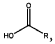
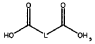
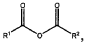
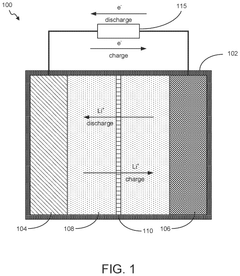
Binder and Conductive Additive Choices for ORB Electrodes: Practical Recipes
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ORB Electrode Development Background and Objectives
Organic radical batteries (ORBs) have emerged as a promising energy storage technology, offering unique advantages in terms of high power density, long cycle life, and environmental friendliness. The development of ORB electrodes represents a critical area of research, with a focus on optimizing binder and conductive additive choices to enhance overall battery performance.
The evolution of ORB technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first explored the potential of organic radical compounds as active materials in batteries. Since then, significant progress has been made in understanding the electrochemical behavior of these materials and their integration into practical battery systems. The primary goal of ORB electrode development is to create high-performance, stable, and cost-effective electrodes that can compete with traditional inorganic battery technologies.
One of the key challenges in ORB electrode development lies in the selection of appropriate binders and conductive additives. These components play crucial roles in maintaining the structural integrity of the electrode and ensuring efficient electron transport throughout the active material. The choice of binder and conductive additive can significantly impact the electrode's performance, including its capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability.
Recent technological trends in ORB electrode development have focused on exploring novel binder materials that can effectively accommodate the volume changes associated with the redox reactions of organic radical compounds. Additionally, researchers are investigating advanced conductive additives, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene derivatives, to enhance the overall conductivity of the electrode matrix.
The objectives of current research in this field are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a drive to develop binder systems that can maintain strong adhesion between the active material particles and the current collector while allowing for efficient ion transport. Secondly, researchers aim to optimize the type and concentration of conductive additives to achieve a balance between enhanced conductivity and minimal inactive material content.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable electrode formulations. This includes the exploration of water-based binder systems and the use of bio-derived conductive additives. These efforts align with the broader goal of creating more sustainable energy storage solutions.
As the field of ORB technology continues to advance, the development of practical recipes for electrode fabrication becomes increasingly important. These recipes must consider not only the electrochemical performance but also the scalability and manufacturability of the electrodes. The ultimate aim is to establish standardized protocols for ORB electrode preparation that can be readily adopted by industry for large-scale production.
The evolution of ORB technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first explored the potential of organic radical compounds as active materials in batteries. Since then, significant progress has been made in understanding the electrochemical behavior of these materials and their integration into practical battery systems. The primary goal of ORB electrode development is to create high-performance, stable, and cost-effective electrodes that can compete with traditional inorganic battery technologies.
One of the key challenges in ORB electrode development lies in the selection of appropriate binders and conductive additives. These components play crucial roles in maintaining the structural integrity of the electrode and ensuring efficient electron transport throughout the active material. The choice of binder and conductive additive can significantly impact the electrode's performance, including its capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability.
Recent technological trends in ORB electrode development have focused on exploring novel binder materials that can effectively accommodate the volume changes associated with the redox reactions of organic radical compounds. Additionally, researchers are investigating advanced conductive additives, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene derivatives, to enhance the overall conductivity of the electrode matrix.
The objectives of current research in this field are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a drive to develop binder systems that can maintain strong adhesion between the active material particles and the current collector while allowing for efficient ion transport. Secondly, researchers aim to optimize the type and concentration of conductive additives to achieve a balance between enhanced conductivity and minimal inactive material content.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable electrode formulations. This includes the exploration of water-based binder systems and the use of bio-derived conductive additives. These efforts align with the broader goal of creating more sustainable energy storage solutions.
As the field of ORB technology continues to advance, the development of practical recipes for electrode fabrication becomes increasingly important. These recipes must consider not only the electrochemical performance but also the scalability and manufacturability of the electrodes. The ultimate aim is to establish standardized protocols for ORB electrode preparation that can be readily adopted by industry for large-scale production.
Market Analysis for ORB Electrode Applications
The market for ORB (Organic Radical Battery) electrodes is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance energy storage solutions. As environmental concerns and the push for renewable energy sources intensify, ORB technology has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
The global market for ORB electrodes is primarily segmented into consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and grid storage applications. In the consumer electronics sector, ORB technology offers advantages such as faster charging times and improved safety, making it attractive for smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices. The electric vehicle market presents a substantial opportunity for ORB electrodes, as automakers seek batteries with higher energy density and longer lifespans.
Grid storage applications represent another key growth area for ORB electrodes. As renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prevalent, the need for efficient and reliable energy storage systems increases. ORB technology's ability to provide rapid charge and discharge cycles makes it well-suited for grid stabilization and peak shaving applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the ORB electrode market, with Japan and South Korea leading in research and development. North America and Europe are also significant markets, driven by stringent environmental regulations and investments in clean energy technologies.
The market is characterized by intense competition among established battery manufacturers and innovative startups. Key players are focusing on improving electrode performance through advanced binder and conductive additive formulations. This has led to increased research and development activities, with a particular emphasis on enhancing cycle life, energy density, and cost-effectiveness.
Challenges in the ORB electrode market include scaling up production to meet growing demand, reducing manufacturing costs, and addressing concerns about long-term stability. However, ongoing advancements in materials science and electrode design are steadily overcoming these hurdles.
The future outlook for the ORB electrode market is promising, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade. Factors such as increasing adoption of electric vehicles, expansion of renewable energy infrastructure, and growing awareness of sustainable technologies are expected to drive market expansion. As research continues to improve electrode performance and manufacturing processes, ORB technology is poised to capture a larger share of the global energy storage market.
The global market for ORB electrodes is primarily segmented into consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and grid storage applications. In the consumer electronics sector, ORB technology offers advantages such as faster charging times and improved safety, making it attractive for smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices. The electric vehicle market presents a substantial opportunity for ORB electrodes, as automakers seek batteries with higher energy density and longer lifespans.
Grid storage applications represent another key growth area for ORB electrodes. As renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prevalent, the need for efficient and reliable energy storage systems increases. ORB technology's ability to provide rapid charge and discharge cycles makes it well-suited for grid stabilization and peak shaving applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the ORB electrode market, with Japan and South Korea leading in research and development. North America and Europe are also significant markets, driven by stringent environmental regulations and investments in clean energy technologies.
The market is characterized by intense competition among established battery manufacturers and innovative startups. Key players are focusing on improving electrode performance through advanced binder and conductive additive formulations. This has led to increased research and development activities, with a particular emphasis on enhancing cycle life, energy density, and cost-effectiveness.
Challenges in the ORB electrode market include scaling up production to meet growing demand, reducing manufacturing costs, and addressing concerns about long-term stability. However, ongoing advancements in materials science and electrode design are steadily overcoming these hurdles.
The future outlook for the ORB electrode market is promising, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade. Factors such as increasing adoption of electric vehicles, expansion of renewable energy infrastructure, and growing awareness of sustainable technologies are expected to drive market expansion. As research continues to improve electrode performance and manufacturing processes, ORB technology is poised to capture a larger share of the global energy storage market.
Current Challenges in Binder and Conductive Additive Selection
The selection of binders and conductive additives for ORB (Organic Radical Battery) electrodes presents several significant challenges in the current research and development landscape. One of the primary issues is achieving an optimal balance between electrode stability and electrochemical performance. Traditional binders, such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), often fail to provide sufficient adhesion and flexibility for ORB electrodes, leading to capacity fading and poor cycle life.
Another challenge lies in the compatibility between the binder and the organic active materials. Many organic radical compounds are sensitive to certain solvents used in binder preparation, which can lead to degradation or loss of electrochemical activity. This necessitates the development of new binder systems that can be processed using benign solvents while maintaining strong adhesion properties.
The selection of conductive additives also poses difficulties. Carbon-based additives, such as carbon black or graphene, are commonly used but can sometimes interfere with the redox reactions of organic radical compounds. Finding the right type and proportion of conductive additive that enhances electron transfer without compromising the active material's performance is a delicate balance.
Furthermore, the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of binders and additives are becoming increasingly important considerations. There is a growing demand for eco-friendly, water-based binder systems and sustainable conductive additives that can replace traditional petroleum-based materials. However, these alternatives often struggle to match the performance of conventional options.
The scalability of binder and additive production for large-scale ORB manufacturing is another significant hurdle. Many promising materials perform well in laboratory settings but face challenges in scaling up to industrial production levels. This includes issues related to consistency, cost, and processability in large-scale electrode fabrication.
Lastly, the long-term stability of binders and additives in ORB systems remains a concern. The organic nature of the active materials in ORBs can lead to complex interactions with binders and additives over time, potentially affecting the battery's performance and lifespan. Developing materials that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles without degradation or loss of functionality is crucial for the commercial viability of ORB technology.
Another challenge lies in the compatibility between the binder and the organic active materials. Many organic radical compounds are sensitive to certain solvents used in binder preparation, which can lead to degradation or loss of electrochemical activity. This necessitates the development of new binder systems that can be processed using benign solvents while maintaining strong adhesion properties.
The selection of conductive additives also poses difficulties. Carbon-based additives, such as carbon black or graphene, are commonly used but can sometimes interfere with the redox reactions of organic radical compounds. Finding the right type and proportion of conductive additive that enhances electron transfer without compromising the active material's performance is a delicate balance.
Furthermore, the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of binders and additives are becoming increasingly important considerations. There is a growing demand for eco-friendly, water-based binder systems and sustainable conductive additives that can replace traditional petroleum-based materials. However, these alternatives often struggle to match the performance of conventional options.
The scalability of binder and additive production for large-scale ORB manufacturing is another significant hurdle. Many promising materials perform well in laboratory settings but face challenges in scaling up to industrial production levels. This includes issues related to consistency, cost, and processability in large-scale electrode fabrication.
Lastly, the long-term stability of binders and additives in ORB systems remains a concern. The organic nature of the active materials in ORBs can lead to complex interactions with binders and additives over time, potentially affecting the battery's performance and lifespan. Developing materials that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles without degradation or loss of functionality is crucial for the commercial viability of ORB technology.
Existing Binder and Conductive Additive Formulations
01 Binder composition for ORB electrodes
Various binder compositions are used in ORB electrodes to improve electrode performance and stability. These may include polymeric binders, such as PVDF, or water-soluble binders like CMC. The choice of binder affects the electrode's mechanical strength, conductivity, and cycling performance.- Binder composition for ORB electrodes: Various binder compositions are used in ORB (Oxygen-Releasing Battery) electrodes to improve electrode stability and performance. These binders may include polymeric materials such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). The choice of binder affects the electrode's mechanical strength, ionic conductivity, and overall battery performance.
- Conductive additives for ORB electrodes: Conductive additives are incorporated into ORB electrodes to enhance electronic conductivity. Common additives include carbon black, graphene, carbon nanotubes, and conductive polymers. These materials improve the electrode's ability to transfer electrons, leading to better overall battery performance and reduced internal resistance.
- Optimization of binder and conductive additive ratios: The ratio of binder to conductive additive in ORB electrodes is crucial for balancing mechanical stability and electrical conductivity. Researchers focus on optimizing these ratios to achieve the best combination of electrode integrity, conductivity, and electrochemical performance. This optimization process often involves experimental studies and computational modeling.
- Novel materials for ORB electrode components: Researchers are exploring novel materials for use as binders and conductive additives in ORB electrodes. These include bio-based binders, nanostructured carbon materials, and hybrid organic-inorganic composites. The goal is to improve electrode performance, increase energy density, and enhance the sustainability of battery production.
- Electrode fabrication techniques: Advanced fabrication techniques are being developed to optimize the integration of binders and conductive additives in ORB electrodes. These methods include spray coating, electrospinning, and 3D printing. The focus is on achieving uniform distribution of components, controlling porosity, and enhancing the electrode's structural integrity and electrochemical properties.
02 Conductive additives for ORB electrodes
Conductive additives are incorporated into ORB electrodes to enhance their electrical conductivity. Common additives include carbon black, graphene, and carbon nanotubes. These materials improve electron transport within the electrode, leading to better overall battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimization of binder and conductive additive ratios
The ratio between binder and conductive additive in ORB electrodes is crucial for balancing mechanical stability and electrical conductivity. Researchers optimize these ratios to achieve the best combination of electrode integrity and performance, often through experimental studies and computational modeling.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel materials for ORB electrode components
Innovative materials are being developed for use as binders and conductive additives in ORB electrodes. These may include bio-derived binders, nanostructured carbon materials, or hybrid organic-inorganic composites. Such materials aim to improve electrode performance while addressing sustainability concerns.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for ORB electrode fabrication
Advanced processing techniques are employed to optimize the integration of binders and conductive additives in ORB electrodes. These may include novel mixing methods, coating processes, or post-treatment techniques that enhance the distribution and interaction of electrode components, leading to improved battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ORB Electrode Materials Industry
The competitive landscape for "Binder and Conductive Additive Choices for ORB Electrodes" is characterized by a mature industry with significant market potential. The technology is well-established, with major players like Samsung Electronics, LG Chem, and DuPont de Nemours leading the field. These companies have extensive research and development capabilities, allowing them to innovate and improve existing formulations. Emerging players such as Sila Nanotechnologies and Log 9 Materials are introducing novel approaches, potentially disrupting the market with advanced materials. The market size is substantial, driven by the growing demand for high-performance batteries in various applications, including electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shin-Etsu Chemical has developed a specialized binder and conductive additive formulation for ORB electrodes, focusing on high-performance and durability. Their binder system is based on a silicone-modified acrylic polymer, which offers excellent adhesion and flexibility while providing enhanced thermal stability[1]. For conductive additives, Shin-Etsu uses a combination of vapor-grown carbon fibers (VGCF) and acetylene black, creating a highly conductive network within the electrode structure[2]. The typical recipe includes 2-4% binder and 1.5-2.5% conductive additive by weight. Shin-Etsu's formulation also incorporates a small amount of their proprietary silane coupling agent, which improves the interface between the active material and the binder, enhancing overall electrode performance[3].
Strengths: Excellent thermal stability, highly conductive network, improved active material-binder interface. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized materials, may require careful handling of VGCF during manufacturing.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed an innovative binder and conductive additive solution for ORB electrodes, leveraging their expertise in materials science. Their approach uses a fluoropolymer-based binder system, specifically a modified polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) with enhanced adhesion properties[1]. For conductive additives, DuPont employs a proprietary carbon black formulation with optimized particle size distribution and surface treatment, ensuring uniform dispersion and excellent conductivity[2]. The typical recipe includes 3-5% binder and 1-2% conductive additive by weight. Additionally, DuPont's formulation incorporates a small amount of ceramic nanoparticles as a functional additive, which helps to stabilize the electrode-electrolyte interface and improve cycling performance[3].
Strengths: Enhanced adhesion properties, uniform dispersion of conductive additives, improved electrode-electrolyte interface stability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized materials, may require specific processing conditions.
Innovative Binder and Conductive Additive Combinations
Battery with novel components
PatentWO2018191289A1
Innovation
- The development of acidified metal oxide (AMO) nanomaterials with controlled surface acidity, synthesized using a single-pot hydrothermal method, which are used in battery electrodes and electrolytes to enhance capacity, cyclability, and longevity by incorporating acidic species that are not superacidic, thereby avoiding the drawbacks of traditional acidic components.
Ultra high capacity performance battery cell
PatentActiveUS12113199B1
Innovation
- The development of battery cells with electrodes containing nanoparticle-sized metal oxides and conductive carbon, where the metal oxide is either acidified or non-acidified, allowing for controlled surface acidity to enhance reactivity and capacity, and the use of acidic species in electrolytes to improve battery performance.
Environmental Impact of Electrode Materials
The environmental impact of electrode materials in ORB (Organic Radical Battery) electrodes is a critical consideration in the development and implementation of sustainable energy storage solutions. The choice of binders and conductive additives plays a significant role in determining the overall environmental footprint of these electrodes.
Traditional binders used in battery electrodes, such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), have been associated with environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature and the use of toxic solvents in their processing. However, recent advancements in binder technology have led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives. Water-based binders, such as carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), have gained attention for their reduced environmental impact and improved processing characteristics.
Conductive additives, typically carbon-based materials like carbon black or carbon nanotubes, also contribute to the environmental profile of ORB electrodes. While these materials enhance the electrode's electrical conductivity, their production often involves energy-intensive processes and potential environmental hazards. Researchers are exploring more sustainable options, such as bio-derived carbon materials or conductive polymers, to mitigate these concerns.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of electrode materials is crucial in evaluating their overall environmental impact. This includes considering the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, energy consumption during production, and end-of-life disposal or recycling options. For ORB electrodes, the use of organic radical compounds as active materials offers potential advantages in terms of recyclability and reduced toxicity compared to conventional inorganic battery materials.
Efforts to minimize the environmental footprint of ORB electrodes also focus on optimizing the ratio of active material to binder and conductive additives. By maximizing the content of active material while maintaining electrode performance, manufacturers can reduce the overall material consumption and associated environmental impacts. Additionally, research into electrode fabrication techniques that require less energy and fewer resources, such as roll-to-roll processing or additive manufacturing, is ongoing.
The recyclability of ORB electrode materials is another crucial aspect of their environmental impact. Developing efficient recycling processes for these electrodes, including the separation and recovery of binders and conductive additives, is essential for creating a closed-loop system and reducing waste. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy and contributes to the overall sustainability of ORB technology.
Traditional binders used in battery electrodes, such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), have been associated with environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature and the use of toxic solvents in their processing. However, recent advancements in binder technology have led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives. Water-based binders, such as carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), have gained attention for their reduced environmental impact and improved processing characteristics.
Conductive additives, typically carbon-based materials like carbon black or carbon nanotubes, also contribute to the environmental profile of ORB electrodes. While these materials enhance the electrode's electrical conductivity, their production often involves energy-intensive processes and potential environmental hazards. Researchers are exploring more sustainable options, such as bio-derived carbon materials or conductive polymers, to mitigate these concerns.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of electrode materials is crucial in evaluating their overall environmental impact. This includes considering the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, energy consumption during production, and end-of-life disposal or recycling options. For ORB electrodes, the use of organic radical compounds as active materials offers potential advantages in terms of recyclability and reduced toxicity compared to conventional inorganic battery materials.
Efforts to minimize the environmental footprint of ORB electrodes also focus on optimizing the ratio of active material to binder and conductive additives. By maximizing the content of active material while maintaining electrode performance, manufacturers can reduce the overall material consumption and associated environmental impacts. Additionally, research into electrode fabrication techniques that require less energy and fewer resources, such as roll-to-roll processing or additive manufacturing, is ongoing.
The recyclability of ORB electrode materials is another crucial aspect of their environmental impact. Developing efficient recycling processes for these electrodes, including the separation and recovery of binders and conductive additives, is essential for creating a closed-loop system and reducing waste. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy and contributes to the overall sustainability of ORB technology.
Performance Testing and Quality Control Methods
Performance testing and quality control methods are crucial for ensuring the reliability and consistency of ORB electrodes. A comprehensive approach to testing involves evaluating both the physical and electrochemical properties of the electrodes. Physical tests typically include measurements of thickness, weight, and surface morphology. Thickness uniformity is particularly important for ensuring consistent performance across the electrode surface. Weight measurements can provide insights into the loading of active materials and the overall composition of the electrode.
Electrochemical performance testing is essential for assessing the functionality of ORB electrodes. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a widely used technique that provides information on the redox behavior and reversibility of the electrode reactions. Galvanostatic charge-discharge tests are employed to evaluate the capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability of the electrodes. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is valuable for investigating the electrode kinetics and internal resistance.
Quality control methods often involve statistical process control (SPC) techniques to monitor and maintain consistency in electrode production. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as capacity retention, coulombic efficiency, and internal resistance are tracked over time to identify trends and potential issues. Batch-to-batch variability is carefully monitored, with acceptance criteria established for critical parameters.
Advanced characterization techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are employed to assess the structural and morphological properties of the electrodes. These methods can reveal information about the distribution of binders and conductive additives, as well as the overall electrode microstructure.
Accelerated aging tests are often conducted to predict long-term performance and identify potential failure modes. These tests may involve cycling at elevated temperatures or under more aggressive charge-discharge conditions. The results from accelerated testing can be used to estimate the expected lifetime of the electrodes under normal operating conditions.
Standardization of testing protocols is essential for ensuring reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and production facilities. Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and ASTM International have developed standardized test methods for battery components, including electrodes. Adherence to these standards facilitates quality control and benchmarking against industry norms.
Electrochemical performance testing is essential for assessing the functionality of ORB electrodes. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a widely used technique that provides information on the redox behavior and reversibility of the electrode reactions. Galvanostatic charge-discharge tests are employed to evaluate the capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability of the electrodes. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is valuable for investigating the electrode kinetics and internal resistance.
Quality control methods often involve statistical process control (SPC) techniques to monitor and maintain consistency in electrode production. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as capacity retention, coulombic efficiency, and internal resistance are tracked over time to identify trends and potential issues. Batch-to-batch variability is carefully monitored, with acceptance criteria established for critical parameters.
Advanced characterization techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are employed to assess the structural and morphological properties of the electrodes. These methods can reveal information about the distribution of binders and conductive additives, as well as the overall electrode microstructure.
Accelerated aging tests are often conducted to predict long-term performance and identify potential failure modes. These tests may involve cycling at elevated temperatures or under more aggressive charge-discharge conditions. The results from accelerated testing can be used to estimate the expected lifetime of the electrodes under normal operating conditions.
Standardization of testing protocols is essential for ensuring reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and production facilities. Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and ASTM International have developed standardized test methods for battery components, including electrodes. Adherence to these standards facilitates quality control and benchmarking against industry norms.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!