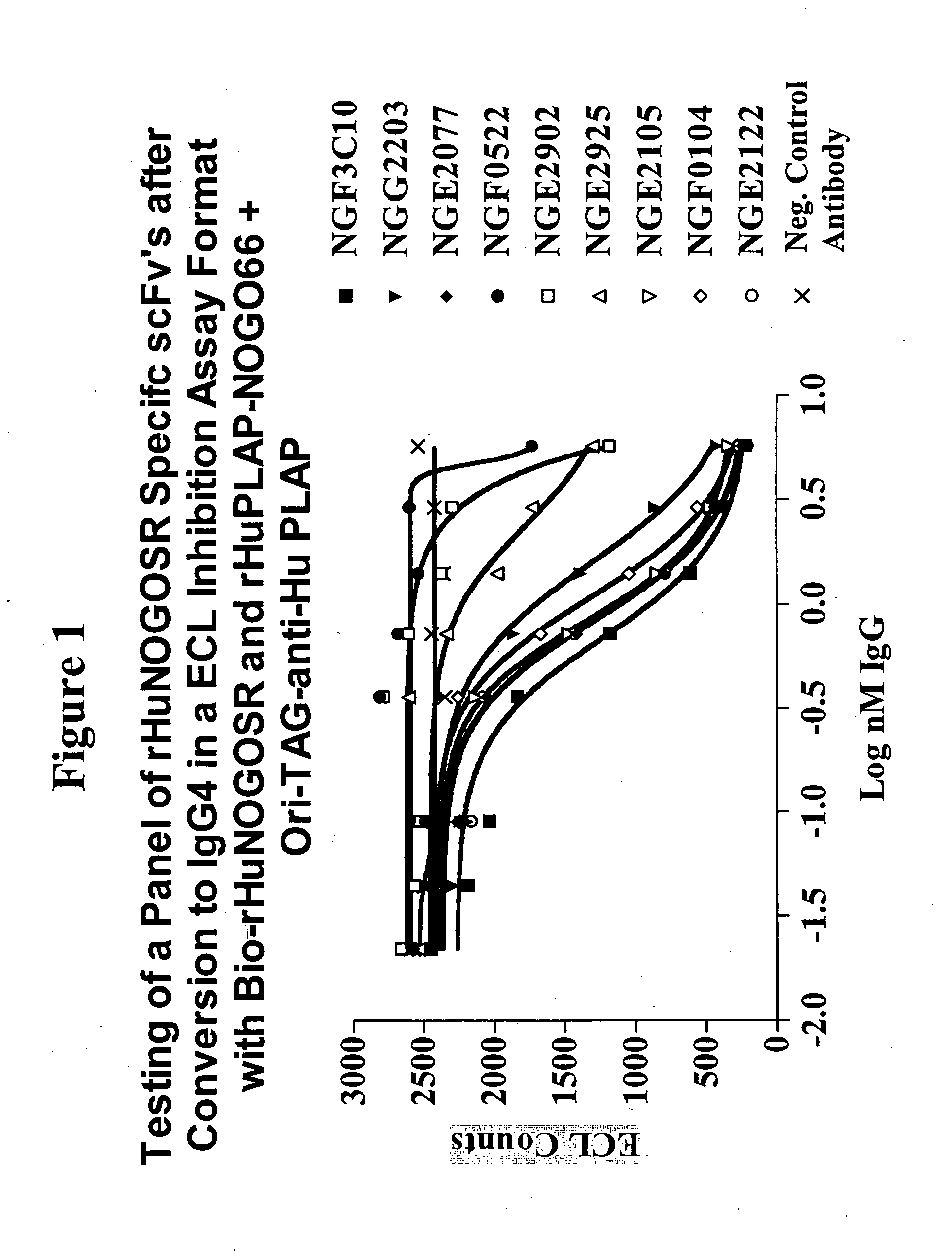
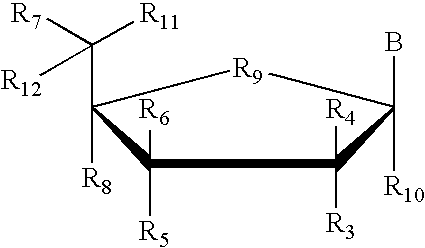
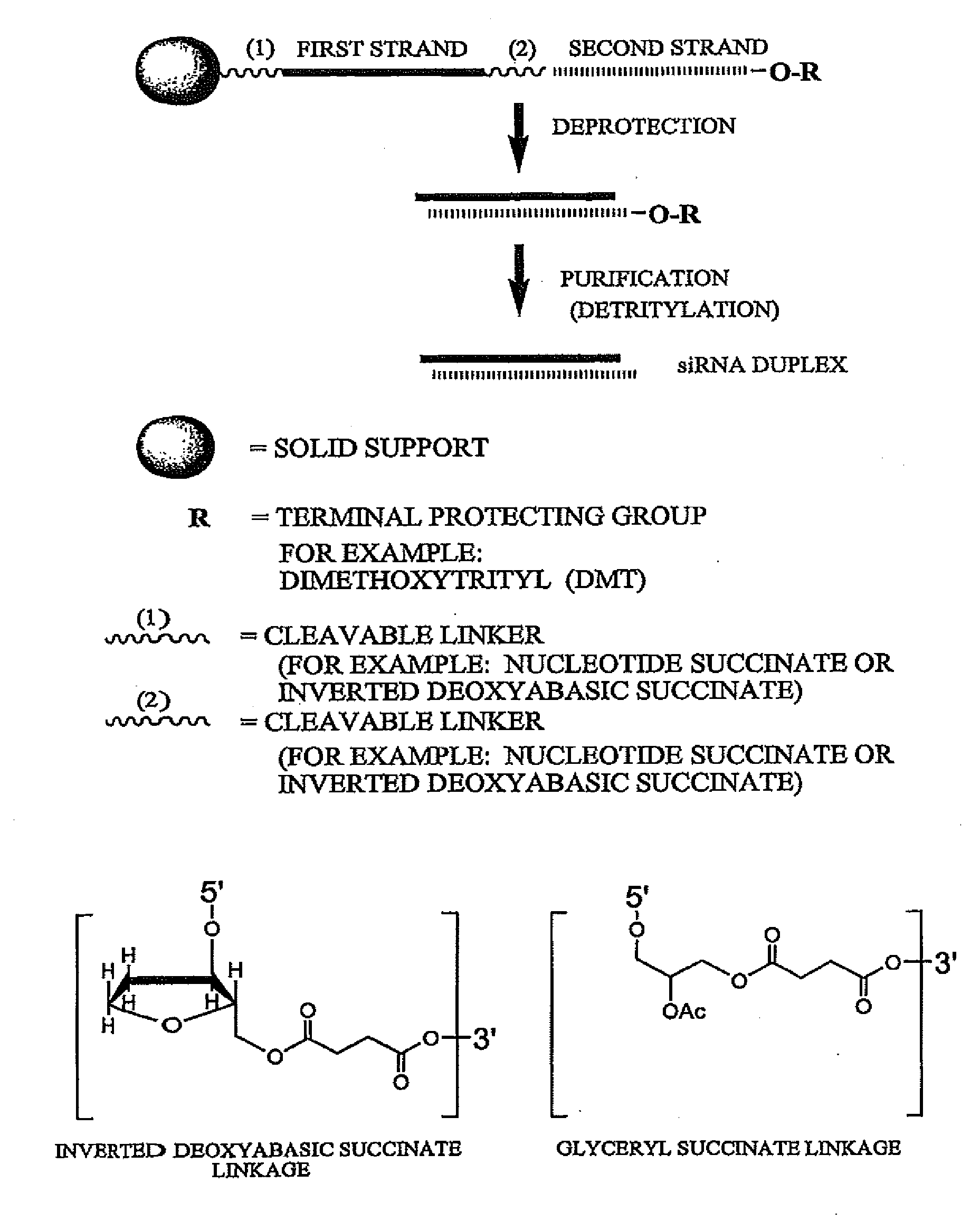
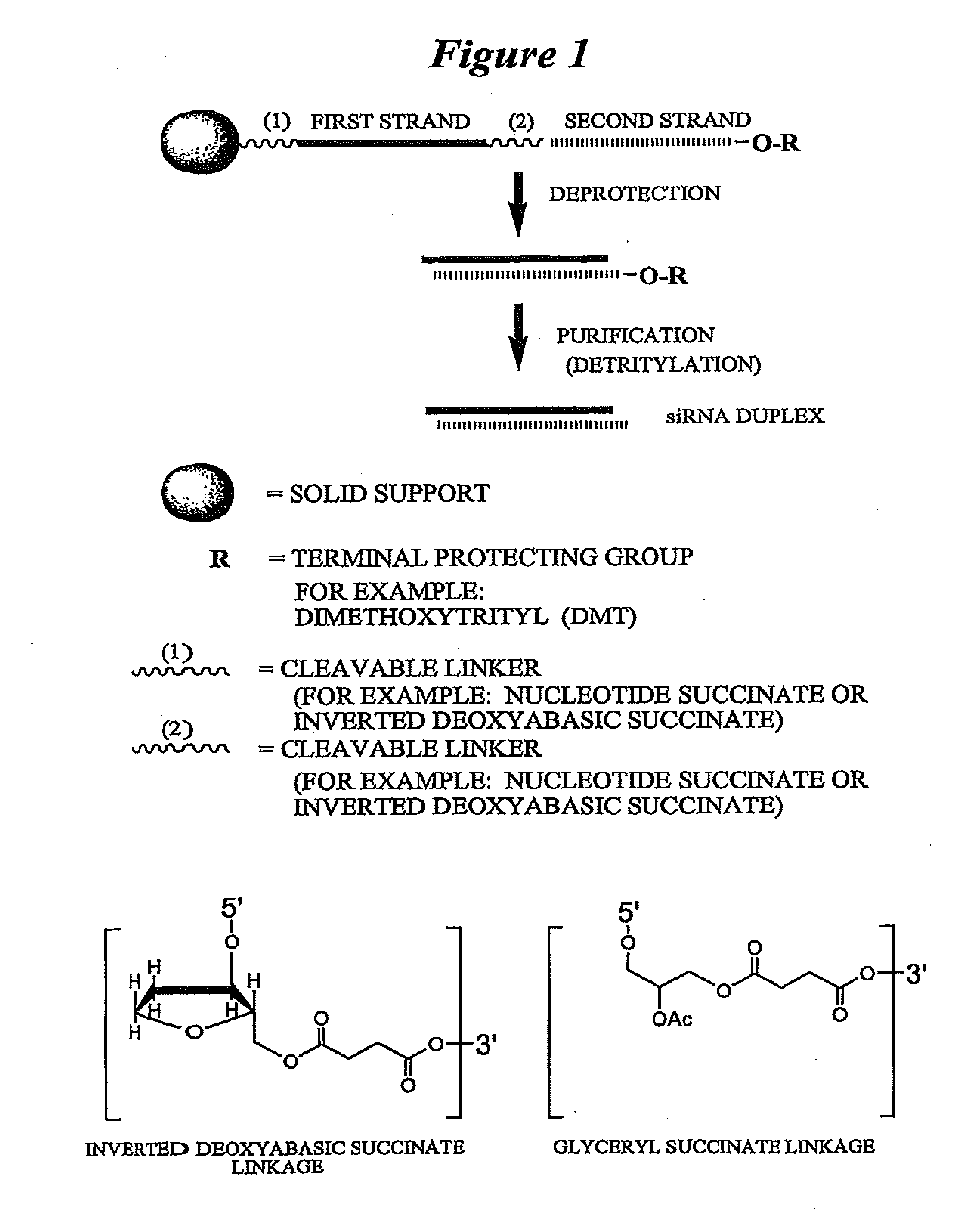
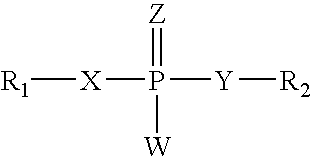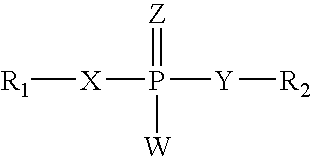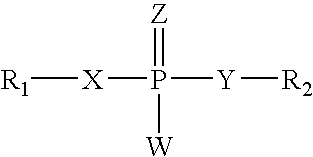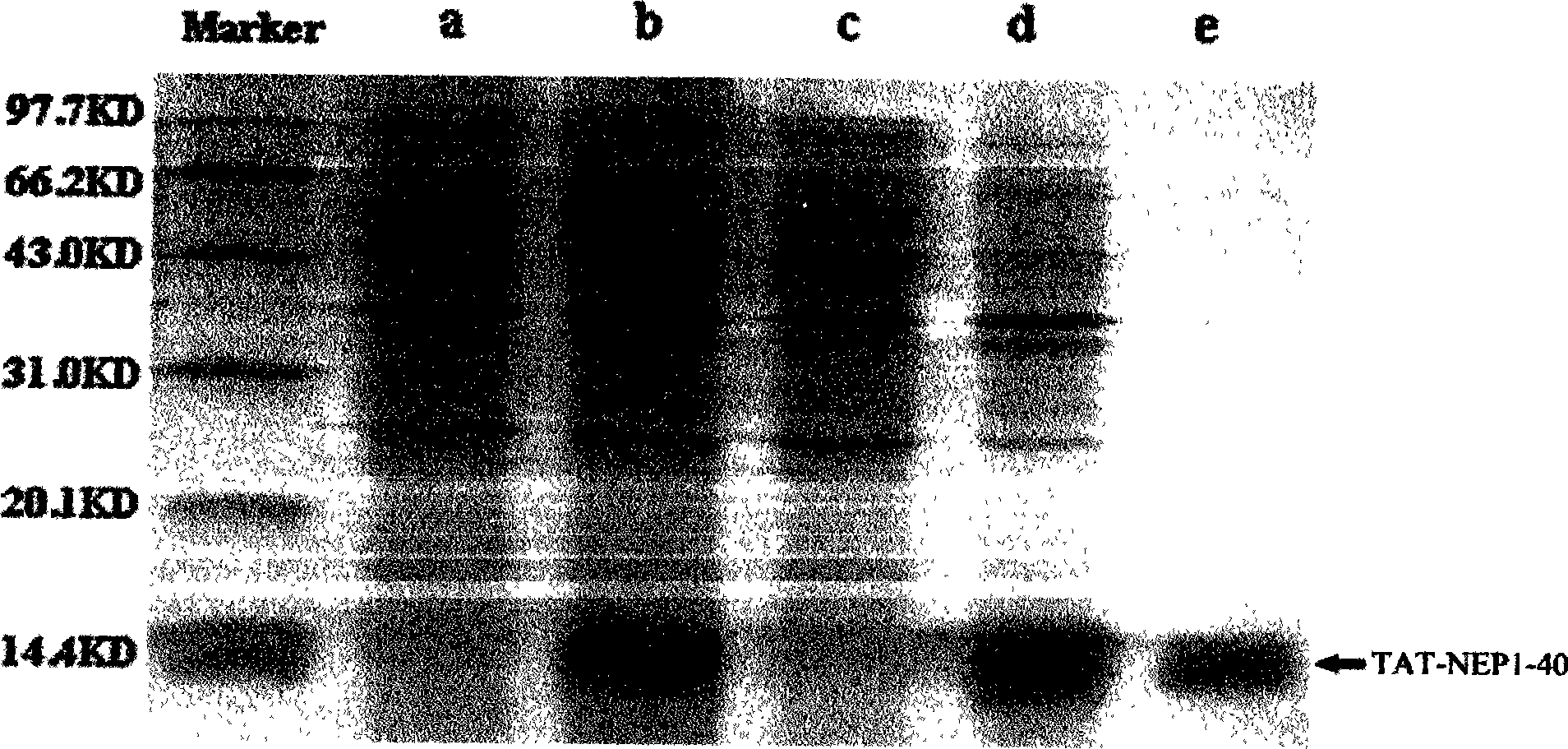Patents
Literature
42 results about "Nogo Receptors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
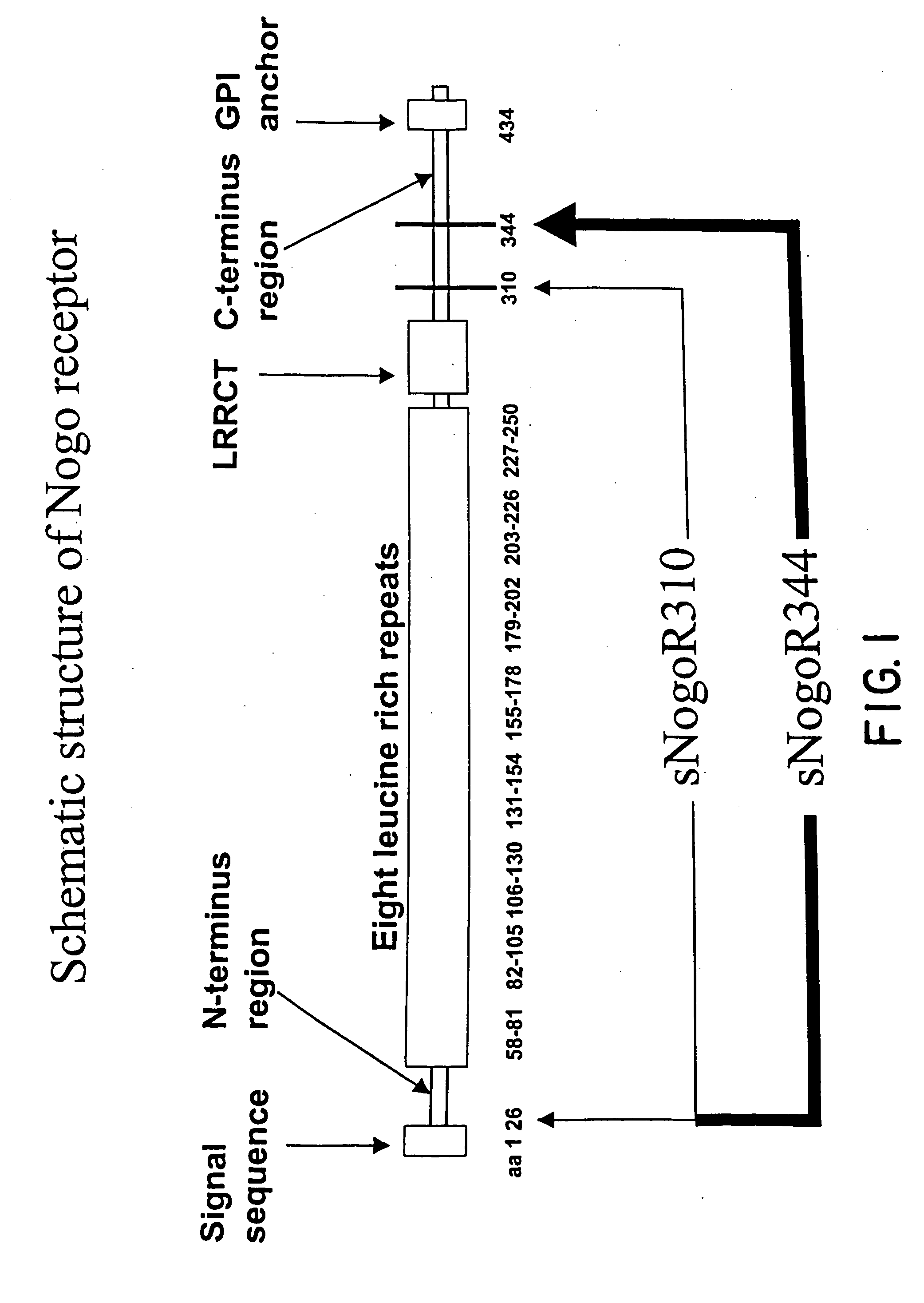
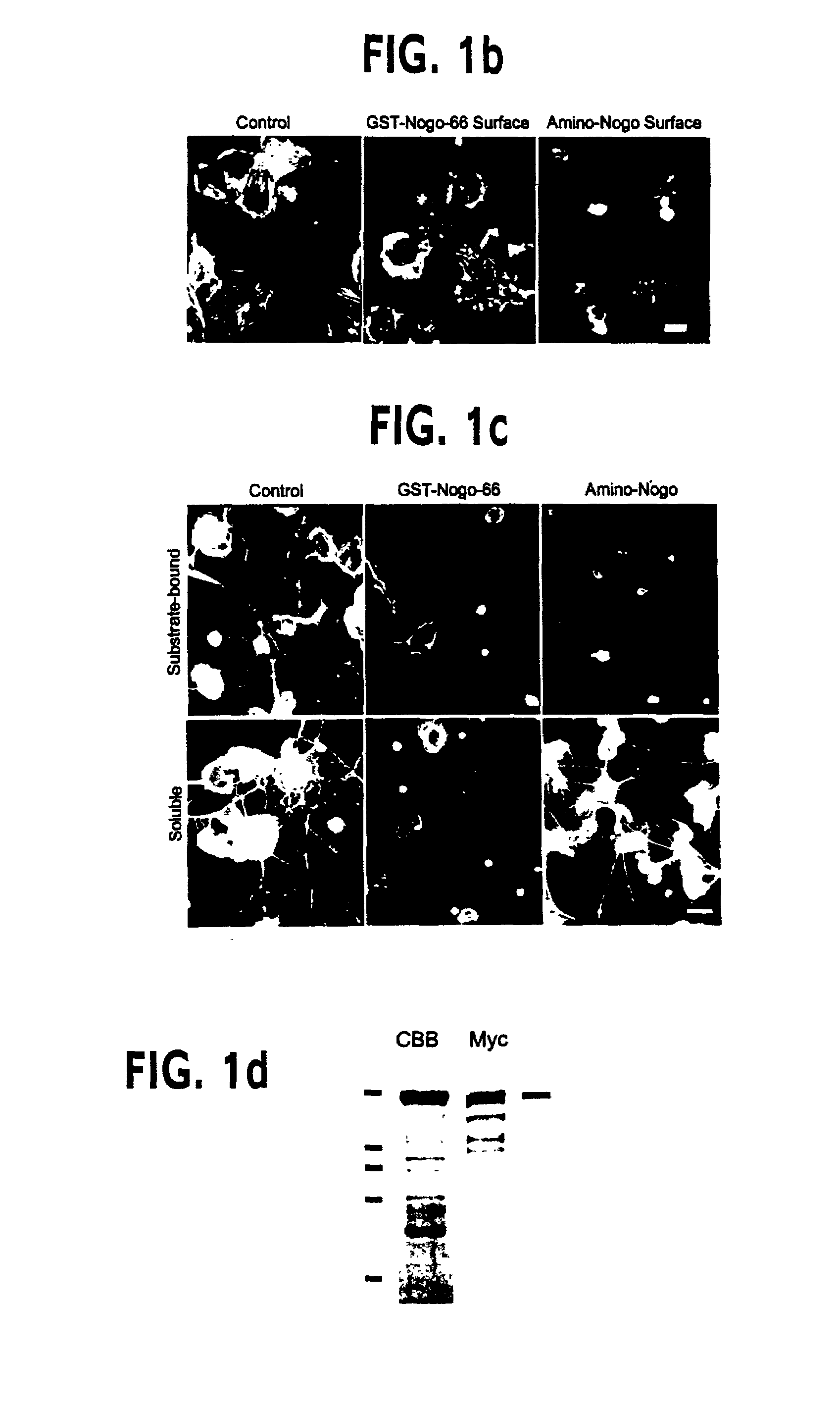
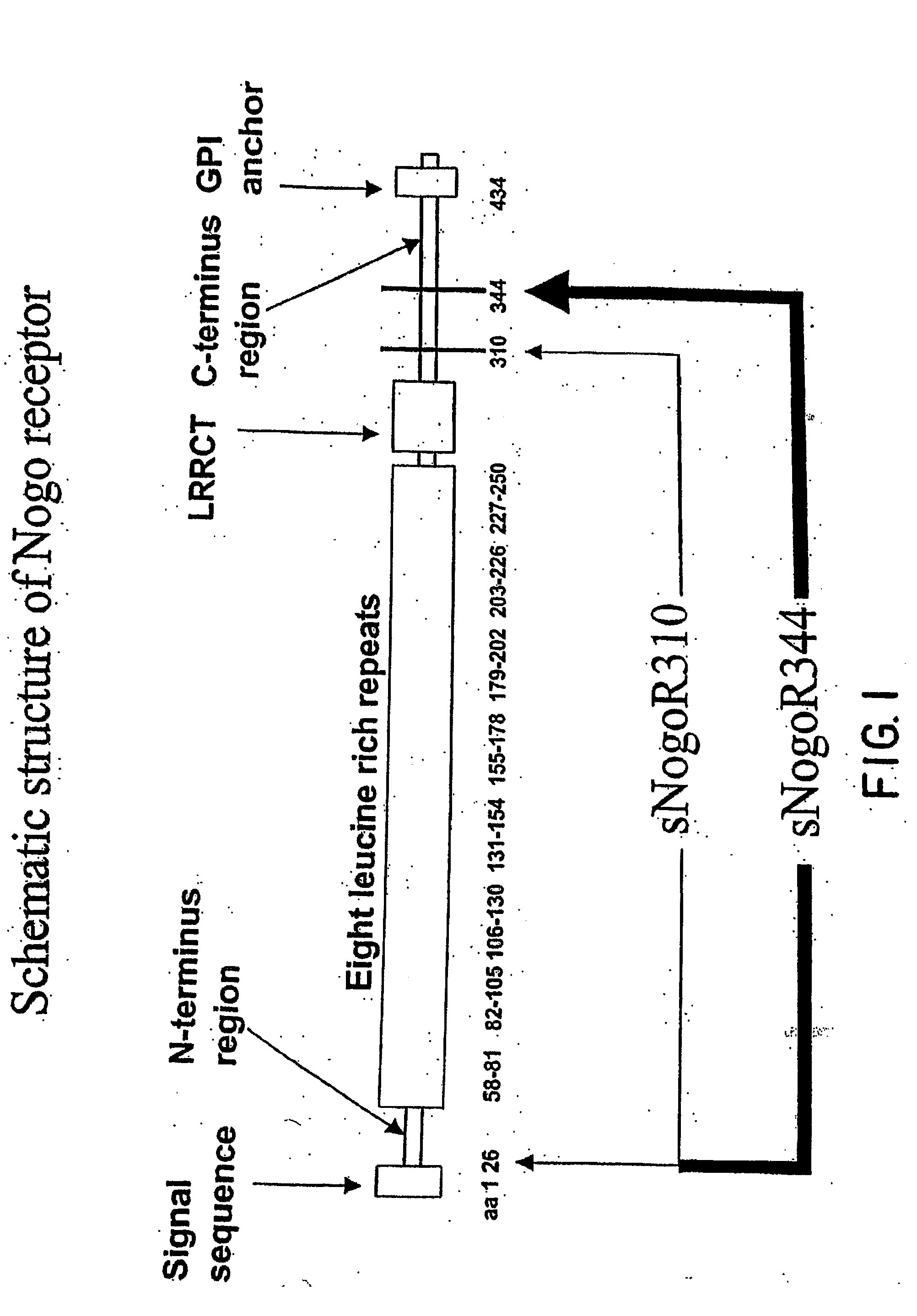
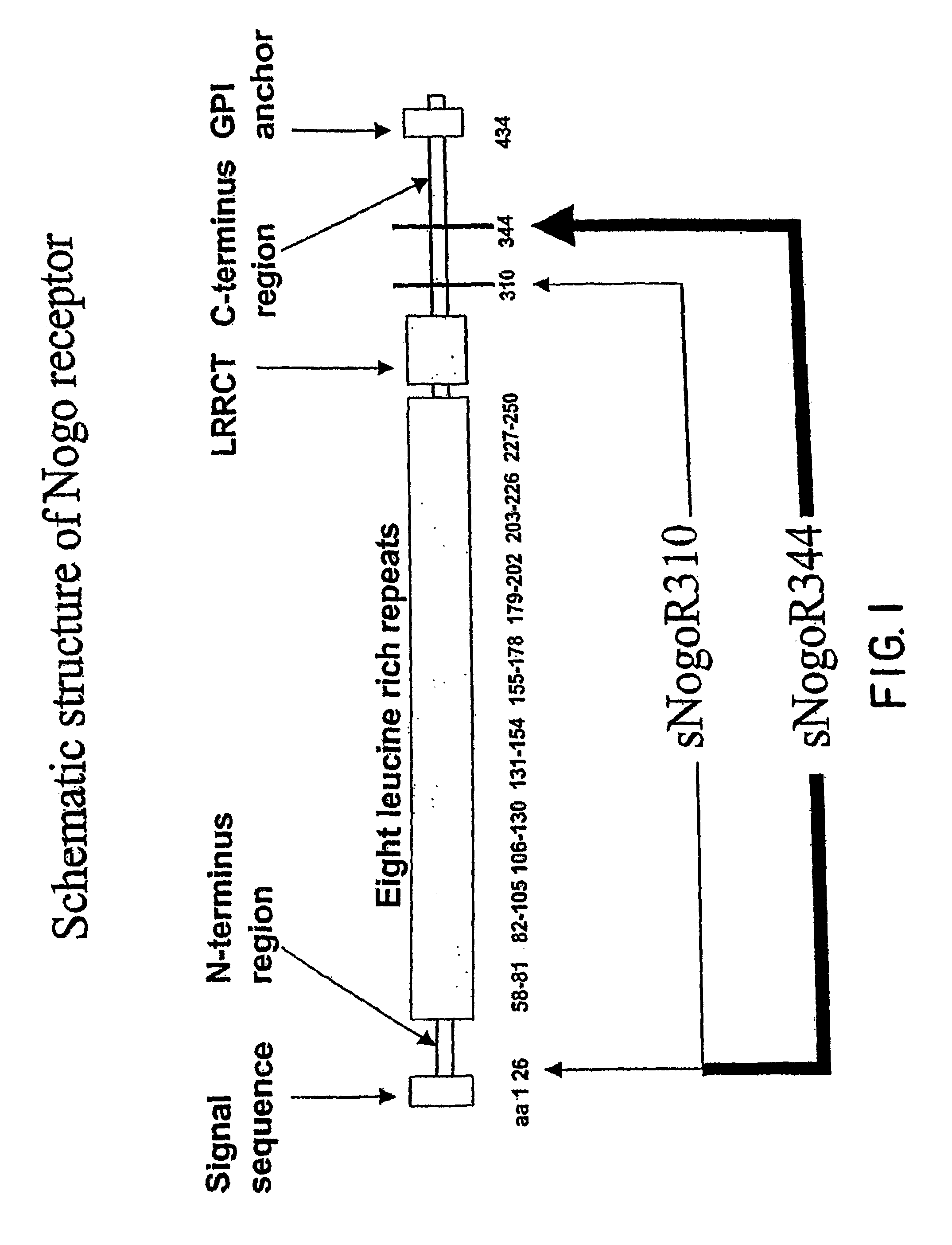
Reticulon 4 receptor (RTN4R) also known as Nogo-66 Receptor (NgR) or Nogo receptor 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RTN4R gene. This gene encodes the receptor for reticulon 4, oligodendrocytemyelin glycoprotein and myelin-associated glycoprotein.
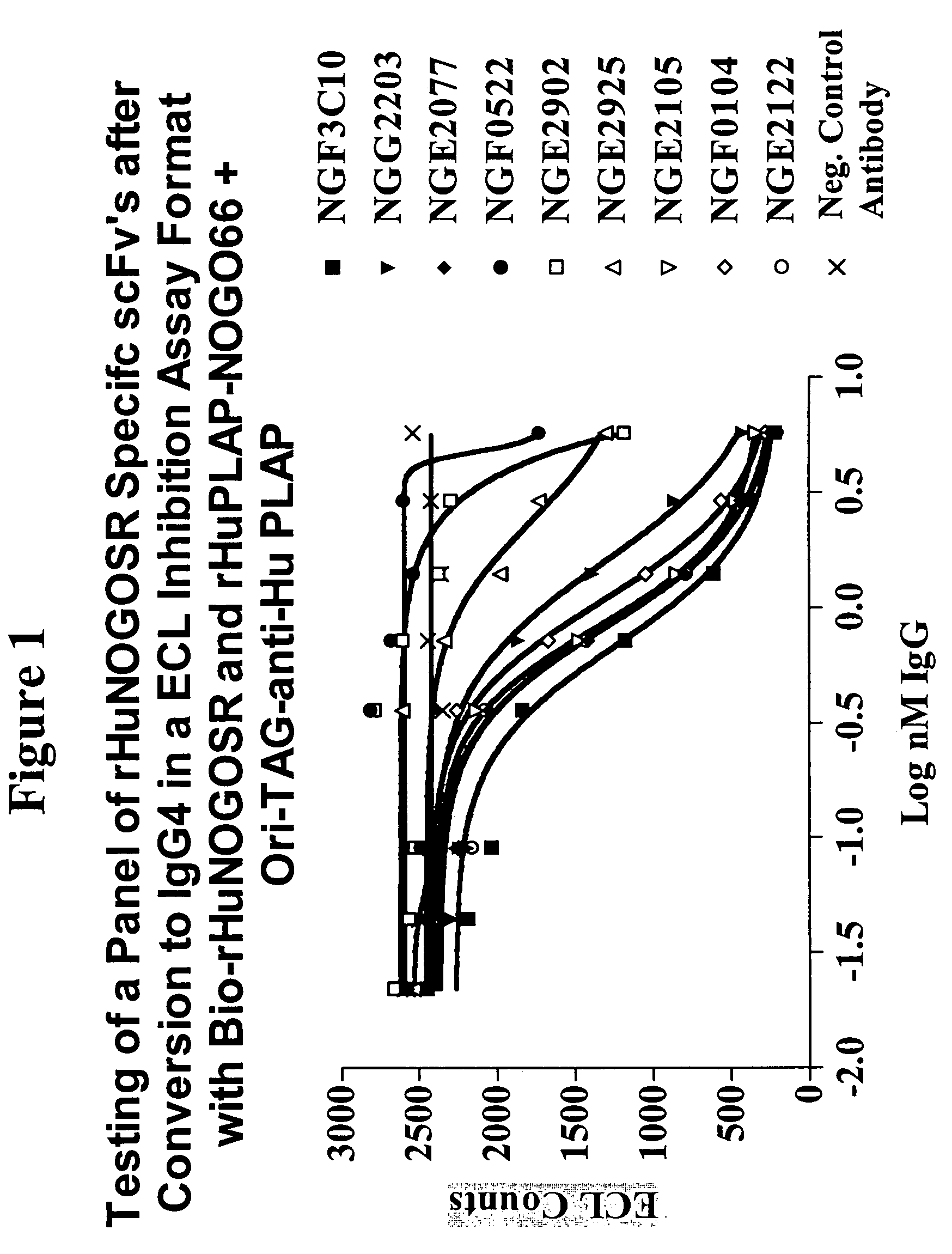
Antibodies against Nogo receptor
ActiveUS20050215770A1Promote neuronalPromote axonal regenerationAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNervous system diseaseNogo Receptors
The present invention relates to antibodies and related molecules that specifically bind to the Nogo receptor (NogoR). Such antibodies have uses, for example, in the treatment of spinal cord injury, brain trauma, paralysis, degenerative nervous system diseases, and stroke. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding anti-NogoR antibodies, vectors and host cells containing these nucleic acids, and methods for producing the same.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
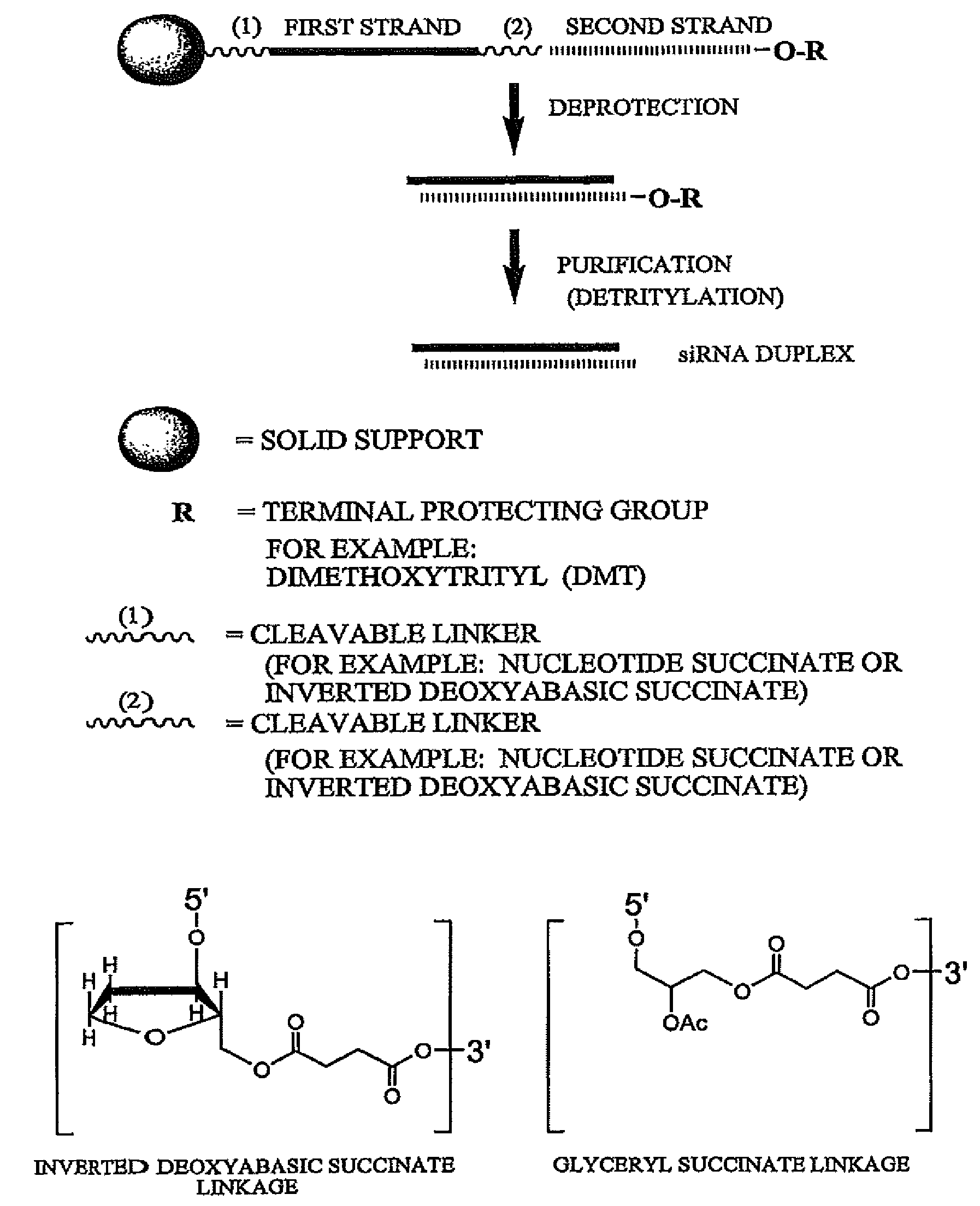
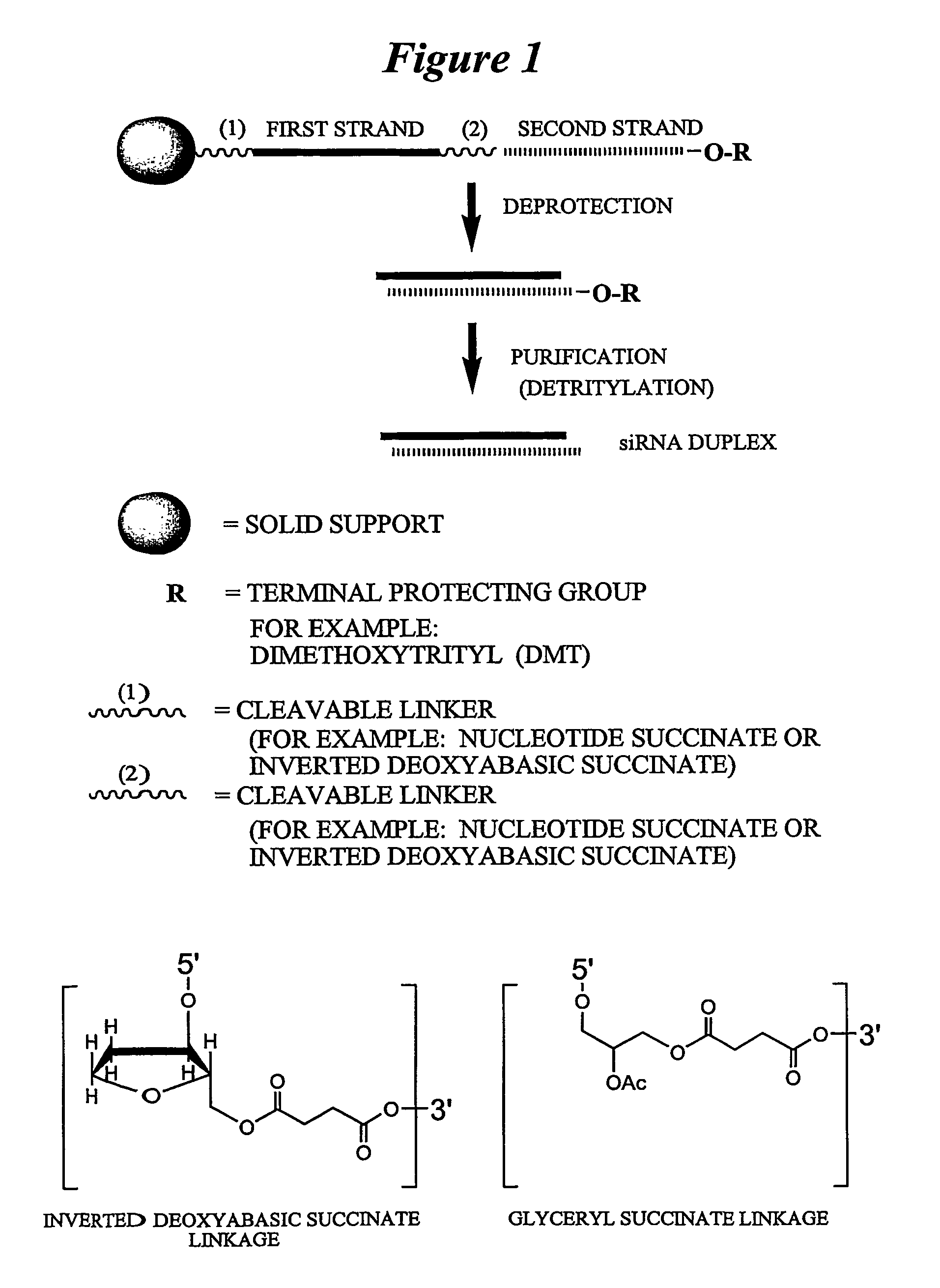
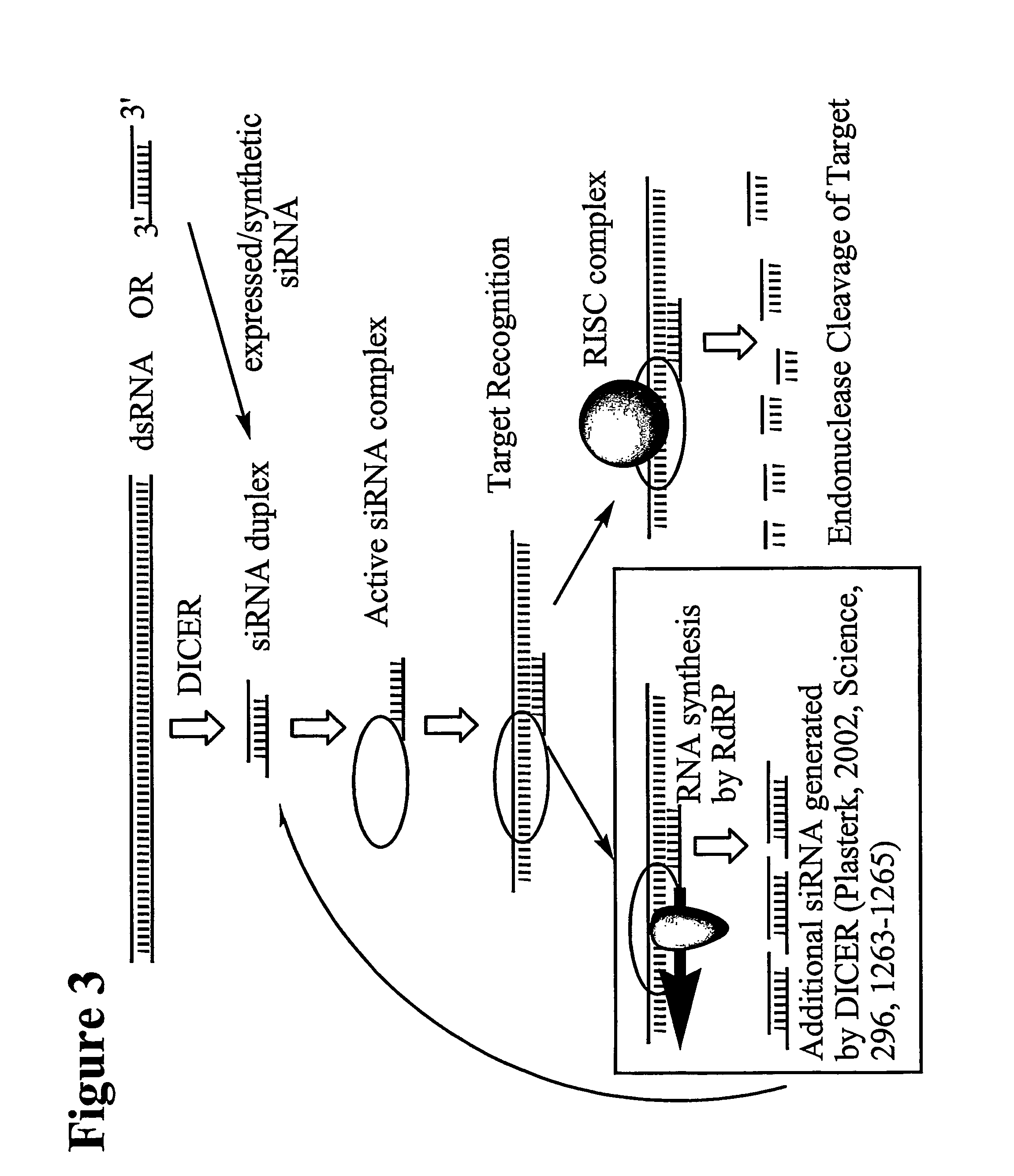
RNA interference mediated inhibition of NOGO and NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering RNA
InactiveUS20050261212A1Preserve activityImprove compound stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRegulator genePolynucleotide
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications associated with Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, the invention relates to small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against NOGO and NOGO receptor (NOGOr) polypeptide and polynucleotide targets.
Owner:RIBOZYME PHARMA INC
Antibodies against Nogo receptor
InactiveUS20050214288A1Promote neuronalPromote axonal regenerationBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRisk strokeNervous system disease
The present invention relates to antibodies and related molecules that specifically bind to the Nogo receptor (NogoR). Such antibodies have uses, for example, in the treatment of spinal cord injury, brain trauma, paralysis, degenerative nervous system diseases, and stroke. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding anti-NogoR antibodies, vectors and host cells containing these nucleic acids, and methods for producing the same.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Nogo receptor antagonists
ActiveUS20050271655A1Inhibit bindingReduce inhibitionFungiBacteriaAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
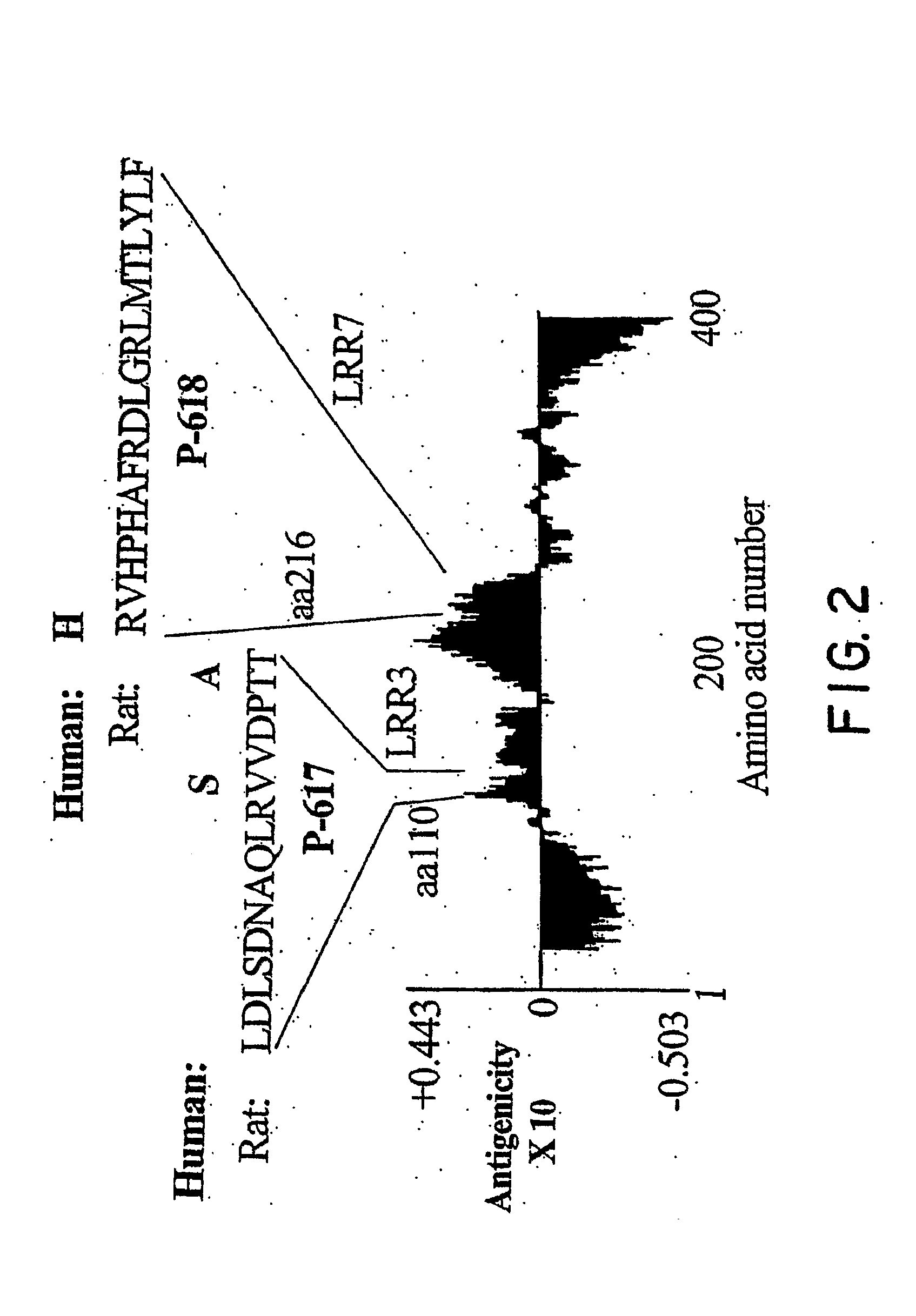
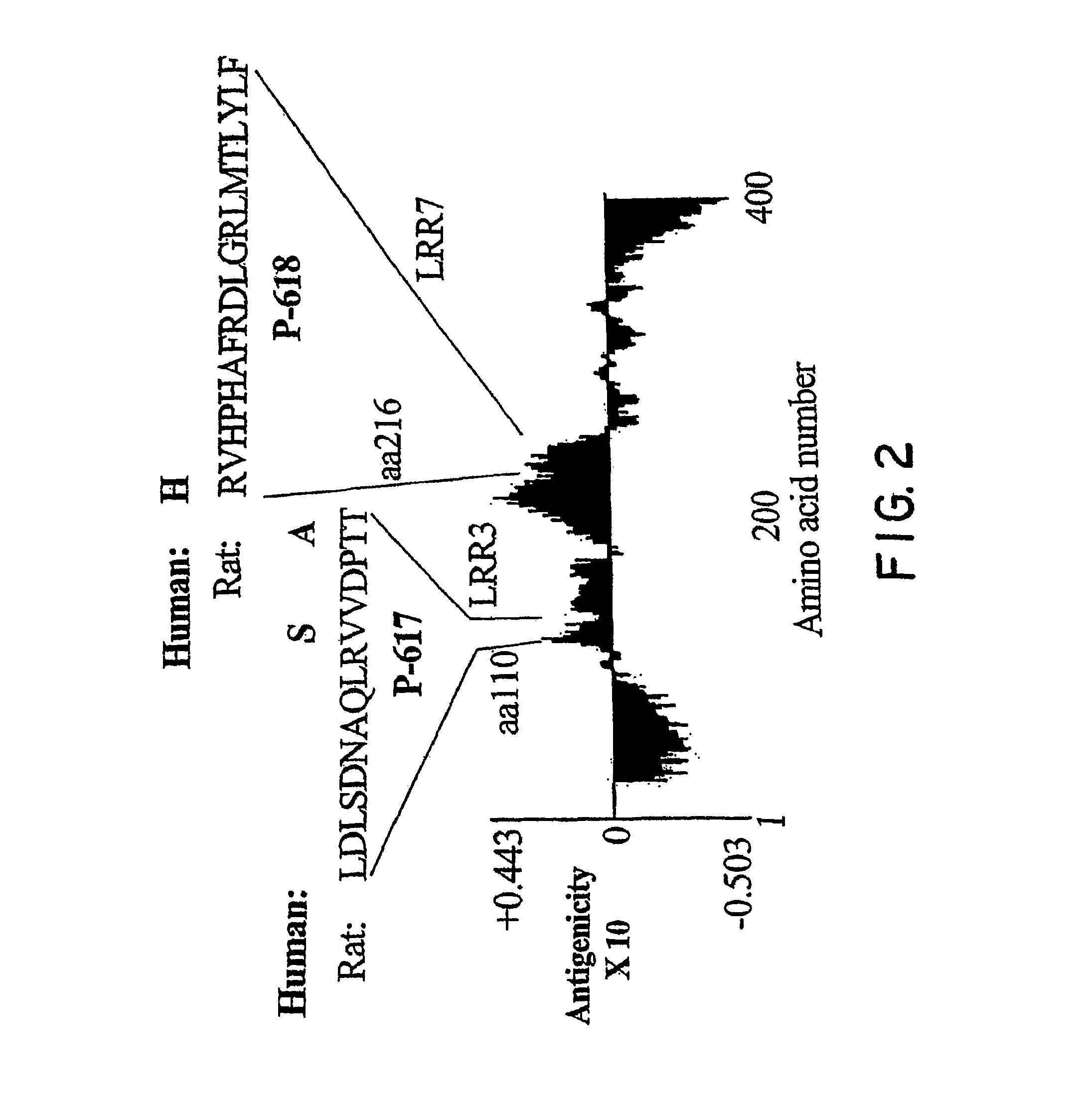
Disclosed are immunogenic Nogo receptor-1 polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same. Also disclosed are compositions comprising, and methods for making and using, such Nogo receptor antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Nogo receptor-mediated blockade of axonal growth
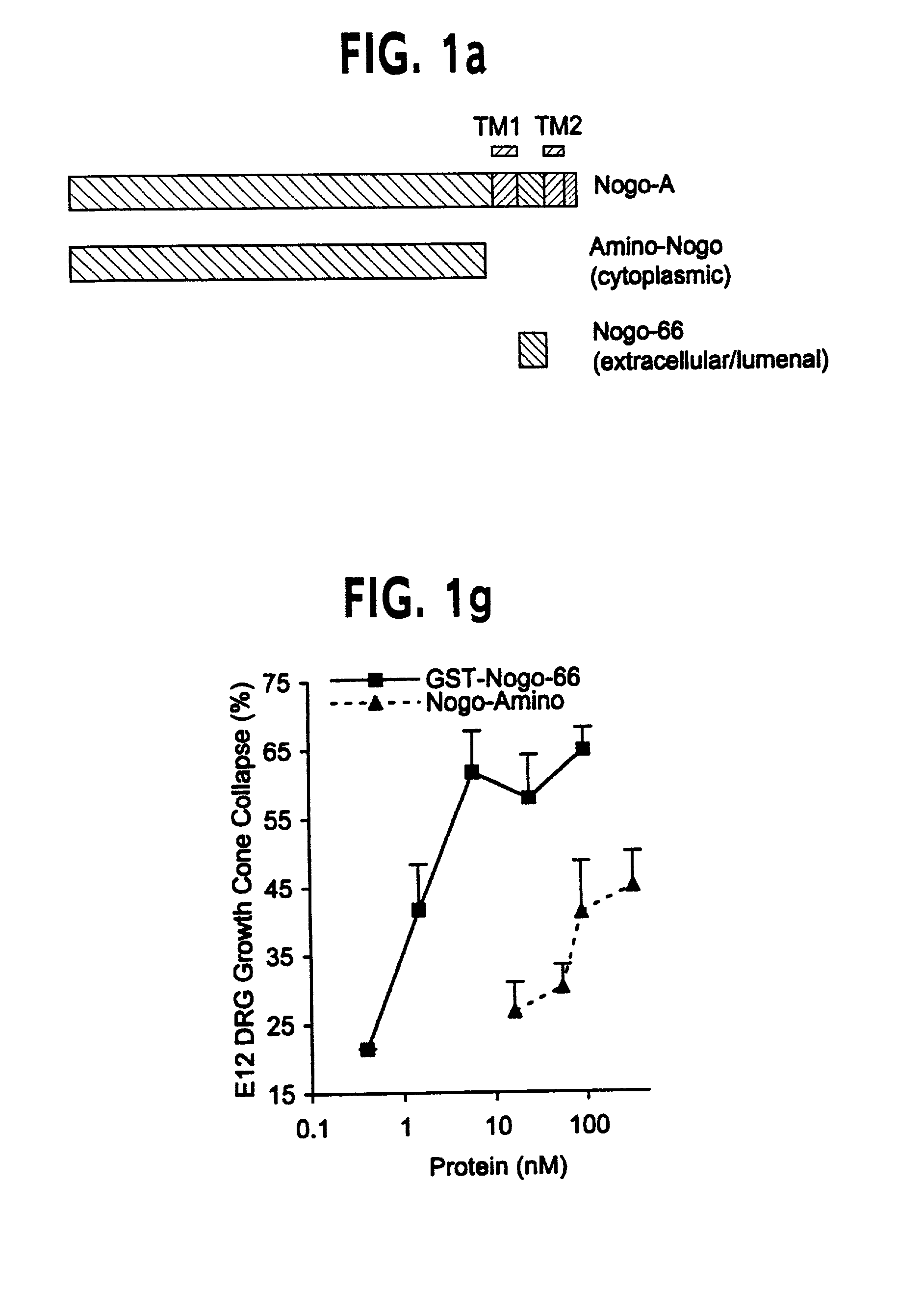
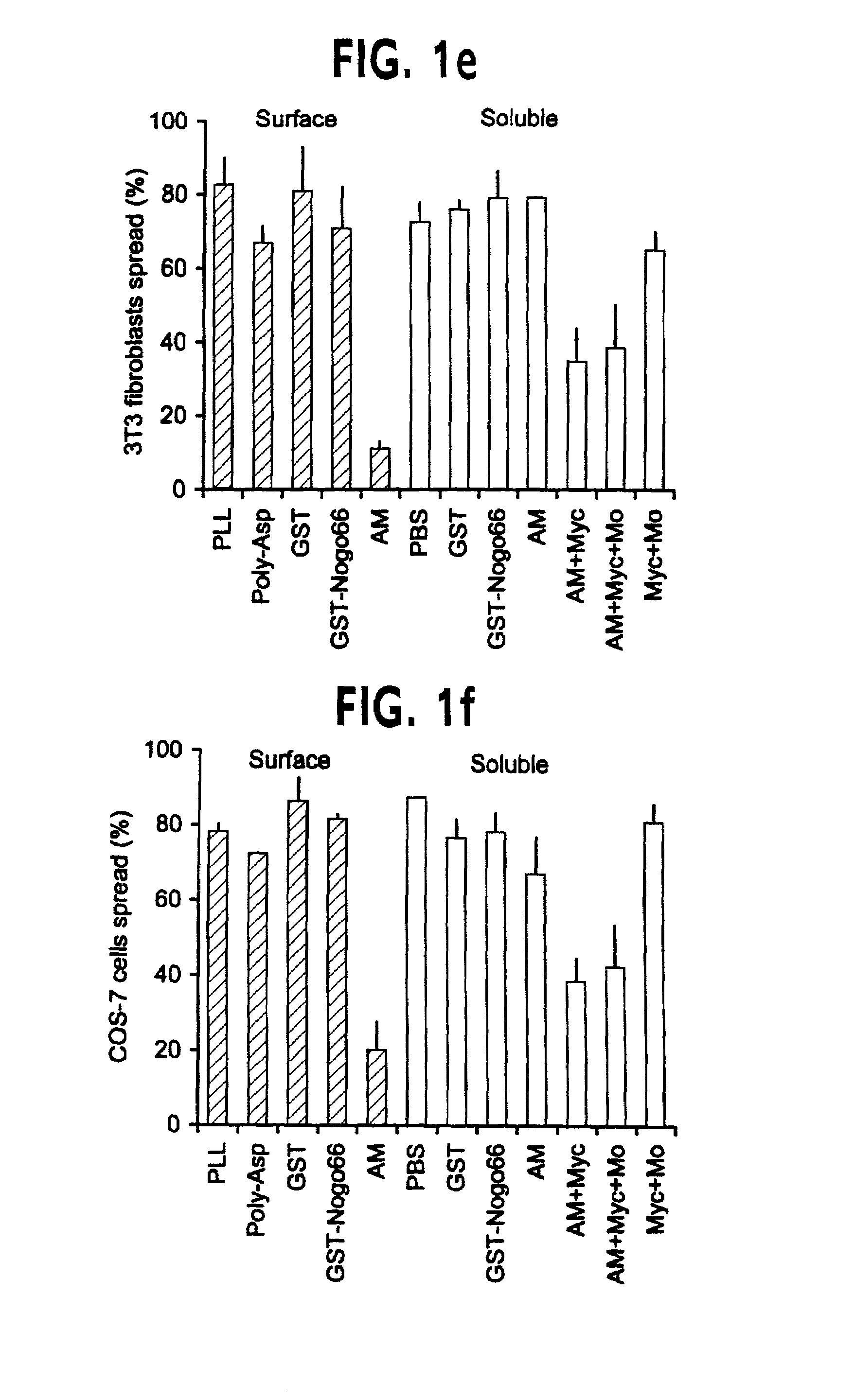
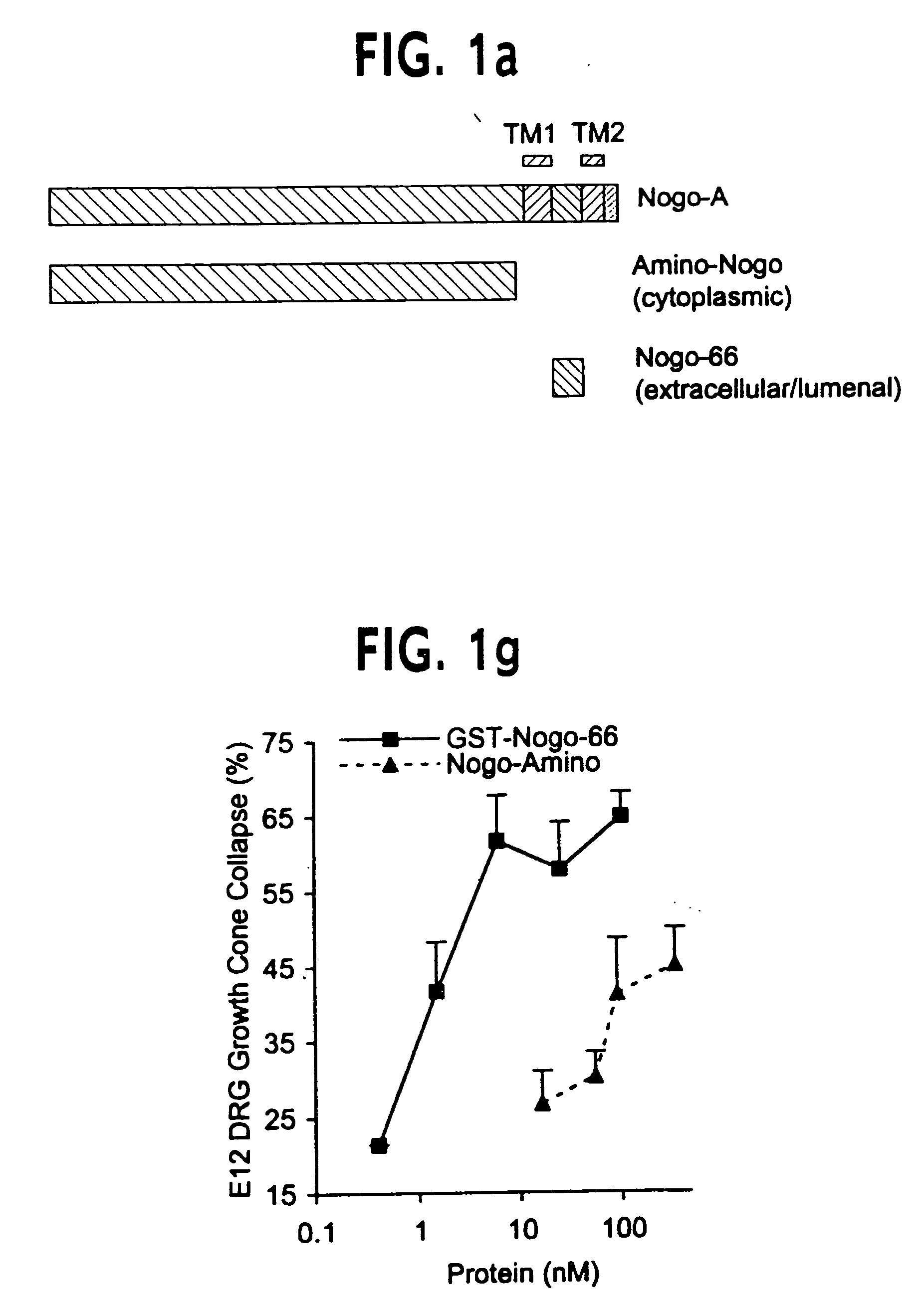
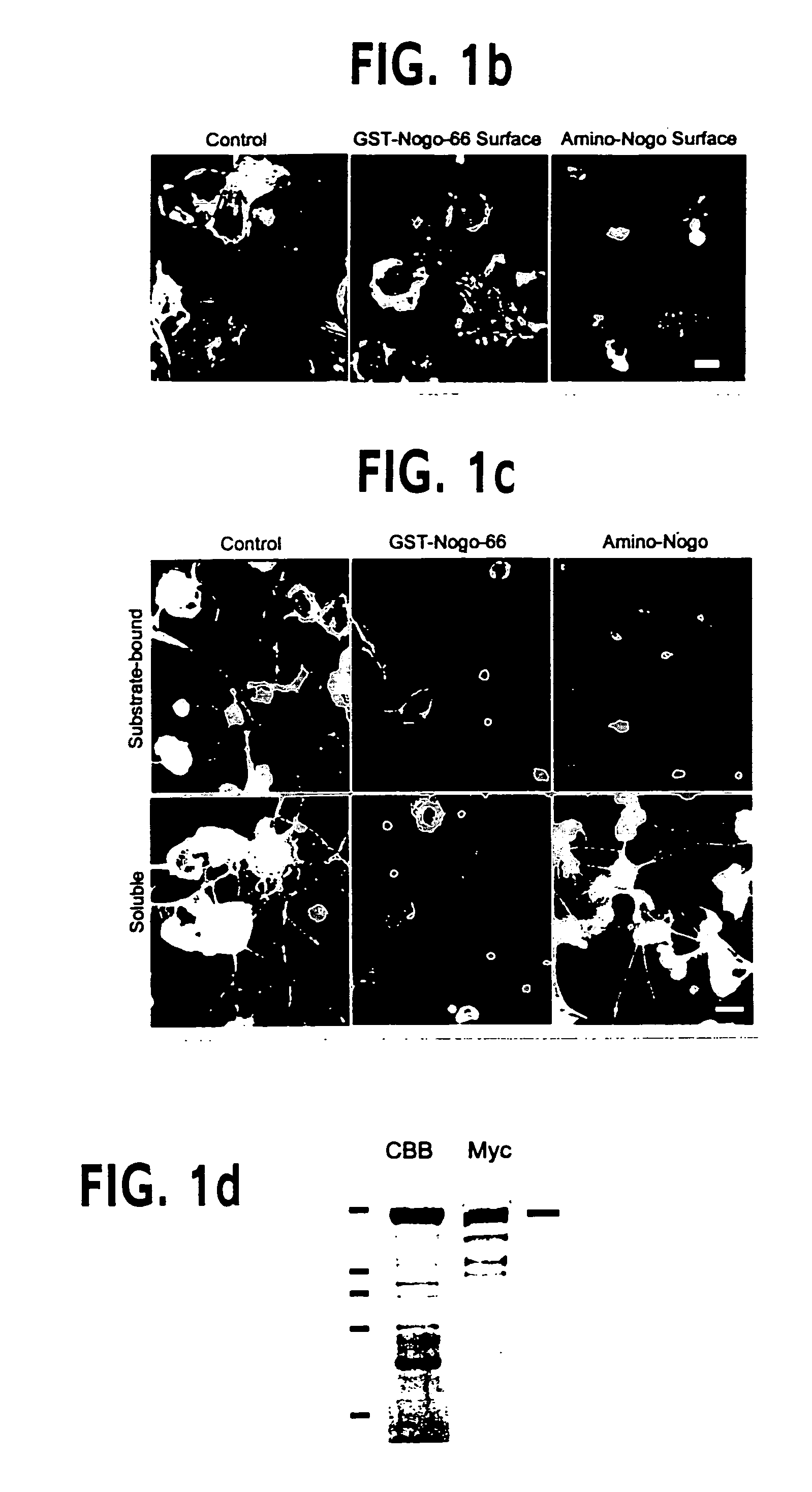
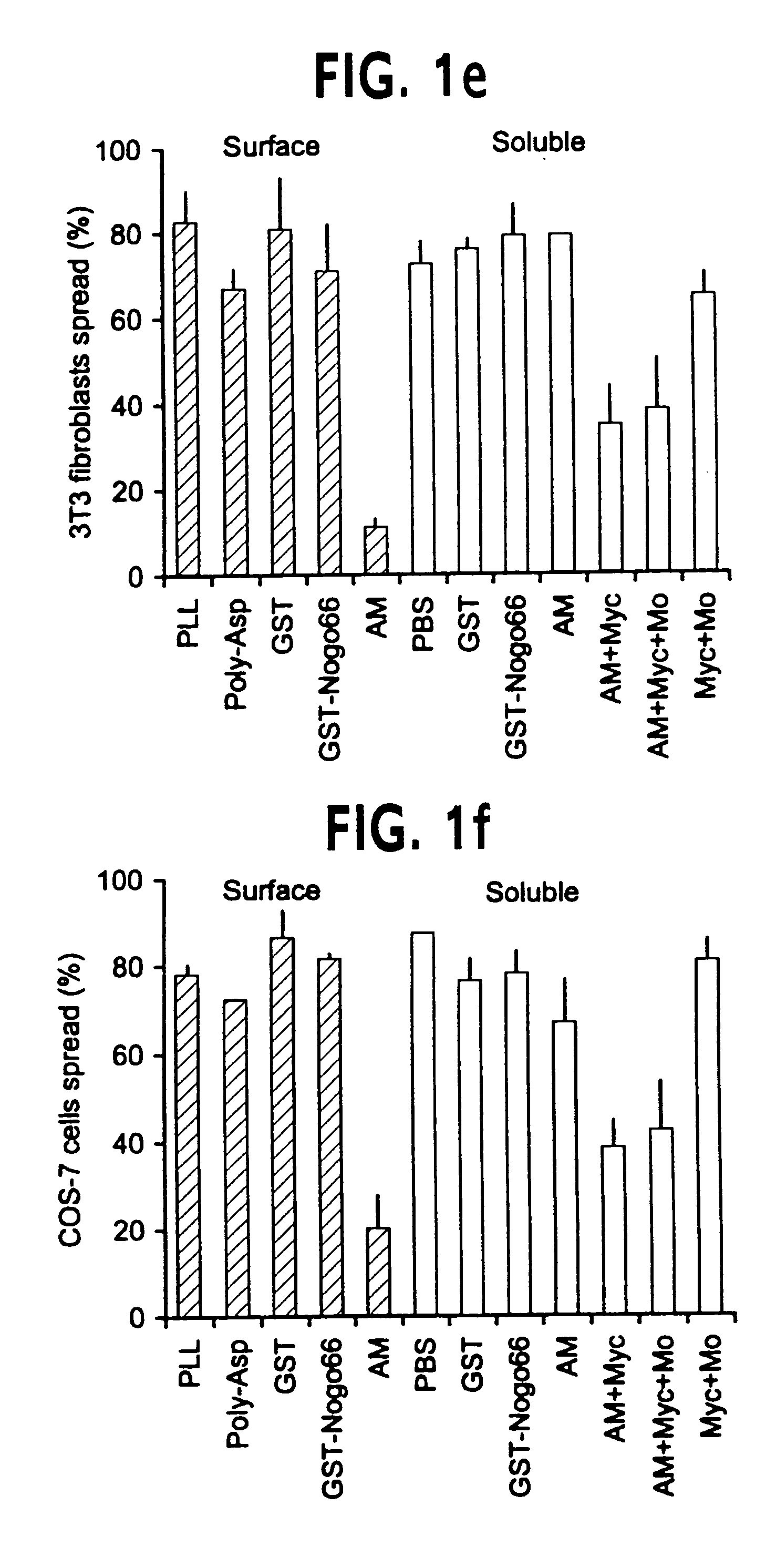
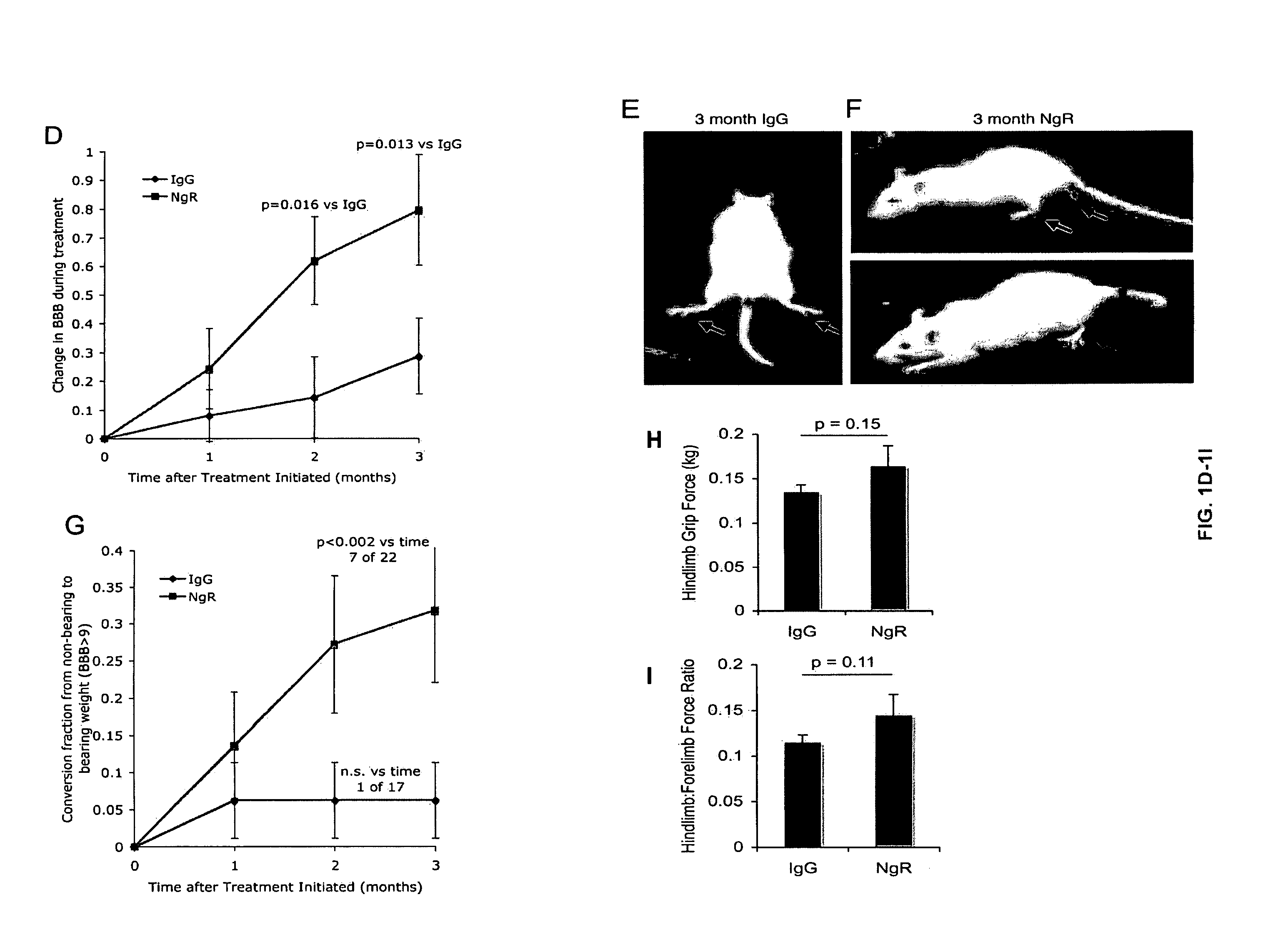
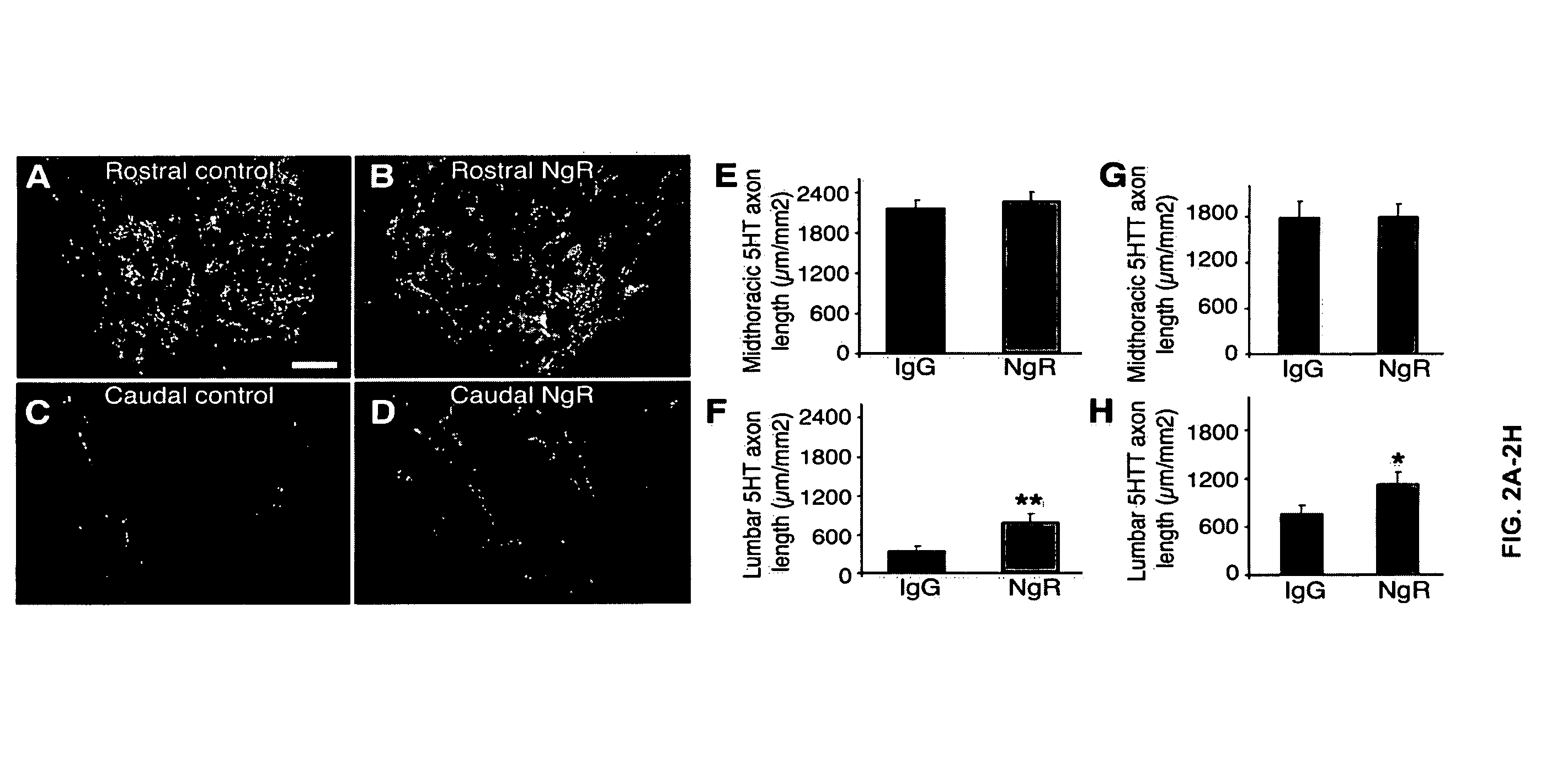
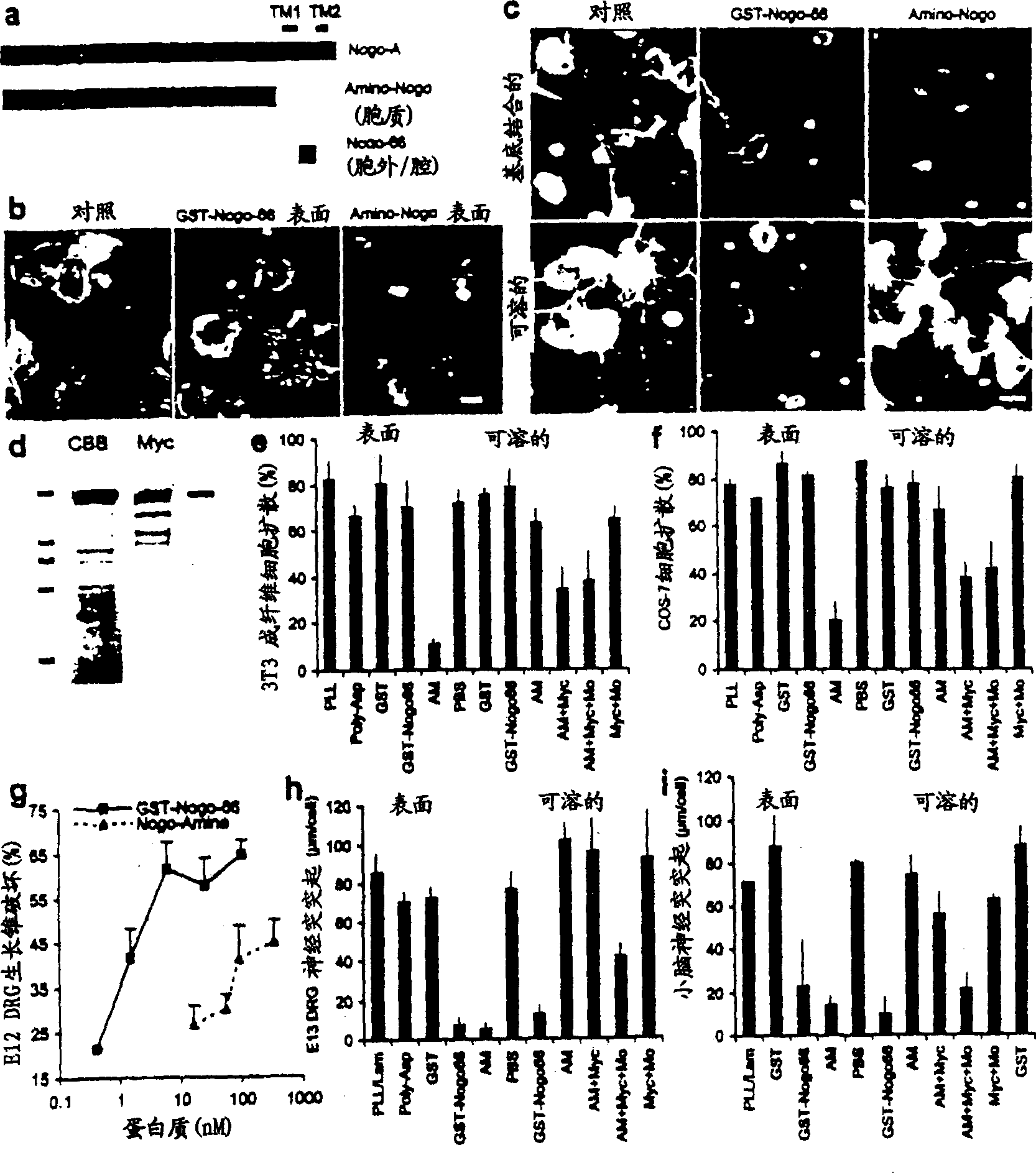
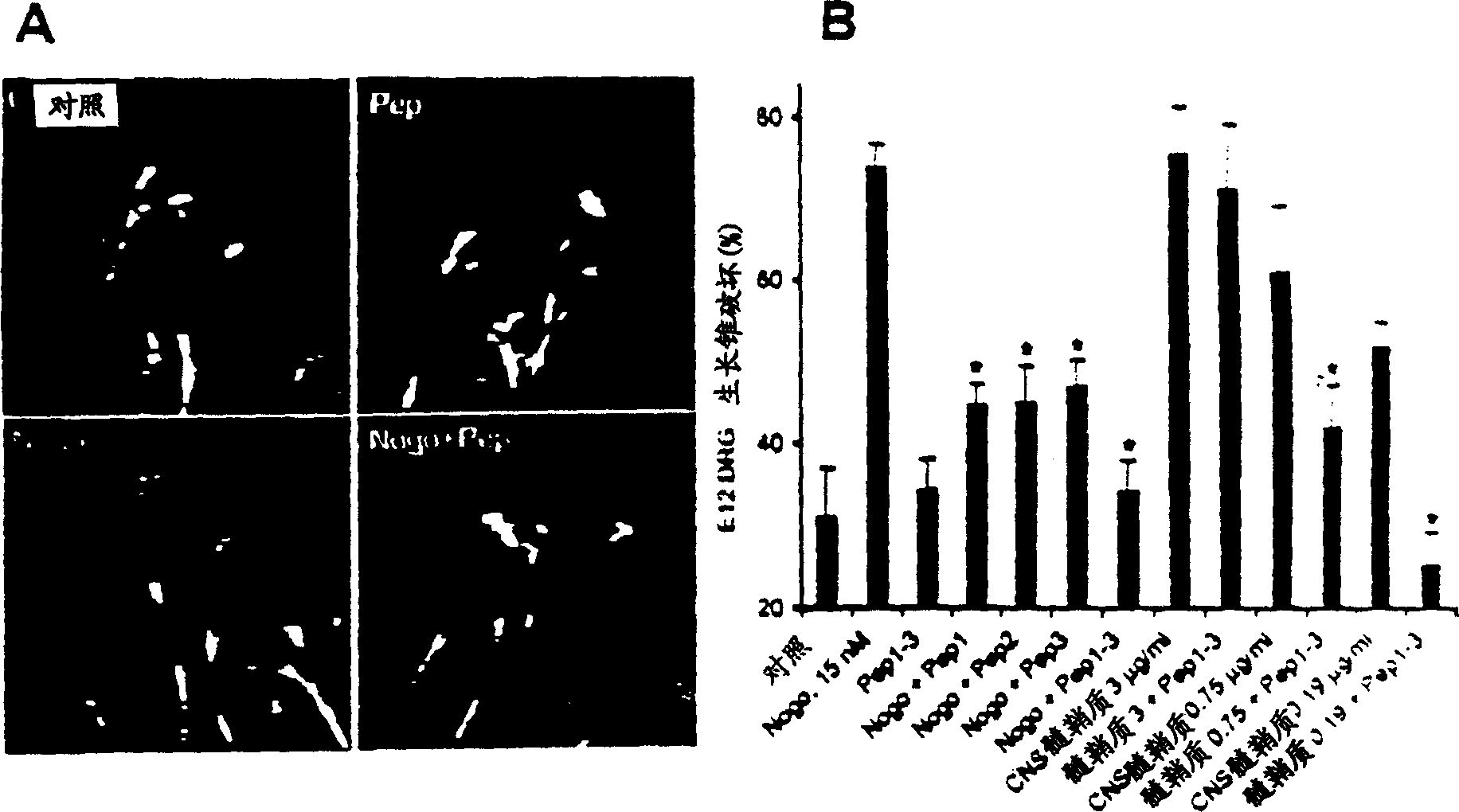
Disclosed are NgR proteins and biologically active Nogo (ligand) protein fragments. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for modulating the expression or activity of the Nogo and NgR protein. Also disclosed are peptides which block Nogo-mediated inhibition of axonal extension. The compositions and methods of the invention are useful in the treatment of cranial or cerebral trauma, spinal cord injury, stroke or a demyelinating disease.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Nogo receptor antagonists
ActiveUS7465705B2Inhibit bindingReduce inhibitionFungiBacteriaAntigen Binding FragmentNK1 receptor antagonist
Disclosed are immunogenic Nogo receptor-1 polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same. Also disclosed are compositions comprising, and methods for making and using, such Nogo receptor antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
RNA interference mediated inhibition of NOGO and NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050182008A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDouble strandNogo Receptors
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor genes, such as NOGO-A, NOGO-B, NOGO-C, NOGO-66 receptor, NI-35, NI-220, NI-250, myelin-associated glycoprotein, tenascin-R, and NG-2
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for Treating Neurological Disorders
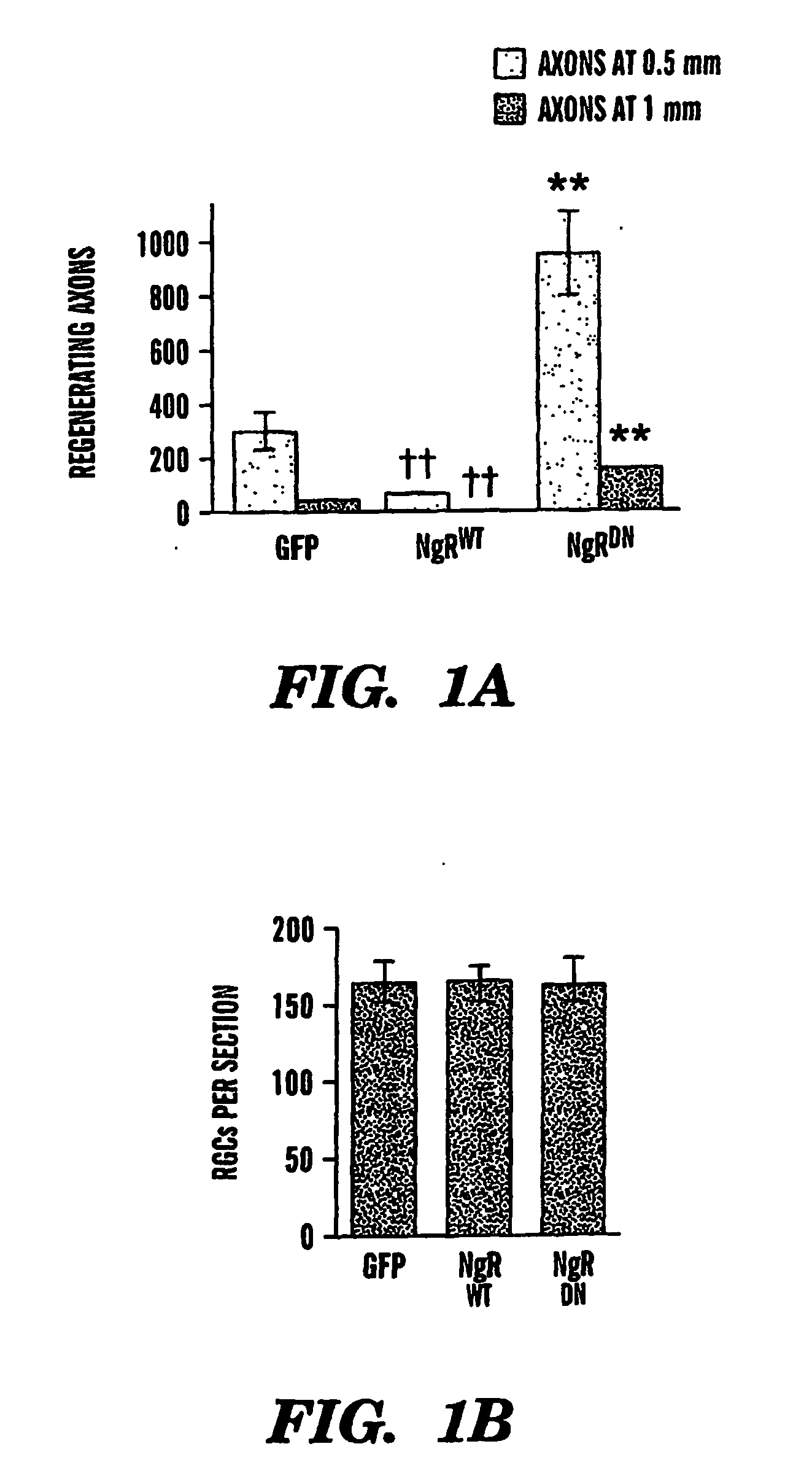
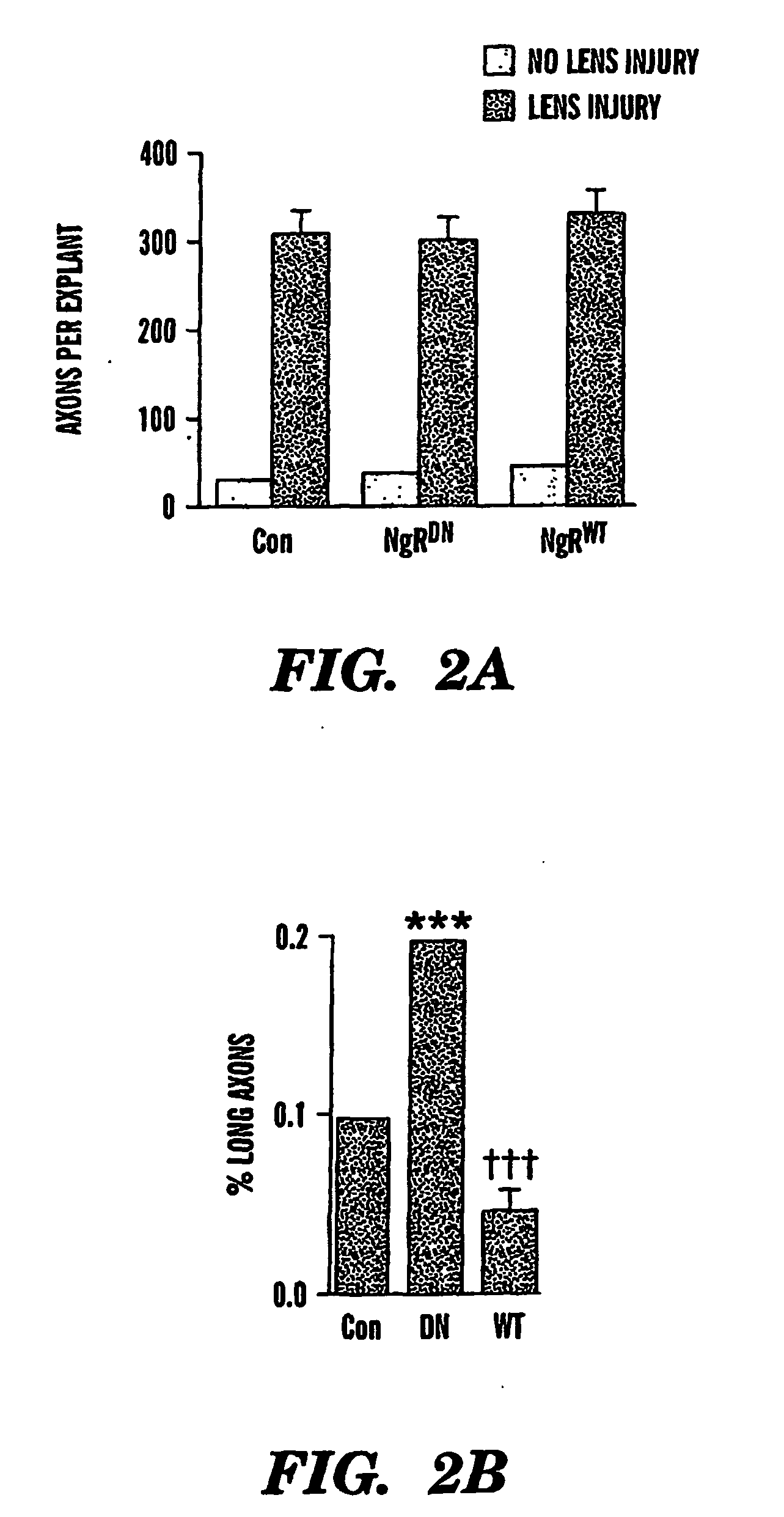
The present invention is based on the discovery that suppressing the activity of the Nogo receptor (NgR) alone does not result in extensive axon regeneration unless the intrinsic growth program of neurons is also activated Accordingly, the present invention is directed to methods of stimulating axon regeneration using a combination therapy wherein agents that inhibit NgR activity or downstream pathways activated by inhibitory signals are combined with agents that activate the growth pathway of neurons (e.g. polypeptide growth factors, activators of macrophages, purine nucleosides, or hexoses).
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Nogo Receptor Antagonists
ActiveUS20090099078A1Inhibit bindingReduce inhibitionSenses disorderNervous disorderAntigen Binding FragmentNucleotide
Disclosed are immunogenic Nogo receptor-1 polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same. Also disclosed are Nogo receptor antagonist polynucleotides. Also disclosed are compositions comprising, and methods for making and using, such Nogo receptor antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof, nucleic acids encoding the same and antagonist polynucleotides.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Nogo receptor antagonists
ActiveUS8669345B2Inhibit bindingReduce inhibitionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideAntigen Binding Fragment
Disclosed are immunogenic Nogo receptor-1 polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same. Also disclosed are Nogo receptor antagonist polynucleotides. Also disclosed are compositions comprising, and methods for making and using, such Nogo receptor antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof, nucleic acids encoding the same and antagonist polynucleotides.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
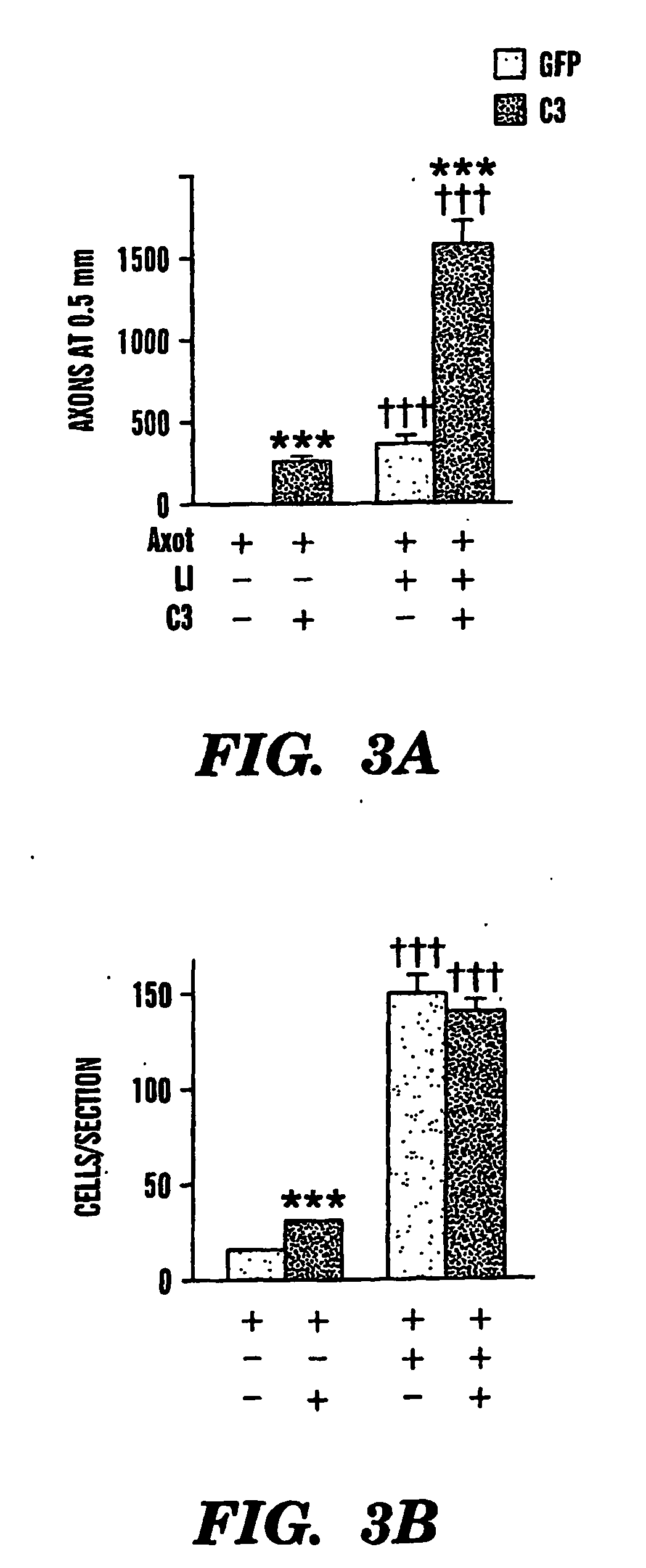
Reducing NgR-p75 mediated inhibition of axon regeneration
InactiveUS20060104973A1Reducing axon growth inhibitionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiochemistryNogo Receptors
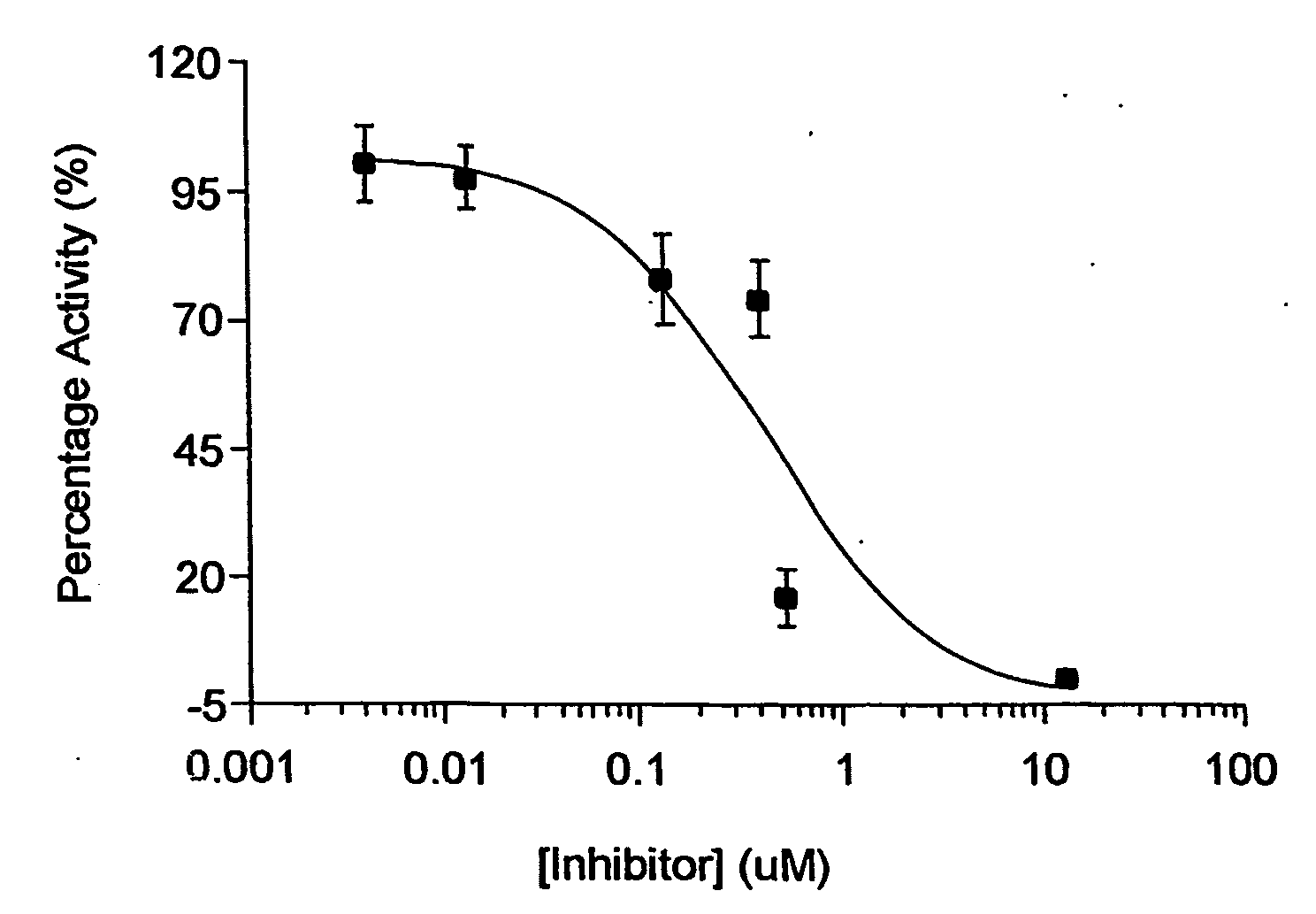
Inhibitors of Nogo Receptor (NgR)-p75 binding are used to reduce NgR-p75 binding mediated axon growth inhibition. Mixtures of NgR and p75 are used in pharmaceutical screens to characterize agents as inhibiting binding of NgR to p75 and promoting axon regeneration.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Method for treating neurological disorders
InactiveUS20110071088A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention is based on the discovery that suppressing the activity of the Nogo receptor (NgR) alone does not result in extensive axon regeneration unless the intrinsic growth program of neurons is also activated. Accordingly, the present invention is directed to methods of stimulating axon regeneration using a combination therapy wherein agents that inhibit NgR activity or downstream pathways activated by inhibitory signals are combined with agents that activate the growth pathway of neurons (e.g. polypeptide growth factors, activators of macrophages, purine nucleosides, or hexoses).
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Methods relating to peripheral administration of nogo receptor polypeptides
InactiveUS20120058125A1Enhanced Aβ clearanceImprove memory functionSenses disorderNervous disorderBlood plasmaNogo Receptors
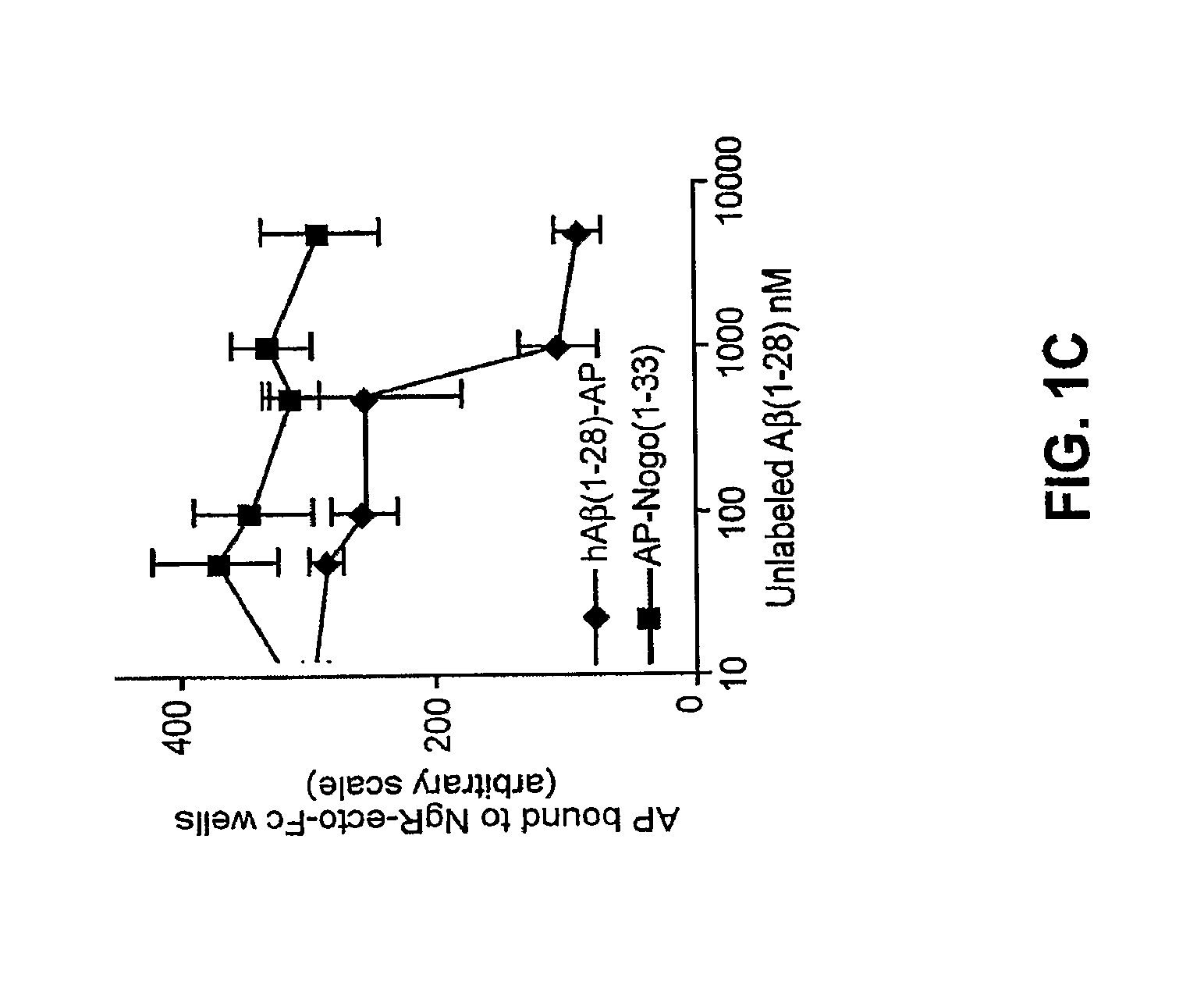
This invention relates to methods of treating diseases involving accumulation of Aβ plaques, including Alzheimer's Disease by the peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. The invention also provides methods of increasing the plasma to brain ratio of Aβ peptide and enhancing Aβ peptide clearance via peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. This invention also provides methods of improving memory function or inhibiting memory loss via the peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. The invention also provides methods of decreasing the size and number of Aβ plaques in a mammal via peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Nogo receptor-mediated blockade of axonal growth
Owner:YALE UNIV
Antibodies against nogo receptor
ActiveUS7973139B2Promote regenerationPrevent or ameliorate one or more symptomsAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRisk strokeNervous system disease
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Nogo Receptor Antagonists
InactiveUS20080274112A1Conducive to survivalInhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen Binding FragmentBiochemistry
Disclosed are immunogenic Nogo receptor-1 polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same. Also disclosed are compositions comprising, and methods for making and using, such Nogo receptor antibodies, antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof and nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Treatment of Conditions Involving Dopaminergic Neuronal Degeneration Using Nogo Receptor Antagonists
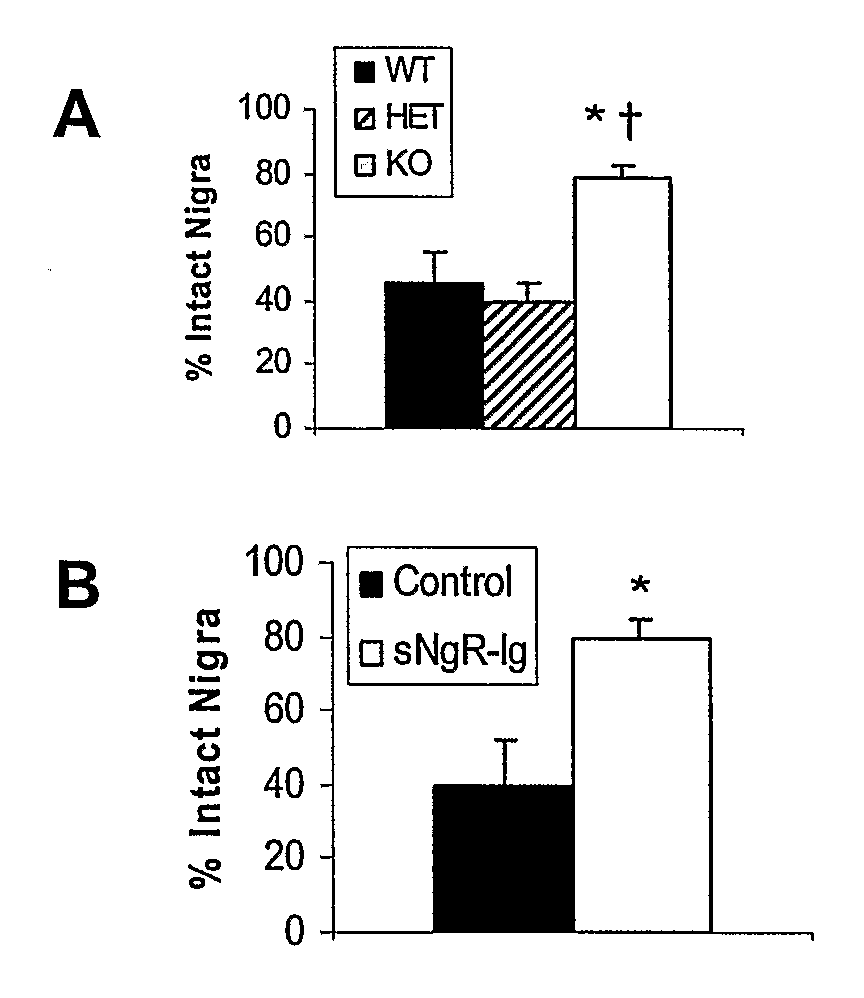
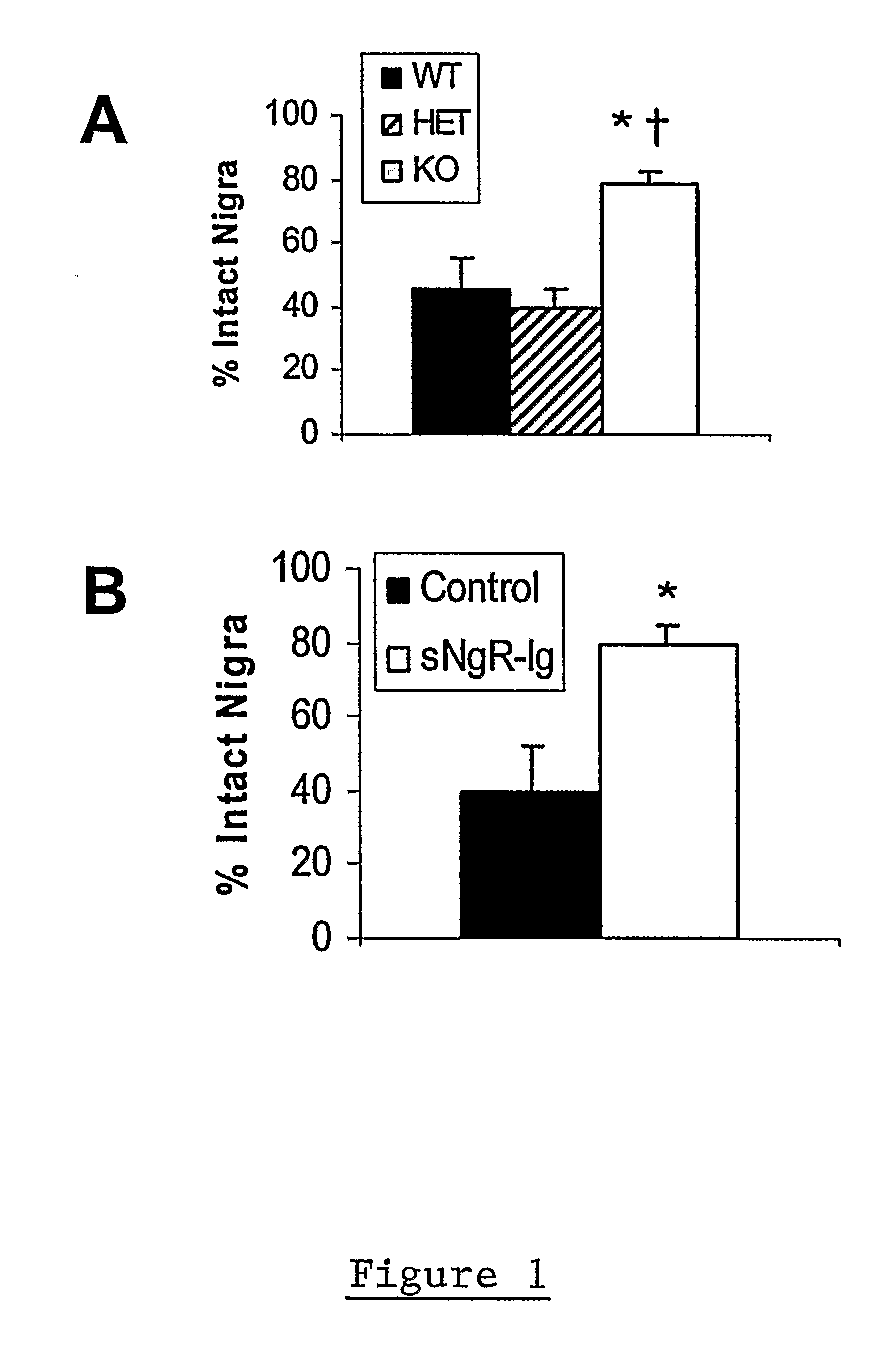
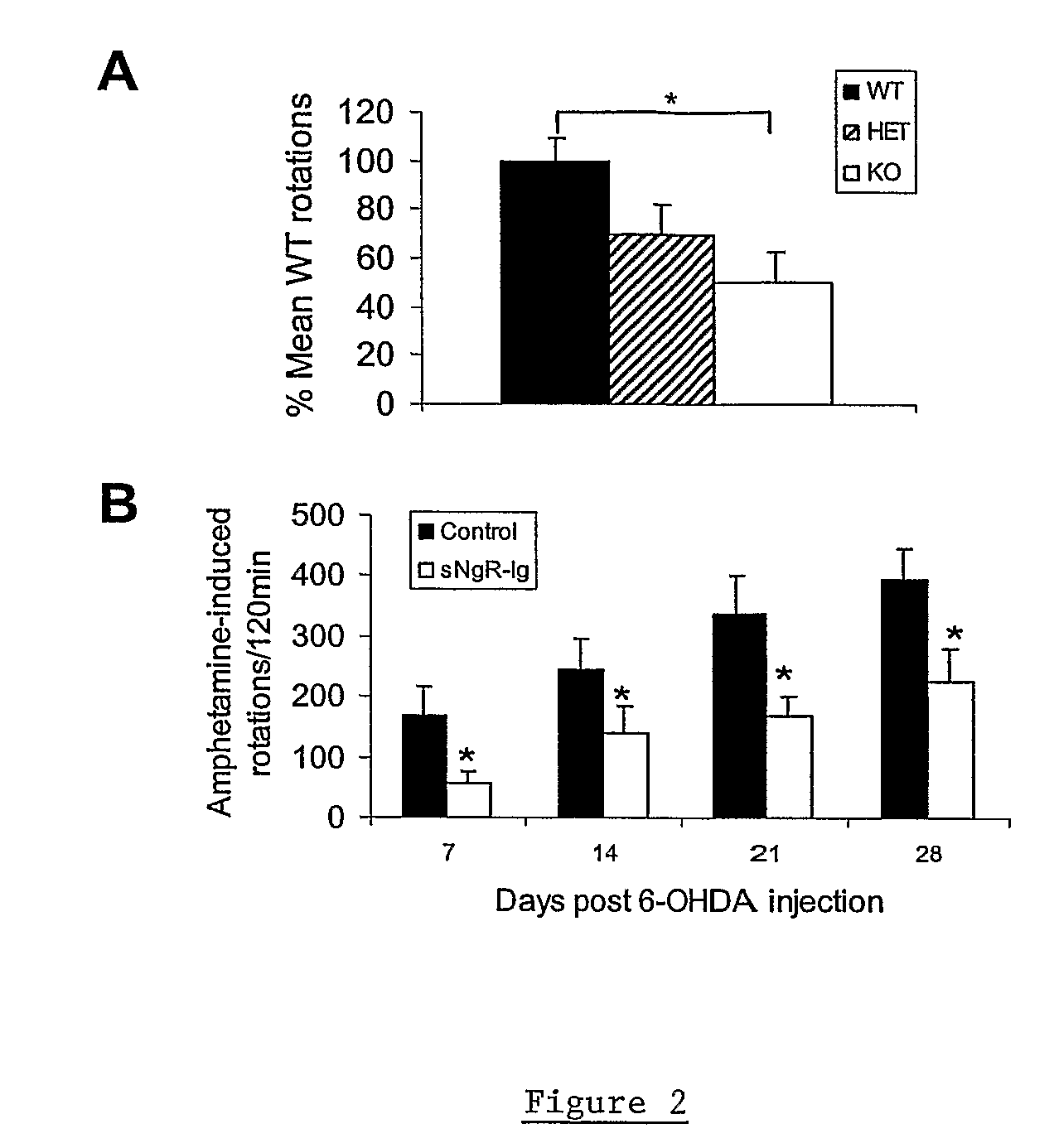
The invention provides methods for promoting regeneration or survival of dopaminergic neurons in a mammal displaying signs or symptoms of dopaminergic neuronal degeneration, including a human with Parkinson's disease, using Nogo receptor antagonists.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Antibodies against Nogo receptor
InactiveUS20050214289A1Promote neuronalPromote axonal regenerationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsNervous system diseaseNogo Receptors
The present invention relates to antibodies and related molecules that specifically bind to the Nogo receptor (NogoR). Such antibodies have uses, for example, in the treatment of spinal cord injury, brain trauma, paralysis, degenerative nervous system diseases, and stroke. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding anti-NogoR antibodies, vectors and host cells containing these nucleic acids, and methods for producing the same.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
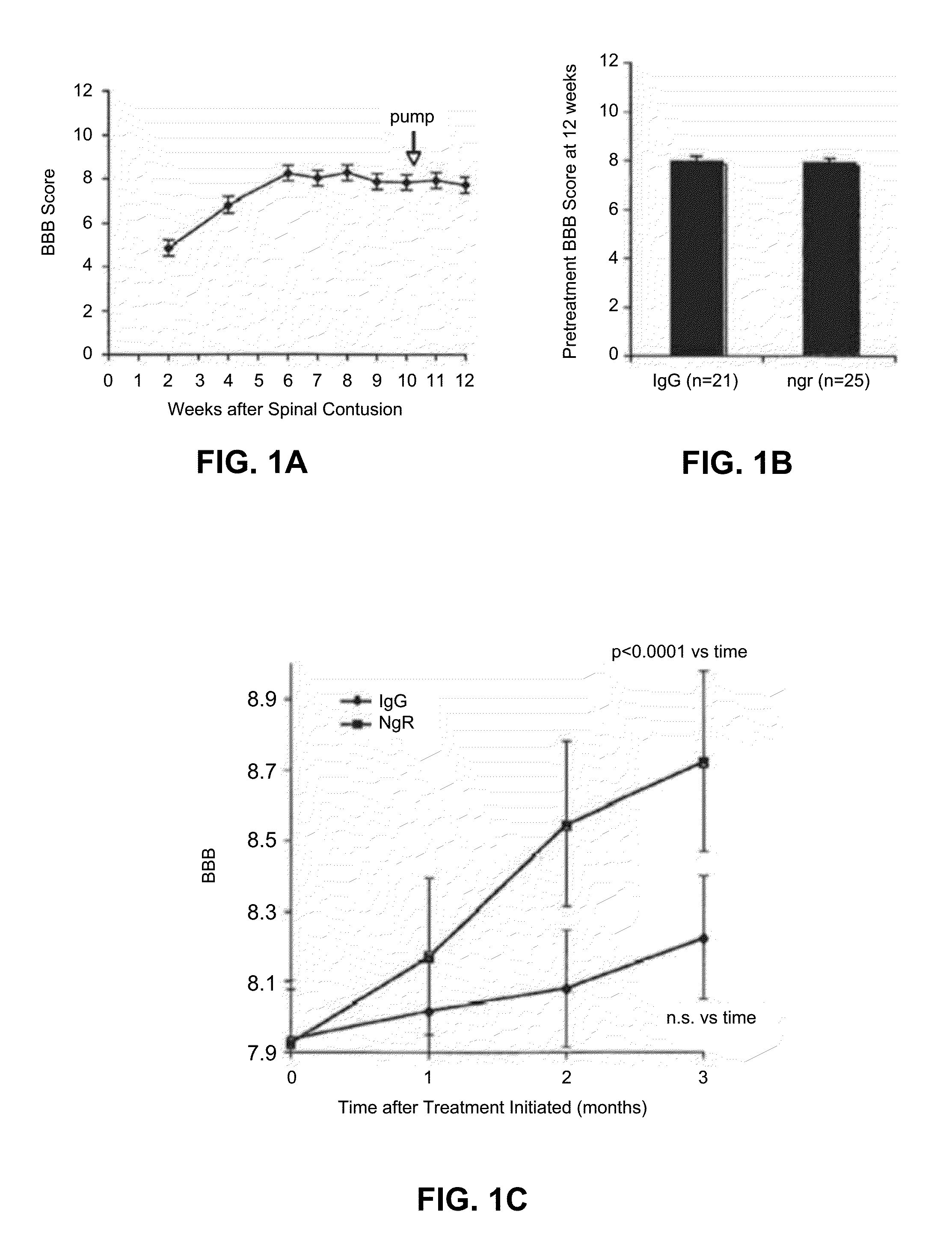
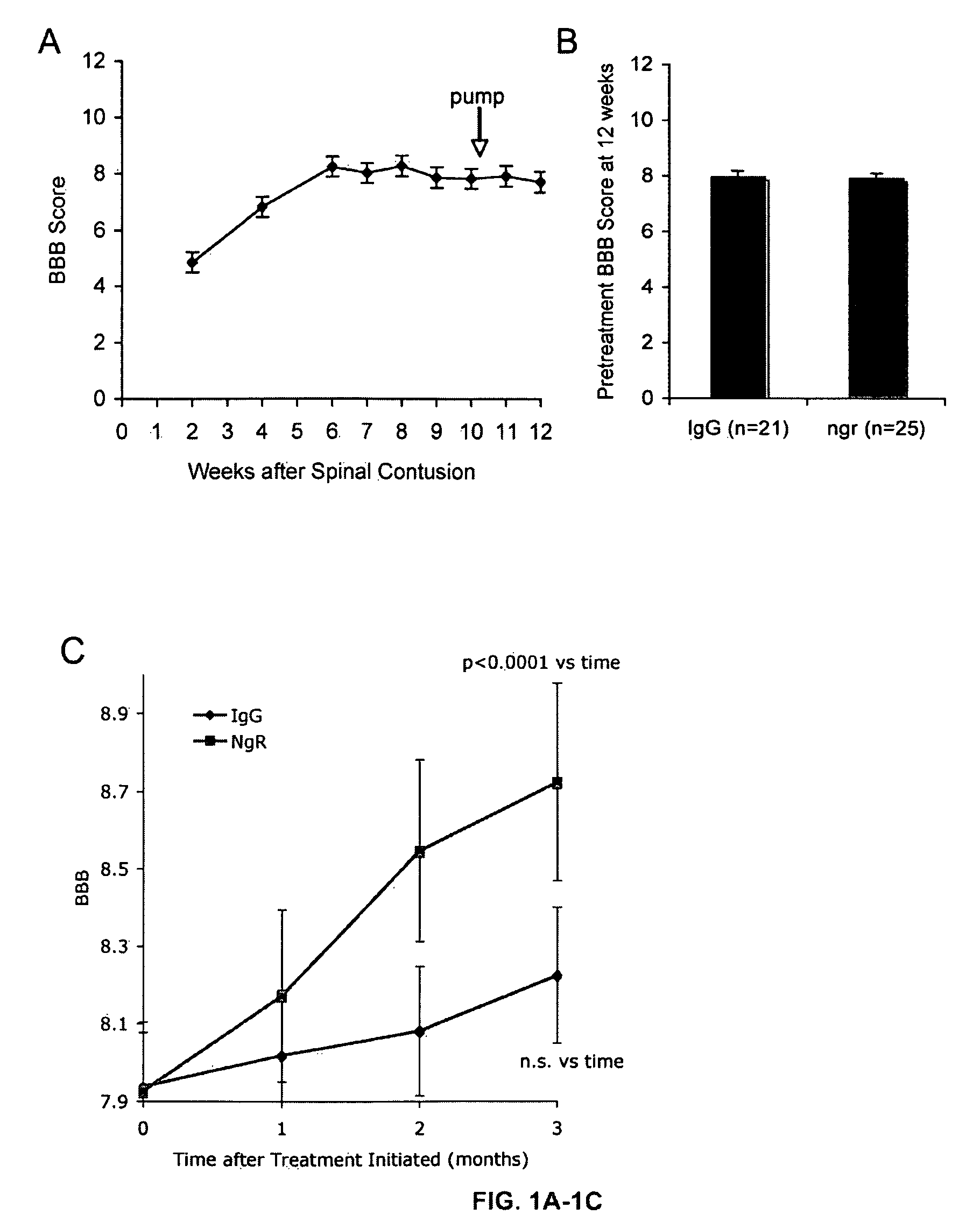
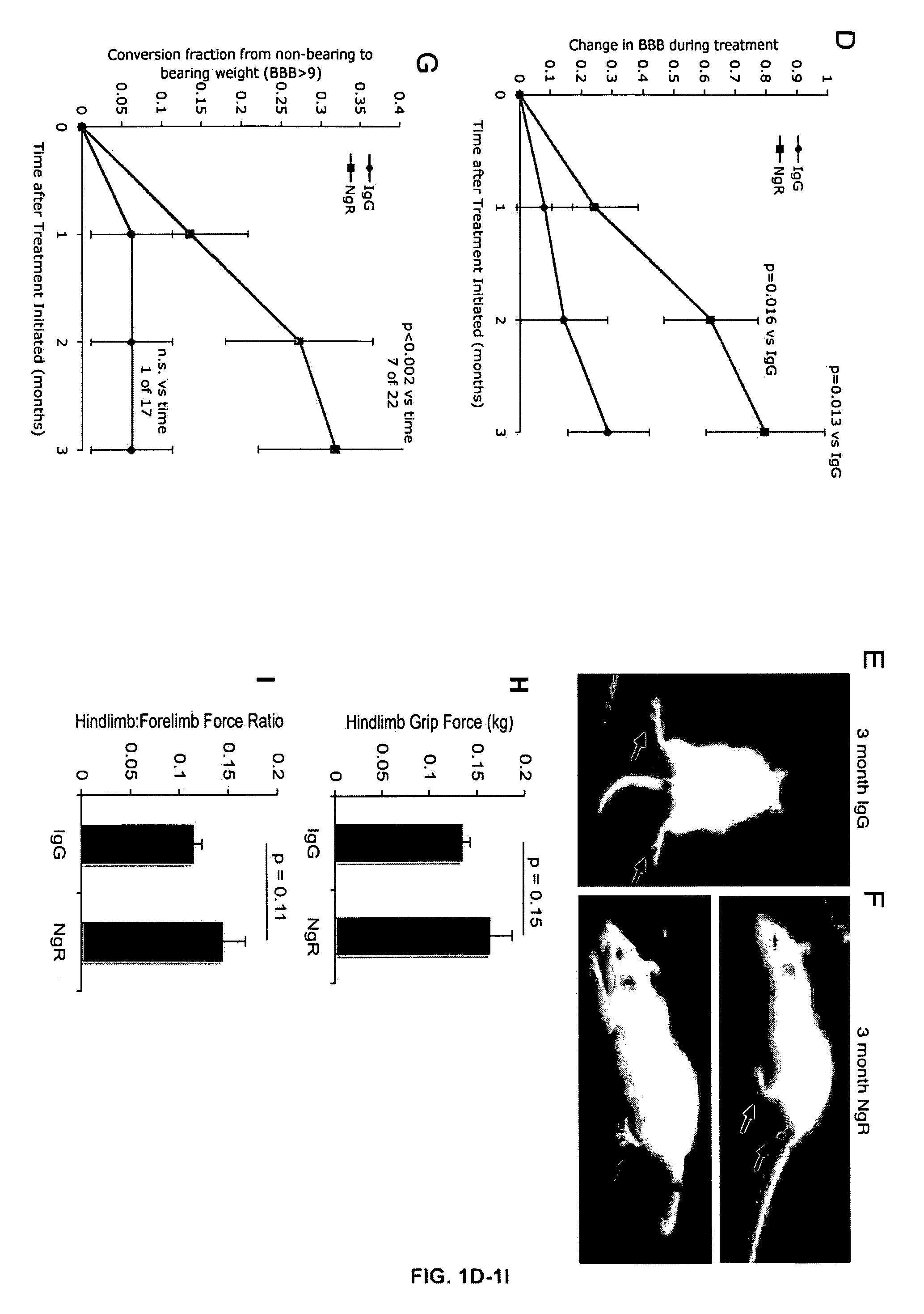
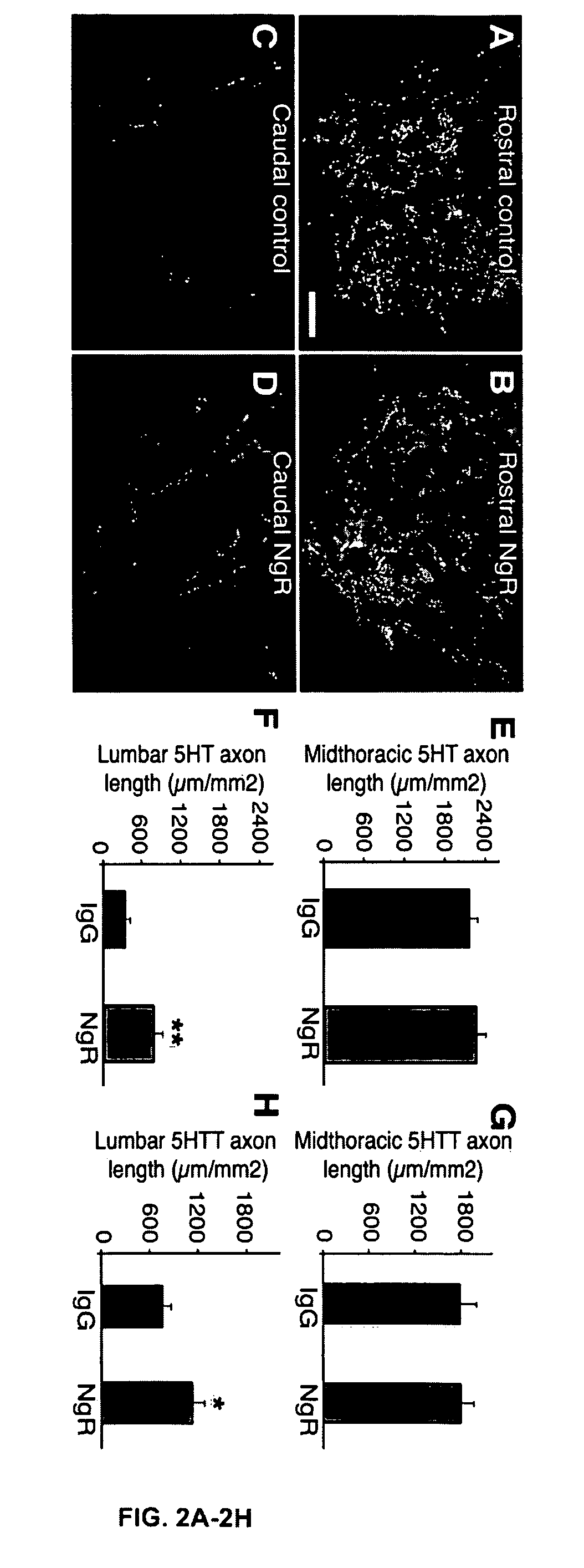
Reactivation of Axon Growth and Recovery in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury
ActiveUS20110117094A1Stimulates axonal growthPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
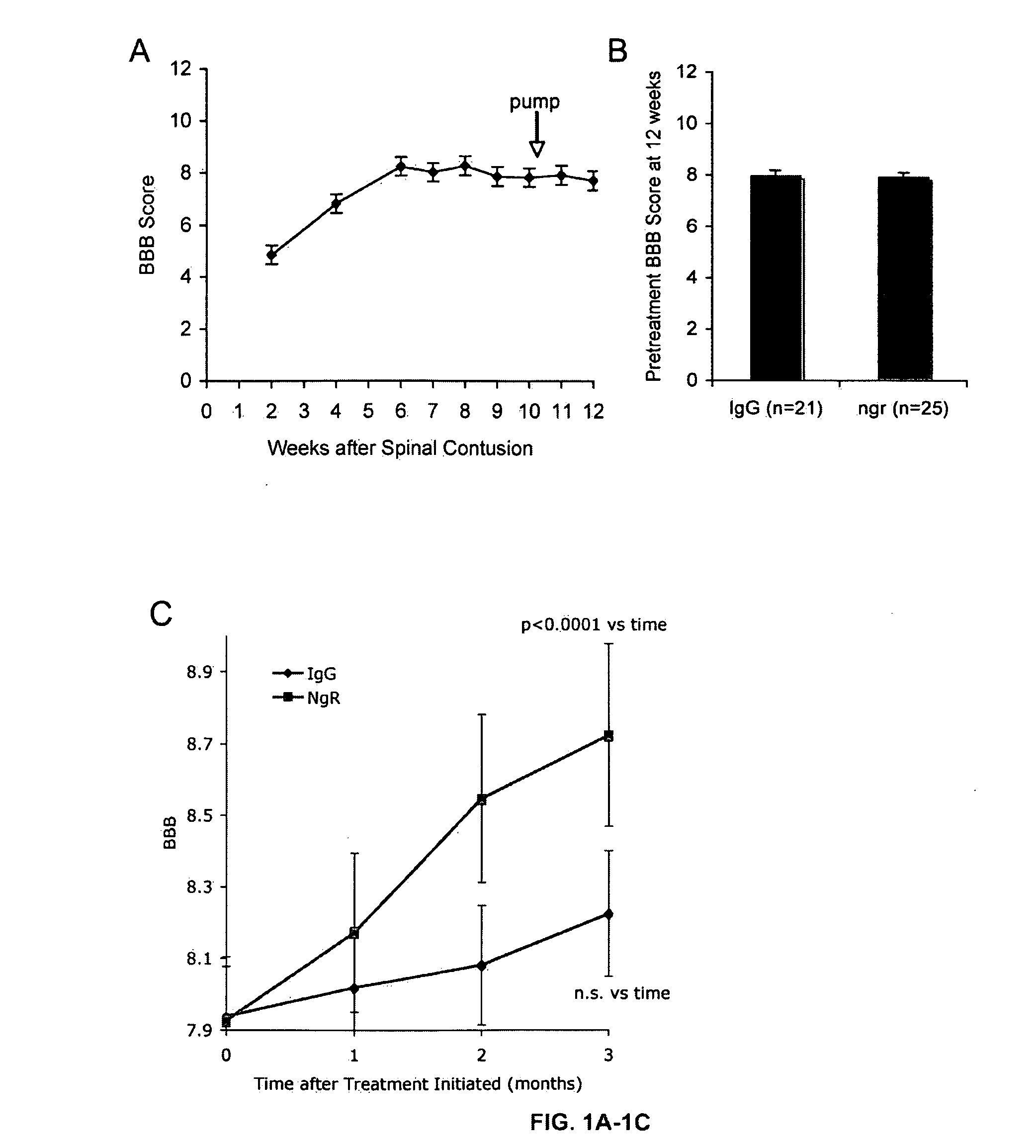
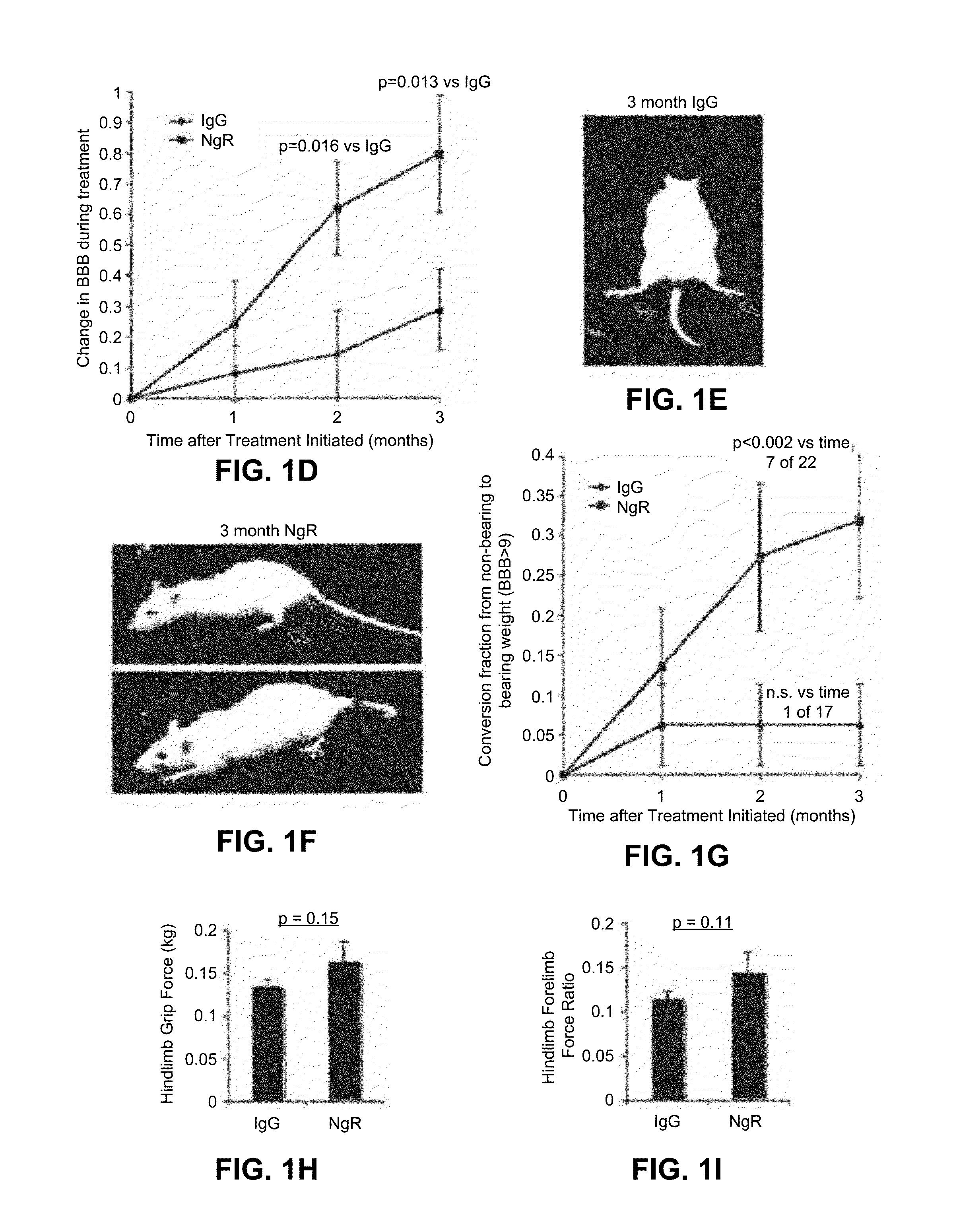
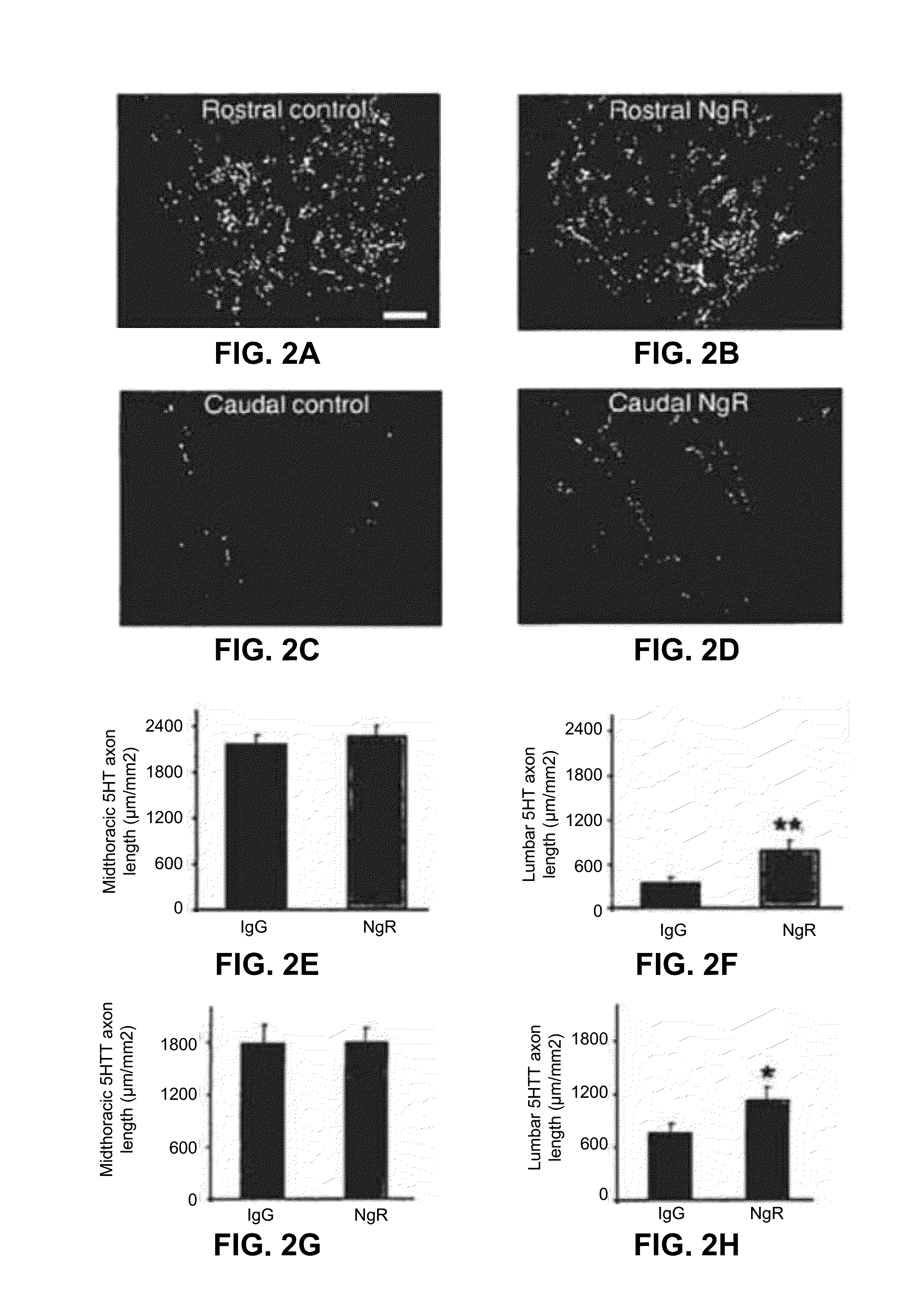
Disclosed are methods of treating chronic nervous system diseases or injuries, e.g., chronic spinal cord injury, using Nogo receptor antagonists, including Nogo receptor-1 (NgR1) polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof, and polynucleotides. Also disclosed are methods of noninvasively monitoring axonal growth during and after treatment with an axonal growth promoting agent.
Owner:YALE UNIV
NOGO receptor-mediated blockade of axonal growth
Disclosed are Nogo receptor proteins and biologically active Nogo (ligand) protein fragments. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for modulating the expression or activity of the Nogo and Nogo receptor protein. Also disclosed are peptides which block Nogo-mediated inhibition of axonal extension. The compositions and methods of the invention are useful in the treatment of cranial or cerebral trauma, spinal cord injury, stroke or a demyelinating disease.
Owner:YALE UNIV
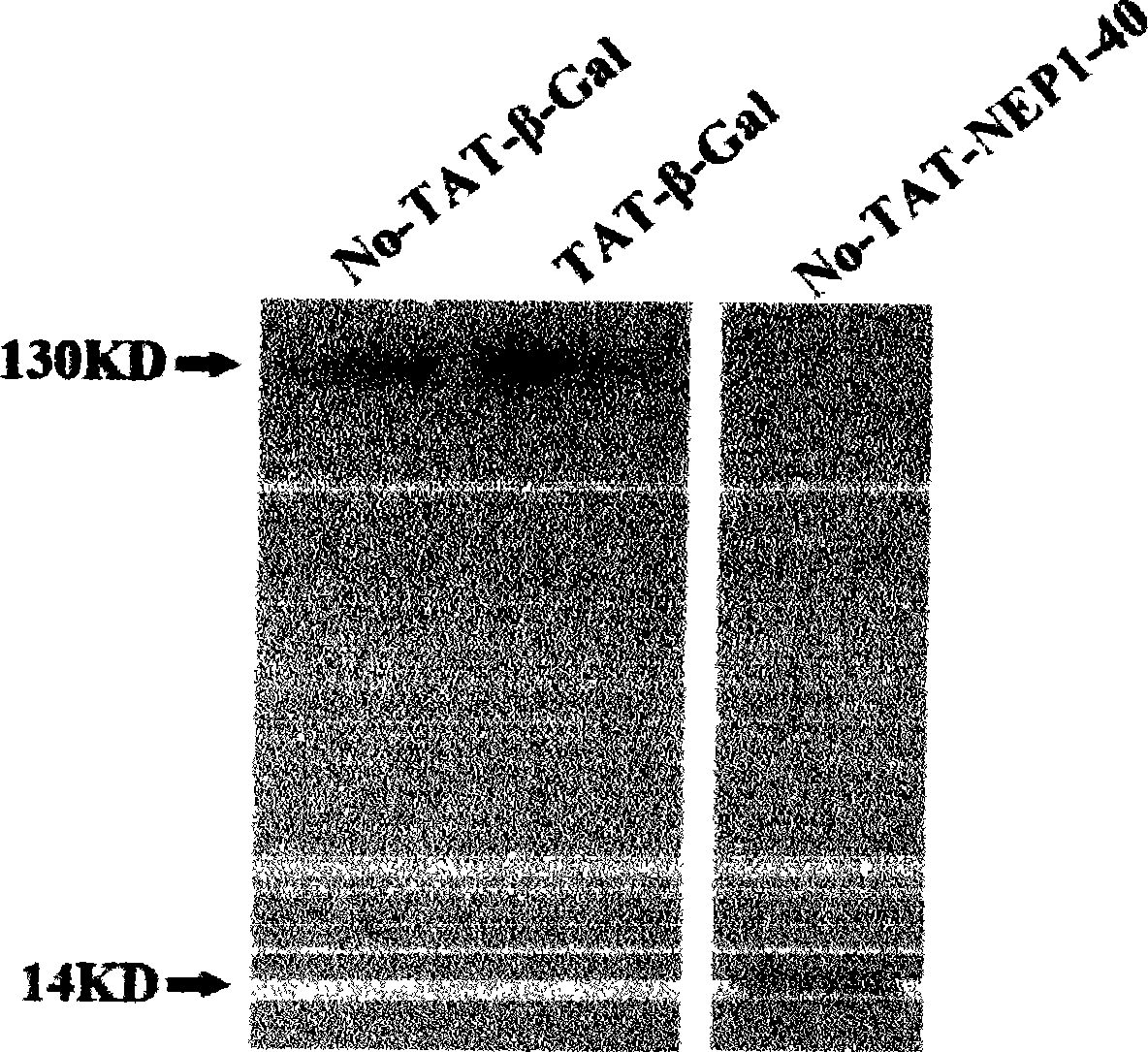
TAT-LBD-NEP1-40 fusion protein, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103113473AOvercome limitationsLittle side effectsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemNogo Receptors
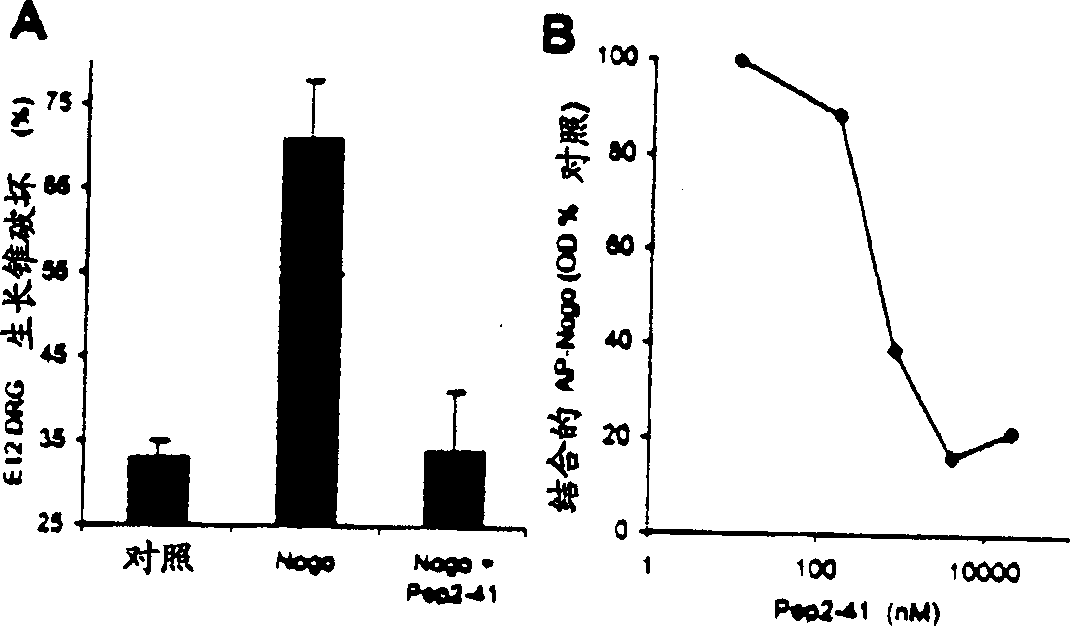
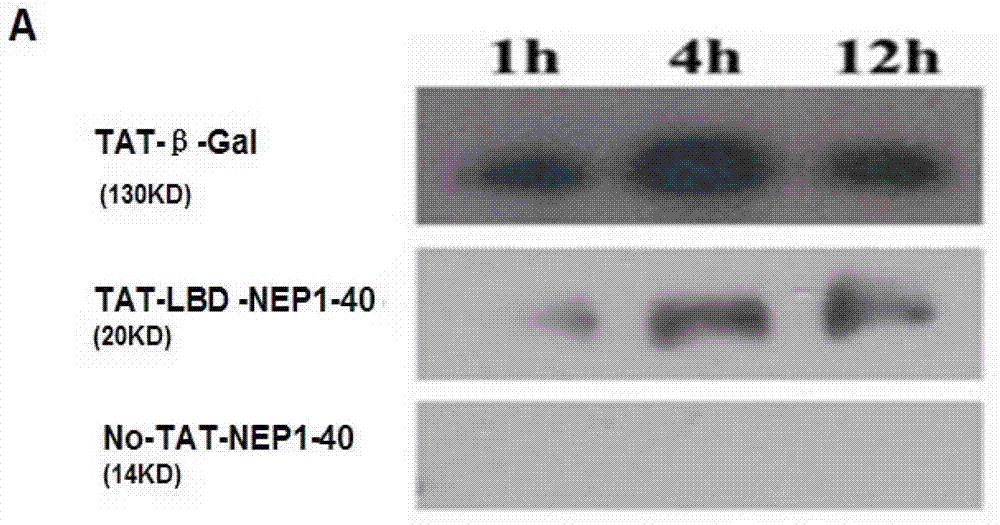
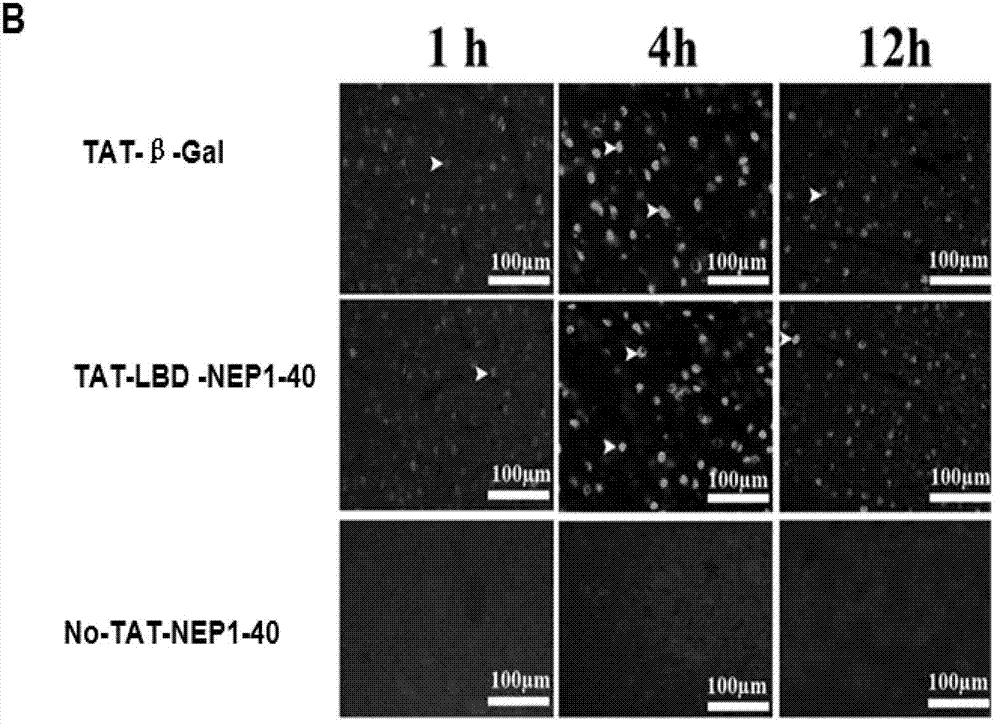
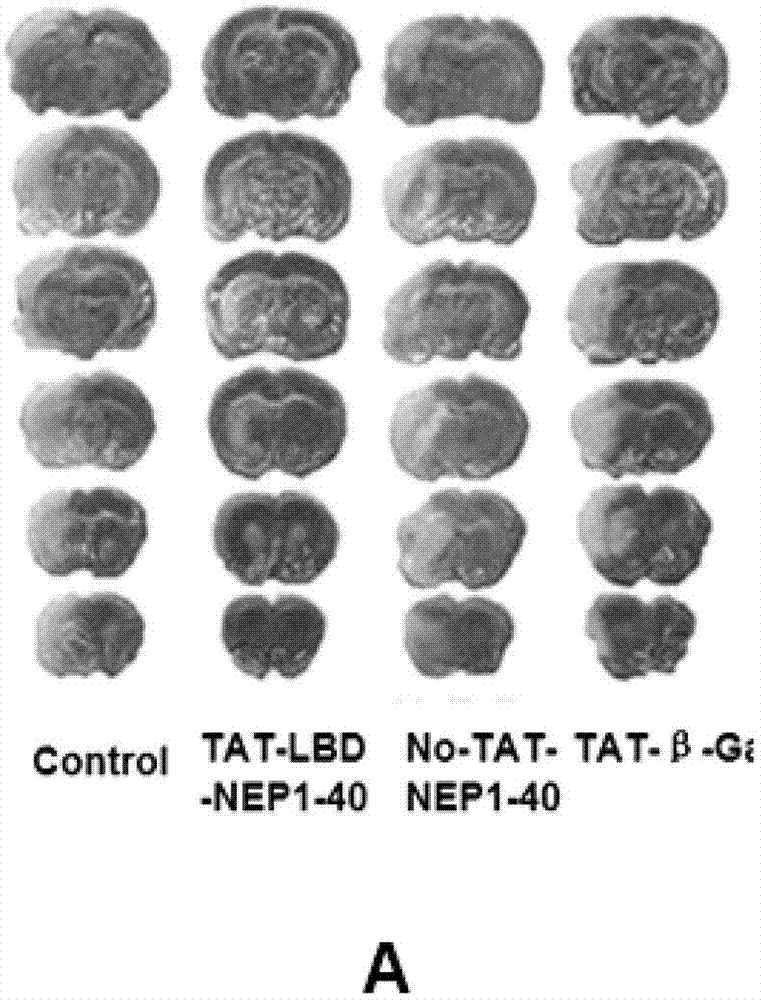
The invention discloses a TAT-LBD-NEP1-40 fusion protein, a construction method and an application thereof for treating central lesion. The TAT-LBD-NEP1-40 fusion protein constructed by the invention remains selective antagonistic activity of NEP1-40 to a Nogo receptor and has the advantages of high transduction efficiency and easy transmission of blood and spine barriers and blood brain barrier, so that the limit of NEP1-40 is overcome so as to avoid the deficiency of extra damage to nervous tissues caused by micro-injection of NEP1-40 or micro pump implantation and difficulty for NEP1-40 to pass through blood and spine barriers and blood brain barrier to meet corresponding biological concentration. The infusion protein provided by the invention can be massively prepared, and is low in cost and high in activity. The infusion protein can be used to treat various CNS (Central Nervous System) damages such as cerebral ischemia and anoxia, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral trauma and spinal cord injury, promote regeneration of nervous tissues and neural functional recovery, and treat CNS damages.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
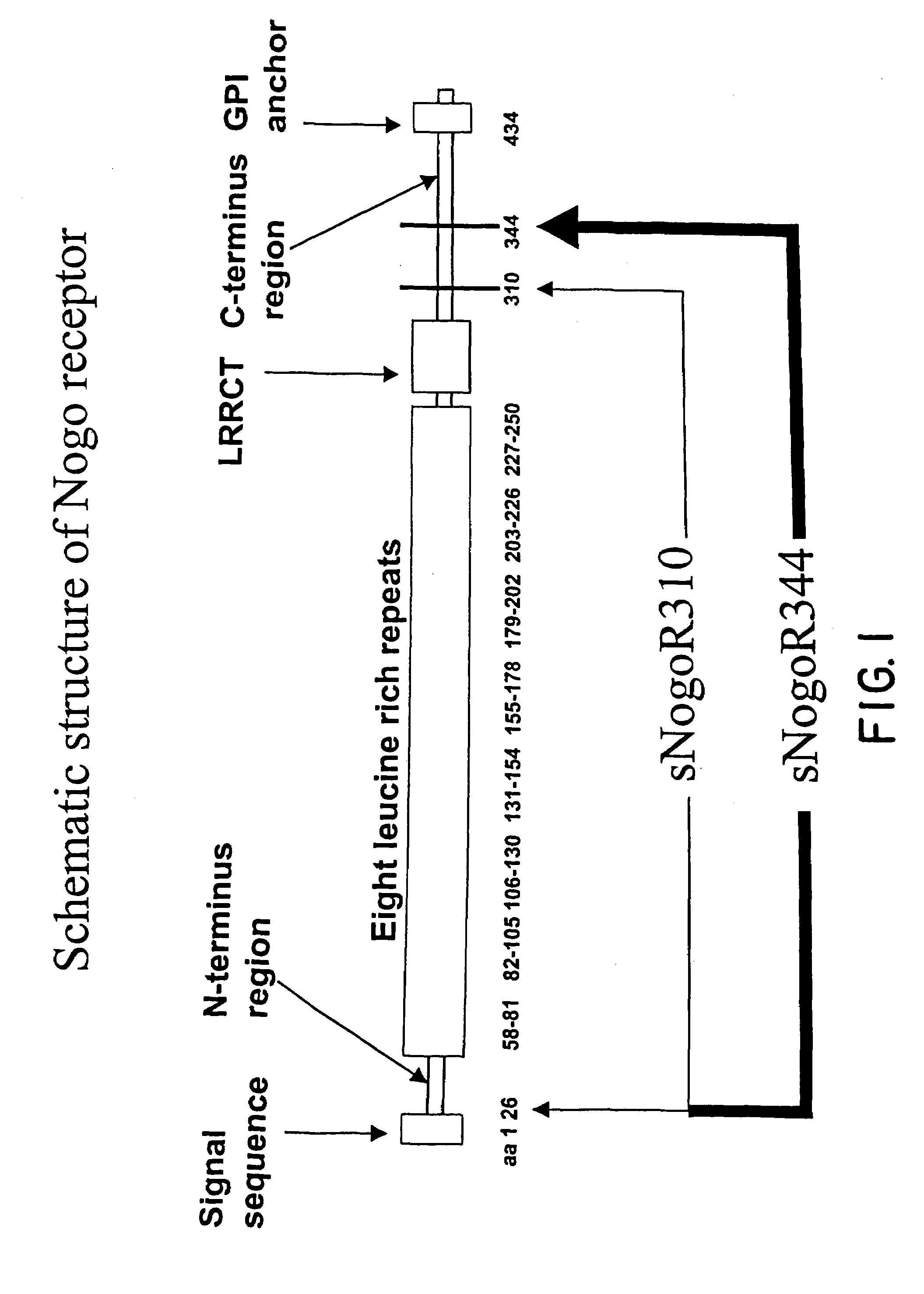
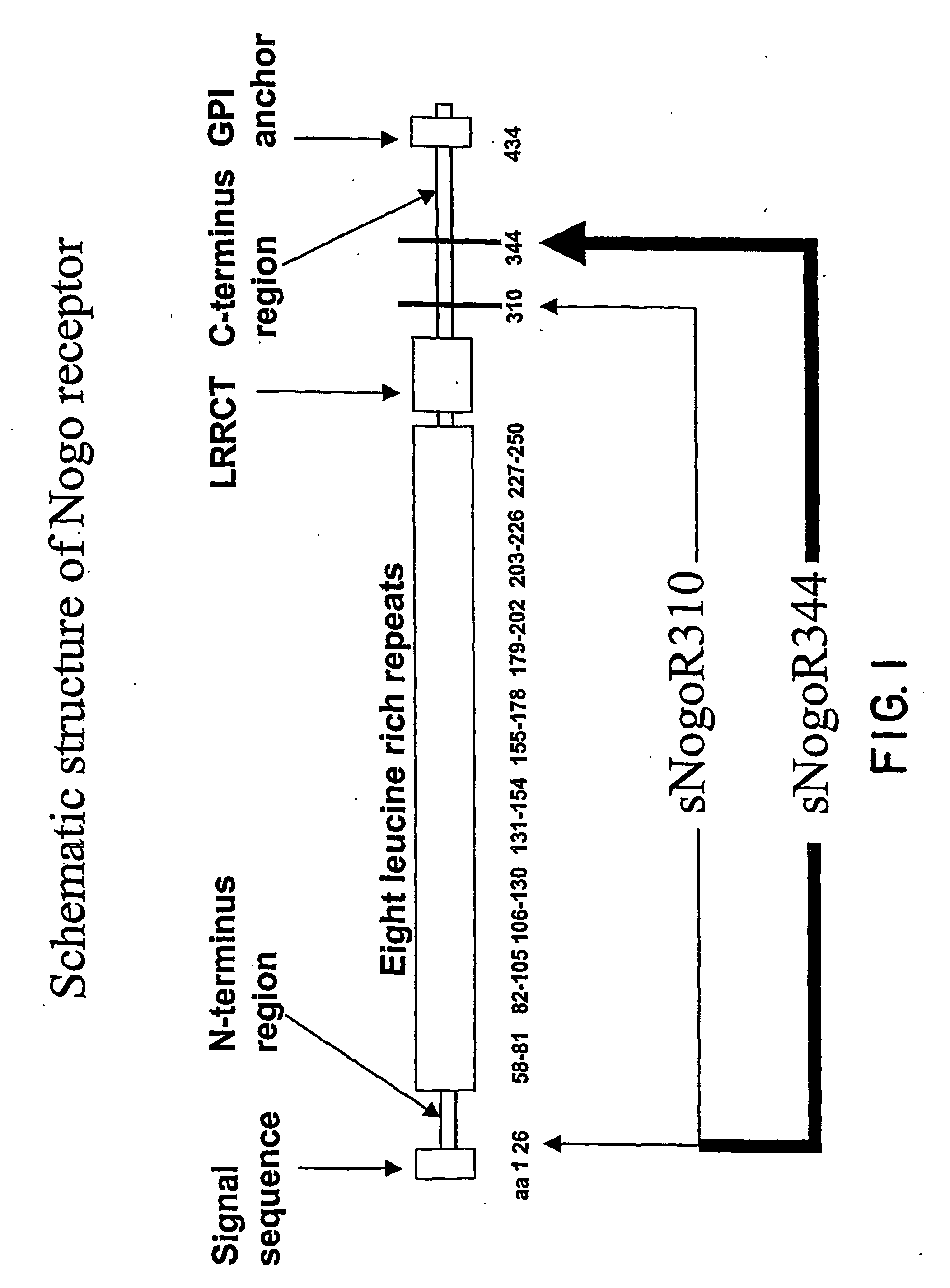
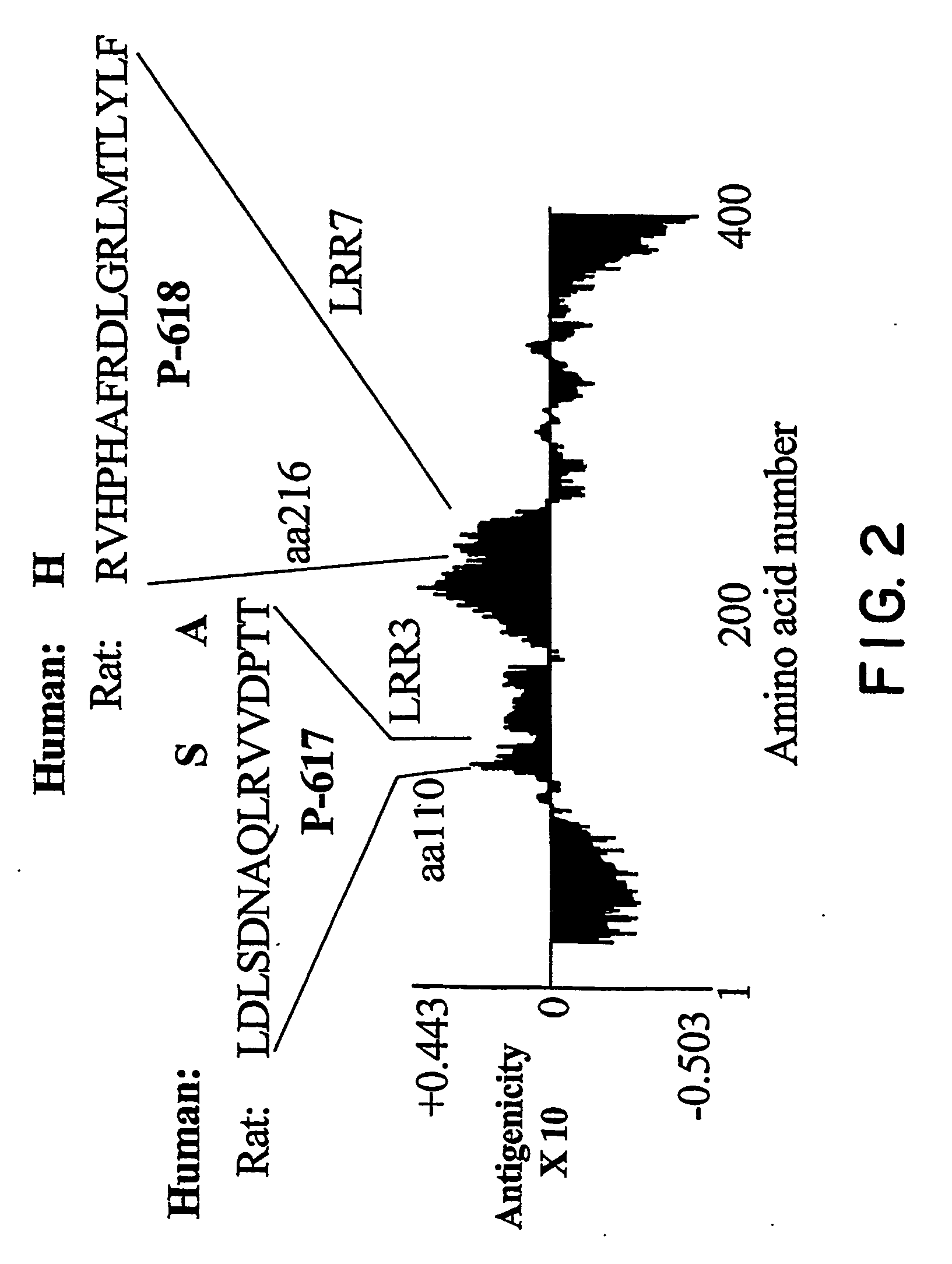
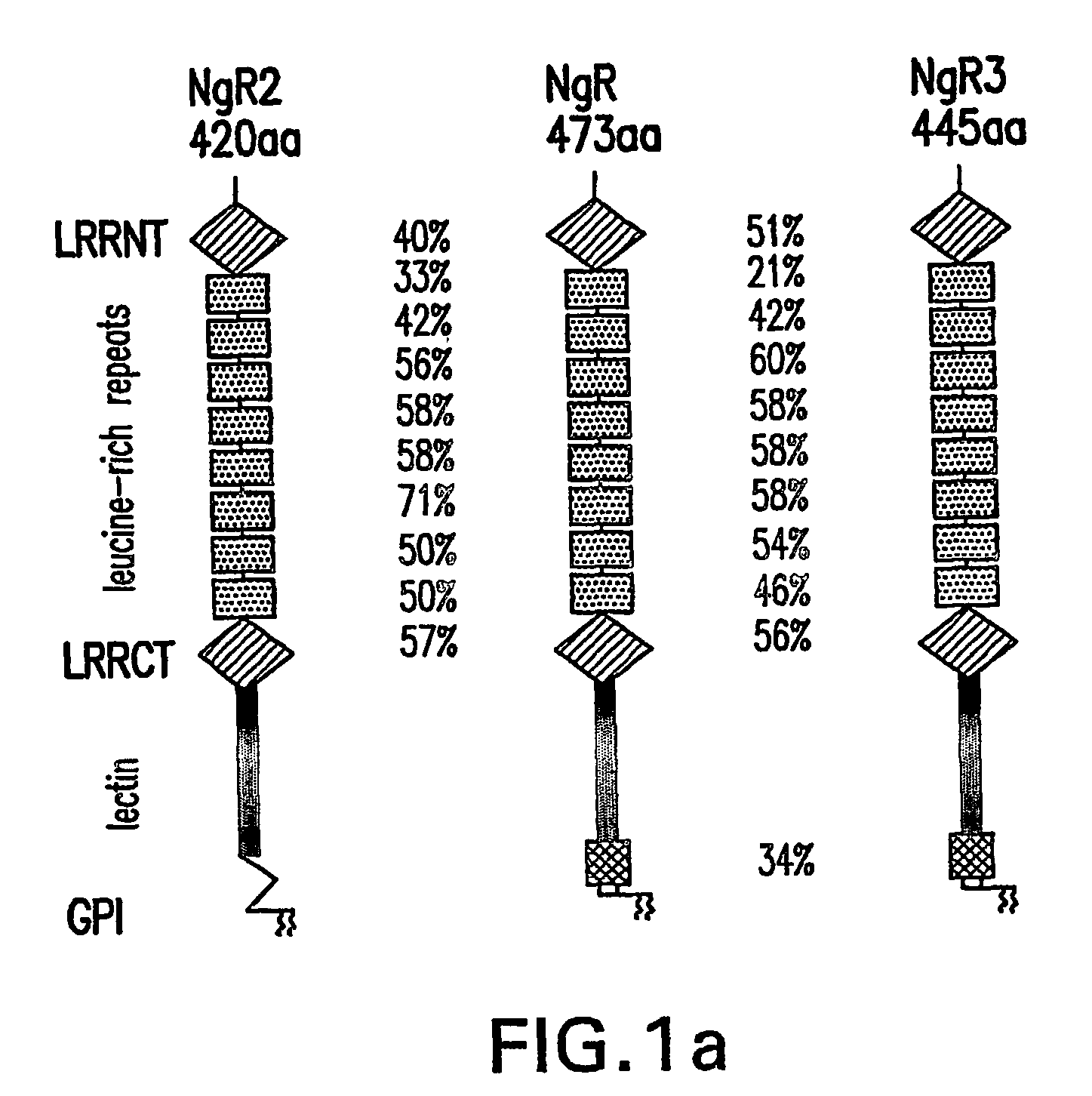
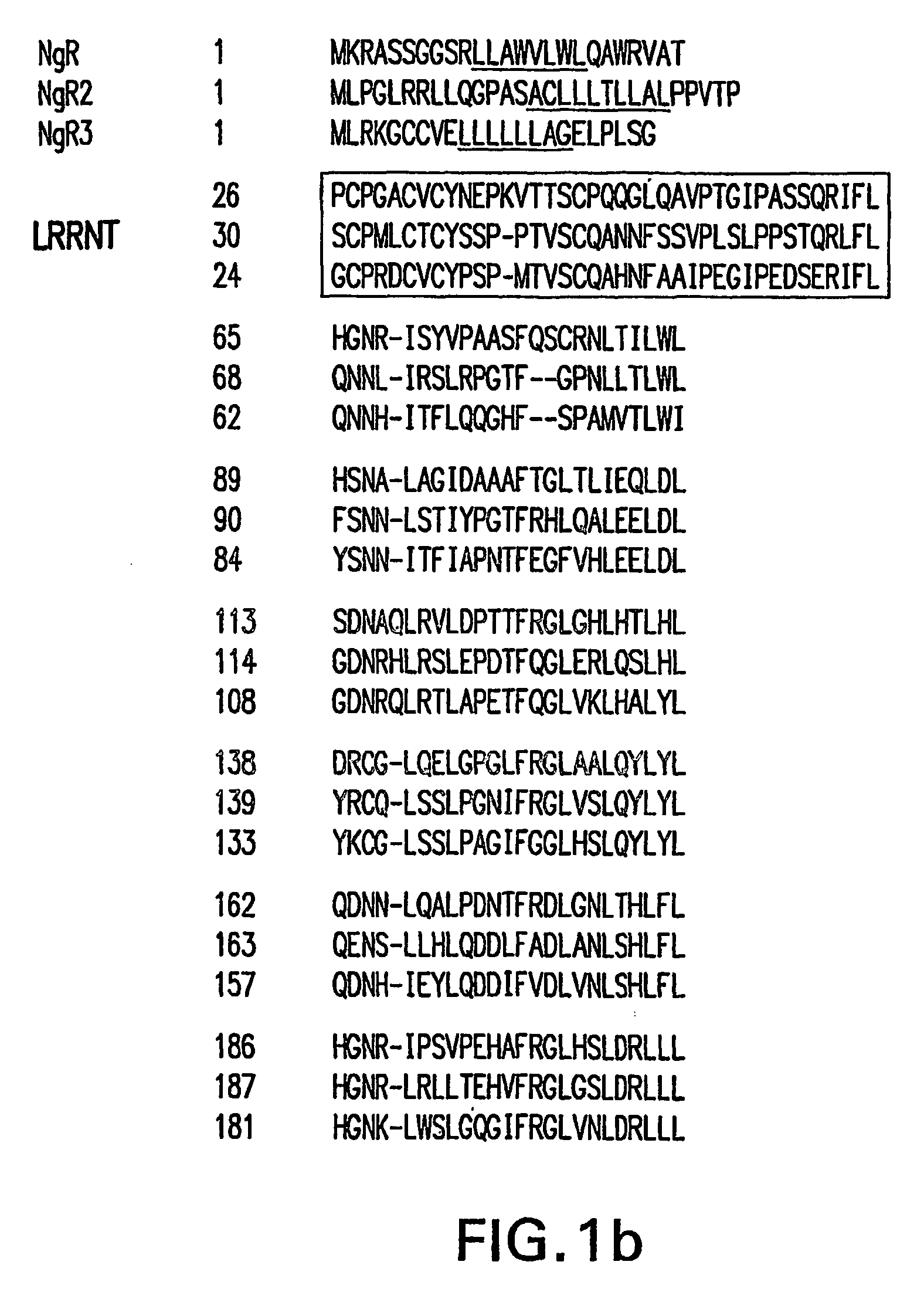
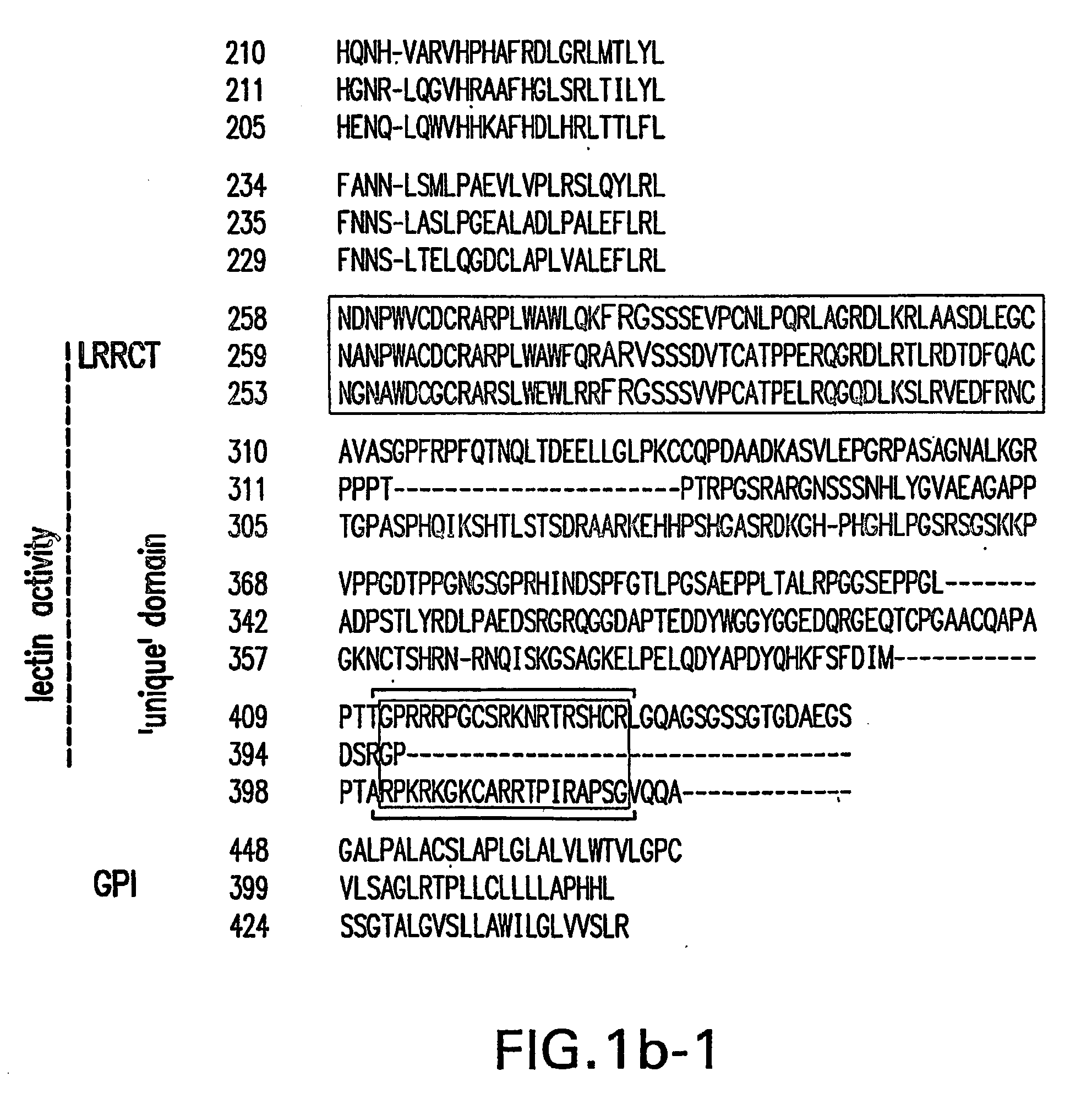
Identification of novel nogo-receptors and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20070032406A1Organic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseAntibody fragments
Disclosed are compositions relating to the Nogo receptor (NgR) family as well as fragments, chimeras, and variants thereof. The invention provides polypeptides, nucleic acids, vectors, expression systems, and antibodies and antibody fragments related to the NgRs as well as uses thereof. Such uses include modulation neurite outgrowth in a subject and treatment of central nervous system disorders in a subject, as well as, methods of identifying and screening compounds that can be used for modulating neurite outgrowth in a subject or in treatment of central nervous system disorders in a subject.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
RNA interference mediated inhibition of NOGO and NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS7691999B2Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesFhit geneNogo Receptors
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor genes, such as NOGO-A, NOGO-B, NOGO-C, NOGO-66 receptor, NI-35, NI-220, NI-250, myelin-associated glycoprotein, tenascin-R, and NG-2.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
TAT protein transduction modified NEP1-40 fusion protein and use thereof
InactiveCN101418046APreserve penetrationSolve the problem of not being able to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB)Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemHigh activity
The invention discloses a preparation method for TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein and application in treating the injuries of a central nervous system, CNS. The TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein is characterized in that the TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein comprises the protein transduction domain (PTD) of a transactivating transduction protein TAT of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Nogo extracellular peptide residues 1-40, NEP1-40. The fusion protein retains the selective antagonistic activity of the NEP1-40 to a Nogo receptor, NgR, and has the advantages of high transduction efficiency and easy penetration of BBB and BCSB, thereby overcoming the limitation of the NEP1-40, avoiding the extra injuries on nervous tissues caused by the mode of injecting the NEP1-40 through microinjection or miniature pump implantation, and overcoming the problem that the NEP1-40 can hardly pass BBB and BCSB to reach corresponding biological concentration. The fusion protein can be prepared in a large quantity, has a low cost and high activity, and can be used for treating a plurality of CNS injuries including cerebral ischemia, cerebral anoxia, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral trauma, spinal core injury, and the like, and promoting the regeneration and functional rehabilitation of nervous tissues.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
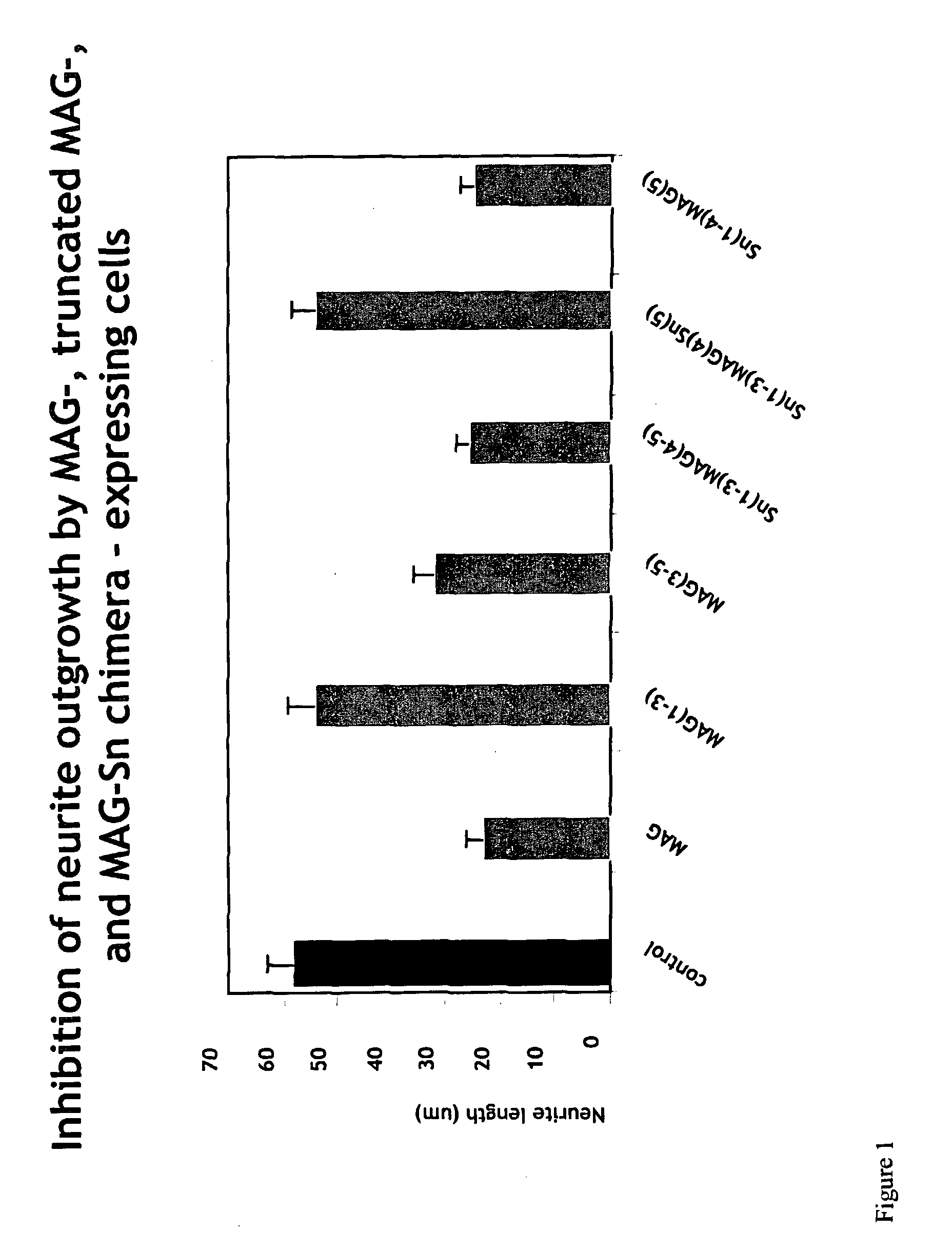
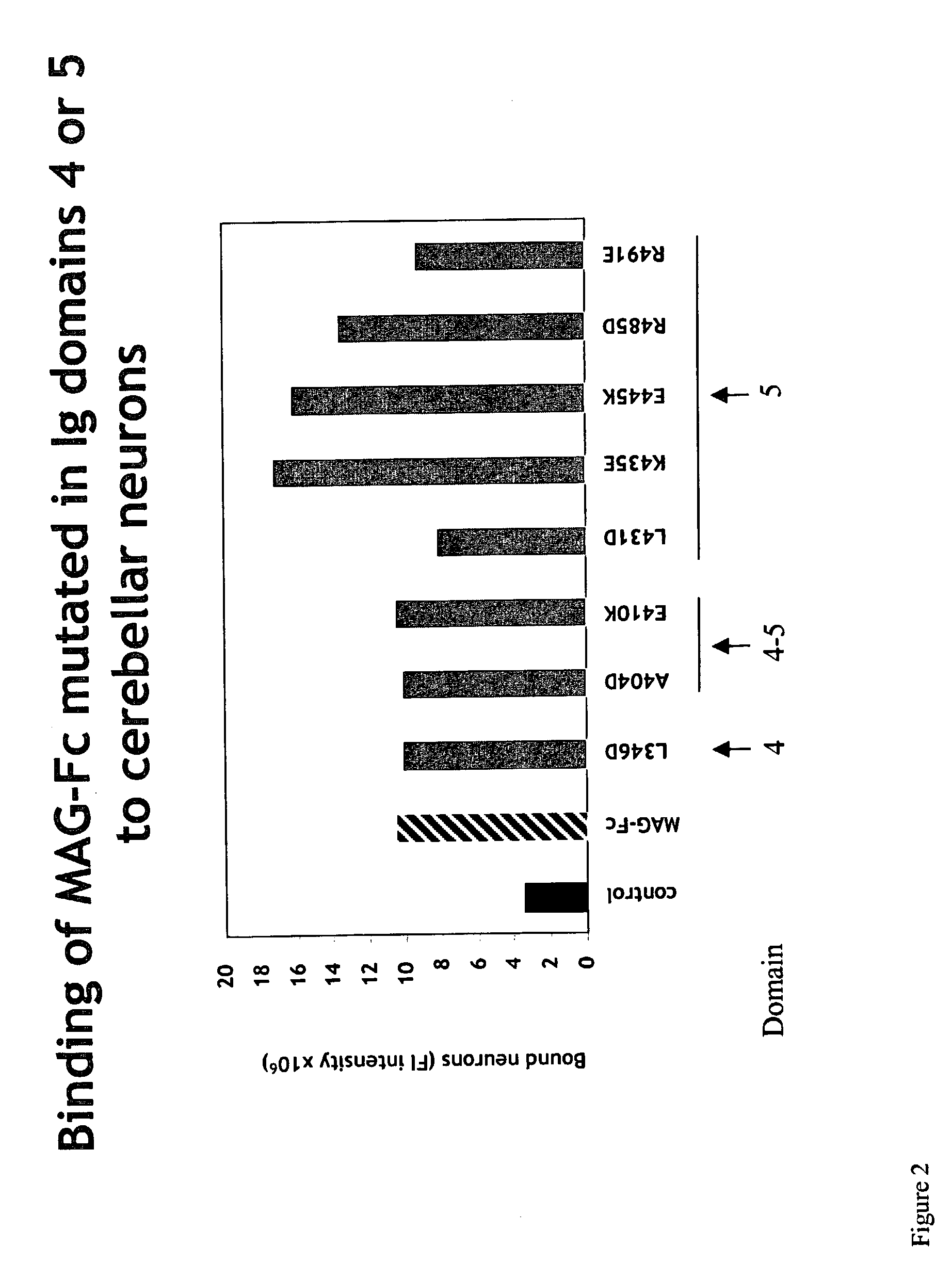
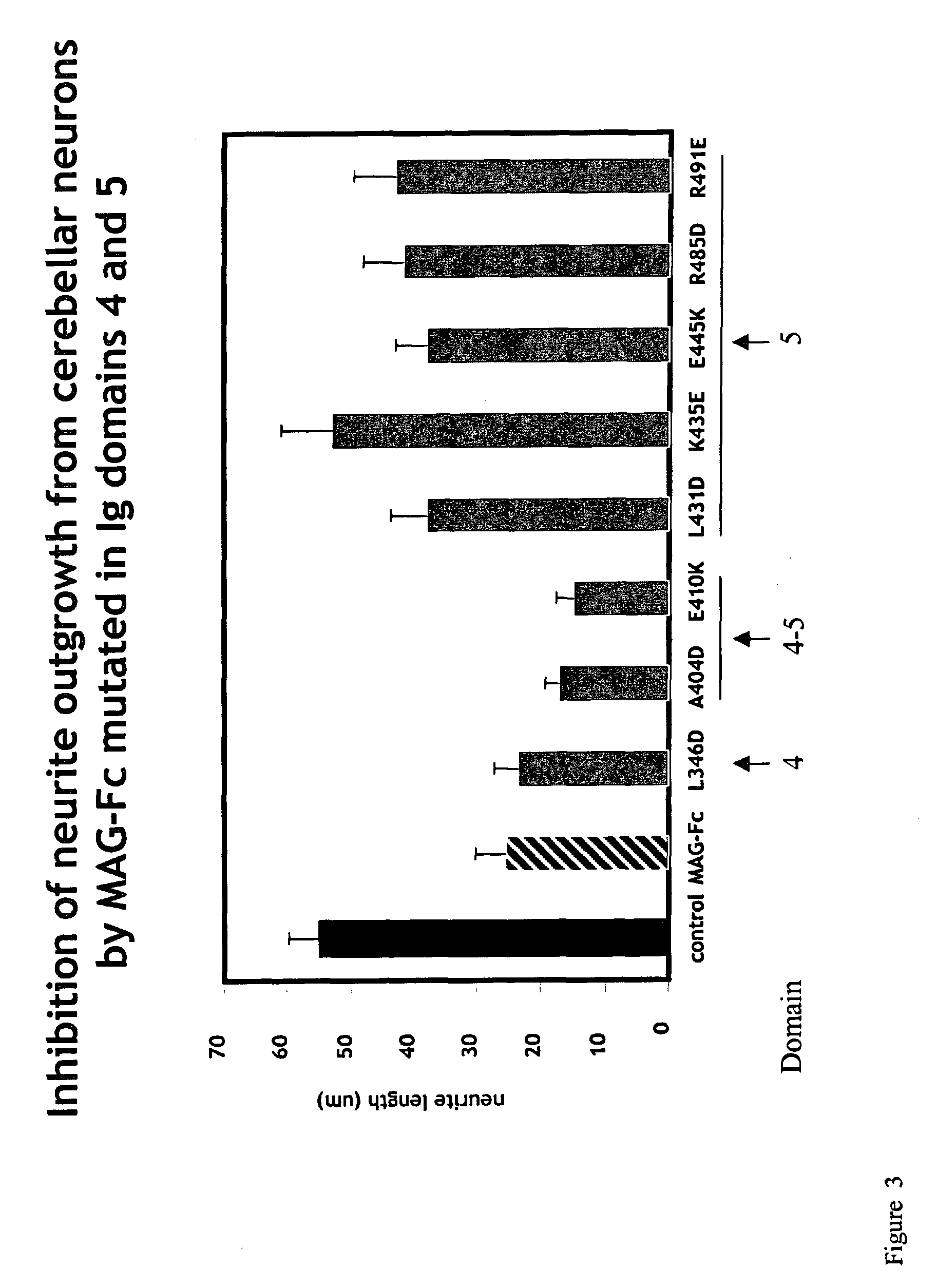
Inhibitors of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) activity for regulating neural growth and regeneration
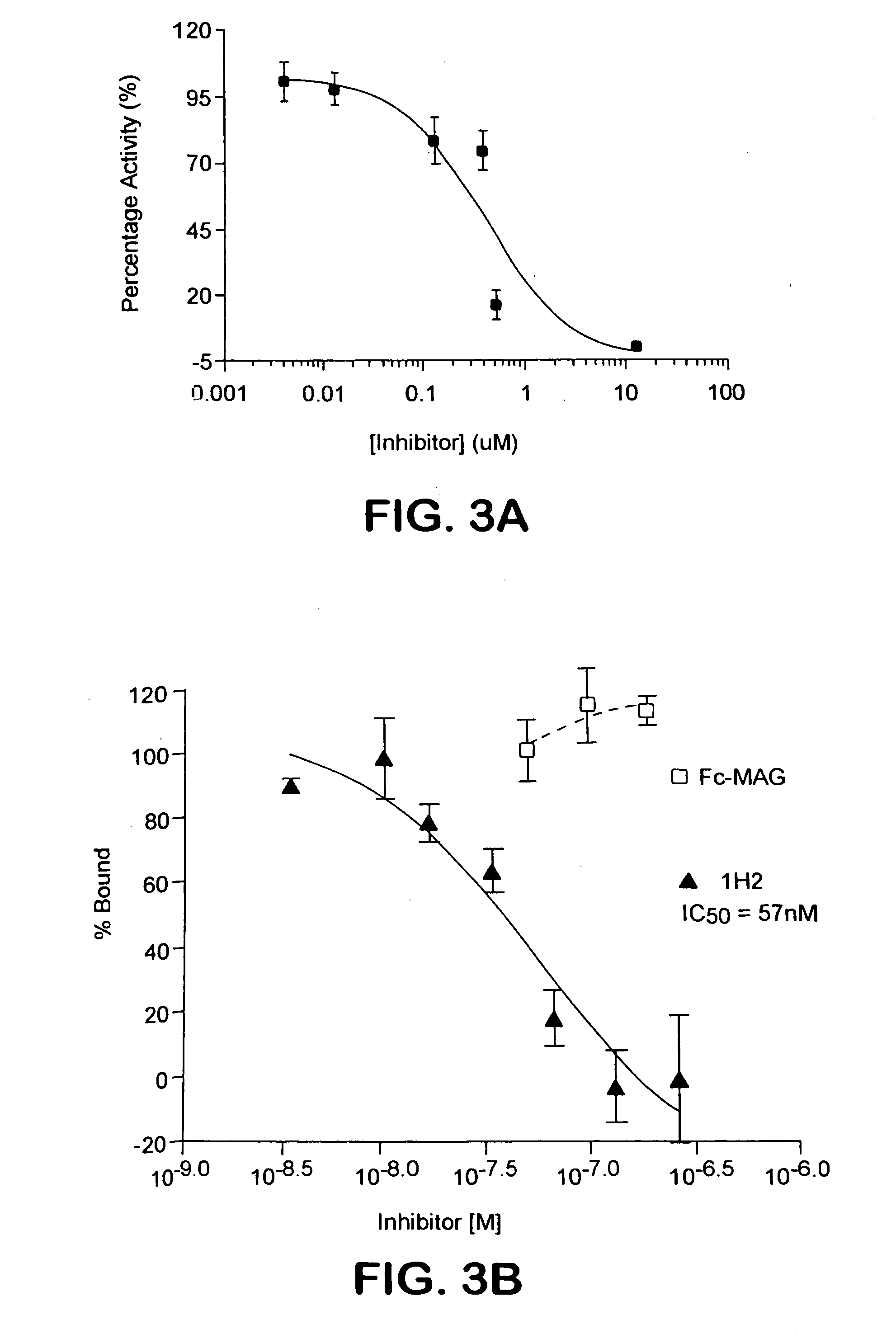
InactiveUS7842666B2Reduce and eliminate abilityPromote or inhibit)Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
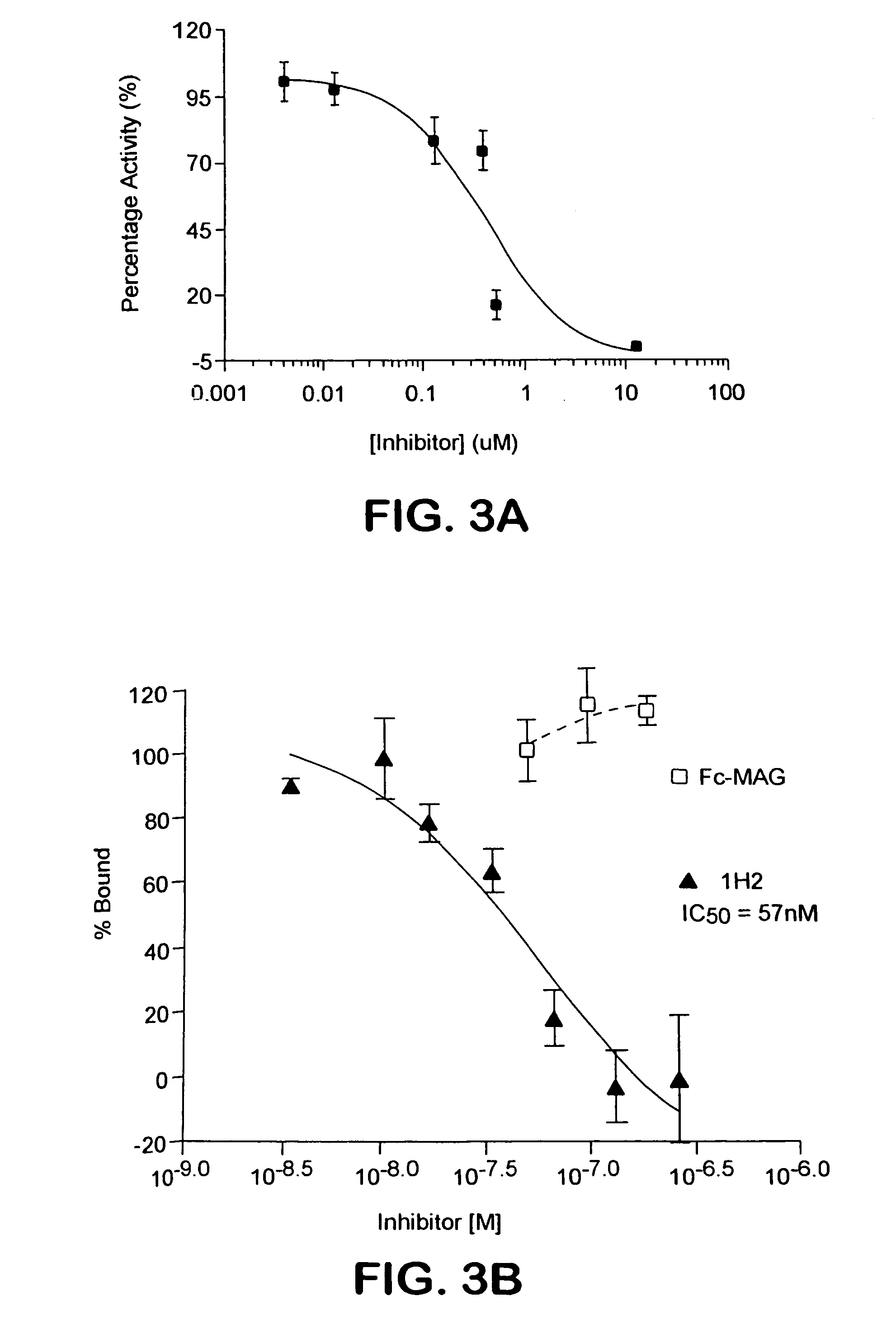
The present invention relates generally to products, compositions and methods useful for promoting neural repair and regeneration. The products and compositions of this invention include myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) derivatives that are inhibitors of endogenous MAG (e.g., mutant MAG proteins) and Nogo Receptor (NgR) binding inhibitors that are peptides derived from MAG, Nogo and OMgp that can bind to NgR and block NgR signaling. Peptides that can bind and activate NgR signaling are also provided. Inhibitory MAG derivatives and NgR binding inhibitors are useful for blocking the inhibition of neural regeneration mediated by proteins such as MAG, Nogo and / or OMgp in the nervous system. These inhibitors are also useful for treating neural degeneration associated with injuries, disorders or diseases.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Reactivation of Axon Growth and Recovery in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury
InactiveUS20150307583A1Promote growthOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntigen Binding FragmentGrowth promoting
Disclosed are methods of treating chronic nervous system diseases or injuries, e.g., chronic spinal cord injury, using Nogo receptor antagonists, including Nogo receptor-1 (NgR1) polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof, and polynucleotides. Also disclosed are methods of noninvasively monitoring axonal growth during and after treatment with an axonal growth promoting agent.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Rna interference mediated inhibition of nogo and nogo receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (sina)
InactiveUS20070185043A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryMyelin sheathNogo Receptors
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor genes, such as NOGO-A, NOGO-B, NOGO-C, NOGO-66 receptor, NI-35, NI-220, NI-250, myelin-associated glycoprotein, tenascin-R, and NG-2
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Reactivation of axon growth and recovery in chronic spinal cord injury
ActiveUS8992918B2Promote growthOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntigen Binding FragmentGrowth promoting
Disclosed are methods of treating chronic nervous system diseases or injuries, e.g., chronic spinal cord injury, using Nogo receptor antagonists, including Nogo receptor-1 (NgR1) polypeptides, Nogo receptor-1 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof, soluble Nogo receptors and fusion proteins thereof, and polynucleotides. Also disclosed are methods of noninvasively monitoring axonal growth during and after treatment with an axonal growth promoting agent.
Owner:YALE UNIV
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF NOGO AND NOGO RECEPTOR GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
InactiveUS20090093431A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFhit geneNogo Receptors
This inventon relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of NOGO and / or NOGO receptor genes, such as NOGO-A, NOGO-B, NOGO-C, NOGO-66 receptor, NI-35, NI-220, NI-250, myelin-associated glycoprotein, tenascin-R, and NG-2
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods Relating to Peripheral Administration of Nogo Receptor Polypeptides
InactiveUS20120219567A1Improve clearanceImprove memory functionSenses disorderNervous disorderBlood plasmaNogo Receptors
This invention relates to methods of treating diseases involving accumulation of Aβ plaques, including Alzheimer's Disease by the peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. The invention also provides methods of increasing the plasma to brain ratio of Aβ peptide and enhancing Aβ peptide clearance via peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. This invention also provides methods of improving memory function or inhibiting memory loss via the peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides. The invention also provides methods of decreasing the size and number of Aβ plaques in a mammal via peripheral administration of soluble Nogo receptor polypeptides.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com