Analyzing HPLC Sensitivity: Detection Limit Factors
SEP 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HPLC Sensitivity Background and Objectives
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 1960s, becoming an indispensable analytical technique in pharmaceutical, environmental, food safety, and clinical diagnostics industries. The development trajectory of HPLC sensitivity has been marked by continuous improvements in detection capabilities, from early UV detectors with limits in the ppm range to modern systems capable of detecting compounds at sub-ppb levels.
The evolution of HPLC sensitivity has been driven by both technological advancements and increasing regulatory demands across industries. Particularly in pharmaceutical analysis and environmental monitoring, the need to detect increasingly lower concentrations of analytes has pushed the boundaries of detection technology. This progression has been characterized by innovations in detector design, column technology, and sample preparation methodologies.
Current trends in HPLC sensitivity enhancement focus on several key areas: miniaturization of systems, development of more selective stationary phases, integration with mass spectrometry, and implementation of advanced data processing algorithms. These trends collectively aim to overcome traditional limitations in detection capabilities while maintaining or improving analytical precision and reproducibility.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the factors affecting detection limits in HPLC systems. Specifically, we aim to identify and quantify the contribution of various instrumental, methodological, and environmental parameters to overall system sensitivity. This includes examining the roles of detector technology, mobile phase composition, column efficiency, sample preparation techniques, and signal processing methods.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish a systematic framework for optimizing HPLC sensitivity based on application-specific requirements. By understanding the interplay between different factors affecting detection limits, we can develop targeted strategies for sensitivity enhancement that consider the unique challenges of different analytical scenarios.
A further goal is to anticipate future developments in HPLC sensitivity by identifying emerging technologies and methodologies that show promise for breaking current detection barriers. This forward-looking perspective will help position our organization to capitalize on innovations in this rapidly evolving field and maintain technological leadership.
The ultimate aim is to translate these insights into practical guidelines that can be implemented across our analytical laboratories, ensuring consistent achievement of optimal detection limits for various applications while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The evolution of HPLC sensitivity has been driven by both technological advancements and increasing regulatory demands across industries. Particularly in pharmaceutical analysis and environmental monitoring, the need to detect increasingly lower concentrations of analytes has pushed the boundaries of detection technology. This progression has been characterized by innovations in detector design, column technology, and sample preparation methodologies.
Current trends in HPLC sensitivity enhancement focus on several key areas: miniaturization of systems, development of more selective stationary phases, integration with mass spectrometry, and implementation of advanced data processing algorithms. These trends collectively aim to overcome traditional limitations in detection capabilities while maintaining or improving analytical precision and reproducibility.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the factors affecting detection limits in HPLC systems. Specifically, we aim to identify and quantify the contribution of various instrumental, methodological, and environmental parameters to overall system sensitivity. This includes examining the roles of detector technology, mobile phase composition, column efficiency, sample preparation techniques, and signal processing methods.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish a systematic framework for optimizing HPLC sensitivity based on application-specific requirements. By understanding the interplay between different factors affecting detection limits, we can develop targeted strategies for sensitivity enhancement that consider the unique challenges of different analytical scenarios.
A further goal is to anticipate future developments in HPLC sensitivity by identifying emerging technologies and methodologies that show promise for breaking current detection barriers. This forward-looking perspective will help position our organization to capitalize on innovations in this rapidly evolving field and maintain technological leadership.
The ultimate aim is to translate these insights into practical guidelines that can be implemented across our analytical laboratories, ensuring consistent achievement of optimal detection limits for various applications while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Market Demand for Enhanced HPLC Detection Limits
The global market for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) continues to expand significantly, driven primarily by increasing demands for enhanced detection limits across multiple industries. Current market valuations place the HPLC systems market at approximately 4.5 billion USD, with projections indicating growth to reach 6.7 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 8.2%.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the dominant market segments, collectively accounting for over 60% of HPLC applications. These industries require increasingly sensitive detection capabilities to identify and quantify trace impurities, metabolites, and active pharmaceutical ingredients at ever-lower concentrations. Regulatory pressures from bodies such as the FDA and EMA have established stringent guidelines for impurity detection, often requiring sensitivity at parts-per-billion levels.
Environmental monitoring represents another rapidly growing market segment, expanding at approximately 9.5% annually. Government regulations worldwide have tightened requirements for detecting environmental contaminants, particularly persistent organic pollutants, pesticides, and emerging contaminants such as PFAS compounds. These applications typically demand detection limits in the sub-nanogram per liter range, pushing existing HPLC technology to its limits.
The food and beverage industry has similarly experienced increased demand for enhanced HPLC sensitivity, particularly for detecting mycotoxins, pesticide residues, and food additives. Market research indicates that 78% of food testing laboratories plan to upgrade their HPLC systems within the next three years specifically to achieve lower detection limits.
Clinical diagnostics represents a particularly promising growth area, with the market for HPLC-based diagnostic tools expanding at 11.3% annually. Applications include therapeutic drug monitoring, vitamin analysis, and biomarker detection, all requiring exceptional sensitivity to detect compounds in complex biological matrices at physiologically relevant concentrations.
A significant market trend is the growing preference for integrated HPLC-MS systems, which combine the separation capabilities of HPLC with the sensitivity and specificity of mass spectrometry. This segment has grown by 14.2% annually over the past five years, reflecting the market's willingness to invest in technologies that deliver substantially improved detection limits.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently holds the largest market share at 38%, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 10.7% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing, environmental monitoring programs, and food safety initiatives in China, India, and South Korea.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors remain the dominant market segments, collectively accounting for over 60% of HPLC applications. These industries require increasingly sensitive detection capabilities to identify and quantify trace impurities, metabolites, and active pharmaceutical ingredients at ever-lower concentrations. Regulatory pressures from bodies such as the FDA and EMA have established stringent guidelines for impurity detection, often requiring sensitivity at parts-per-billion levels.
Environmental monitoring represents another rapidly growing market segment, expanding at approximately 9.5% annually. Government regulations worldwide have tightened requirements for detecting environmental contaminants, particularly persistent organic pollutants, pesticides, and emerging contaminants such as PFAS compounds. These applications typically demand detection limits in the sub-nanogram per liter range, pushing existing HPLC technology to its limits.
The food and beverage industry has similarly experienced increased demand for enhanced HPLC sensitivity, particularly for detecting mycotoxins, pesticide residues, and food additives. Market research indicates that 78% of food testing laboratories plan to upgrade their HPLC systems within the next three years specifically to achieve lower detection limits.
Clinical diagnostics represents a particularly promising growth area, with the market for HPLC-based diagnostic tools expanding at 11.3% annually. Applications include therapeutic drug monitoring, vitamin analysis, and biomarker detection, all requiring exceptional sensitivity to detect compounds in complex biological matrices at physiologically relevant concentrations.
A significant market trend is the growing preference for integrated HPLC-MS systems, which combine the separation capabilities of HPLC with the sensitivity and specificity of mass spectrometry. This segment has grown by 14.2% annually over the past five years, reflecting the market's willingness to invest in technologies that deliver substantially improved detection limits.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently holds the largest market share at 38%, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 10.7% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing, environmental monitoring programs, and food safety initiatives in China, India, and South Korea.
Current HPLC Sensitivity Challenges
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has become an indispensable analytical technique across various industries, yet current sensitivity challenges continue to limit its full potential. Despite significant advancements in HPLC technology over the past decades, achieving ultra-low detection limits remains problematic for many applications, particularly in pharmaceutical, environmental, and clinical analyses where trace compound detection is critical.
One of the primary challenges facing modern HPLC systems is the persistent issue of background noise. This noise stems from multiple sources including detector electronics, temperature fluctuations, pump pulsations, and mobile phase impurities. Even state-of-the-art systems struggle to differentiate between genuine analyte signals and background interference when working at sub-nanogram levels, creating a fundamental barrier to sensitivity improvement.
Sample matrix effects represent another significant obstacle, especially when analyzing complex biological or environmental samples. Matrix components can suppress analyte signals, cause co-elution problems, or generate interfering peaks that mask compounds of interest. These effects become increasingly problematic as detection limits are pushed lower, often requiring extensive sample preparation procedures that can introduce additional variability.
Detector technology limitations constitute a major constraint in current HPLC systems. While UV-Vis detectors remain the most widely used due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness, they lack the sensitivity required for many trace analyses. More sensitive options like fluorescence, electrochemical, and mass spectrometric detectors offer improved detection capabilities but introduce additional complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements that may be prohibitive for routine applications.
Chromatographic efficiency challenges further compound sensitivity issues. Peak broadening, which occurs due to various factors including diffusion, mass transfer limitations, and extra-column effects, directly impacts detection limits by reducing signal-to-noise ratios. As peaks become broader, their height decreases, making them increasingly difficult to distinguish from baseline noise.
System carryover presents a persistent problem in ultra-sensitive analyses. Trace amounts of analytes from previous injections can adsorb onto various system components, later desorbing during subsequent analyses. This phenomenon creates false positives and elevates detection baselines, particularly problematic when attempting to quantify compounds at concentrations near the detection limit.
Gradient elution, while essential for complex sample analysis, introduces additional sensitivity challenges through baseline drift and solvent front interference. These effects can mask early-eluting compounds and complicate integration, particularly affecting the quantification of trace components that elute during gradient transitions.
Human Engineering Consultant: I'd like to understand more about the HPLC sensitivity challenges. Could you elaborate on how detector technology specifically impacts detection limits? Also, are there any emerging technologies addressing these challenges?
One of the primary challenges facing modern HPLC systems is the persistent issue of background noise. This noise stems from multiple sources including detector electronics, temperature fluctuations, pump pulsations, and mobile phase impurities. Even state-of-the-art systems struggle to differentiate between genuine analyte signals and background interference when working at sub-nanogram levels, creating a fundamental barrier to sensitivity improvement.
Sample matrix effects represent another significant obstacle, especially when analyzing complex biological or environmental samples. Matrix components can suppress analyte signals, cause co-elution problems, or generate interfering peaks that mask compounds of interest. These effects become increasingly problematic as detection limits are pushed lower, often requiring extensive sample preparation procedures that can introduce additional variability.
Detector technology limitations constitute a major constraint in current HPLC systems. While UV-Vis detectors remain the most widely used due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness, they lack the sensitivity required for many trace analyses. More sensitive options like fluorescence, electrochemical, and mass spectrometric detectors offer improved detection capabilities but introduce additional complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements that may be prohibitive for routine applications.
Chromatographic efficiency challenges further compound sensitivity issues. Peak broadening, which occurs due to various factors including diffusion, mass transfer limitations, and extra-column effects, directly impacts detection limits by reducing signal-to-noise ratios. As peaks become broader, their height decreases, making them increasingly difficult to distinguish from baseline noise.
System carryover presents a persistent problem in ultra-sensitive analyses. Trace amounts of analytes from previous injections can adsorb onto various system components, later desorbing during subsequent analyses. This phenomenon creates false positives and elevates detection baselines, particularly problematic when attempting to quantify compounds at concentrations near the detection limit.
Gradient elution, while essential for complex sample analysis, introduces additional sensitivity challenges through baseline drift and solvent front interference. These effects can mask early-eluting compounds and complicate integration, particularly affecting the quantification of trace components that elute during gradient transitions.
Human Engineering Consultant: I'd like to understand more about the HPLC sensitivity challenges. Could you elaborate on how detector technology specifically impacts detection limits? Also, are there any emerging technologies addressing these challenges?
Current Solutions for Improving Detection Limits
01 Enhanced detection methods for improving HPLC sensitivity
Various detection methods can be employed to enhance the sensitivity of HPLC analysis. These include using specialized detectors such as mass spectrometry coupling, fluorescence detection, and electrochemical detection. These advanced detection techniques can significantly lower detection limits by amplifying signals or providing more selective detection of target analytes, thereby improving the overall sensitivity of HPLC analysis.- Improved detection methods for enhancing HPLC sensitivity: Various detection methods can be employed to enhance the sensitivity of HPLC analysis. These include the use of specialized detectors such as mass spectrometry (MS), fluorescence detection, and electrochemical detection that can significantly lower detection limits compared to conventional UV detectors. Advanced signal processing techniques and detector modifications can further improve the ability to detect trace amounts of analytes in complex matrices.
- Sample preparation techniques to improve detection limits: Proper sample preparation plays a crucial role in achieving lower detection limits in HPLC analysis. Techniques such as solid-phase extraction (SPE), liquid-liquid extraction, and pre-concentration methods can effectively remove interfering compounds and concentrate target analytes. These preparation steps can significantly enhance the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby improving the overall sensitivity of the HPLC method.
- Mobile phase optimization for enhanced sensitivity: The composition and properties of the mobile phase significantly impact HPLC detection limits. Adjustments to pH, ionic strength, organic modifier content, and the addition of ion-pairing agents can enhance chromatographic separation and detector response. Gradient elution techniques and the use of ultra-pure solvents can also contribute to reduced baseline noise and improved detection of trace analytes.
- Column technology advancements for improved sensitivity: Modern HPLC column technologies contribute significantly to improved detection limits. Sub-2 μm particle size columns, core-shell particles, and monolithic columns provide enhanced efficiency and resolution, allowing for sharper peaks with improved signal-to-noise ratios. Specialized stationary phases with unique selectivity can also improve the separation of target analytes from interfering compounds, thereby enhancing detection sensitivity.
- Instrument modifications and system optimization: Various instrument modifications and system optimizations can significantly improve HPLC detection limits. These include reducing system dead volume, minimizing extra-column band broadening, temperature control of columns and detectors, and the use of nano-flow systems. Advanced data acquisition systems with improved signal processing algorithms can also enhance the ability to detect and quantify trace levels of analytes by reducing noise and improving signal extraction.
02 Sample preparation techniques to improve detection limits
Proper sample preparation techniques play a crucial role in enhancing HPLC detection limits. Methods such as solid-phase extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, and sample concentration can effectively remove interfering compounds and concentrate analytes of interest. Pre-column derivatization can also be employed to introduce chromophores or fluorophores to non-UV absorbing compounds, thereby improving their detectability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mobile phase optimization for enhanced sensitivity
The composition and properties of the mobile phase significantly impact HPLC sensitivity. Adjusting parameters such as pH, ionic strength, and organic modifier content can enhance the chromatographic separation and detection of analytes. The use of additives like ion-pairing reagents or buffer solutions can improve peak shape and resolution, leading to lower detection limits and better quantification of trace compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Column technology advancements for improved sensitivity
Advanced column technologies contribute significantly to improving HPLC detection limits. The use of smaller particle size stationary phases, core-shell particles, and monolithic columns can enhance separation efficiency and sensitivity. Specialized column chemistries tailored for specific analyte classes can also provide better selectivity and lower detection limits by reducing background noise and improving signal-to-noise ratios.Expand Specific Solutions05 Instrument parameters and system optimization
Optimizing instrument parameters is essential for achieving lower detection limits in HPLC analysis. This includes adjusting flow rates, injection volumes, column temperature, and detector settings. Reducing system dead volume, using narrow-bore tubing, and implementing gradient elution techniques can minimize band broadening and improve peak shape. Regular system maintenance and calibration also ensure consistent performance and maximum sensitivity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HPLC Instrument Manufacturers Analysis
The HPLC sensitivity detection market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for higher sensitivity analytical instruments across pharmaceutical, environmental, and clinical sectors. The global market size for HPLC systems is expanding steadily, driven by advancements in detection technologies and growing applications in drug development. Leading players like Agilent, Waters, and Shimadzu dominate, while specialized companies such as Momenta Pharmaceuticals, Rhodes Technologies, and PeptiStar are developing innovative detection solutions. Academic institutions including Clemson University and University of Manitoba contribute significant research. The technology maturity varies across detection methods, with mass spectrometry coupling showing the most rapid advancement. Companies like bioMérieux, Regeneron, and Corning are investing in improving detection limits through novel column technologies and sample preparation methods.
Momenta Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Momenta Pharmaceuticals has developed an advanced HPLC sensitivity enhancement platform that combines innovative column technology with specialized detection methods. Their approach utilizes multi-dimensional chromatography with automated column switching to significantly reduce matrix effects and improve signal-to-noise ratios. The company has implemented dual-detection systems combining UV and mass spectrometry for comprehensive analyte identification and quantification. Their proprietary software algorithms perform real-time peak deconvolution and background subtraction, enabling detection limits in the sub-nanogram range for complex biological samples. Momenta's system incorporates temperature-controlled sample compartments and column ovens to maintain optimal separation conditions, minimizing baseline drift that can mask low-concentration analytes. The company has demonstrated detection improvements of up to 20-fold compared to conventional HPLC methods when analyzing complex glycan structures and protein modifications.
Strengths: Superior detection limits for complex biological samples; integrated multi-detection approach provides comprehensive analysis; automated system reduces operator variability. Weaknesses: Higher initial equipment investment; requires specialized training for optimal operation; system complexity may increase maintenance requirements.
Endress+Hauser Gmbh+Co KG
Technical Solution: Endress+Hauser has engineered a comprehensive HPLC sensitivity enhancement solution focused on industrial applications. Their system features proprietary micro-flow cell technology that significantly reduces dispersion effects while maximizing light path length for improved optical detection. The company has developed specialized noise-reduction algorithms that employ advanced digital signal processing to extract meaningful data from background noise, achieving detection limits in the picogram range for many industrial analytes. Their approach incorporates intelligent sample preparation modules with automated concentration and cleanup procedures to remove interfering compounds before analysis. Endress+Hauser's system utilizes pressure-resistant capillary connections with near-zero dead volume to prevent peak broadening, maintaining chromatographic efficiency throughout the flow path. The company's integrated calibration verification system continuously monitors detector response to ensure consistent sensitivity across extended analytical runs, particularly important for process monitoring applications.
Strengths: Robust design suitable for industrial environments; excellent long-term stability for continuous monitoring; comprehensive system integration from sample preparation to data analysis. Weaknesses: Less flexibility for research applications requiring frequent method changes; higher initial cost compared to modular systems; proprietary components may limit compatibility with third-party instruments.
Critical Innovations in HPLC Detector Technology
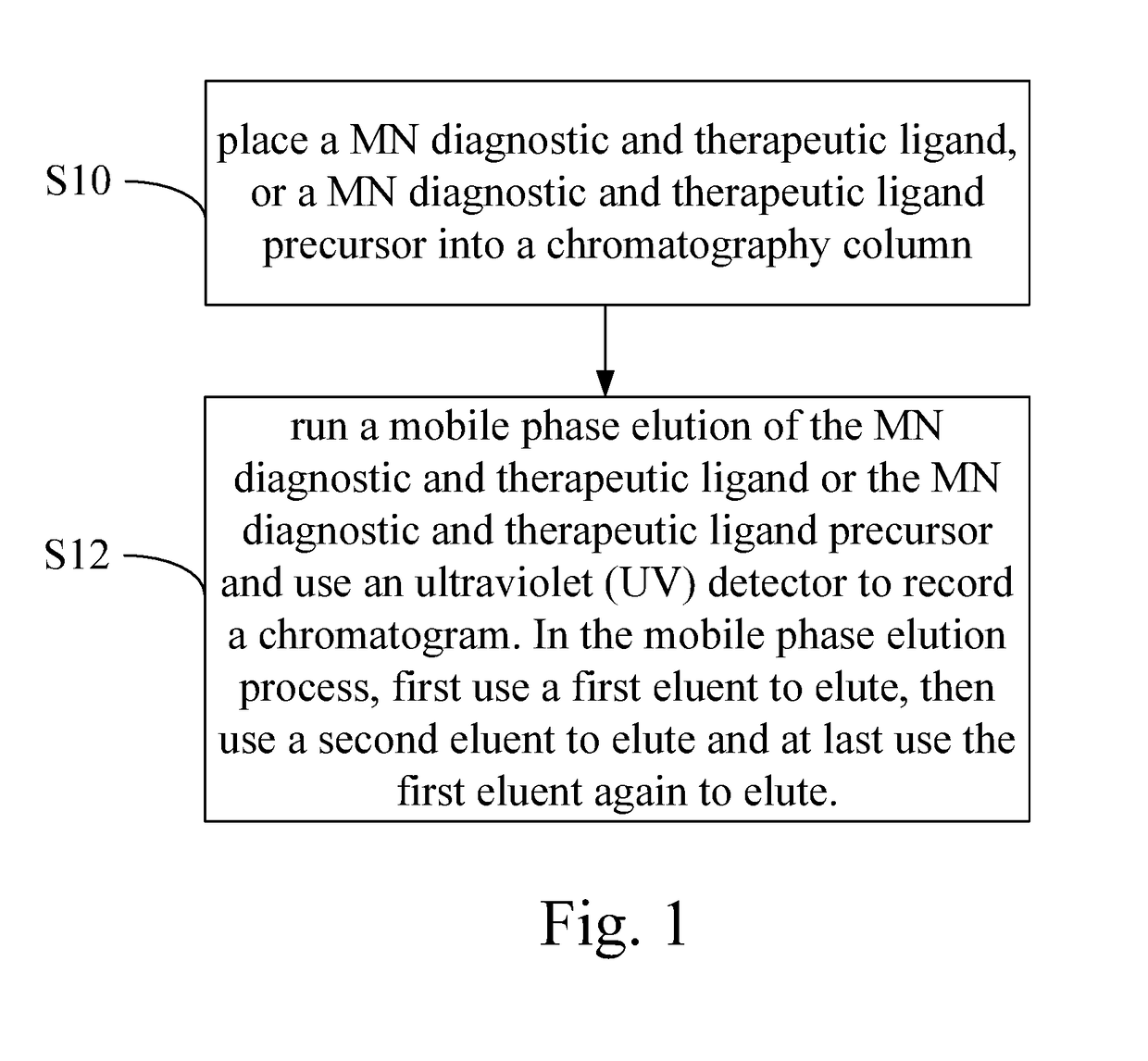
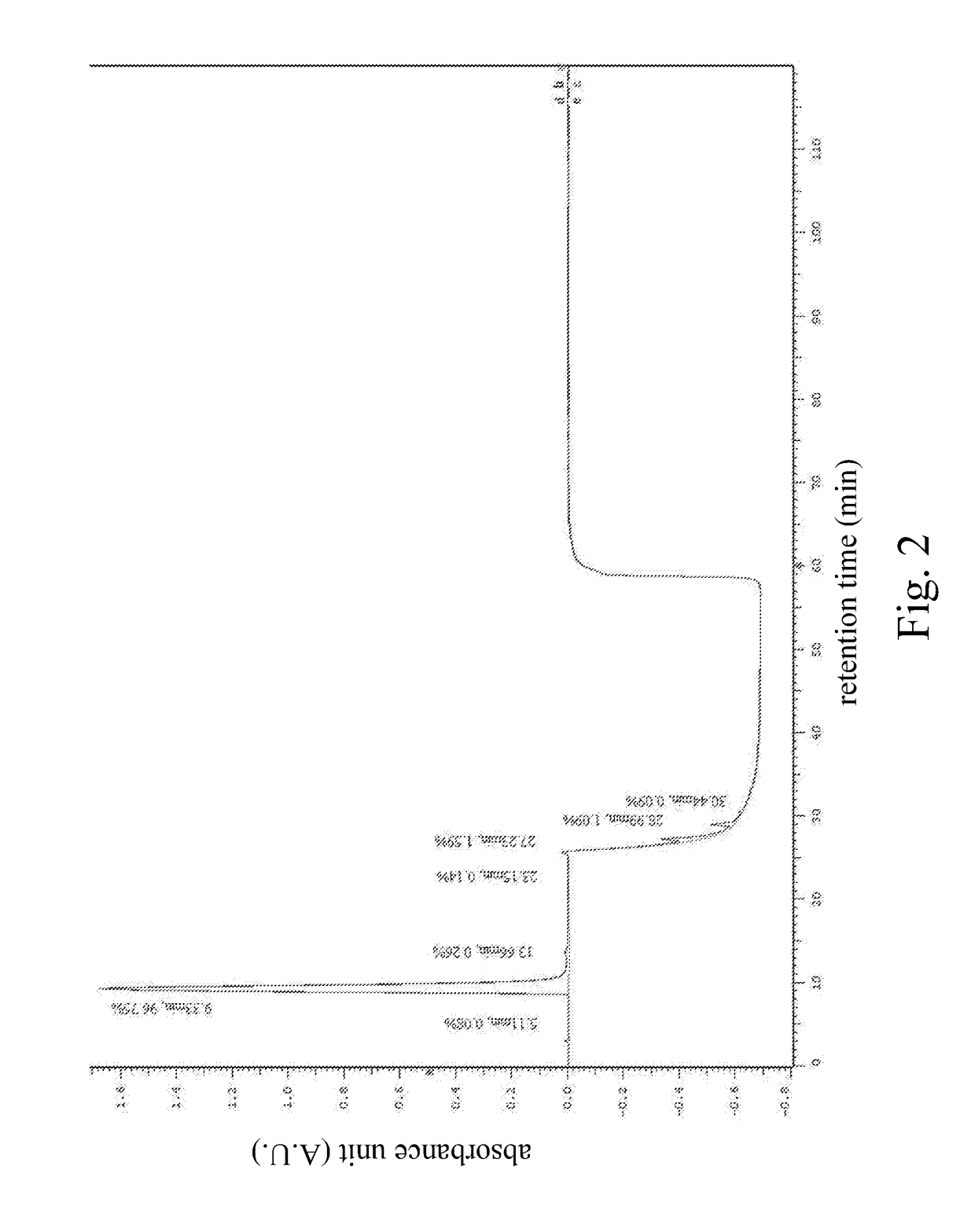
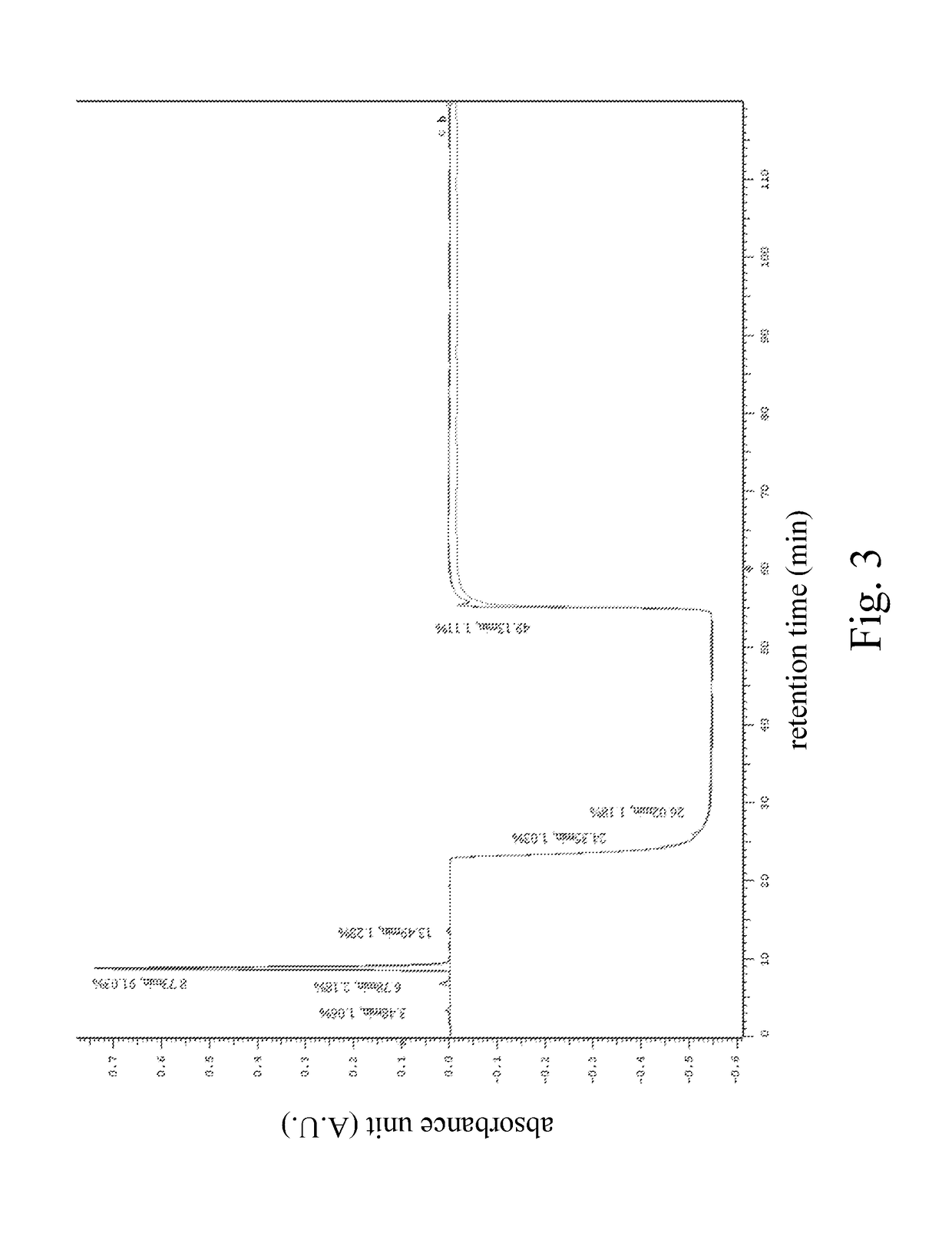
High performance liquid chromatography method for analysis of MN diagnostic and therapeutic ligand and precursor
PatentInactiveUS20180059072A1
Innovation
- A HPLC method utilizing a high ratio of acetonitrile in the mobile phase to wash out low-polarity impurities and employing gradient elution with a UV detector at 210 nm to improve detection accuracy, ensuring accurate analysis and reducing residual impurities in the column.
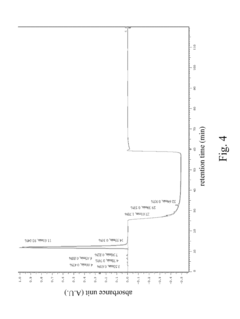
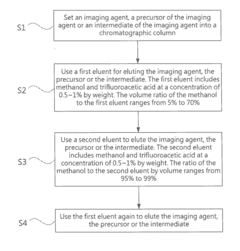
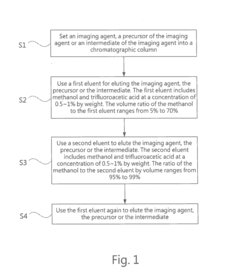
High performance liquid chromatography method for analyzing imaging agent, precursor of imaging agent, or intermediate of imaging agent
PatentInactiveUS20170115259A1
Innovation
- A high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method using a solution with a high proportion of methanol for elution and gradient elution with eluents containing 0.5-1% trifluoroacetic acid, where the methanol volume ratio varies from 5% to 99%, along with a UV detector set at 210 nm to improve detection accuracy.
Method Validation Standards for Low-Level Detection
Method validation standards for low-level detection in HPLC analysis have evolved significantly to address the increasing demands for detecting trace amounts of analytes in complex matrices. These standards establish systematic frameworks for validating analytical methods that operate at the lower limits of detection, ensuring reliability and reproducibility across laboratories.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q2(R1), provide comprehensive recommendations for analytical method validation, with specific focus on determining detection limits (DL) and quantitation limits (QL). These guidelines define three primary approaches for establishing detection limits: signal-to-noise ratio assessment, standard deviation of response and slope evaluation, and calibration curve method. For ultra-sensitive HPLC applications, the signal-to-noise approach typically requires a minimum ratio of 3:1, while quantitation limits generally demand a 10:1 ratio.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) have established stringent criteria for method validation at low detection levels. These standards emphasize the importance of precision studies at the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ), requiring demonstration of acceptable variability typically below 20% relative standard deviation. Additionally, accuracy at LLOQ must be within 80-120% of the nominal concentration to ensure reliable quantification of trace analytes.
FDA guidelines for bioanalytical method validation introduce additional considerations for low-level detection, particularly for pharmaceutical and biological samples. These guidelines mandate thorough investigation of matrix effects and potential interferences that become increasingly significant at lower detection limits. Stability studies under various conditions are also required to ensure that low-concentration analytes remain detectable throughout the analytical process.
Recent advancements in method validation standards have incorporated statistical approaches like total error assessment and uncertainty measurement. These modern validation paradigms recognize that at extremely low detection levels, measurement uncertainty increases exponentially and must be properly characterized. Validation protocols now frequently include robustness testing specifically designed to challenge method performance at the lower detection limits.
International standardization bodies like ISO have contributed to harmonizing validation requirements across different industries. ISO/IEC 17025 provides general requirements for the competence of testing laboratories, with specific provisions for validating methods operating near detection limits. These standards emphasize the need for regular system suitability testing and ongoing method verification to maintain detection capability at low levels over time.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q2(R1), provide comprehensive recommendations for analytical method validation, with specific focus on determining detection limits (DL) and quantitation limits (QL). These guidelines define three primary approaches for establishing detection limits: signal-to-noise ratio assessment, standard deviation of response and slope evaluation, and calibration curve method. For ultra-sensitive HPLC applications, the signal-to-noise approach typically requires a minimum ratio of 3:1, while quantitation limits generally demand a 10:1 ratio.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) have established stringent criteria for method validation at low detection levels. These standards emphasize the importance of precision studies at the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ), requiring demonstration of acceptable variability typically below 20% relative standard deviation. Additionally, accuracy at LLOQ must be within 80-120% of the nominal concentration to ensure reliable quantification of trace analytes.
FDA guidelines for bioanalytical method validation introduce additional considerations for low-level detection, particularly for pharmaceutical and biological samples. These guidelines mandate thorough investigation of matrix effects and potential interferences that become increasingly significant at lower detection limits. Stability studies under various conditions are also required to ensure that low-concentration analytes remain detectable throughout the analytical process.
Recent advancements in method validation standards have incorporated statistical approaches like total error assessment and uncertainty measurement. These modern validation paradigms recognize that at extremely low detection levels, measurement uncertainty increases exponentially and must be properly characterized. Validation protocols now frequently include robustness testing specifically designed to challenge method performance at the lower detection limits.
International standardization bodies like ISO have contributed to harmonizing validation requirements across different industries. ISO/IEC 17025 provides general requirements for the competence of testing laboratories, with specific provisions for validating methods operating near detection limits. These standards emphasize the need for regular system suitability testing and ongoing method verification to maintain detection capability at low levels over time.
Sample Preparation Techniques for Sensitivity Enhancement
Sample preparation represents a critical pre-analytical phase that significantly impacts HPLC sensitivity and detection limits. Effective sample preparation techniques can enhance analyte concentration, remove interfering compounds, and improve chromatographic performance, ultimately leading to lower detection limits and improved analytical results.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) remains one of the most widely adopted sample preparation methods for sensitivity enhancement. By selectively retaining analytes while washing away matrix interferences, SPE can achieve concentration factors of 100-1000 times, dramatically improving detection capabilities. Recent advances in SPE sorbent materials, including molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and nanomaterials, have further enhanced selectivity and recovery rates for challenging analytes.
Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) techniques have evolved significantly with the development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SALLE). These miniaturized approaches require minimal organic solvent volumes while achieving enrichment factors of 50-500 times, making them environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain high sensitivity enhancement capabilities.
Derivatization strategies represent another powerful approach for improving HPLC sensitivity, particularly for compounds lacking strong chromophores or fluorophores. Pre-column derivatization with reagents such as dansyl chloride, 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC-Cl), or o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) can introduce detectable moieties to otherwise difficult-to-detect analytes, lowering detection limits by 10-100 fold for UV or fluorescence detection.
Automated sample preparation systems have revolutionized the field by improving reproducibility and reducing human error. Technologies such as online SPE-HPLC systems, robotic sample handlers, and microfluidic devices enable consistent sample processing while minimizing contamination risks. These systems have demonstrated up to 30% improvement in method detection limits compared to manual preparation techniques.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD) has emerged as an effective technique for complex biological and environmental samples. By combining sample disruption, homogenization, and extraction in a single process, MSPD reduces sample handling steps while achieving excellent clean-up and concentration. Studies have shown MSPD can improve detection limits by 5-20 times compared to traditional extraction methods for challenging matrices.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) represent energy-based approaches that accelerate extraction kinetics and improve analyte recovery. These techniques have demonstrated particular utility for plant materials and environmental samples, with extraction efficiencies improved by 15-40% compared to conventional methods, directly translating to enhanced sensitivity in subsequent HPLC analysis.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) remains one of the most widely adopted sample preparation methods for sensitivity enhancement. By selectively retaining analytes while washing away matrix interferences, SPE can achieve concentration factors of 100-1000 times, dramatically improving detection capabilities. Recent advances in SPE sorbent materials, including molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and nanomaterials, have further enhanced selectivity and recovery rates for challenging analytes.
Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) techniques have evolved significantly with the development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SALLE). These miniaturized approaches require minimal organic solvent volumes while achieving enrichment factors of 50-500 times, making them environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain high sensitivity enhancement capabilities.
Derivatization strategies represent another powerful approach for improving HPLC sensitivity, particularly for compounds lacking strong chromophores or fluorophores. Pre-column derivatization with reagents such as dansyl chloride, 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC-Cl), or o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) can introduce detectable moieties to otherwise difficult-to-detect analytes, lowering detection limits by 10-100 fold for UV or fluorescence detection.
Automated sample preparation systems have revolutionized the field by improving reproducibility and reducing human error. Technologies such as online SPE-HPLC systems, robotic sample handlers, and microfluidic devices enable consistent sample processing while minimizing contamination risks. These systems have demonstrated up to 30% improvement in method detection limits compared to manual preparation techniques.
Matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD) has emerged as an effective technique for complex biological and environmental samples. By combining sample disruption, homogenization, and extraction in a single process, MSPD reduces sample handling steps while achieving excellent clean-up and concentration. Studies have shown MSPD can improve detection limits by 5-20 times compared to traditional extraction methods for challenging matrices.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) represent energy-based approaches that accelerate extraction kinetics and improve analyte recovery. These techniques have demonstrated particular utility for plant materials and environmental samples, with extraction efficiencies improved by 15-40% compared to conventional methods, directly translating to enhanced sensitivity in subsequent HPLC analysis.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!