Patents
Literature
373results about "Synchronisation transmitters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
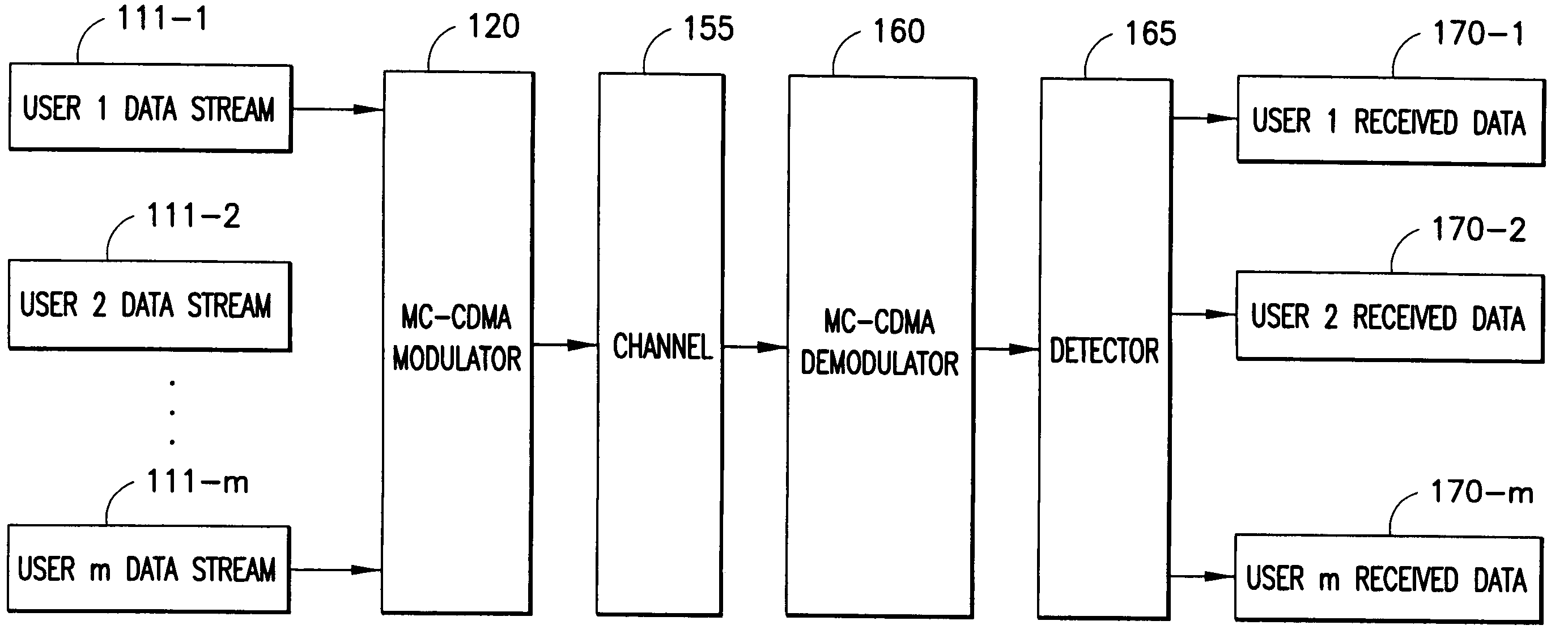
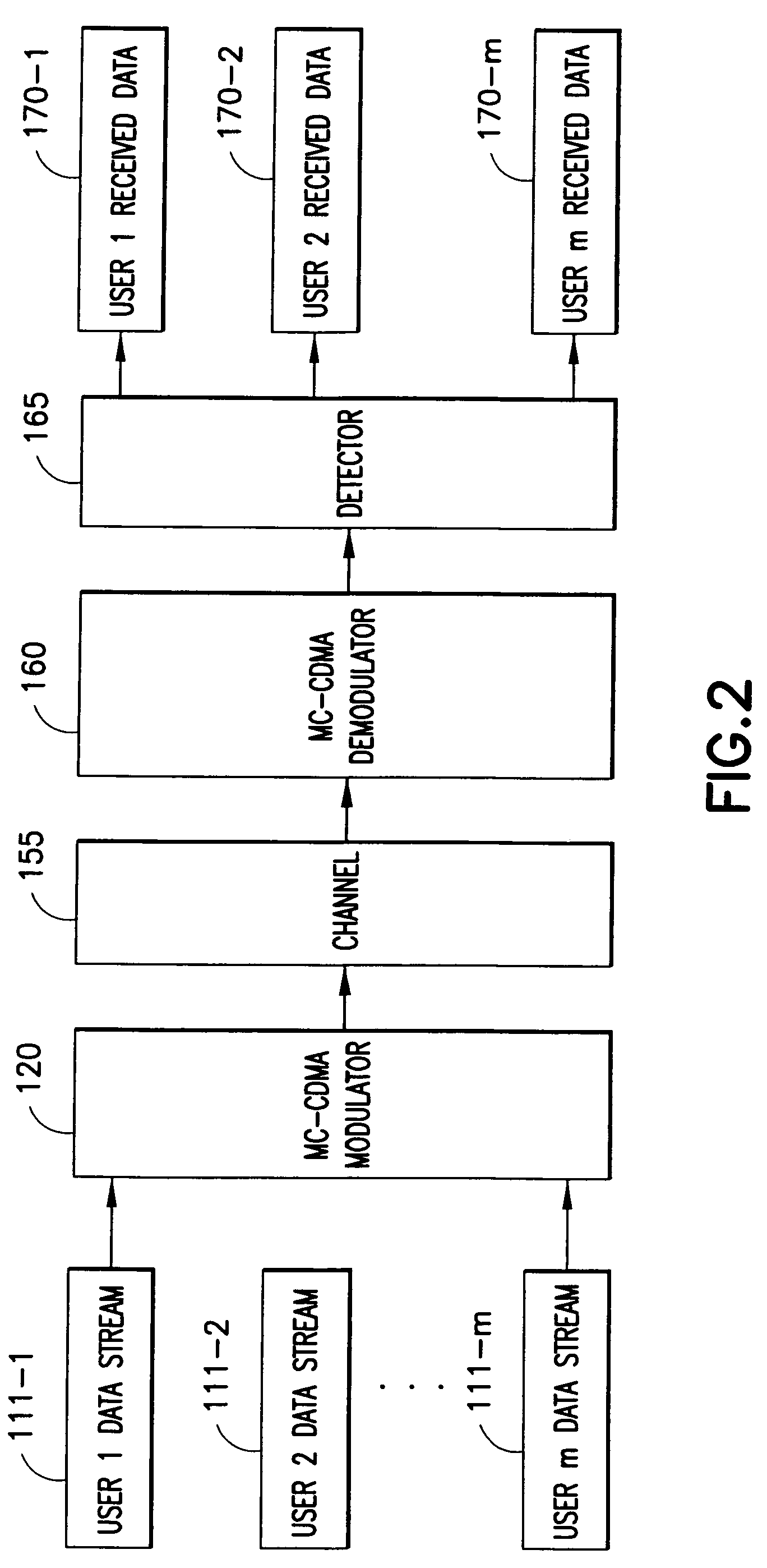
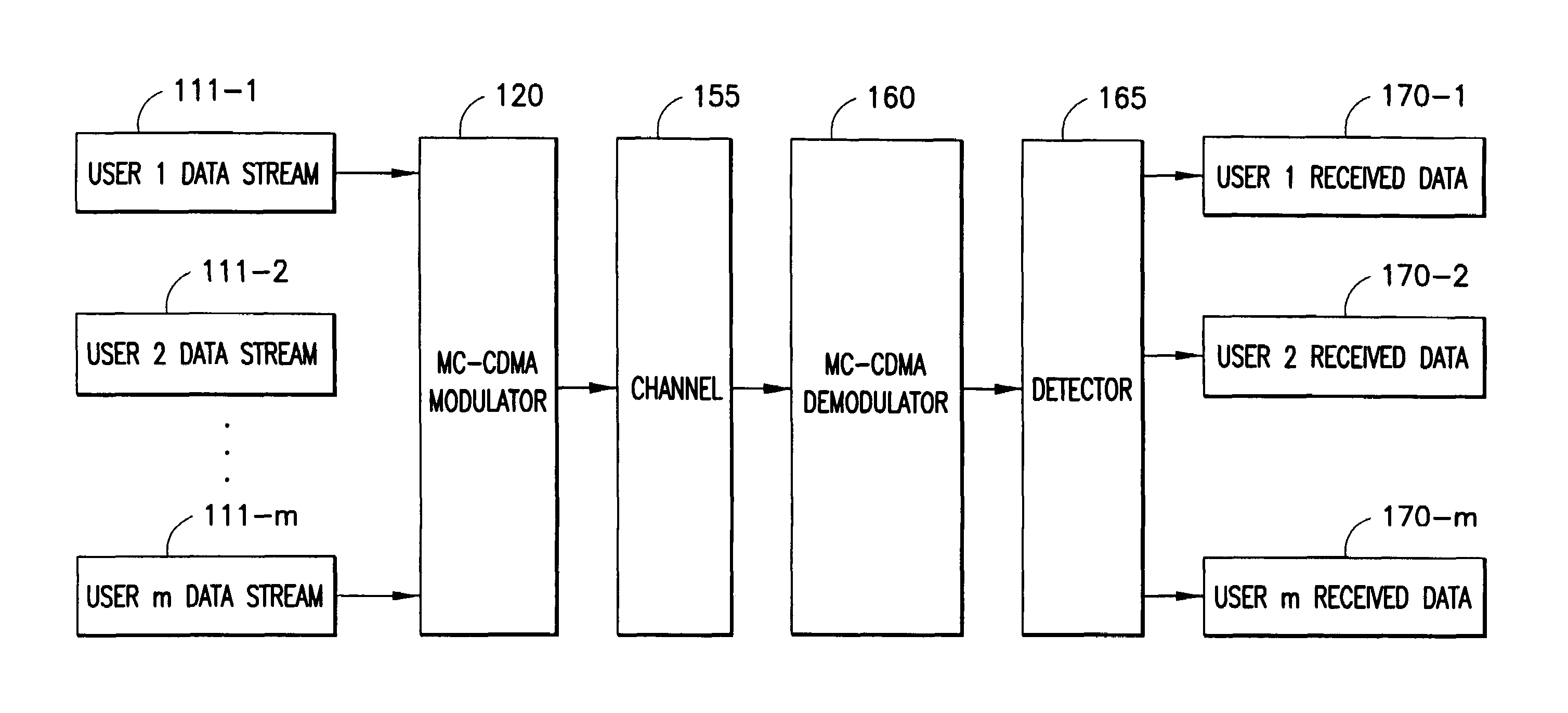
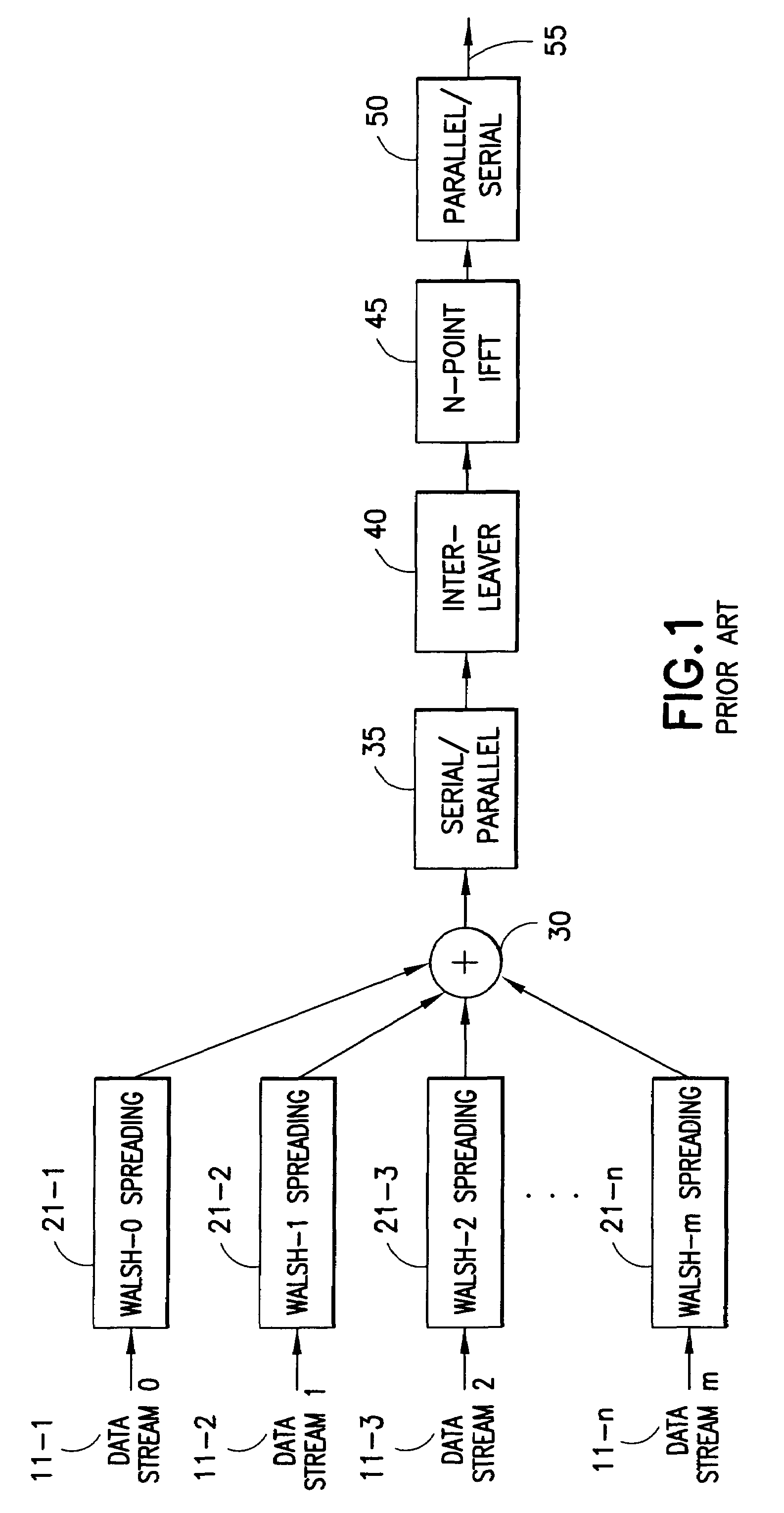
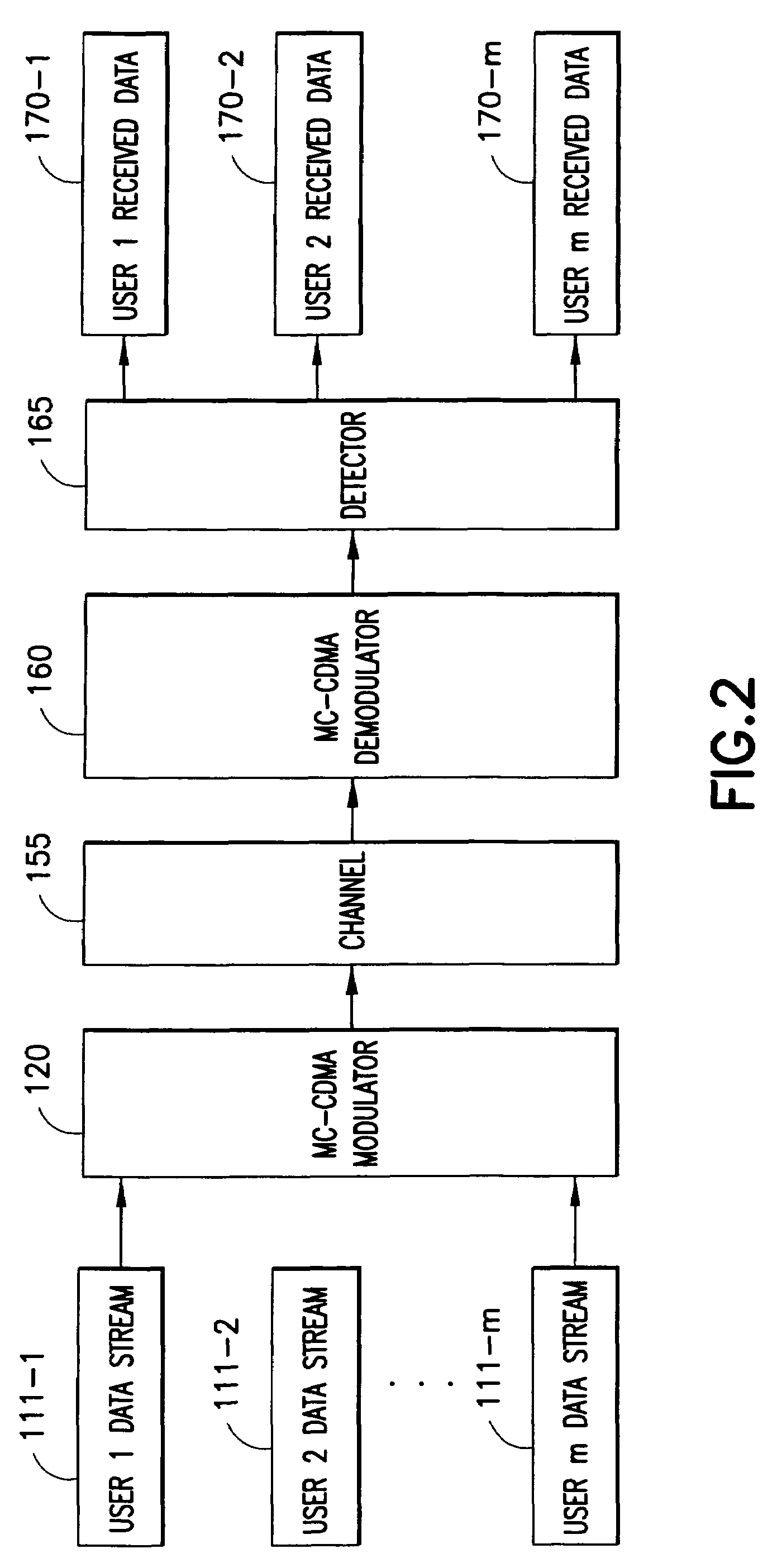
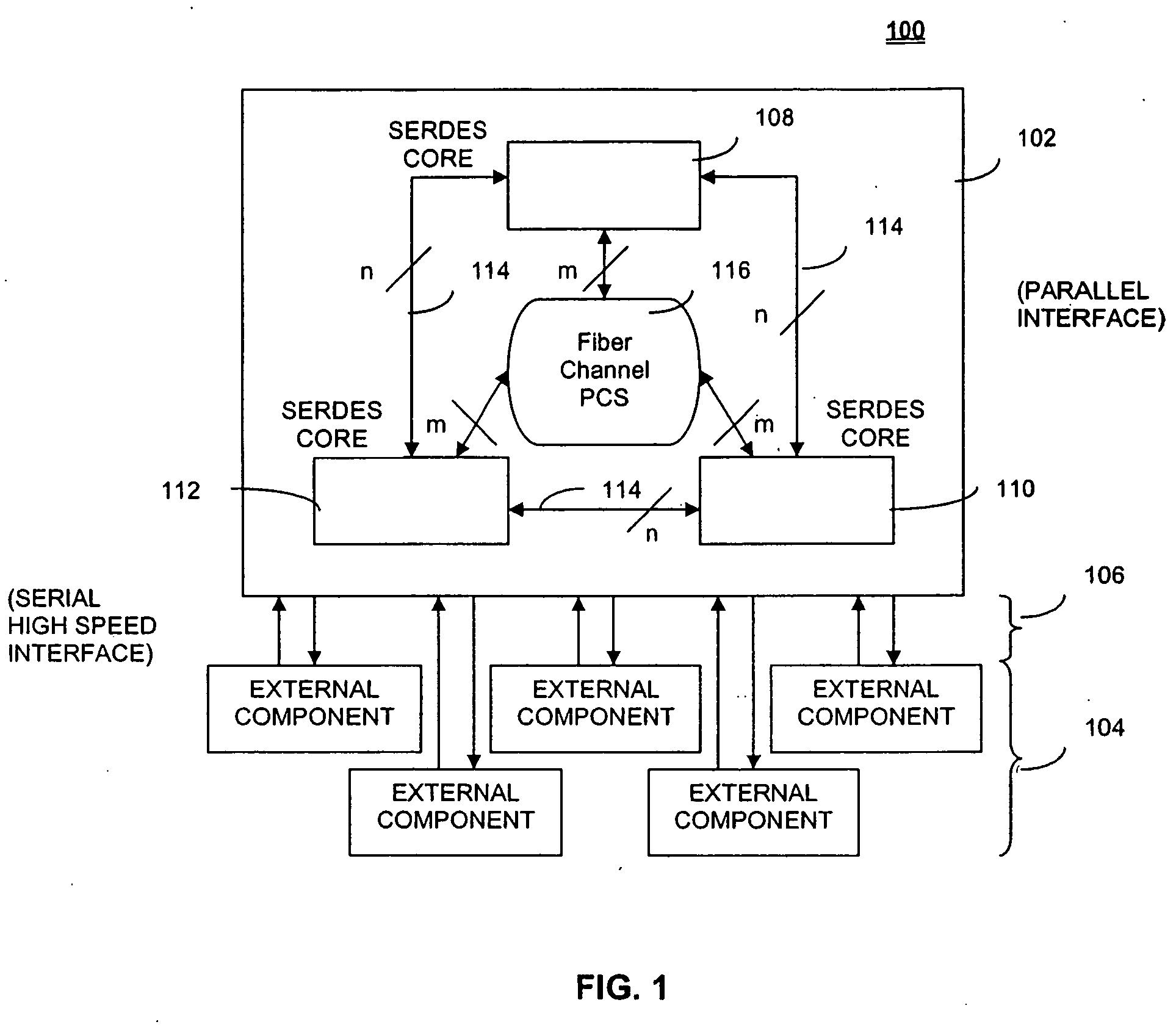
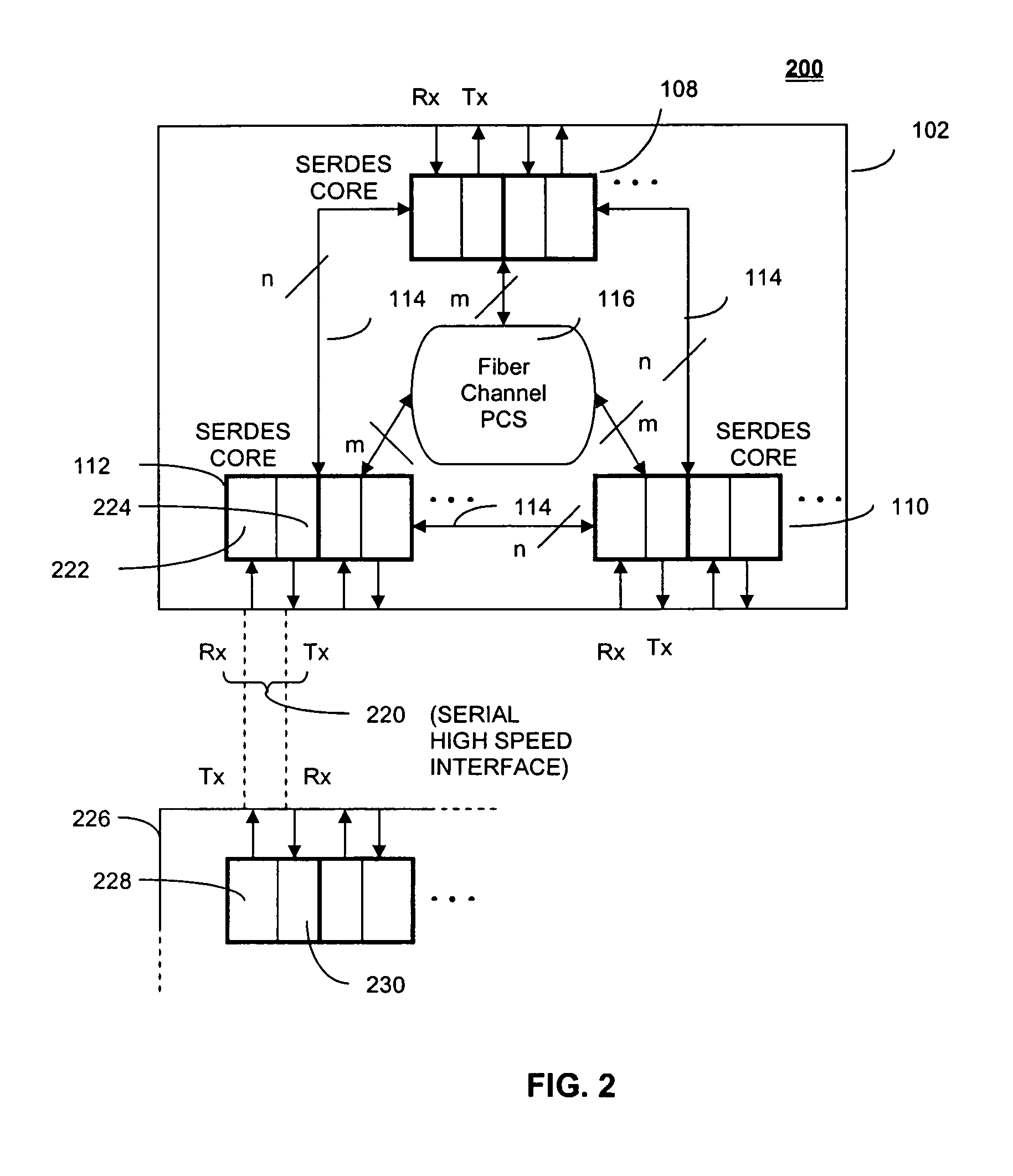
Multiple user adaptive modulation scheme for MC-CDMA
InactiveUS20050157670A1Keep in syncMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransmission path divisionModem devicePerformance tuning
In a multi-user frequency domain spreading downlink MC-CDMA system. a group of sub-carriers can be replaced by an equivalent sub-carrier of a conventional OFDM modem for purposes of resource allocation to improve the system performance. The chips for a given user are spread only within the group. Confinement insures synchronization between different users' chips that is essential to the recovering and separation of user symbols at the receiver. There is no limit imposed on the group size, which permits different spreading code lengths to be used for different scenarios or for performance tuning.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
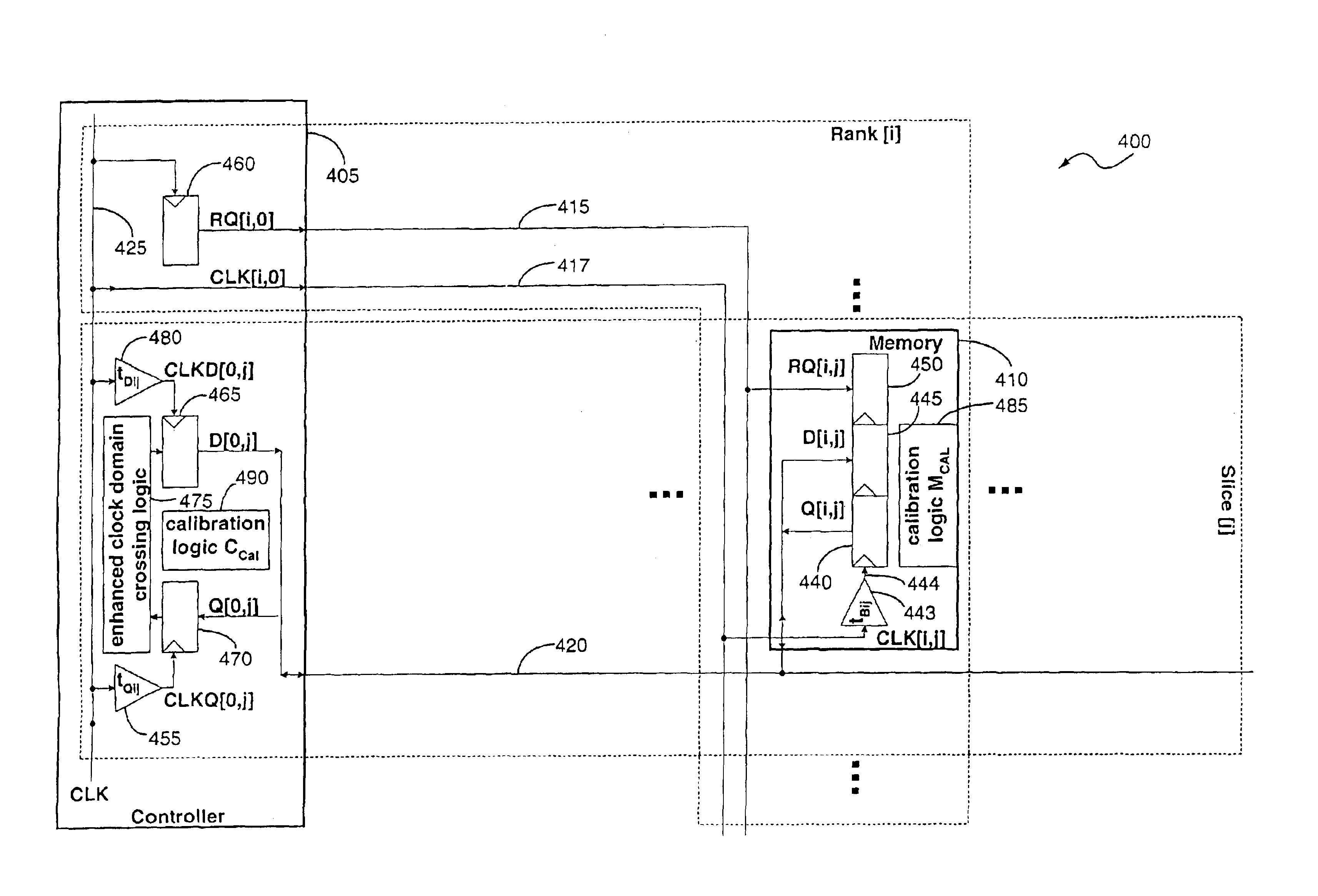
Timing calibration apparatus and method for a memory device signaling system
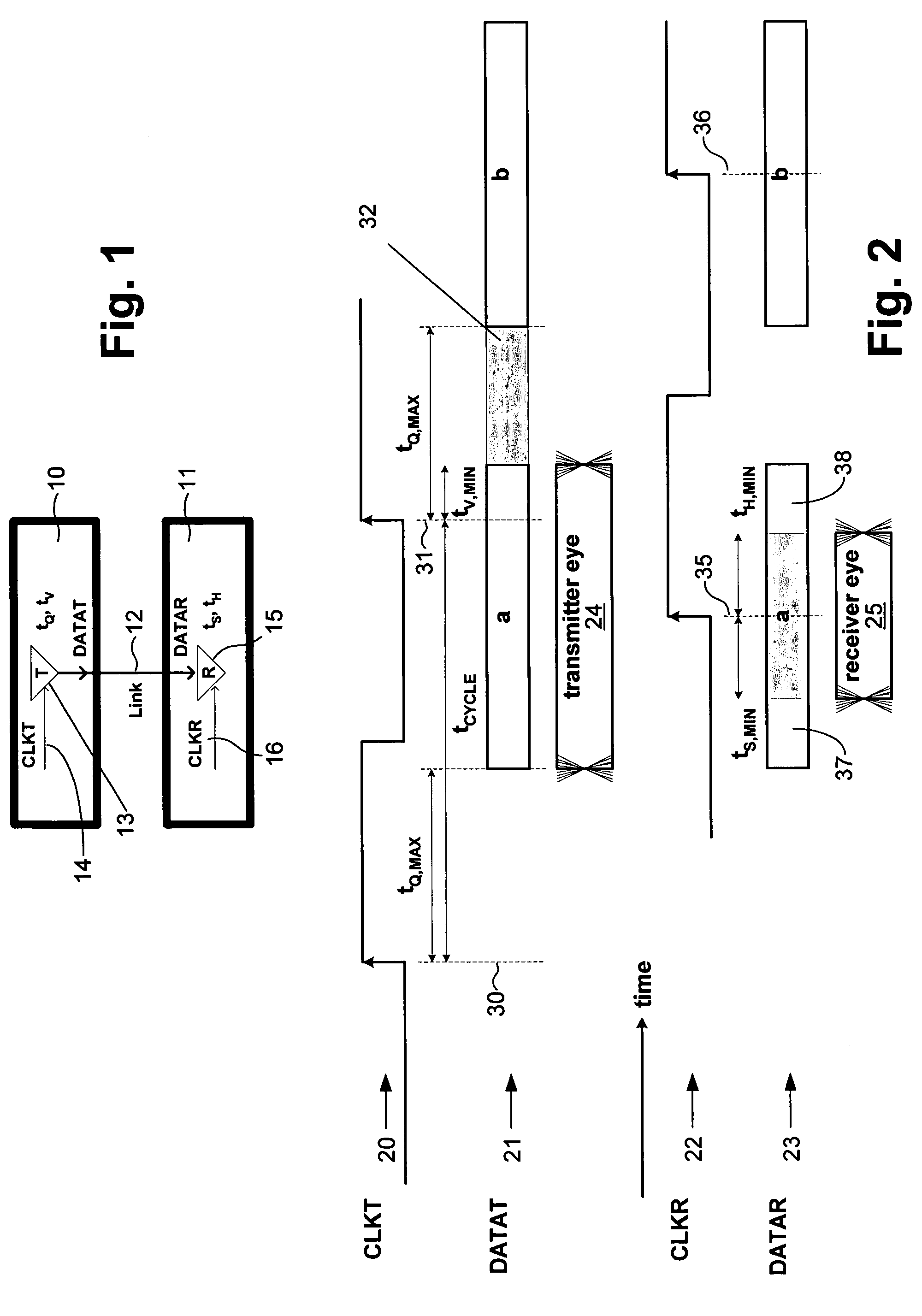
A memory system includes a memory controller and a memory component coupled to each other. An interface of the memory component is configured to receive a first signal from the memory controller with read request information, retrieve the read data information from the memory core in response to the request information, and transmit to the memory controller a second signal containing the read data information. The read data information includes read data symbols, where the average duration of the read data symbols, measured at the interface, defines a symbol time interval. A first external access time is measured at the interface between a first read request and read data transmitted by the interface in response to the first read request. A second external access time interval is measured at the interface between a second read request and read data transmitted by the interface in response to the second read request. The difference between the first external access time and the second external access time is greater than one-half of the symbol time interval.
Owner:RAMPART ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
Memory device signaling system and method with independent timing calibration for parallel signal paths
InactiveUS20050132158A1Error detection/correctionSolid-state devicesMemory controllerSignaling system
A memory system includes a memory controller and a memory component coupled to each other. The memory controller includes an interface to receive a first signal and a second signal from the memory component, wherein the first signal comprises a first symbol and the second signal comprises a second symbol. A first circuit of the memory controller receives the first signal by sampling the first symbol using a first timing offset relative to a reference clock signal, and a second circuit of the memory controller receives the second signal by sampling the second symbol using a second timing offset relative to the reference clock signal. The first timing offset is independent of the second timing offset.
Owner:RAMPART ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
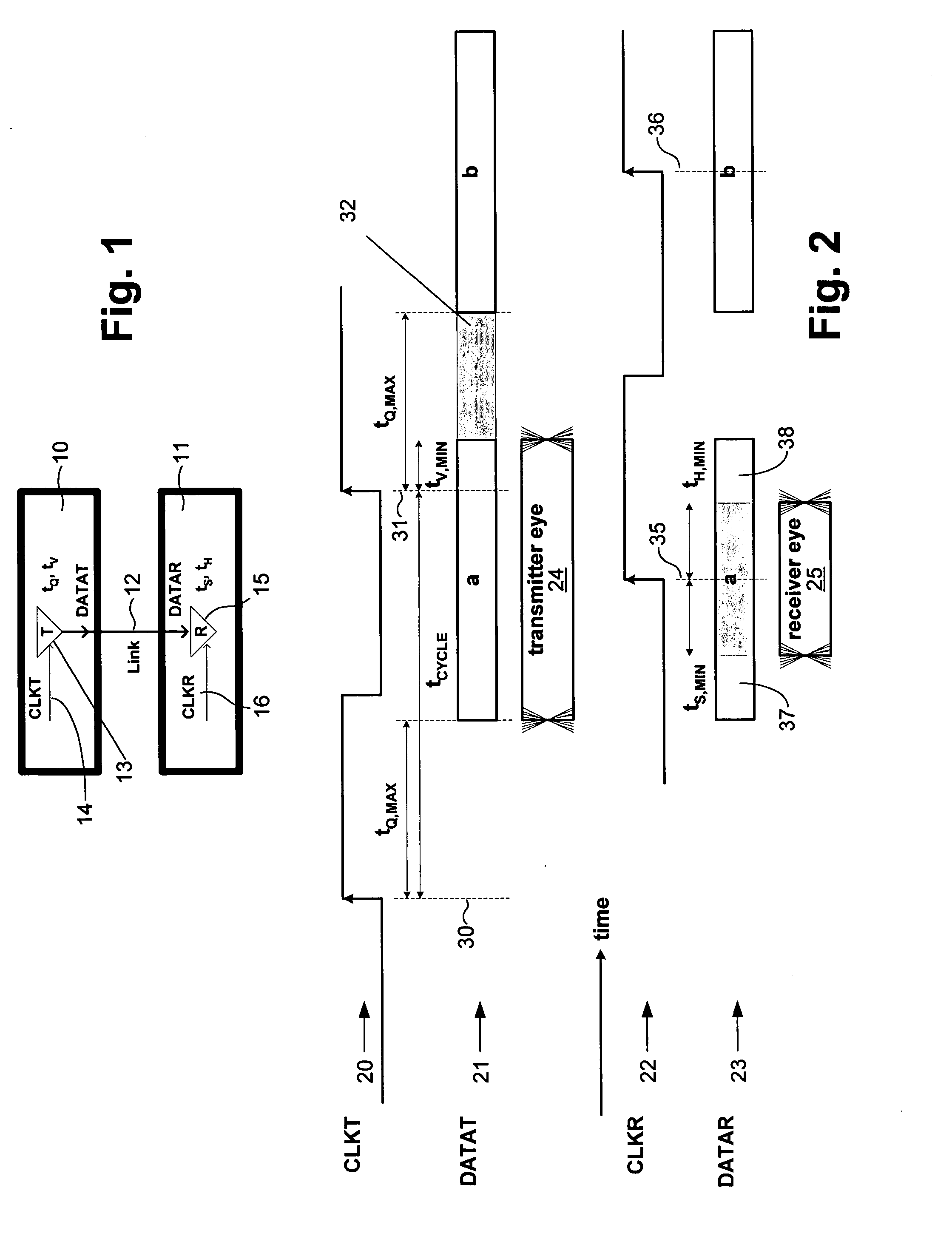
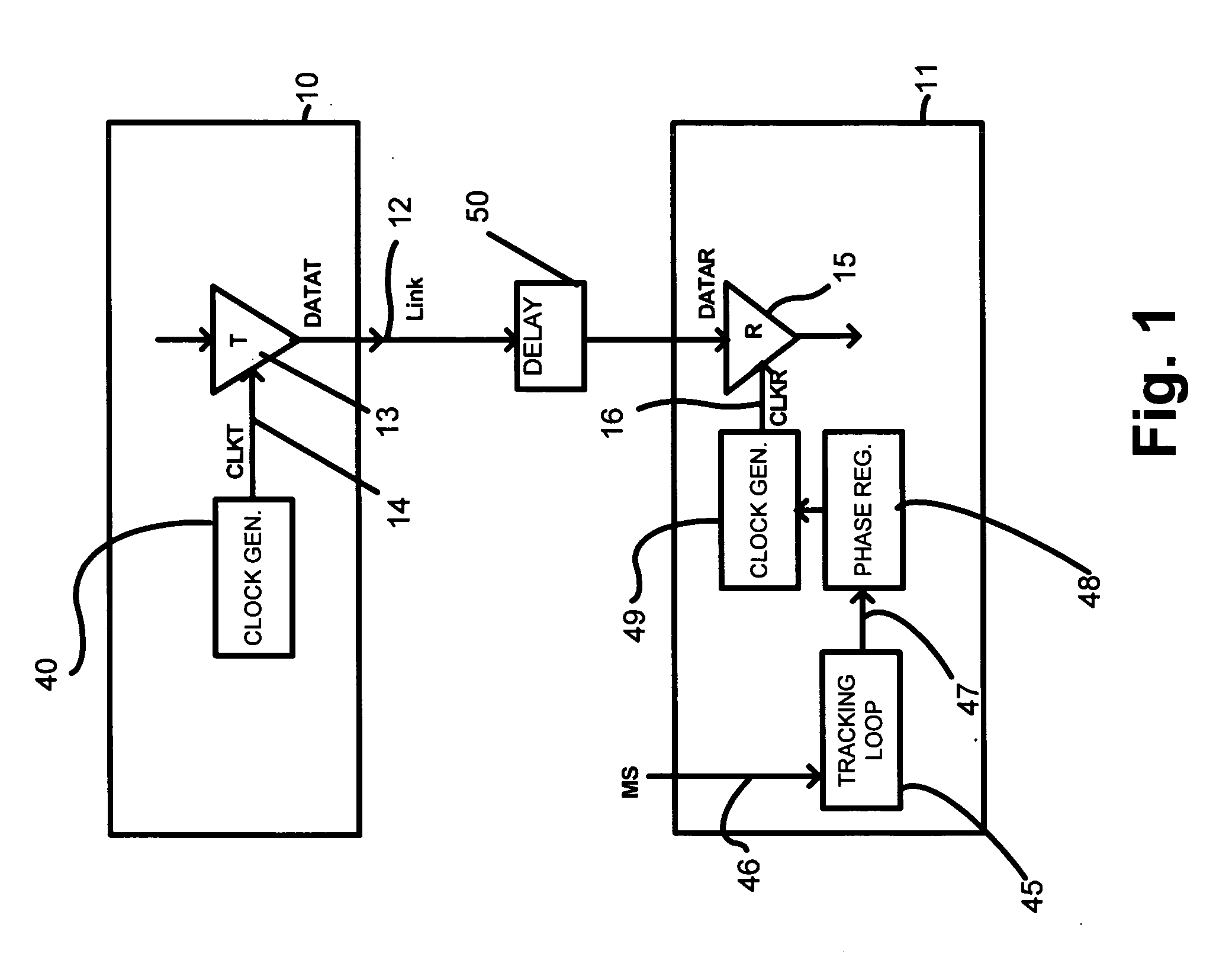
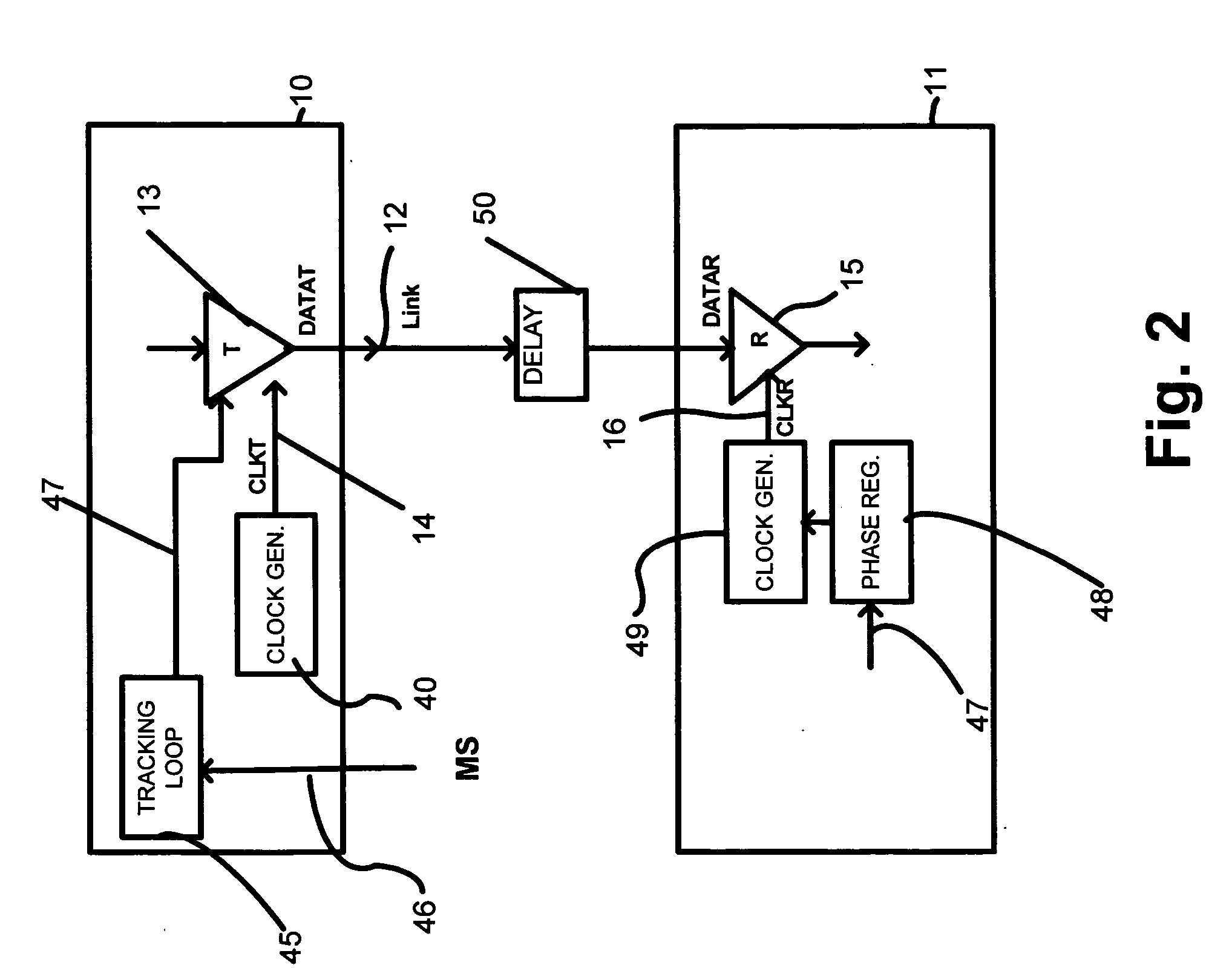
Drift tracking feedback for communication channels
ActiveUS6961862B2Efficiently tracking drift of property of channelReceiver initialisationChannel dividing arrangementsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
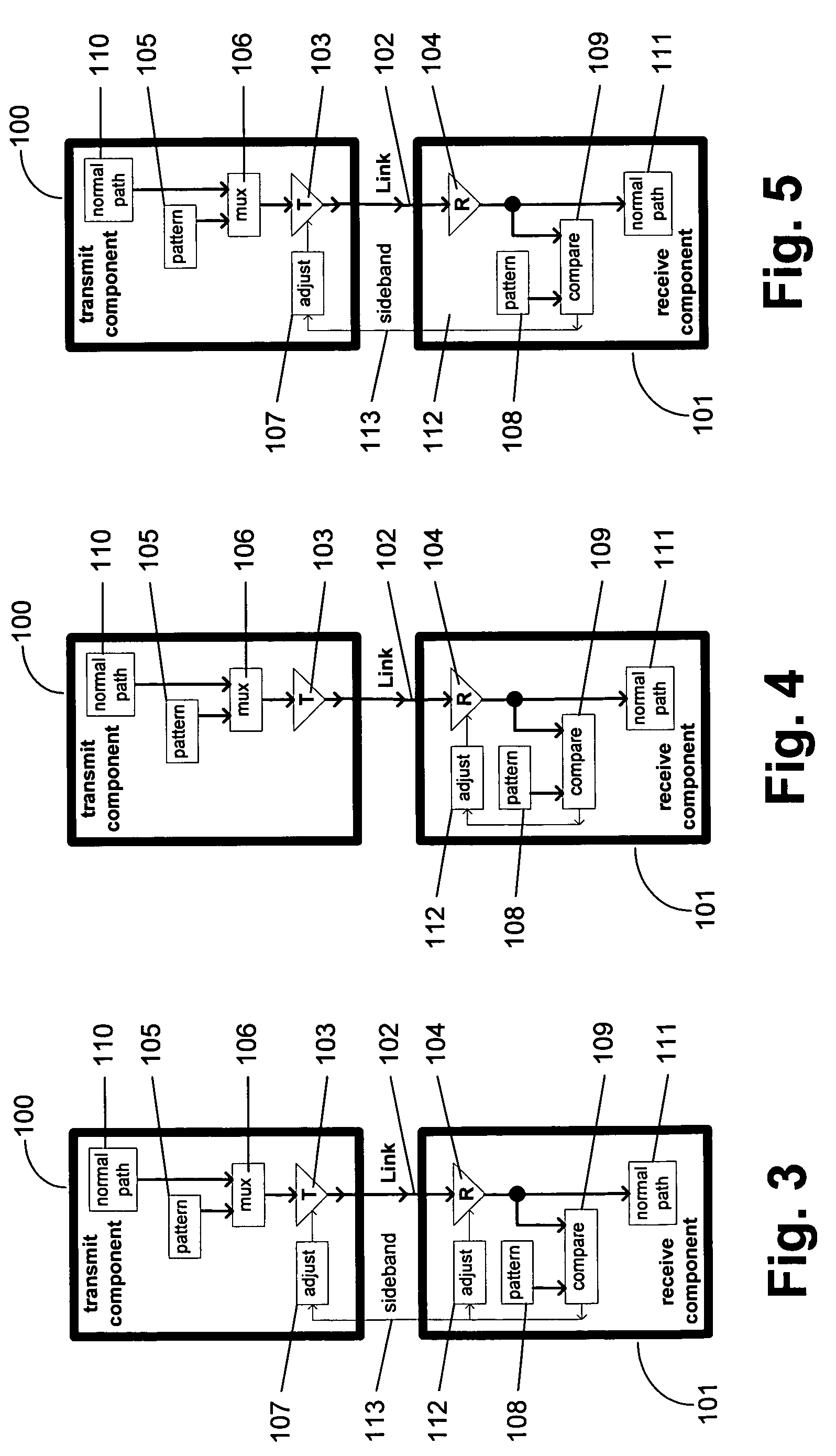
A communication channel includes a first component having a transmitter coupled to a normal signal source, and a second component having a receiver coupled to a normal signal destination. A communication link couples the first and second components. Calibration logic provides for setting an operation value for a parameter of the communication channel, such as by executing an exhaustive calibration sequence at initialization of the link. A tracking circuit, including a monitoring function, tracks drift in the parameter by monitoring a feedback signal that has a characteristic that correlates with drift in the communication channel, and updates, or indicates the need for updating of, the operation value of the parameter in response to the monitoring function.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
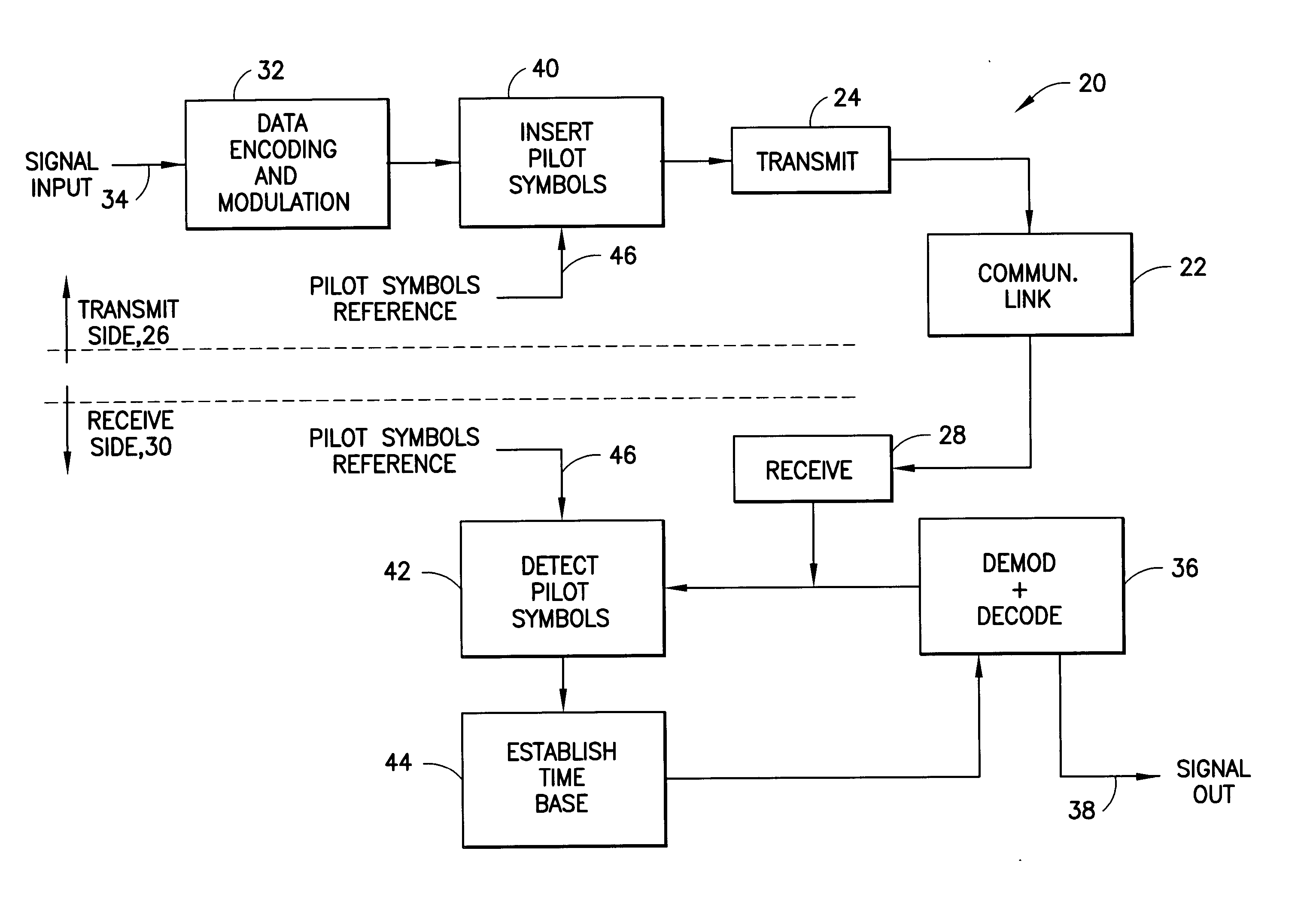
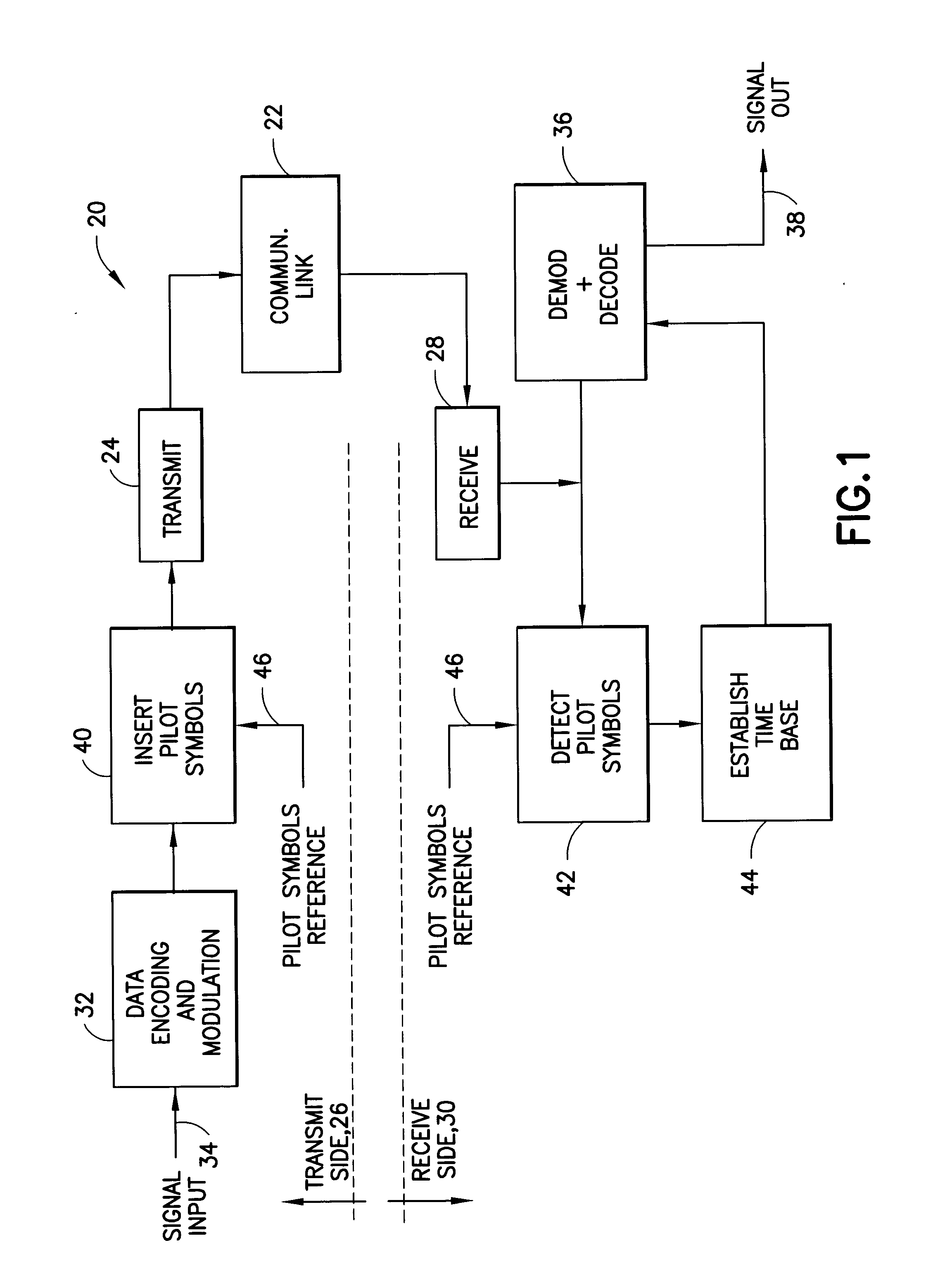
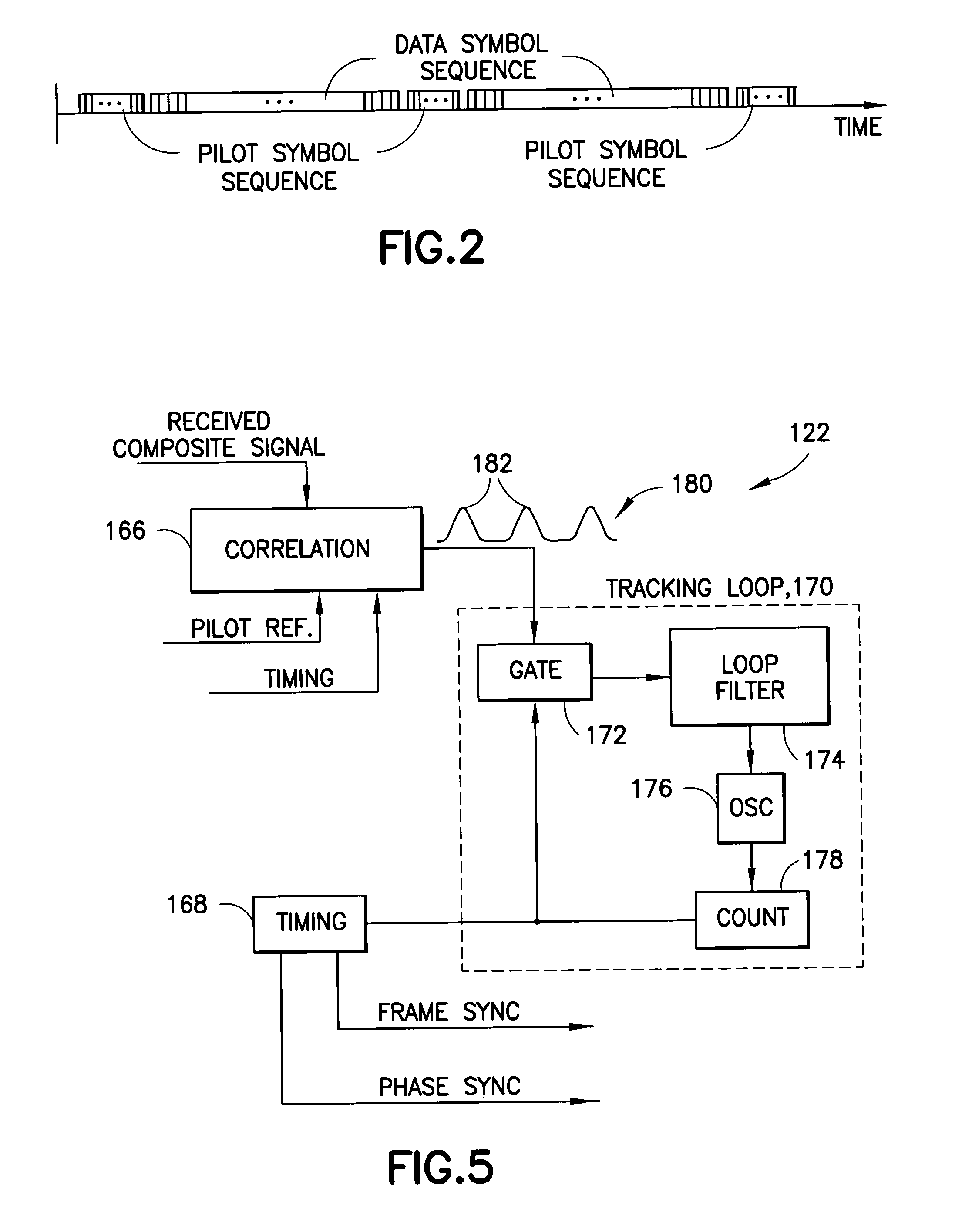
Modem with pilot symbol synchronization
InactiveUS20050047496A1Rapid determinationLess noisySynchronisation transmittersSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCommunications systemModem device
A modem, or a communication system, in its transmission section, has signal-formatting circuitry followed by circuitry for insertion of a sequence of pilot symbols into a sequence of data symbols outputted by the formatting circuitry. Placement of the insertion circuitry after the formatting circuitry permits a variety of formatting options without effecting the sequence of pilot symbols that serves as a time reference useful in detection of a signal transmitted by the modem. The reception section of the modem is equipped correspondingly to process a received composite signal of data symbols having a prescribed format and a sequence of pilot symbols. The reception section extracts the sequence of pilot symbols from the composite signal, and employs the pilot symbols to develop a time base for operation of circuitry for decoding the format of the received composite signal to extract data from the composite signal.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
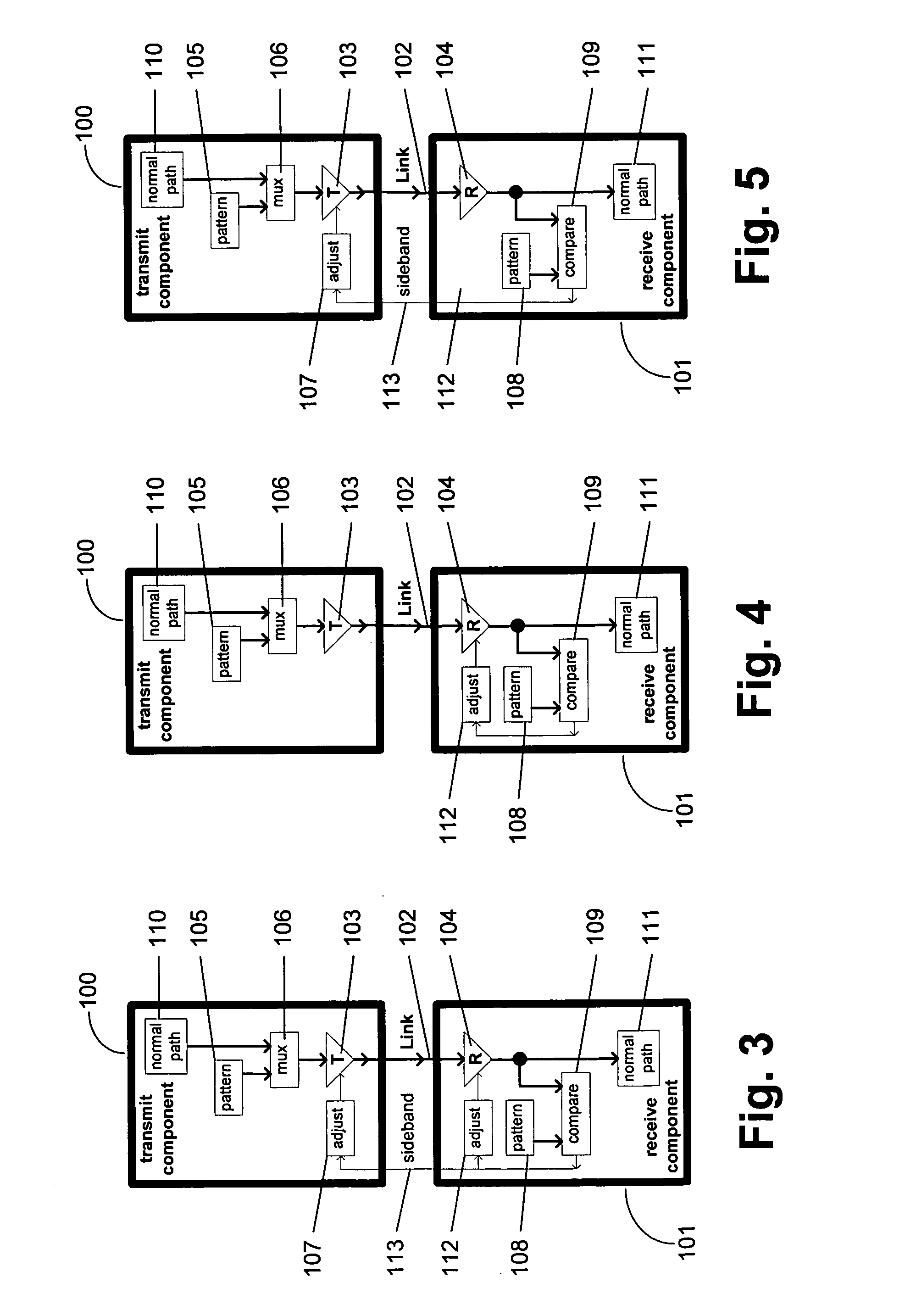
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
ActiveUS7095789B2Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingTelecommunications linkData source
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:K MIZRA LLC
Data sampling method and apparatus with alternating edge sampling phase detection for loop characteristic stabilization
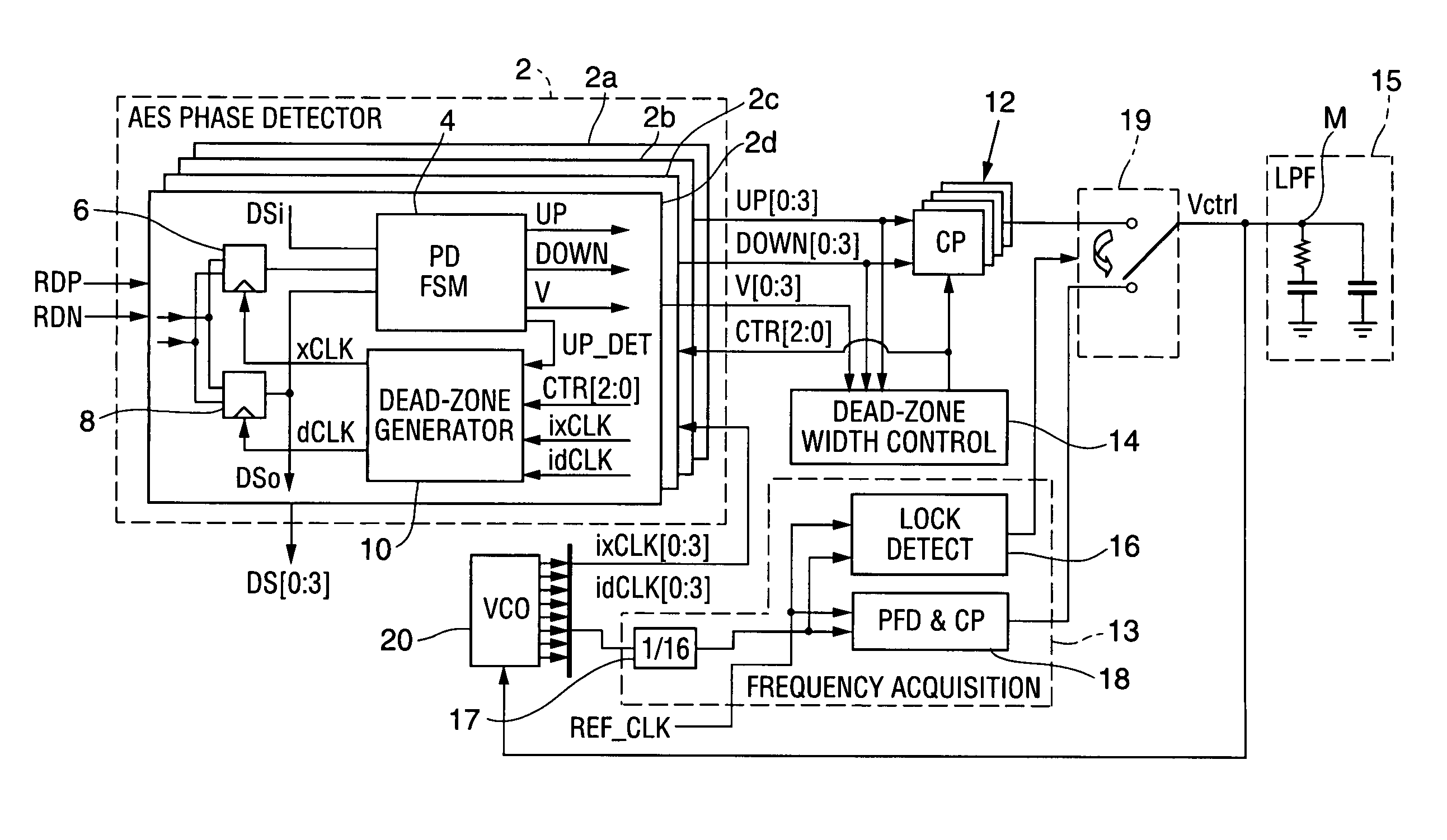
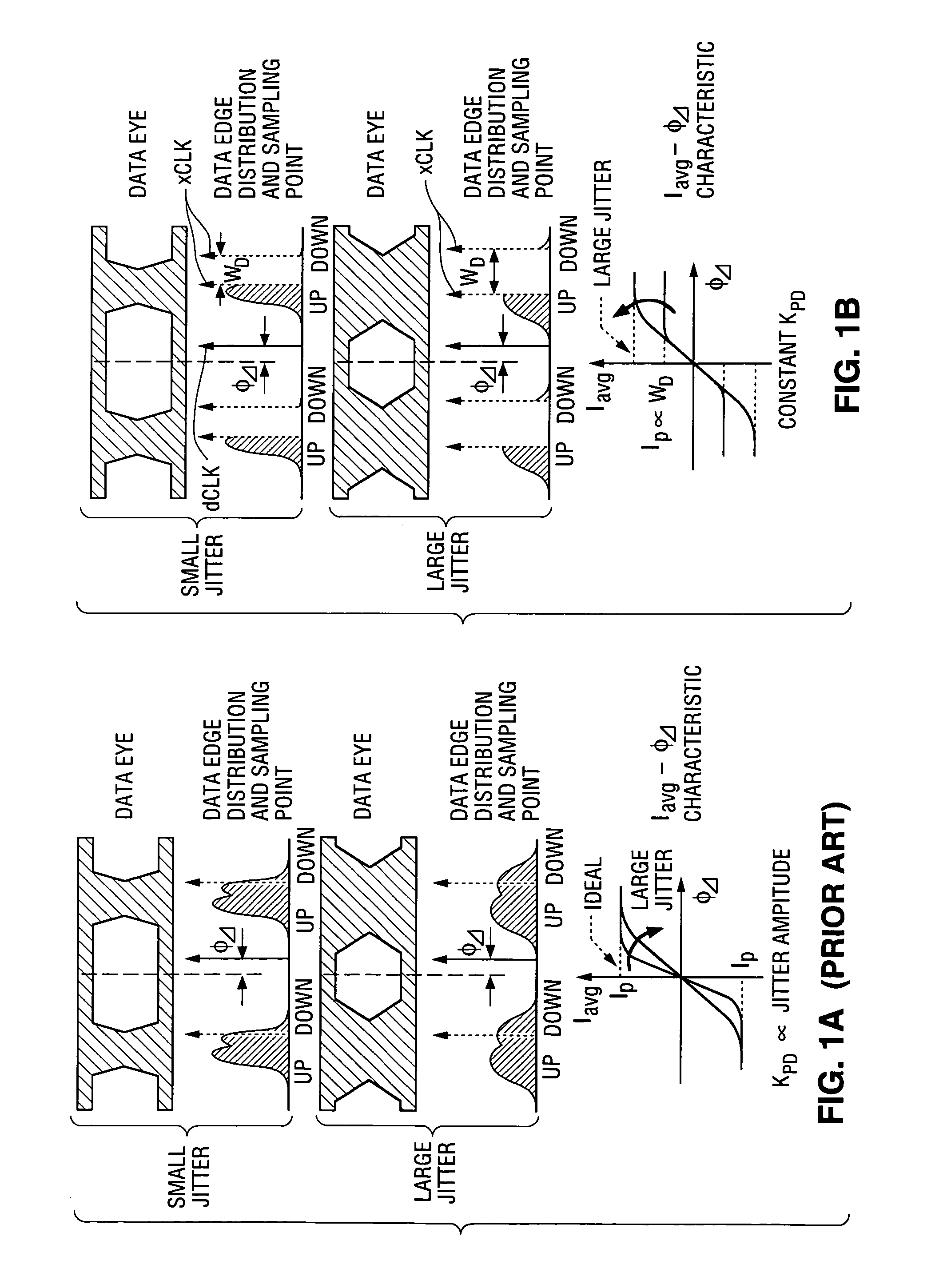
ActiveUS7409031B1Reduce phase differenceIncrease widthPulse automatic controlSynchronisation transmittersPhase detectorData rate
A method and apparatus for 2× oversampling of data having jitter. In some embodiments, the invention is a clock and data recovery device including an alternating edge sampling binary phase detector, and which is configured to stabilize loop characteristics in various jitter environments and can be implemented with small hardware overhead. A transceiver that embodies the invention can be implemented as a CMOS integrated circuit using a 0.18 μm CMOS process, with the transceiver chip being capable of recovering data having a data rate of up to 11.5 Gbps from a signal received over a serial link, while consuming no more than 540 mW from 1.8V supply, and with a bit error rate of less than 10−12.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
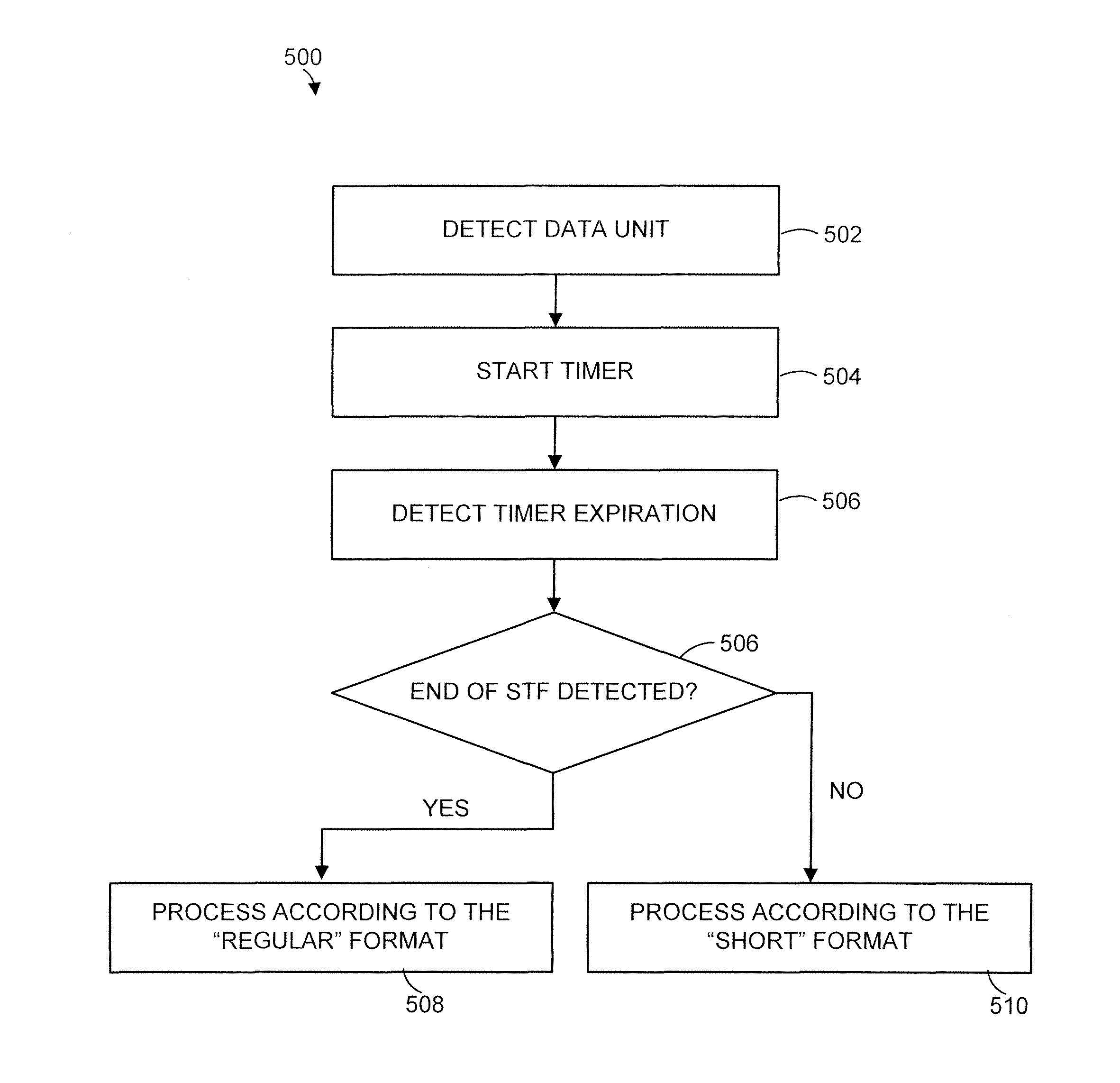
Control physical layer (PHY) data unit
ActiveUS8891592B1Synchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemPhysical layer
In a wireless communication system where communication devices exchange information utilizing physical layer (PHY) data units that conform to a first format, where the first format includes a short training field (STF) that includes exactly N repetitions of a spreading sequence, a method for generating a PHY data unit that conforms to a second format, where the second format has a longer STF than the first format, includes generating an STF of the PHY data unit that includes M instances of the spreading sequence, where M is greater than N, and generating a channel estimation field (CEF).
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Communication channel calibration with nonvolatile parameter store for recovery
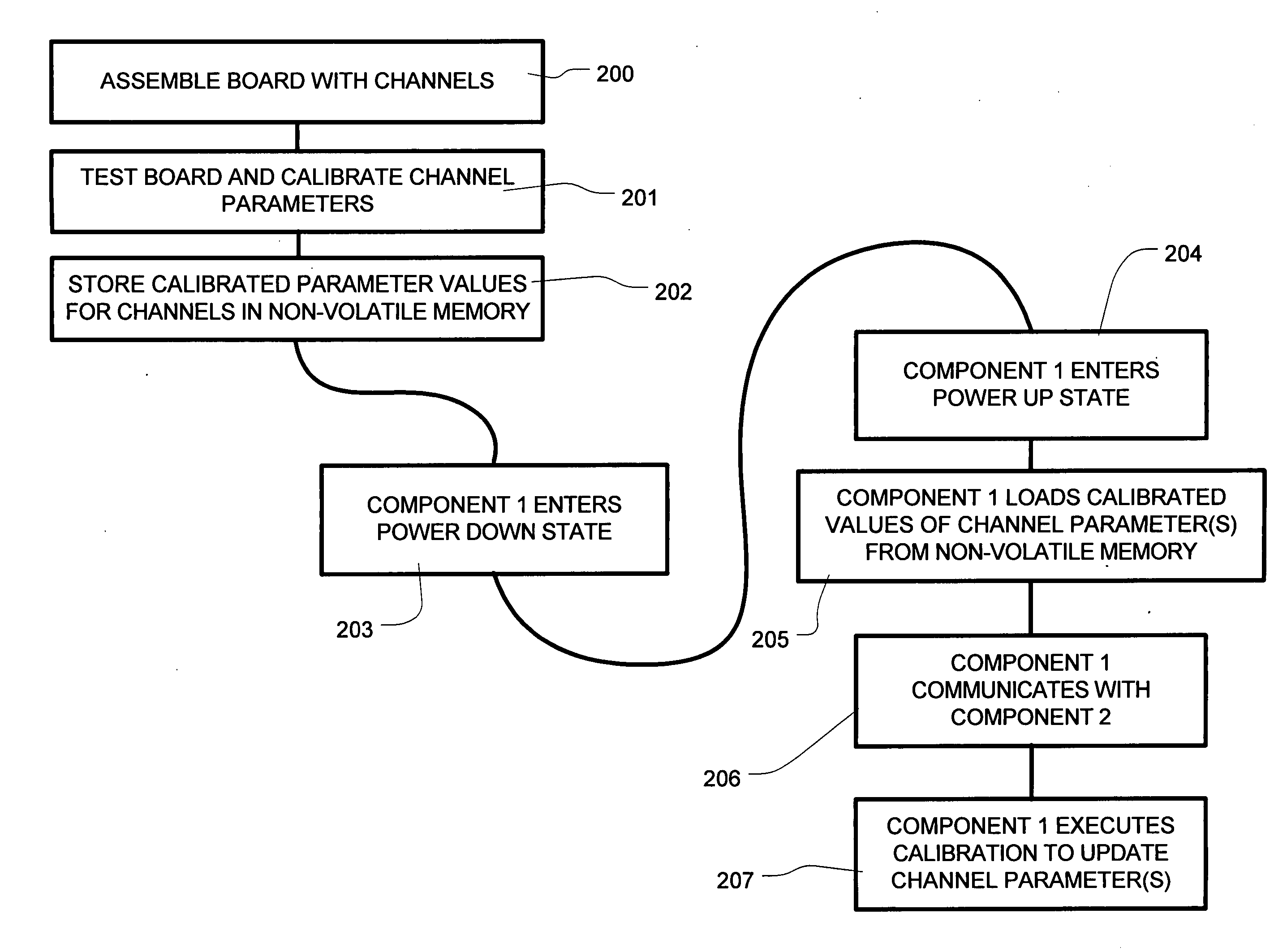
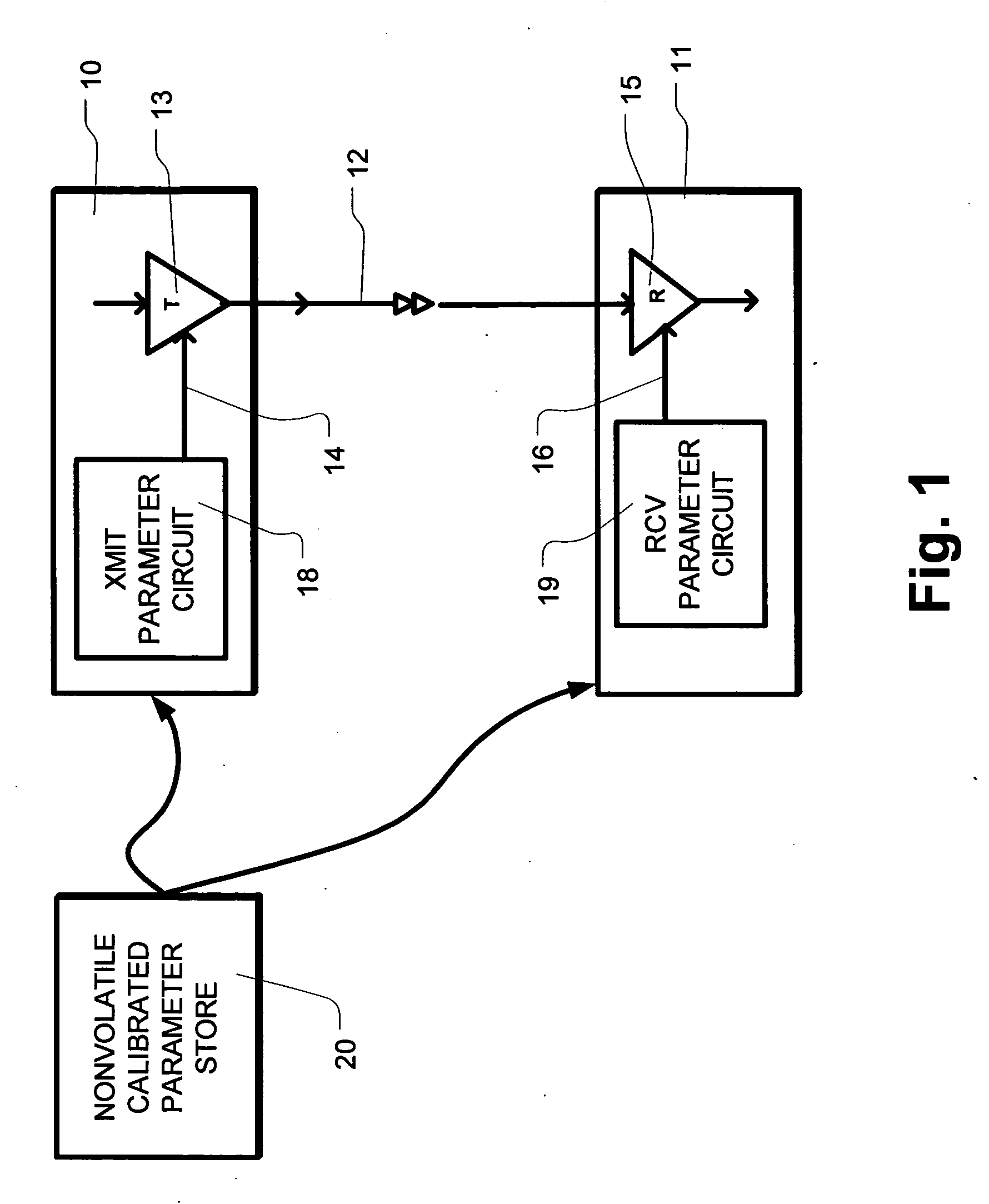
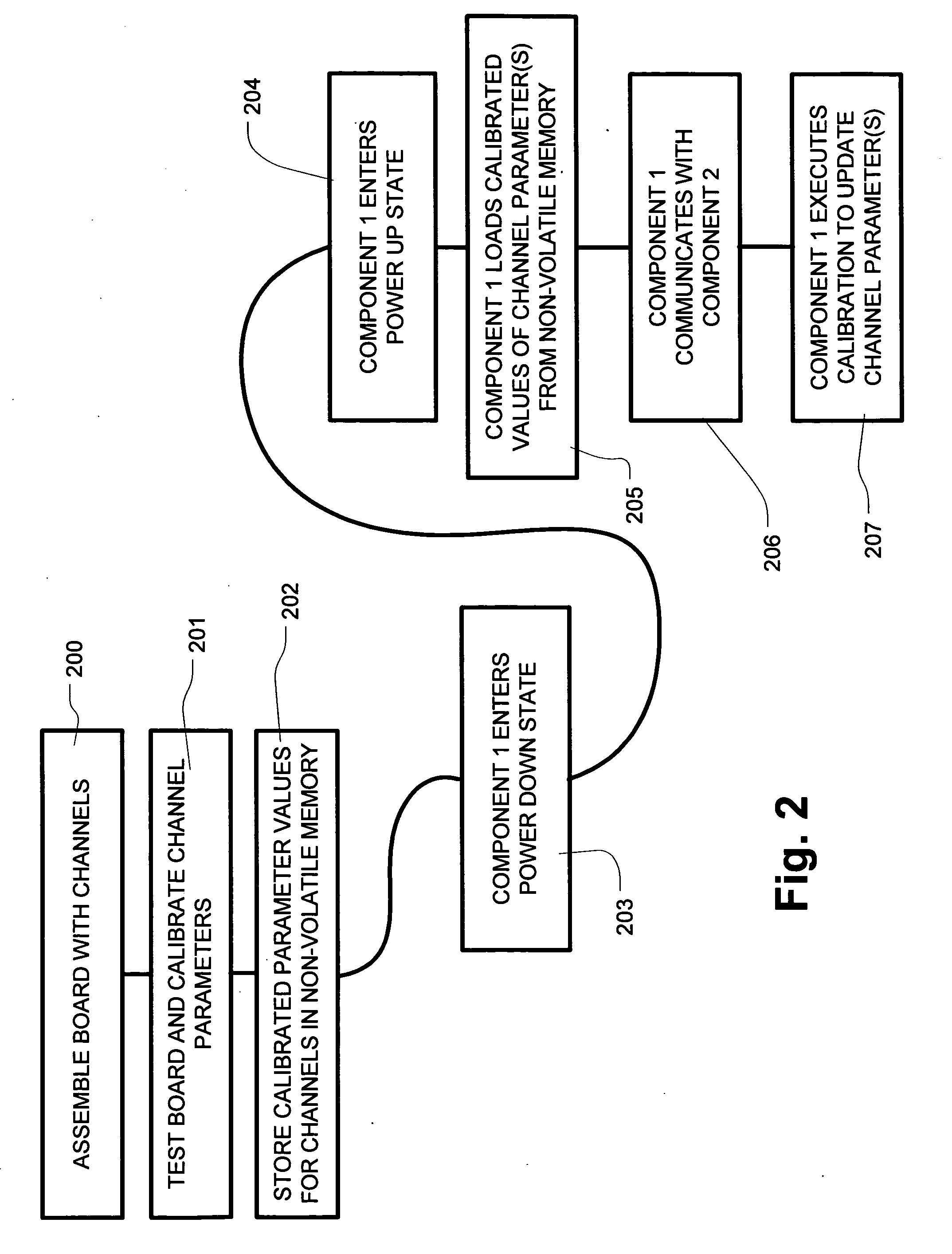
ActiveUS20050265437A1Communicating data very quicklyFast communicationThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionComputer scienceStart up
A communication channel is operated by storing a calibrated parameter value in nonvolatile memory during manufacturing, testing, or during a first operation of the device. Upon starting operation of the communication channel in the field, the calibrated parameter value is obtained from the nonvolatile memory, and used in applying an operating parameter of the communication channel. After applying the operating parameter, communication is initiated on a communication channel. The operating parameter can be adjusted to account for drift immediately after starting up, or periodically. The process of starting operation in the field includes power up events after a power management operation. In embodiments where one component includes memory, steps can be taken prior to a power management operation using the communication channel, such as transferring calibration patterns to be used in calibration procedures.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
ActiveUS20050163203A1Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingTelecommunications linkData source
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
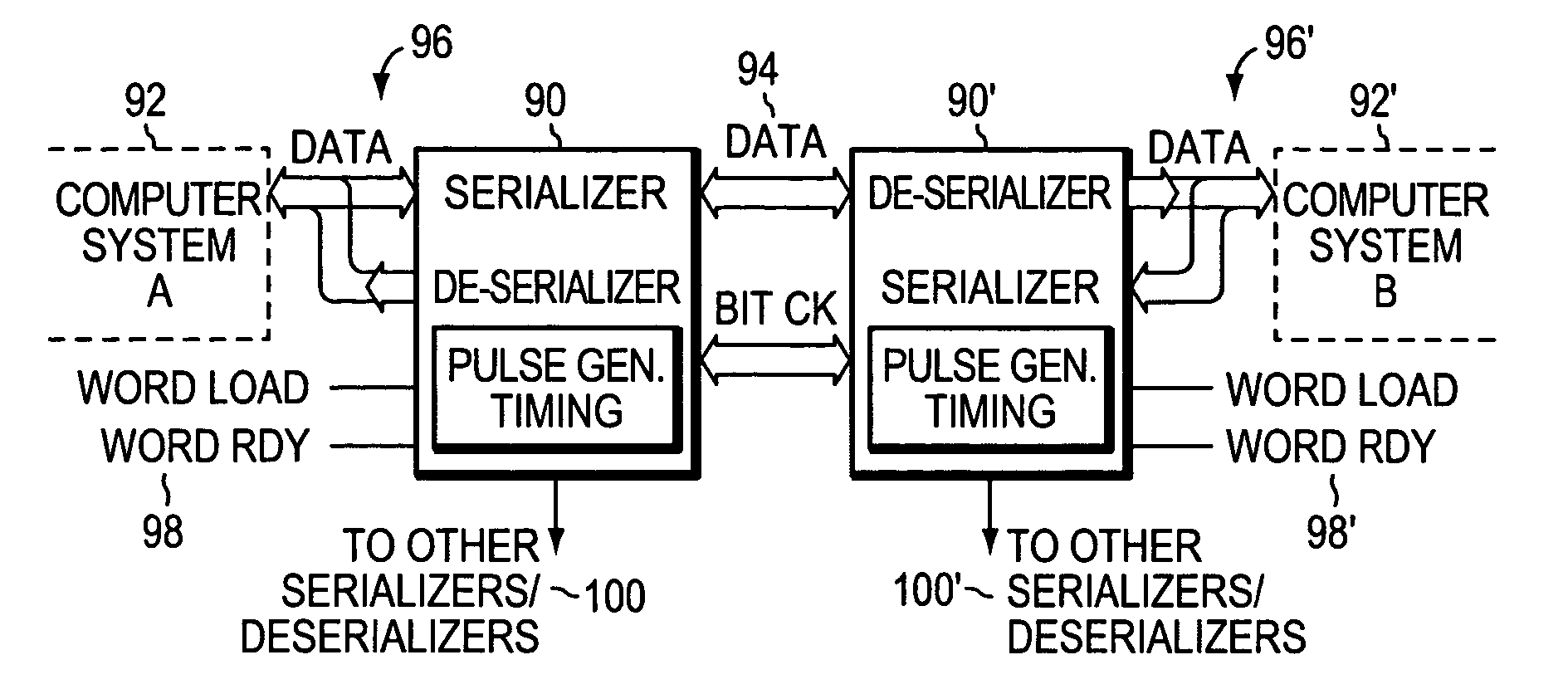
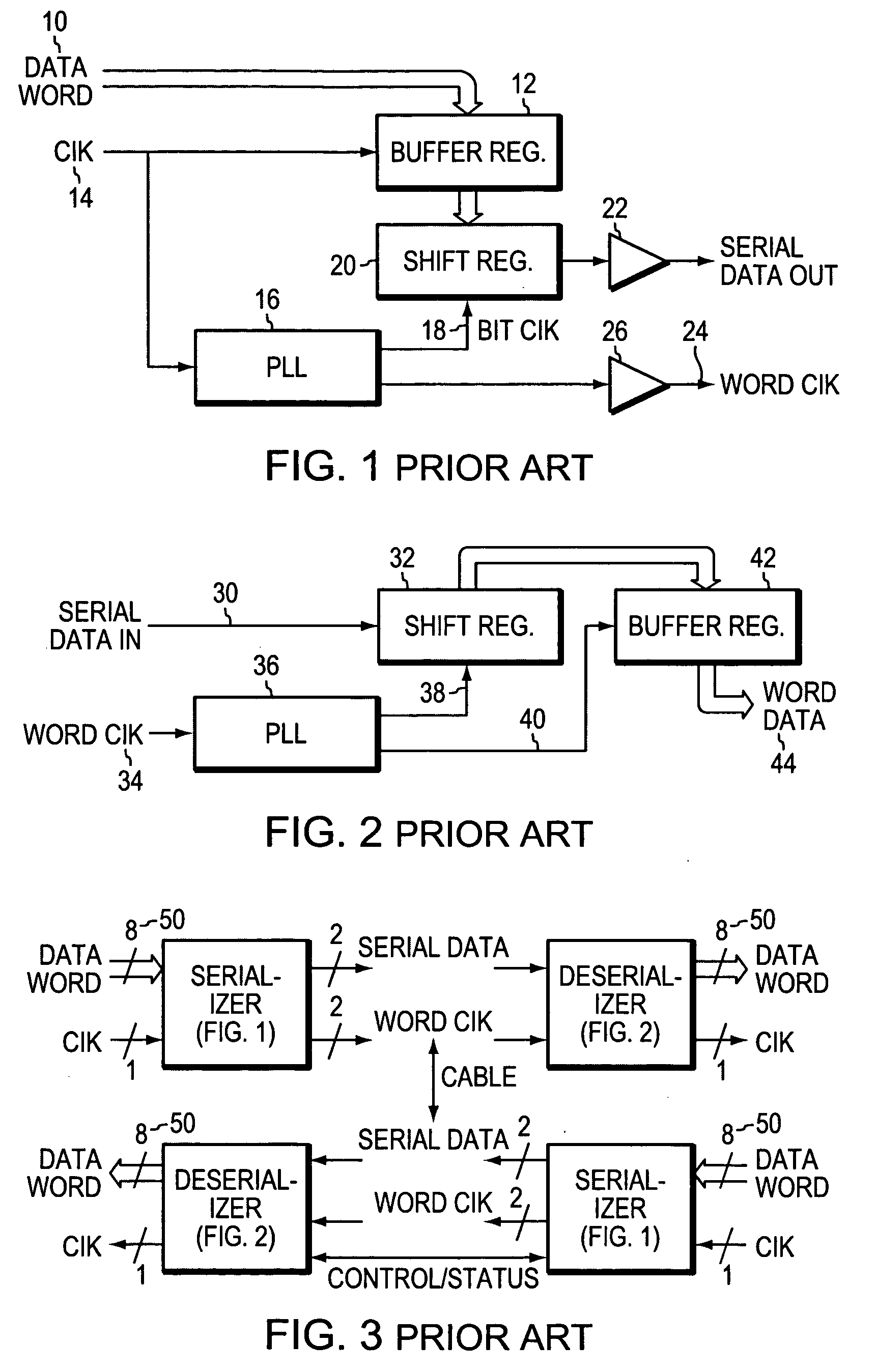
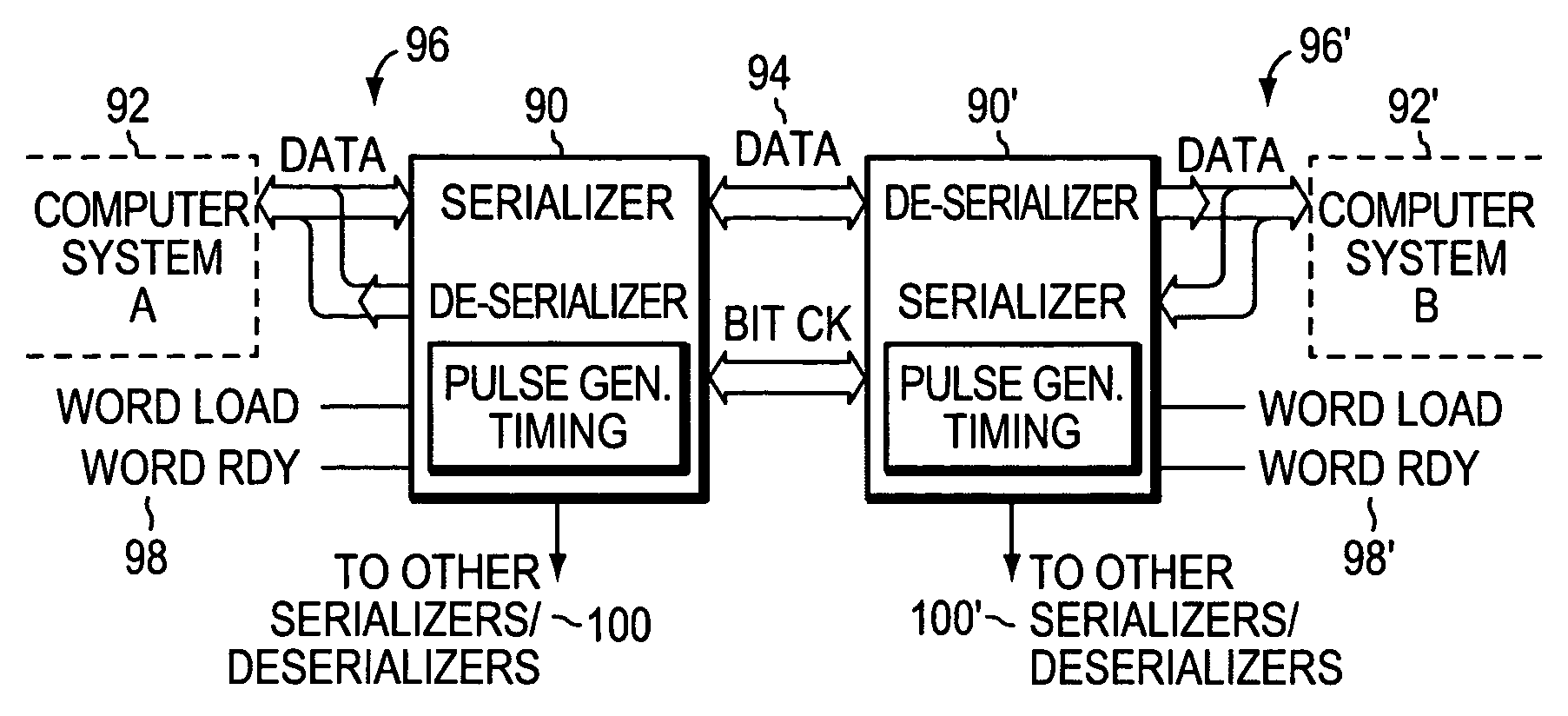
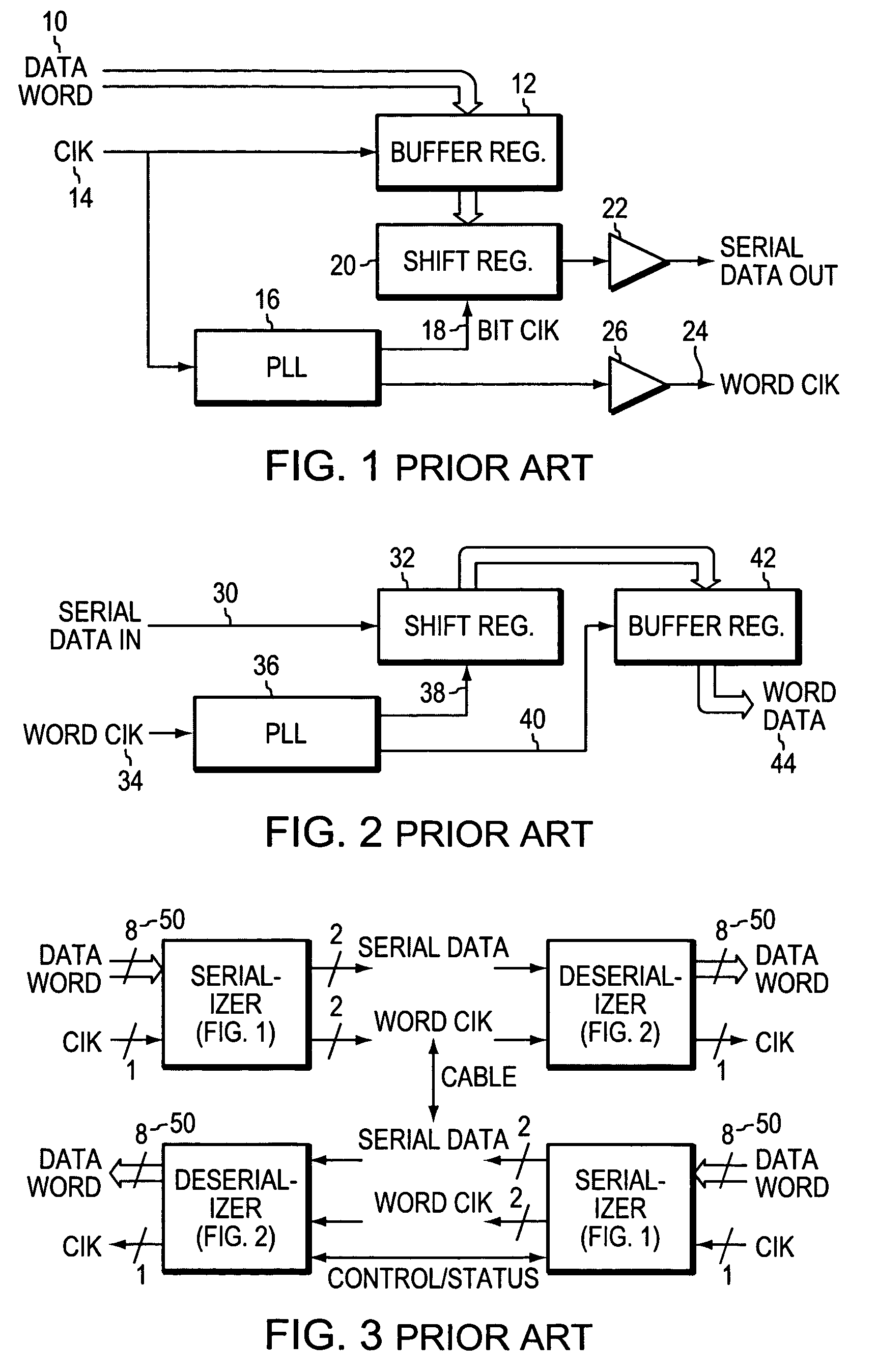
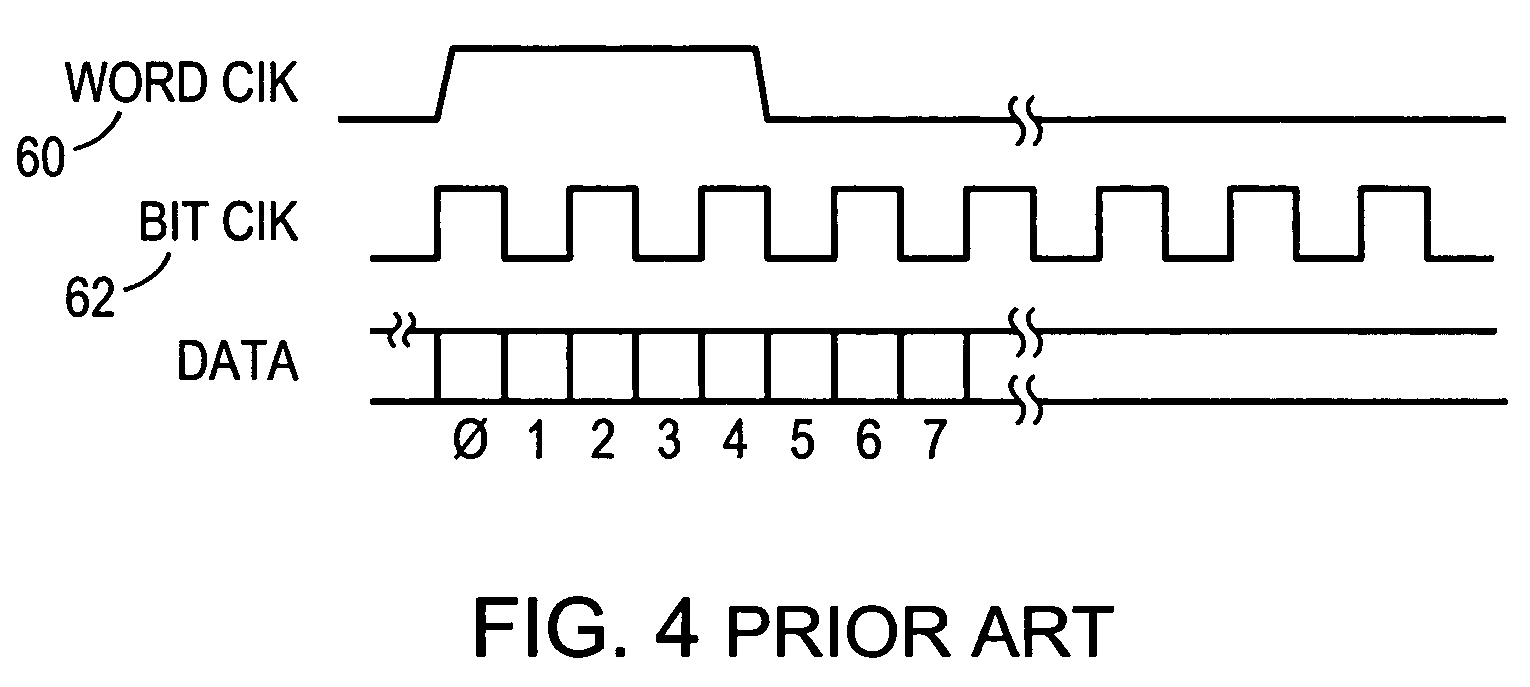
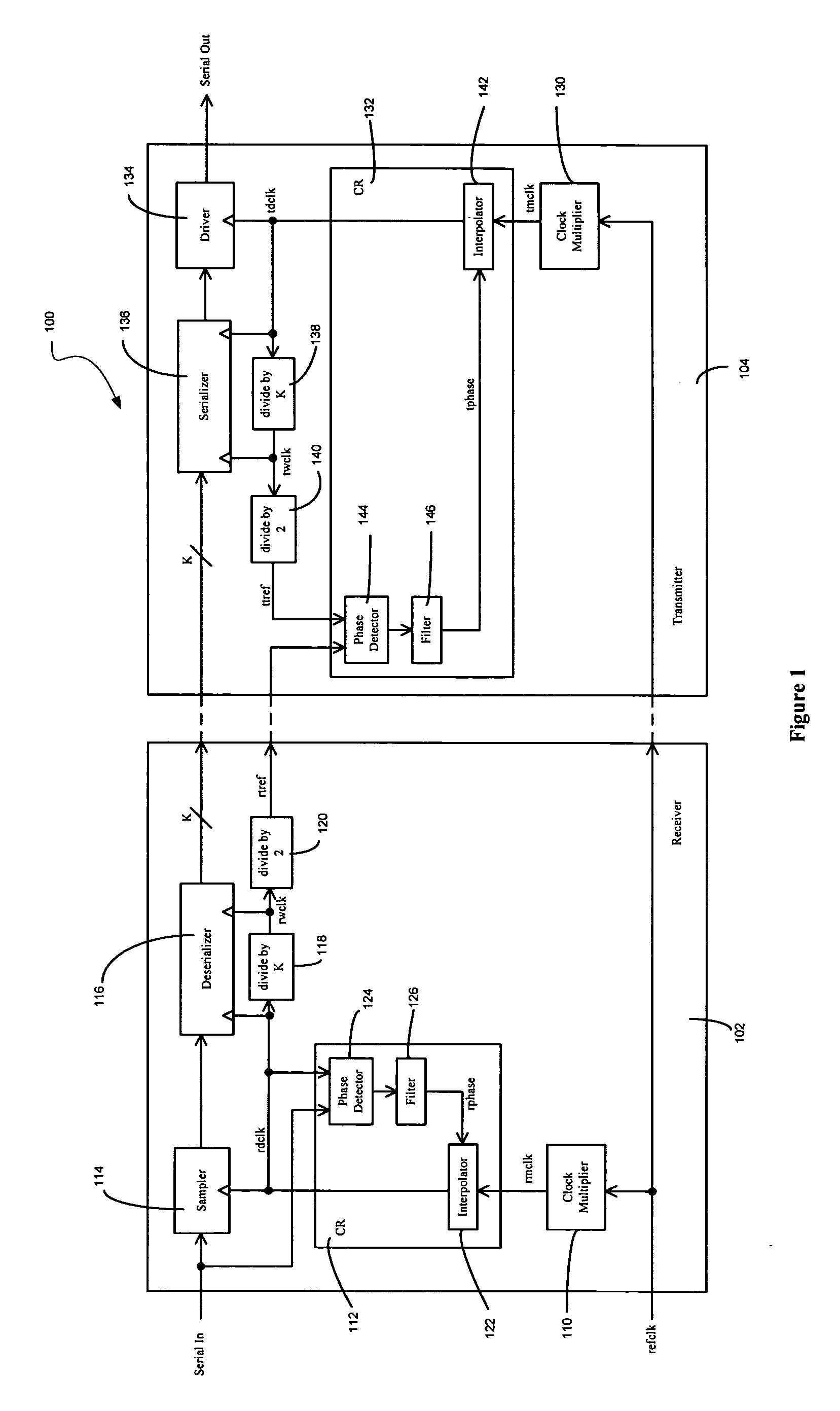
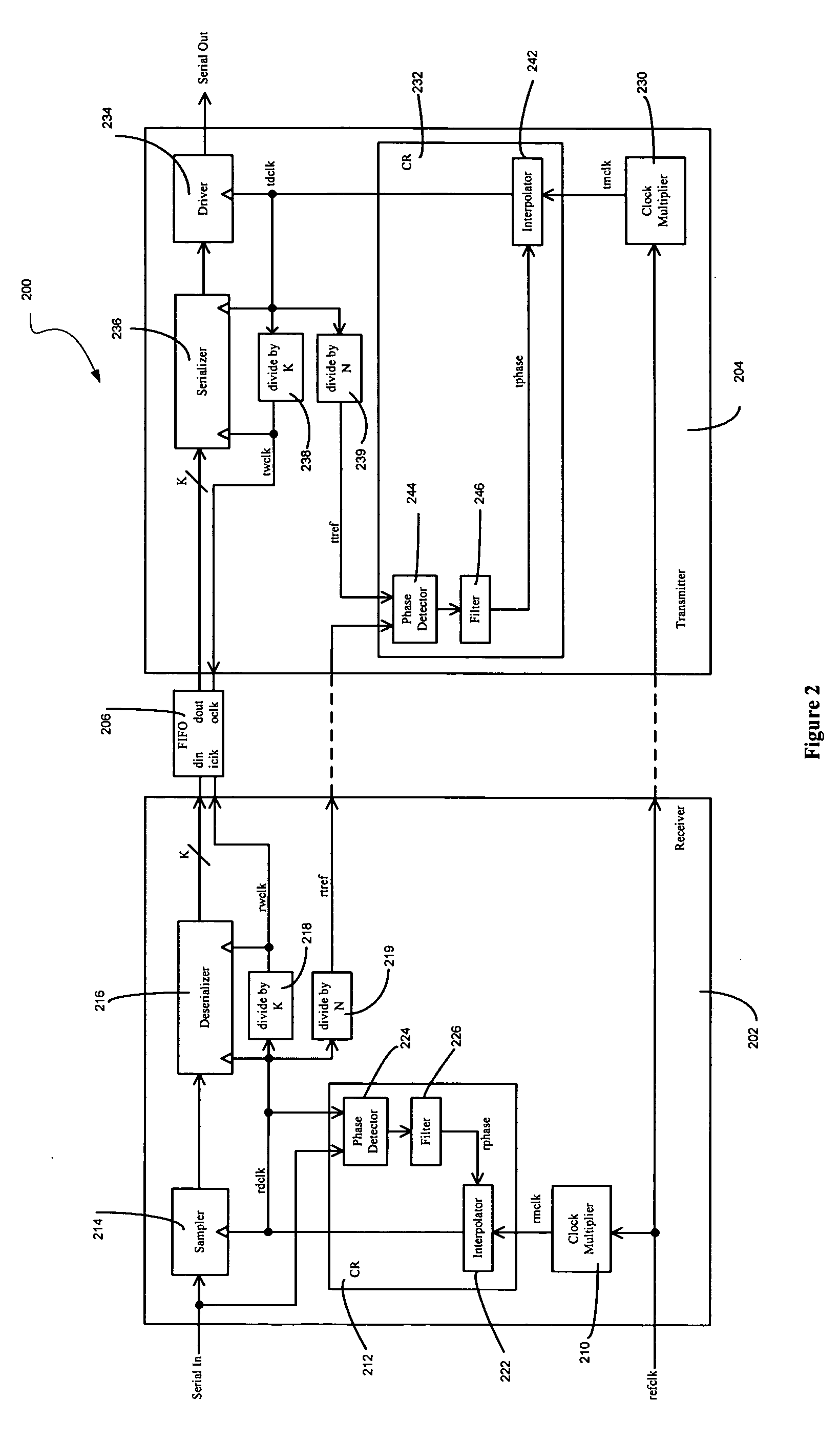
Sending and/or receiving serial data with bit timing and parallel data conversion
A serializer and a deserializer are disclosed and shown operating singly or as a pair. The invention operates independently from any outside system reference clock. The inventive system provides an internal bit clock that serializes the data when sending and de-serializes the data when receiving. A bit clock or pulse travels with the data word bits to define when a bit is stable. The system uses word boundary bits operating with a bit clock to distinguish different data words, as described in the parent application. The system operates either synchronously or asynchronously with the base computer or other such digital system, including I / O devices. The invention finds use where new data to be sent is strobed into the serializer, but also where a change in the data bit content itself will cause the changed data to be loaded into the serializer and sent bit by bit. The system operates where new data is strobed or loaded by the serializer (not the base computer system) when the last data word has been sent. In this case a signal is generated when the last word has been sent in the serializer that causes new data to be loaded for sending. Half duplex and full duplex configurations as disclosed. Similar, corresponding operations occur at the deserializer.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Timestamp predictor for packets over a synchronous protocol
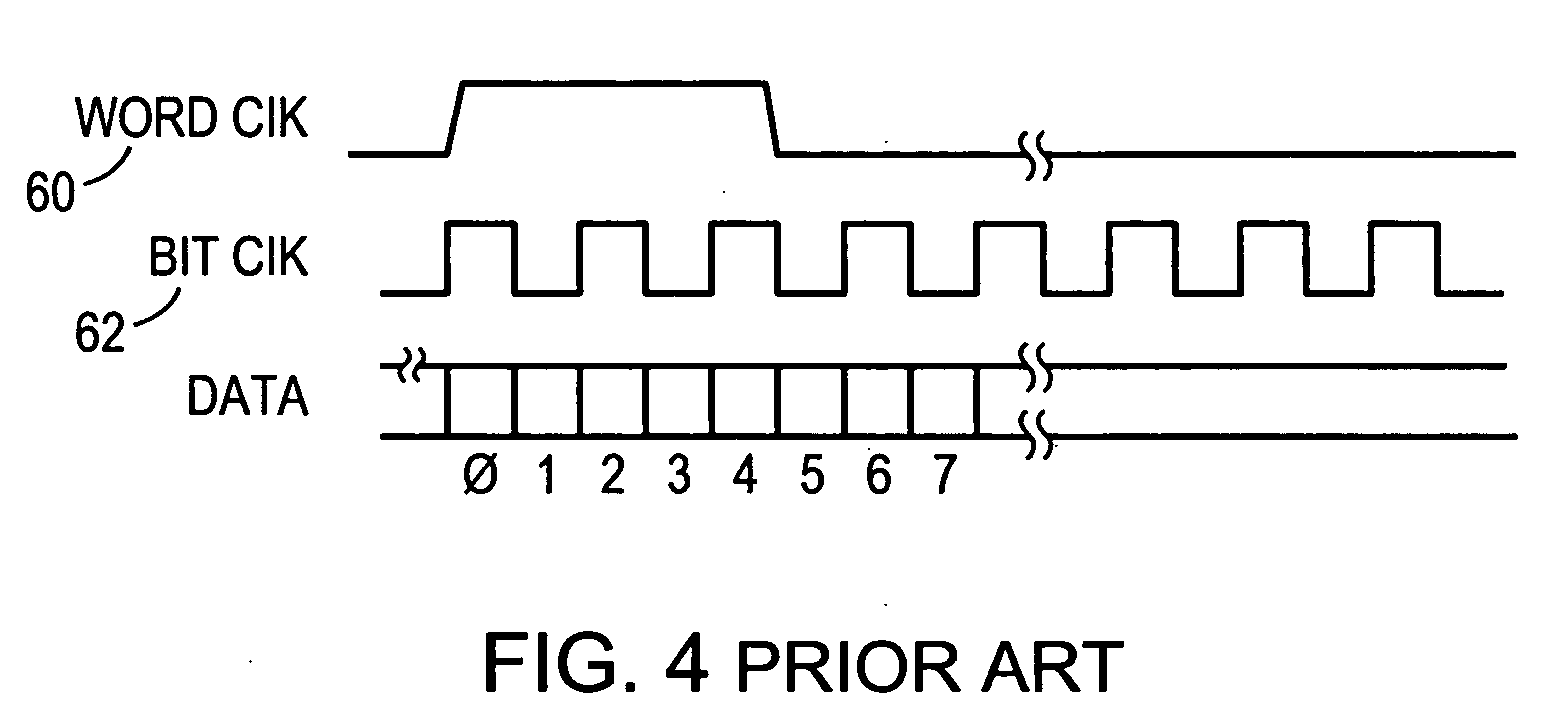
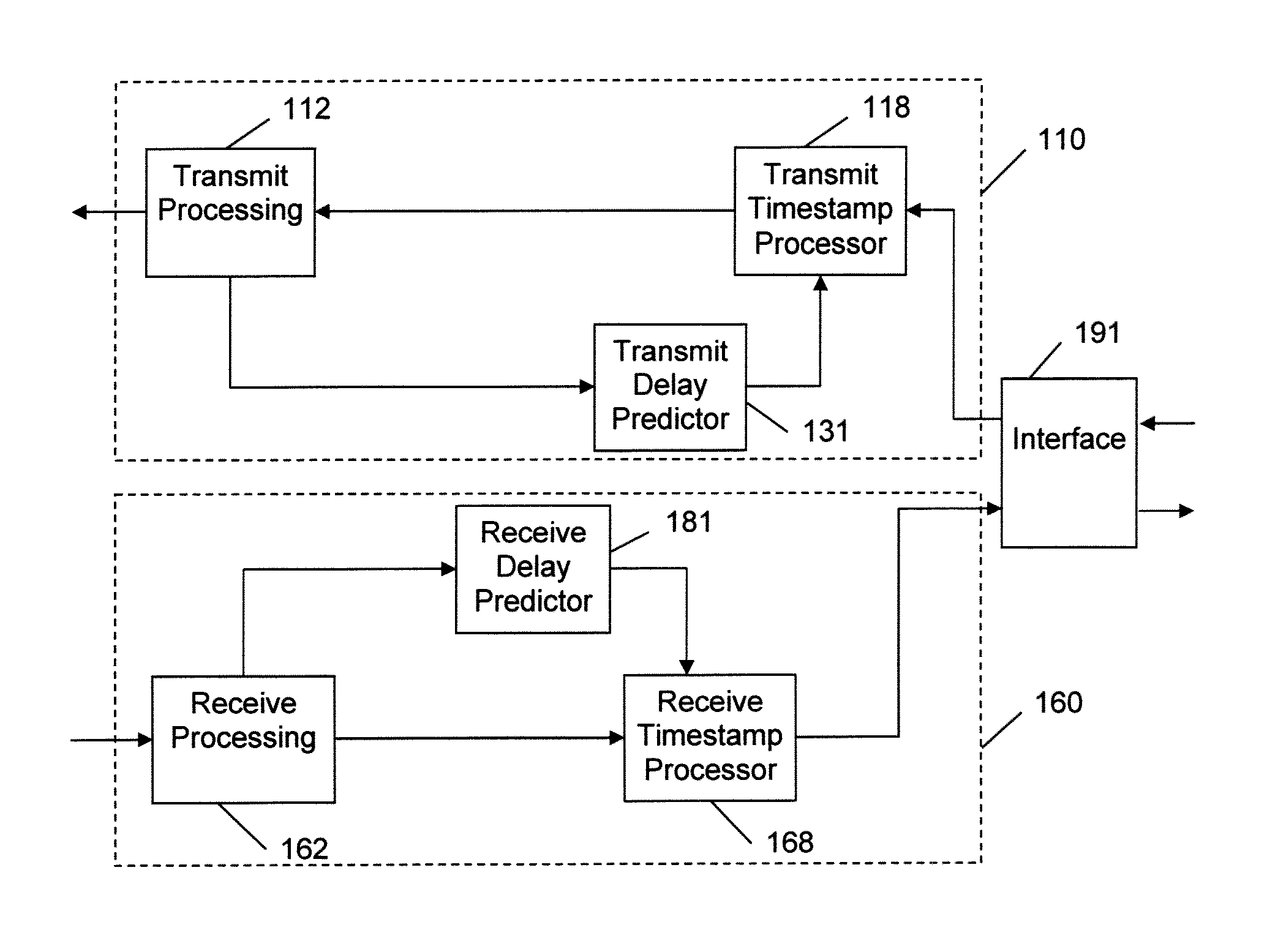
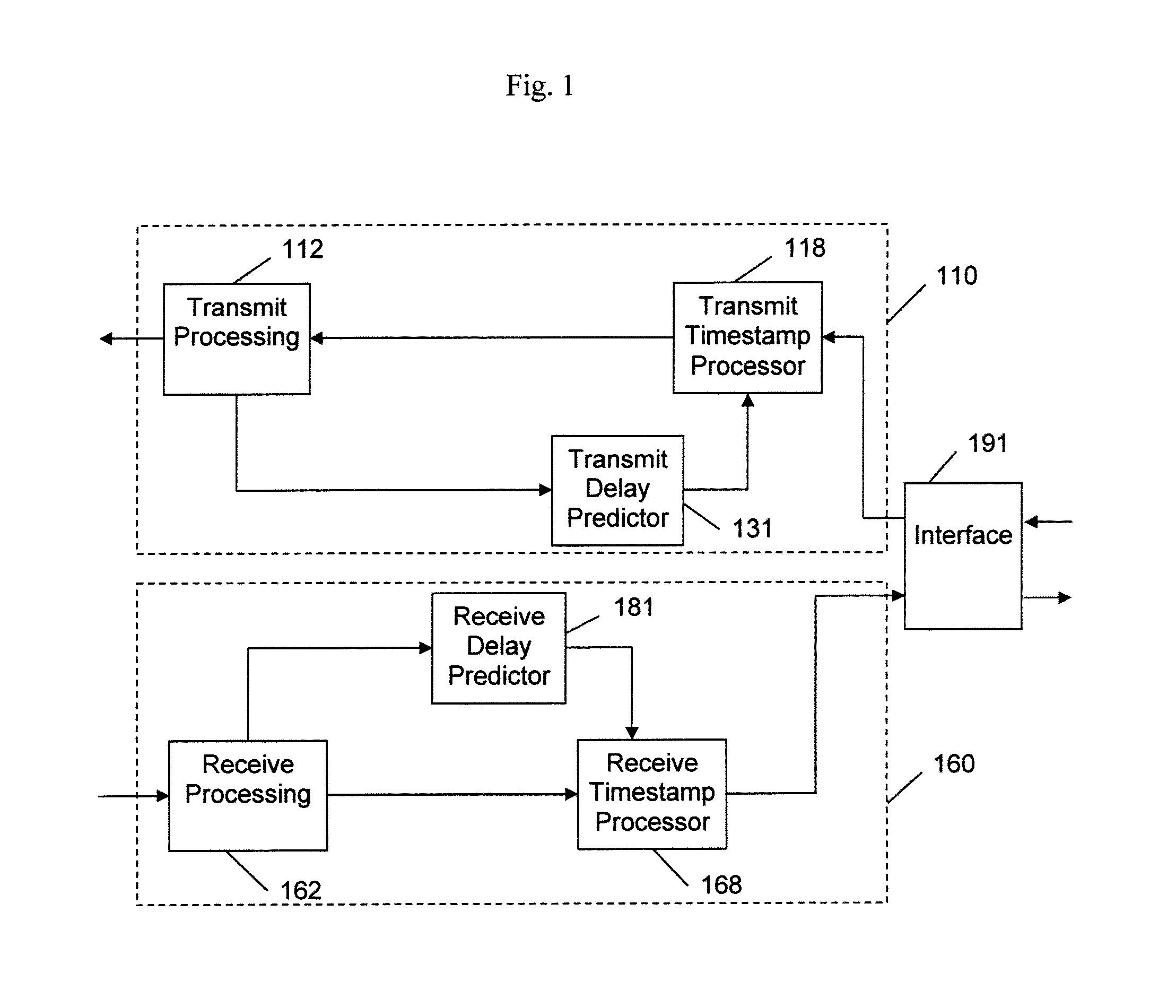
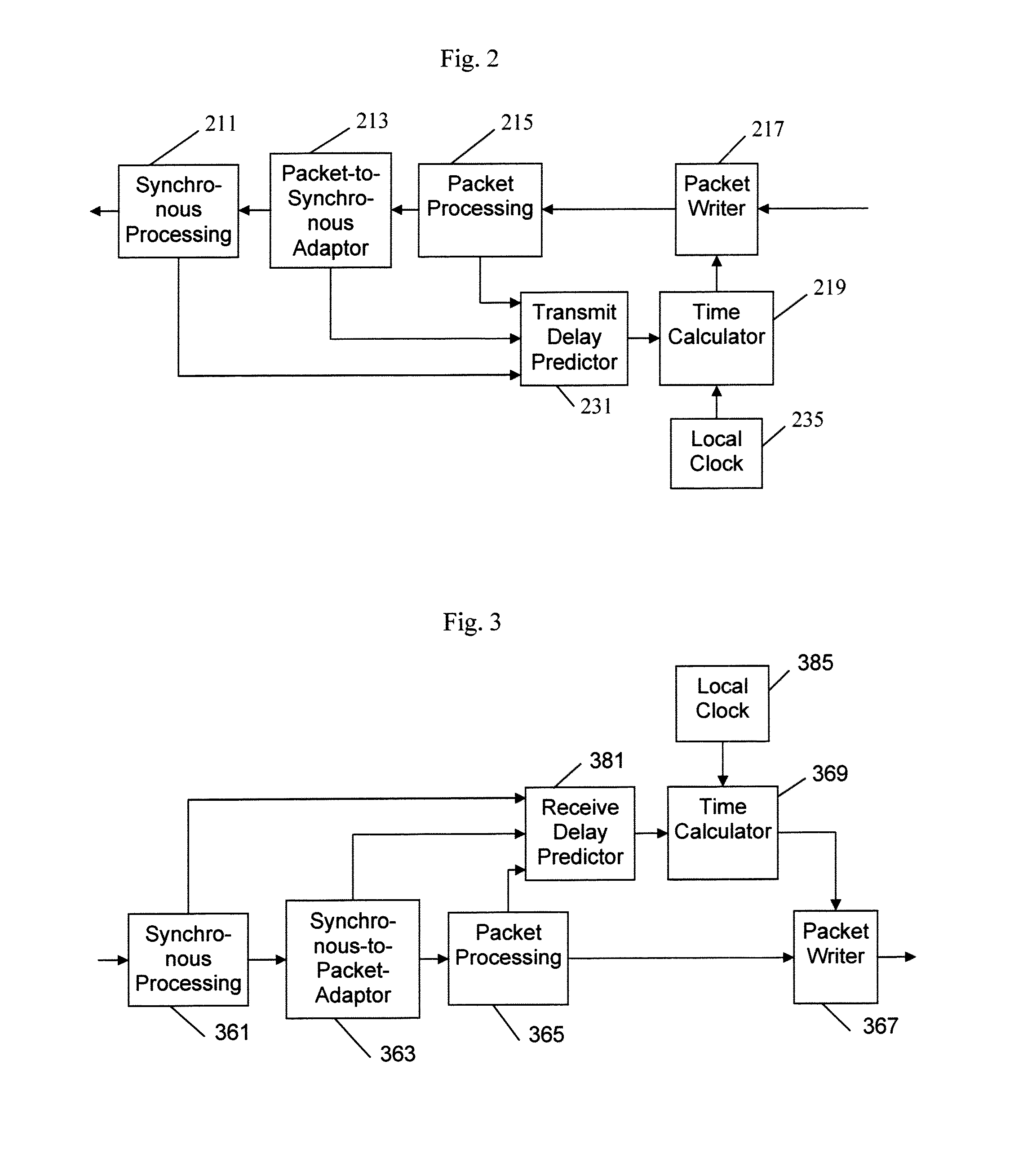
ActiveUS20120082156A1Fully comprehendedTime-division multiplexSynchronisation transmittersTelecommunications linkTimestamp
A physical layer communication device (PHY) transmits and receives signal to and from a communication link using a synchronous protocol. The PHY communicates with a higher-layer device using a packet protocol. Timestamp values contained in timing-related messages in some packets are written or modified by the PHY. Delays incurred in transmitting and receiving the packets are predicted and used in setting the timestamp values.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
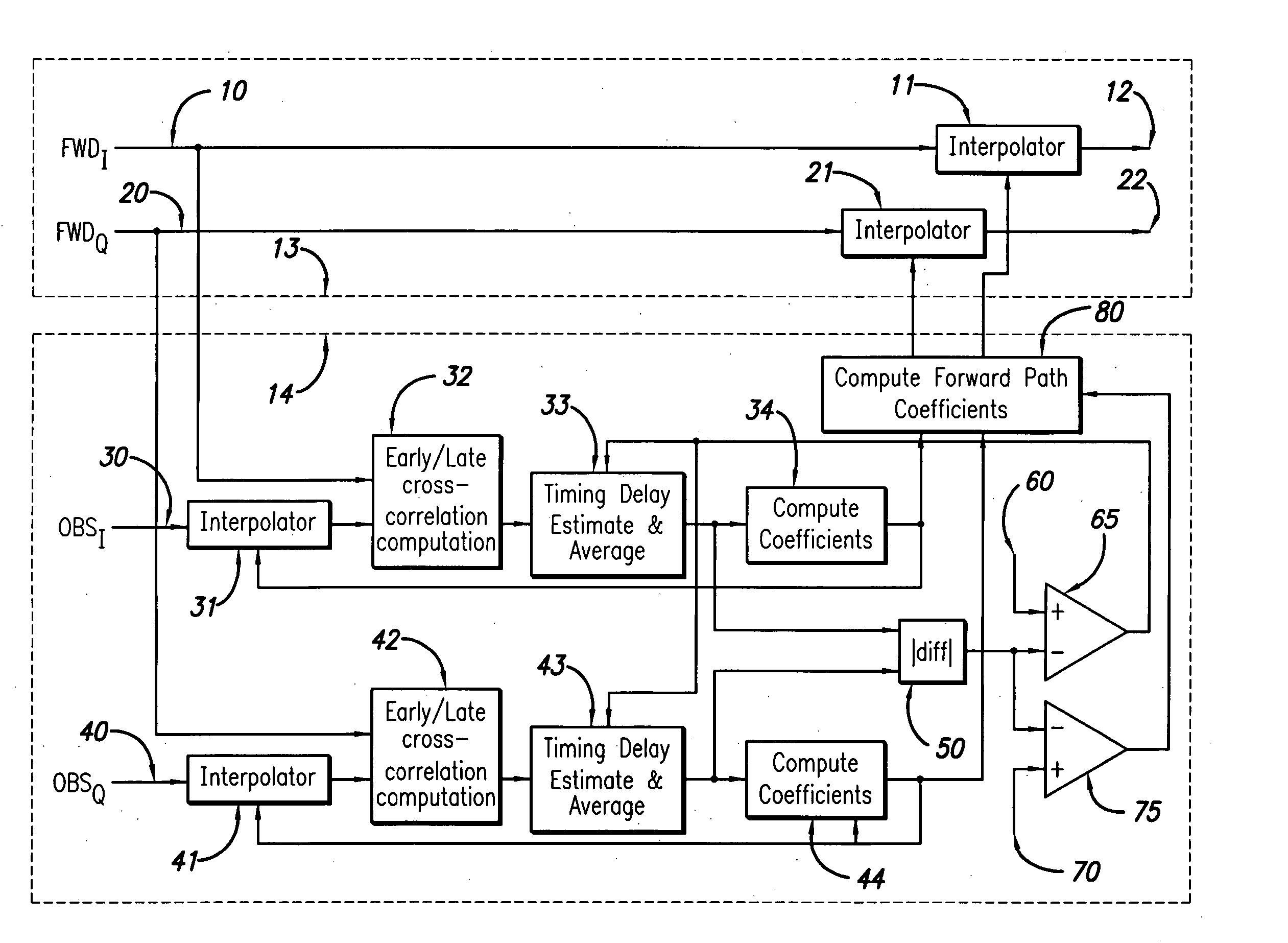
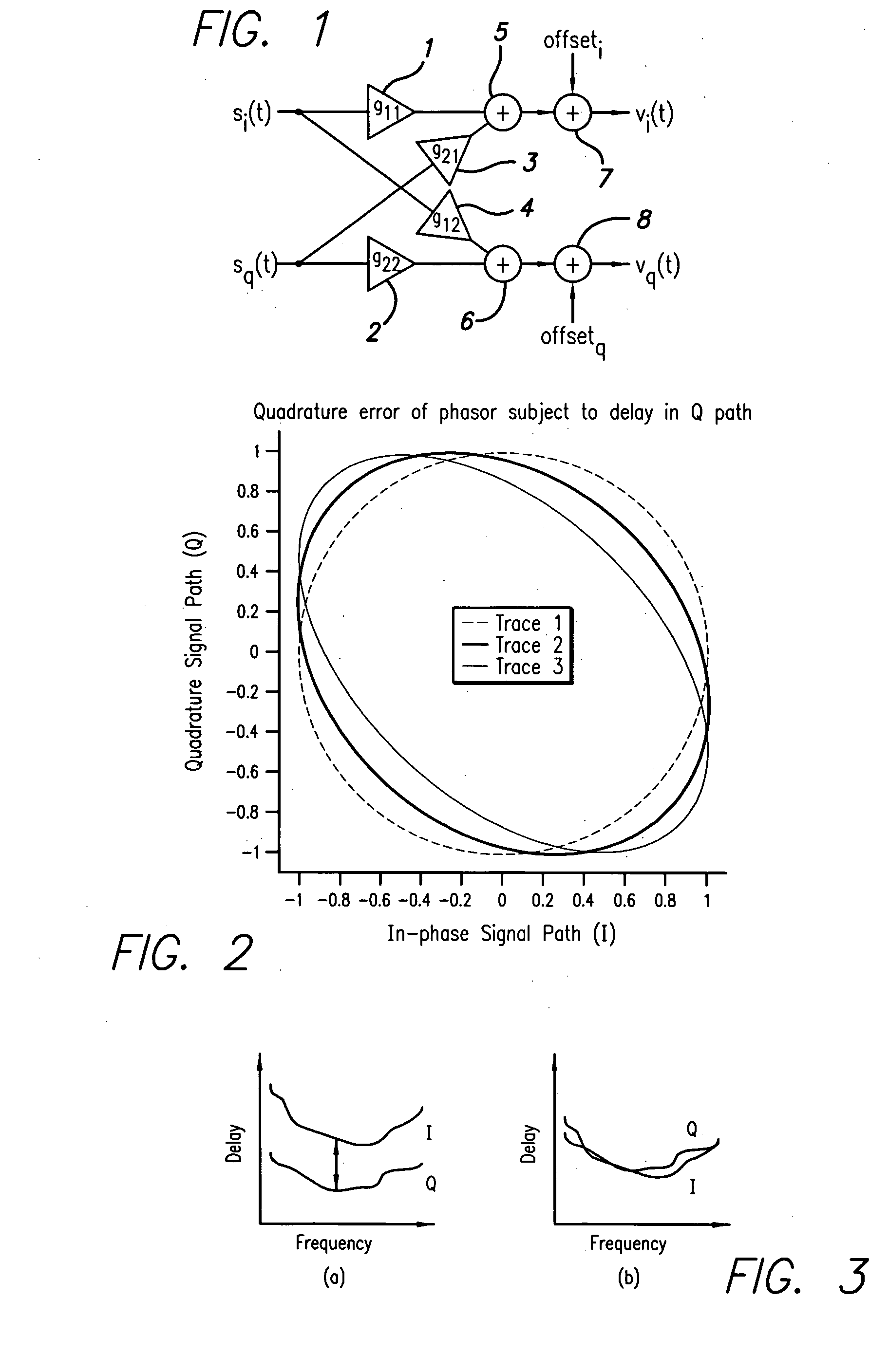
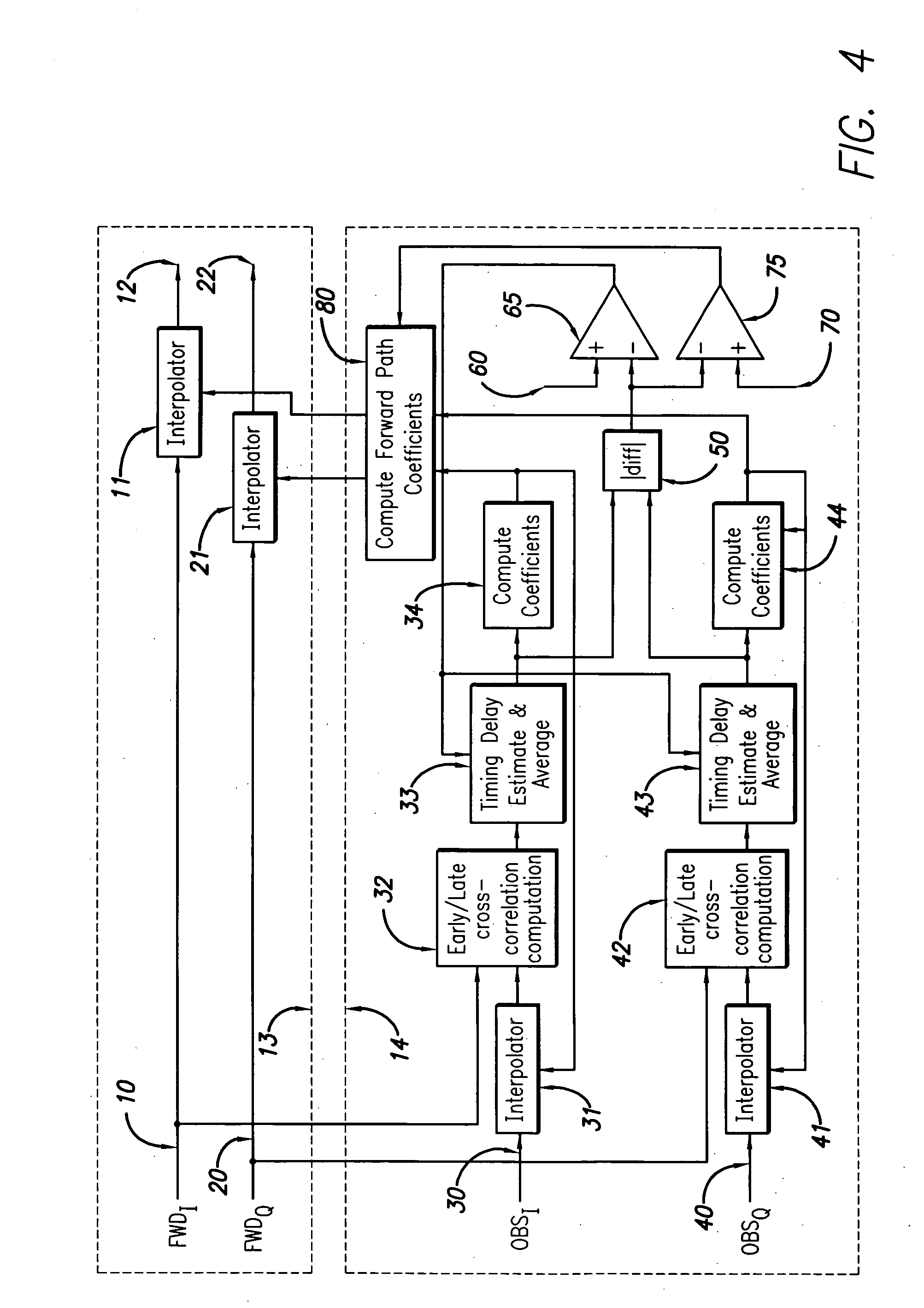
System and method for differential IQ delay compensation in a communications system utilizing adaptive AQM compensation
ActiveUS20060008030A1Synchronisation transmittersAngle modulationQuadrature modulatorCommunications system
A system and method for compensating for the time delay between the in-phase I and the quadrature Q paths of a digitally modulated transmitter incorporating an analog quadrature modulator is disclosed. The time delay between the in-phase I and the quadrature Q paths is computed and used to calibrate a set of interpolation filters in the forward path that compensate for this delay, reducing the frequency dependent degradation in performance of the analog quadrature modulator. The disclosed system and method provides improved compensation of gain, phase and DC offsets in the analog quadrature modulator over a broader bandwidth. Fractional delay interpolation filters may be used to estimate the delay between the in-phase and quadrature paths. This eliminates the need for a factory calibration procedure, speeding up manufacture and reducing costs.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Sending and/or receiving serial data with bit timing and parallel data conversion
A serializer and a deserializer are disclosed and shown operating singly or as a pair. The invention operates independently from any outside system reference clock. The inventive system provides an internal bit clock that serializes the data when sending and de-serializes the data when receiving. A bit clock or pulse travels with the data word bits to define when a bit is stable. The system uses word boundary bits operating with a bit clock to distinguish different data words, as described in the parent application. The system operates either synchronously or asynchronously with the base computer or other such digital system, including I / O devices. The invention finds use where new data to be sent is strobed into the serializer, but also where a change in the data bit content itself will cause the changed data to be loaded into the serializer and sent bit by bit. The system operates where new data is strobed or loaded by the serializer (not the base computer system) when the last data word has been sent. In this case a signal is generated when the last word has been sent in the serializer that causes new data to be loaded for sending. Half duplex and full duplex configurations as disclosed. Similar, corresponding operations occur at the deserializer.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method and apparatus for skew adjustment, data transmission system having skew adjustability
InactiveUS20040223566A1Channel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsData signalEngineering
A data transmission system with which optimal skew adjustment is achieved by a structure transmitting skew adjustment signals in place of data signals and detecting the amount of skew between the clock signals and the data signals. The skew adjustment signals are alternating signals with twice the period of the clock signals, and one signal state persists for a longer time than the other signal state.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
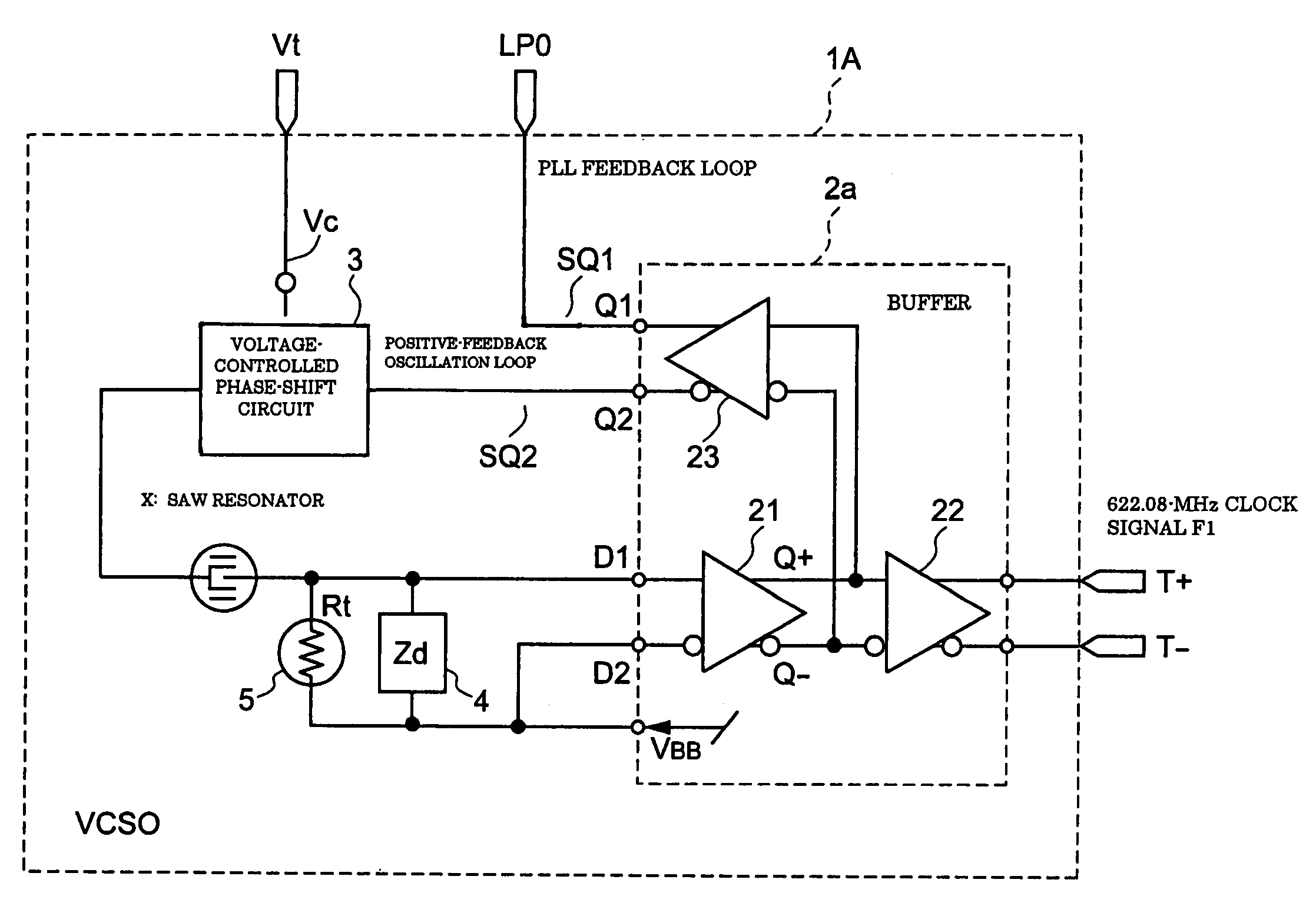
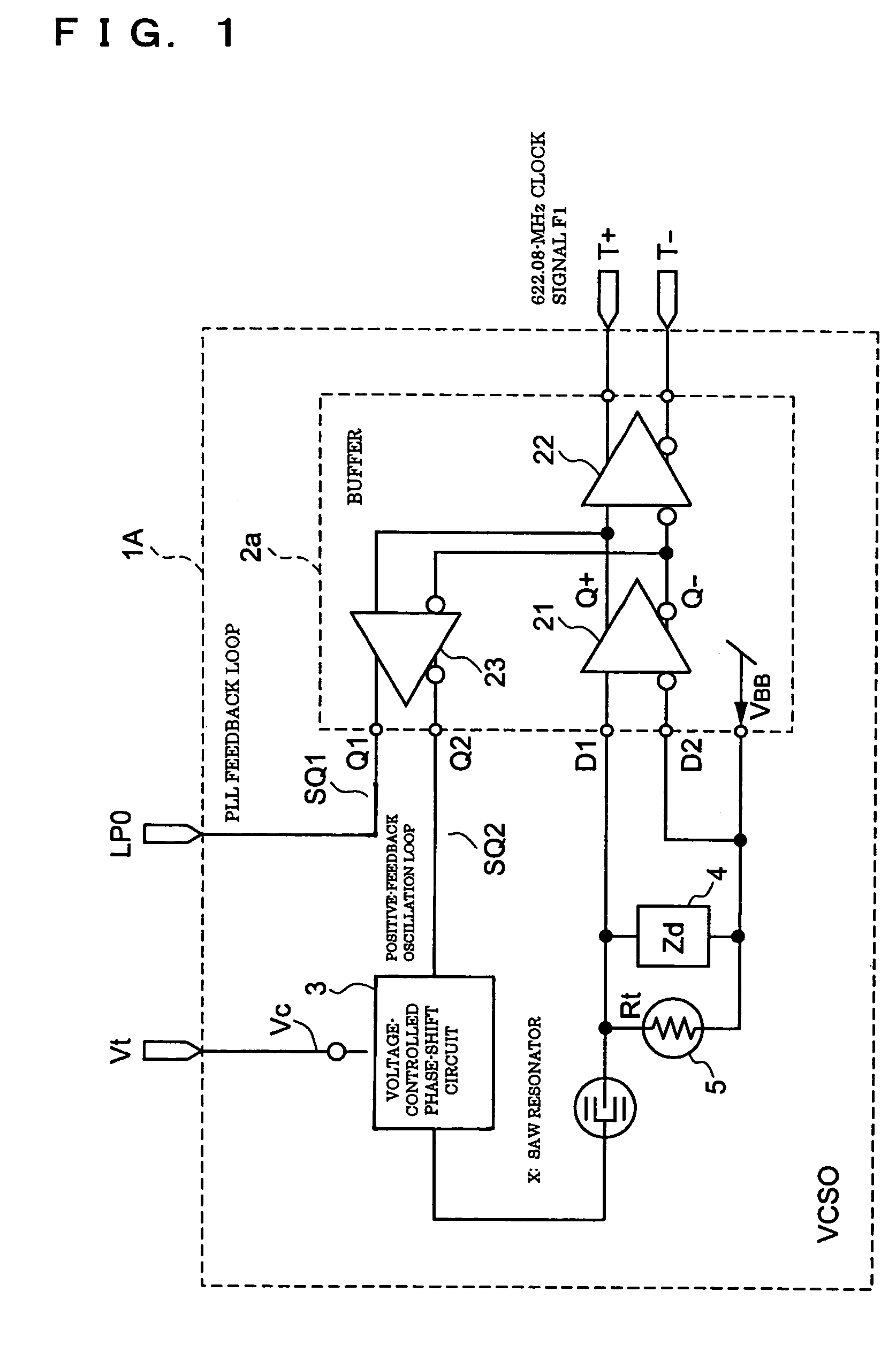
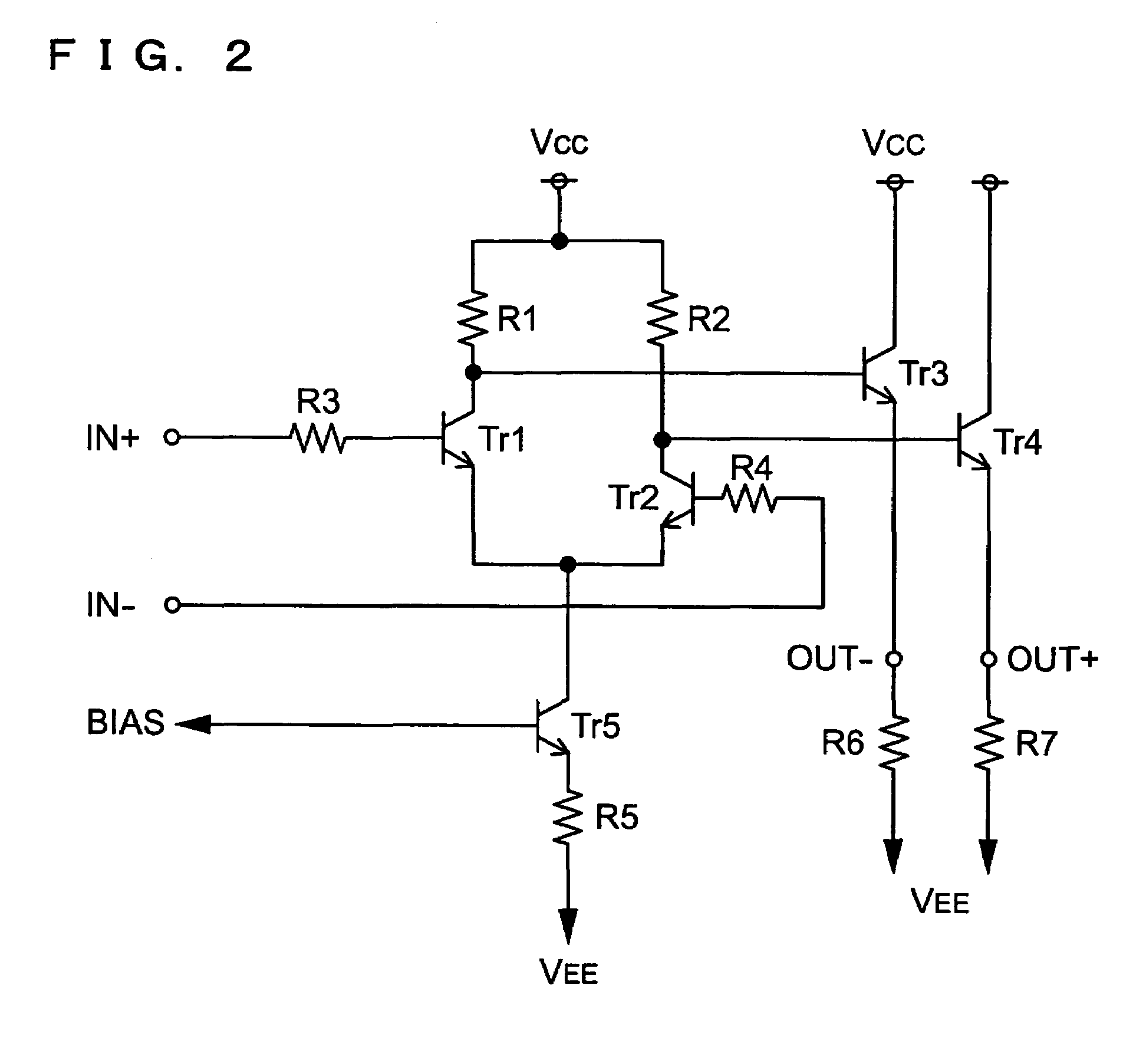
Voltage-controlled oscillator, clock converter, and electronic device
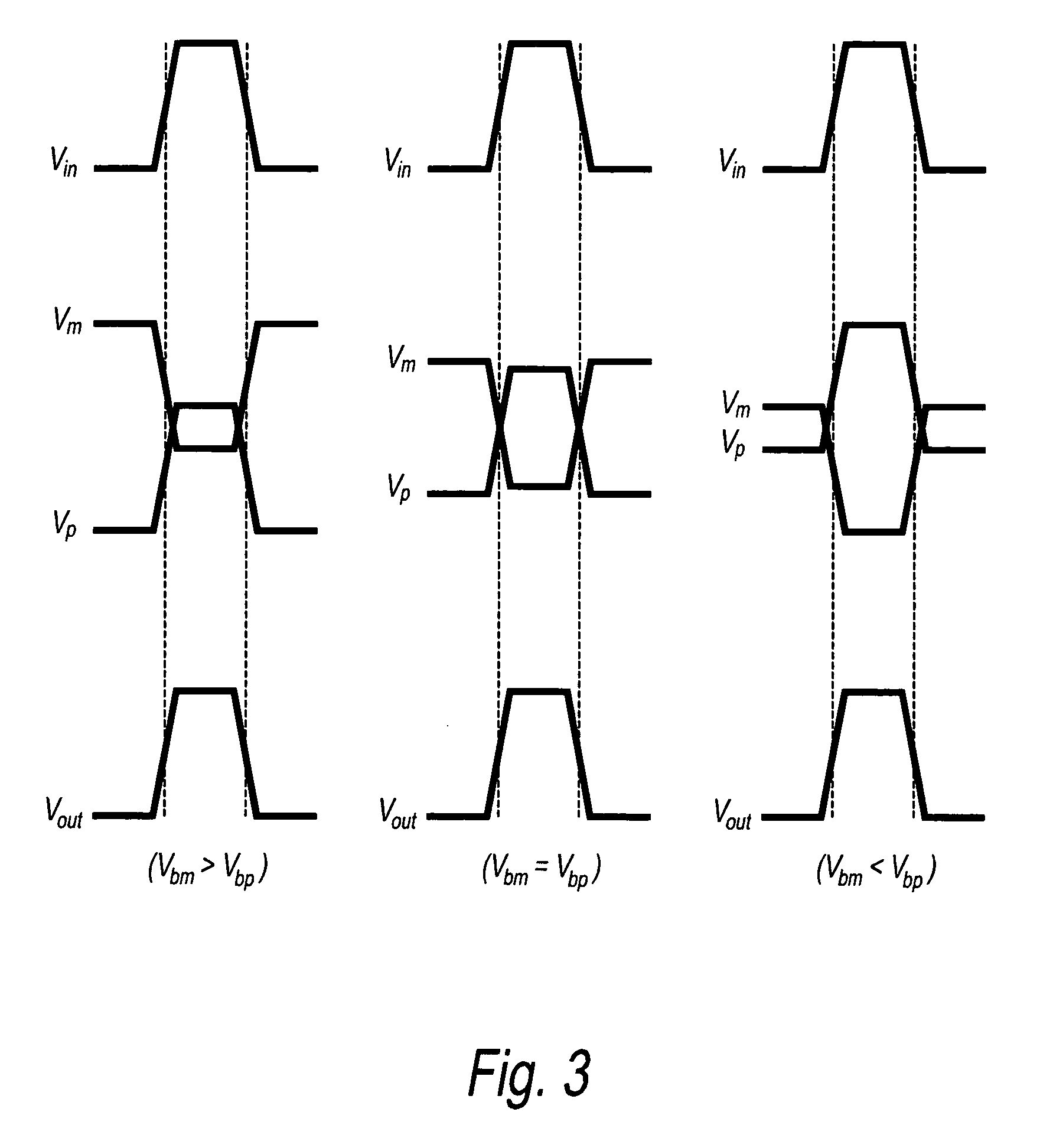
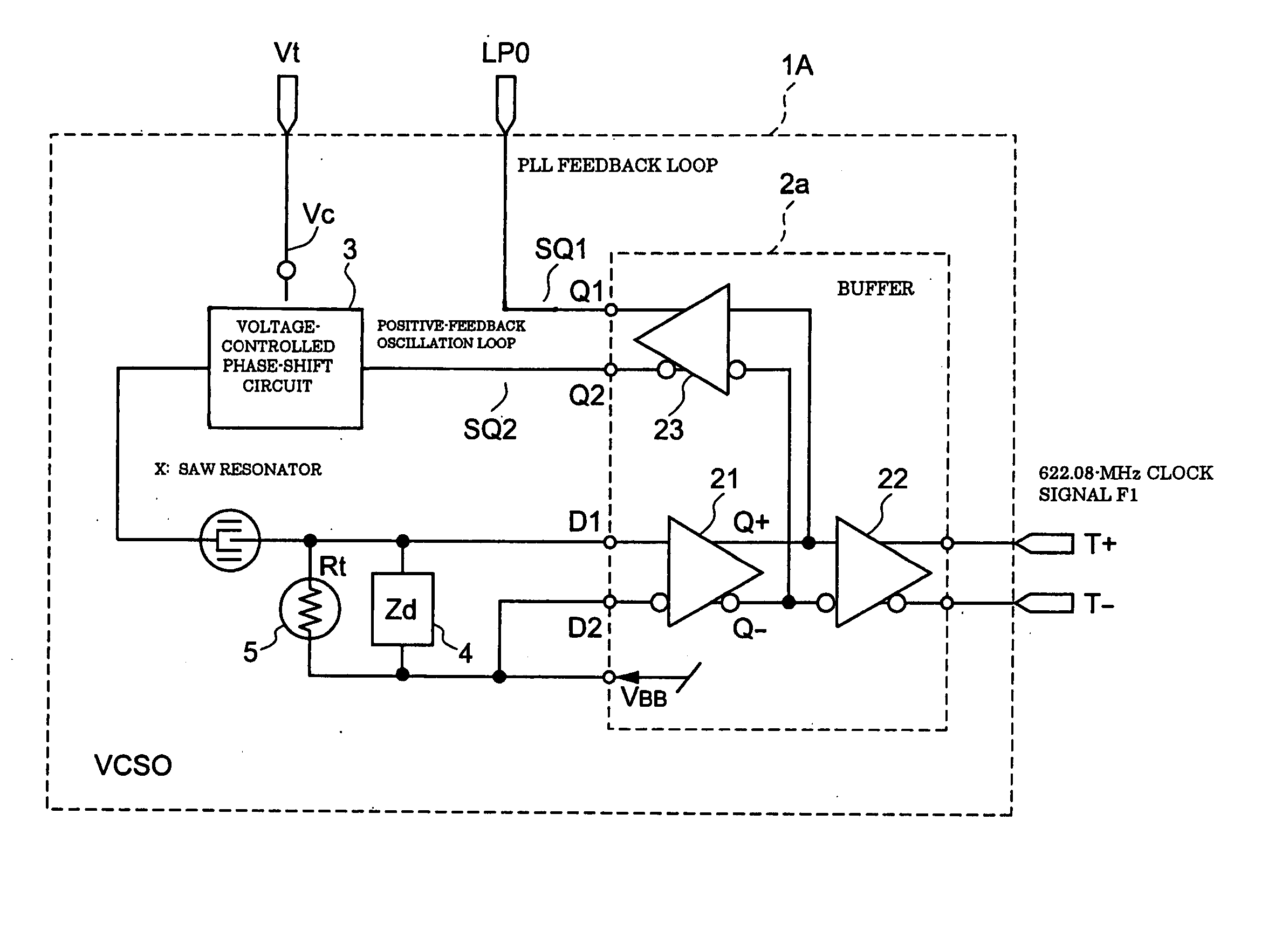
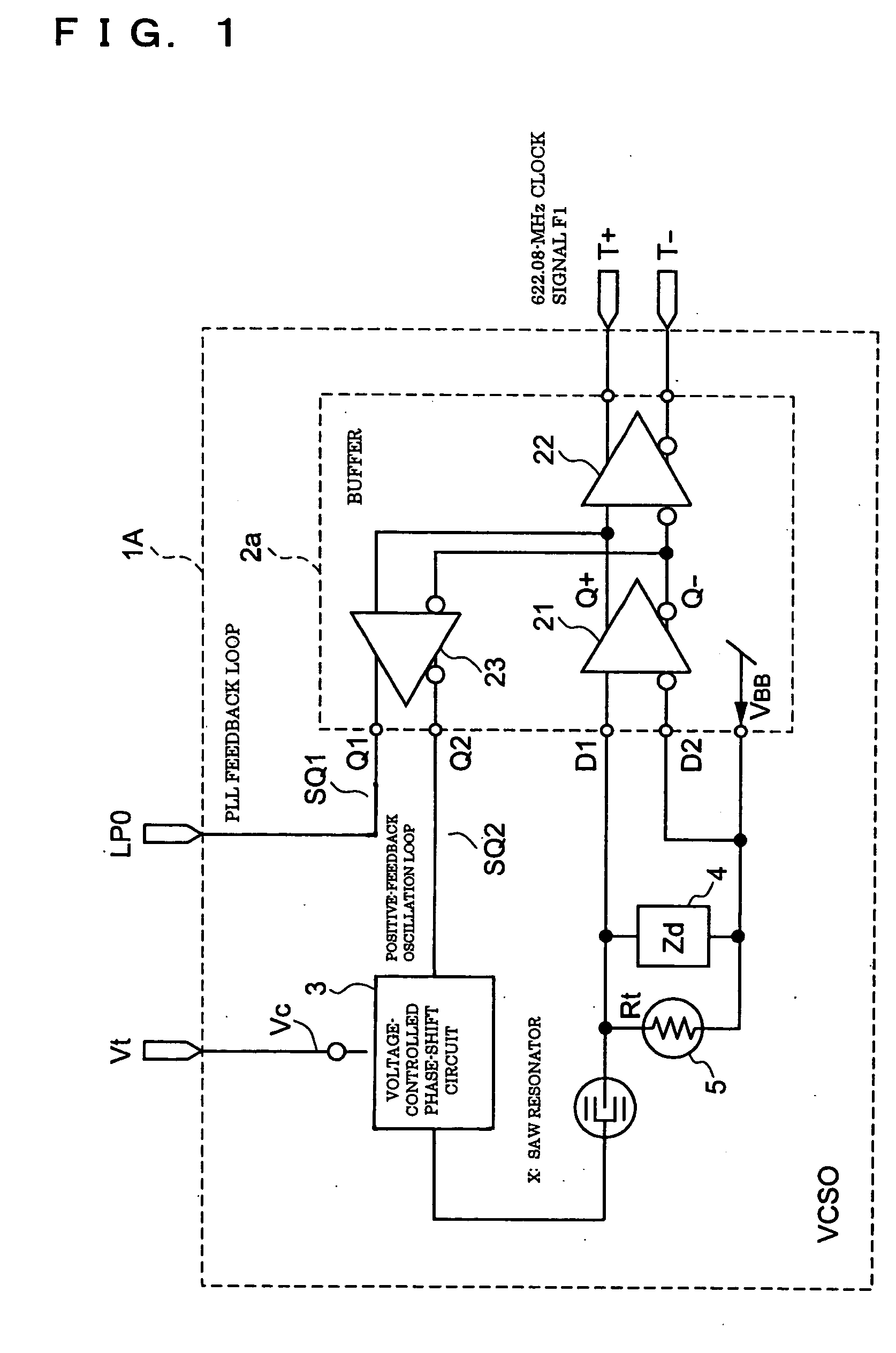
InactiveUS20050122179A1Data transmission is stableStable receptionRadiation pyrometryImpedence networksPropagation delayPhase shifted
A voltage-controlled oscillator includes a voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, outputting a signal with the shift deviated from an input signal by a specified amount with an external control voltage Vt, a SAW resonator, a buffer, inputting a resonance signal having a specified resonance frequency from the SAW resonator, outputting a clock signal with a desired frequency, and outputting a positive-feedback-oscillation-loop output signal, wherein the voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, the SAW resonator, and the buffer construct a positive-feedback oscillation loop, in which the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator is rotated by a specified amount using the temperature characteristic of the propagation delay time of the buffer to correct the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Peer-to-peer network and node of a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20190089716A1Simple processImprove tamper resistanceSynchronisation receiversTime-division multiplexDistributed computingPeer-to-peer
The invention relates to a peer-to-peer network having at least one first node with a first clock module and part of a peer-to-peer application. Also included is at least one second node with a second clock module and part of the peer-to-peer application. At least one communication connection between the first node and the second node is establishable. The first node comprises at least one first synchronization clock module. The second node comprises at least one second synchronization clock module. At least the first synchronization clock module is configured to transmit at least one first synchronization clock message to the second synchronization clock module via the communication connection, the second synchronization clock module is configured to synchronize the clock signal of the second clock module to the clock signal of the first clock module based on synchronization information included in the first synchronization clock message.
Owner:INNOGY INNOVATION GMBH
Drift tracking feedback for communication channels
ActiveUS20050210308A1Efficiently tracking drift of property of channelReceiver initialisationChannel dividing arrangementsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A communication channel includes a first component having a transmitter coupled to a normal signal source, and a second component having a receiver coupled to a normal signal destination. A communication link couples the first and second components. Calibration logic provides for setting an operation value for a parameter of the communication channel, such as by executing an exhaustive calibration sequence at initialization of the link. A tracking circuit, including a monitoring function, tracks drift in the parameter by monitoring a feedback signal that has a characteristic that correlates with drift in the communication channel, and updates, or indicates the need for updating of, the operation value of the parameter in response to the monitoring function.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Multiple user adaptive modulation scheme for MC-CDMA
InactiveUS7123580B2Keep in syncMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransmission path divisionModem deviceCarrier signal
In a multi-user frequency domain spreading downlink MC-CDMA system, a group of sub-carriers can be replaced by an equivalent sub-carrier of a conventional OFDM modem for purposes of resource allocation to improve the system performance. The chips for a given user are spread only within the group. Confinement insures synchronization between different users' chips that is essential to the recovering and separation of user symbols at the receiver. There is no limit imposed on the group size, which permits different spreading code lengths to be used for different scenarios or for performance tuning.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System and method for nonlinearity estimation with reference signals
ActiveUS20190190552A1Limited rangeReduce distortion problemsPower amplifiersReceiver specific arrangementsConstant envelopeDistortion
A transmitter may be configured to generate a reference signal having a non-constant envelope for nonlinearity estimation by a receiver. The transmitter may transmit the reference signal. A receiver may be configured to receive, from the transmitter, the reference signal having the non-constant envelope. The receiver may estimate at least one nonlinearity characteristic based on the reference signal having the non-constant envelope. The receiver may transmit feedback based on the at least one nonlinearity characteristic and / or perform at least one digital post distortion (DPoD) operation based on the at least one nonlinearity characteristic.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
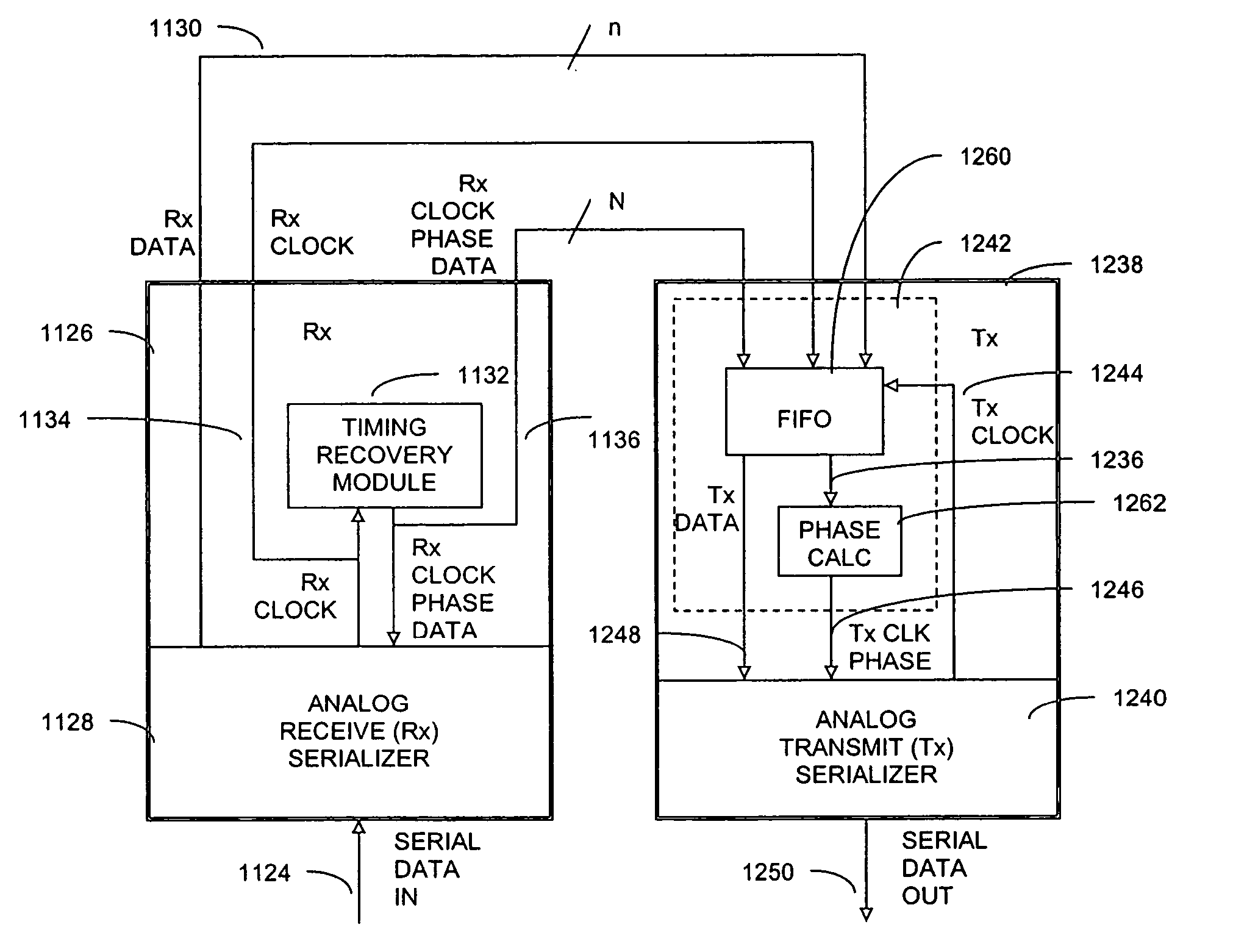
System and method of phase-locking a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase
ActiveUS20050169417A1Parallel/series conversionSynchronisation information channelsPhase differenceTransmission channel
Systems and methods for synchronizing a receive clock signal phase with a transmit clock signal phase are presented. A system includes a receiving channel and a transmitting channel, wherein the transmitting channel synchronizes a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase based on receive clock signal phase data. A method includes storing a previous receive clock signal phase of a receiving channel and identifying a current receive clock signal phase of the receiving channel. The method further includes determining a phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase, and identifying a direction of the phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase. The method further includes adjusting a previous transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel to a current transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel based on the phase difference and direction.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
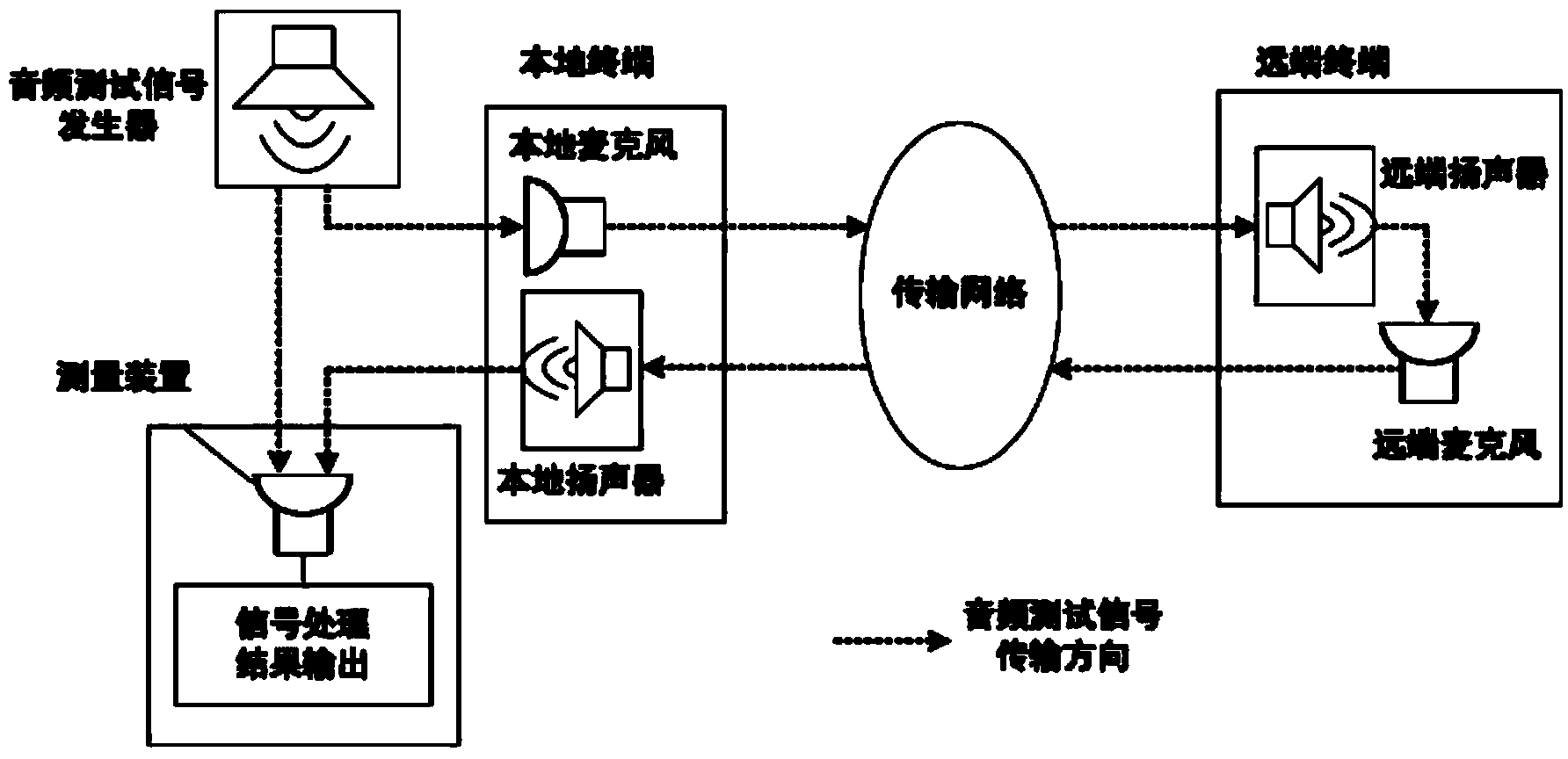
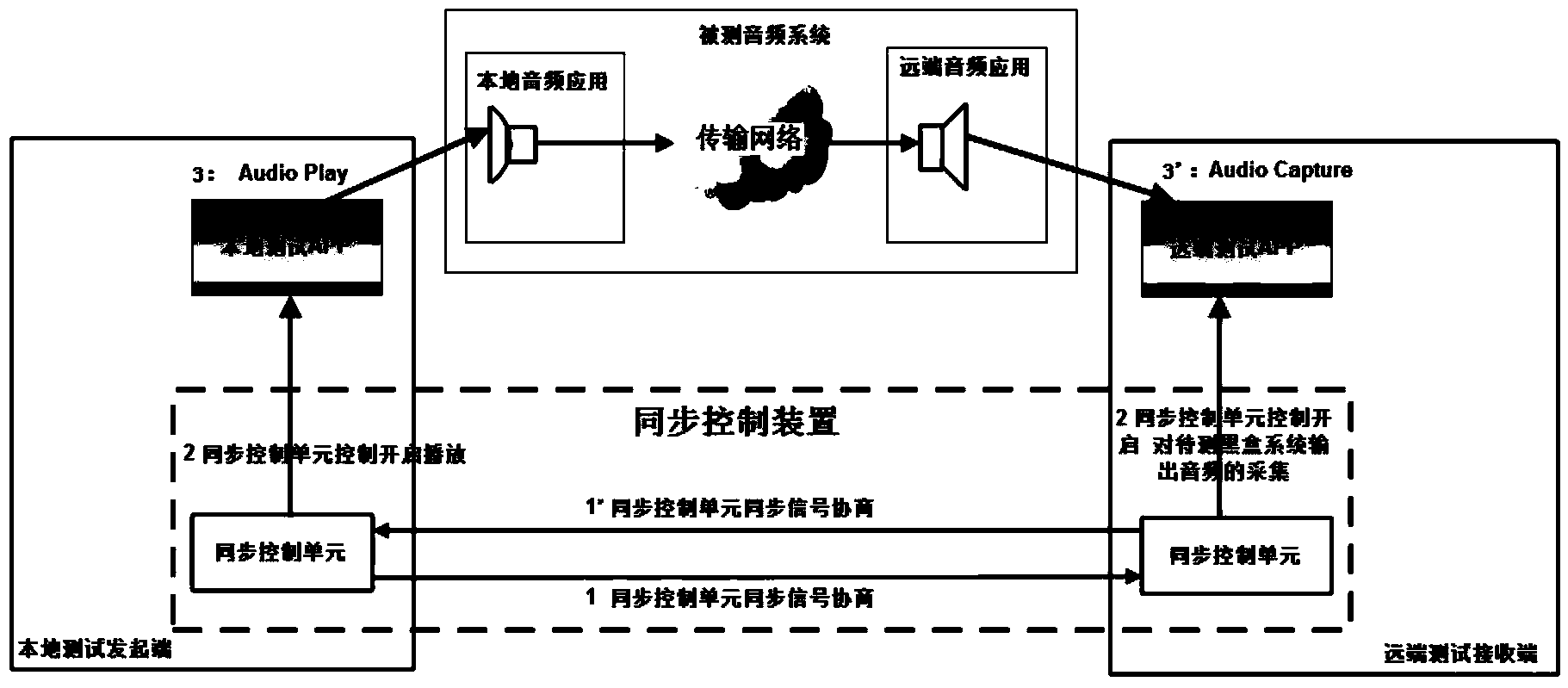
Audio transmission delay measuring method and system
ActiveCN104125022ASolve technical problems with inaccurate calculationsPrevent echoSynchronisation receiversSynchronisation transmittersTransmission delayCodebook
The invention discloses an audio transmission delay measuring method and system. The method comprises performing synchronization operation on transmission of an original audio codebook to be measured between a transmitting end and a receiving end to obtain the transmission starting indicating information, the transmission ending indicating information, the receiving starting indicating information and the receiving ending indicating information of the original audio codebook; enabling the transmitting end to respond to the transmission starting indicating information and transmit the original audio codebook to be measured to the receiving end and to respond to the transmission ending indicating information and stop transmitting the original audio codebook to the receiving end, and enabling the receiving end to respond to the receiving starting indicating information and collect the original audio codebook transmitted by the transmitting end and to respond to the receiving ending indicating information and stop collecting the original audio codebook transmitted by the transmitting end; obtaining audio transmission delay according to the testing audio codebook collected by the receiving end and the original audio codebook prestored in the receiving end. The audio transmission delay measuring method and system solves the problem of inaccurate computation of audio transmission delay in the prior art.
Owner:TENCENT TECH CHENGDU
Voltage-controlled oscillator, clock converter, and electronic device
InactiveUS7012476B2Excellent frequency temperature characteristicsStable receptionRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlVoltage controlVoltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator includes a voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, outputting a signal with the shift deviated from an input signal by a specified amount with an external control voltage Vt, a SAW resonator, a buffer, inputting a resonance signal having a specified resonance frequency from the SAW resonator, outputting a clock signal with a desired frequency, and outputting a positive-feedback-oscillation-loop output signal, wherein the voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, the SAW resonator, and the buffer construct a positive-feedback oscillation loop, in which the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator is rotated by a specified amount using the temperature characteristic of the propagation delay time of the buffer to correct the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and method for synchronization of isochronous data streams over a wireless communication link
InactiveUS20070100473A1Synchronisation arrangementPosition fixationTelecommunications linkData stream
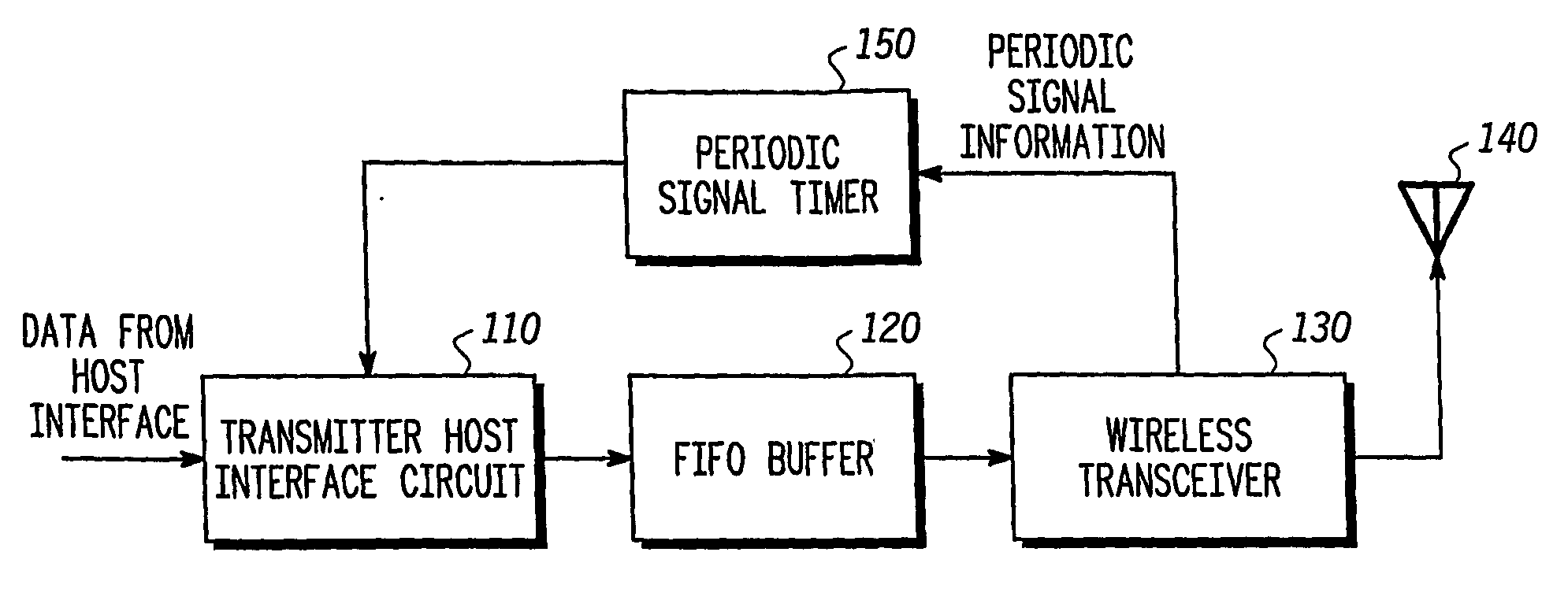
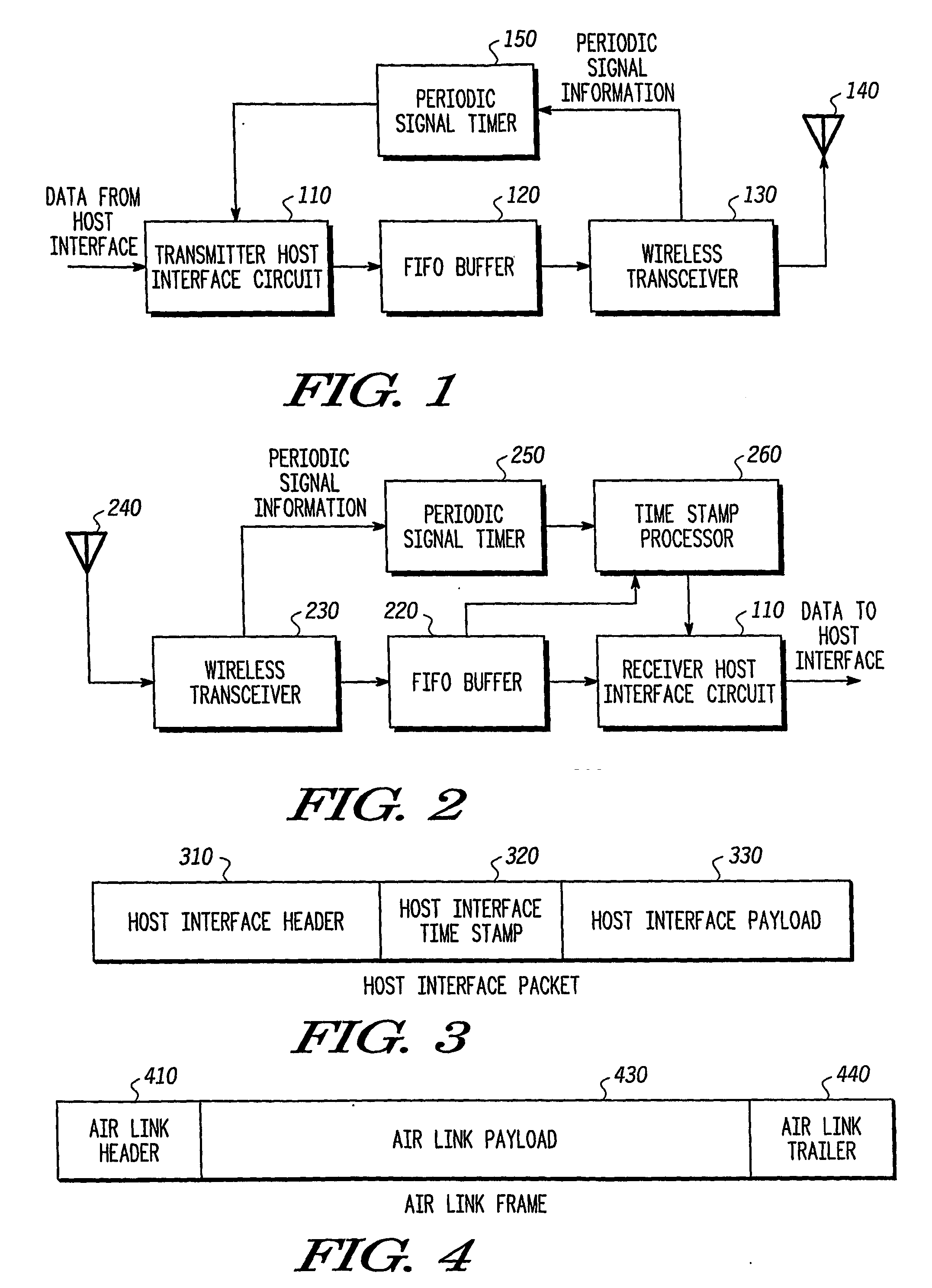
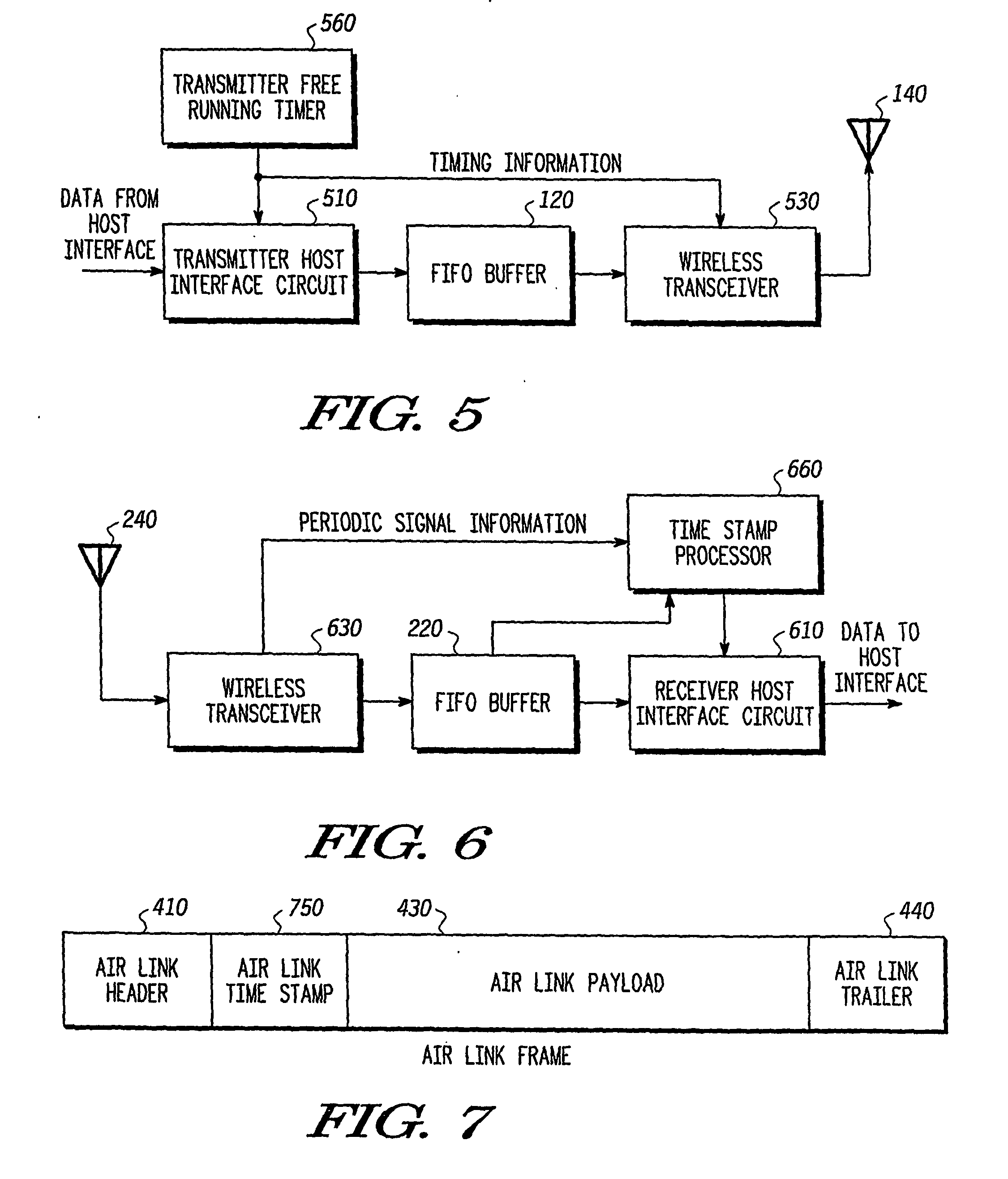
A transmitter (500) is provided for transmitting host data over a wireless channel. The transmitter (500) includes a free-running timer (560) that provides a series of increasing free-running timing values; a host interface circuit (510) that receives host data from a local host circuit and a first free-running timing value from the series of increasing free-running timing values; a detection circuit (530) for detecting a global synchronizing event and receiving a second free-running timing value from the series of increasing free-running timing values, and for placing the host data and the first free-running timing value into a host interface packet; and a wireless transceiver (530) for adding the second free-running timing value and an identifier for the global synchronizing event to the host interface packet to form an air link frame, and transmitting the air link frame over a wireless channel to a remote wireless device.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
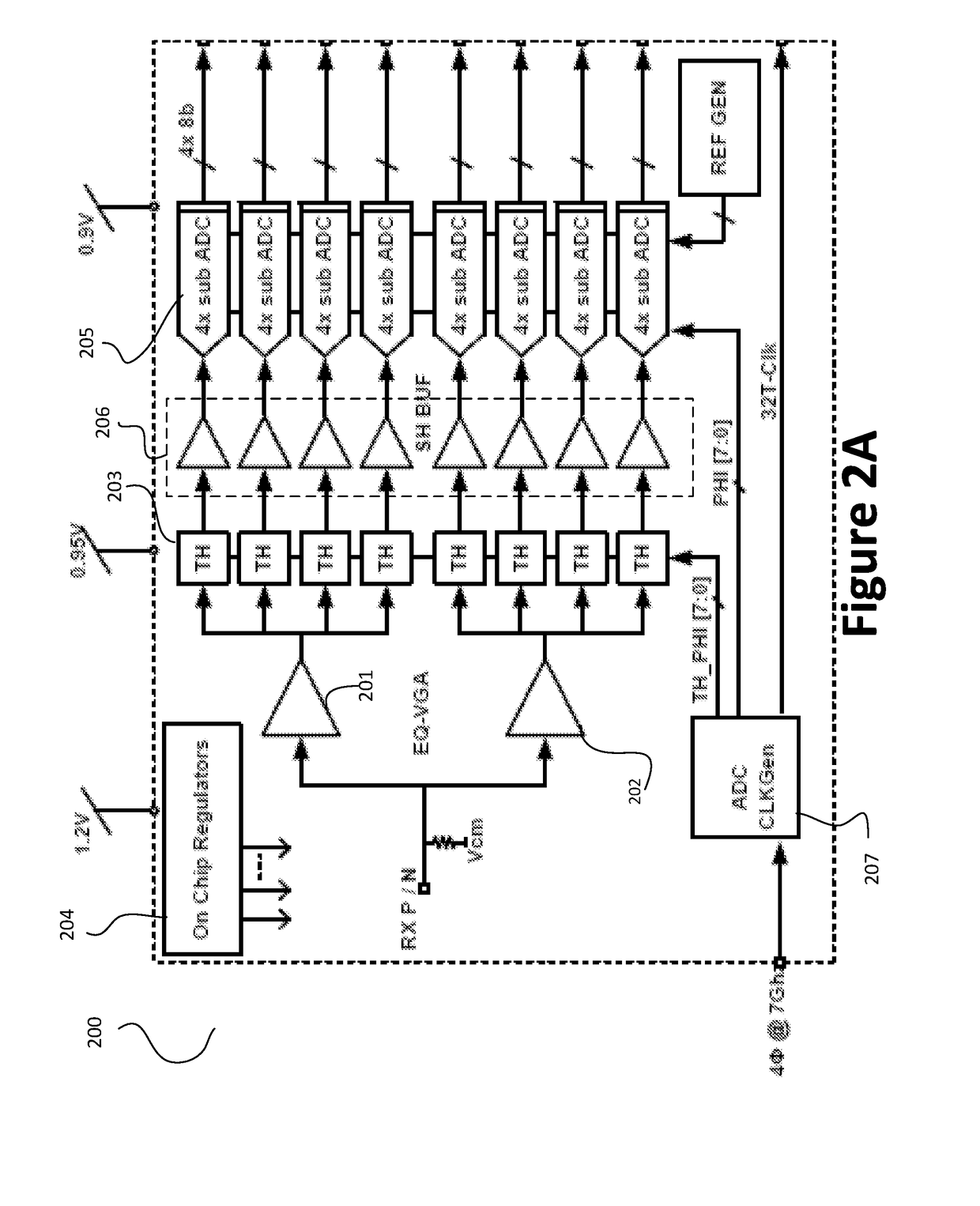
Pam4 transceivers for high-speed communication
ActiveUS20170257168A1Reduce power consumptionReduce noisePulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversAudio power amplifierTransceiver
The present invention is directed to data communication. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention provide a transceiver that processes an incoming data stream and generates a recovered clock signal based on the incoming data stream. The transceiver includes a voltage gain amplifier that also performs equalization and provides a driving signal to track and hold circuits that hold the incoming data stream, which is stored by shift and holder buffer circuits. Analog to digital conversion is then performed on the buffer data by a plurality of ADC circuits. Various DSP functions are then performed over the converted data. The converted data are then encoded and transmitted in a PAM format. There are other embodiments as well.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
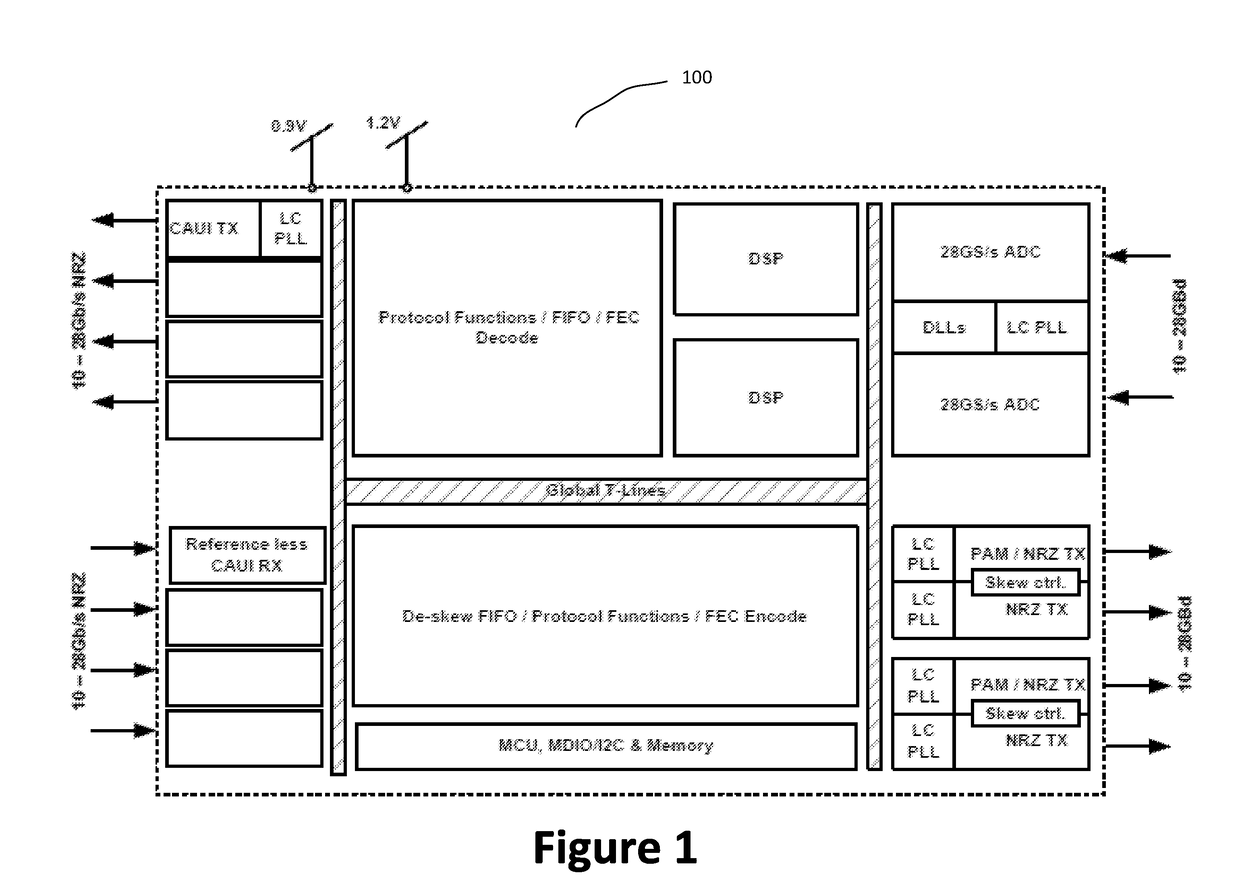
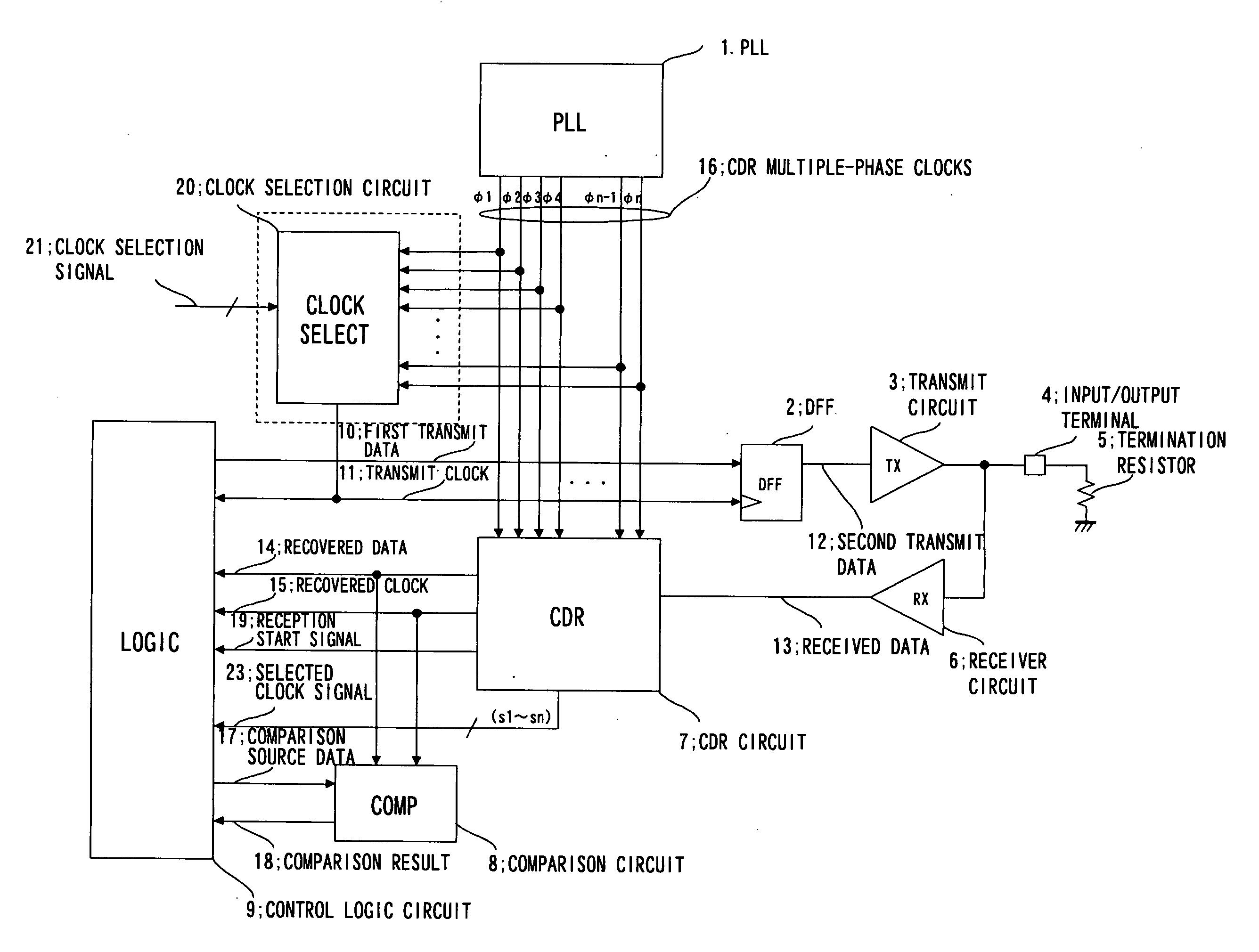
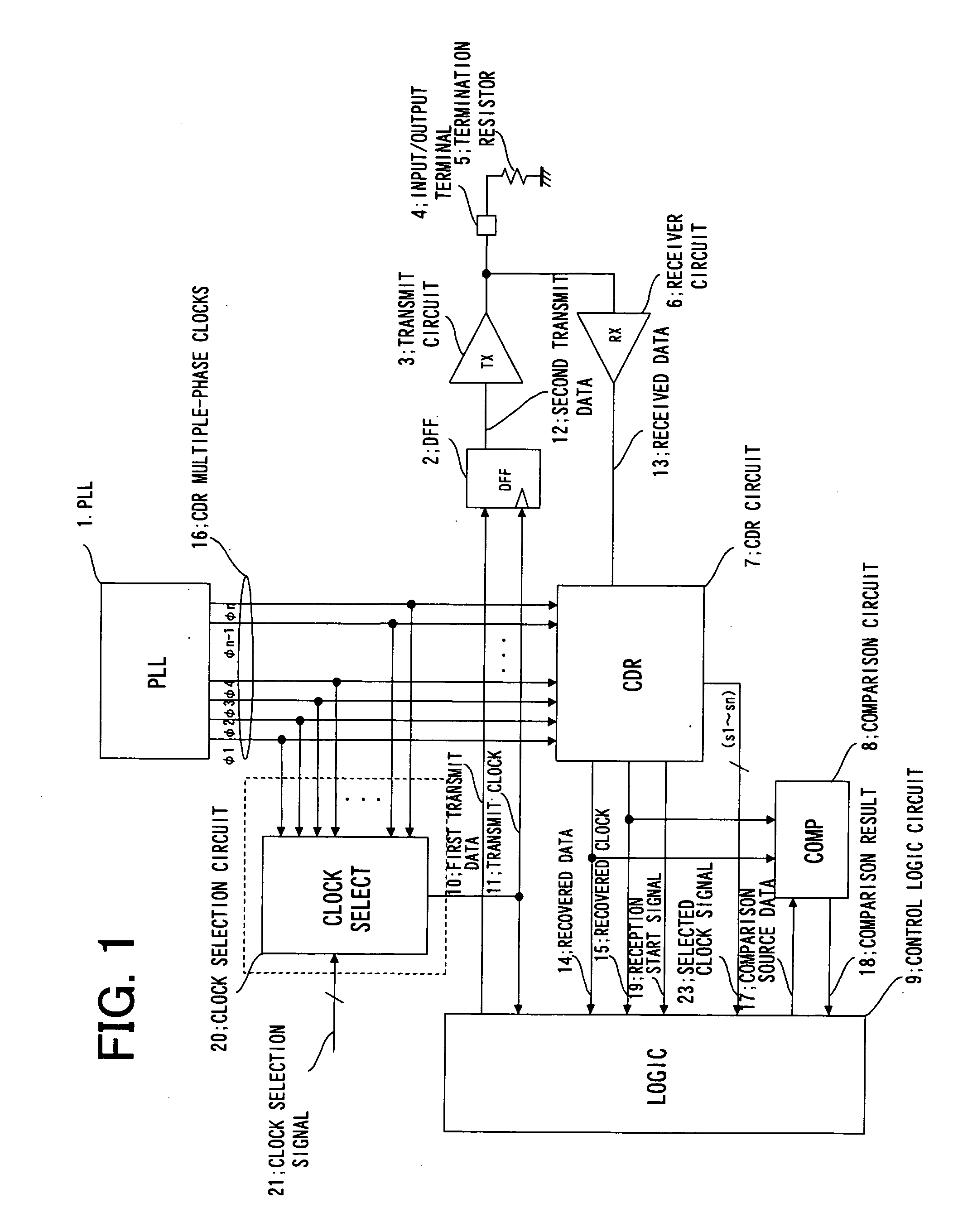
Communication device
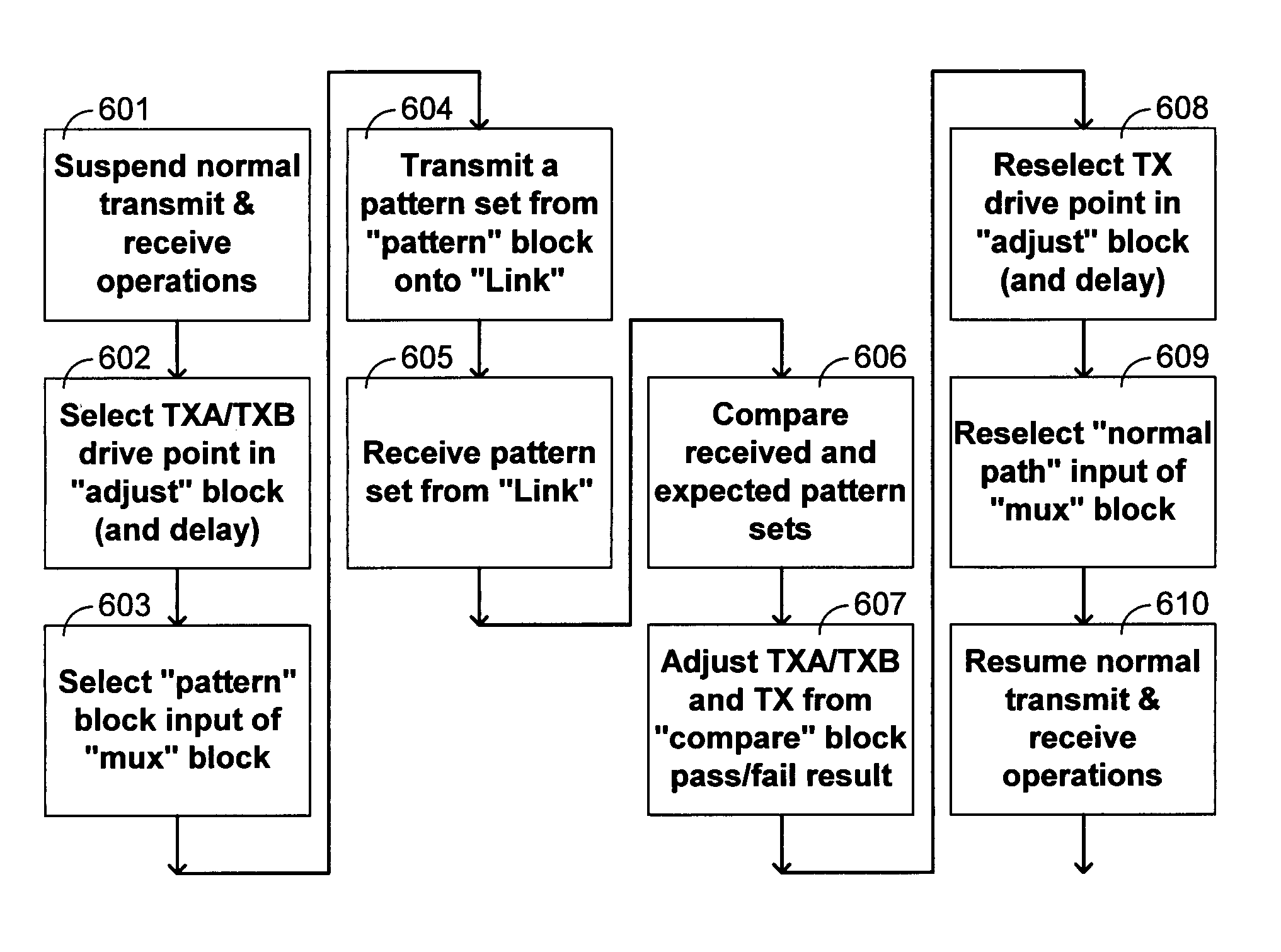
InactiveUS20070127614A1Increase speedError preventionPulse automatic controlCircuit delayDelayed time
Disclosed is a communication circuit including a clock selection circuit (20) which receives CDR multiple-phase clocks (16) from a PLL (1) to a CDR circuit (7), selects one of the CDR multiple-phase clock signals (16) responsive to a clock selection signal (21), and outputs the selected clock signal. At a time of the loopback test, the clock signal selected by the clock selection circuit (20) is used as a transmit clock (11). Transmit data is looped back from an input / output terminal (4) to a receiver circuit (6). Data from the receiver circuit (6) is supplied to the CDR circuit (7), and comparison between recovered data from the CDR circuit (7) and expected value data is made by a comparison circuit (8), thereby conducting the test. By changing a phase of the transmit clock (11) by the clock selection circuit (20), a delay time (=tTx+tRx) which is a sum of a transmit circuit delay time (tTx) and a receiver circuit delay time (tRx) can be varied.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Bearer integration method and apparatus for the bearer integration method
InactiveUS7123630B1Increase the number ofRaise the possibilitySynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsTime-division multiplexing
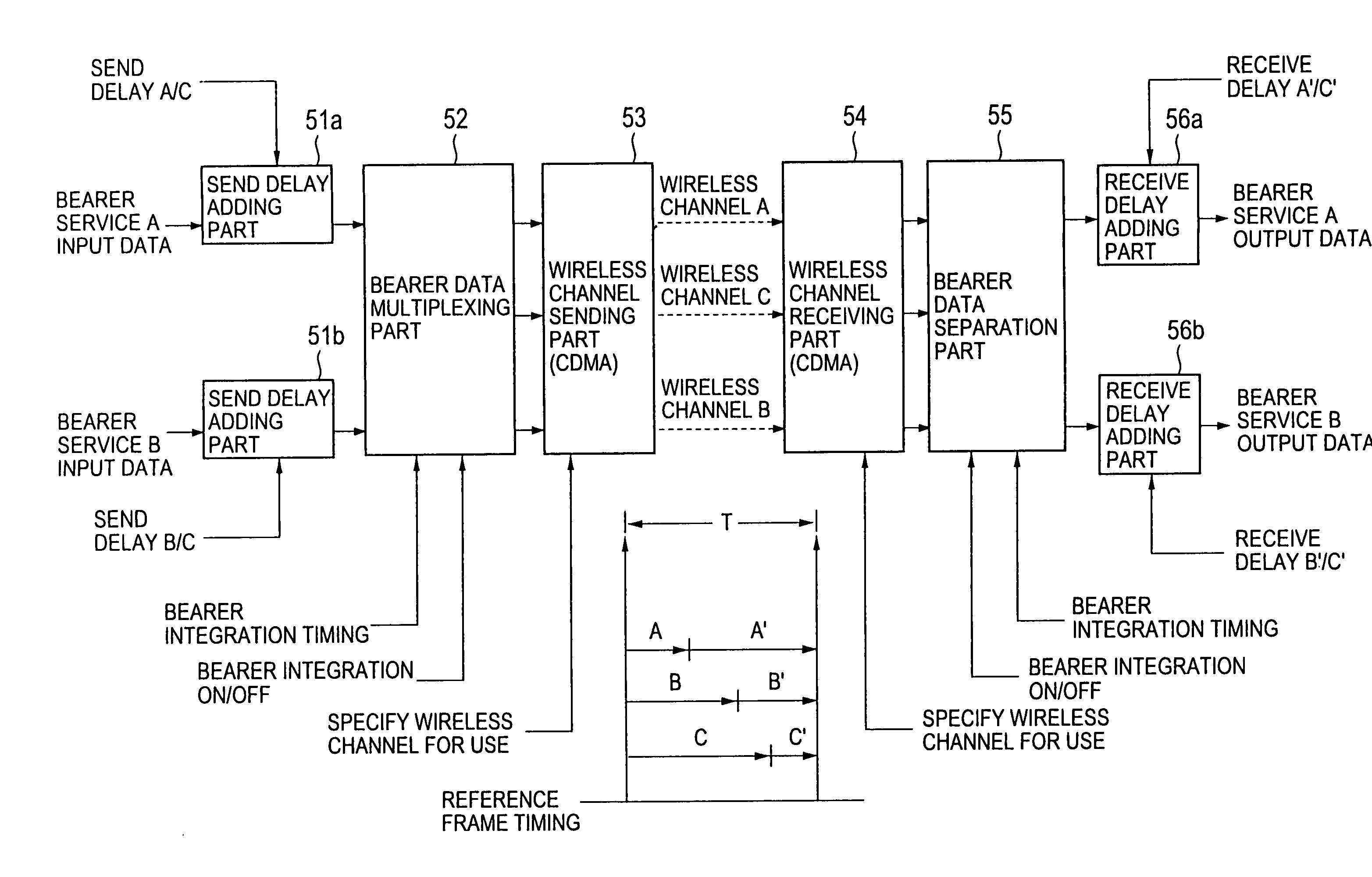
A bearer integration method for integrating a plurality of bearer services into a wireless channel by performing time-division multiplexing / demultiplexing is provided, in which bearer service data is input in synchronization with reference frame timing of a period T in a sending side, the bearer service data is delayed by one frame period by allocating delays A (0≦A≦T) and A′ (=T−A) between the sending side and a receiving side, the bearer service data is output in the receiving side, and the bearer service data is integrated into a wireless channel with another bearer service data in which delays B (A≦B≦T) and B′ (=T−B) are allocated between the sending side and the receiving side.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
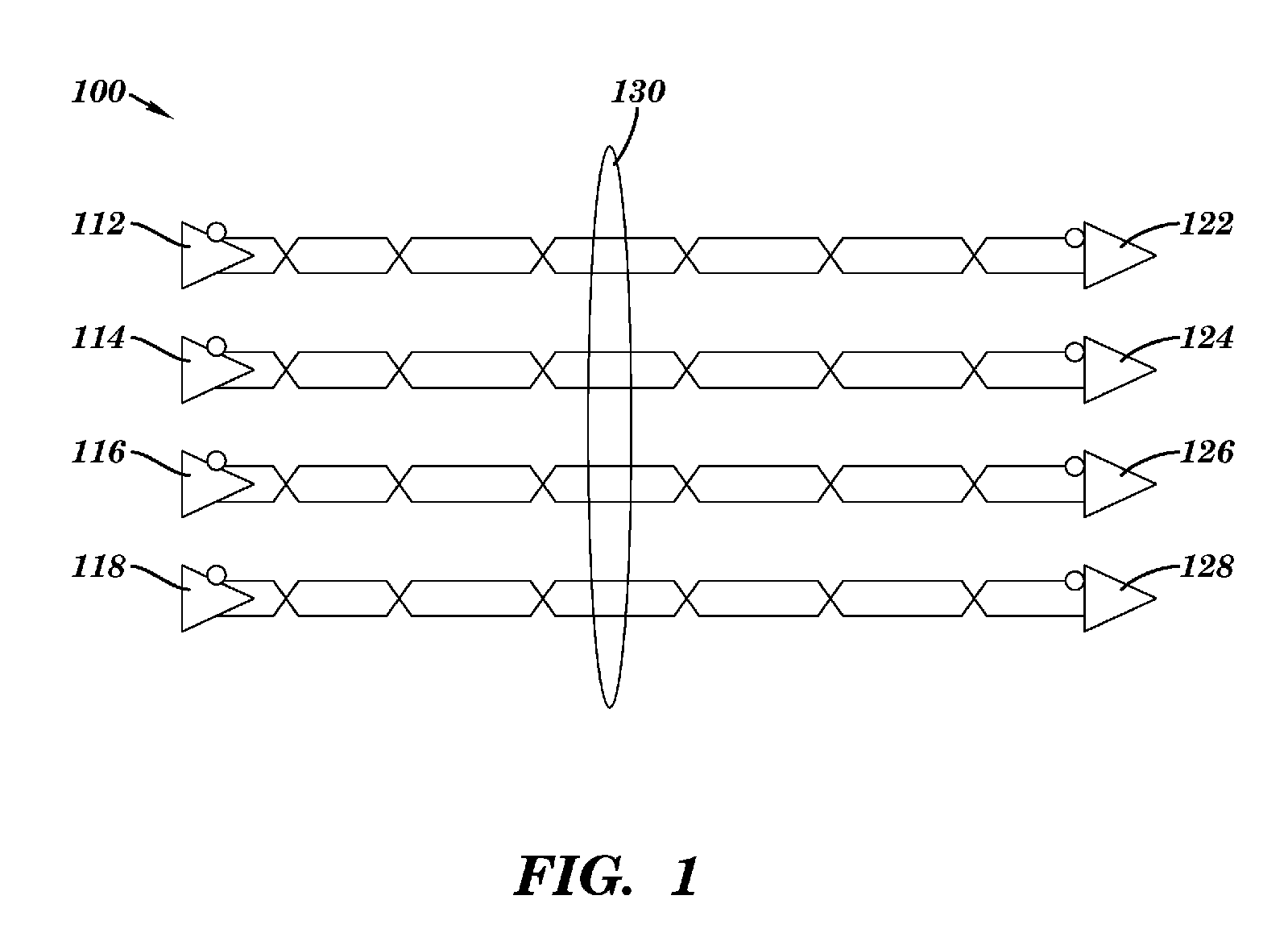
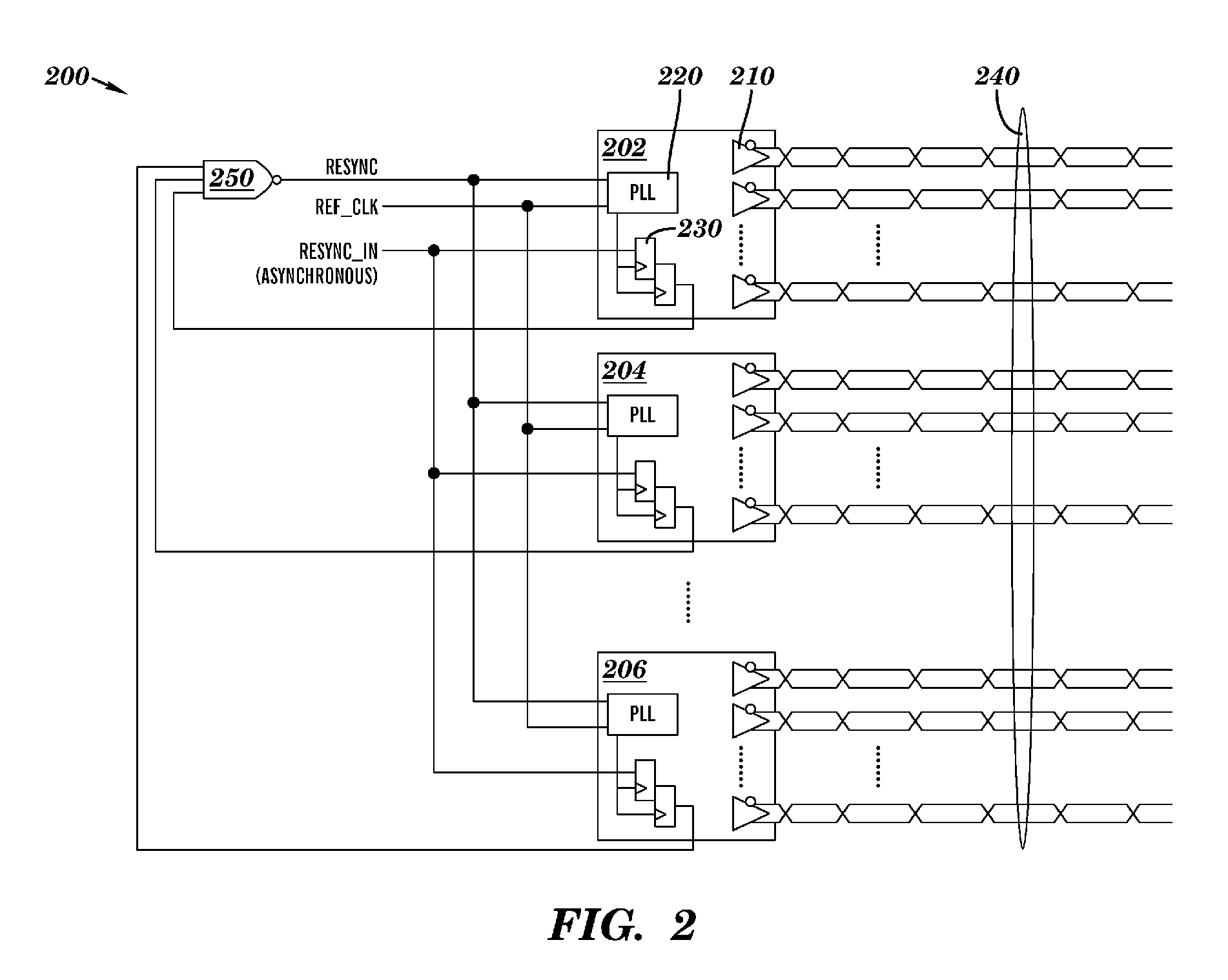
Multi-channel synchronization architecture
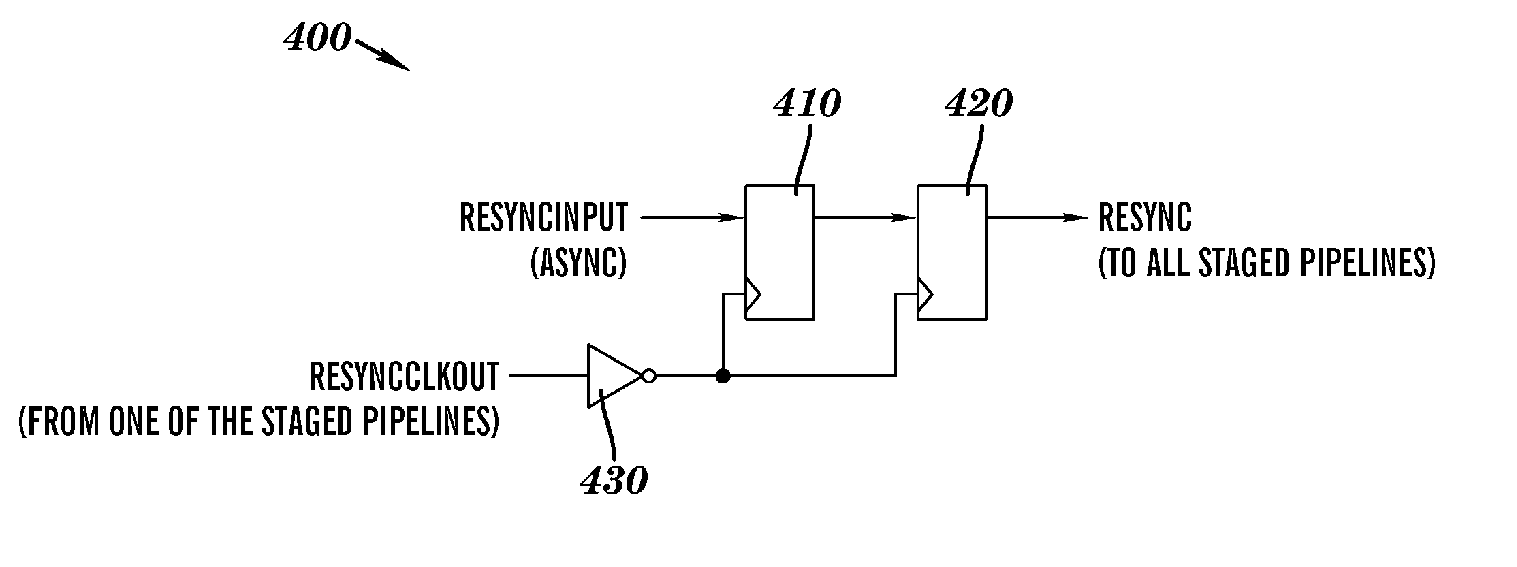
InactiveUS20070002845A1Minimize impactSynchronisation transmittersNetwork connectionsCommunications systemMulti link
The present invention provides a robust global timing resynchronization architecture, a multi-link communications system including the same, and a method for minimizing the effects of resynchronization signal skew, reference clock skew, and PLL static phase error variations on resynchronization of multi-link communications systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
CDR-based clock synthesis
A clock signal can be synthesized by performing a clock and data recovery (CDR) operation on a potentially noisy clock source signal which has a known transition density. The CDR operation produces a desired clock signal in response to the clock source signal. In order to reduce crosstalk between plesiochronous receive and transmit clock domains of a serial data transceiver, a single common PLL is used both to recover the receive clock from the received data and to synthesize the transmit clock from a potentially noisy transmit clock source signal.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC +1
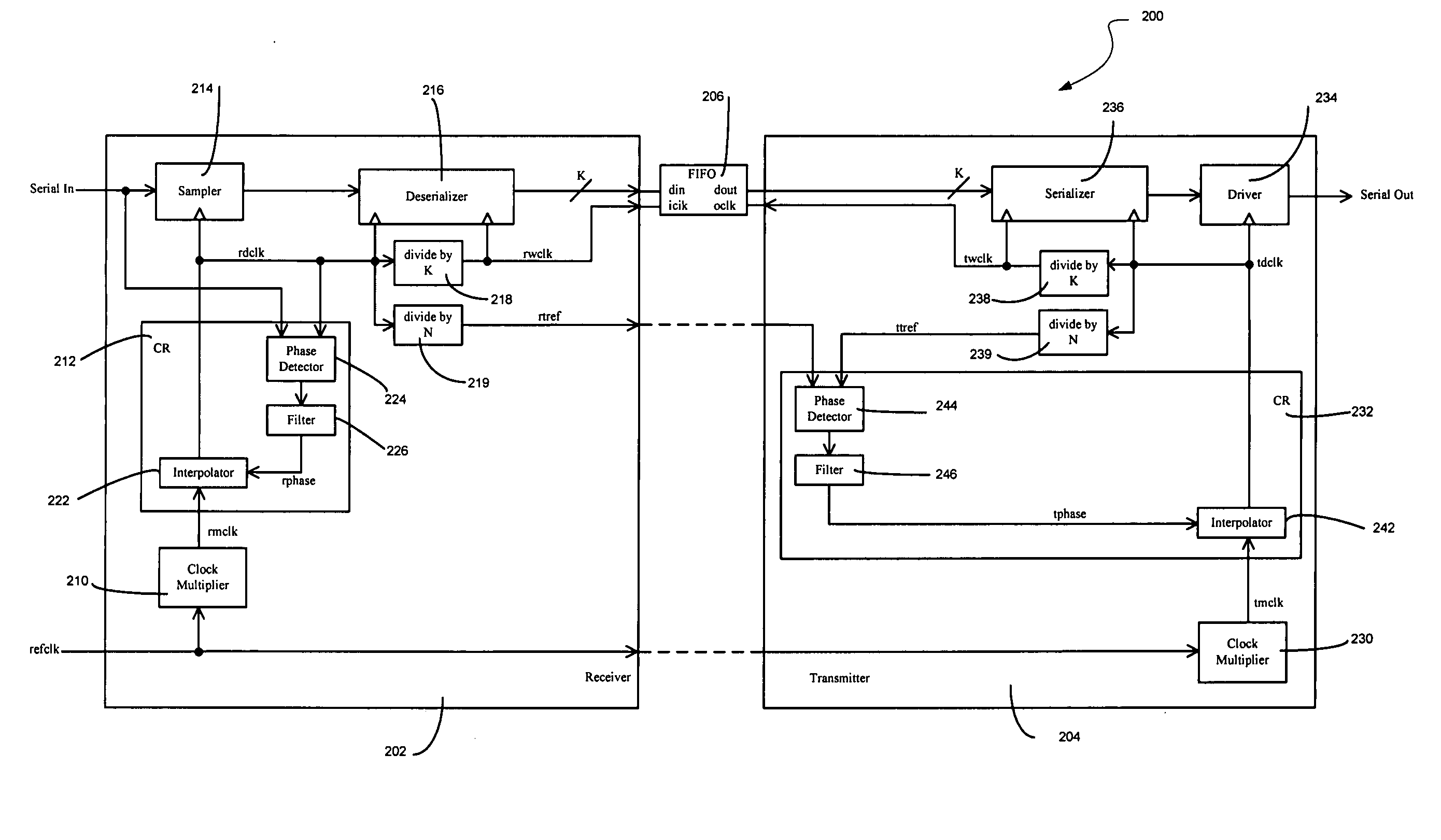
Pleisiochronous repeater system and components thereof
A pleisiochronous repeater system and components thereof are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, a pleisiochronous repeater system component may be realized as a receiver circuit comprising a clock multiplier that multiplies a reference clock signal by an integer multiple to generate a data clock signal. The receiver circuit may also comprise a divider circuit that generates a timing reference signal having a frequency that is not an integer divisor of a frequency of the reference clock signal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com