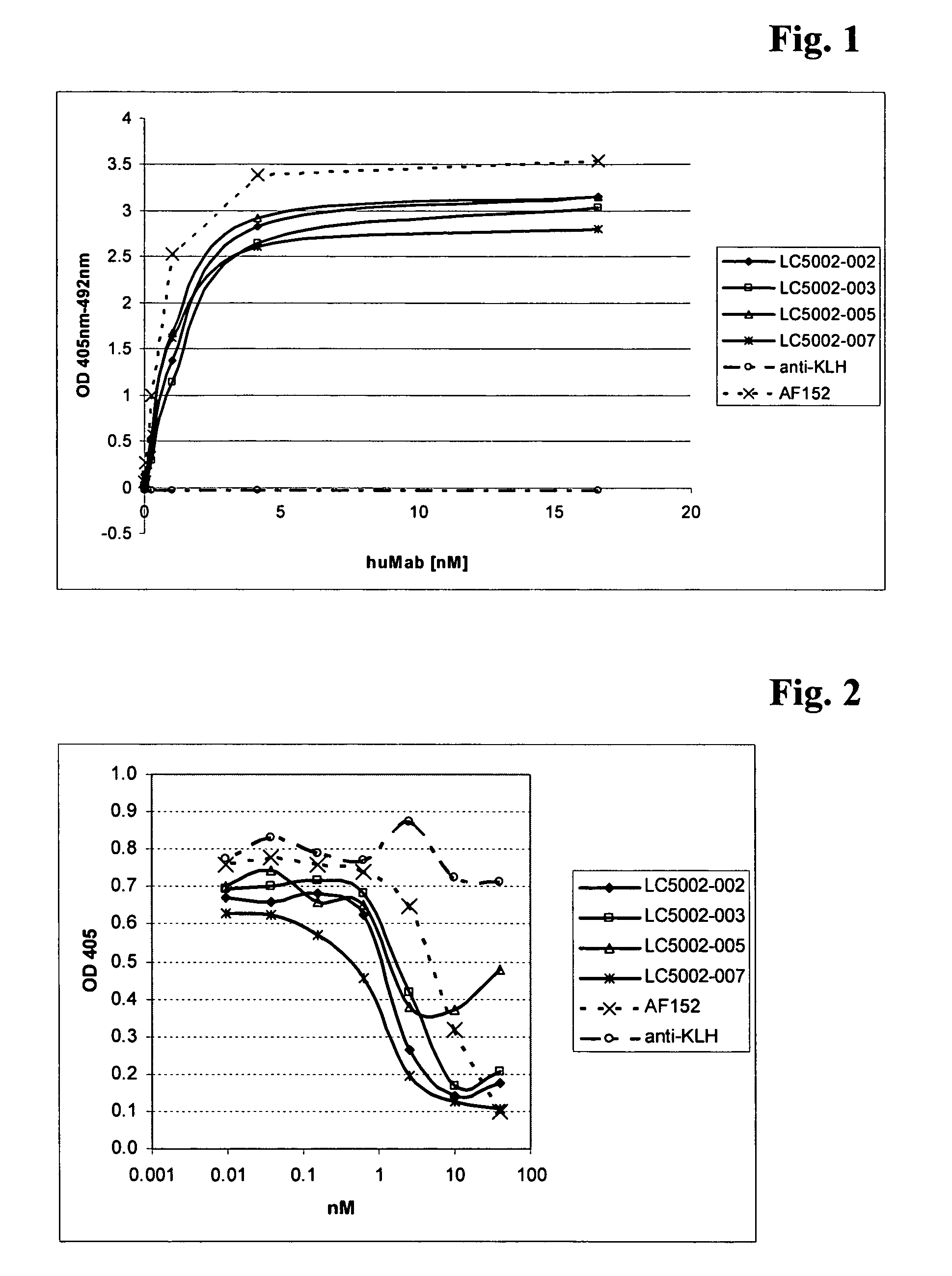
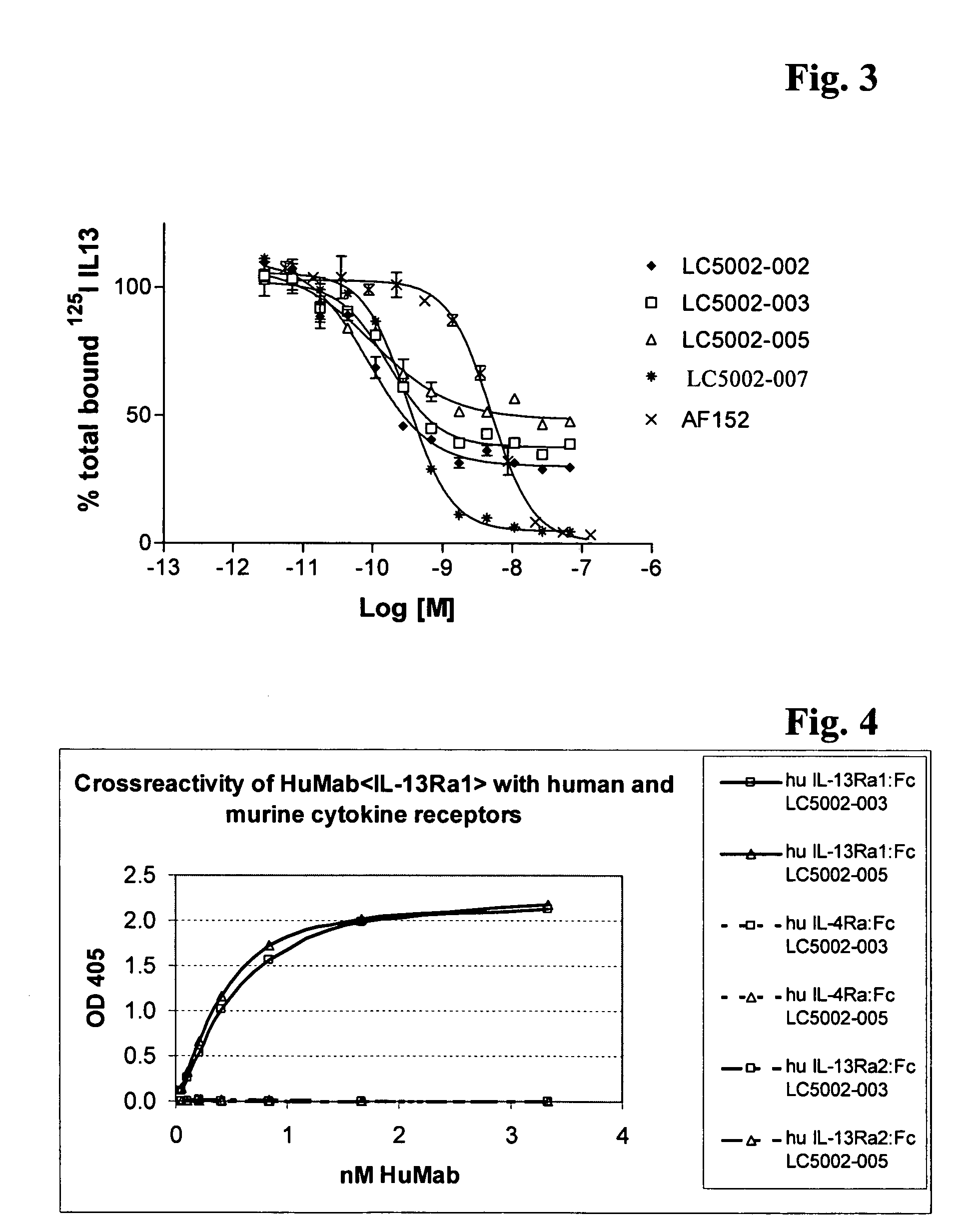
Antibodies against IL-13 receptor alpha1 and uses thereof
The instant specification discloses an antibody binding to IL-13Rα1, inhibiting IL-13 bioactivity and comprising a variable heavy and a variable light chain, characterized in that the variable heavy chain amino acid sequence CDR3 of this antibody is selected from the group consisting of the heavy chain CDR3 sequences of SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9, and this antibody is useful in the treatment of asthma and allergic diseases.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Assays to Identify Irreversibly Binding Inhibitors of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention relates to a method of identifying an inhibitor of a receptor tyrosine kinase that irreversibly binds to the kinase. Specifically, the method comprises using a variety of assays, either alone or in combination, to identify compounds that irreversibly bind to tyrosine kinases. More specifically, there are four assays, which are novel variations of a basic enzyme assay and identify irreversible binding inhibitors.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Inhibitor which is deactivatable by a reagent produced by a target cell
The invention relates to molecules inhibiting biologically active compounds and further comprising moieties specifically cleavable by a reagent produced by a target cell. More specifically, the invention relates to inhibitors that bind, inhibit, suppress, neutralize, or decrease activity of a biologically active agent. Inhibitors comprise at least one moiety that bind, inhibit, suppress, neutralize, or decrease activity of a biologically active agent and at least one moiety that can be cleaved specifically by a reagent produced by target cells. The cleavage deactivates the inhibitor. Following cleavage, the active agent is liberated into the local environment. Administration of the inhibitor alone or together with the active agent suppress the compound's activity until it reaches the proximity of a target cell. This targeted specific release enables the agent concentration in a site to reach levels that have desired therapeutic effects without systemic toxicity. The invention also relates to production and uses of the inhibitors in diagnosis and treatment of a disease.
Owner:VYTACERA BIO LLC
Oligonucleotide antagonist for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)
InactiveUS7309786B2Strong specificityHigh affinitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsL929 cellHigh concentration
The present invention relates to a group of new oligonucleotides sequences with human tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibiting activity, which includes DNA sequences and RNA sequences. These oligonucleotides or aptamer can specifically be bound to TNF-α and inhibit the cytoxicity of TNF-α to L929 cells. Therefore, the aptamer of the present invention may be used to detect TNF-α and provide a therapeutic method for diseases related to the increasing level of TNF-α. Compared with other TNF antagonists such as monoclonal antibody and soluble receptor, the present invention has high specificity, high affinity, quick penetration to target tissue, rapid plasma clearance, and lower immunogenecity. Turthermore, it can be used repeatedly and keeps high concentration in target tissue and the like. It has the advantages of affinity and specificity similar to monoclonal antibodies and also has permeability and pharmacokinetics characteristics similar to small molecular polypeptide. The present invention also refers to derivative of the oligonucleotides sequence, including modified sequence. The present invention may further be manufactured as medicine for therapy and diagnosis of TNF-α related diseases.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Reducing NgR-p75 mediated inhibition of axon regeneration
InactiveUS20060104973A1Reducing axon growth inhibitionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiochemistryNogo Receptors
Inhibitors of Nogo Receptor (NgR)-p75 binding are used to reduce NgR-p75 binding mediated axon growth inhibition. Mixtures of NgR and p75 are used in pharmaceutical screens to characterize agents as inhibiting binding of NgR to p75 and promoting axon regeneration.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
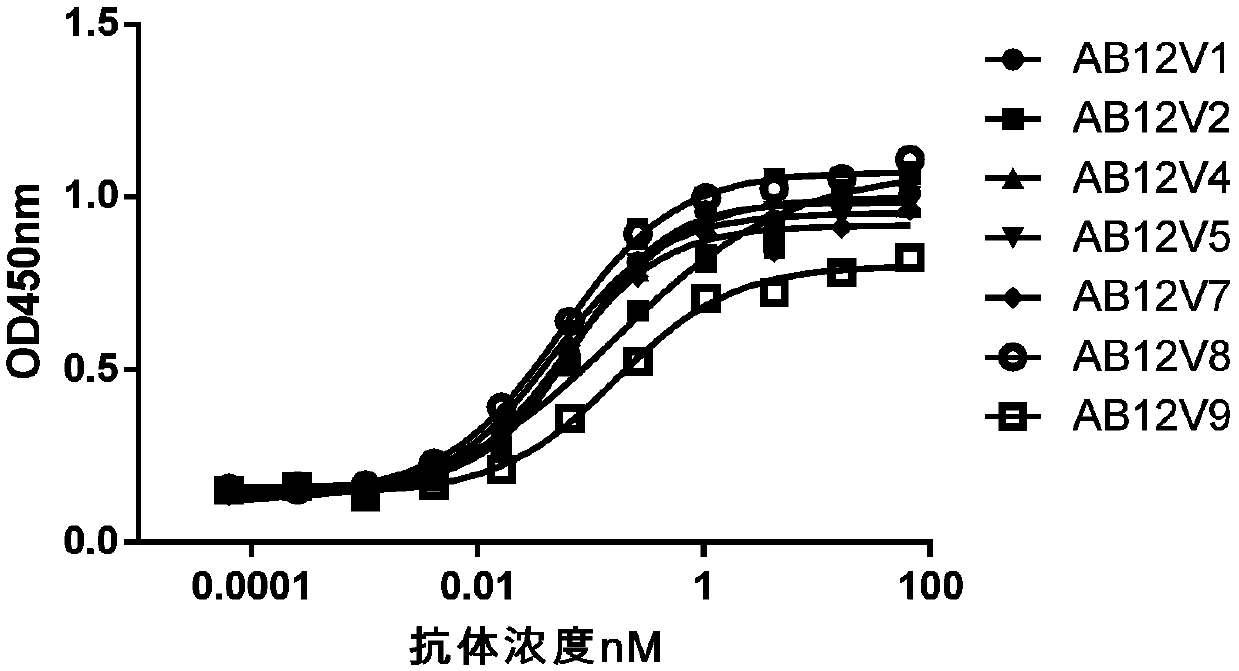
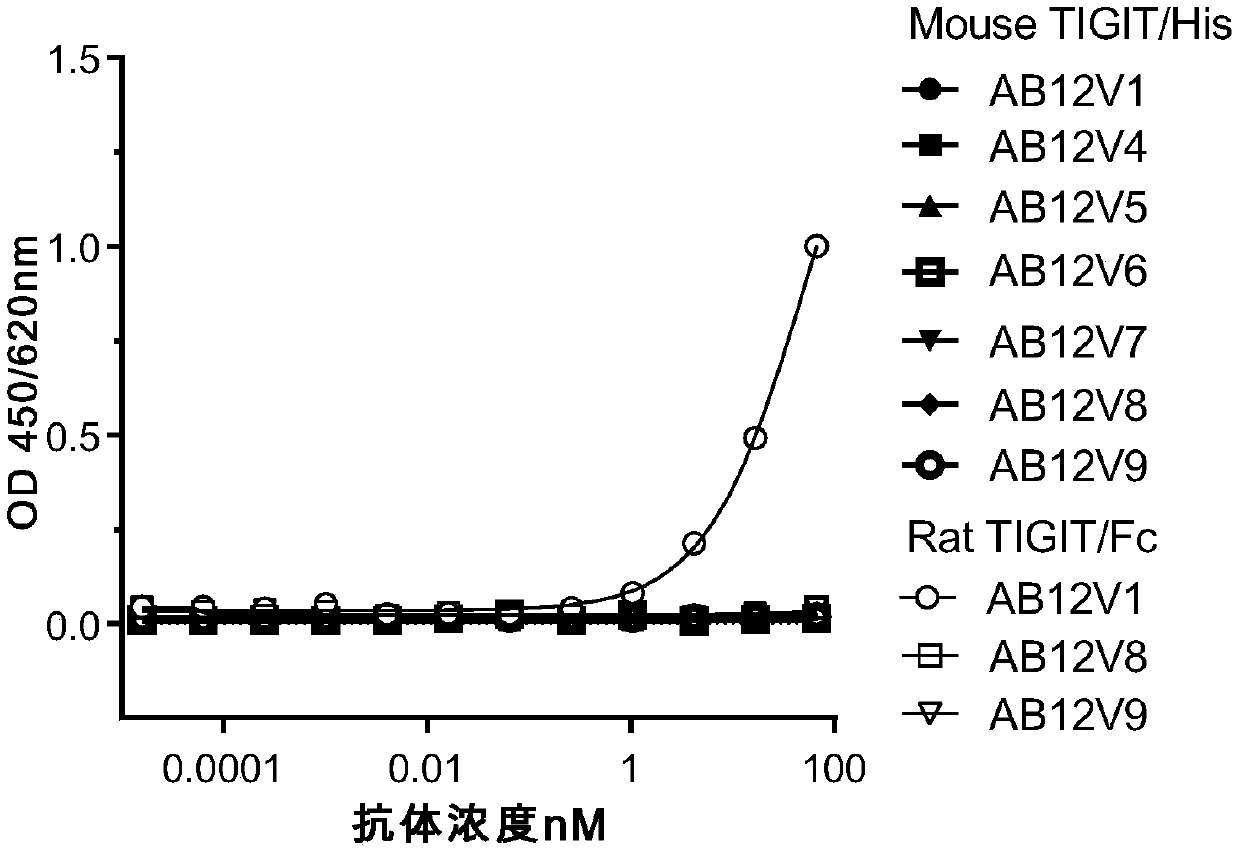
Anti-TIGIT antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveCN111196852AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsIntracellular signallingAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention relates to the field of disease treatment and immunology, and in particular, to anti-TIGIT antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof, nucleic acid molecules encoding the anti-TIGIT antibody and the antigen-binding fragment, and a preparation method thereof. The anti-TIGIT antibody or the antigen binding fragment thereof provided by the invention has high specificity andhigh affinity to TIGIT, can effectively block the binding of TIGIT and a ligand thereof, and inhibits and / or blocks intracellular signal transduction mediated by the binding of TIGIT and the ligand thereof. Therefore, the invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, and to the use thereof in the preparation of a medicine for enhancing immune cell activity, enhancing immune response, or for preventing and / or treating tumors, infections or infectious diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN BIOTECH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
Method of detecting surrogate markers in a serum sample
ActiveUS20130137598A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompetitive bindingCholesterol
The invention provides a method of detecting surrogate markers for active tuberculosis in a serum sample. The surrogate markers are selected from serum mycolic acid antigen, serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies or both. The method includes the steps of combining the serum sample with a labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acids to produce a combined serum sample, the antibody or fragment thereof not substantially cross-reacting with cholesterol and the label being selected so that binding of the labelled antibody to immobilized mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin produces a detectable signal and combining a blank sample with the labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acid to produce a combined blank sample. The method includes exposing both samples to immobilised mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin or a synthetic analogue or analogues thereof so that the labelled immunoglobulin antibodies or fragments thereof in each sample bind to the immobilised antigen to produce detectable signals. If the surrogate markers are present, the signal produced by the blank sample will be stronger than that produced by the serum sample because of inhibition of binding of the labelled antibody in the serum sample arising from prior binding of the labelled antibody with the mycolic acid antigen in the serum sample or by competitive binding of serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies in the serum sample to the immobilised mycolic acid antigen or both.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA
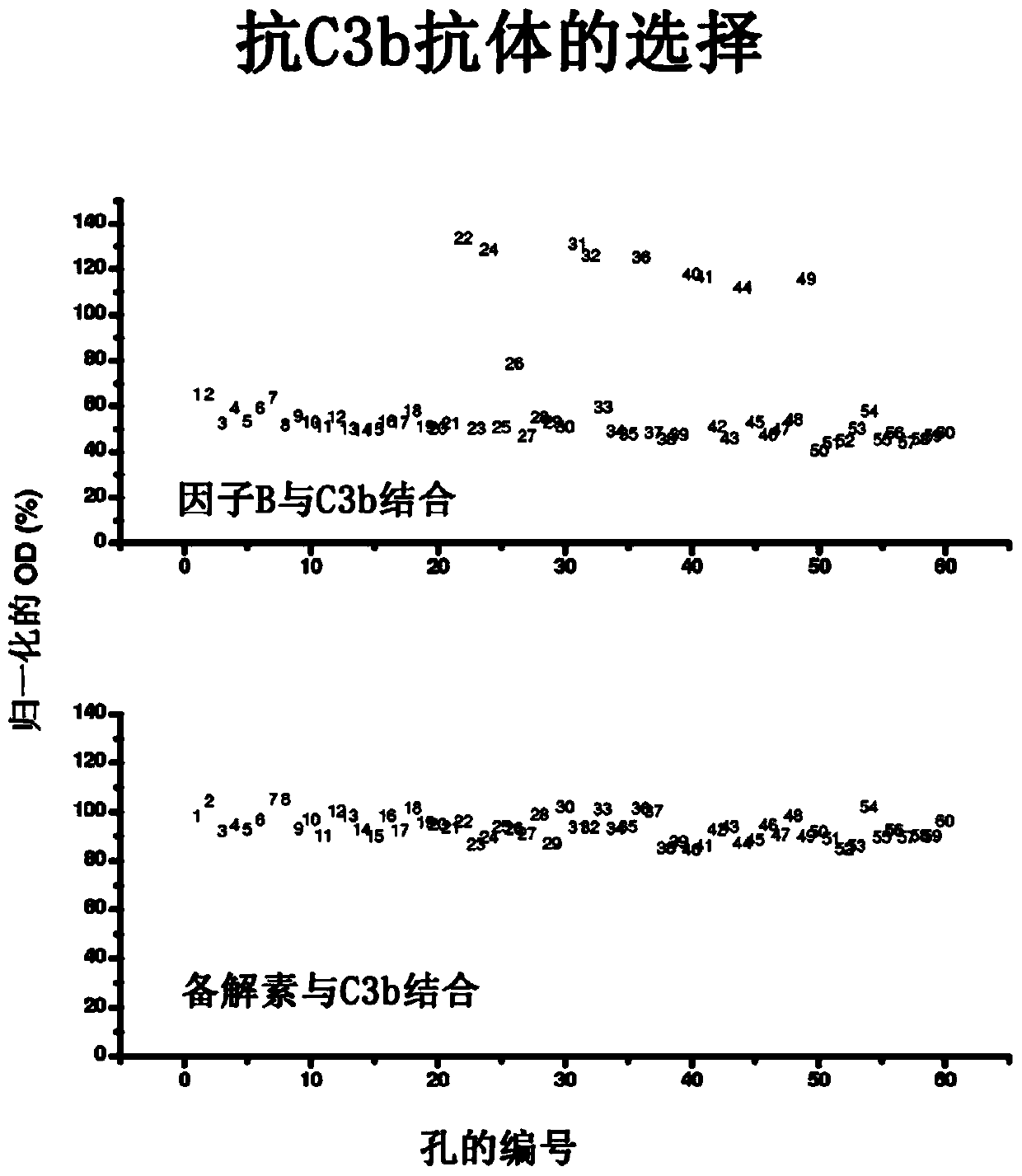
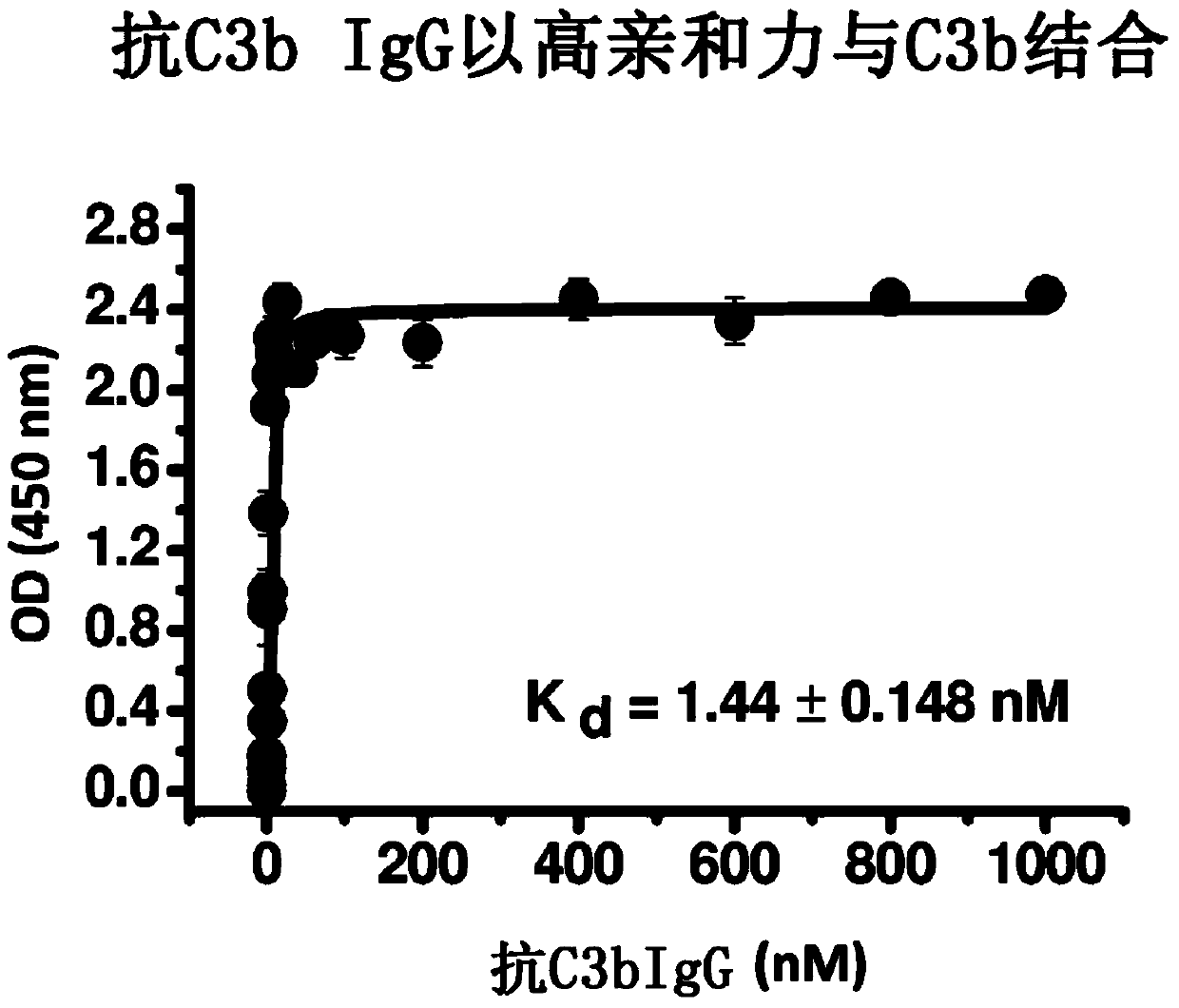
Humanized and chimeric anti-factor c3 antibodies and uses thereof
A method of inhibiting complement activation mediated by C3b inhibitors in a subject is provided. The method includes administering a C3b inhibitor to the subject to inhibit at least one of C3b binding to factors B and properdin, to inhibit C3 cleavage, to inhibit the activation of neutrophils, monocytes, platelets, and endothelium; or to inhibit the formation of C3a, C5a, and MAC.
Owner:NOVELMED THERAPEUTICS
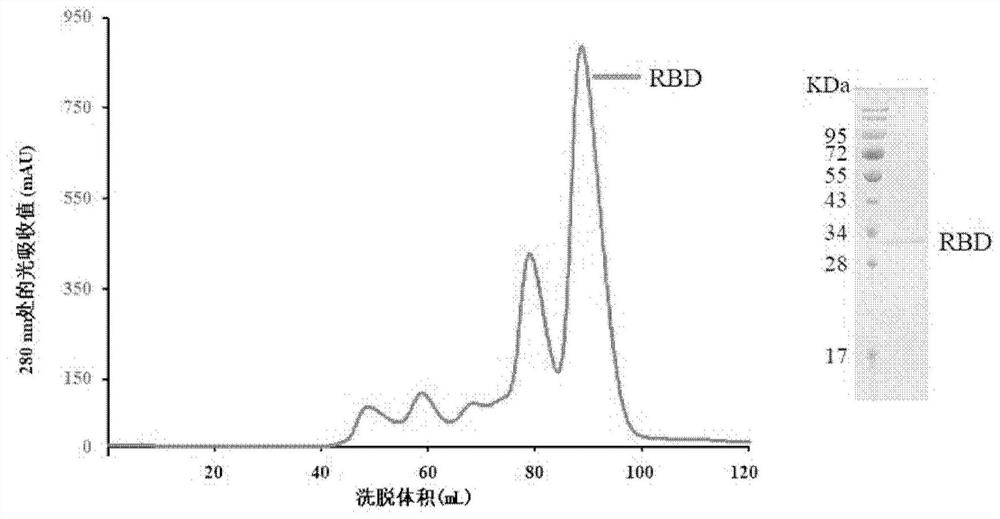
Fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody
ActiveCN112794899AAvoid infectionHigh neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsDiagnosis treatmentMutant strain
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and discloses a fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody for resisting novel coronavirus and application of the fully human monoclonal neutralizing antibody. B-type lymphocytes are screened from blood of a new coronal pneumonia rehabilitation patient, and the affinity constant of the obtained antibody and a virus receptor binding domain (RBD) is 1.19 nM. X-ray crystal diffraction is used for analyzing the three-dimensional structure of the antibody and RBD compound, it is found that the binding epitope of the antibody and the binding epitope of a host cell receptor (ACE2) are highly overlapped, binding of the RBD and the ACE2 can be competitively blocked, and infection of the RBD and the ACE2 is inhibited. The antibody can cope with certain genetic mutations of viruses, the half effective concentration of the antibody for blocking pseudoviruses (accumulated B.1. 1.7 mutant strain genes and D614G) from infecting host cells is 0.57 ng / mL, and the antibody has the advantages of safety, high efficiency and broad spectrum, and is expected to be used as a neutralizing antibody drug for diagnosing, treating and preventing new coronal pneumonia.
Owner:SUZHOU YUZHIBO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Fluorohydroxyproline derivatives useful in the preparation of proteolysis targeted chimeras
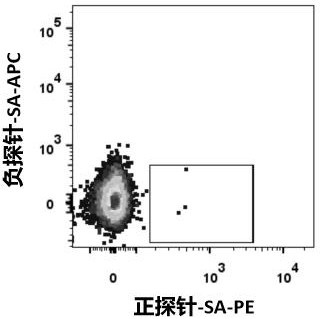
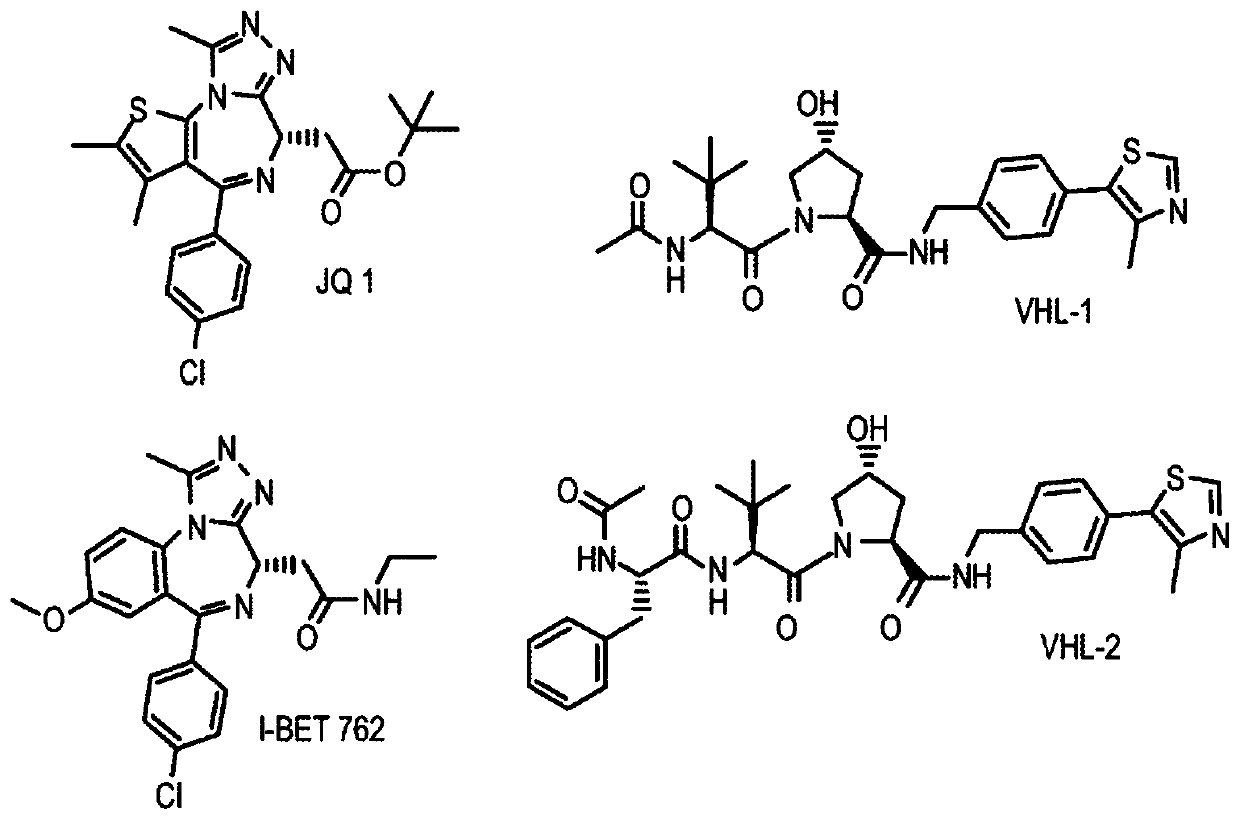
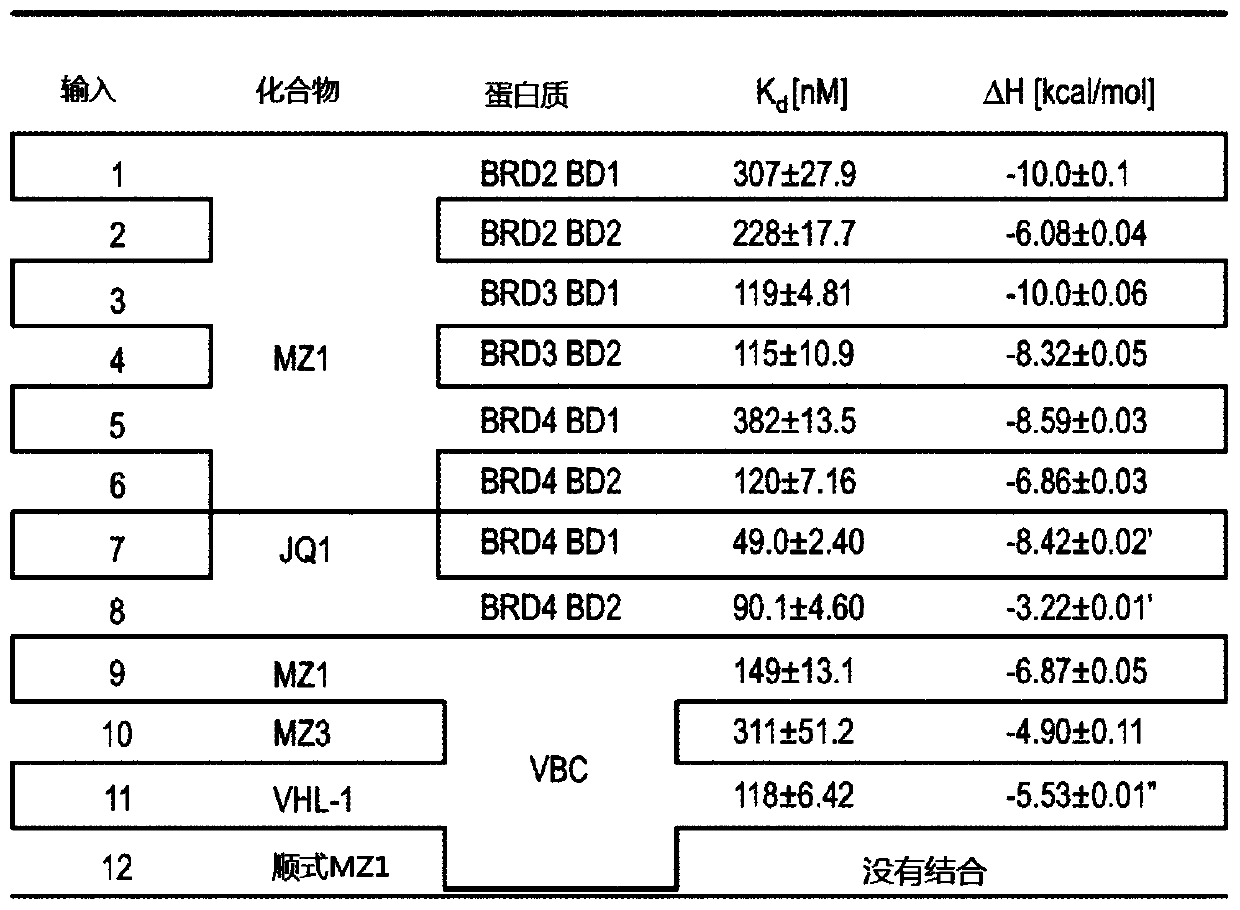
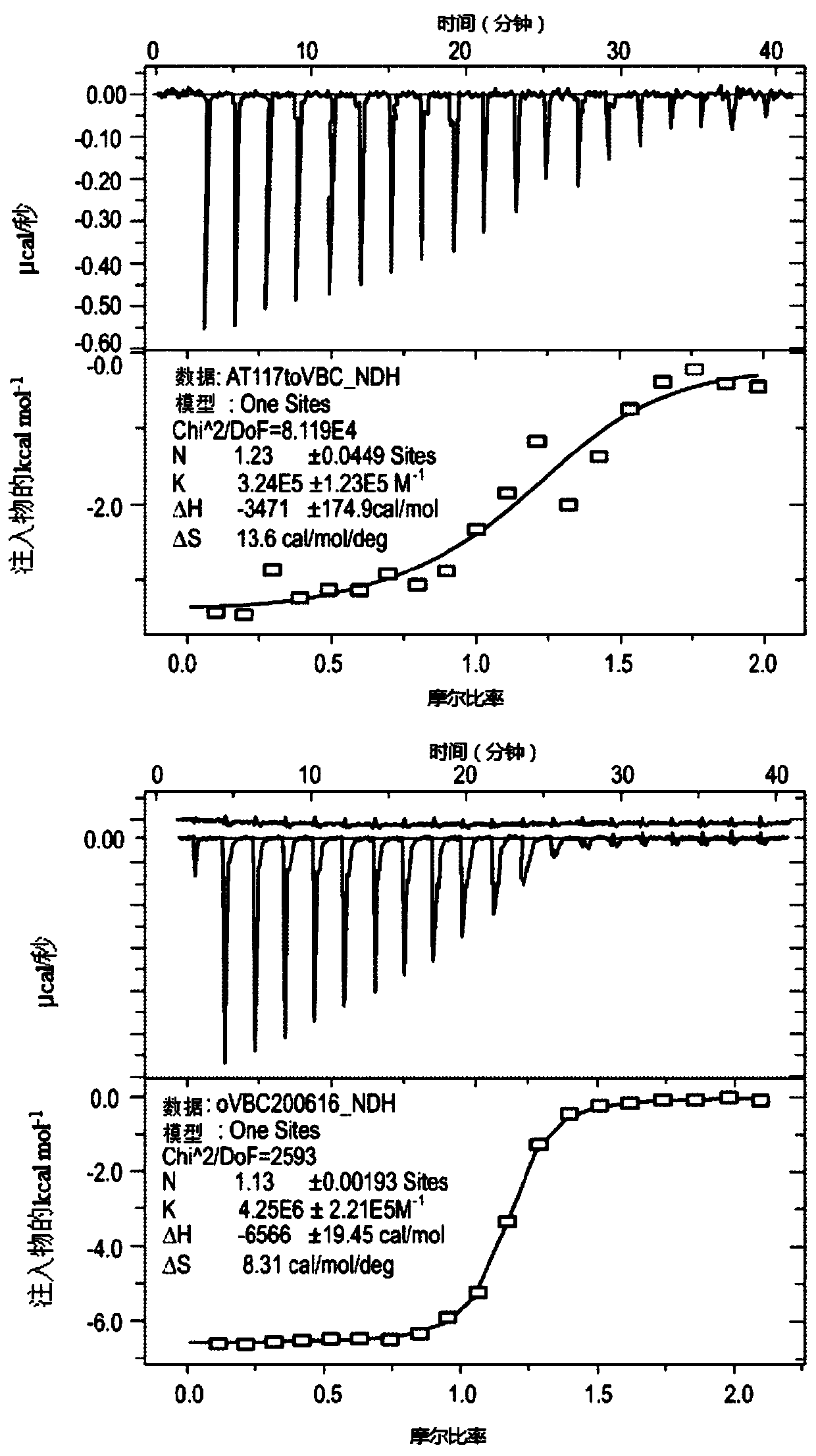
There is provided novel small molecule E3 ubiquitin ligase protein binding ligand compounds, and to their utility in PROteolysis Targeted Chimeras (PROTACs), as well as processes for their preparationthereof, and use in medicine. There is particularly provided novel small molecule E3 ubiquitin ligase protein binding inhibitorcompounds based on a fluorohydroxyproline scaffold, to their utility asligands in synthesizing novel PROTACs, and to synthetic methods therefor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DUNDEE
Method for detecting residual kanamycin
InactiveCN105651850ASensitive detectionRealize detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesKanamycinEnzyme digestion
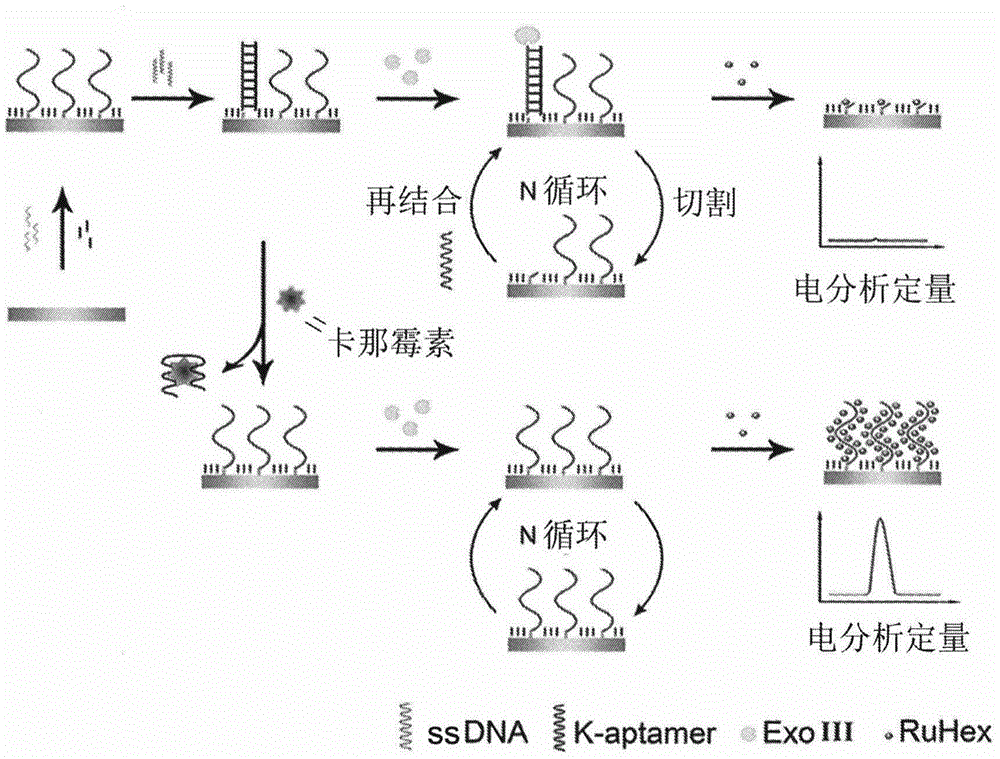
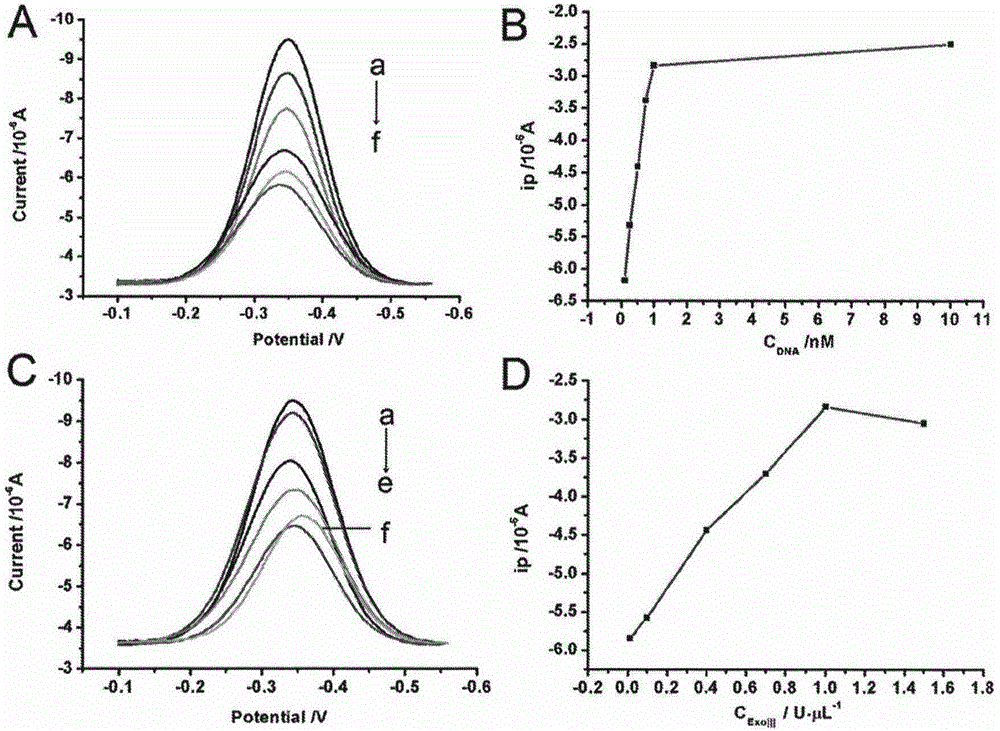
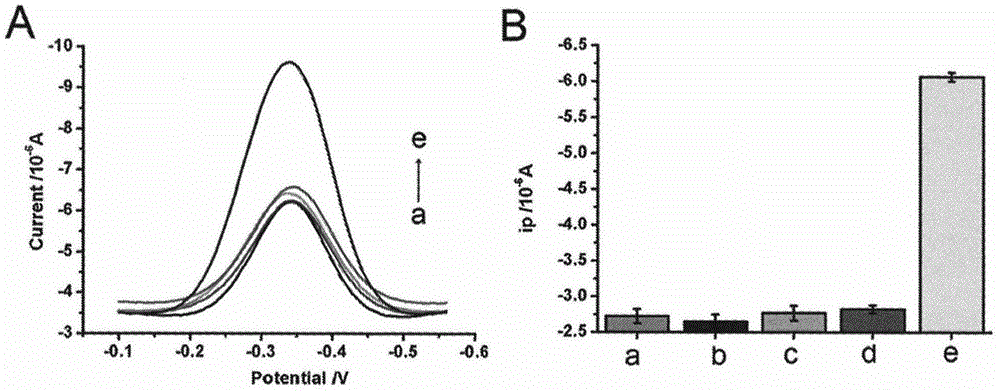
The invention discloses a method for detecting residual kanamycin and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analysis chemistry, wherein the detection method is based on aptamer initiated cyclic enzyme digestion of exonuclease III (Exo III). According the method, mercapto self-assembly is utilized, single stranded DNA (ssDNA) that is complementary with kanamycin aptamer (K-aptamer) is grafted on the surface of a gold electrode, then a little amount of K-aptamer is added, and the K-aptamer is matched with ssDNA to form a little amount of double stranded DNA (dsDNA). Then Exo III is added, the ssDNA in dsDNA can be specifically digested by Exo III, thus the residual aptamers are released, the released aptamers can combine with ssDNA to form dsDNA, another enzyme digestion is triggered then, and after several circulations, the modified ssDNA is completely digested by enzymes. Kanamycin exists in the system, through the combination between kanamycin and aptamers, the circulation enzyme digestion is inhibited, thus ssDNA is preserved, and the amount of preserved ssDNA is related with the concentration of kanamycin. An electro-analysis method is used to absorb electrical signal molecules namely hexaammine ruthenium (RuHeX) through static electricity absorption so as to quantitatively detect residual kanamycin; and the method has high sensitivity and can sensitively detect residual kanamycin in milk.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Fluorescent biosensing method used for detecting low molecular ligand target protein and based on combination of inhibition of click chemistry reaction
InactiveCN104792753ARealize quantitative detectionHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetClick chemistry
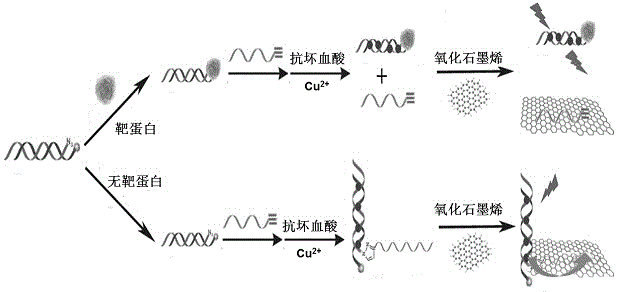
The invention discloses a fluorescent biosensing method used for detecting low molecular ligand target protein and based on combination of inhibition of a click chemistry reaction. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), specific molecular recognition of oligonucleotide DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) chain end modified low molecular ligands and target protein of the low molecular ligands; (2), combination of inhibition of the click chemistry reaction; (3), fluorescent quantitation detection based on a fluorescence quenching nanoprobe system comprising copper nanoparticles and graphene oxide. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, simplicity and convenience in operation and good universality, thereby having great potential application value in fields of clinical diagnosis, drug research and development and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Application of hydroquinone farnesyl group compound
ActiveCN105213363APrevent proliferationMetabolism disorderDigestive systemTyrosineTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a hydroquinone farnesyl group compound and application of a pharmaceutical salt thereof in serving as an alpha-glucosidase, protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 1B or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, or in preparing drug for treating and / or preventing type-II diabetes or hyperlipidemia, or in preparing drug or functional healthcare products having hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic functions, or in preparing drug or functional healthcare products having a function of treating or preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or in preparing drug or functional healthcare products having liver protection effect, or in preparing drug or functional healthcare products for preventing and / or treating cancer or inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, or in serving as an RXRalpha receptor binding inhibitor, or in preparing drug serving as the RXRalpha receptor binding inhibitor. The inhibitors, the drug, food or the healthcare products prepared through the hydroquinone farnesyl group compound and the pharmaceutical salt are free of toxic and side effect and remarkable in treatment effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIO SINCERITY PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN112979802AImprove bindingEnsuring biological activity in vivoNervous disorderAntipyreticImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention provides an anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody and application thereof. By taking recombinant human IL-33 as an immunogen, a murine anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is prepared through a hybridoma technique; binding activity analysis is carried out on the murine antibody, blocking activity analysis is carried out on binding of IL-33 and ST2, sequencing is carried out, a human-mouse chimeric anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is constructed, and kinetic parameters of the chimeric antibody are detected. On the basis of performance analysis of the murine antibody and the chimeric antibody, a humanized anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is constructed by adopting a CDRs transplantation technology and a complementary determining region (CDR) mutation design, kinetic parameters and affinity of the humanized antibody are detected, and IL33-induced cytokine release is blocked. The anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody has relatively high affinity to IL-33, can effectively block binding of IL-33 and a receptor ST2 thereof, inhibits immune response related to an IL-33 / ST2 pathway, and has a good application prospect in treatment of asthma, inflammatory diseases, diabetes and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:MABWELL (SHANGHAI) BIOSCIENCE CO LTD
Stereochemical control of the DNA binding affinity, sequence specificity, and orientation-preference of chiral hairpin polyamides in the minor groove
InactiveUS7049061B1Inhibit expressionTightly boundBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPolyamideMinor groove
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
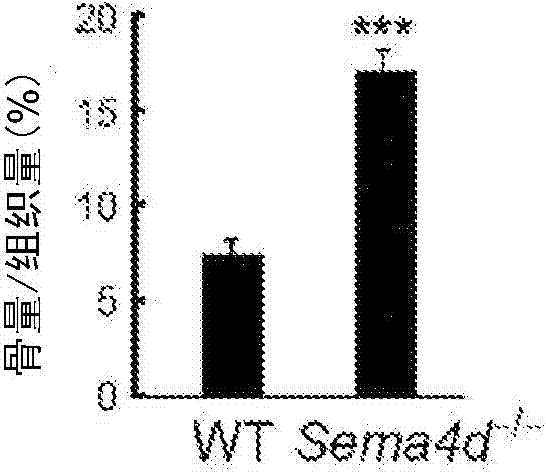
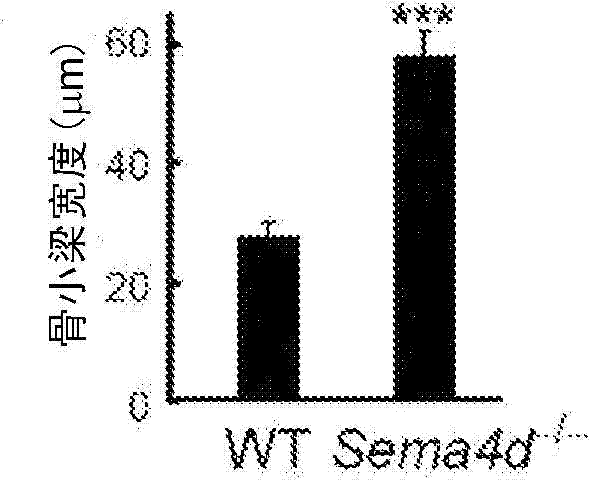
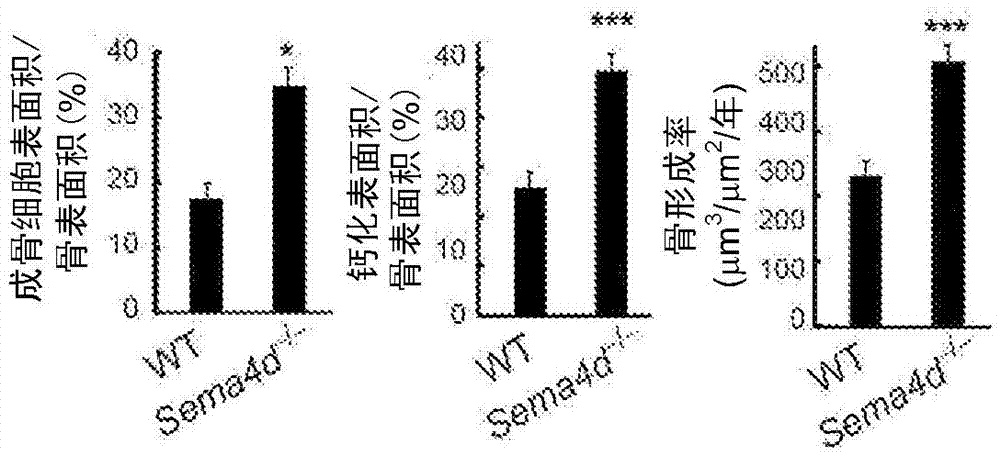
Osteogenesis promoter
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an osteogenesis promoter for directly promoting osteogenesis by osteoblasts, and an agent for preventing and treating bone disease. The present invention is characterized in that a binding inhibitor substance of semaphorin 4D and plexin B1 is used. For the binding inhibitor substance, suitable examples include anti-semaphorin 4D antibody, anti-plexin B1 antibody, and protein comprising the extracellular domain of plexin B1.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
Assays for detecting inhibitors of binding between COX-2 and PDZ proteins
The invention provides an assay for determining whether a test agent is a COX modulator. In general terms, the assay includes: determining whether a test agent modulates binding of a PDZ-containing polypeptide to a COX PL-containing polypeptide. The PDZ-containing polypeptide may contain the PDZ domain of PDZ domain of MAGI1, TIP-1, MAST2, PSD95, or SHANK. The assays may be done in a cell-free environment or in a cellular environment, particularly using a neuronal cell. The invention finds use in a variety of therapeutic applications, including for identifying agents for use in treating cancer, pain, inflammation and neuronal conditions caused by acute insult, e.g., stroke.
Owner:ARBOR VITA CORP
Crystallization of IGF-1
Crystalline IGF-1 is provided along with a method for production thereof. Crystallizing IGF-1 comprises the steps of mixing an aqueous solution comprising IGF-1 with a reservoir solution comprising a precipitant to form a mixture; and crystallizing the mixture, optionally also recrystallizing and isolating the crystalline IGF-1. In addition, a method for identifying IGF-1 indirect agonists is provided using a detergent as a standard for the level of inhibition of binding of IGFBP-1 or IGFBP-3 to IGF-1 and / or using the coordinates of the binding pockets of IGF-1 to which a candidate indirect agonist binds for structure-based drug design.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
SH2 domain binding inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds represented by the formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or isomer thereof, wherein R1-R6 are as defined in the specification. These compounds are targeted for use as inhibitors of SH2 domain binding with a phosphoprotein, and are contemplated for use in a number of diseases including cancer. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
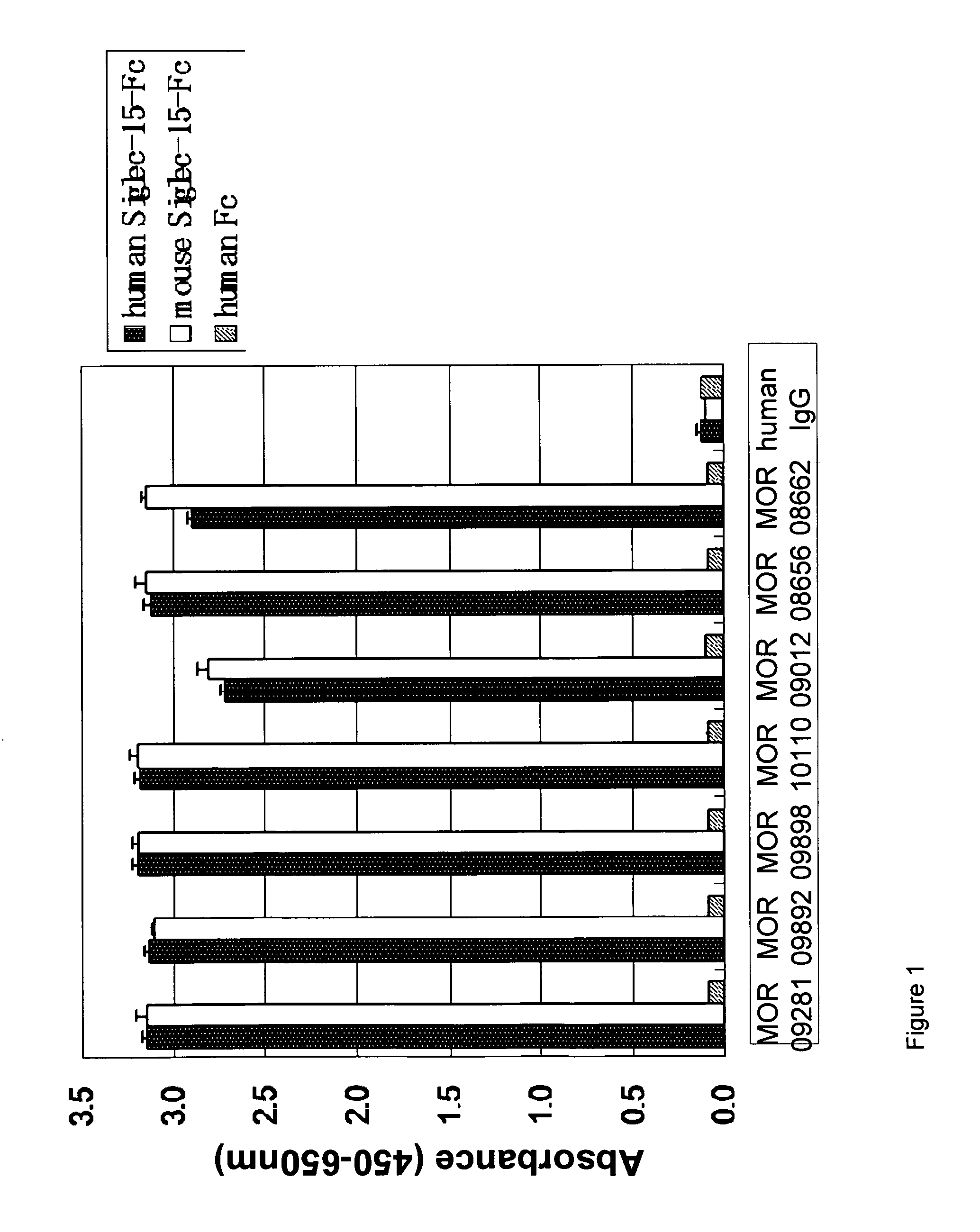
Antibody targeting osteoclast-related protein Siglec-15
InactiveUS9114131B2Inhibit differentiation and maturationAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainAntibody targeting
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
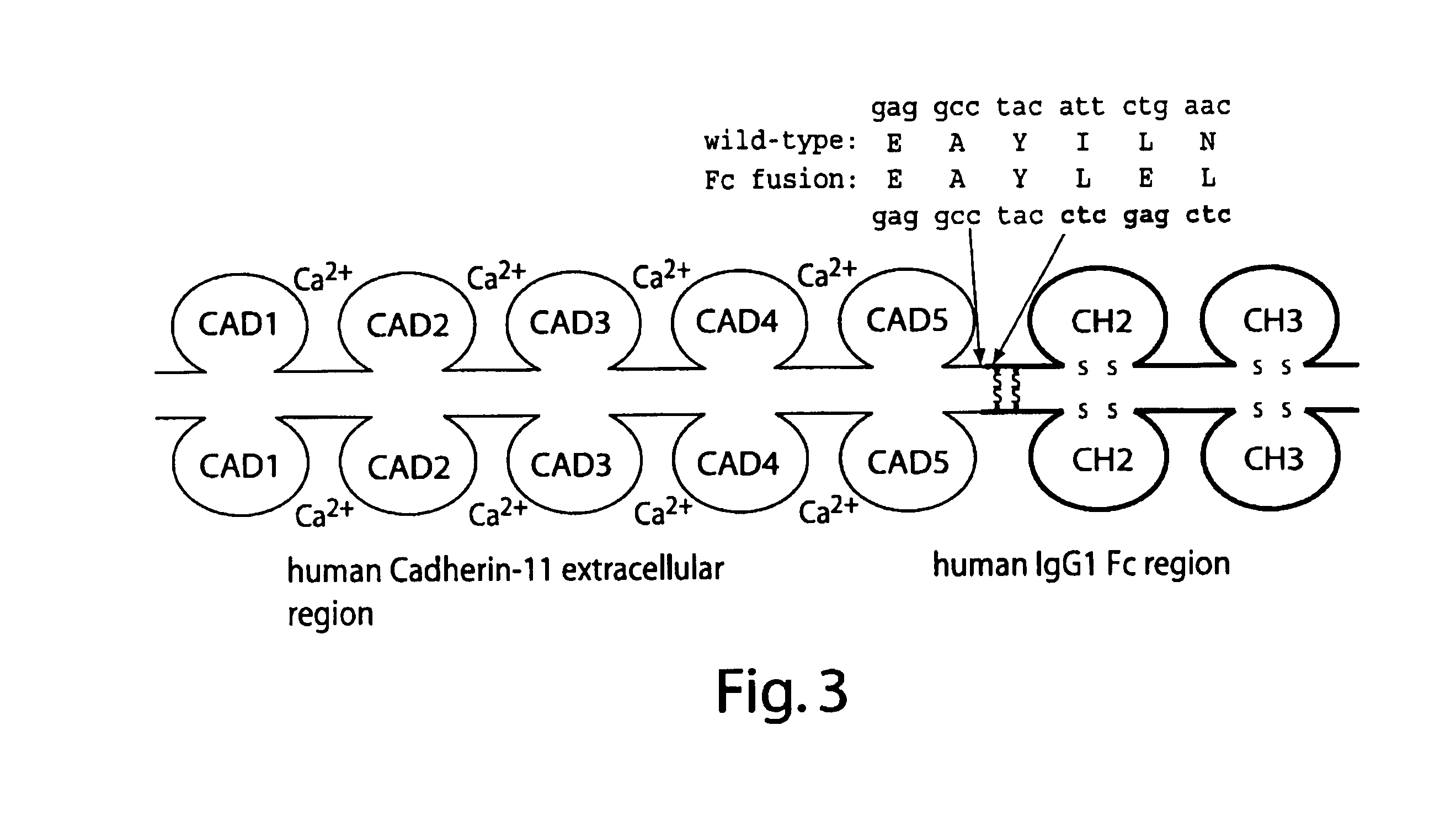
Methods and compositions for treatment of inflammatory disease using cadherin-11 modulating agents
InactiveUS6964768B2Inhibit bindingAvoid stickingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntipyreticApoptosisSecretion
A method for treating inflammatory joint diseases by inhibiting cadherin-11 mediated cellular function using a cadherin-11 modulating agent is provided. Also provided are screening assays for identifying pharmaceutical lead compounds capable of modulating cellular functions of cadherin-11 such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, factor secretion, and binding of cadherin-11 to cadherin-11 counter-receptor inhibiting binding of cadherin-11 to its counter-receptor either in the context of a cell or in soluble form.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods for detecting Th1 cells
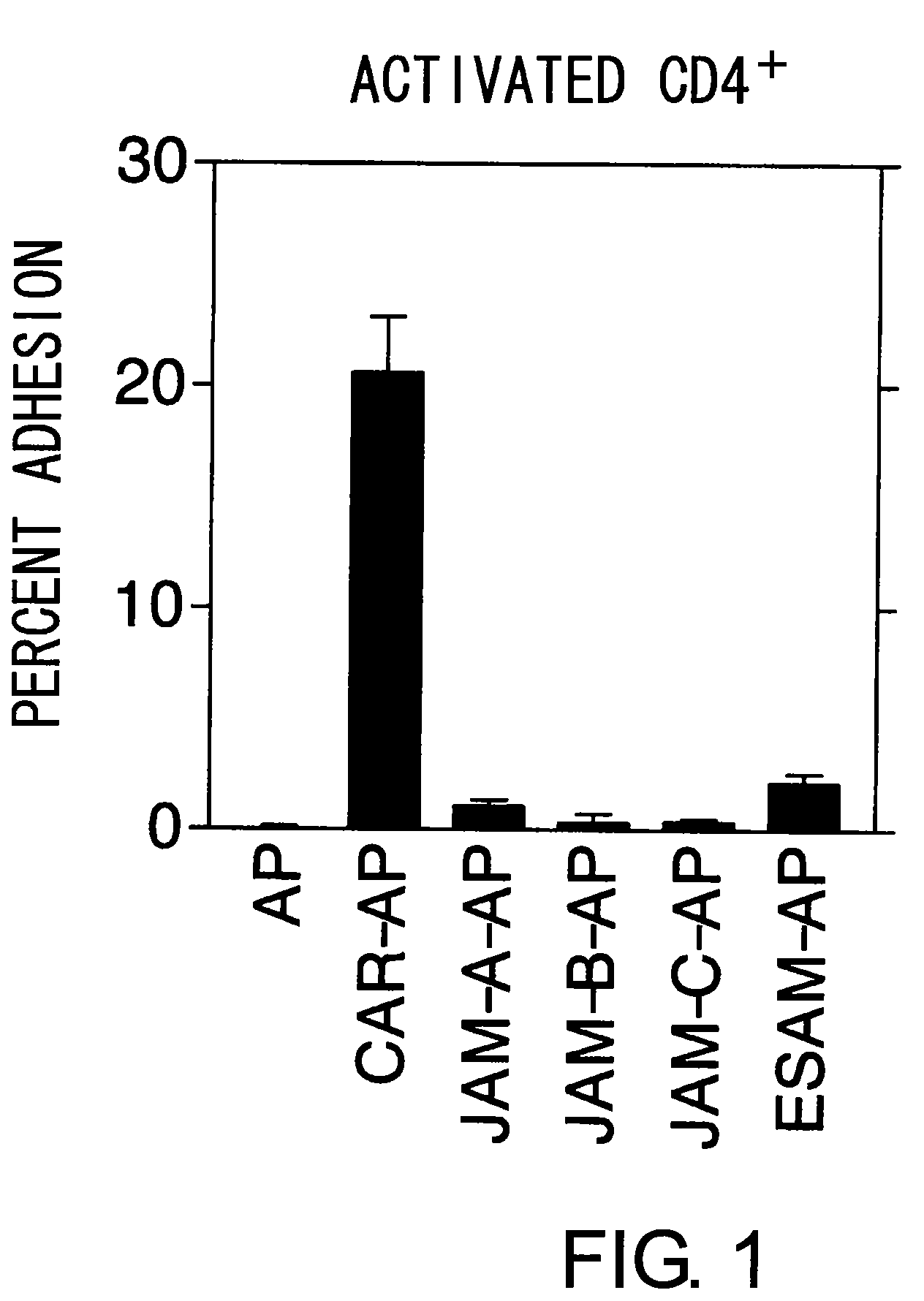
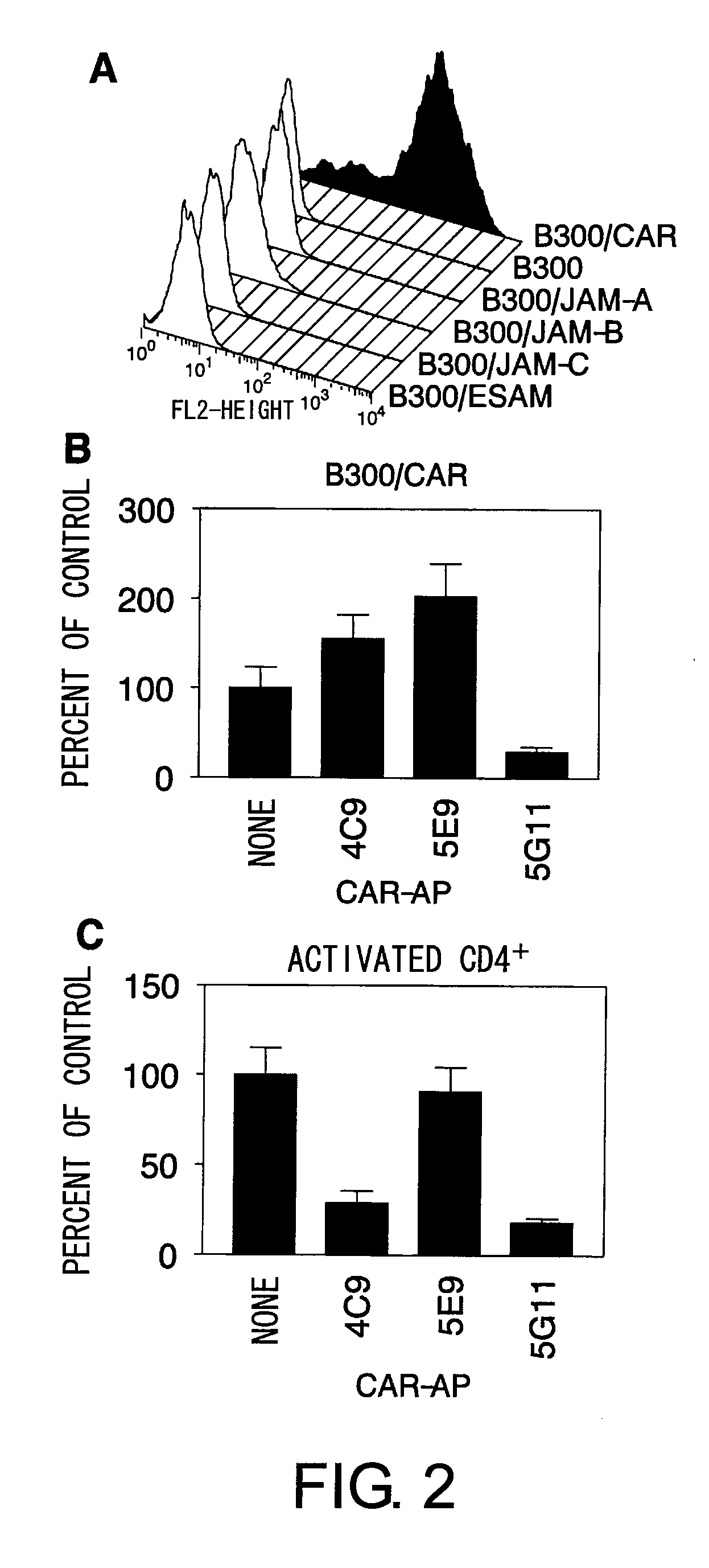
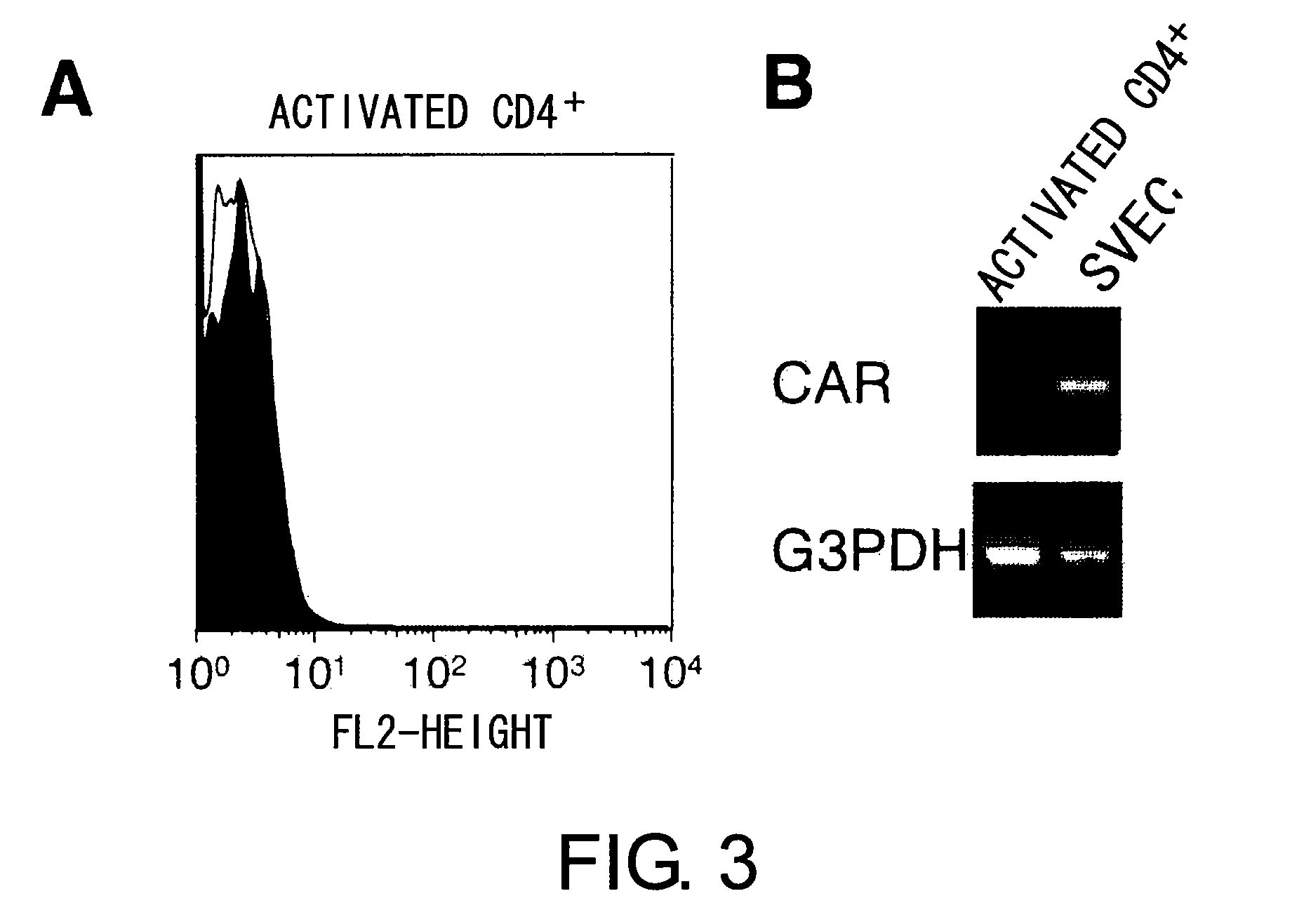
InactiveUS8017344B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansActivated LymphocyteBinding inhibition
The inventors discovered that the adhesion molecule CAR, known to be localized in intracellular adhesion sites, functioned as an adhesion molecule for activated lymphocytes. Further, the inventors identified CARL, a novel CAR ligand expressed in lymphocytes, and clarified that the ligand was expressed selectively in Th1 cells. In addition, they found that anti-CAR antibodies could inhibit the adhesion of activated lymphocytes to CAR molecules. Thus, the present invention provides methods for detecting Th1 cells using CAR or anti-CARL antibodies, and methods of screening for inhibitors suppressing the adhesion of Th1 cells using the binding between CAR and CARL as an index. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of screening for inhibitors of the binding between CAR and CARL, antibodies that inhibit the binding between CAR and CARL, and therapeutic compositions comprising these antibodies. These are expected to be useful in diagnosing diseases, such as inflammation, in which infiltration of Th1 cells is involved, and in providing pharmaceutical agents for alleviating such diseases.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
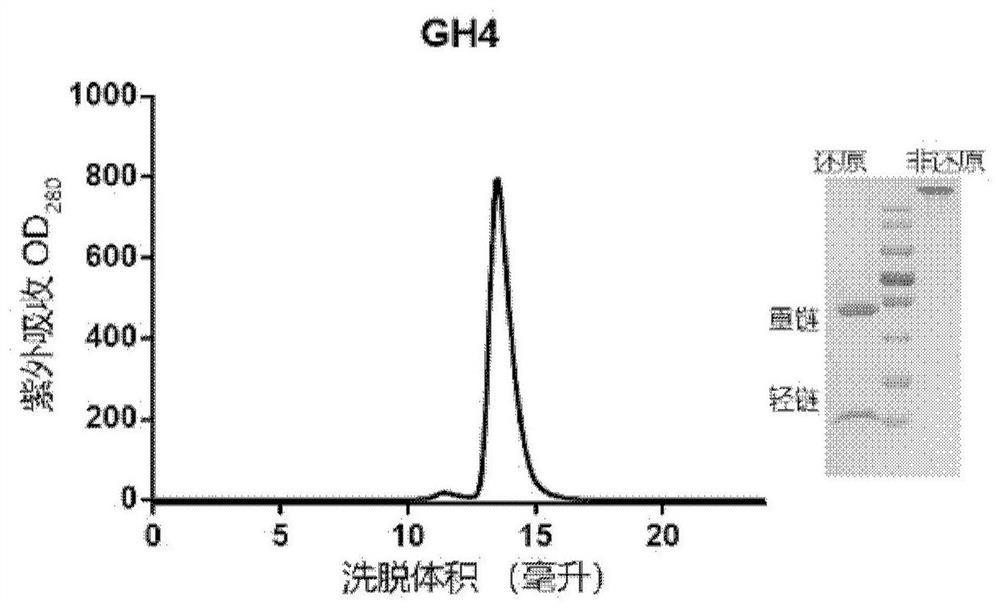
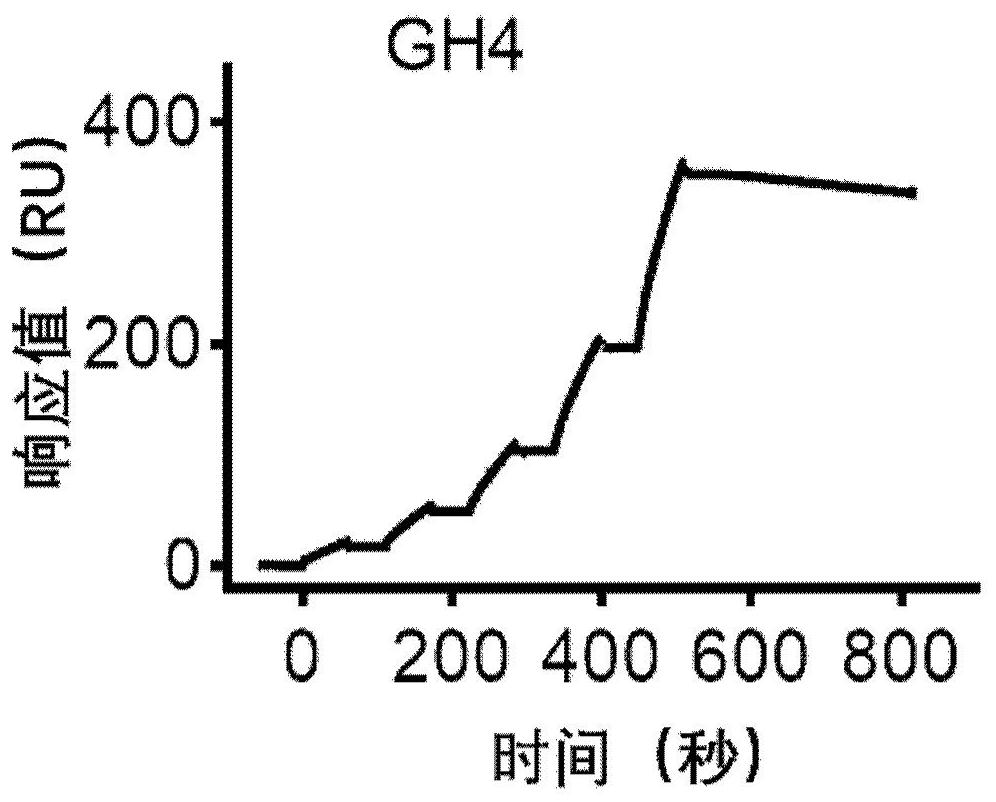
Humanized monoclonal antibody of novel coronavirus and application thereof
ActiveCN113292649ABinding blockGood neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding inhibition
The invention relates to a novel human monoclonal antibody of coronavirus and application of the novel human monoclonal antibody. The antibody can be specifically combined with the 2019-nCoV RBD, the combination of the 2019-nCoV RBD and ACE2 is blocked, and the infection of the 2019-nCoV is inhibited.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-IL-1beta (anti-interleukin-1beta) antibody as well as medicine composition and application thereof
InactiveCN110818793AEffective combinationBinding blockAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntigenAutoimmune condition
The invention belongs to the field of immunology and relates to an anti-IL-1beta (anti-interleukin-1beta) antibody as well as a medicine composition and application thereof. Specially, the invention relates to the anti-IL-1beta antibody or an antigen binding fragment thereof. The heavy chain variable region of the antibody comprises HCDR1-3 (heavy chain complementary determining region 1-3) of which amino acid sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO:17-19 in the description respectively; and the light chain variable region of the antibody comprises LCDR1-3 (light chain complementary determining region 1-3) of which amino acid sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO:20-22 in the description respectively. The antibody provided by the invention is capable of effectively binding human IL-1beta, blocking binding of IL-1beta with a receptor IL-1R1 and inhibiting activation of a downstream signal channel of IL-1beta, and has the potential of preparing medicines for preventing and treating autoimmune diseases, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes of children and adults, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, gouty arthritis, cardiovascular diseases or tumors.
Owner:AKESO BIOPHARMA
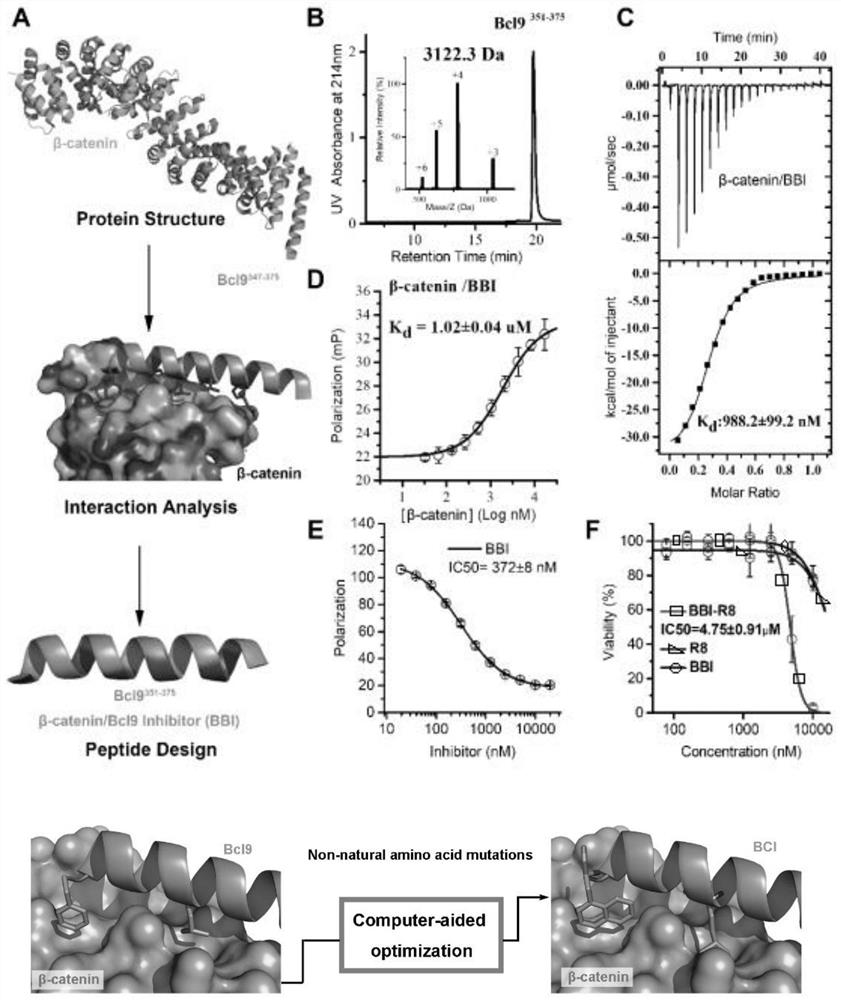
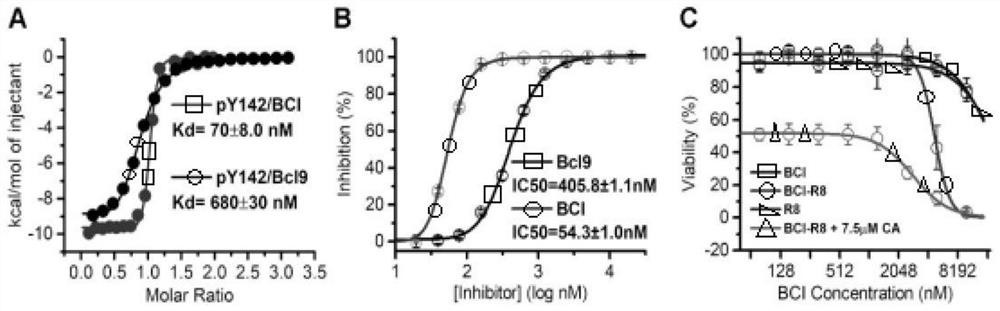
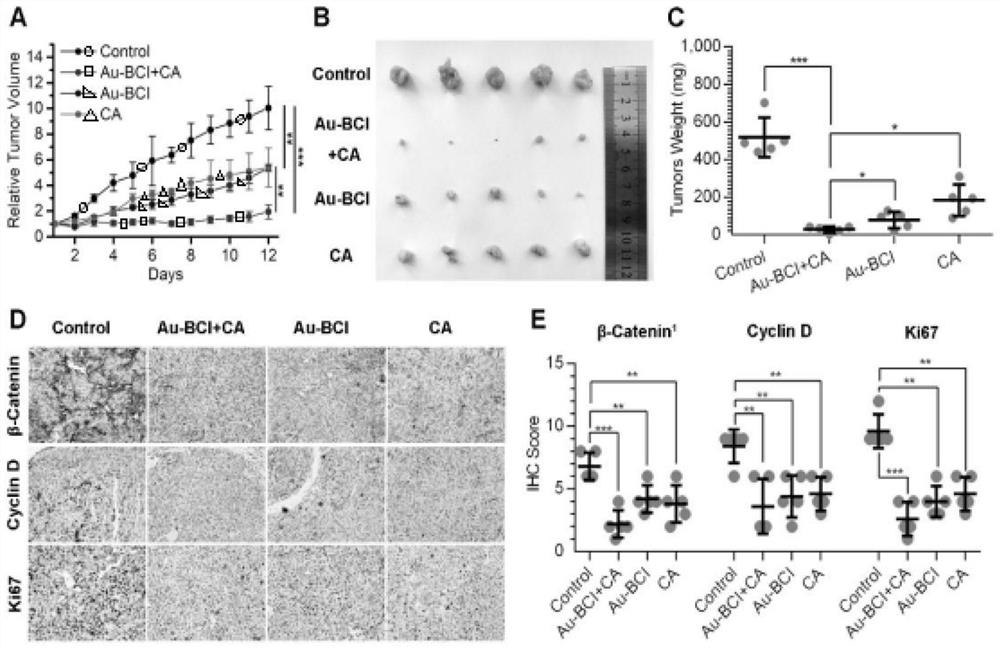
Polypeptide specifically combined with beta-catenin protein with high affinity, and application and synthesis method of polypeptide
ActiveCN111909242AThe synthesis method is simple and easy to obtainInhibit onPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseCancer cell
The invention discloses a polypeptide specifically combined with beta-catenin protein with high affinity, and application and a synthesis method of the polypeptide. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is LEHRERSLQT(X1)RDIQRML(X2)P, wherein X1 is leucine, norleucine or homoleucine, and X2 is phenylalanine, 1-naphthyl alanine, 2-naphthyl alanine, 2-anthryl alanine or 9-anthryl alanine. The polypeptide is used for inhibiting growth of cancer cells. By the polypeptide, various tumor treatment targets can be achieved. The polypeptide inhibits opening of a beta-catenin protein-mediated Wnt signal pathway by inhibiting mutual combination of the beta-catenin protein and BCL9 in the cancer cells, so that growth of tumors is inhibited, self-apoptosis of the cells is induced, and the tumor disease treatment targets are achieved. The synthesis method of the polypeptide is simple and easy to implement, and the final product has high yield efficiency, has mass production potential, and has great drug clinical transformation potential.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Application of paeonol in preparing medicament for preventing and treating disease of TOPK activity abnormal elevation
InactiveCN106727455APrevent and/or treat inflammationPrevent and/or treat tumorsAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseInflammatory factors
The invention discloses a novel effect and molecular mechanism of Paeonol and aims to provide an application of paeonol in preparing a medicament for preventing and treating a disease of TOPK activity abnormal elevation. Paeonol inhibits photodermatoses (sunburn and chronic actinic dermatosis) induced by ultraviolet rays (UV), which is realized by combining protein kinase (TOPK) originated from a T-LAK cell, inhibiting the activity thereof and blocking a TOPK signal channel. Immunopathology indicates that TOPK, P38 and JNK in skin lesion of photodermatoses are increased in expression. In a cell experiment, the activity of TOPK affects phosphorylation of P38 and JNK induced by UV. Through a molecular docking experiment, paeonol can be directly combined with TOPK to inhibit activation of TOPK and inhibit phosphorylation of p38, JNK and H2AX and secretion of inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-alpha. An animal experiment also verifies a cell experimental result.
Owner:史飞
Nucleic acid aptamer specifically binding to P-glycoprotein, and preparation method and application of nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN111304208AInhibitory functionStrong specificityBiological testingDNA preparationAptamerChemical synthesis
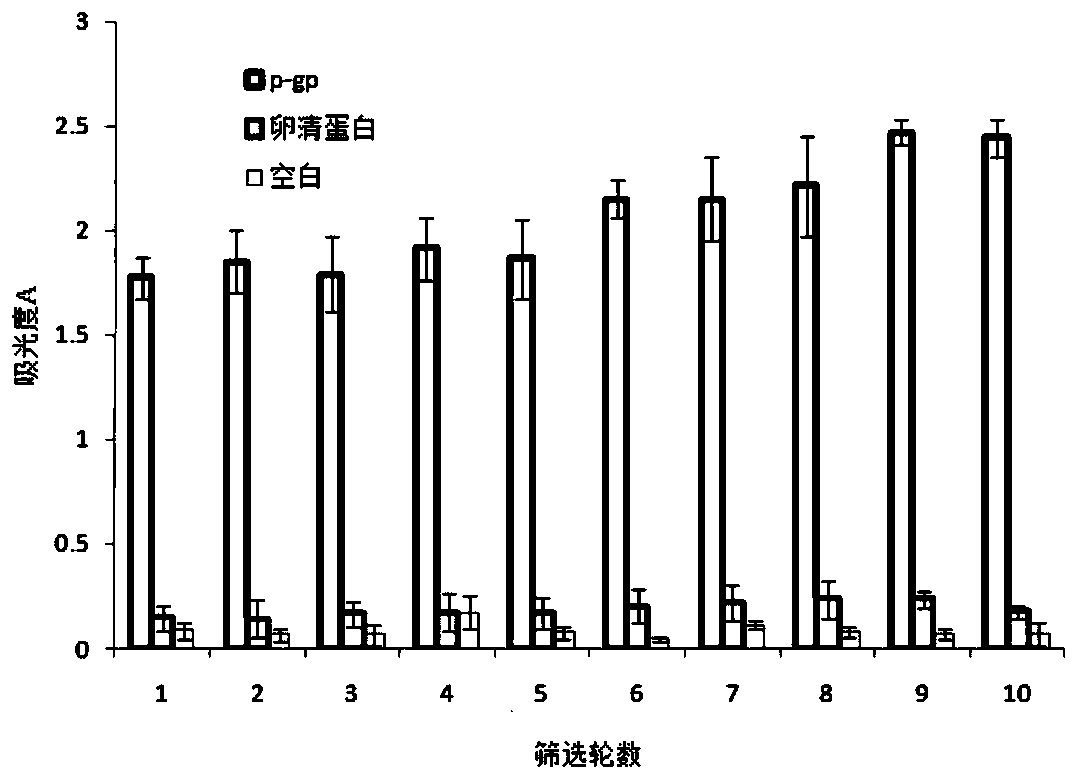
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer specifically binding to P-glycoprotein (P-gp), and a preparation method and application of the nucleic acid aptamer, and belongs to the technical fieldof biology. The nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer is selected from SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.14 in sequence tables; the nucleic acid aptamer is prepared by screening, amplifying and sequencing an original random oligonucleotide library through an SELEX technology in combination with surface modified magnetic beads; the nucleic acid aptamer is small in molecular weight, can be chemically synthesized, and is low in cost; the affinity and the specificity are high; marking is facilitated; and the repeatability and the stability are high, and storage is easy. The nucleic acid aptamer can be made into a fluorescent molecular probe, and fluorescent visualization and quantification of P-gp on in-vitro tissues and cells of an organism are realized; and the nucleic acid aptamer can be specifically bound with P-gp, inhibits the function of P-gp, and becomes a potential nucleic acid type inhibitor of the function of P-gp.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com