Patents
Literature
69results about "Line impedence variation compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
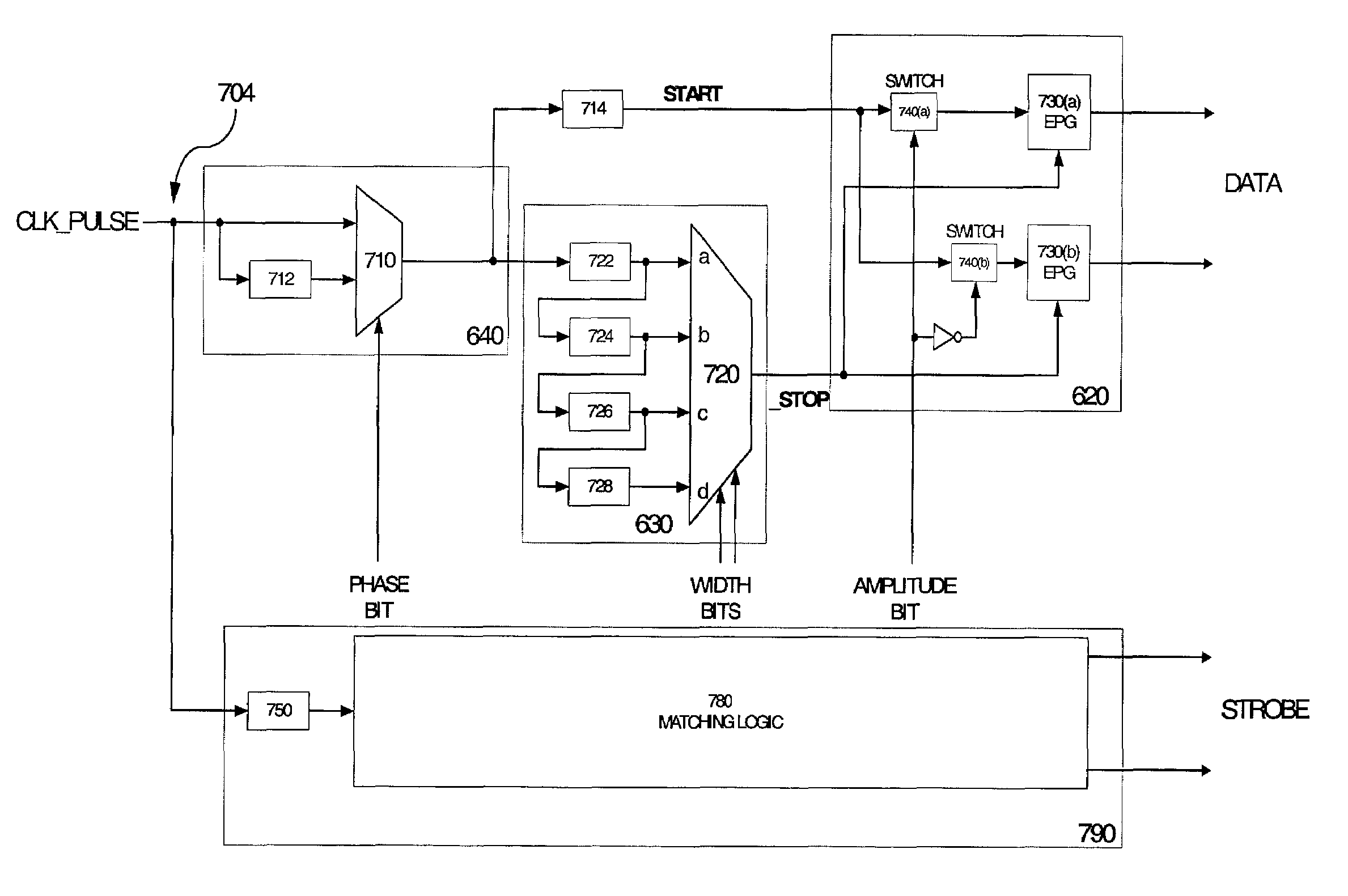
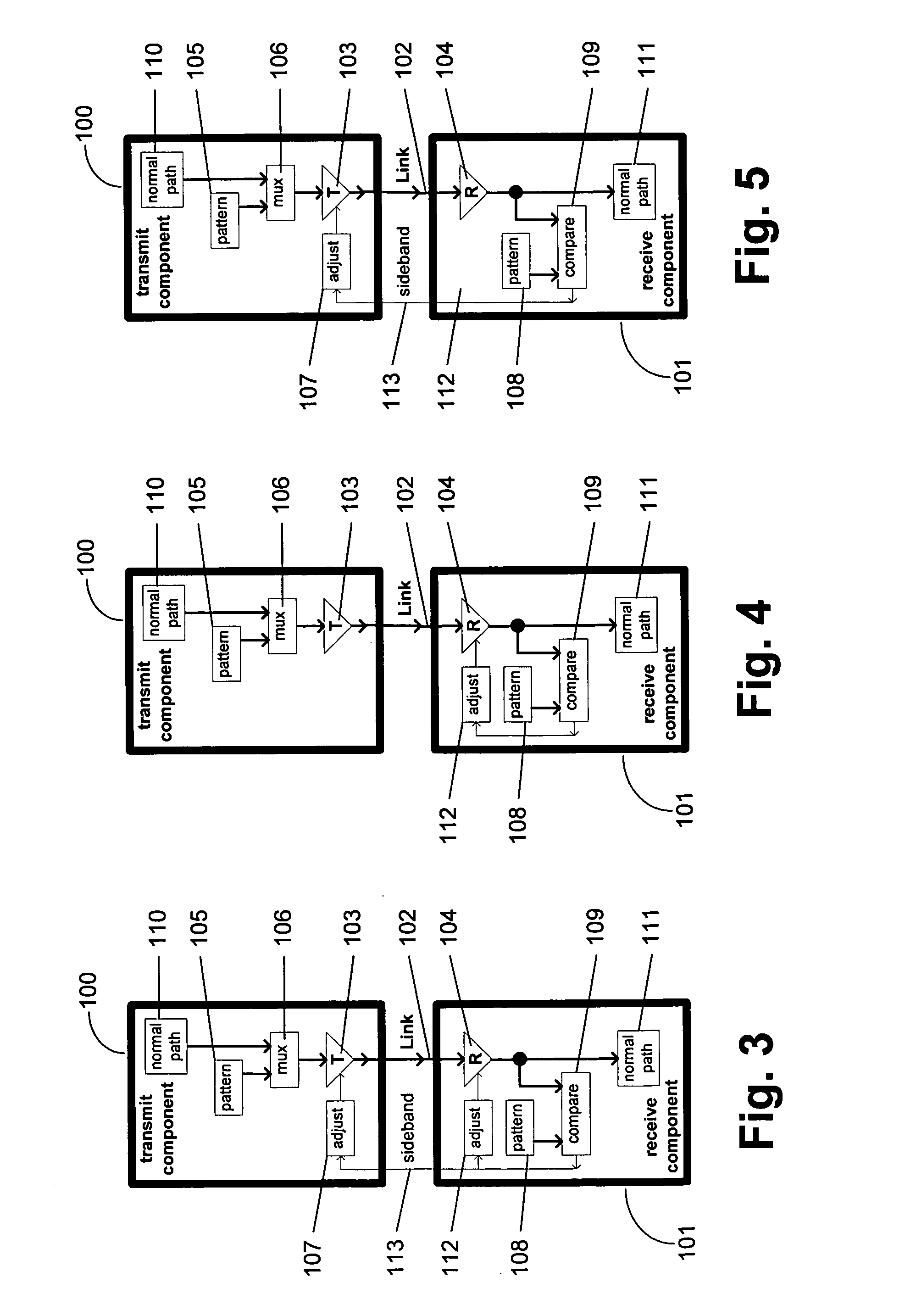
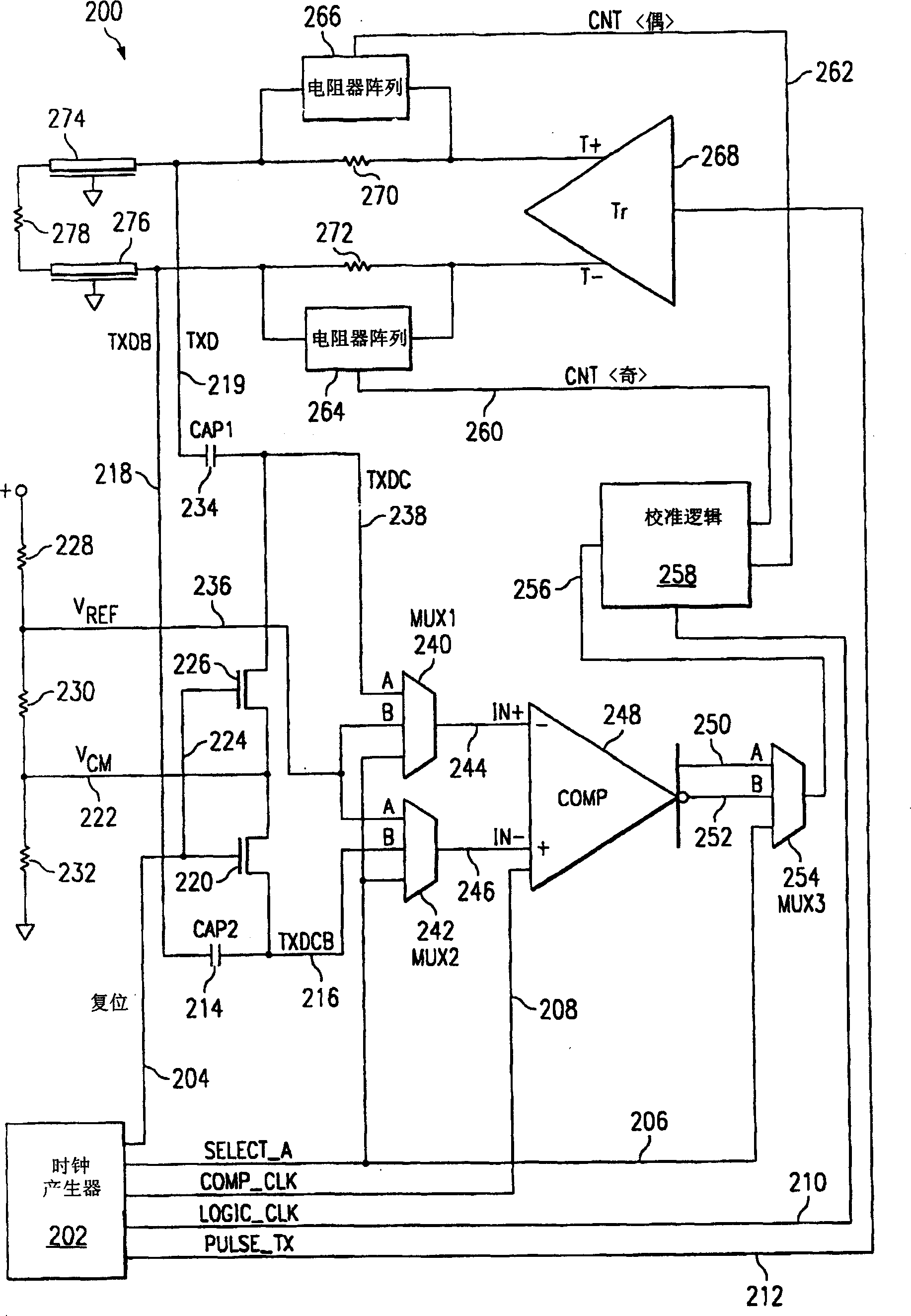
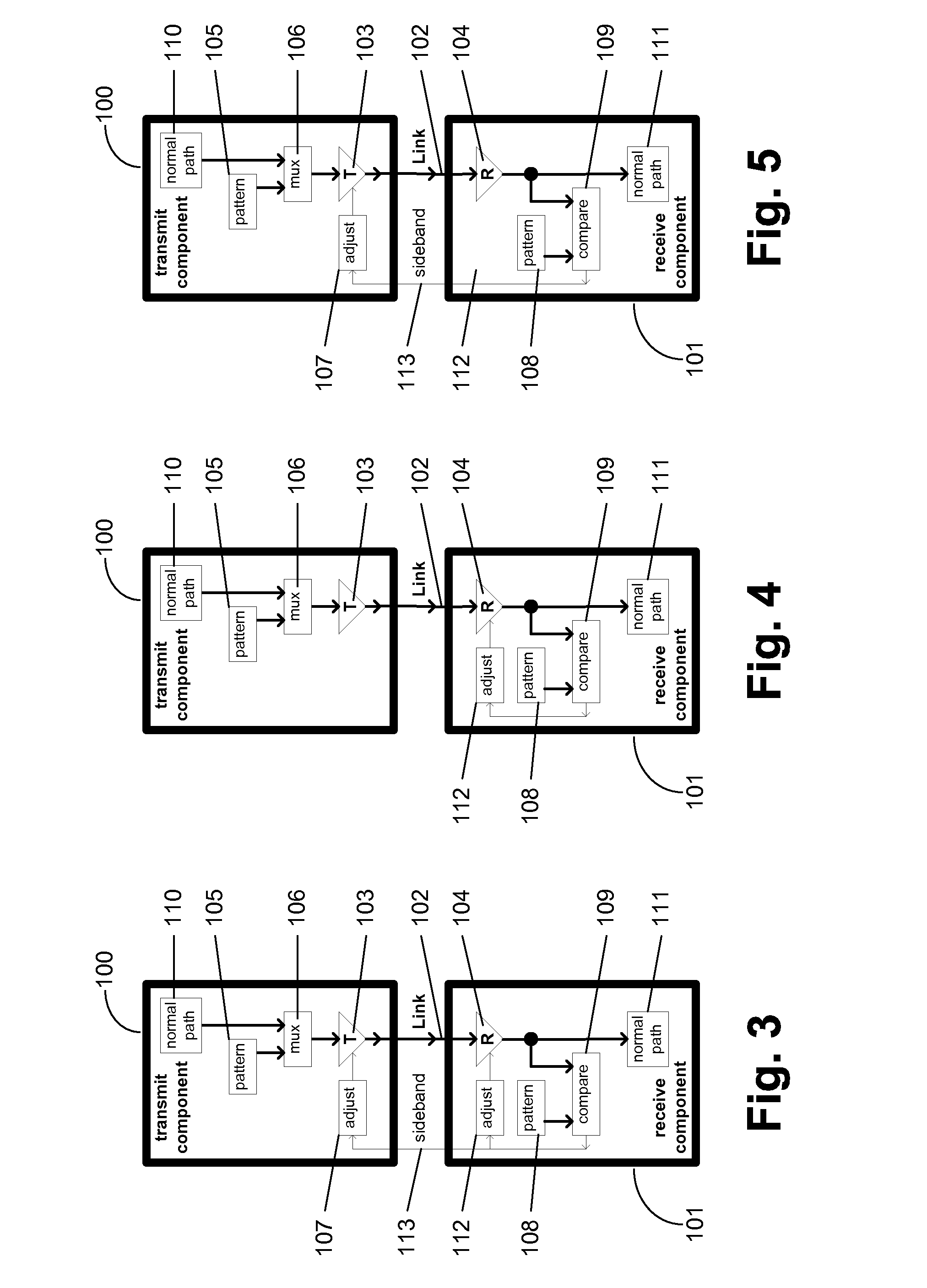
Symbol-based signaling device for an electromagnetically-coupled bus system
InactiveUS7075996B2Printed circuit assemblingLine impedence variation compensationComplementary pairChipset
The present invention provides a chipset for transferring data through an electromagnetically coupled bus system. The chipset includes a modulator, a matching circuit and a demodulator. The modulator modifies a clock to encode multiple bits in a complementary pair of symbols. The matching circuit modifies the clock signal to generate a complementary pair of reference signals that is transmitted with the complementary symbol pair, and the demodulator decodes a second set of bits from selected properties of a complementary pair of transferred symbols.
Owner:INTEL CORP
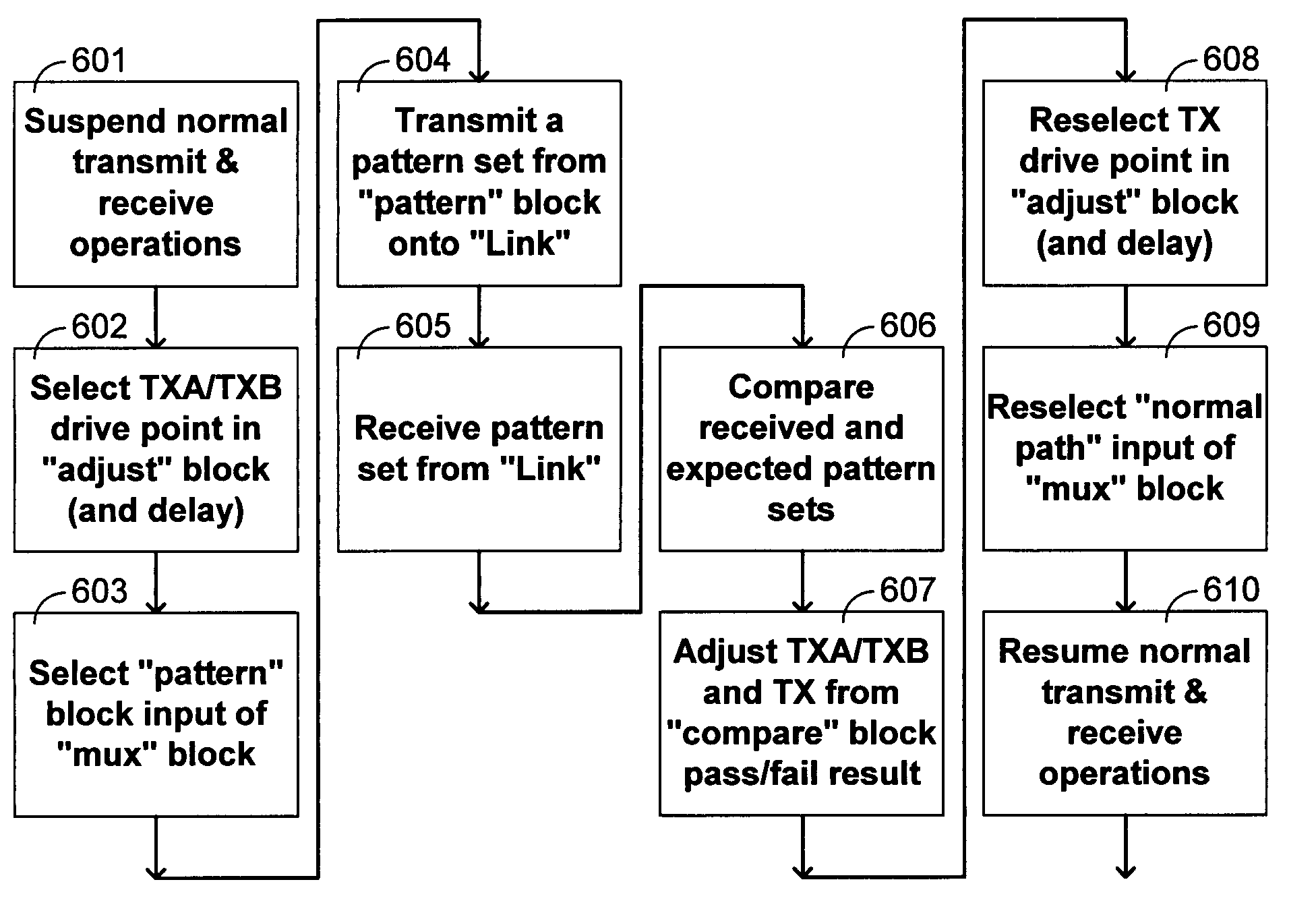
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
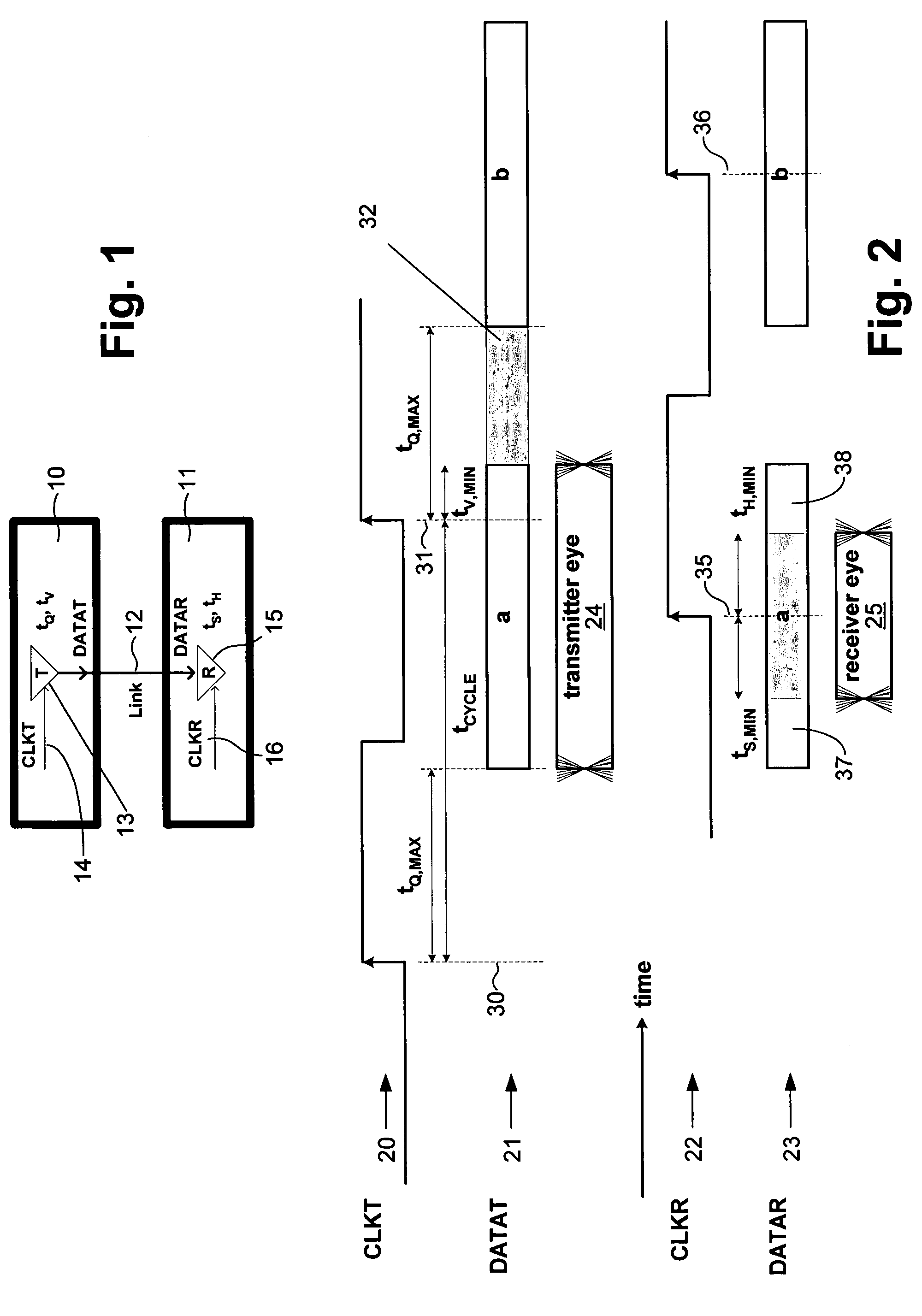
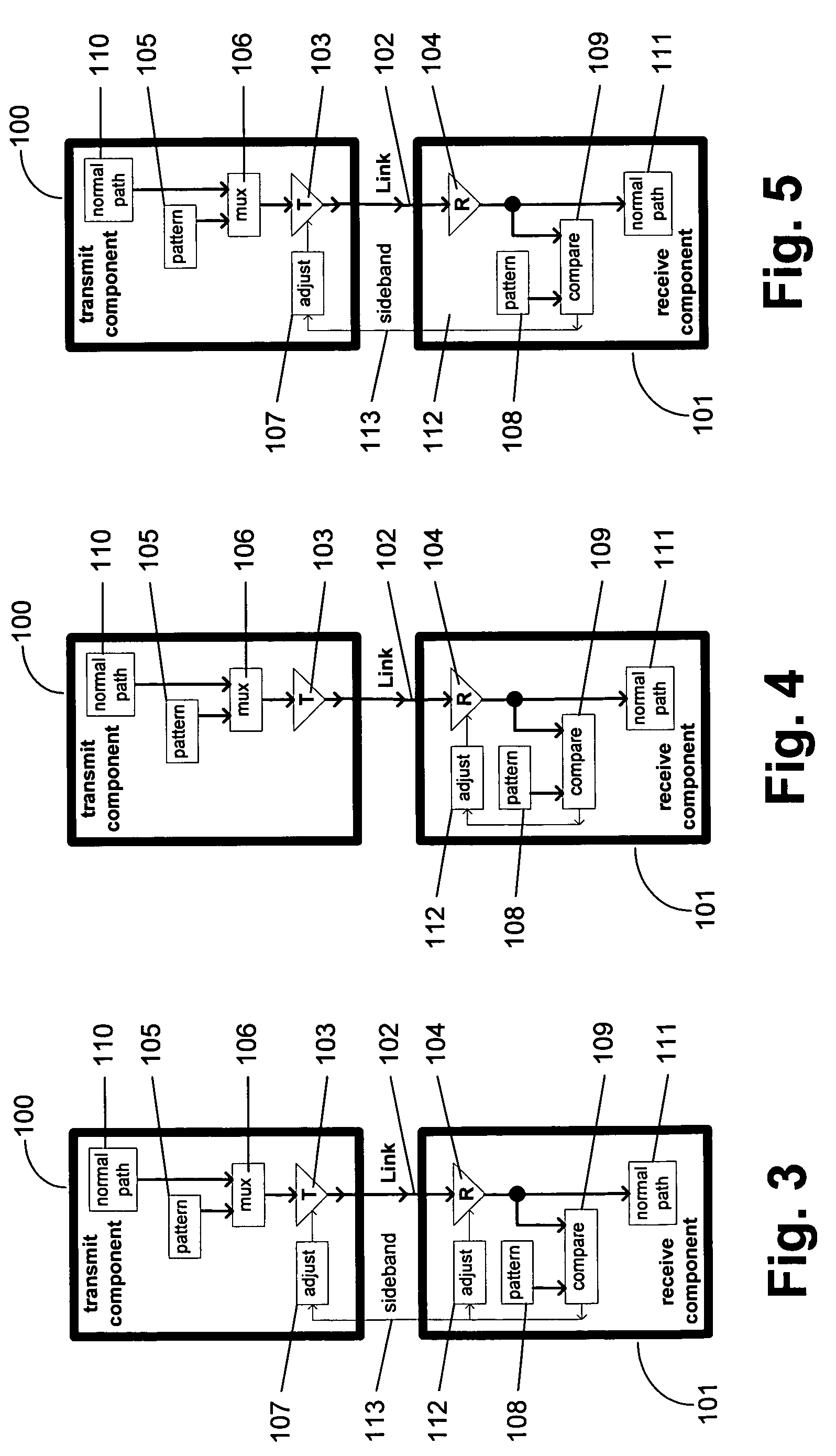
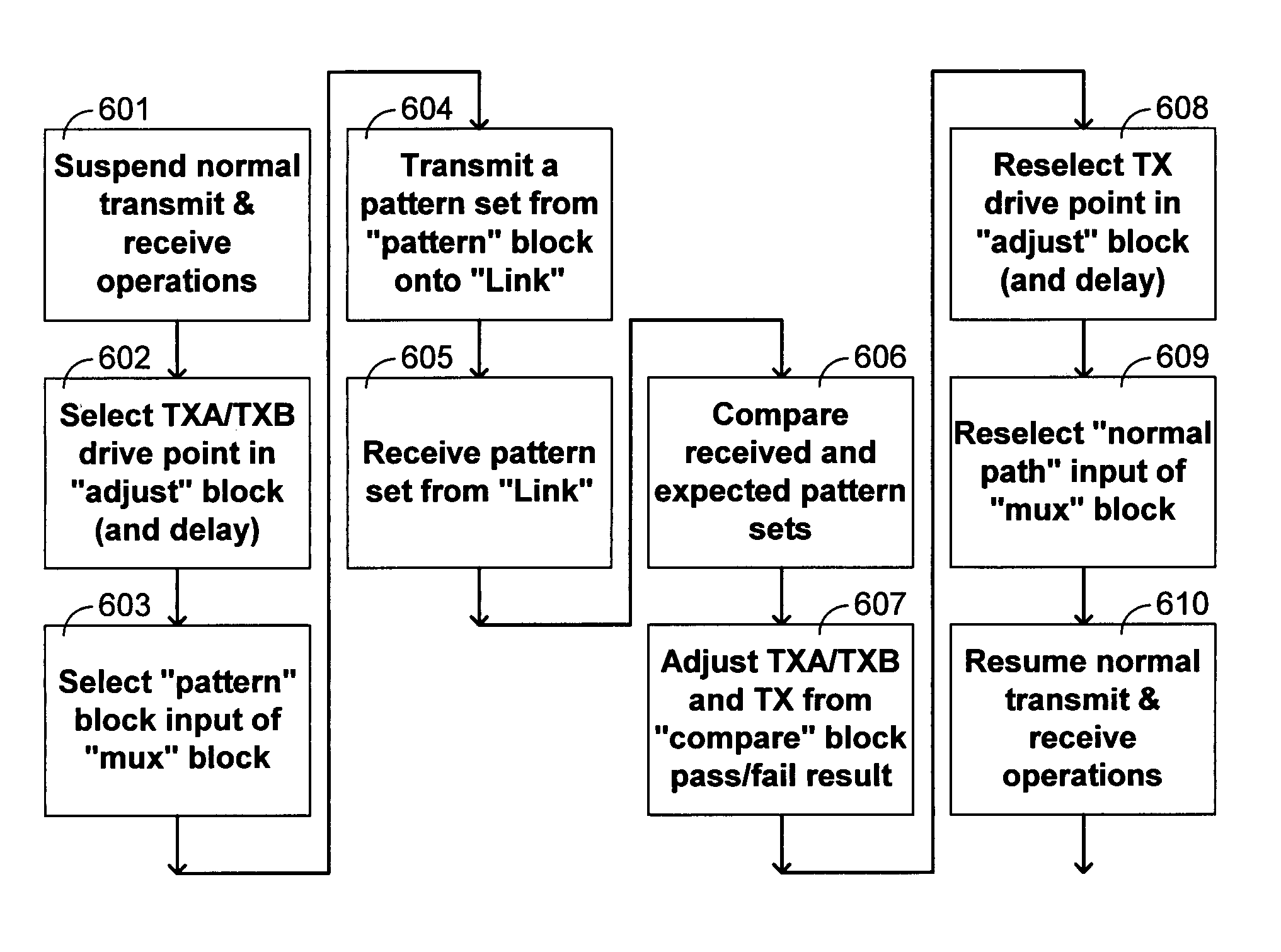
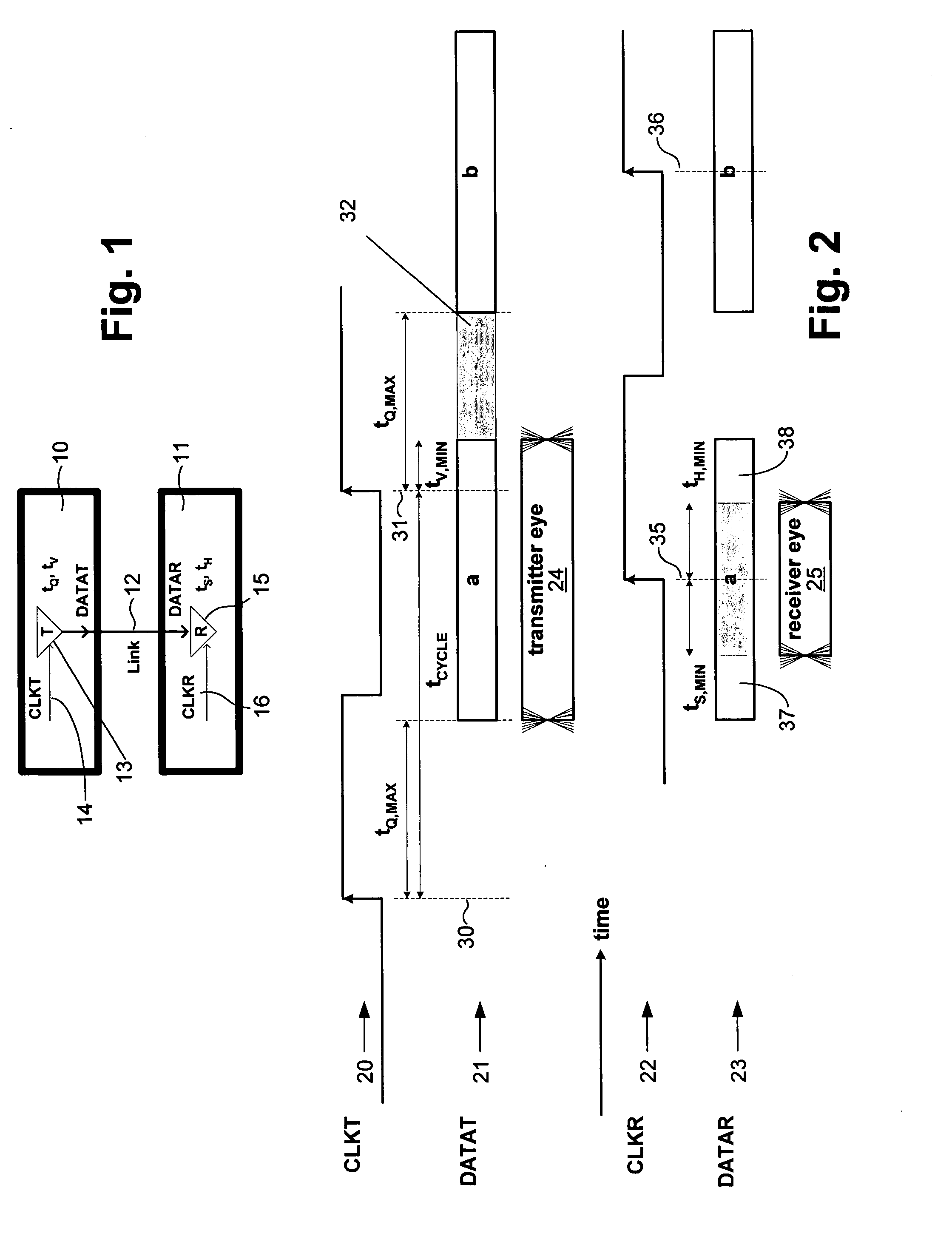
ActiveUS7095789B2Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingTelecommunications linkData source
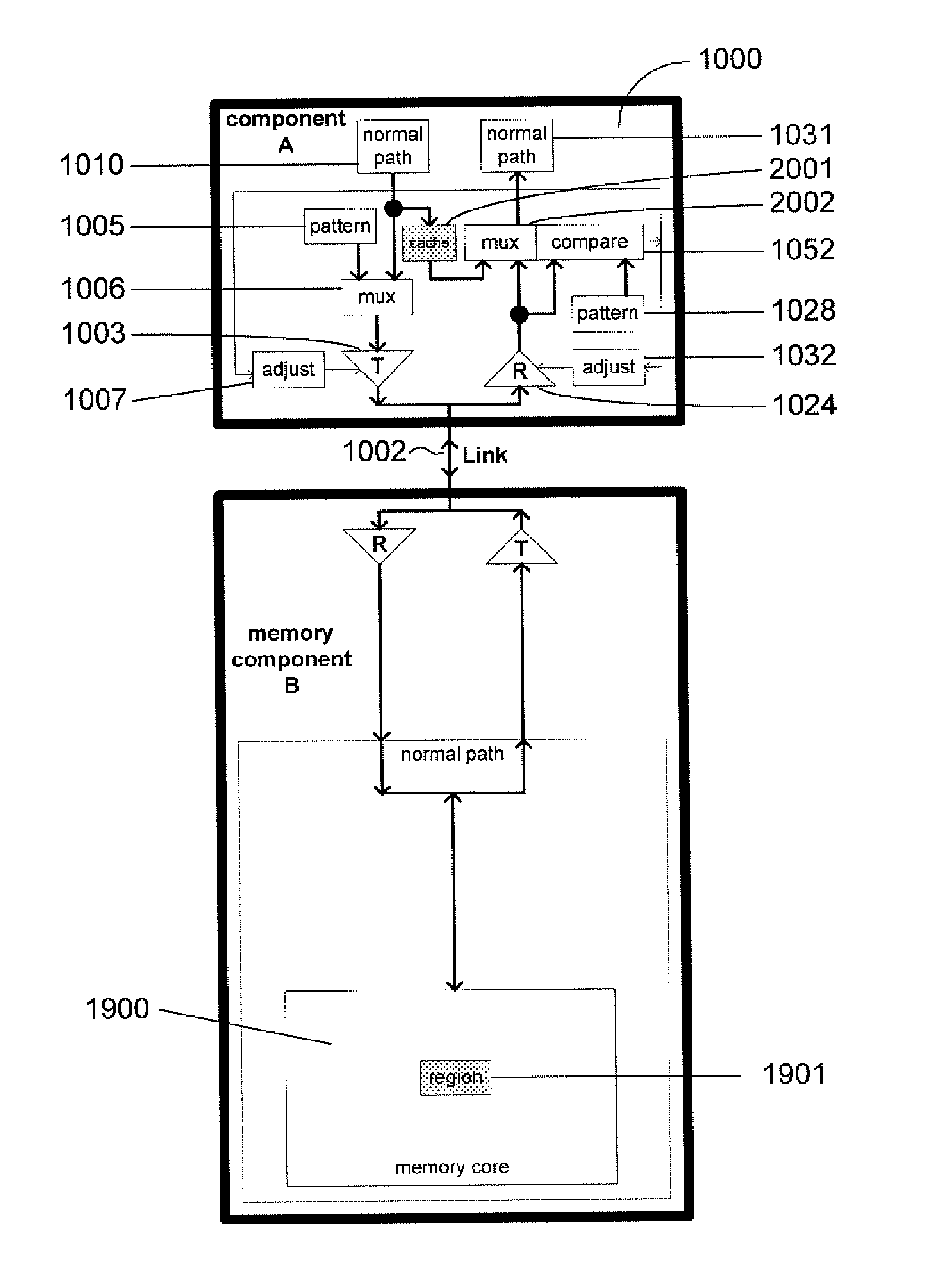
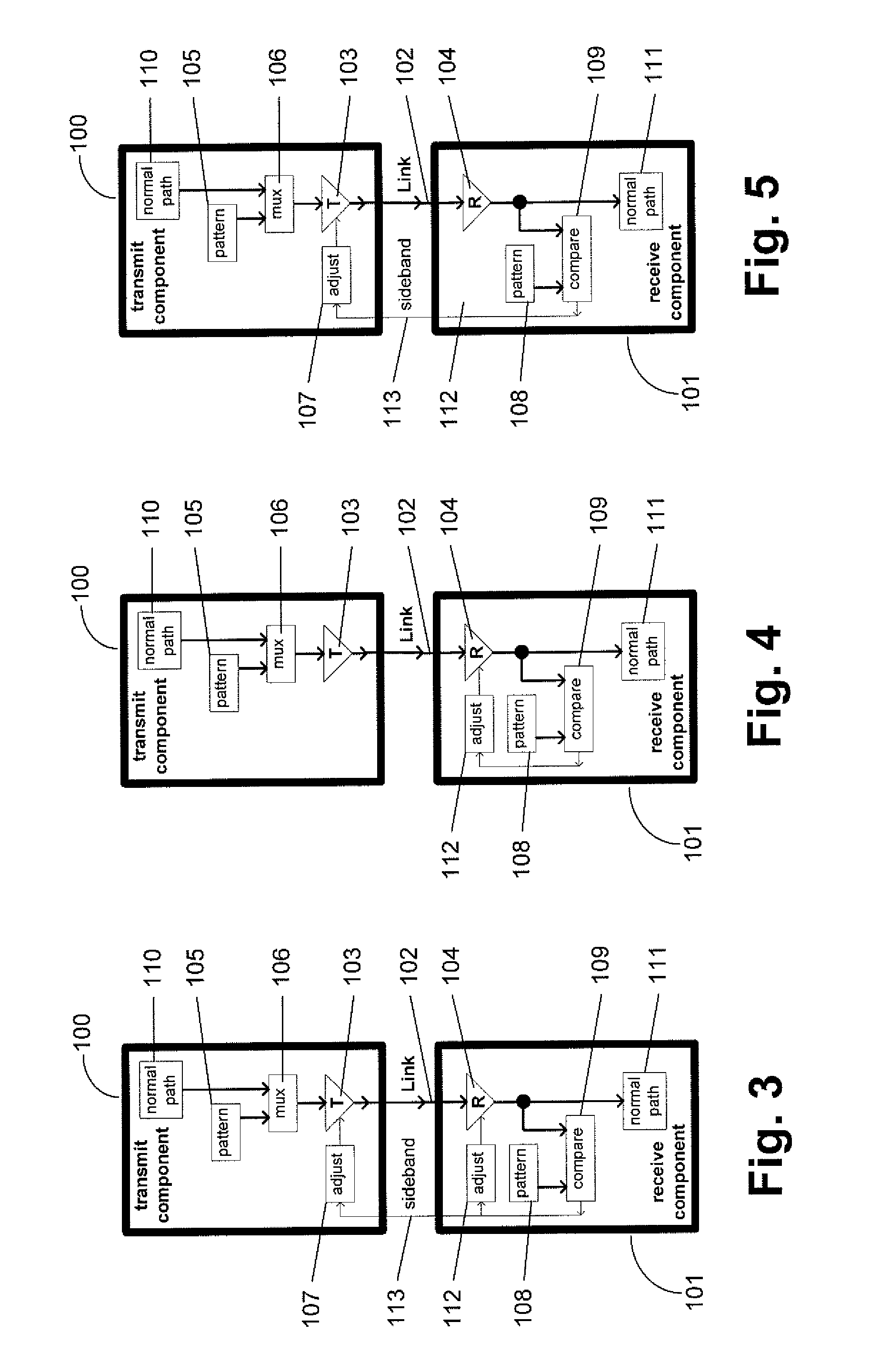
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:K MIZRA LLC
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
ActiveUS20050163203A1Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingTelecommunications linkData source
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
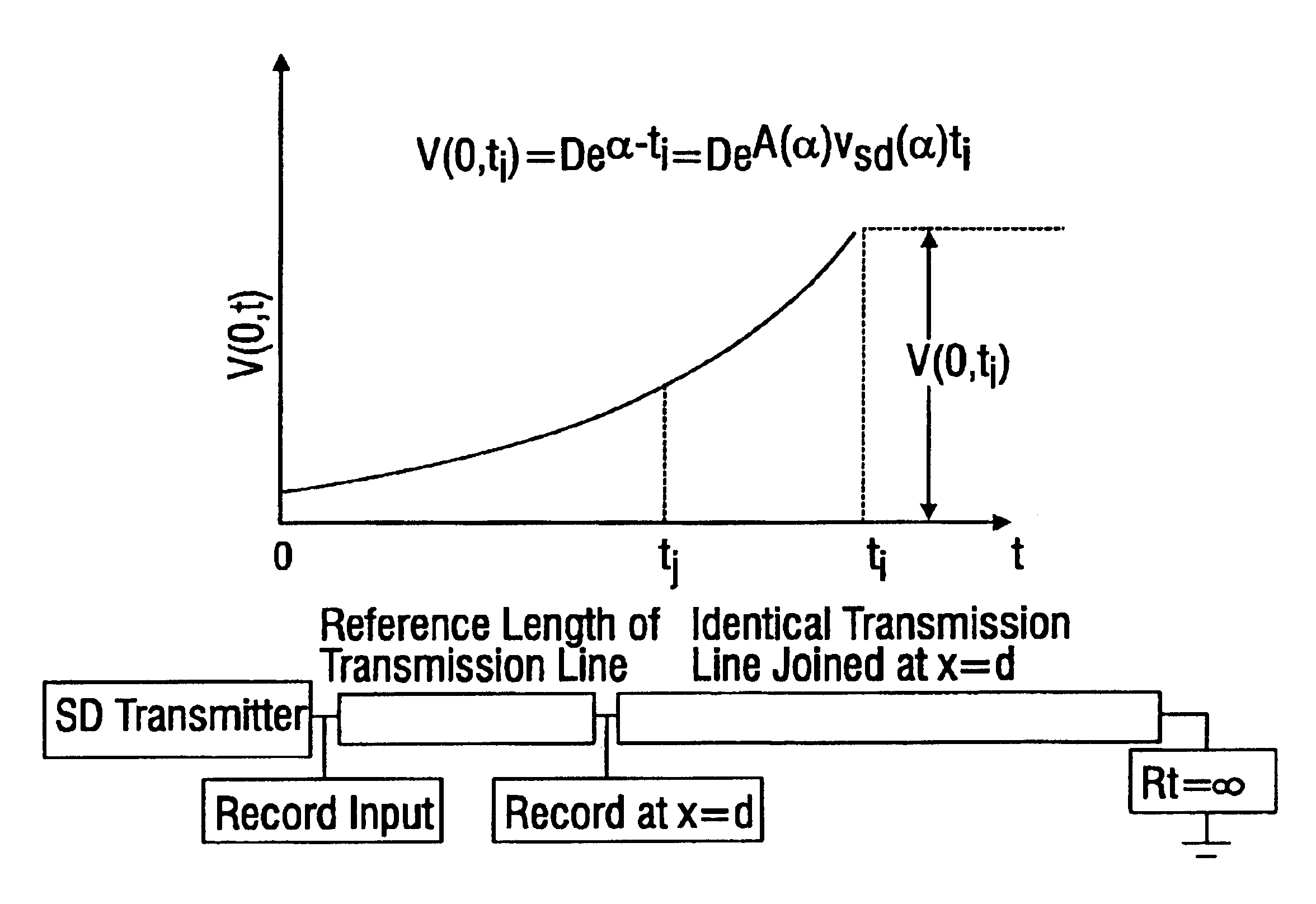
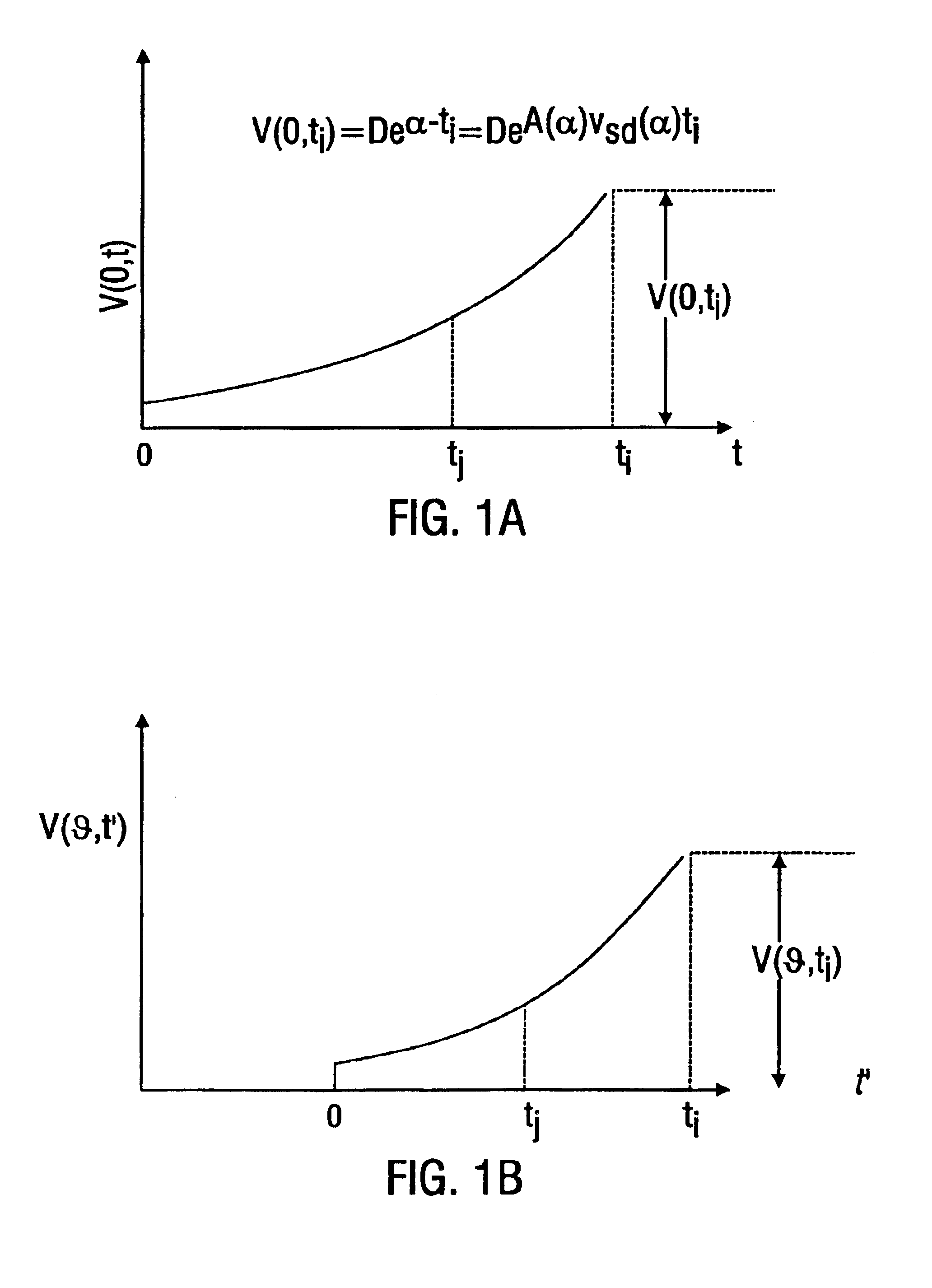
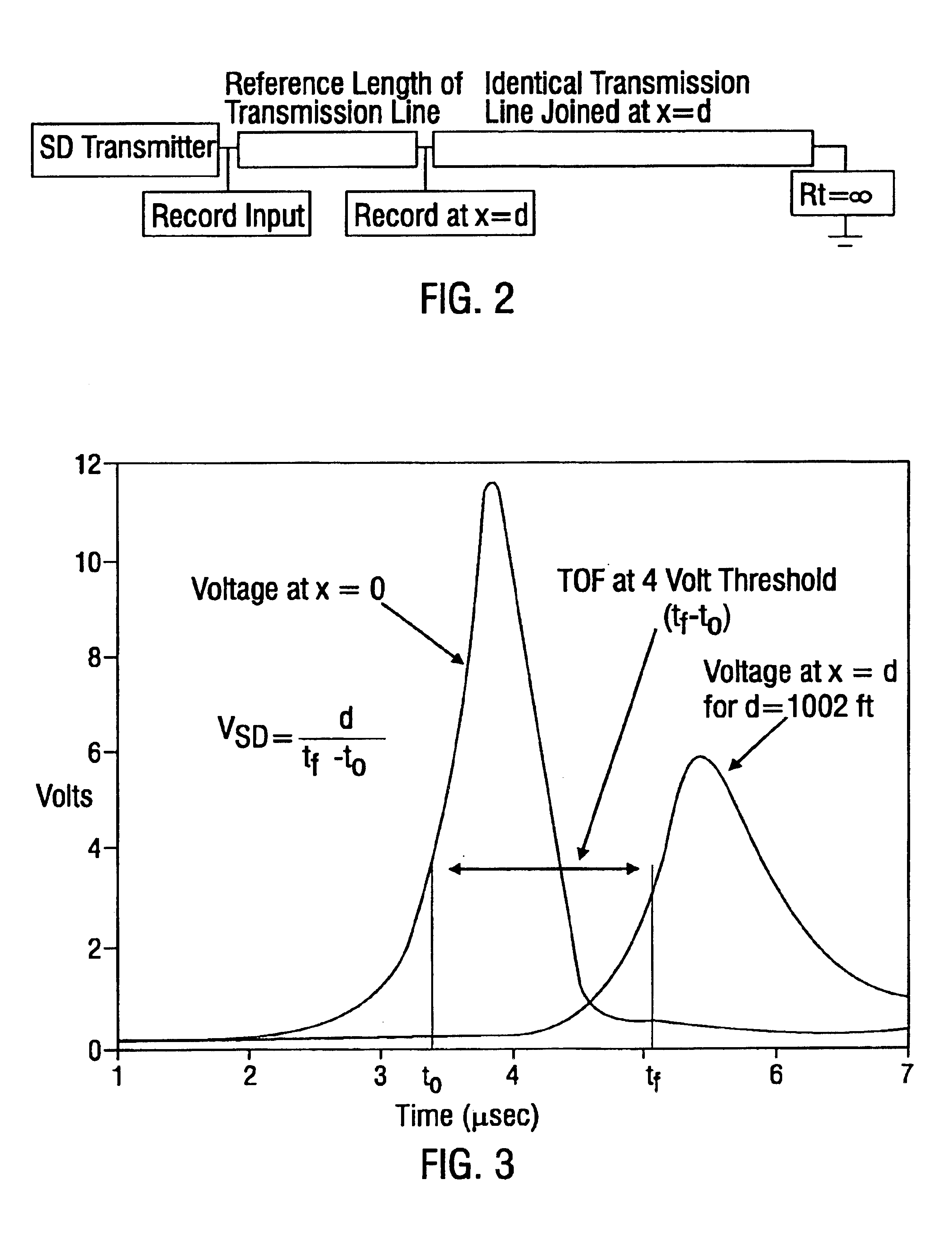
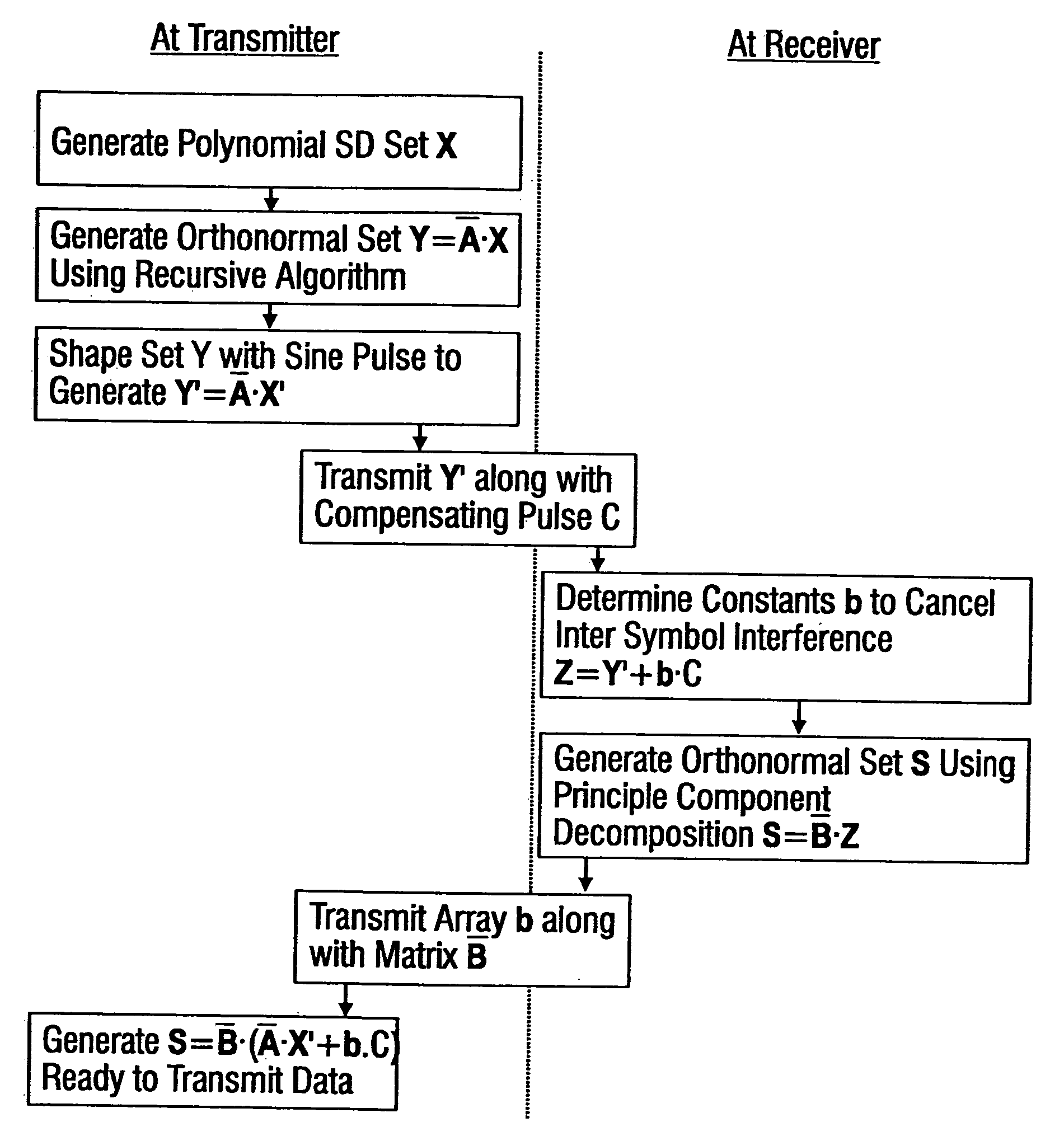
Methods for transmitting a waveform having a controllable attenuation and propagation velocity
InactiveUS6847267B2Transmission control/equlisationLine impedence variation compensationSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
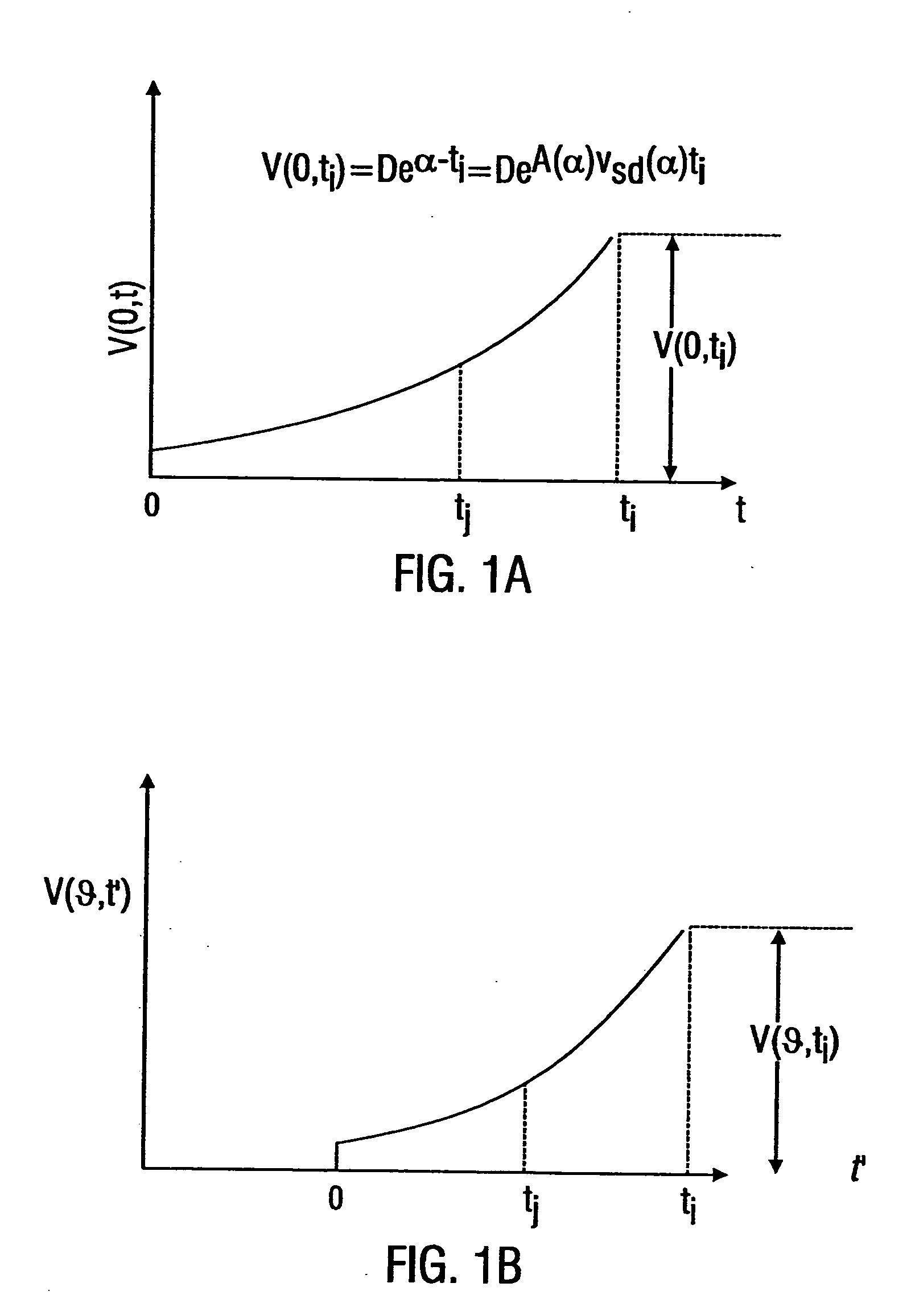
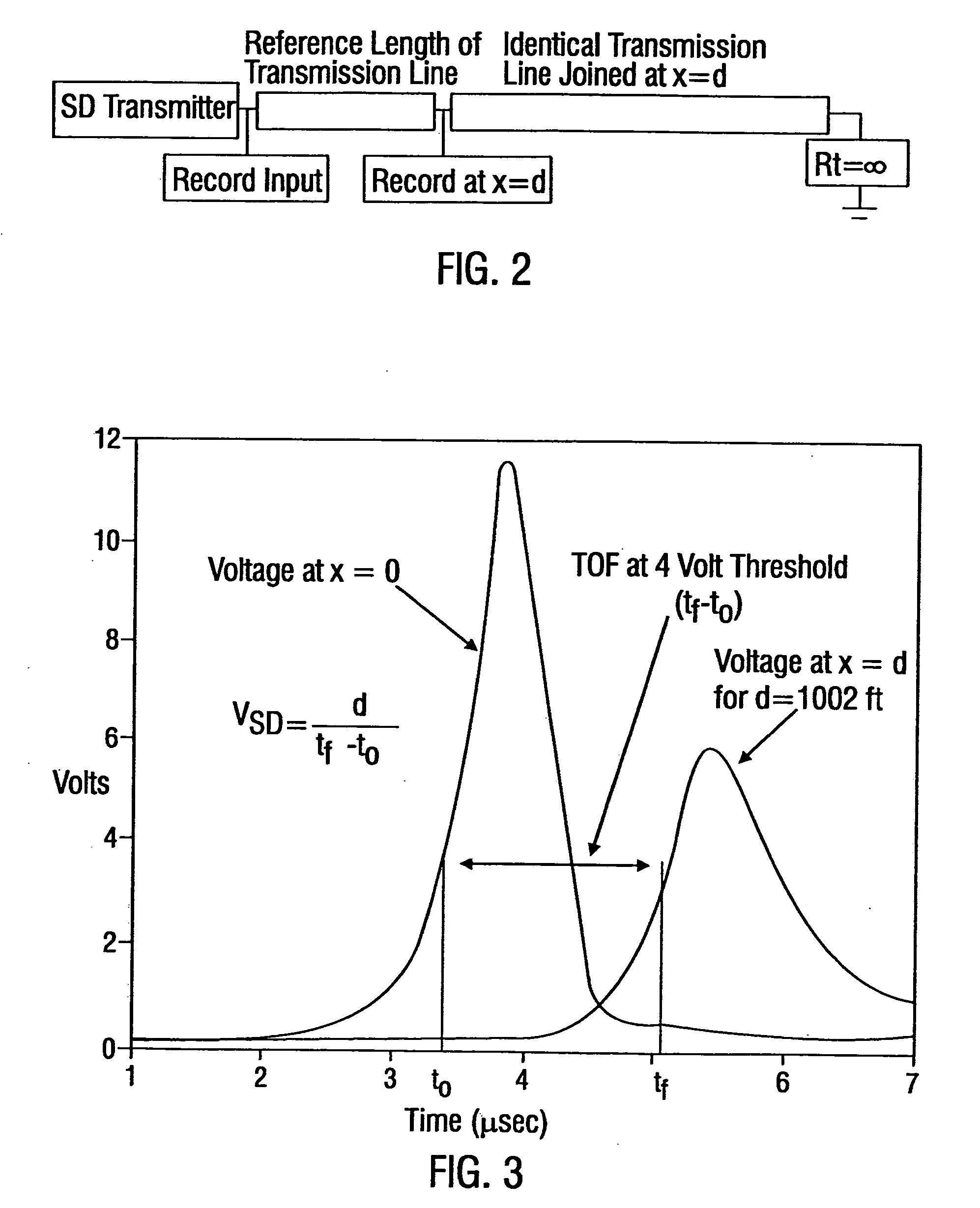
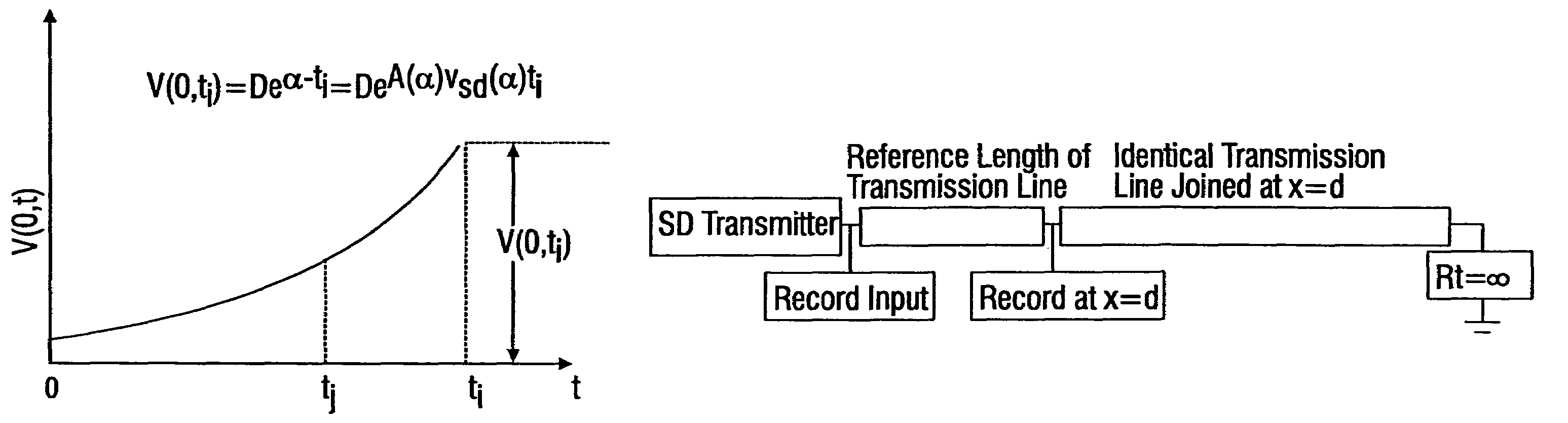
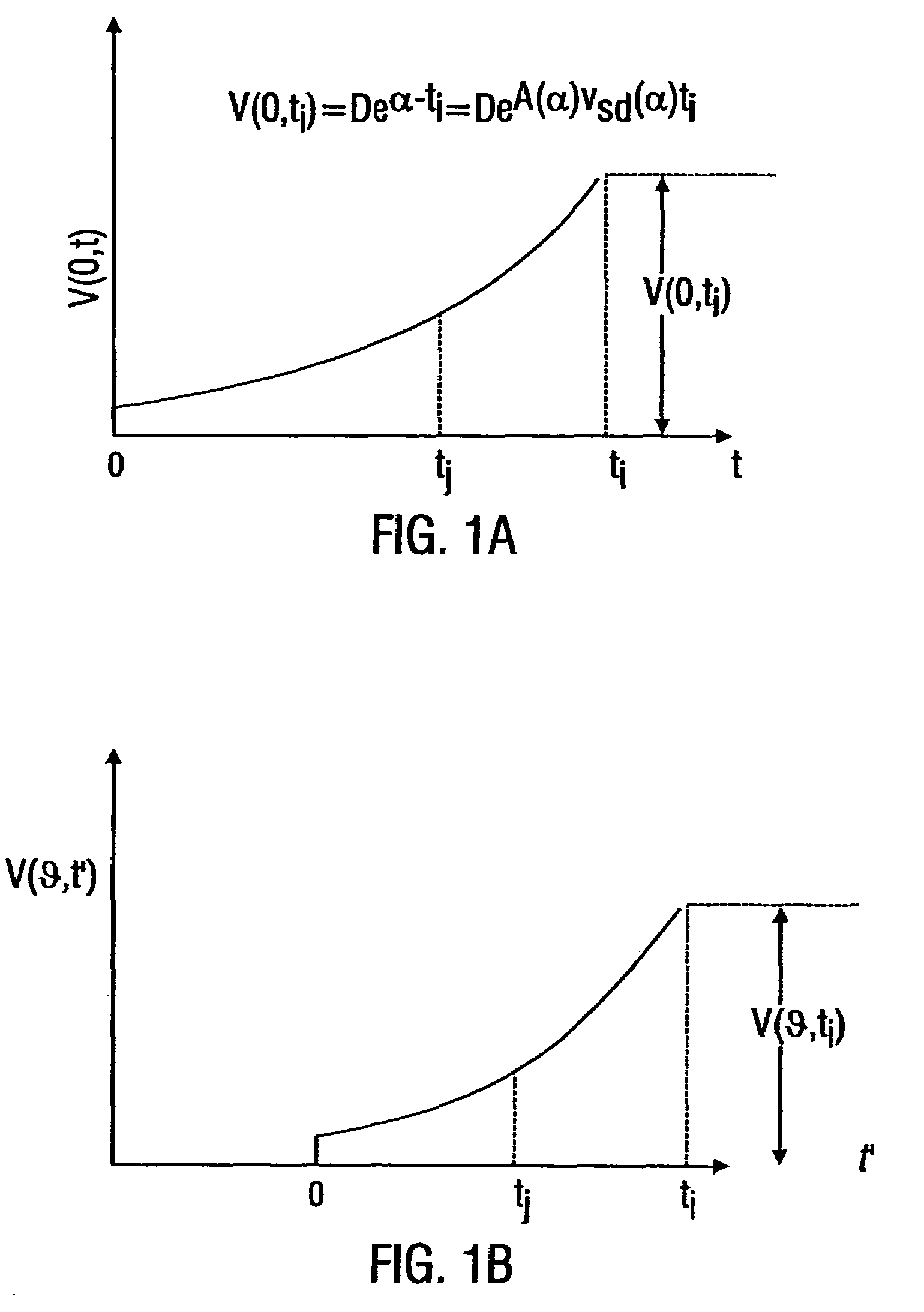
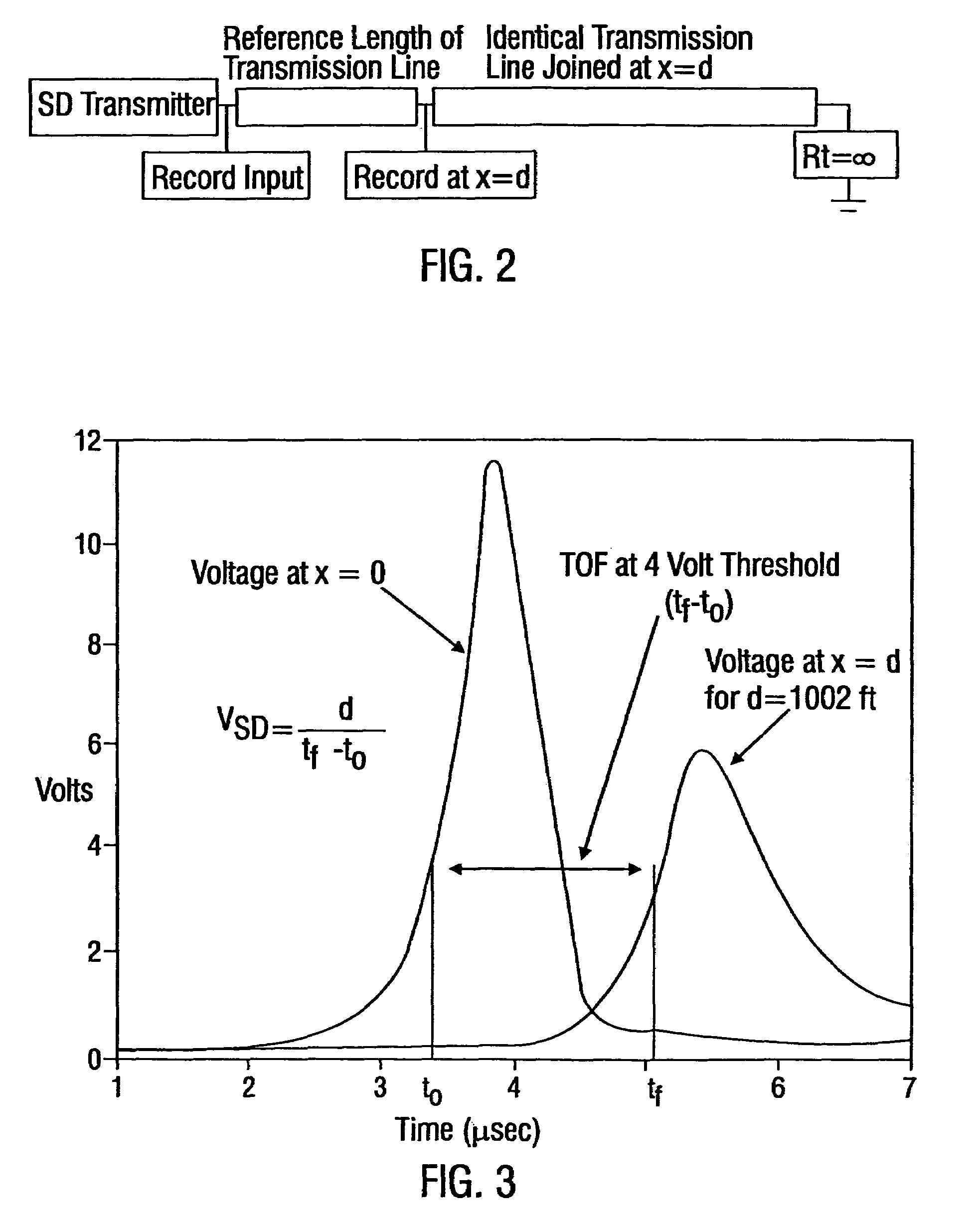
Systems and methods are described for transmitting a waveform having a controllable attenuation and propagation velocity. An exemplary method comprises: generating an exponential waveform, the exponential waveform (a) being characterized by the equation Vin=De−A<sub2>SD< / sub2>(x−v<sub2>SD< / sub2>t), where D is a magnitude, Vin is a voltage, t is time, ASD is an attenuation coefficient, and VSD is a propagation velocity; and (b) being truncated at a maximum value. An exemplary apparatus comprises: an exponential waveform generator; an input recorder coupled to an output of the exponential waveform generator; a transmission line under test coupled to the output of the exponential waveform generator; an output recorder coupled to the transmission line under test; an additional transmission line coupled to the transmission line under test; and a termination impedance coupled to the additional transmission line and to a ground.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for propagating a non sinusoidal signal without distortion in dispersive lossy media
InactiveUS20050213684A1Reducing interconnect delayReduce delaysLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
Systems and methods are described for transmitting a waveform having a controllable attenuation and propagation velocity. An exemplary method comprises: generating an exponential waveform, the exponential waveform (a) being characterized by the equation Vin=De−A<sub2>SD< / sub2>[x−v<sub2>SD< / sub2>t], where D is a magnitude, Vin is a voltage, t is time, ASD is an attenuation coefficient, and vSD is a propagation velocity; and (b) being truncated at a maximum value. An exemplary apparatus comprises: an exponential waveform generator; an input recorder coupled to an output of the exponential waveform generator; a transmission line under test coupled to the output of the exponential waveform generator; an output recorder coupled to the transmission line under test; an additional transmission line coupled to the transmission line under test; and a termination impedance coupled to the additional transmission line and to a ground.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
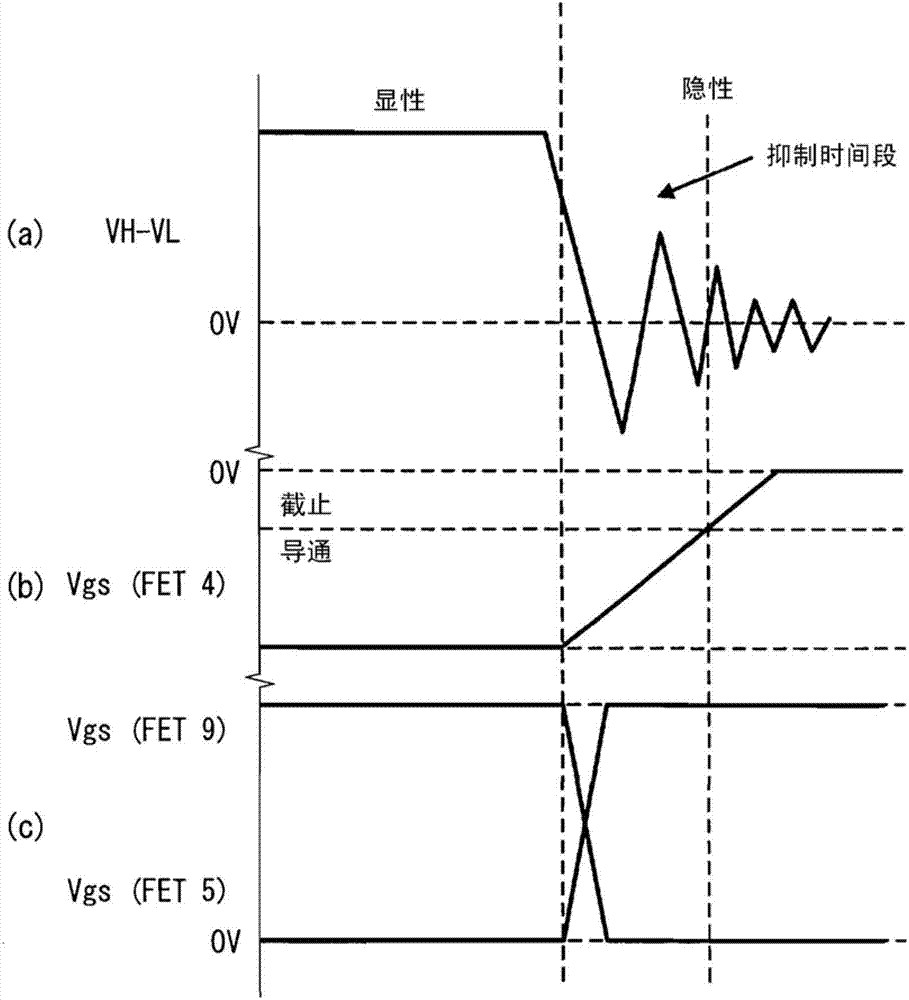
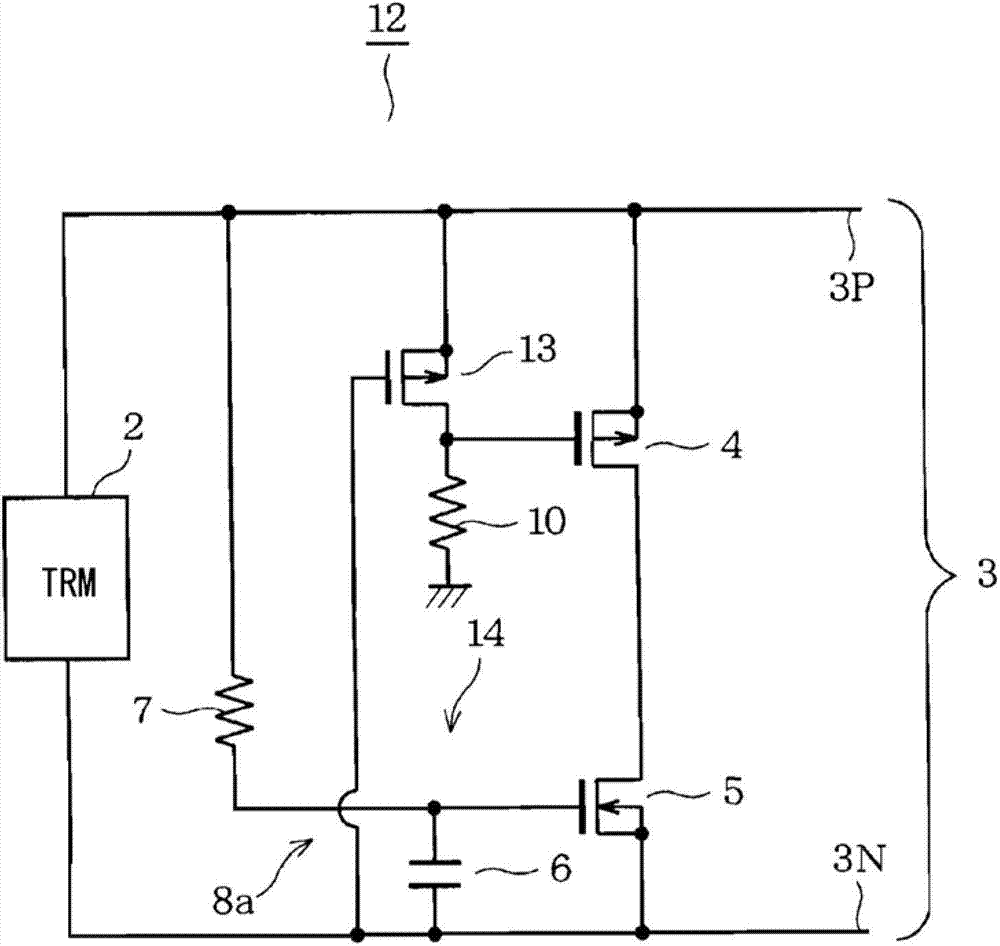
Ringing suppression circuit
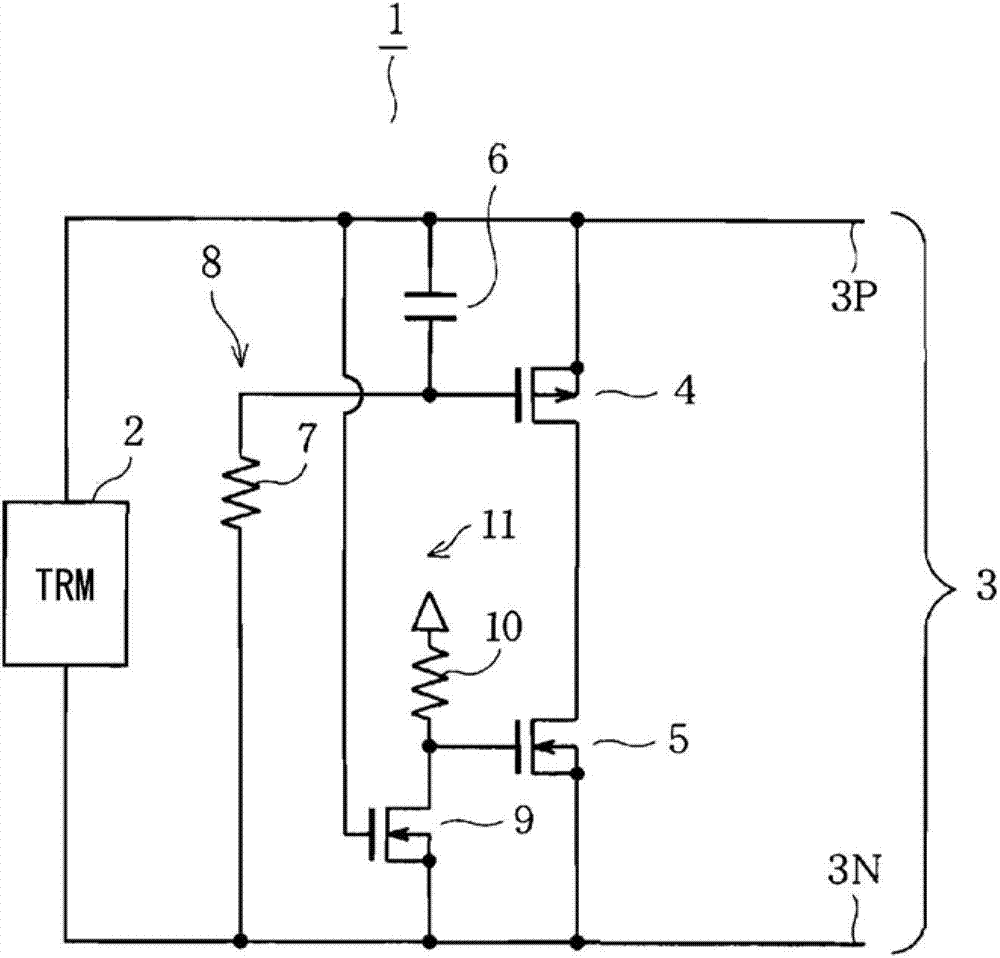
ActiveCN102790735ALine impedence variation compensationRinging signal bypassing circuitsMOSFETDifferential signaling
An inter-line switching element formed of a MOSFET(4,5,7) is provided between a pair of signal lines(3P,3N). When the level of a differential signal changes from high to low, a control circuit turns on the FET for a fixed period thereby to suppress ringing by decreasing the impedance between the signal lines(3P,3N) when the level of the differential signal transitions, and causing the energy of the distortion of the differential signal waveform to be absorbed by the on-resistance of the FET(4,5,7).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Modems
InactiveUS20050243983A1Significant differenceLine impedence variation compensationPower distribution line transmissionElectrical conductorModem device
A modem for receiving and transmitting data from and to a conductor comprises an output drive for transmitting data to the conductor, a receiver for receiving data from the conductor and impedance matching means for matching the impedance of the receiver input with the impedance of the conductor, wherein the gain of the output drive, the receiver gain and the impedance of the receiver input are all adjustable.
Owner:VETCO GRAY CONTROLS
Repeaters with fast transitions from low-power standby to low-frequency signal transmission
ActiveUS20190288743A1Line impedence variation compensationPulse automatic controlEngineeringLow power dissipation
Repeaters are described that operate to rapidly transition from low-power standby states to a low frequency signal transmission state. Bandwidth for high-frequency signal transmission is preserved.
Owner:PERICOM SEMICON
Power supply system, powered device, and power reception method
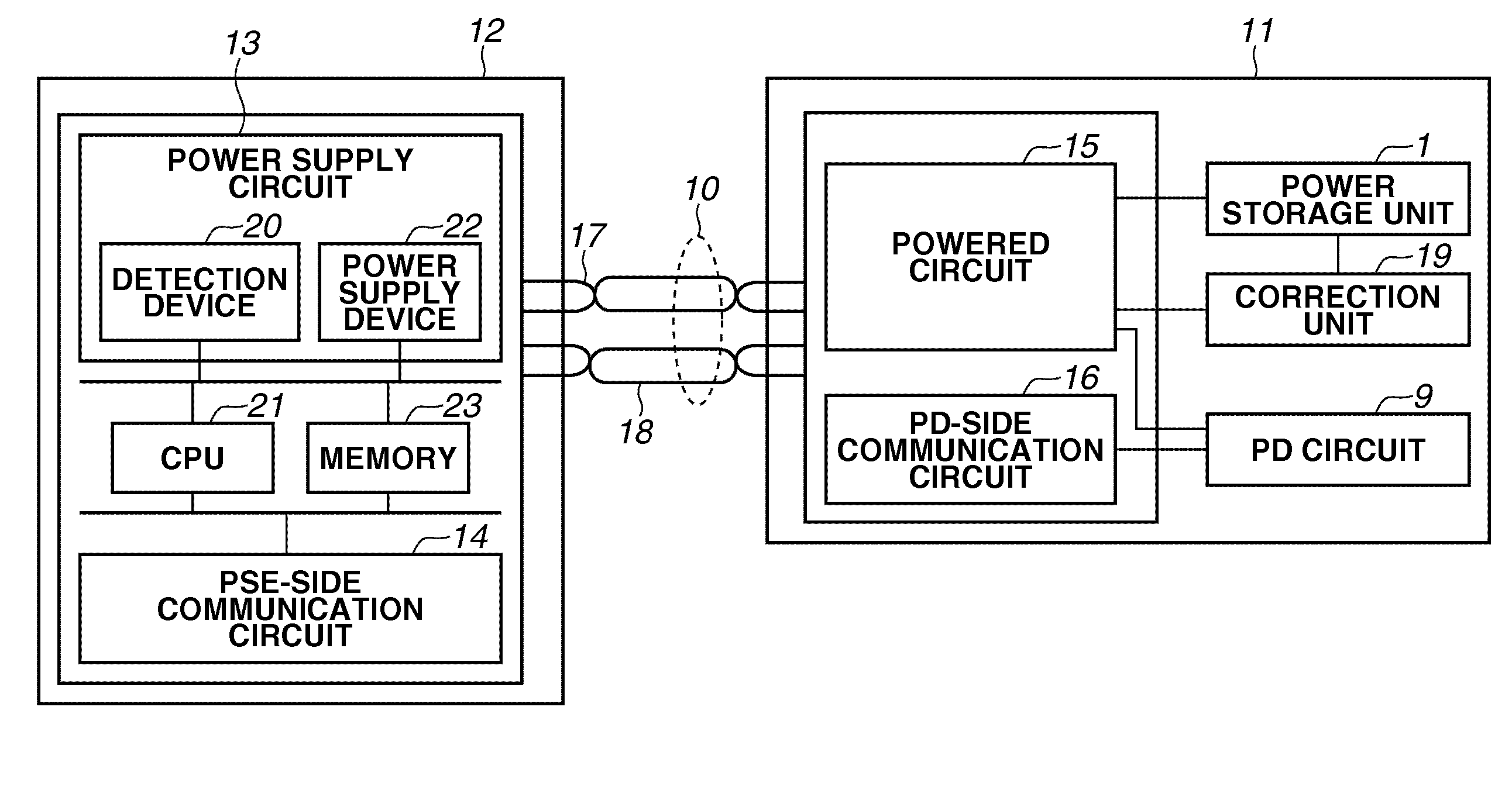
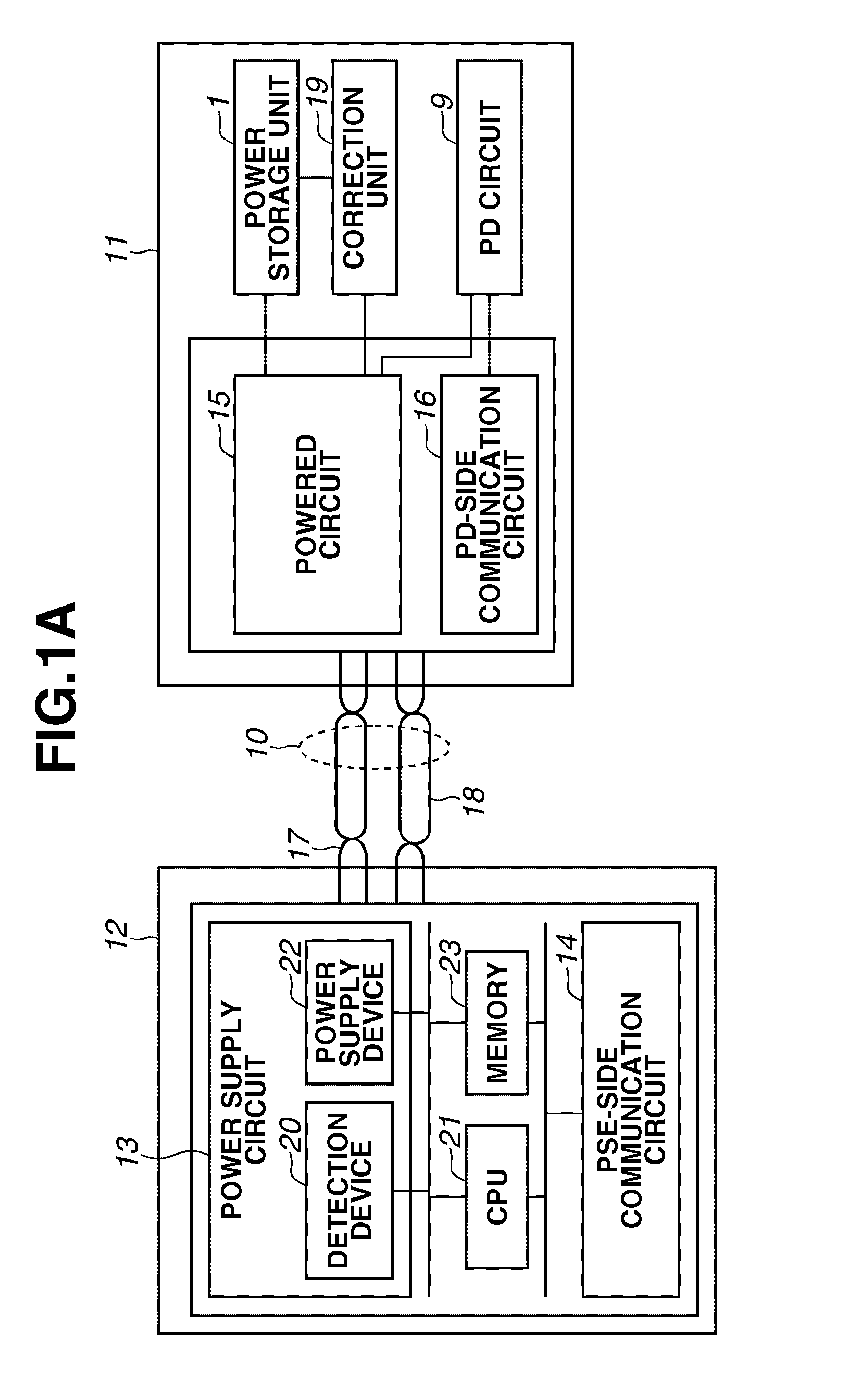
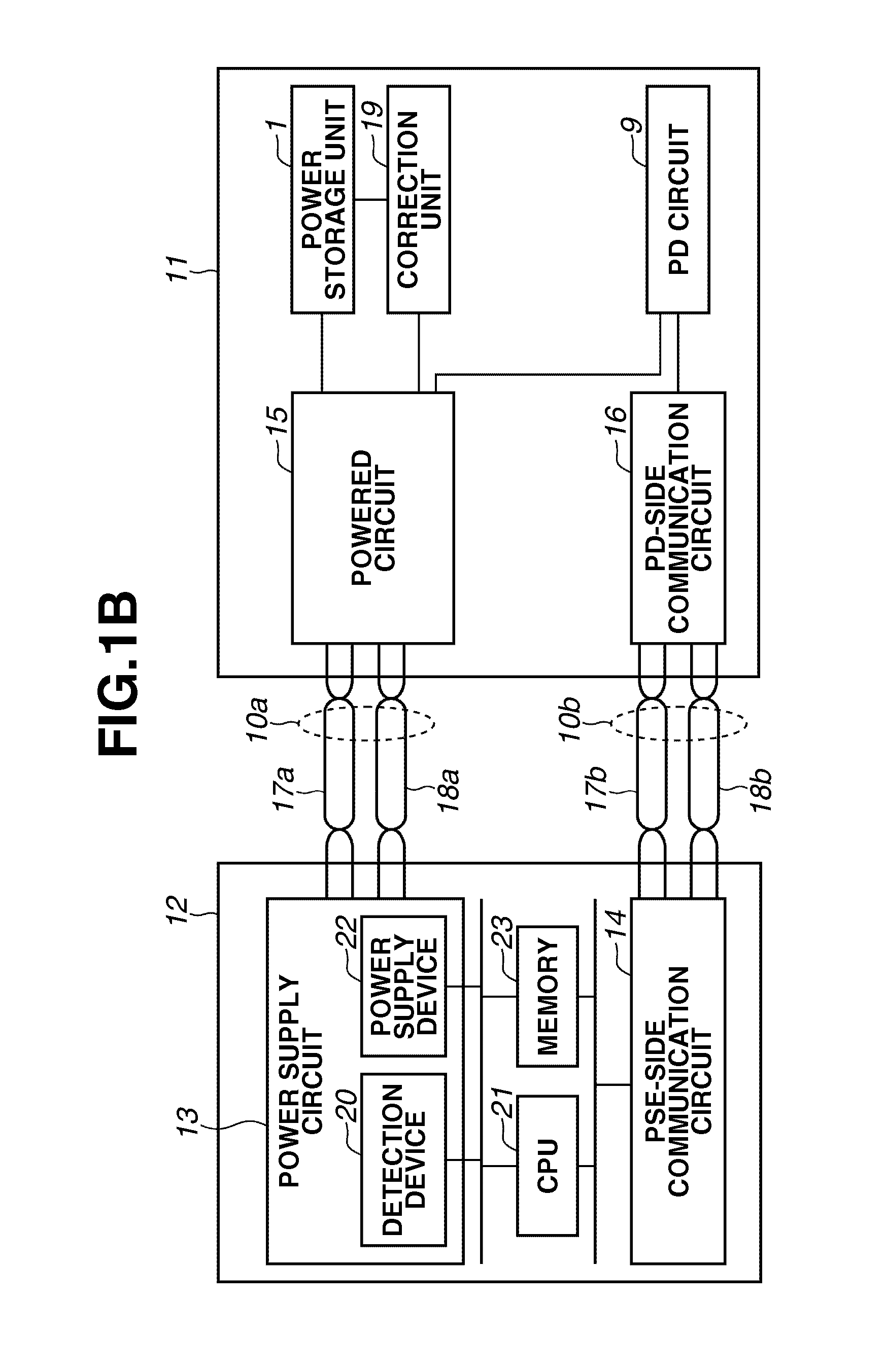
InactiveUS20110202784A1Improve connectivitySmooth connectionLine impedence variation compensationDigital data processing detailsElectricityEngineering
Power sourcing equipment starts power supply after outputting a detection signal to a transmission line and detecting that a powered device is connected with the transmission line. The powered device includes a power storage unit configured to store power obtained from the detection signal output from the power sourcing equipment, and a correction unit configured to correct an impedance unbalance in the transmission line. The power storage unit provides the stored power to the correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
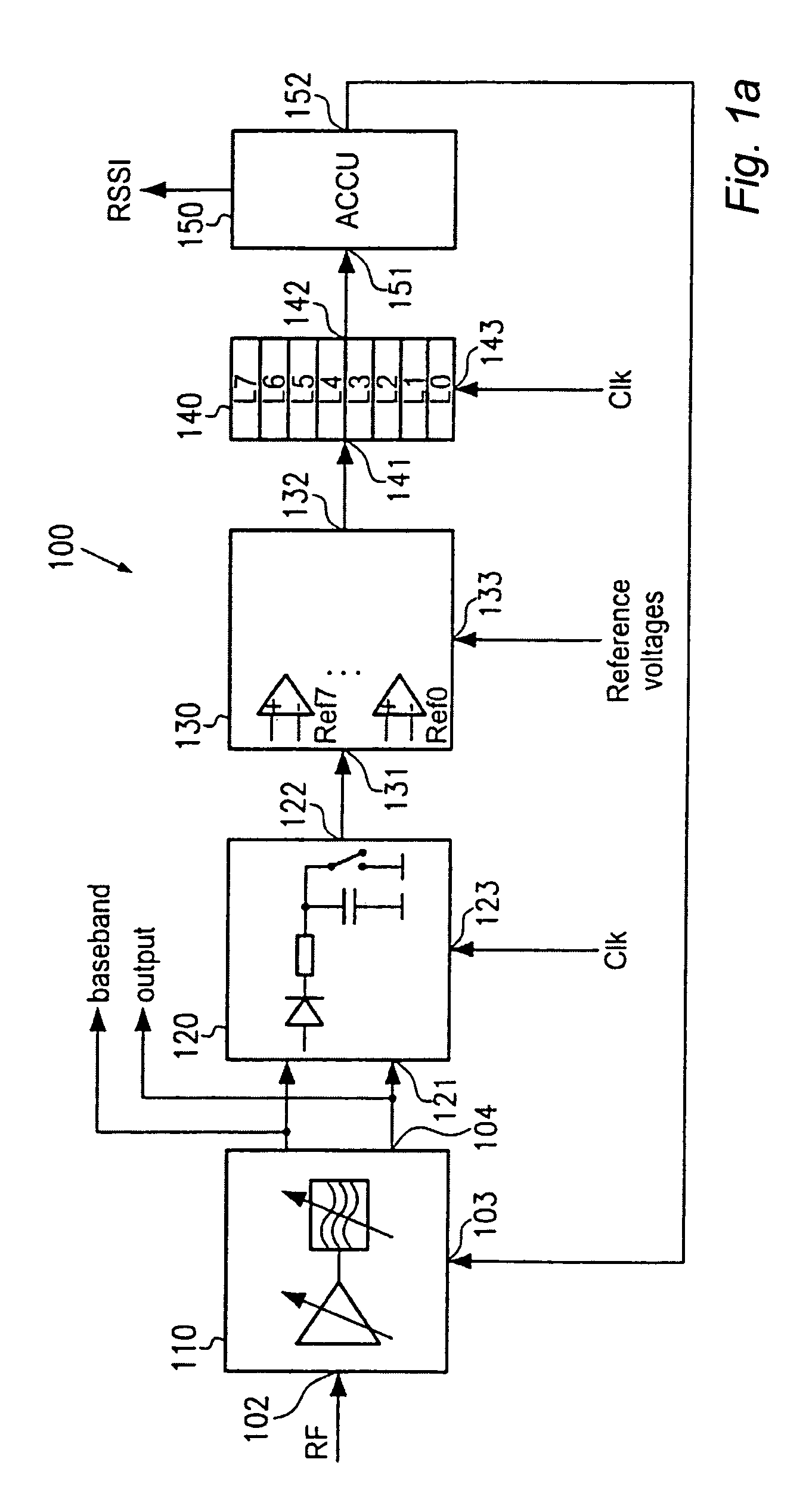
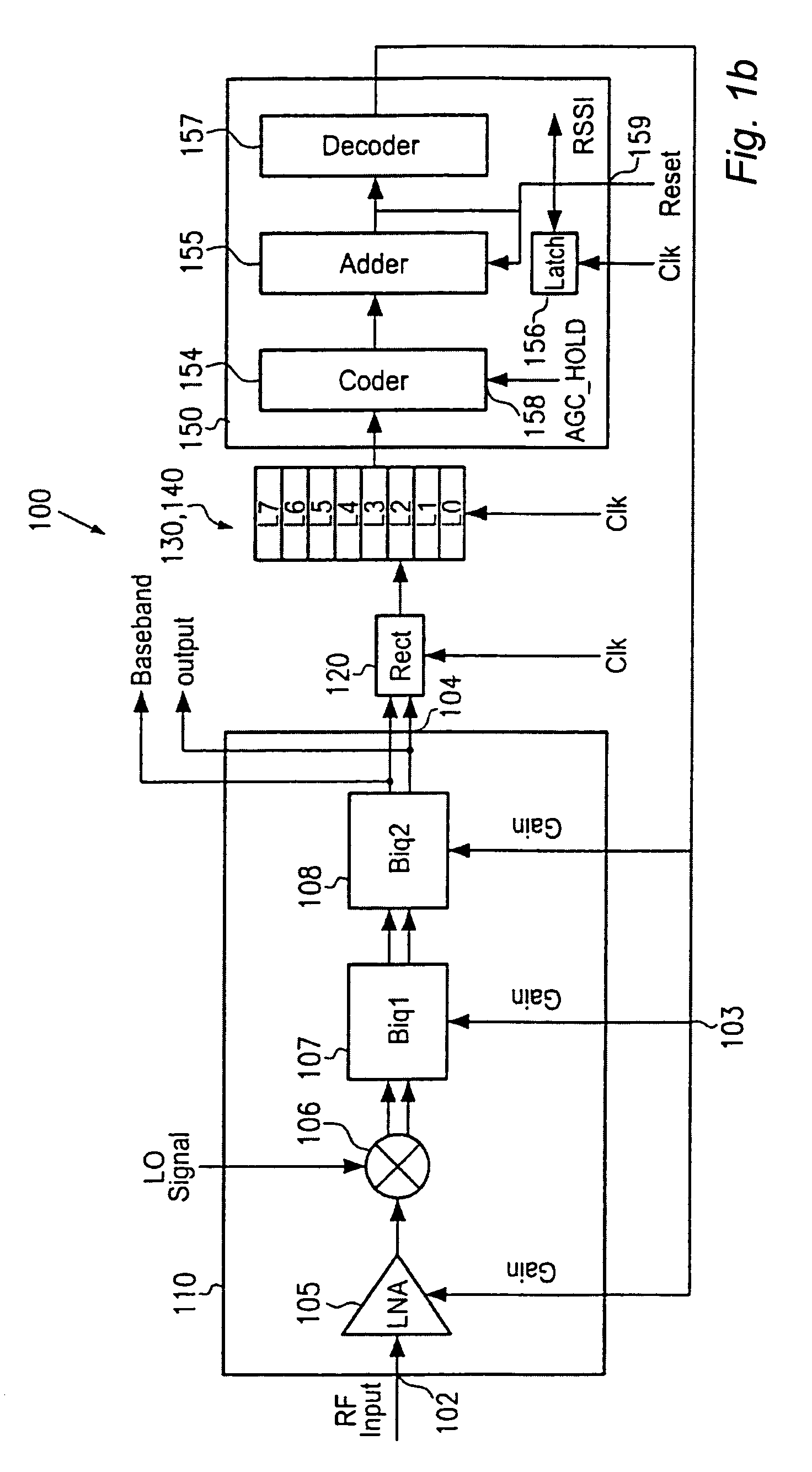
Digital automatic gain control for transceiver devices
ActiveUS7184729B2Effective gain controlSimple designTransmission control/equlisationLine impedence variation compensationDigital topologyTransceiver
An automatic gain controller for transceiver elements uses a digital topology to achieve an efficient and rapid gain settling so that an output signal of the variable gain section is within a predefined range. In one embodiment, an input signal is periodically sampled and latched so as represent the gain excess of a variable gain section. An accumulator, including an adder having saturation characteristics and a latch as a feedback element, creates a number for a new gain setting so that the variable gain section may adapt to the new gain setting within one clock period. In one example, a gain range of 84 dB is controllable and settling is achieved within 3 clock periods at most.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
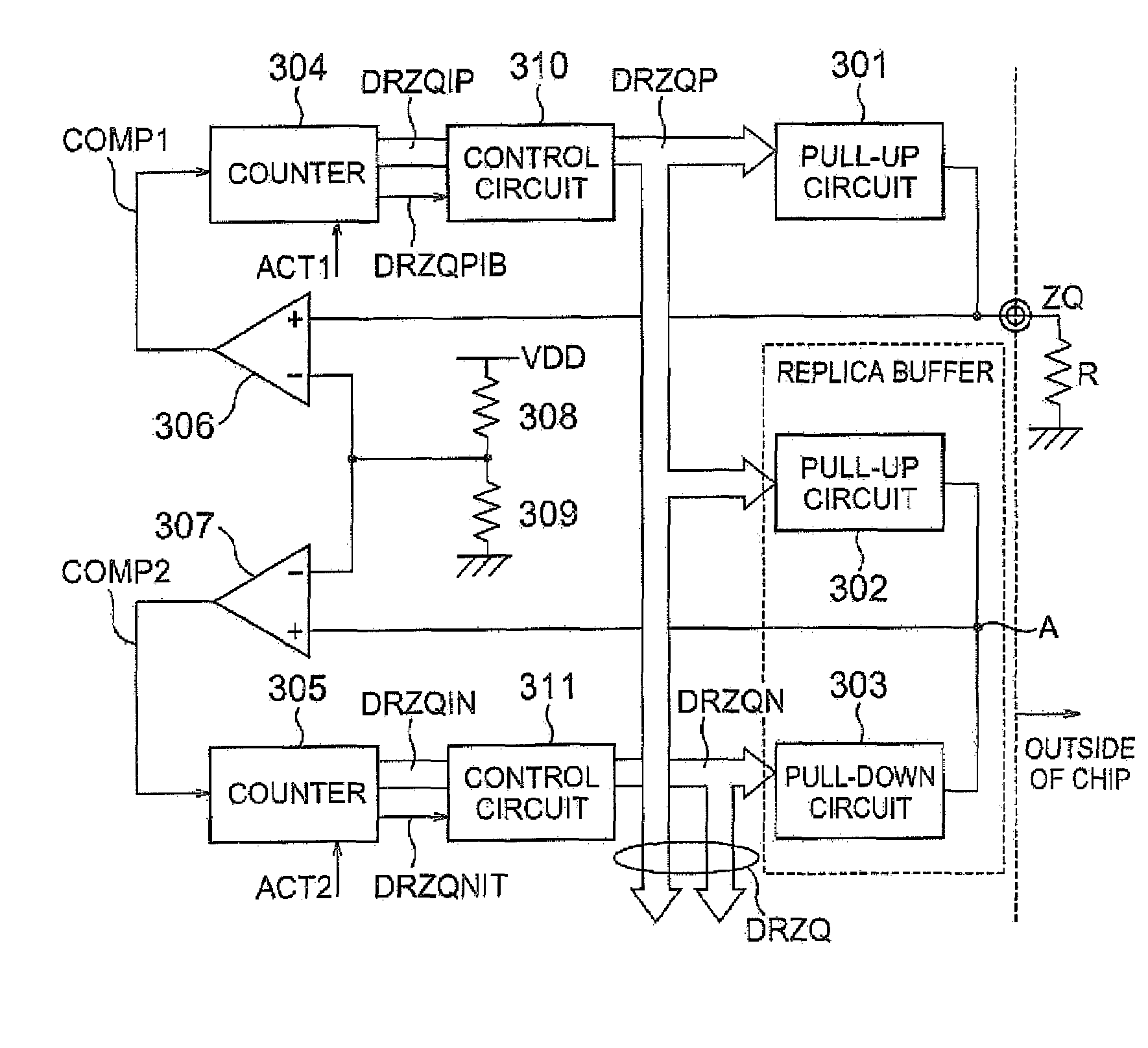
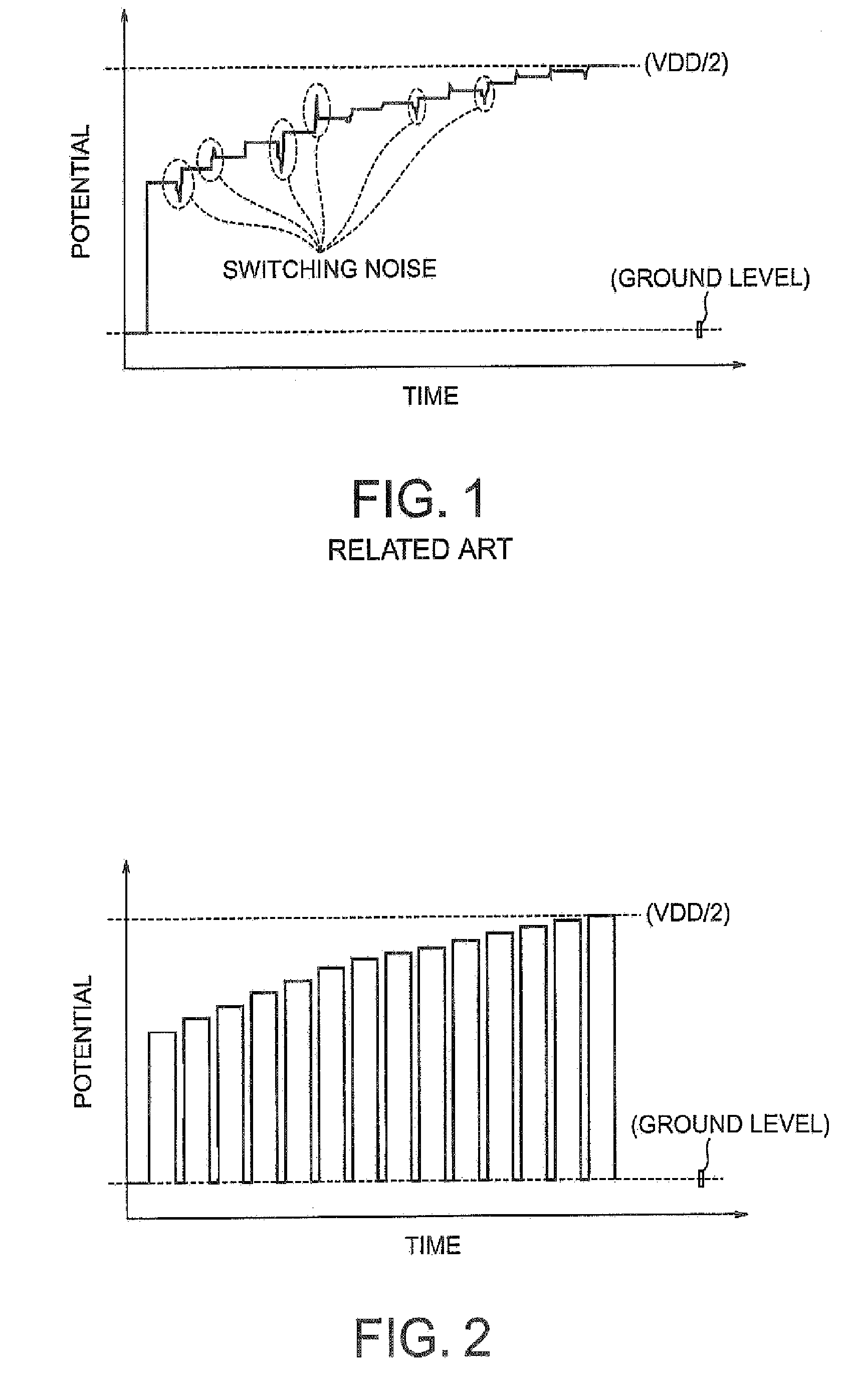
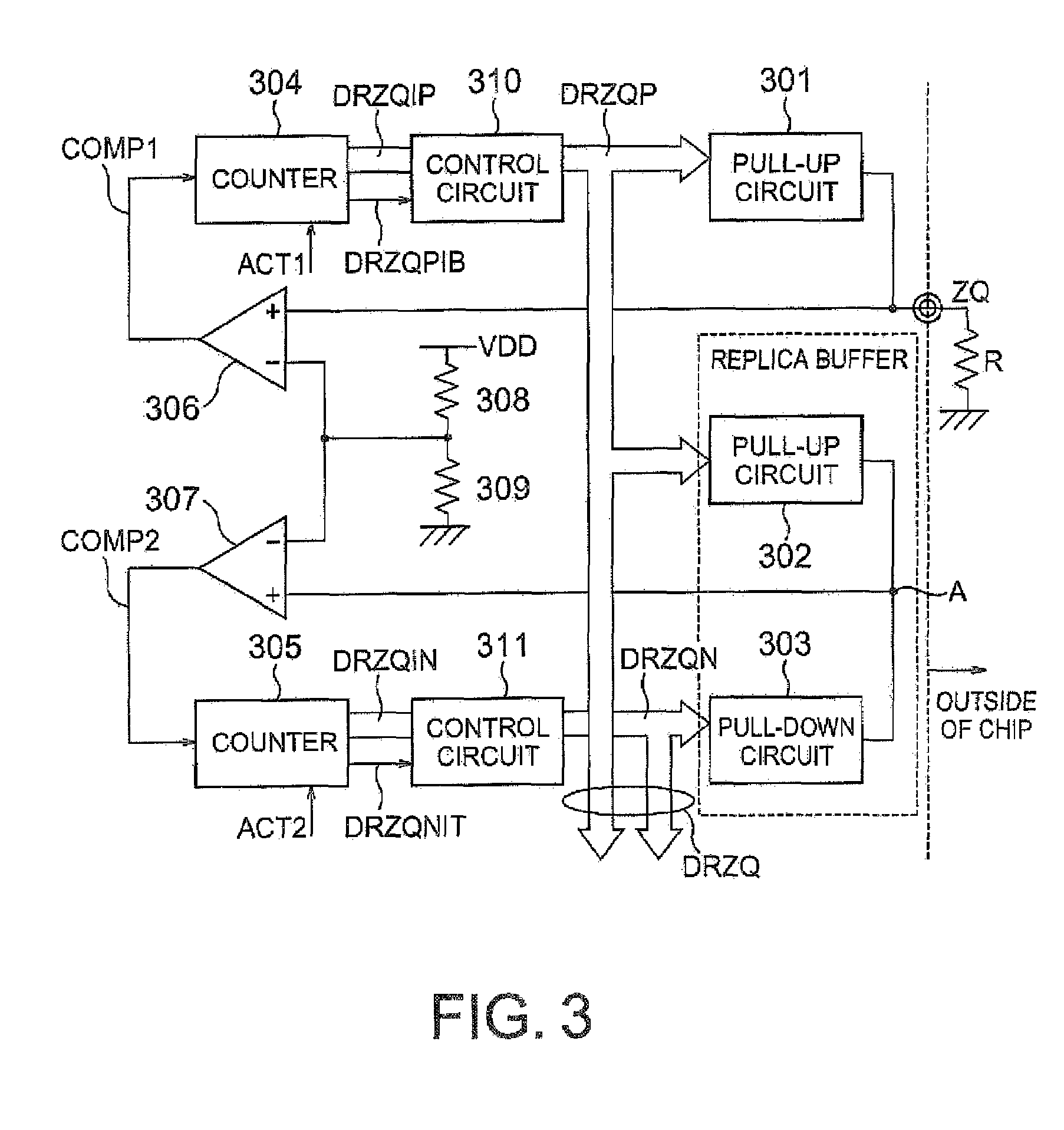
Calibration circuit and semiconductor device incorporating the same
ActiveUS7595645B2Stable levelStable comparisonLine impedence variation compensationDigital storageEngineeringElectrical impedance
Impedance adjusting transistors are once inactivated on every occasion of changing an impedance adjusting code. After restoring the potential to an initially set potential by once inactivating the impedance adjusting transistors, the state of the transistors is switched according to the impedance adjusting code. By starting the potential from the initially set potential at the time of switching the state of the transistors, no switching noise is generated. Since no switching noise is generated, a comparator always carries out stable comparison and judgment and thus there is obtained a calibration circuit that ensures stable outputs.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Test switching circuit for a high speed data interface
InactiveCN1715943ADetection errorReduce power consumptionLine impedence variation compensationDigital circuit testingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Test switching circuit for a high speed data interface ( 1 ) of an integrated circuit comprising switching transistors (T 1 -T 6 ) which switch in a test mode a termination resistor output stage ( 15 ) of a data transmission signal path ( 17 ) to a termination resistor input stage ( 18 ) of a data reception signal path ( 25 ) to form an internal feedback test loop within said integrated circuit.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
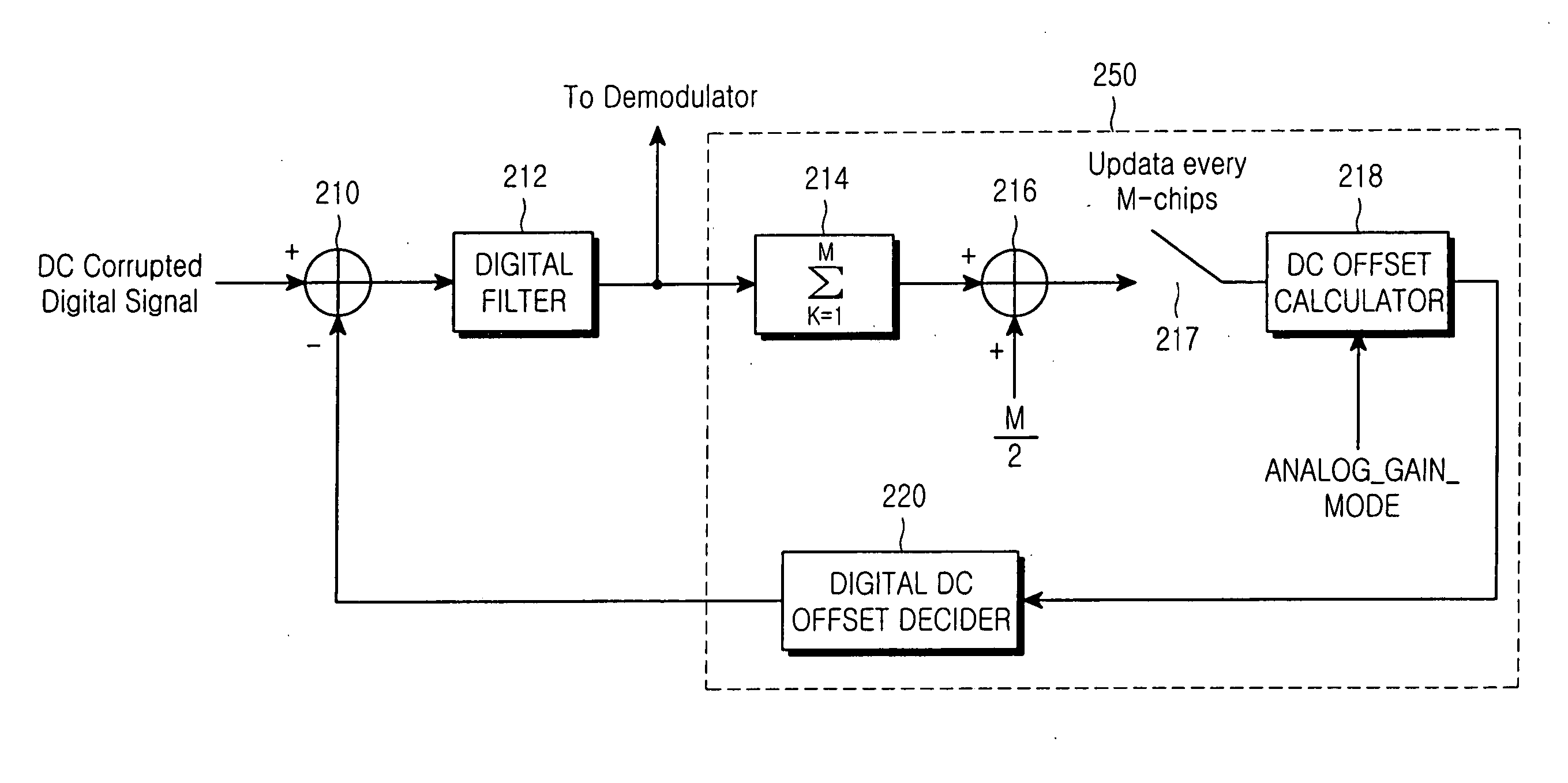
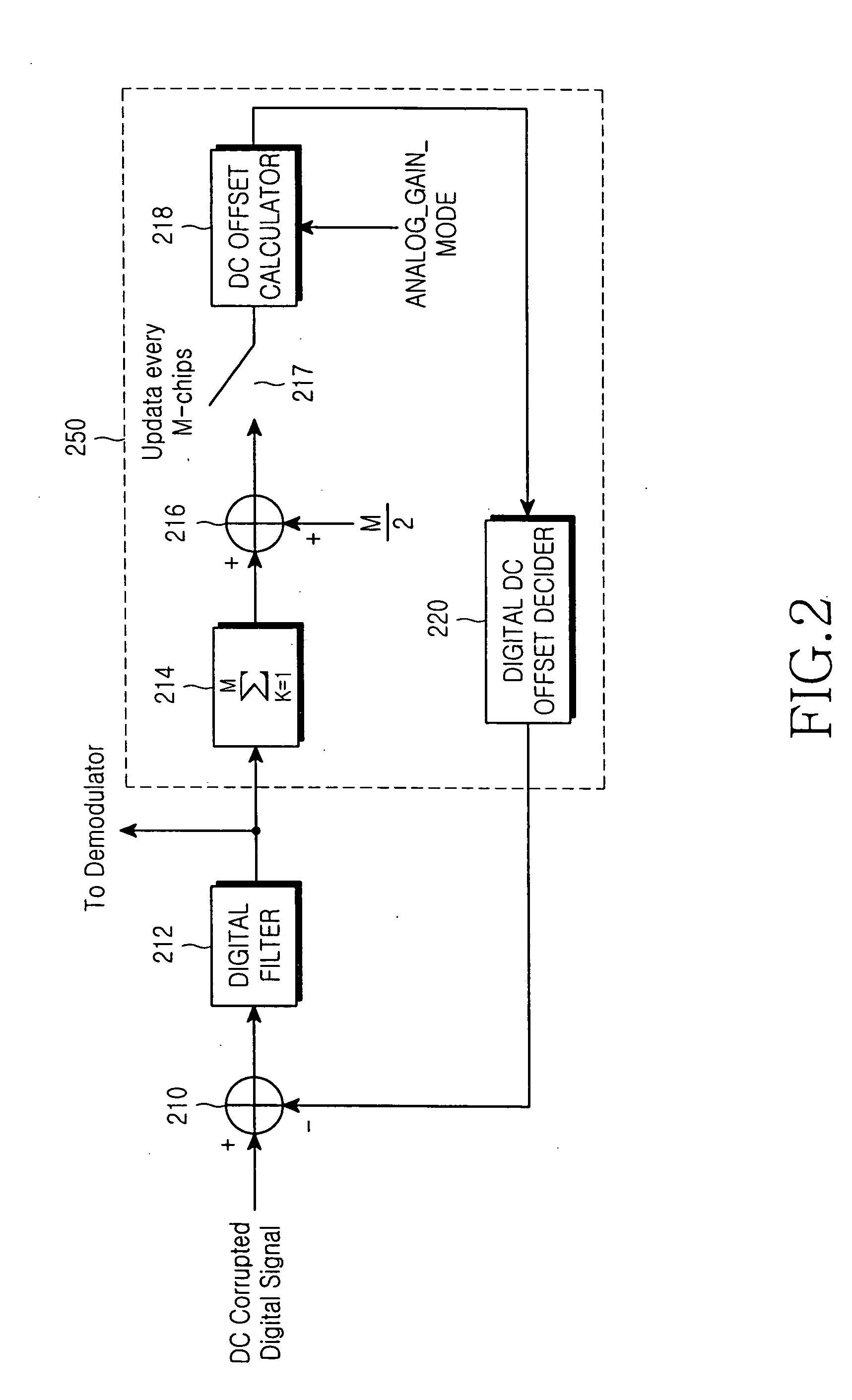
Apparatus and method for removing DC offset in a frequency direct-conversion device
InactiveUS20050136874A1Avoid damageAvoid saturationLine impedence variation compensationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemEngineering
An apparatus for removing a DC offset during frequency direct conversion in a reception device of a wireless communication system. In the apparatus, an adder receives a digital baseband signal comprising a DC component, receives an estimated DC offset value, and calculates a difference between the digital baseband signal with the DC component and the estimated DC offset value. A DC offset calculator receives gain mode information of an analog element of the reception device, and calculates the estimated DC offset value according to the gain mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
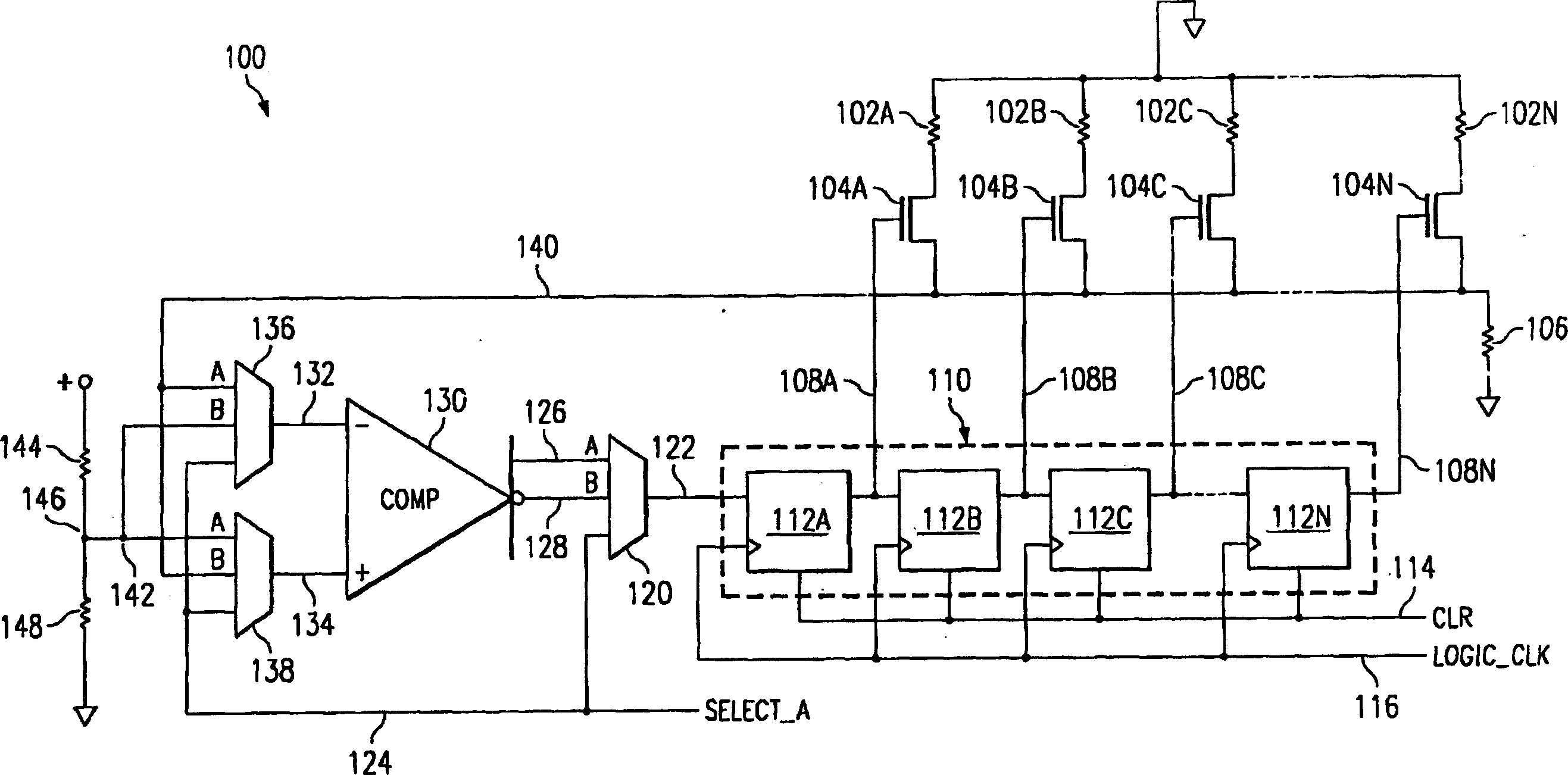
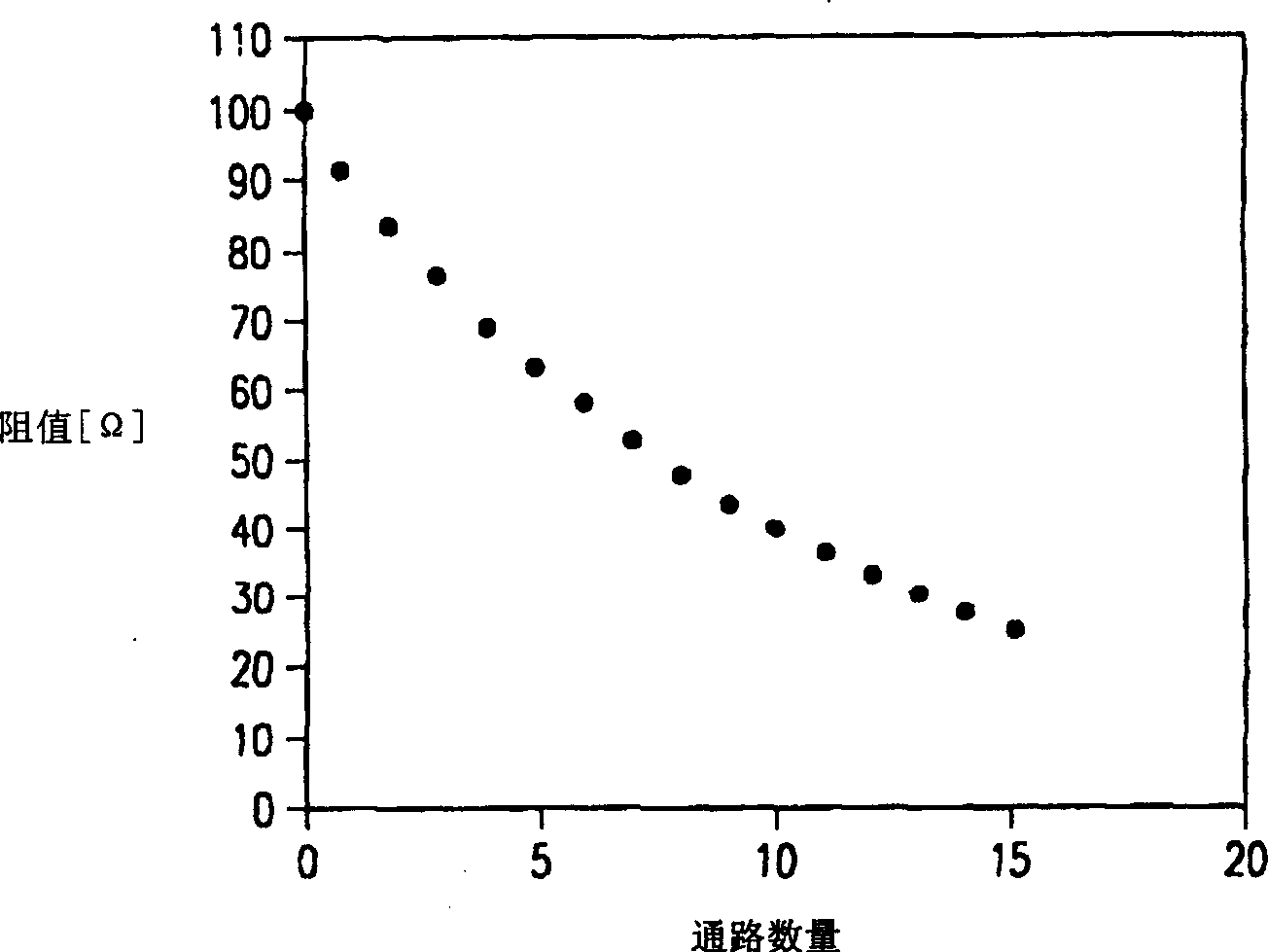
Impedance calibrating circuit
InactiveCN1499798AInput/output impedence modificationLine impedence variation compensationEngineeringComparator
An impedance calibration circuit for a serial ATA (SATA) transmitter has a resistor in series with each leg of the differential output of the transmitter. An array of selectable resistors is in parallel with each of the series resistors. Resistors in the array are selected to be in parallel with the series resistors. A calibration circuit utilizes a comparator to determine when the minimum error in the impedance calibration is reached. Offset errors in the comparator are compensated for by a circuit which determines the center of alternate ones and zeros generated by the comparator when the input signals are within the offset of the comparator, which should be the point of minimum error in the calibration.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
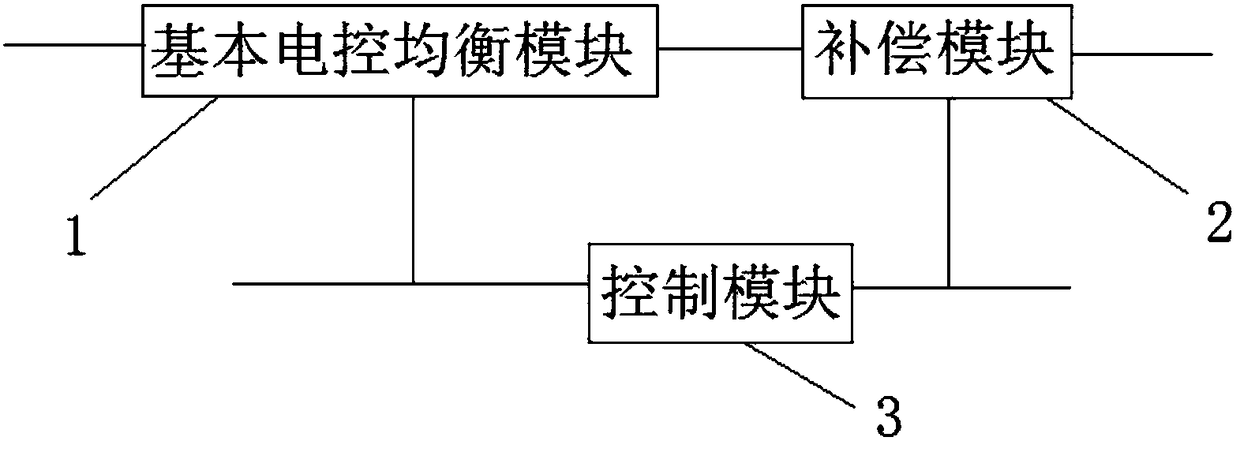
High-precision adjustable electric control equalization circuit of cable television network
ActiveCN108200368AImprove frequency response characteristicsImprove featuresImpedence matching networksTelevision system detailsElectricityComputer module
A high-precision adjustable electric control equalization circuit of a cable television network comprises one or more basic electric control equalization modules with an adjustable slope. The circuitalso comprises a control module and one or more compensation modules. The control module is electrically connected to the basic electric control equalization modules so as to control the slope changesof the basic electric control equalization modules. The control module is electrically connected to the compensation modules so as to generate a compensation signal according to the slope changes ofthe basic electric control equalization modules. The output of the basic electric control equalization modules is electrically connected to the input of the compensation modules so as to output a complete signal after the two are overlaid. The high-precision adjustable electric control equalization circuit of the cable television network can obtain good signal waveform flatness at each slope.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS INC
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
InactiveUS20060291574A1Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationSynchronisation error correctionTelecommunications linkData source
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:K MIZRA LLC
Methods for propagating a non sinusoidal signal without distortion in dispersive lossy media
InactiveUS7375602B2Reduce the clock skewMinimum coaxial cable delay measuredLine impedence variation compensationCorrect operation testingUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
Systems and methods are described for transmitting a waveform having a controllable attenuation and propagation velocity. An exemplary method comprises: generating an exponential waveform, the exponential waveform (a) being characterized by the equation Vin=De−A<sub2>SD< / sub2>[x−v<sub2>SD< / sub2>t], where D is a magnitude, Vin is a voltage, t is time, ASD is an attenuation coefficient, and vSD is a propagation velocity; and (b) being truncated at a maximum value. An exemplary apparatus comprises: an exponential waveform generator; an input recorder coupled to an output of the exponential waveform generator; a transmission line under test coupled to the output of the exponential waveform generator; an output recorder coupled to the transmission line under test; an additional transmission line coupled to the transmission line under test; and a termination impedance coupled to the additional transmission line and to a ground.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Scheme for controlling rise-fall times in signal transitions
ActiveUS7737747B2Input/output impedence modificationLine impedence variation compensationElectrical resistance and conductanceFall time
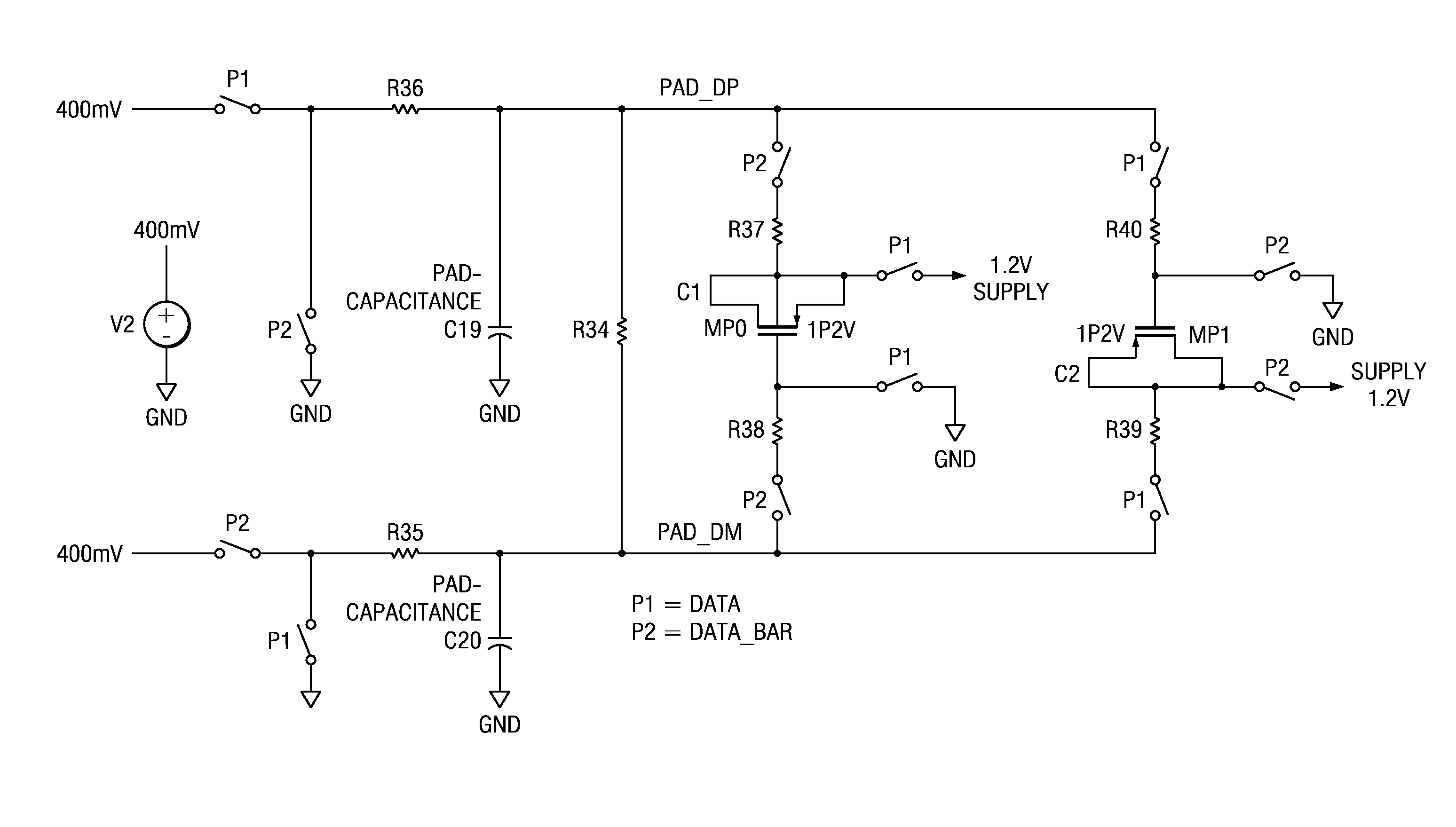
A serial interface interacting with a transmission pad system circuitry wherein a differential impedance is reckoned across the system voltage source, includes a scheme for controlling transmitter rise-fall transitions (to selectively speed up or slow down transitions) without requiring additional timing controls or affecting reflection coefficient of the transmitter port. The scheme uses at least one pre-charged capacitor, e.g., PMOS capacitor, interacting with the transmitter pad and connected through resistances or otherwise across the differential impedance with a switch. A modified scheme uses first and second parallely connected PMOS capacitors connectable with the transmission pad by switches, which may be NMOS switches. The scheme may be used in a MIPI D-PHY compliant DSI transmitter operating at, for e.g. 800 Mbps, and low signal common-modes. The scheme controls signal transition times of high speed circuitry including transmitters and uses a DATA signal which is already available to the circuitry.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
MOS linear region impedance curvature correction
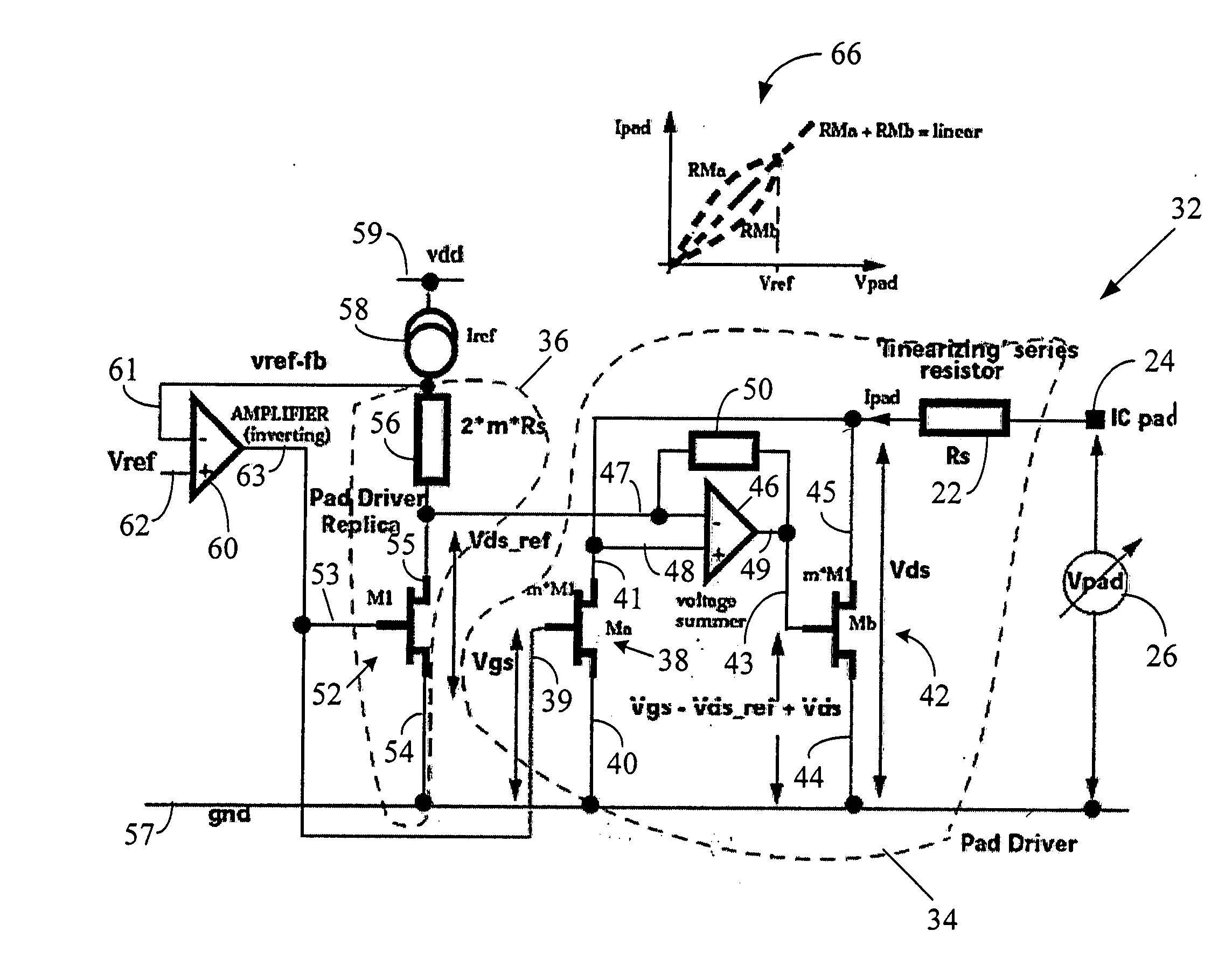
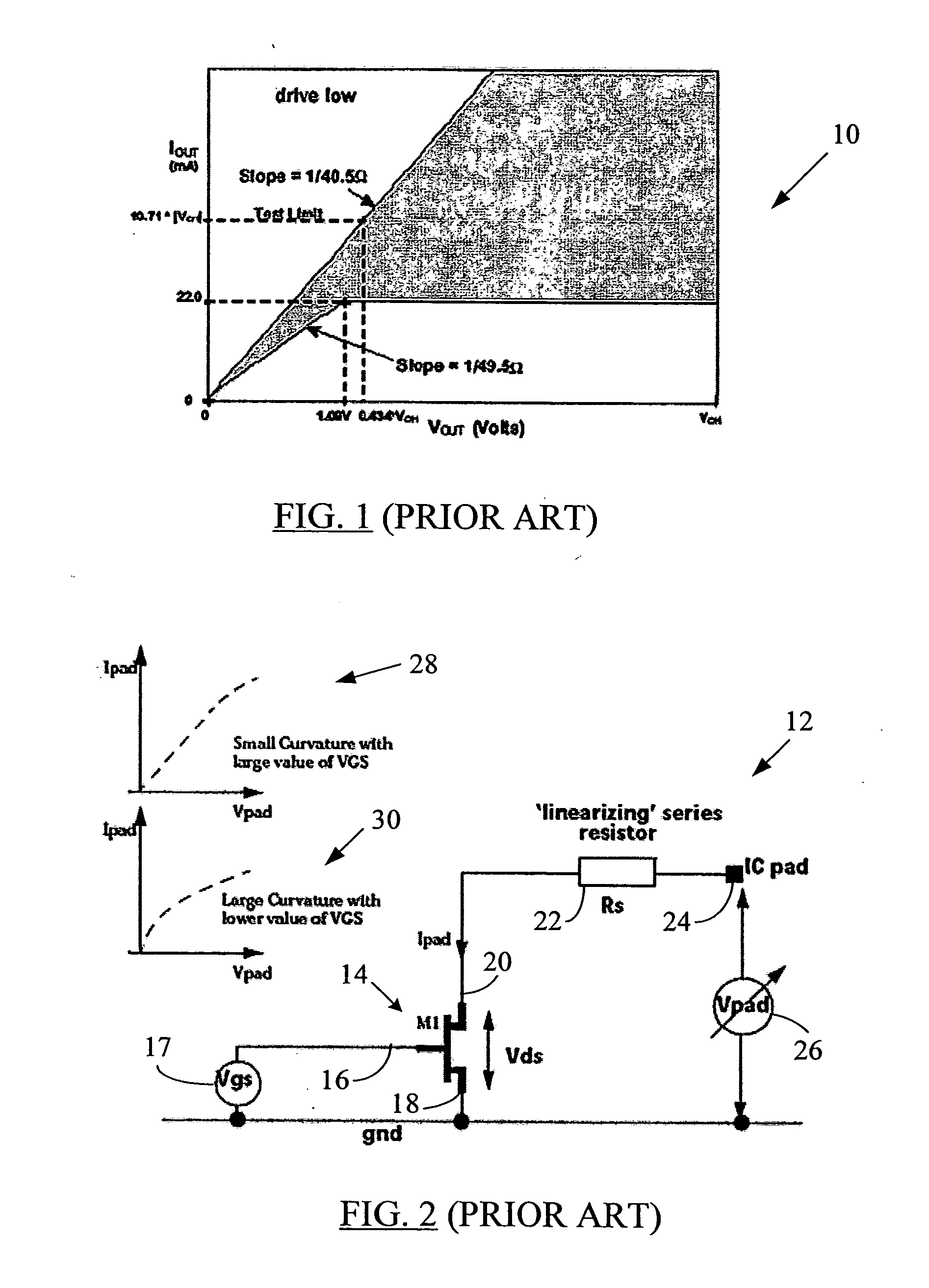
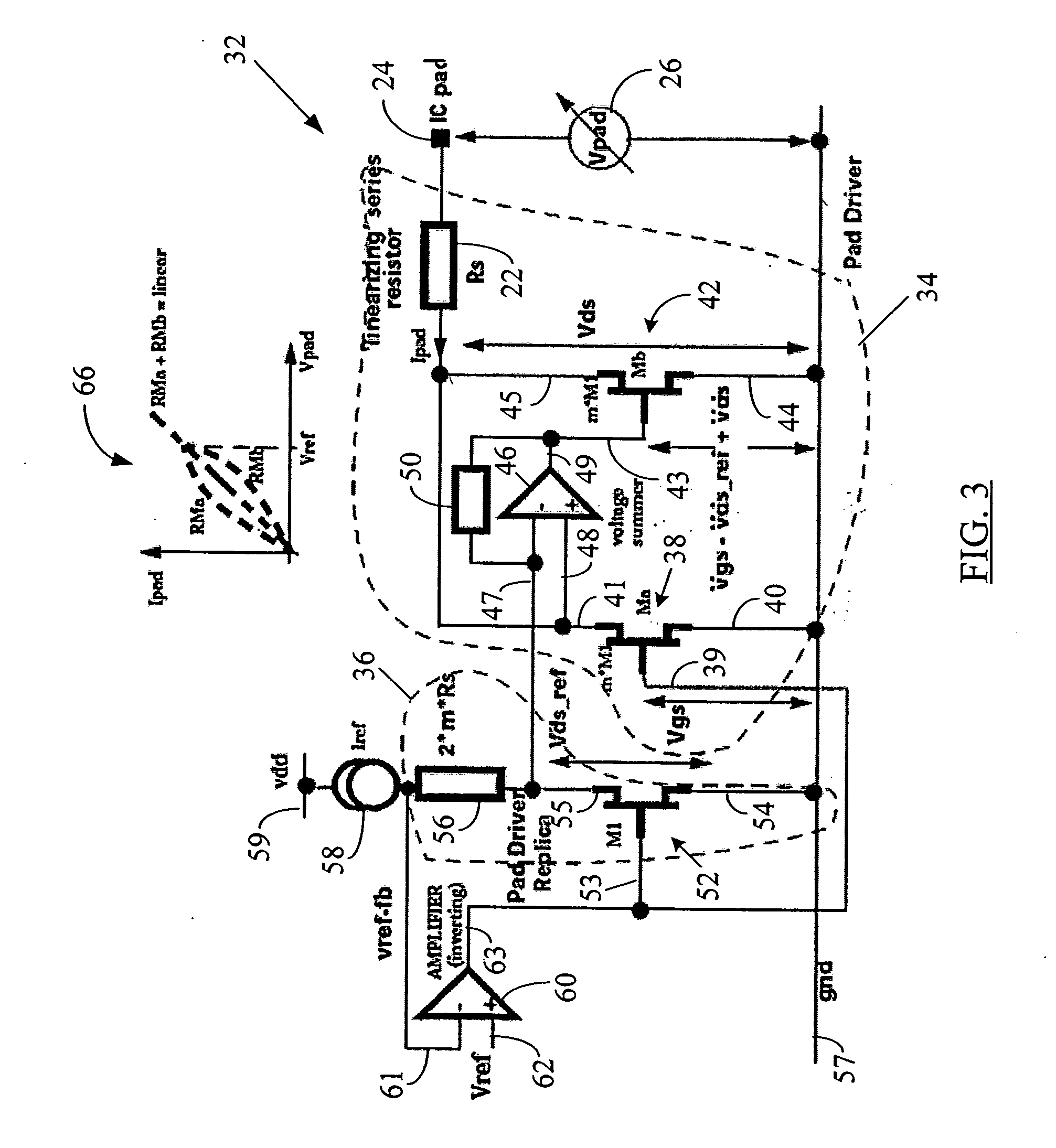
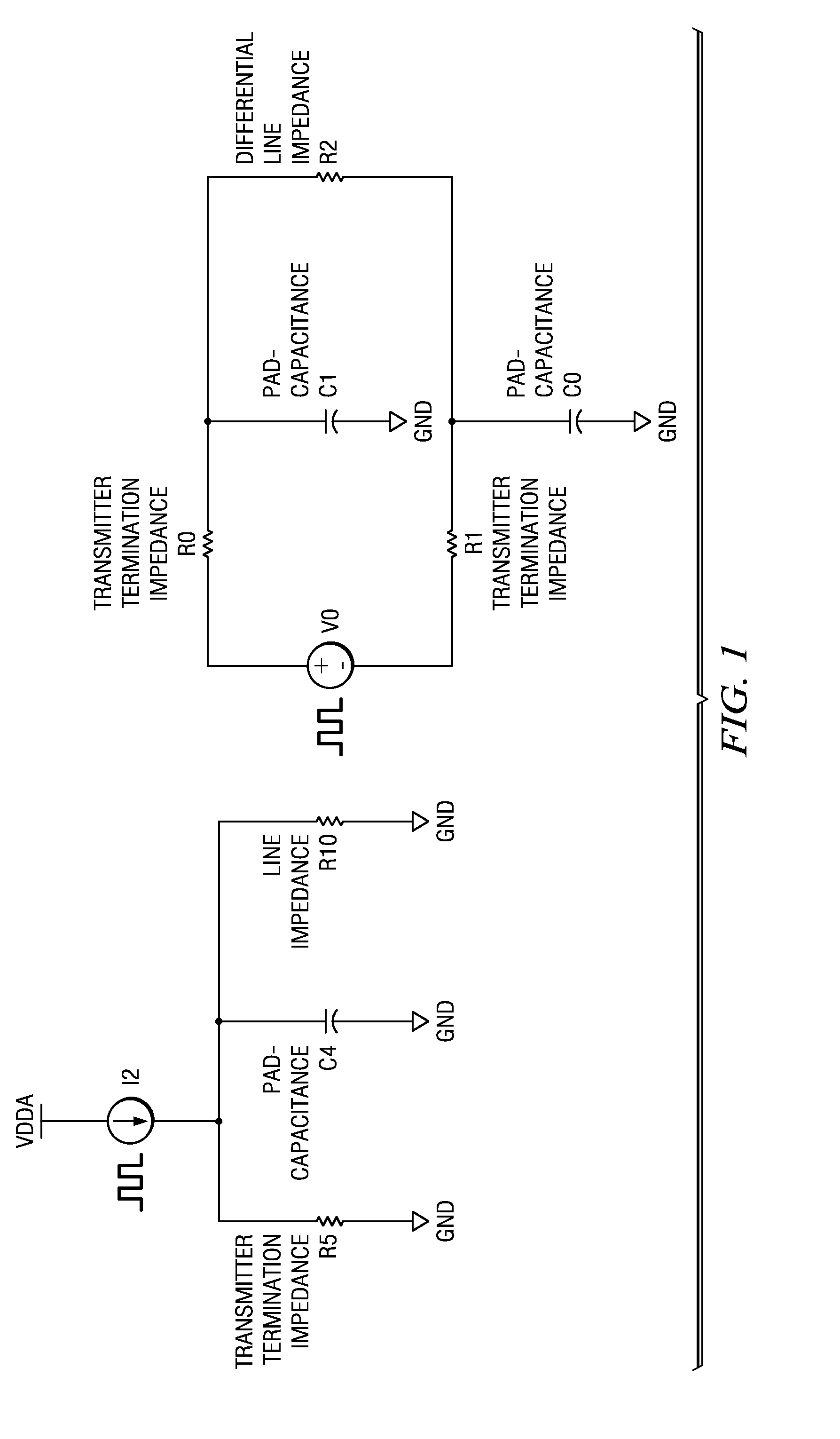
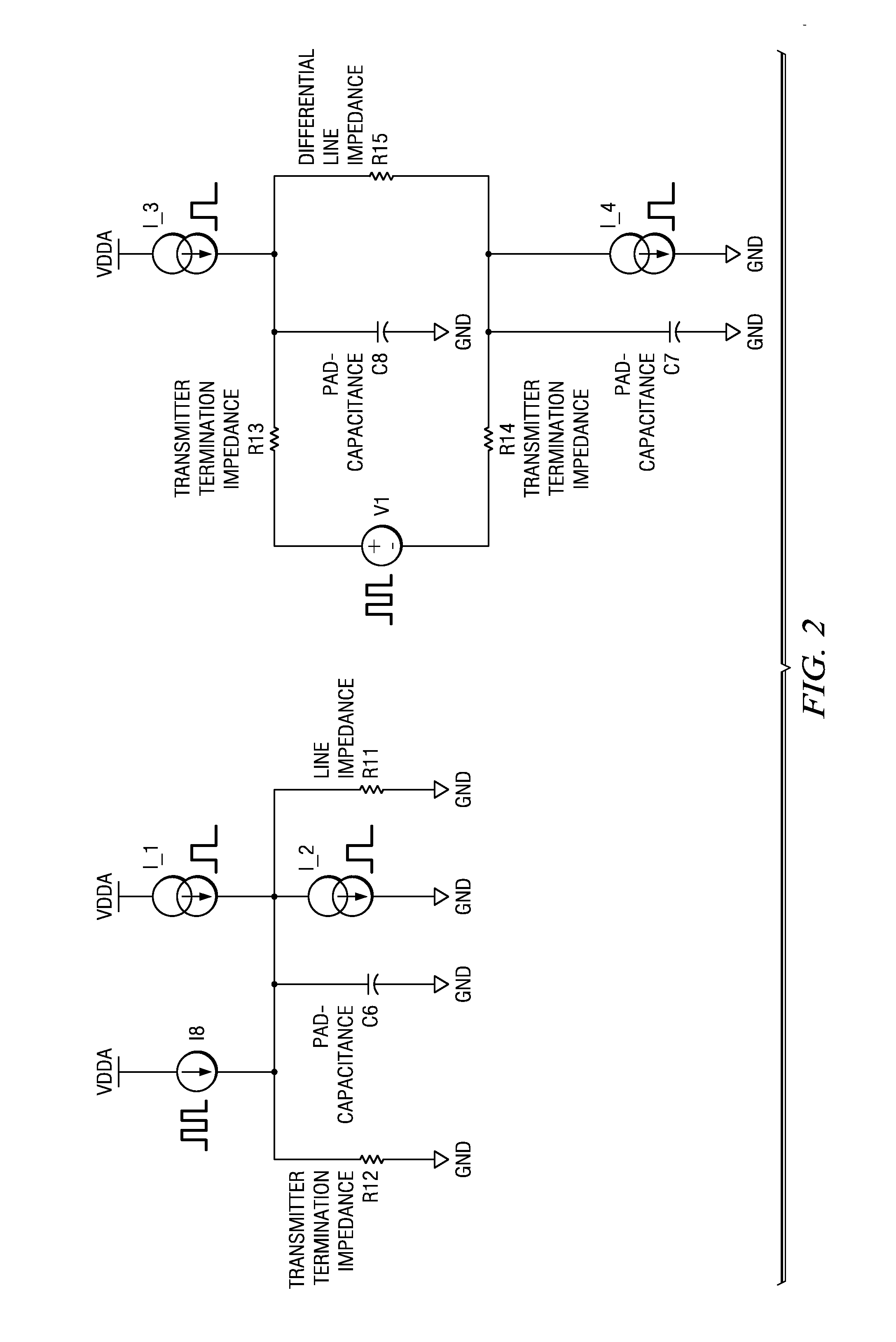
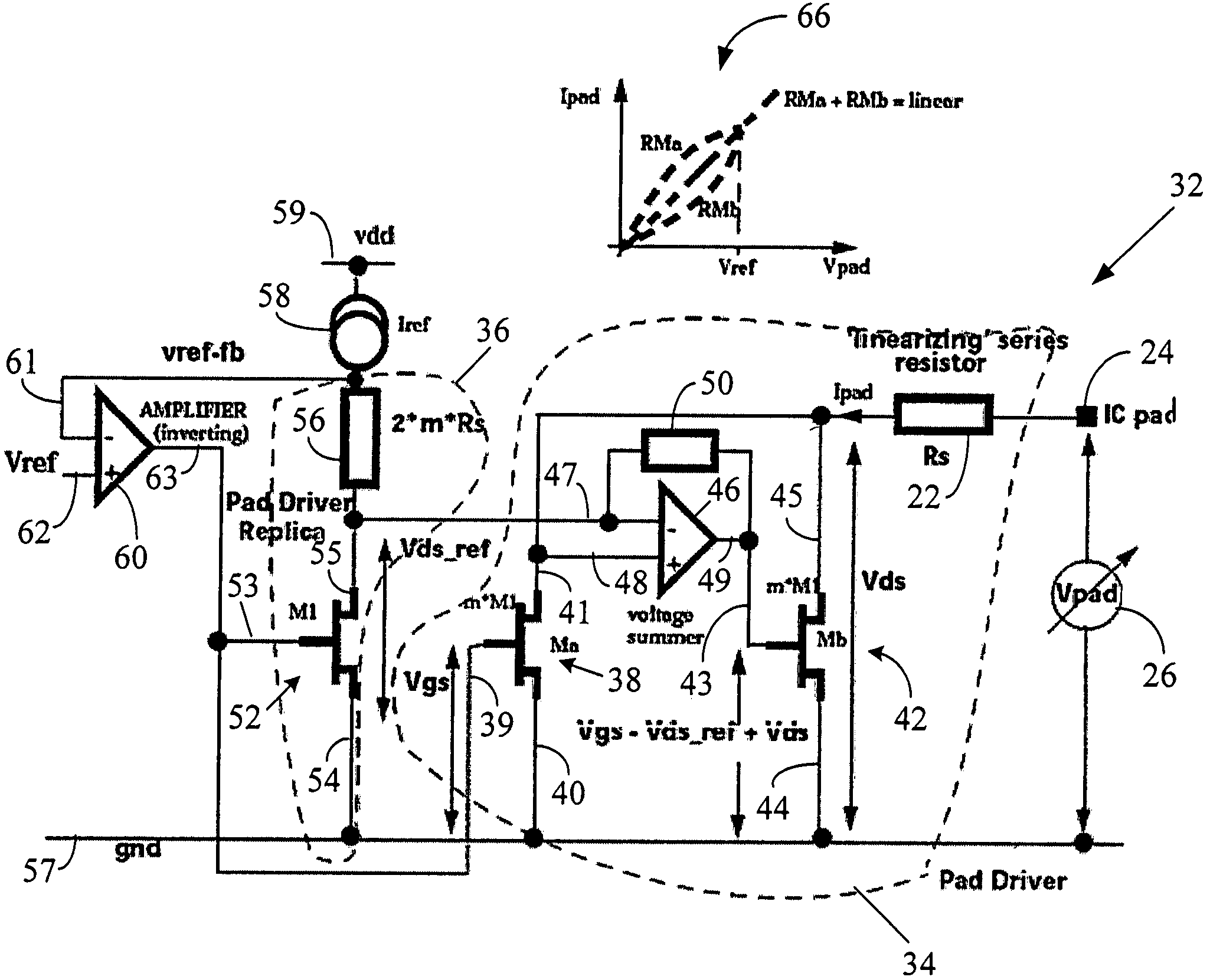
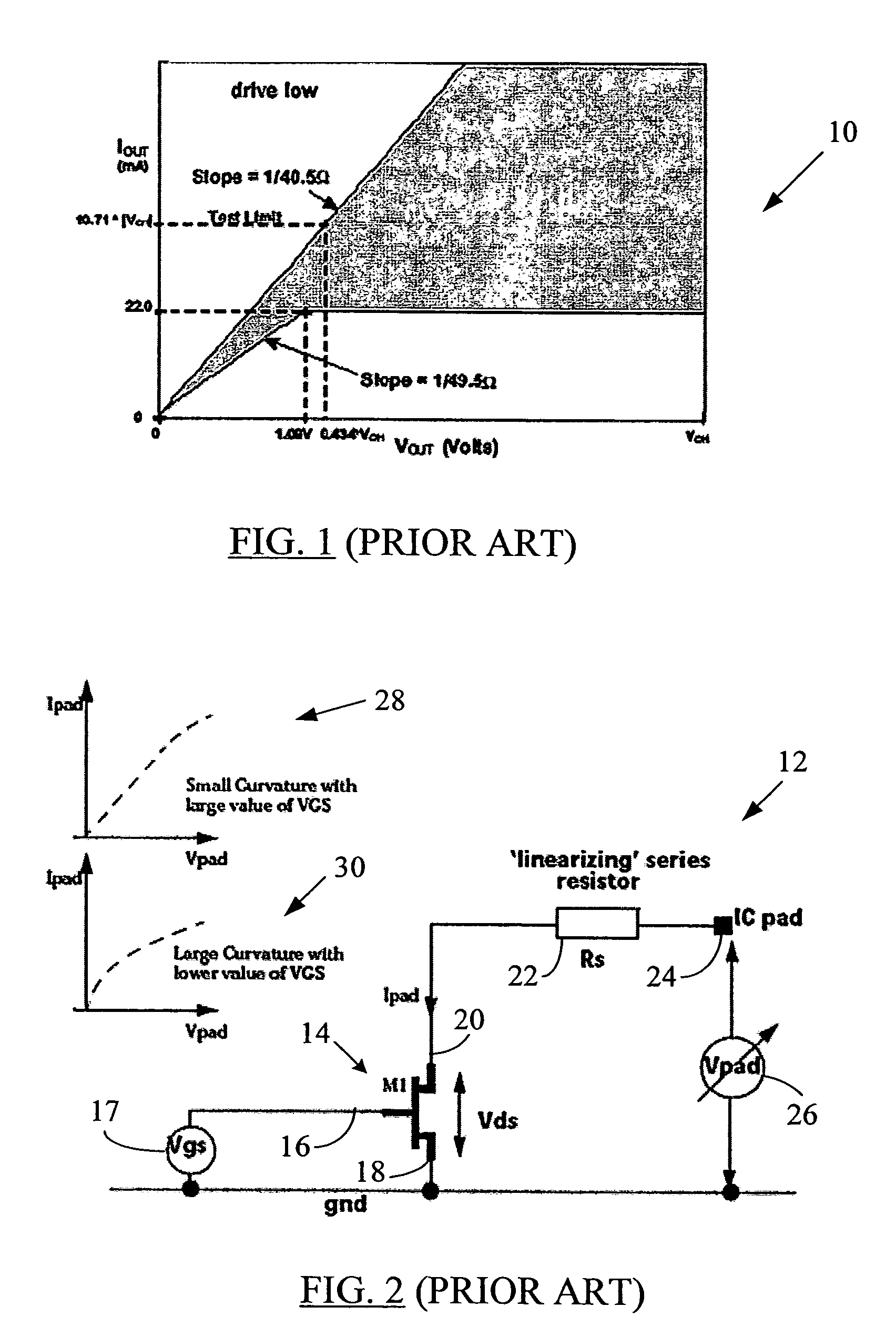
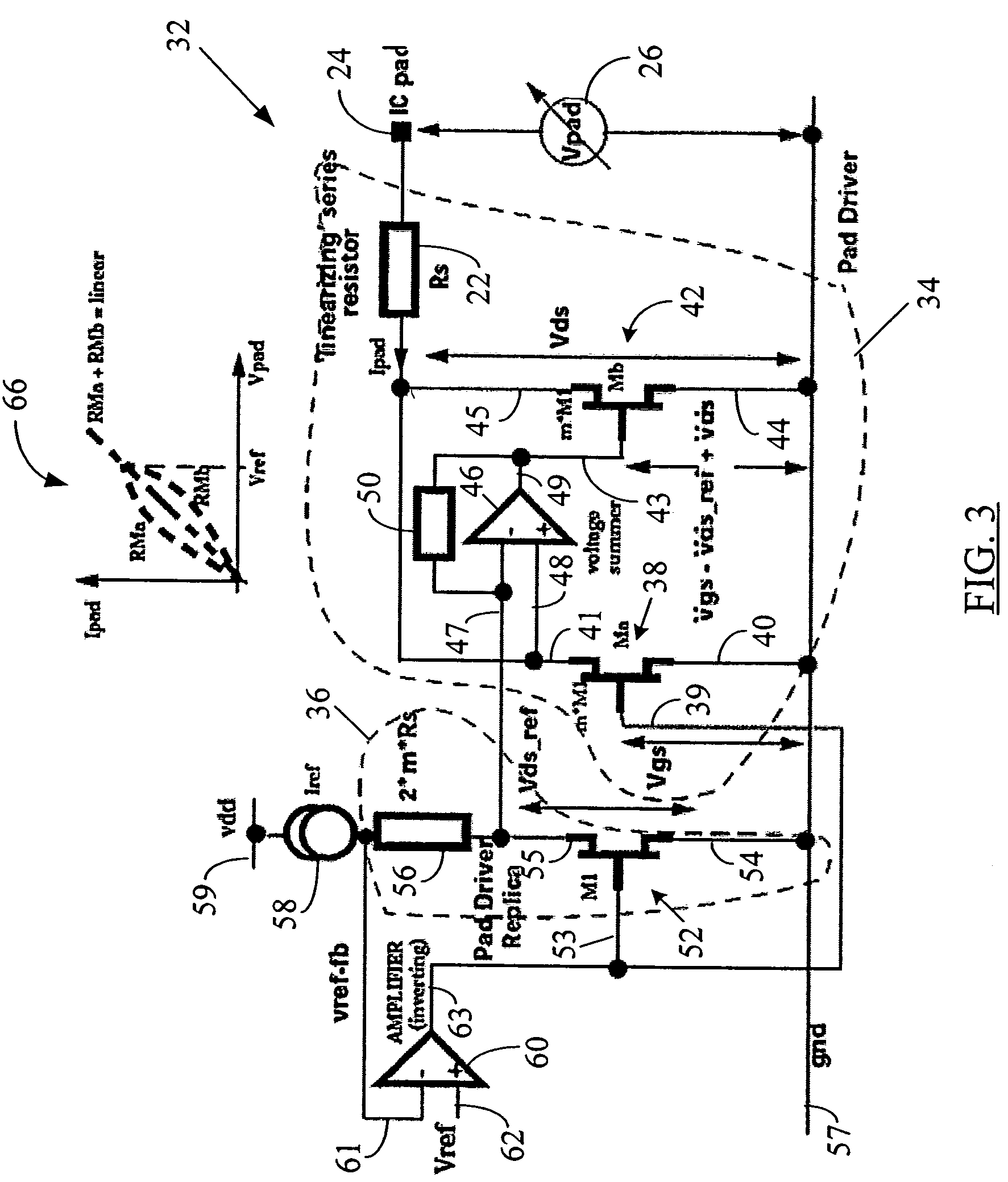
ActiveUS20050088199A1Improve linearityTight impedance controlReliability increasing modificationsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionManufacturing technologyLinear region
A system and method to correct or cancel MOS linear region impedance curvature employing an analog solution to trim out the MOS linear region impedance curvature while accommodating PVT spreads in values of internal or external precision resistors. The linear region curvature correction may be obtained by using two MOS transistors in the pad driver / buffer and operating the transistors so as to proportionately increase output impedance of one of them when the output impedance of the other decreases, and vice versa. A linear pad impedance may be maintained over a range of Vpad values, while also maintaining the Vgs supplied to pad driver transistors at its maximum possible value to obtain greater linearity. The approach of the present disclosure relaxes the requirements on the voltage / current references used in the MOS pad drivers and makes tight impedance control possible, especially in a situation where the MOS fabrication process (typically all currently used processes) does not have available an internal precision resistor with a reasonably well controlled value.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
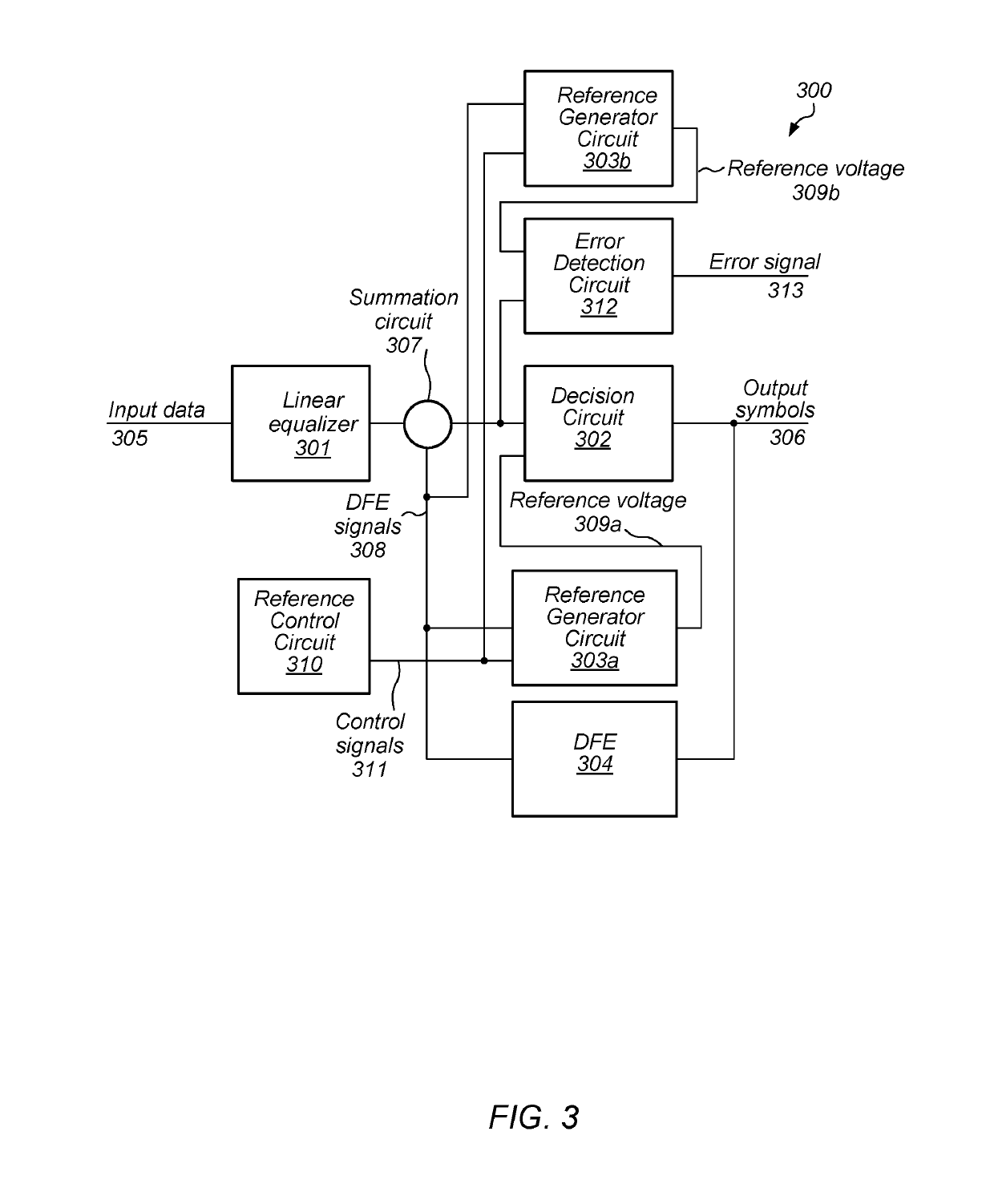
Fast-settling voltage reference generator for serdes applications
ActiveUS10348535B1Line impedence variation compensationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDecision circuitData stream
A reference generator for use with serial link data communication is disclosed. Broadly speaking, a decision circuit may perform a comparison between a particular data symbol included in a serial data stream and a difference between a voltage level of a first signal and a voltage level of a second signal, and generate an output data value based on a result of the comparison. A reference generator circuit may selectively sink a first current value from either the first signal or the second signal based upon another output data value generated from another data symbol included in the serial data stream that was to received prior to the particular data symbol.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Serial communication method and interface circuit
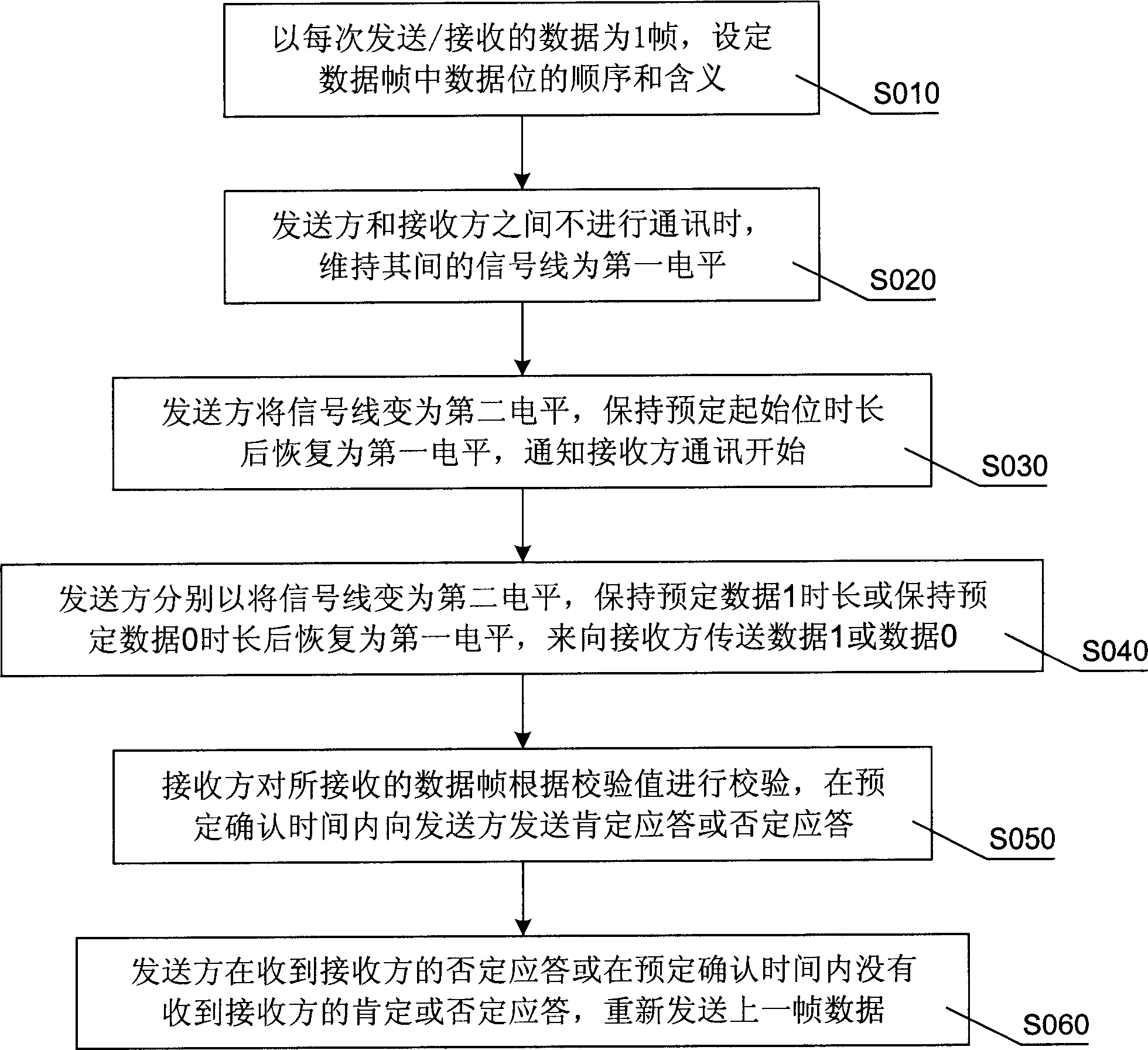
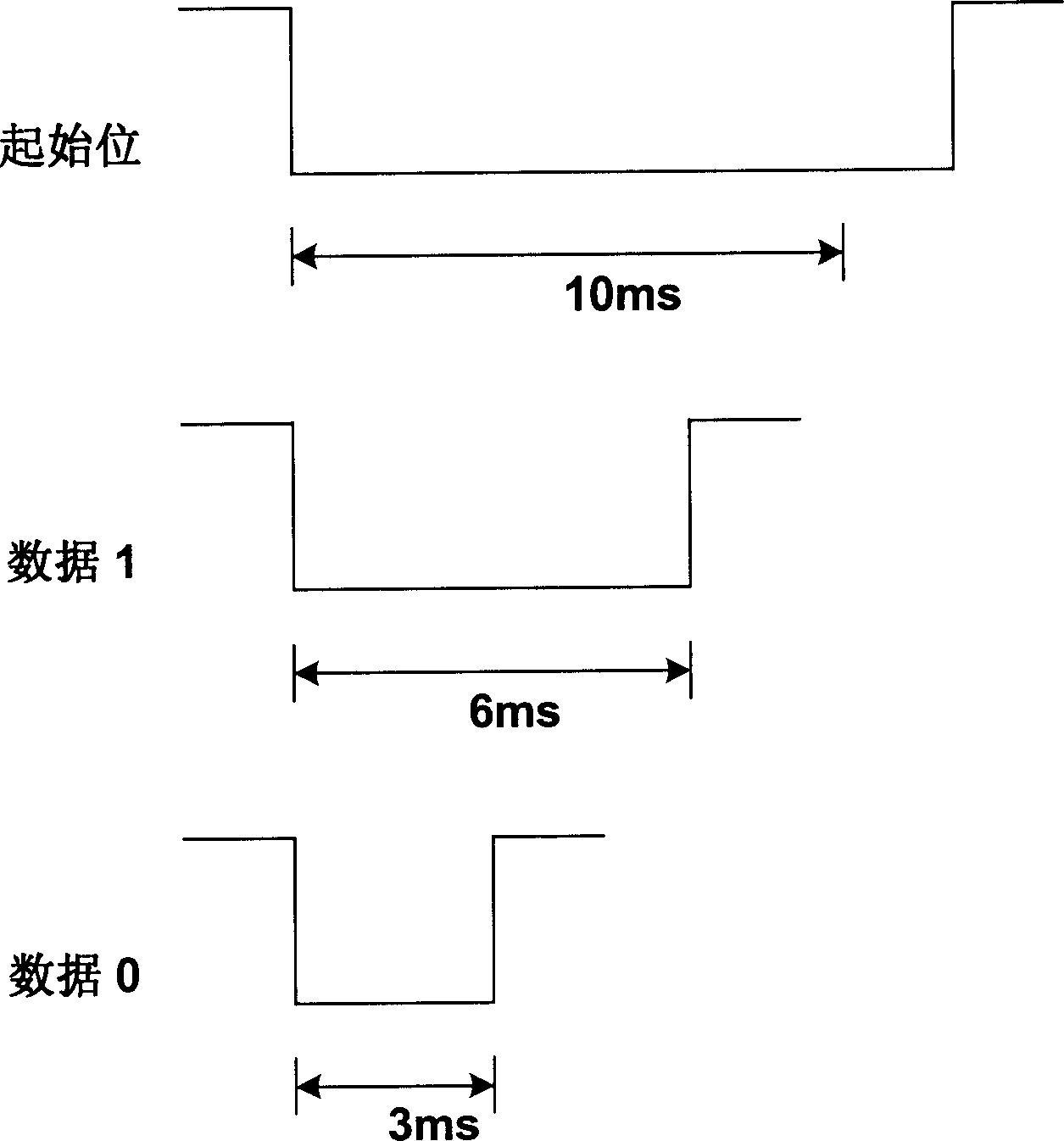
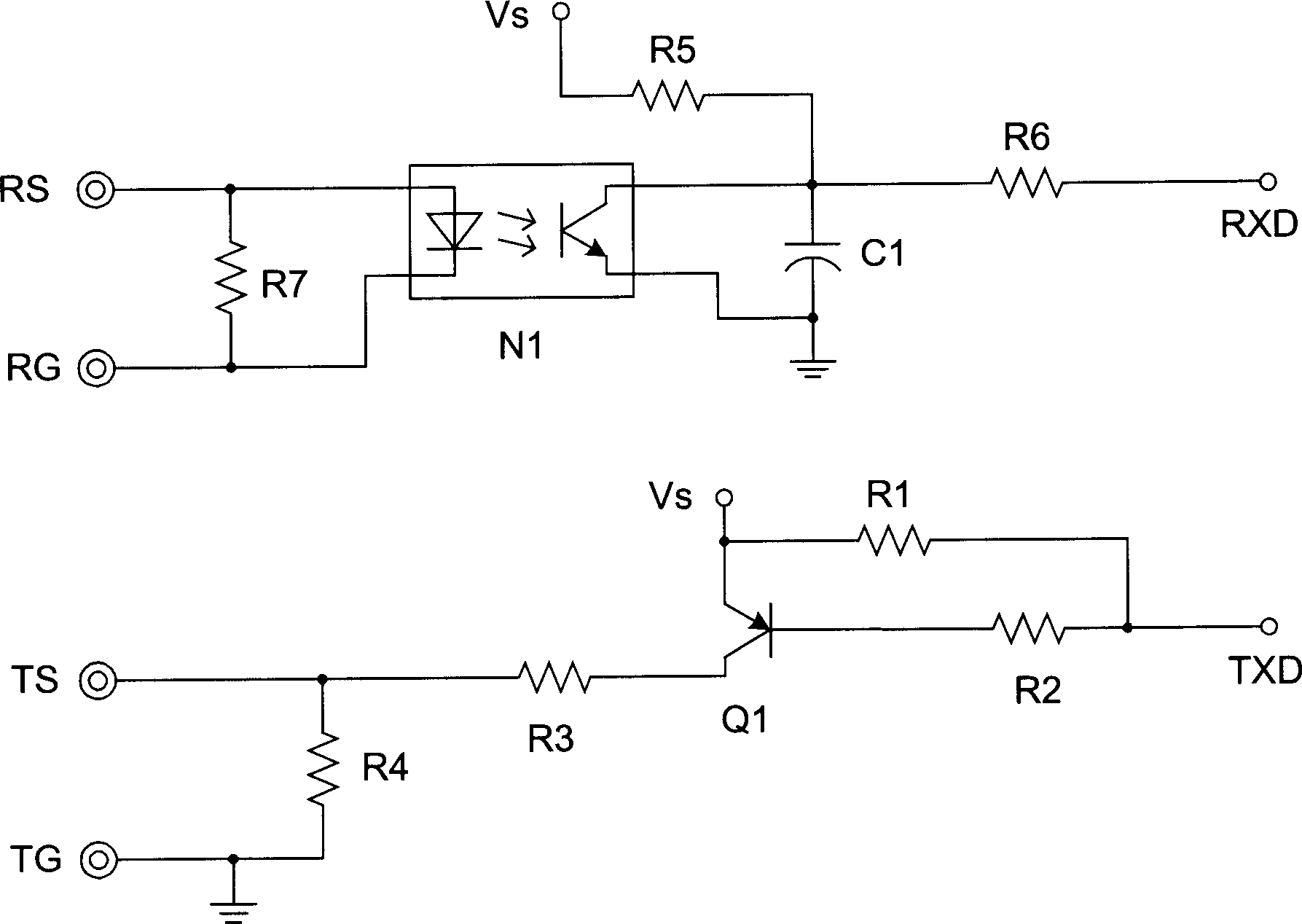
ActiveCN1893404AImprove anti-interference abilityLine impedence variation compensationLine-faulsts/interference reductionElectricityData transmission
Carrying out data transmission based on signal line and ground wire between transmitter and receiver, the method in serial comm. includes parts and sequences: when not carrying comm. between transmitter and receiver, maintaining signal line at first level; transmitter sets signal line to second level, and after maintains prearranged time lengths of start bit, data 1, or 0, restores level to first level to indicate starting comm. data 1, or 0. There are different time lengths among start bit, data 1, or 0. The disclosed interface circuit includes interface circuits of transmitter and receiver. Signal lines and ground wire are connected between interface circuits. When transmitting end has no input or is in high level, the receiving end is in high level; when low level is inputted to the transmitting end, the receiving end is at low level. The invention enhances interference-killing feature for serial comm. without need of transmitter and receiver of possessing same reference clock.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Scheme for controlling rise-fall times in signal transitions
ActiveUS20090058480A1Input/output impedence modificationLine impedence variation compensationControl signalPre-charge
A serial interface interacting with a transmission pad system circuitry wherein a differential impedance is reckoned across the system voltage source, includes a scheme for controlling transmitter rise-fall transitions (to selectively speed up or slow down transitions) without requiring additional timing controls or affecting reflection coefficient of the transmitter port. The scheme uses at least one pre-charged capacitor, e.g., PMOS capacitor, interacting with the transmitter pad and connected through resistances or otherwise across the differential impedance with a switch. A modified scheme uses first and second parallely connected PMOS capacitors connectable with the transmission pad by switches, which may be NMOS switches. The scheme may be used in a MIPI D-PHY compliant DSI transmitter operating at, for e.g. 800 Mbps, and low signal common-modes. The scheme controls signal transition times of high speed circuitry including transmitters and uses a DATA signal which is already available to the circuitry.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
MOS linear region impedance curvature correction
ActiveUS7282948B2Increase output impedanceImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceLinear region
A system and method to correct or cancel MOS linear region impedance curvature employing an analog solution to trim out the MOS linear region impedance curvature while accommodating PVT spreads in values of internal or external precision resistors. The linear region curvature correction may be obtained by using two MOS transistors in the pad driver / buffer and operating the transistors so as to proportionately increase output impedance of one of them when the output impedance of the other decreases, and vice versa. A linear pad impedance may be maintained over a range of Vpad values, while also maintaining the Vgs supplied to pad driver transistors at its maximum possible value to obtain greater linearity. The approach of the present disclosure relaxes the requirements on the voltage / current references used in the MOS pad drivers and makes tight impedance control possible, especially in a situation where the MOS fabrication process (typically all currently used processes) does not have available an internal precision resistor with a reasonably well controlled value.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
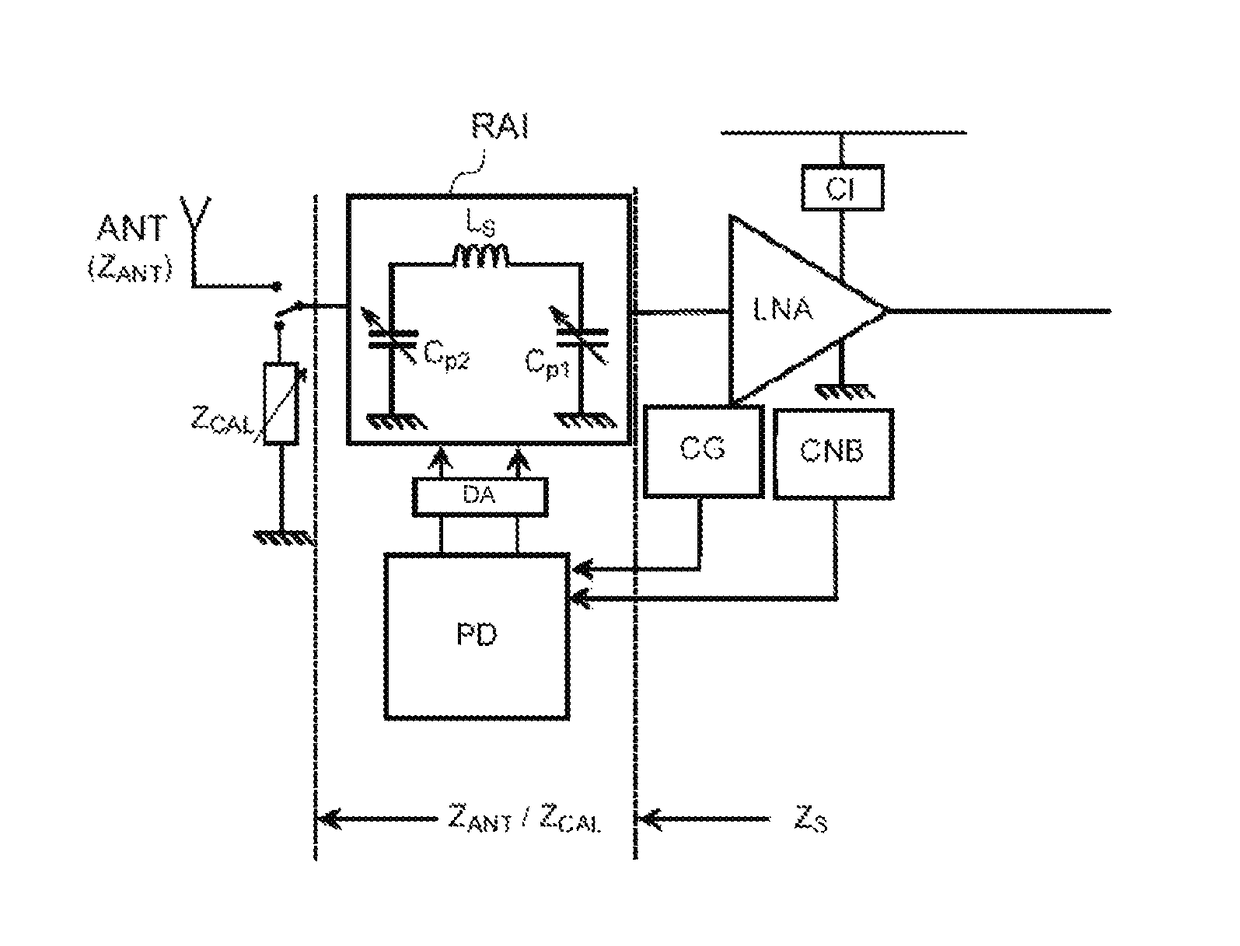
Automatic impedance matching for a radiofrequency reception chain
InactiveUS9935798B2Impedence matching networksMultiple-port networksAudio power amplifierNoise level
An automatic impedance-matching method for a radiofrequency reception chain, which includes an antenna, an amplifier and a configurable impedance-matching network, arranged between the antenna and an input of the amplifier. The method includes two steps: acquiring measurement of a gain of the reception chain and of a noise level at an output of the amplifier and tuning the impedance-matching network according to the measurements. A radiofrequency reception chain allowing the method to be implemented is also provided.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
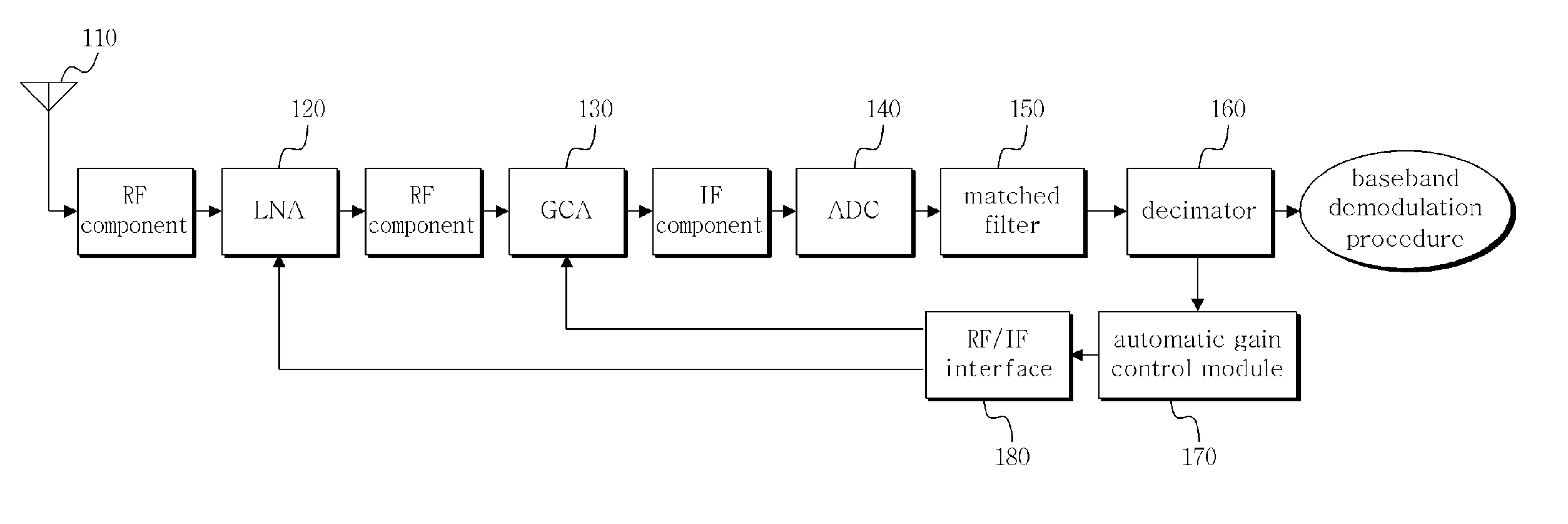
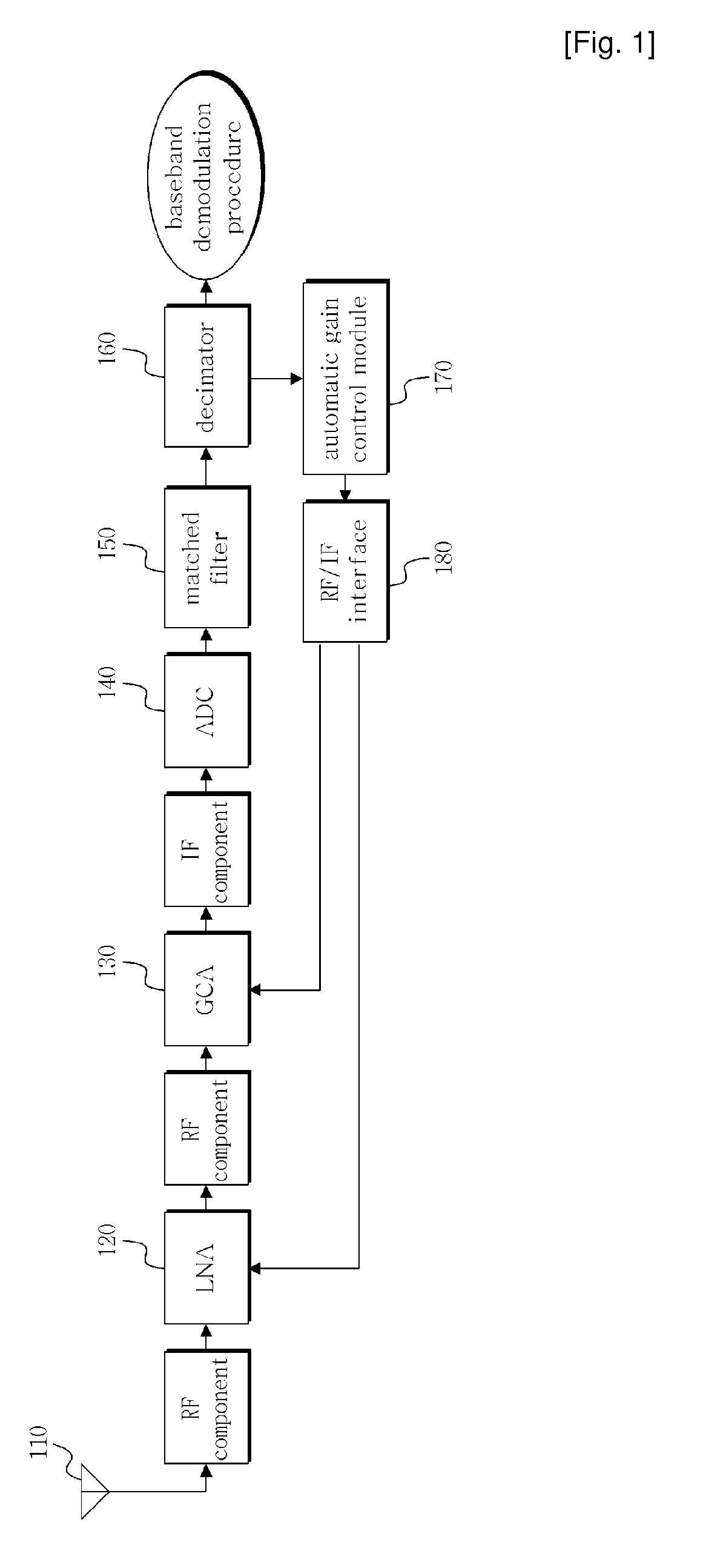
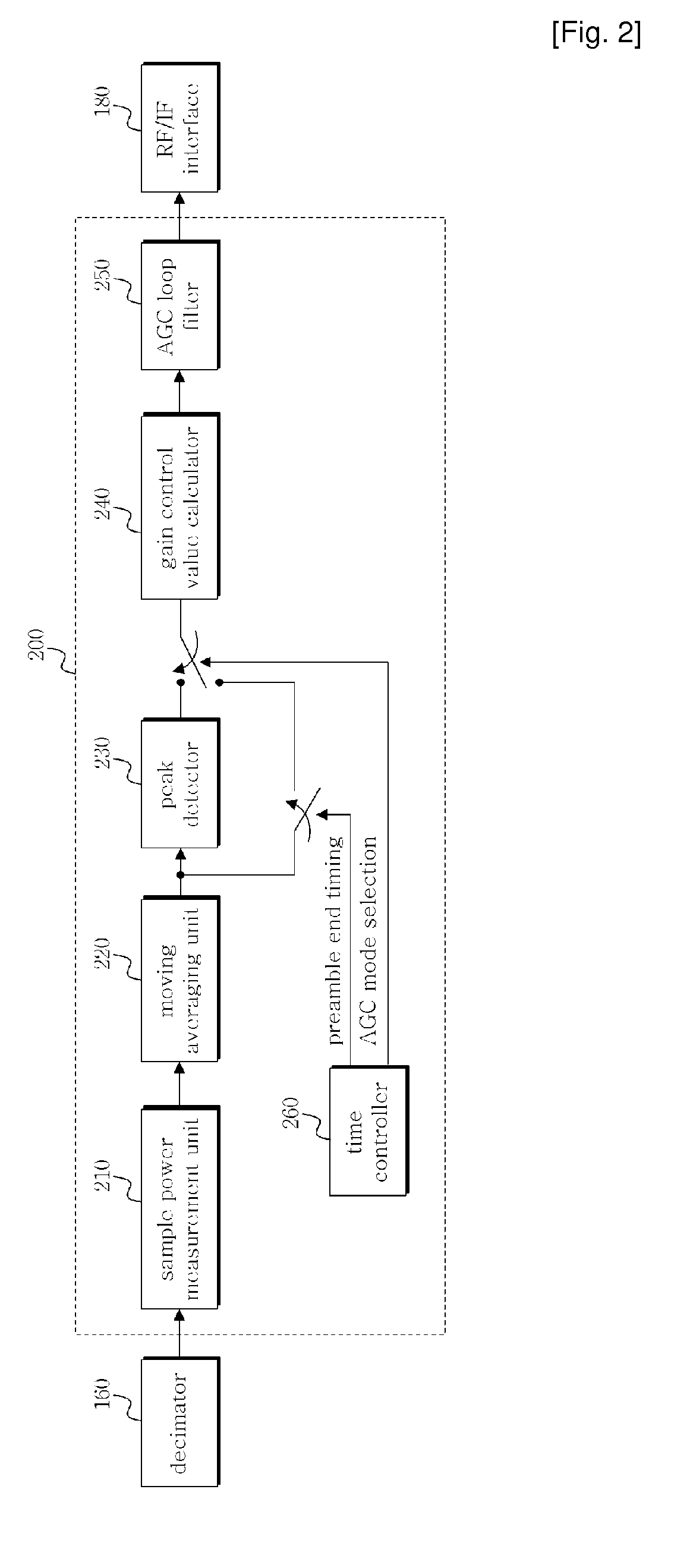
Automatic gain control apparatus and method in wireless telecommunication system
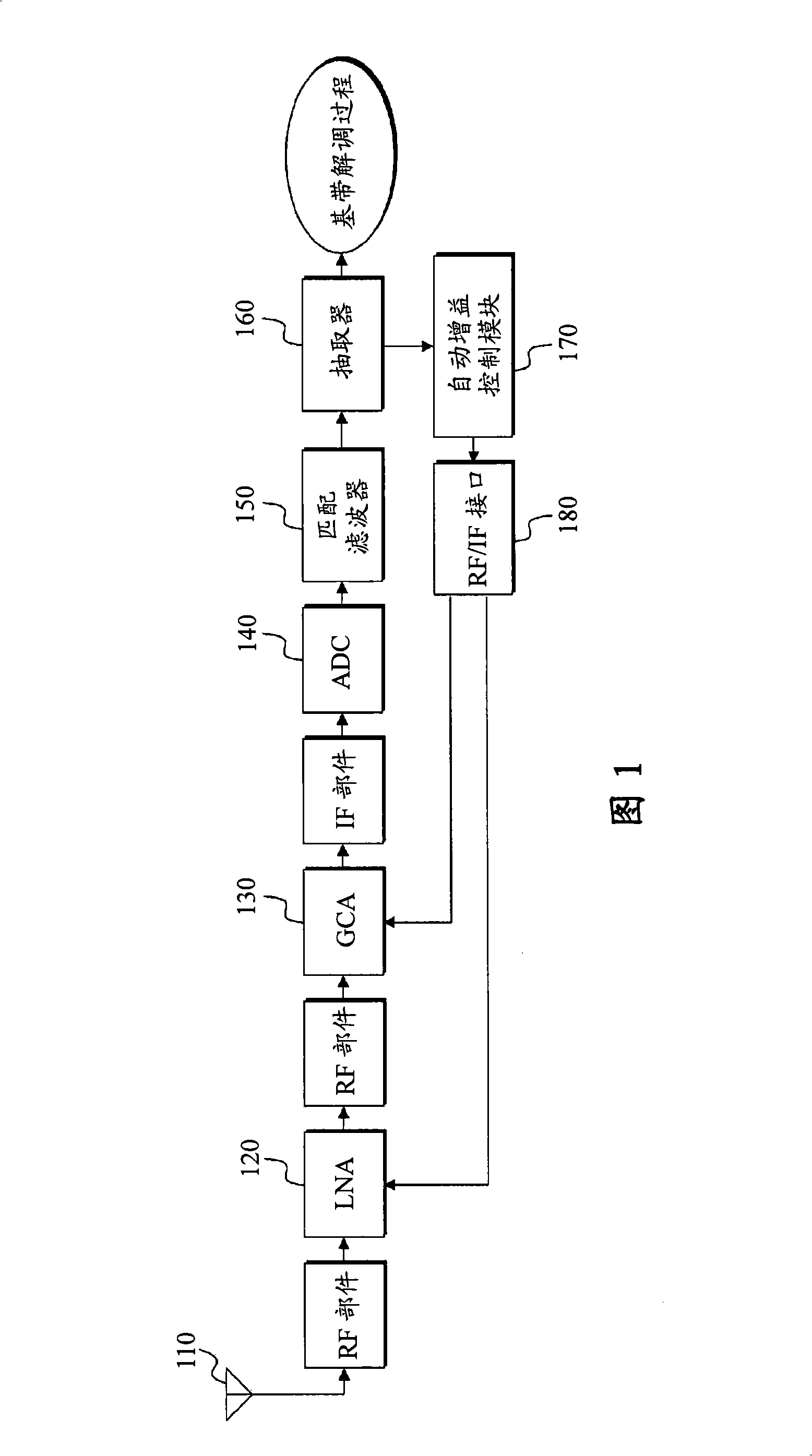
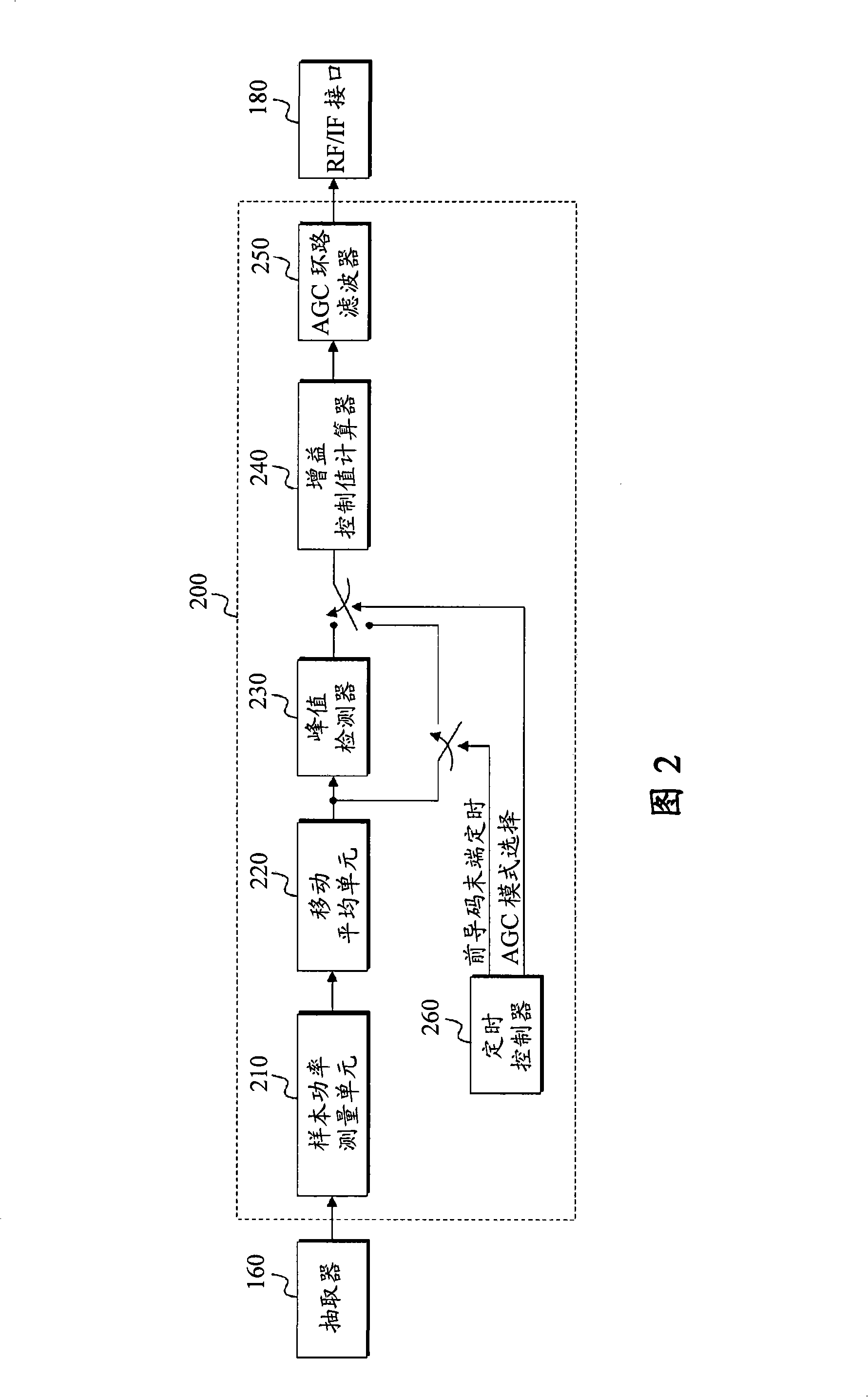
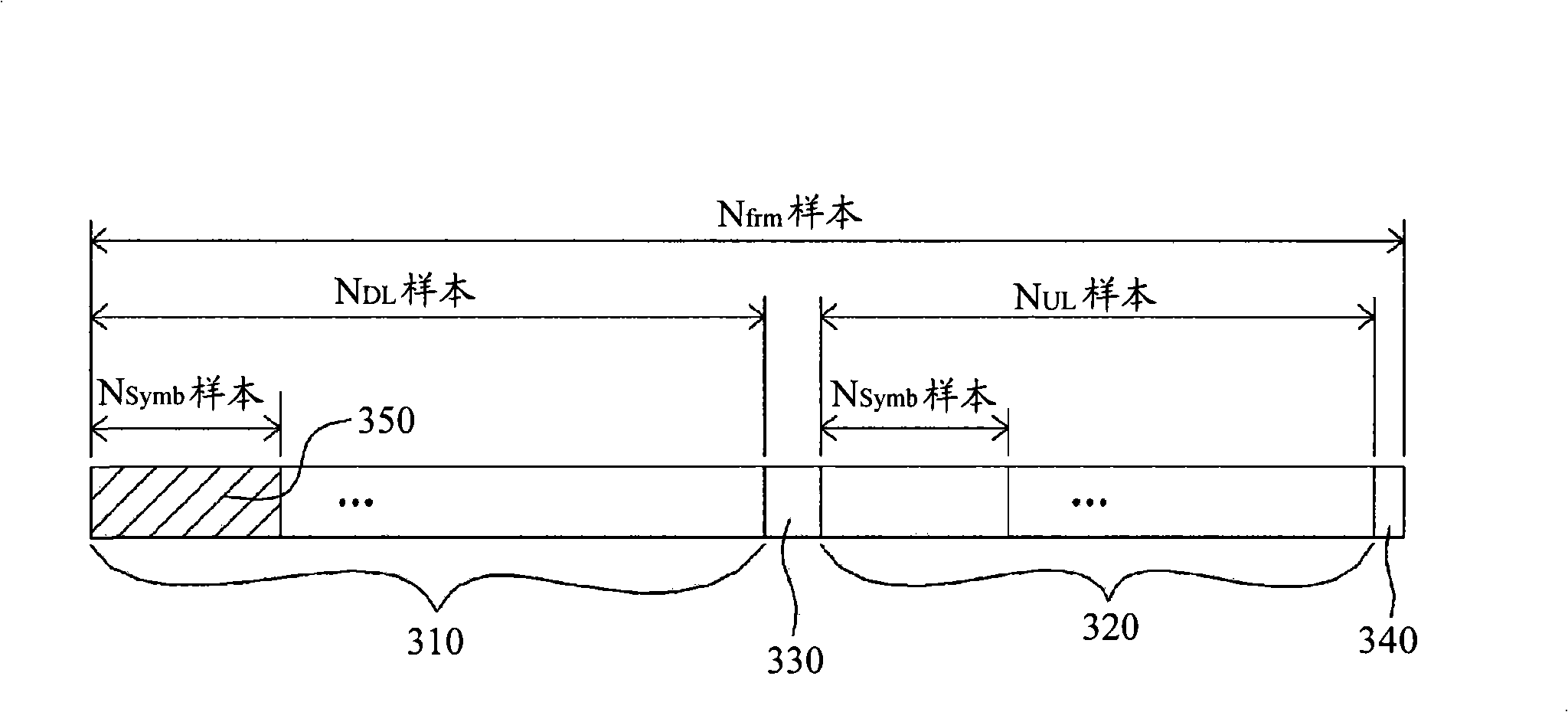
InactiveCN101346957AAutomatic gain controlLine impedence variation compensationModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates to an automatic gain control apparatus and method in a wireless telecommunication system which measures the strength of received signals using preamble symbols and automatically control the gain of an amplifier based on the measurement results. The automatic gain control apparatus and method according to present invention performs automatic gain control of measuring sample power in a sample unit for input signals, acquiring a sample power average value during a unit symbol period, detecting a maximum value during one frame period for the acquired sample power average value and then calculating a gain control value based on it.
Owner:POS DATA CO LTD
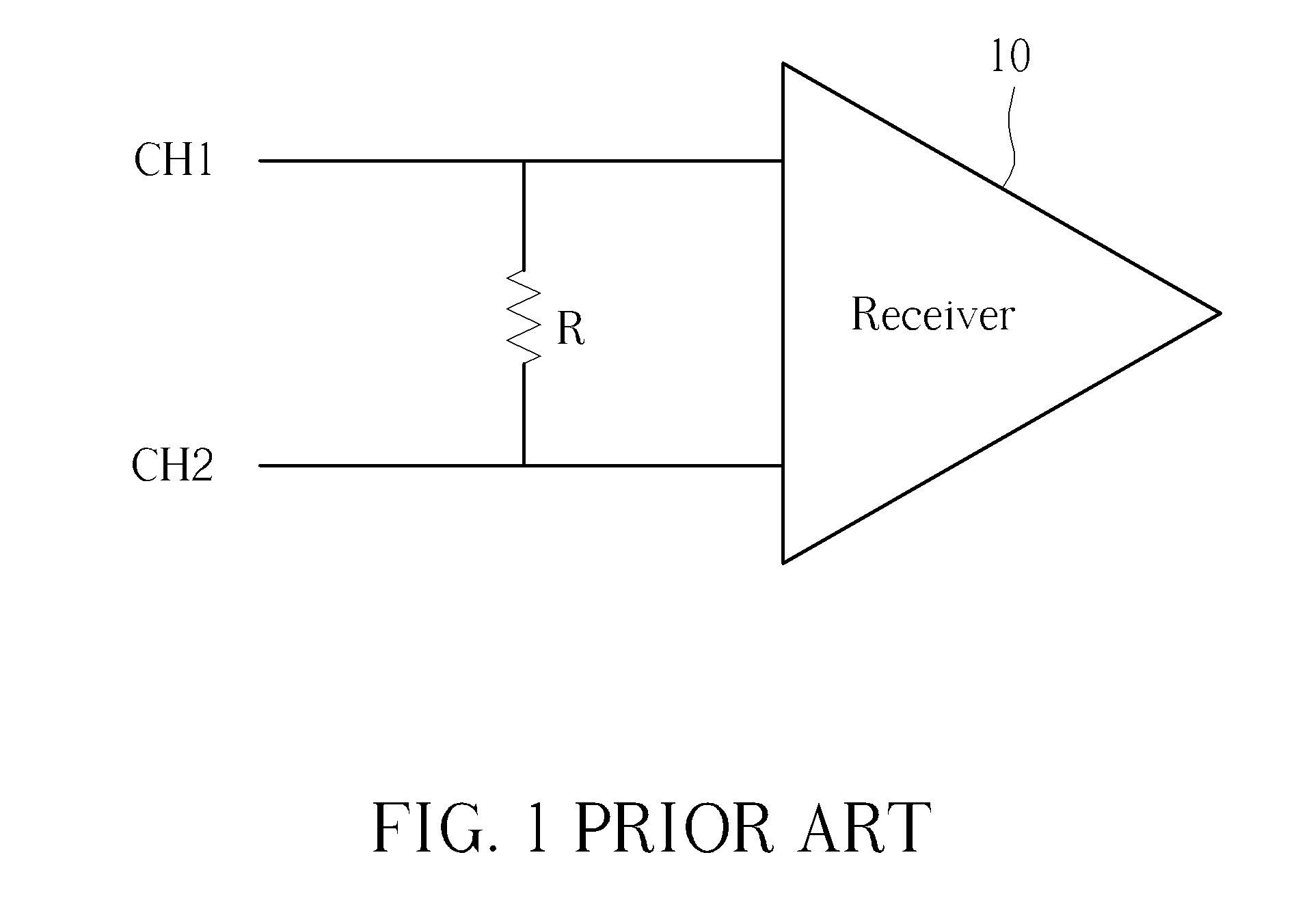
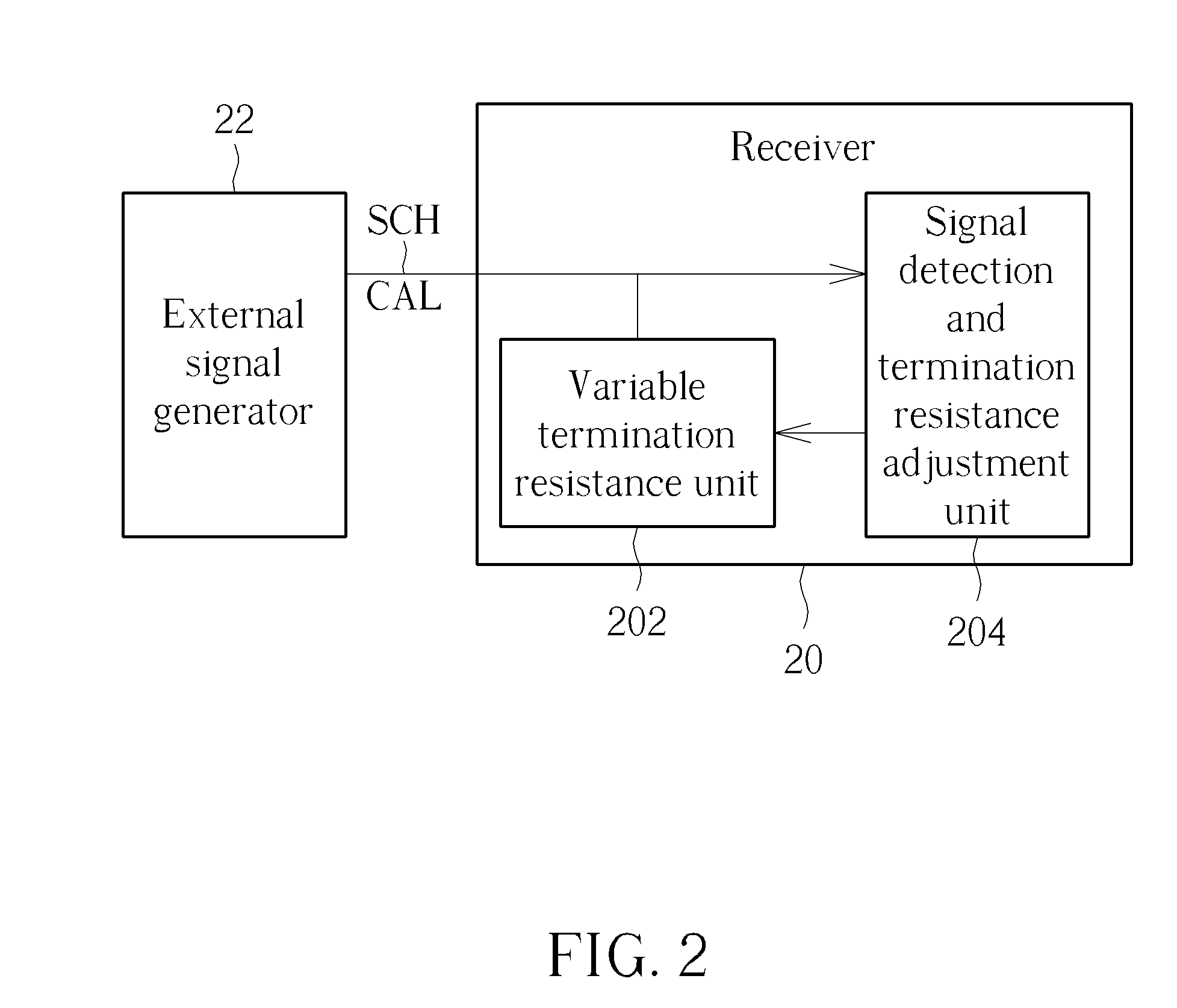
Receiver
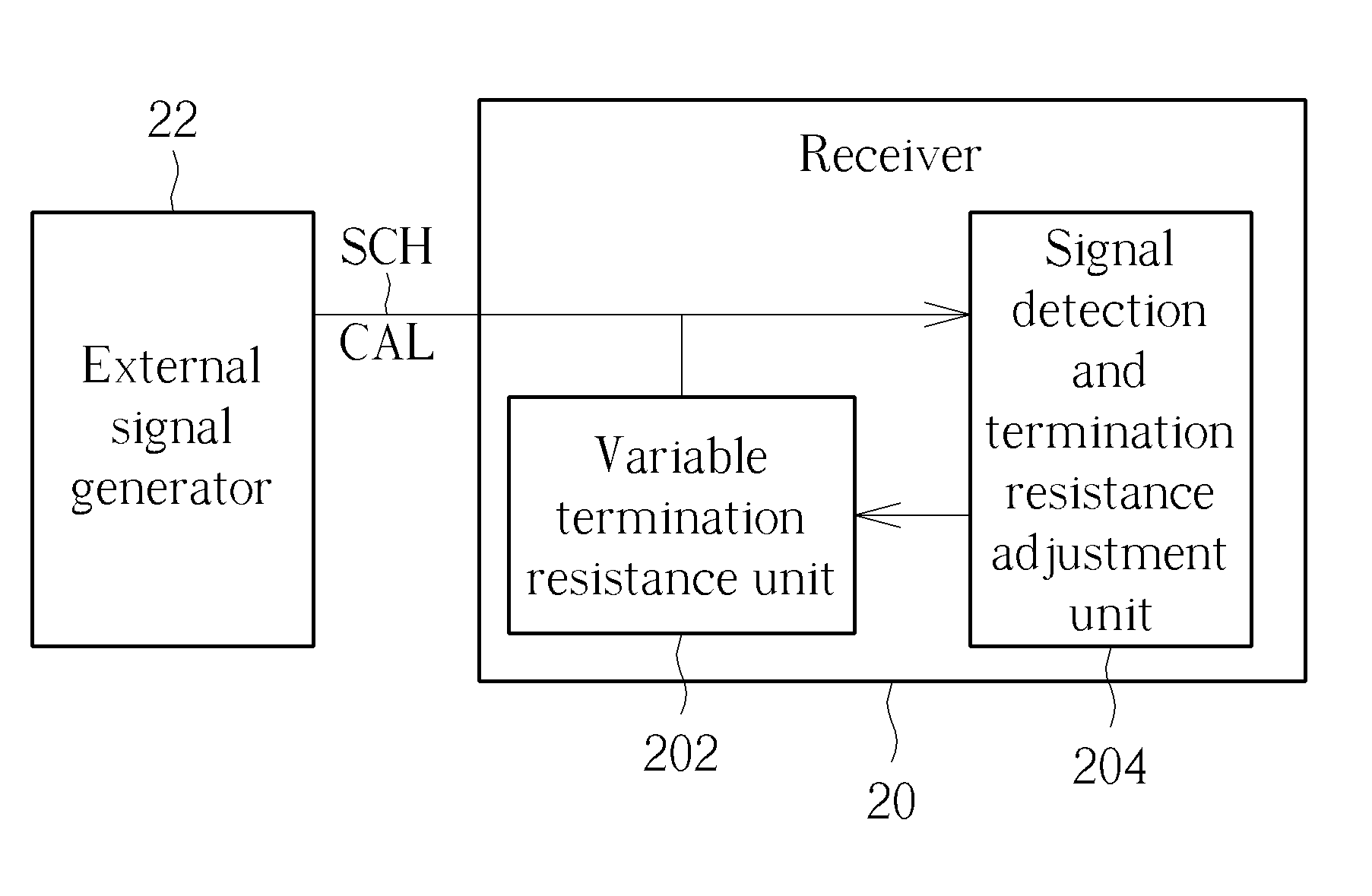
ActiveUS8963578B2Improve accuracyReliability increasing modificationsLine impedence variation compensationImpedance matchingSignal generator
The present invention discloses a receiver capable of enhancing accuracy of signal reception. The receiver includes a variable termination resistance unit, coupled to at least one channel, for utilizing at least one termination resistance corresponding to the at least one channel to perform impedance matching, and a signal detection and termination resistance adjustment unit, for detecting at least one external calibration signal corresponding to the at least one channel from at least one external signal generator, and adjusting the at least one termination resistance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Communication channel calibration for drift conditions
ActiveUS20120155526A1Improve memory utilizationIncrease profitLine impedence variation compensationSynchronisation error correctionTelecommunications linkData source
A method and system provides for execution of calibration cycles from time to time during normal operation of the communication channel. A calibration cycle includes de-coupling the normal data source from the transmitter and supplying a calibration pattern in its place. The calibration pattern is received from the communication link using the receiver on the second component. A calibrated value of a parameter of the communication channel is determined in response to the received calibration pattern. The steps involved in calibration cycles can be reordered to account for utilization patterns of the communication channel. For bidirectional links, calibration cycles are executed which include the step of storing received calibration patterns on the second component, and retransmitting such calibration patterns back to the first component for use in adjusting parameters of the channel at first component.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Automatic Gain Control Apparatus and Method in Wireless Telecommunication System
InactiveUS20080317176A1Easy to getLine impedence variation compensationGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates to an automatic gain control apparatus and method in a wireless telecommunication system which measures the strength of received signals using preamble symbols and automatically control the gain of an amplifier based on the measurement results. The automatic gain control apparatus and method according to present invention performs automatic gain control of measuring sample power in a sample unit for input signals, acquiring a sample power average value during a unit symbol period, detecting a maximum value during one frame period for the acquired sample power average value and then calculating a gain control value based on it.
Owner:POS DATA CO LTD
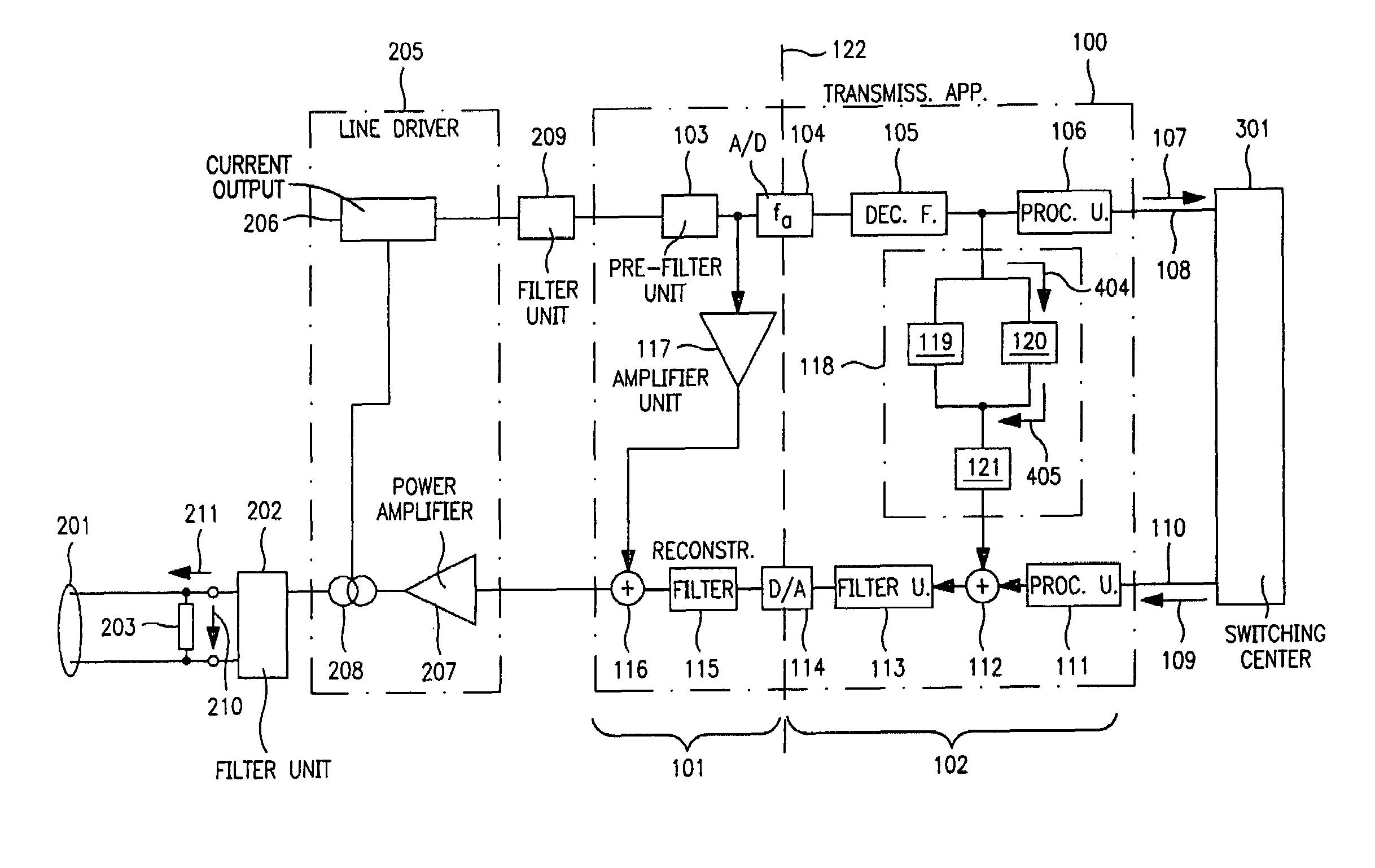
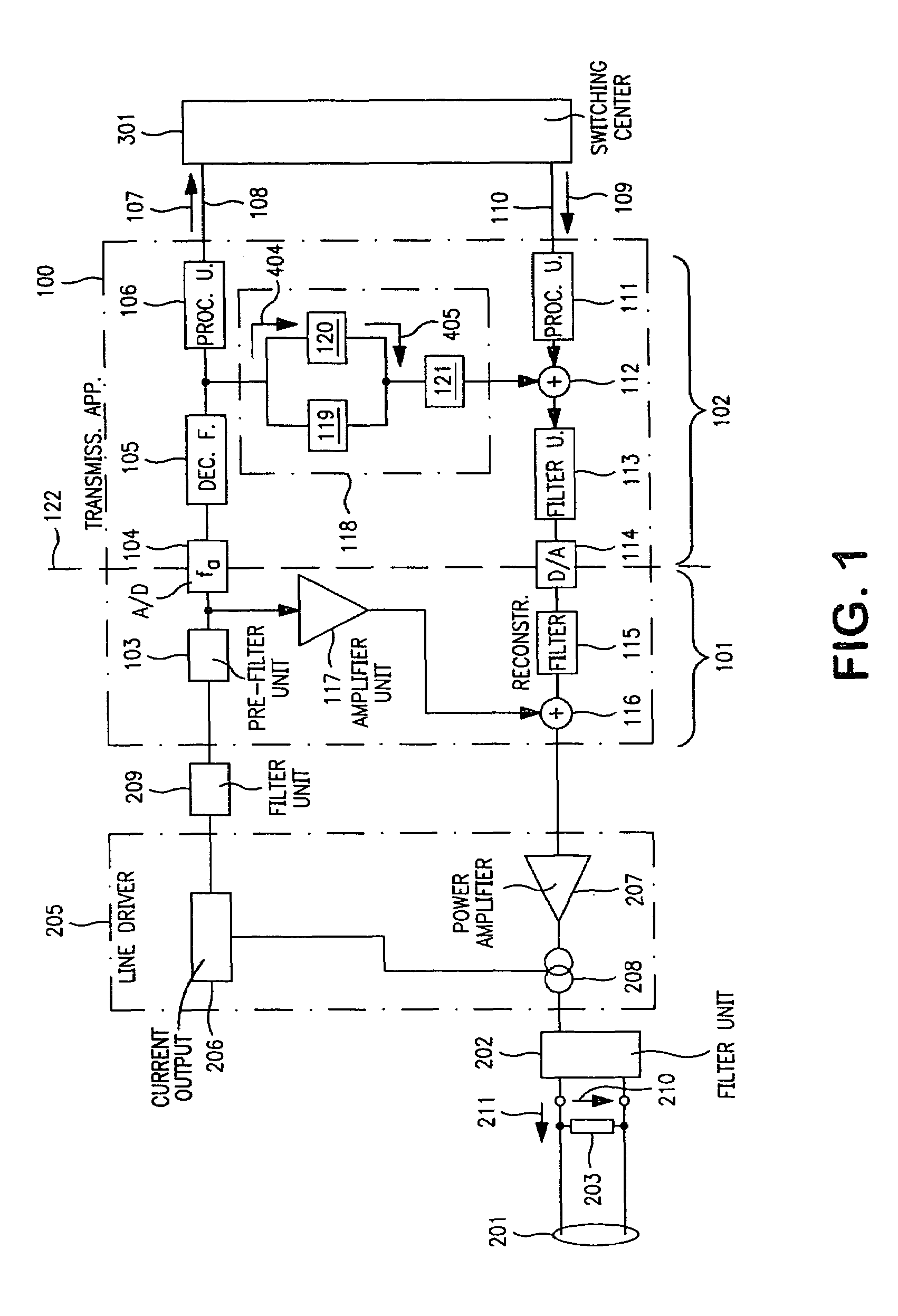
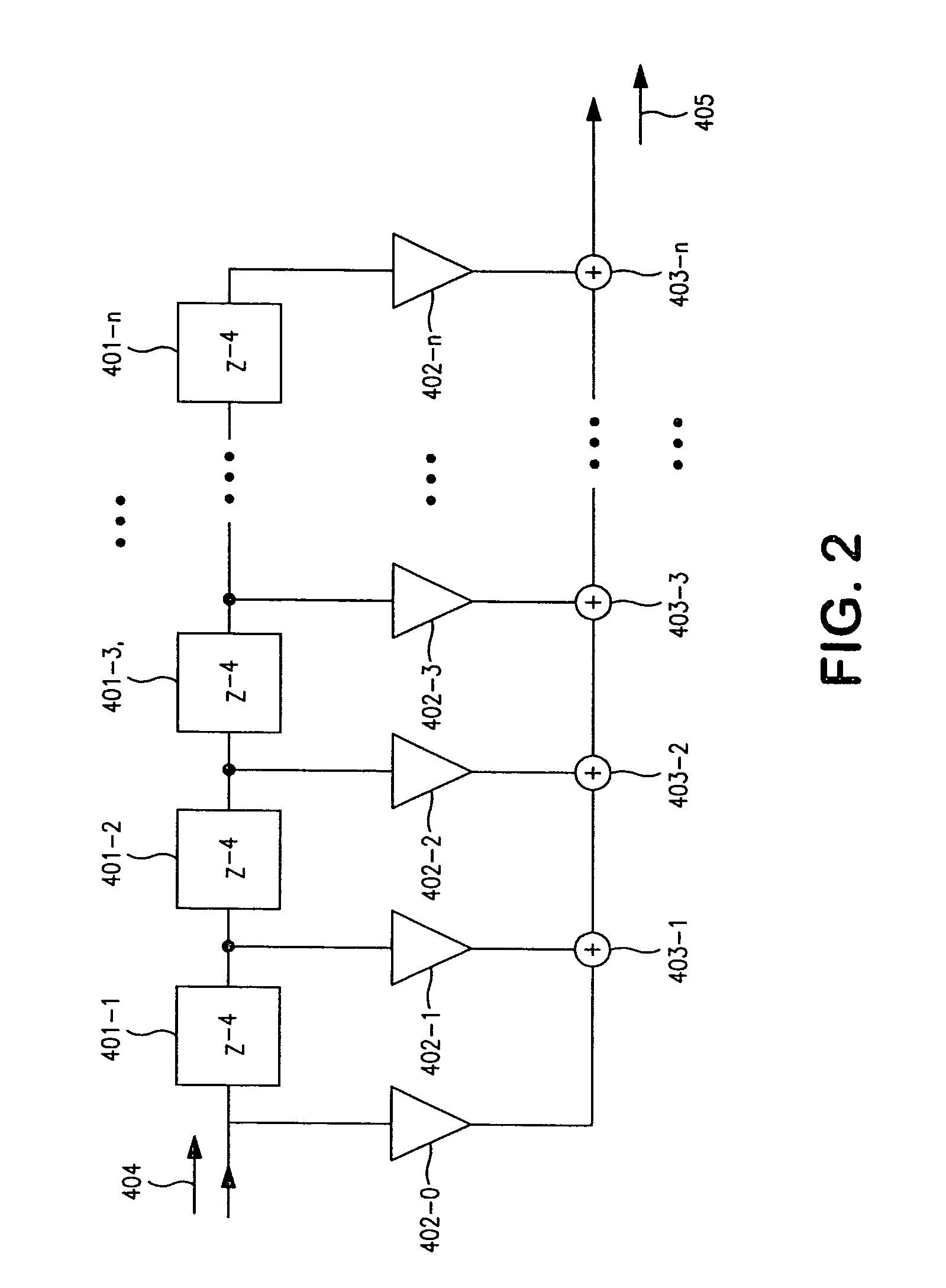
Transmission apparatus with variable impedance matching
ActiveUS7496150B2Reduce circuit complexityReduce rateInterconnection arrangementsLine impedence variation compensationElectricityDigital feedback
The invention provides a transmission apparatus (100) for transmission of electrical signals between a line driver (205), which is connected to a transmission line (201), and a switching center (301), having an analog feedback device (101) for coarse setting of a line voltage level (210) on the transmission line (201), and a digital feedback device (102), which is coupled to the analog feedback device (101) and has a feedback filter device (118), designed such that a filter input signal (404) can be converted to a filter output signal (405) at a rate which is lower than the sampling rate (fa) of an analog / digital converter (104).
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
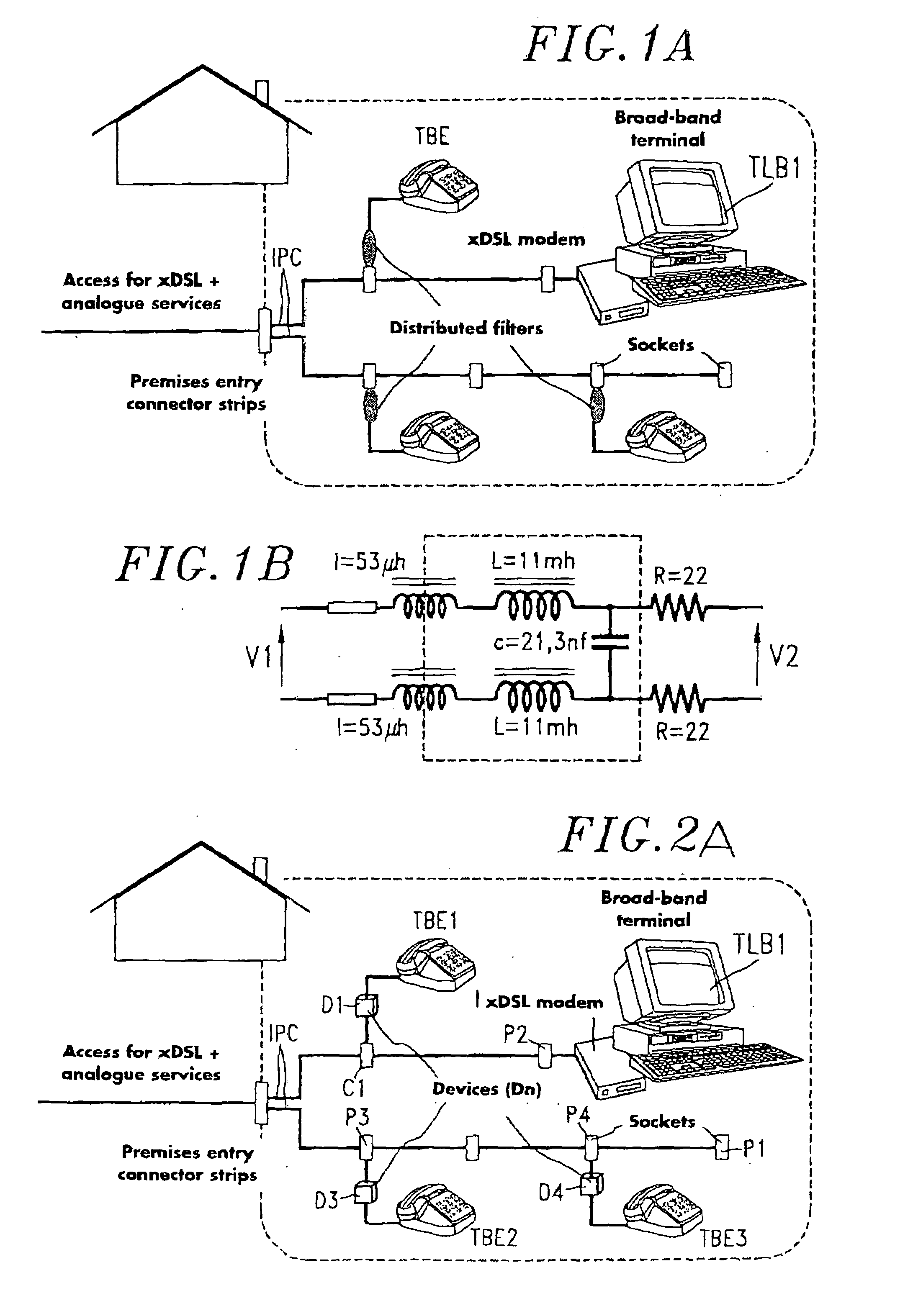
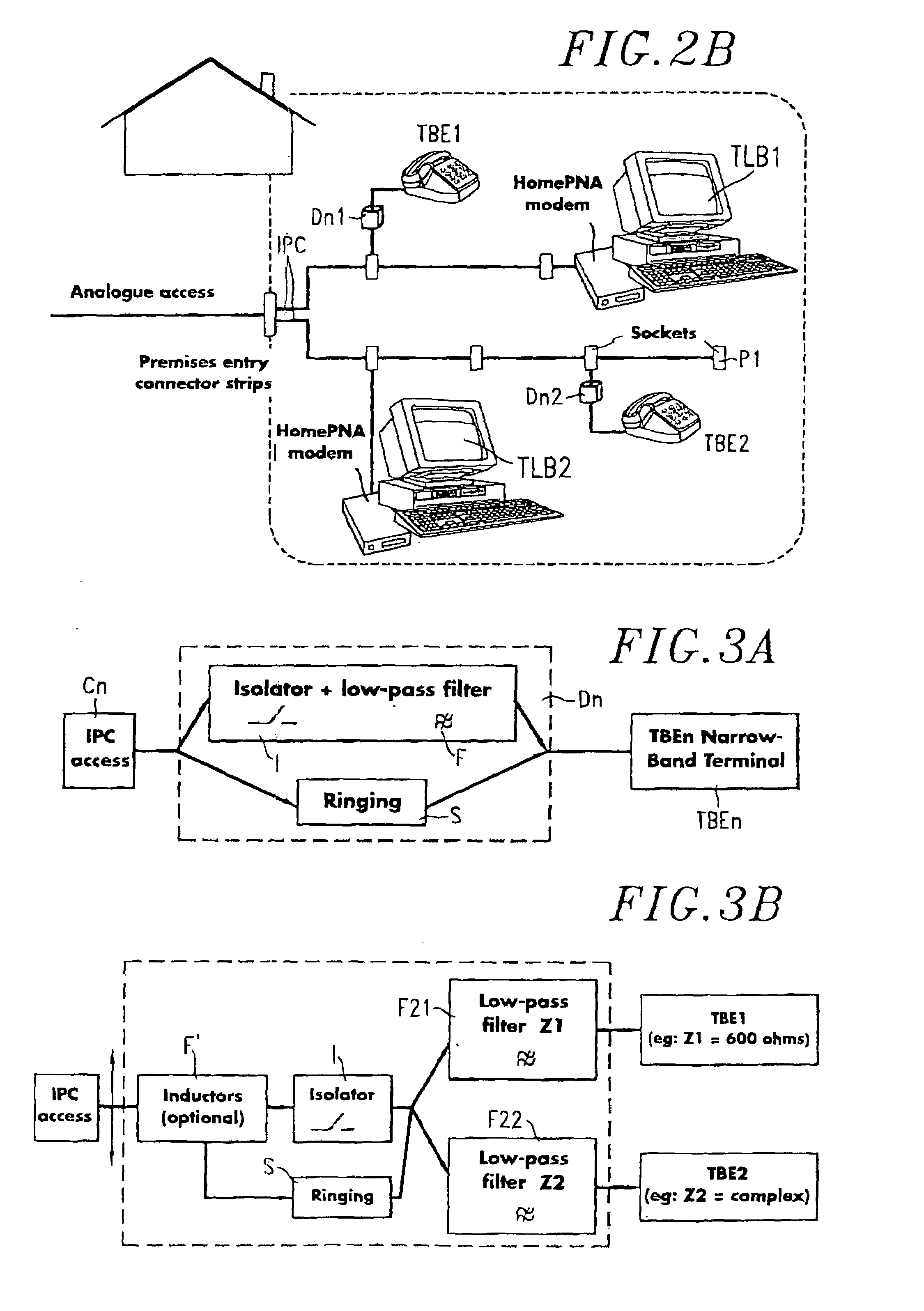
Low-pass filtering device with integrated insulator and private installation comprising same
InactiveUS6980645B1Interconnection arrangementsLine impedence variation compensationAccess networkInput impedance
A filtering device for a narrow-band terminal in a private installation connected to an access network carrying narrow-band services (analogue or ISDN) and broad-band services (xDSL or HomePNA). The device has a low-pass filter associated with an insulation enabling the device to have a high input impedance insulating the installation when the narrow-band terminal is on hook while allowing the ringing signal to pass. Applicable to private telephone-teledata installations.
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC +1
Popular searches
High frequency circuit adaptations Printed circuits structural associations Transmission line coupling arrangements Line-transmission Electric digital data processing Synchronisation transmitters Synchronisation signal speed/phase control Duplex signal operation Resistance/reactance/impedence Fault location by pulse reflection methods
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com