Radical Polymer Electrode Fabrication: Slurry Formulation and Coating Best Practices
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Radical Polymer Evolution
The evolution of radical polymers in electrode fabrication has been a significant area of research and development in recent years. This progression can be traced through several key stages, each marked by important technological advancements and breakthroughs in material science and engineering.
In the early stages, radical polymers were primarily studied for their unique electrochemical properties, with limited practical applications in electrode fabrication. The focus was on understanding the fundamental chemistry and behavior of these materials under various conditions. This foundational research laid the groundwork for future developments in electrode design and manufacturing processes.
As the field progressed, researchers began to explore the potential of radical polymers in energy storage applications, particularly in batteries and supercapacitors. This phase saw the development of novel synthesis methods and the optimization of polymer structures to enhance their electrochemical performance. The introduction of new radical polymer compositions with improved stability and conductivity marked a significant milestone in this evolution.
The next major advancement came with the integration of radical polymers into composite electrode materials. This approach combined the benefits of radical polymers with other conductive materials, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, to create hybrid electrodes with superior performance characteristics. These composite materials demonstrated enhanced charge storage capacity, faster charge/discharge rates, and improved cycling stability.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards more sophisticated electrode fabrication techniques, focusing on the optimization of slurry formulations and coating processes. This stage has been crucial in translating the promising properties of radical polymers into practical, large-scale electrode production. Researchers have developed innovative methods for dispersing radical polymers in slurries, ensuring uniform distribution and optimal electrode morphology.
The latest developments in radical polymer electrode fabrication have centered on tailoring the polymer structure and composition to specific application requirements. This includes the design of radical polymers with tunable redox potentials, enhanced ionic conductivity, and improved mechanical properties. Additionally, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly fabrication processes, aligning with broader trends in green chemistry and manufacturing.
Looking forward, the evolution of radical polymer electrode fabrication is expected to continue, with a focus on scalability, cost-effectiveness, and performance optimization. Emerging areas of research include the development of self-healing radical polymer electrodes, the exploration of bio-inspired radical polymer structures, and the integration of radical polymers into flexible and wearable energy storage devices.
In the early stages, radical polymers were primarily studied for their unique electrochemical properties, with limited practical applications in electrode fabrication. The focus was on understanding the fundamental chemistry and behavior of these materials under various conditions. This foundational research laid the groundwork for future developments in electrode design and manufacturing processes.
As the field progressed, researchers began to explore the potential of radical polymers in energy storage applications, particularly in batteries and supercapacitors. This phase saw the development of novel synthesis methods and the optimization of polymer structures to enhance their electrochemical performance. The introduction of new radical polymer compositions with improved stability and conductivity marked a significant milestone in this evolution.
The next major advancement came with the integration of radical polymers into composite electrode materials. This approach combined the benefits of radical polymers with other conductive materials, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, to create hybrid electrodes with superior performance characteristics. These composite materials demonstrated enhanced charge storage capacity, faster charge/discharge rates, and improved cycling stability.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards more sophisticated electrode fabrication techniques, focusing on the optimization of slurry formulations and coating processes. This stage has been crucial in translating the promising properties of radical polymers into practical, large-scale electrode production. Researchers have developed innovative methods for dispersing radical polymers in slurries, ensuring uniform distribution and optimal electrode morphology.
The latest developments in radical polymer electrode fabrication have centered on tailoring the polymer structure and composition to specific application requirements. This includes the design of radical polymers with tunable redox potentials, enhanced ionic conductivity, and improved mechanical properties. Additionally, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly fabrication processes, aligning with broader trends in green chemistry and manufacturing.
Looking forward, the evolution of radical polymer electrode fabrication is expected to continue, with a focus on scalability, cost-effectiveness, and performance optimization. Emerging areas of research include the development of self-healing radical polymer electrodes, the exploration of bio-inspired radical polymer structures, and the integration of radical polymers into flexible and wearable energy storage devices.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for radical polymer electrode fabrication, particularly in the areas of slurry formulation and coating practices, has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing adoption of energy storage technologies, especially in the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy sectors.
The global lithium-ion battery market, which heavily relies on advanced electrode fabrication techniques, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is largely attributed to the rising demand for EVs, portable electronic devices, and grid energy storage systems. As a result, the need for efficient and cost-effective electrode fabrication methods, including those utilizing radical polymers, has become more pronounced.
In the EV industry, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve battery performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Radical polymer electrode fabrication offers potential advantages in terms of faster charging capabilities, improved energy density, and enhanced cycle life. These benefits align well with the industry's goals of developing more efficient and sustainable transportation solutions.
The renewable energy sector also presents a significant market opportunity for radical polymer electrode technologies. As countries worldwide push for greater adoption of clean energy sources, the demand for large-scale energy storage solutions continues to rise. Radical polymer electrodes could play a crucial role in developing more efficient and durable grid-scale storage systems, helping to address the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources.
Furthermore, the consumer electronics market contributes to the growing demand for advanced electrode fabrication techniques. With consumers expecting longer battery life and faster charging times in their devices, manufacturers are exploring innovative electrode materials and fabrication methods to meet these expectations.
The industrial sector is another area where radical polymer electrode fabrication is gaining traction. Applications in robotics, automation, and portable industrial equipment require high-performance energy storage solutions, driving the need for advanced electrode technologies.
However, it's important to note that the market demand is not without challenges. Cost considerations, scalability issues, and competition from established electrode technologies are factors that may impact the adoption rate of radical polymer electrode fabrication methods. Additionally, regulatory requirements and safety standards in various industries may influence the market dynamics for these new electrode technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for radical polymer electrode fabrication, particularly in slurry formulation and coating practices, is robust and growing. The technology's potential to address key challenges in energy storage across multiple sectors positions it as a promising area for further research and development. As the global push for electrification and sustainable energy solutions continues, the demand for innovative electrode fabrication techniques is expected to remain strong in the coming years.
The global lithium-ion battery market, which heavily relies on advanced electrode fabrication techniques, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is largely attributed to the rising demand for EVs, portable electronic devices, and grid energy storage systems. As a result, the need for efficient and cost-effective electrode fabrication methods, including those utilizing radical polymers, has become more pronounced.
In the EV industry, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve battery performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Radical polymer electrode fabrication offers potential advantages in terms of faster charging capabilities, improved energy density, and enhanced cycle life. These benefits align well with the industry's goals of developing more efficient and sustainable transportation solutions.
The renewable energy sector also presents a significant market opportunity for radical polymer electrode technologies. As countries worldwide push for greater adoption of clean energy sources, the demand for large-scale energy storage solutions continues to rise. Radical polymer electrodes could play a crucial role in developing more efficient and durable grid-scale storage systems, helping to address the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources.
Furthermore, the consumer electronics market contributes to the growing demand for advanced electrode fabrication techniques. With consumers expecting longer battery life and faster charging times in their devices, manufacturers are exploring innovative electrode materials and fabrication methods to meet these expectations.
The industrial sector is another area where radical polymer electrode fabrication is gaining traction. Applications in robotics, automation, and portable industrial equipment require high-performance energy storage solutions, driving the need for advanced electrode technologies.
However, it's important to note that the market demand is not without challenges. Cost considerations, scalability issues, and competition from established electrode technologies are factors that may impact the adoption rate of radical polymer electrode fabrication methods. Additionally, regulatory requirements and safety standards in various industries may influence the market dynamics for these new electrode technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for radical polymer electrode fabrication, particularly in slurry formulation and coating practices, is robust and growing. The technology's potential to address key challenges in energy storage across multiple sectors positions it as a promising area for further research and development. As the global push for electrification and sustainable energy solutions continues, the demand for innovative electrode fabrication techniques is expected to remain strong in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The fabrication of radical polymer electrodes presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must overcome to achieve optimal performance and scalability. One of the primary hurdles lies in the formulation of the slurry, which requires a delicate balance of components to ensure proper electrode functionality.
The selection and ratio of radical polymers, conductive additives, and binders are critical factors that directly impact the electrode's electrochemical properties. Achieving the right combination to maximize conductivity, stability, and capacity while maintaining mechanical integrity is a complex task. The interaction between these components at the molecular level can lead to unexpected behaviors, making it challenging to predict and control the final electrode characteristics.
Another major challenge is the development of coating techniques that can produce uniform and defect-free electrode layers. The viscosity and rheological properties of the slurry must be carefully controlled to ensure even distribution during the coating process. Achieving the optimal thickness and porosity of the electrode layer is crucial for maximizing active material utilization and facilitating ion transport.
The drying process following coating introduces additional complexities. Rapid and uniform drying is essential to prevent cracking, delamination, or uneven distribution of components within the electrode. However, the drying conditions must be carefully optimized to avoid degradation of the radical polymer or alteration of its chemical structure, which could compromise the electrode's performance.
Scalability of the fabrication process from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining consistency in slurry formulation and coating quality across large-scale production runs requires sophisticated process control and quality assurance measures. The transition from small-scale batch processing to continuous manufacturing methods introduces variables that can affect electrode uniformity and performance.
Environmental factors, such as humidity and temperature, can significantly impact the slurry formulation and coating process. Controlling these parameters throughout the manufacturing process is essential but can be technically demanding, especially in large-scale production environments.
The long-term stability of radical polymer electrodes remains a concern, as these materials can be susceptible to degradation over time or during cycling. Developing strategies to enhance the chemical and mechanical stability of the electrodes without compromising their electrochemical performance is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative approaches in materials science and engineering.
The selection and ratio of radical polymers, conductive additives, and binders are critical factors that directly impact the electrode's electrochemical properties. Achieving the right combination to maximize conductivity, stability, and capacity while maintaining mechanical integrity is a complex task. The interaction between these components at the molecular level can lead to unexpected behaviors, making it challenging to predict and control the final electrode characteristics.
Another major challenge is the development of coating techniques that can produce uniform and defect-free electrode layers. The viscosity and rheological properties of the slurry must be carefully controlled to ensure even distribution during the coating process. Achieving the optimal thickness and porosity of the electrode layer is crucial for maximizing active material utilization and facilitating ion transport.
The drying process following coating introduces additional complexities. Rapid and uniform drying is essential to prevent cracking, delamination, or uneven distribution of components within the electrode. However, the drying conditions must be carefully optimized to avoid degradation of the radical polymer or alteration of its chemical structure, which could compromise the electrode's performance.
Scalability of the fabrication process from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining consistency in slurry formulation and coating quality across large-scale production runs requires sophisticated process control and quality assurance measures. The transition from small-scale batch processing to continuous manufacturing methods introduces variables that can affect electrode uniformity and performance.
Environmental factors, such as humidity and temperature, can significantly impact the slurry formulation and coating process. Controlling these parameters throughout the manufacturing process is essential but can be technically demanding, especially in large-scale production environments.
The long-term stability of radical polymer electrodes remains a concern, as these materials can be susceptible to degradation over time or during cycling. Developing strategies to enhance the chemical and mechanical stability of the electrodes without compromising their electrochemical performance is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative approaches in materials science and engineering.
Current Slurry Methods
01 Radical polymer electrode composition
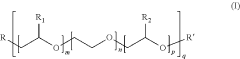
Radical polymer electrodes are composed of organic radical polymers, which are conductive and electrochemically active. These polymers are typically combined with conductive additives and binders to form a slurry. The composition of the slurry is crucial for the performance of the electrode, including factors such as the ratio of active material to additives, the type of binder used, and the solvent system employed.- Slurry formulation for radical polymer electrodes: The slurry formulation for radical polymer electrodes typically includes a combination of active materials, conductive additives, and binders. The active materials are radical polymers, while conductive additives enhance electrical conductivity. Binders ensure cohesion between particles and adhesion to the current collector. The composition and ratio of these components are crucial for optimizing electrode performance.
- Coating techniques for radical polymer electrodes: Various coating techniques are employed for applying the slurry onto current collectors to form radical polymer electrodes. These may include doctor blade coating, slot-die coating, or spray coating. The choice of coating method affects the uniformity, thickness, and adhesion of the electrode layer, which in turn influences the electrode's electrochemical performance and stability.
- Optimization of electrode composition and structure: Researchers focus on optimizing the composition and structure of radical polymer electrodes to enhance their performance. This includes adjusting the ratio of active material to conductive additives, exploring novel binder materials, and developing porous electrode structures. The goal is to improve charge transfer, ion diffusion, and overall electrochemical properties of the electrodes.
- Post-coating treatments for electrode enhancement: After coating, various post-treatment processes can be applied to further improve the properties of radical polymer electrodes. These may include thermal annealing, pressure treatment, or surface modification techniques. Such treatments aim to enhance the mechanical stability, electrical conductivity, and electrochemical performance of the electrodes.
- Integration of radical polymer electrodes in energy storage devices: The integration of radical polymer electrodes into various energy storage devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors, is a key area of research. This involves designing appropriate cell configurations, selecting compatible electrolytes, and optimizing the overall device architecture to leverage the unique properties of radical polymers for improved energy and power density.
02 Slurry preparation techniques
The preparation of radical polymer electrode slurries involves specific techniques to ensure uniform dispersion and optimal electrode properties. This may include the use of high-shear mixing, sonication, or ball milling to break down agglomerates and achieve a homogeneous mixture. The order of addition of components and mixing time are also critical factors in slurry preparation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Coating methods for radical polymer electrodes
Various coating methods are employed to apply the radical polymer slurry onto current collectors. These may include doctor blade coating, slot-die coating, or spray coating. The choice of coating method affects the thickness uniformity, adhesion, and overall performance of the electrode. Proper control of coating parameters such as speed, temperature, and drying conditions is essential for achieving desired electrode characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Additives for enhancing electrode performance
Various additives are incorporated into radical polymer electrode slurries to enhance their performance. These may include conductive carbon materials to improve electrical conductivity, dispersants to prevent agglomeration, and functional additives to enhance specific properties such as cycling stability or rate capability. The selection and optimization of these additives play a crucial role in the overall electrode performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-coating treatments and electrode finishing
After coating, radical polymer electrodes often undergo post-treatment processes to improve their properties. These may include calendering to adjust porosity and increase density, thermal treatments to remove residual solvents or activate certain components, or surface modifications to enhance interfacial properties. These finishing steps are critical for optimizing the electrode's electrochemical performance and mechanical stability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The radical polymer electrode fabrication market is in its early growth stage, characterized by ongoing research and development efforts. The market size is expanding as interest in sustainable energy storage solutions grows. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly but still maturing. Companies like ZEON Corp., LG Energy Solution, and Toyota are leading innovation in electrode materials and manufacturing processes. Established players such as PPG Industries and BASF are leveraging their expertise in chemical formulations to develop advanced slurry compositions. Emerging companies like A123 Systems and CALB Group are focusing on novel electrode designs and coating techniques. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with collaborations between industry and academia, such as the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, driving technological advancements.
ZEON Corp.
Technical Solution: ZEON Corp. has developed advanced radical polymer electrode fabrication techniques, focusing on slurry formulation and coating processes. Their approach involves using specialized binders and conductive additives to enhance the electrochemical performance of radical polymers. The company has optimized the slurry composition by incorporating a combination of organic solvents and water-based systems, which improves the dispersion of active materials and conductive additives[1]. ZEON's coating process utilizes precision-controlled doctor blade techniques, ensuring uniform electrode thickness and density. They have also implemented a multi-layer coating strategy to create gradient structures within the electrode, enhancing both ionic and electronic conductivity[2].
Strengths: Excellent control over electrode microstructure, improved cycling stability, and enhanced rate capability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized materials and multi-step processes.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed a comprehensive approach to radical polymer electrode fabrication, focusing on both slurry formulation and coating techniques. Their slurry formulation incorporates a proprietary blend of radical polymers, conductive carbon, and binders optimized for high-energy density and long cycle life. The company utilizes a dual-solvent system, combining N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) and water, which allows for better dispersion of active materials and reduced environmental impact[3]. For coating, LG Energy Solution employs advanced roll-to-roll techniques with precise tension control and multi-zone drying processes. This ensures uniform electrode thickness and prevents cracking or delamination during the drying phase. Additionally, they have implemented in-line quality control measures using optical and X-ray inspection systems to maintain consistent electrode properties[4].
Strengths: High-throughput production capabilities, excellent quality control, and optimized electrode performance. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production for new radical polymer formulations.
Innovative Formulations
Water based binder composition and application thereof
PatentPendingUS20240178398A1
Innovation
- A self-thickening polymeric latex binder is used, eliminating the need for additional rheology modifiers and preventing hydrogen gas generation, while providing improved adhesion, conductivity, and interconnectivity in the electrodes.
Preparation method of positive electrode slurry, as well as positive electrode plate, secondary battery, battery module, battery pack and electrical apparatus
PatentPendingUS20250070180A1
Innovation
- A multi-step stirring process is employed to prepare the positive electrode slurry, involving the mixing of a positive electrode active material, conductive agent, and first binder to form a dry mixture, followed by the preparation of an adhesive solution with a second binder of lower molecular weight, and finally, the integration of the dry mixture and solvent to achieve the desired slurry properties.
Material Sustainability
Material sustainability is a critical aspect of radical polymer electrode fabrication, particularly in the context of slurry formulation and coating practices. The increasing demand for energy storage devices has led to a growing concern about the environmental impact and long-term viability of electrode materials. In the realm of radical polymer electrodes, sustainability considerations encompass the entire lifecycle of the materials, from sourcing and production to use and end-of-life management.
One of the primary focuses of material sustainability in this field is the selection of environmentally friendly and renewable precursors for radical polymer synthesis. Researchers are exploring bio-based monomers and polymers derived from sustainable sources, such as lignin and cellulose, to replace petroleum-based materials. These alternatives not only reduce the carbon footprint of electrode production but also offer potential improvements in biodegradability and recyclability.
The slurry formulation process presents opportunities for enhancing sustainability through the optimization of solvent usage. Traditional organic solvents used in electrode fabrication often pose environmental and health risks. Efforts are being made to develop aqueous-based slurry formulations that minimize the use of harmful solvents while maintaining or improving electrode performance. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also enhances worker safety during manufacturing.
Coating practices are being reevaluated to minimize material waste and energy consumption. Advanced coating techniques, such as roll-to-roll processing and spray coating, are being optimized to achieve uniform and thin electrode layers with minimal material loss. These improvements in coating efficiency contribute to resource conservation and reduce the overall environmental footprint of electrode production.
The recyclability of radical polymer electrodes is another crucial aspect of material sustainability. Research is ongoing to develop efficient recycling processes that can recover and reuse the active materials from spent electrodes. This includes exploring chemical and mechanical methods to separate the polymer components from other electrode materials, enabling their reintegration into new electrode formulations.
Furthermore, the durability and cycle life of radical polymer electrodes play a significant role in their overall sustainability. Enhancing the stability of these materials through molecular design and protective coatings can extend the operational lifespan of energy storage devices, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing electronic waste.
In conclusion, material sustainability in radical polymer electrode fabrication encompasses a wide range of considerations, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life management. By addressing these aspects through innovative research and development, the field is moving towards more environmentally friendly and economically viable energy storage solutions.
One of the primary focuses of material sustainability in this field is the selection of environmentally friendly and renewable precursors for radical polymer synthesis. Researchers are exploring bio-based monomers and polymers derived from sustainable sources, such as lignin and cellulose, to replace petroleum-based materials. These alternatives not only reduce the carbon footprint of electrode production but also offer potential improvements in biodegradability and recyclability.
The slurry formulation process presents opportunities for enhancing sustainability through the optimization of solvent usage. Traditional organic solvents used in electrode fabrication often pose environmental and health risks. Efforts are being made to develop aqueous-based slurry formulations that minimize the use of harmful solvents while maintaining or improving electrode performance. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also enhances worker safety during manufacturing.
Coating practices are being reevaluated to minimize material waste and energy consumption. Advanced coating techniques, such as roll-to-roll processing and spray coating, are being optimized to achieve uniform and thin electrode layers with minimal material loss. These improvements in coating efficiency contribute to resource conservation and reduce the overall environmental footprint of electrode production.
The recyclability of radical polymer electrodes is another crucial aspect of material sustainability. Research is ongoing to develop efficient recycling processes that can recover and reuse the active materials from spent electrodes. This includes exploring chemical and mechanical methods to separate the polymer components from other electrode materials, enabling their reintegration into new electrode formulations.
Furthermore, the durability and cycle life of radical polymer electrodes play a significant role in their overall sustainability. Enhancing the stability of these materials through molecular design and protective coatings can extend the operational lifespan of energy storage devices, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing electronic waste.
In conclusion, material sustainability in radical polymer electrode fabrication encompasses a wide range of considerations, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life management. By addressing these aspects through innovative research and development, the field is moving towards more environmentally friendly and economically viable energy storage solutions.
Scalability Assessment
The scalability assessment of radical polymer electrode fabrication through slurry formulation and coating processes is crucial for determining the viability of large-scale production. This evaluation encompasses several key aspects that impact the potential for industrial-scale manufacturing.
Firstly, the slurry formulation process must be examined for its adaptability to larger batch sizes. The ability to maintain consistent quality and homogeneity of the slurry mixture when scaling up from laboratory quantities to industrial volumes is paramount. This includes assessing the mixing equipment capacity, the stability of the formulation over extended periods, and the reproducibility of the slurry characteristics across different batch sizes.
The coating process presents its own set of scalability challenges. The transition from small-scale coating techniques to continuous roll-to-roll processes requires careful consideration. Factors such as coating uniformity, thickness control, and adhesion to the substrate must be maintained across larger surface areas. The speed of the coating process and its impact on the final electrode properties are critical parameters that need to be optimized for high-volume production.
Material availability and cost implications also play a significant role in scalability assessment. The supply chain for radical polymers and other electrode components must be evaluated to ensure a steady and economically viable source for large-scale manufacturing. Any rare or specialized materials that may pose supply constraints should be identified and alternatives explored.
Environmental and safety considerations become more pronounced at industrial scales. The assessment should include an analysis of waste management, emissions control, and worker safety protocols associated with handling larger quantities of materials and increased production volumes.
Equipment and infrastructure requirements for scaled-up production need thorough evaluation. This includes assessing the need for specialized machinery, clean room facilities, and quality control systems capable of handling increased throughput while maintaining product specifications.
Lastly, the scalability assessment should consider the flexibility of the manufacturing process to accommodate potential future modifications or improvements in electrode design. The ability to integrate new materials or adjust formulations without significant disruption to the production line is valuable for long-term scalability.
By comprehensively addressing these aspects, the scalability assessment provides crucial insights into the feasibility and challenges of transitioning radical polymer electrode fabrication from laboratory-scale to industrial-scale production.
Firstly, the slurry formulation process must be examined for its adaptability to larger batch sizes. The ability to maintain consistent quality and homogeneity of the slurry mixture when scaling up from laboratory quantities to industrial volumes is paramount. This includes assessing the mixing equipment capacity, the stability of the formulation over extended periods, and the reproducibility of the slurry characteristics across different batch sizes.
The coating process presents its own set of scalability challenges. The transition from small-scale coating techniques to continuous roll-to-roll processes requires careful consideration. Factors such as coating uniformity, thickness control, and adhesion to the substrate must be maintained across larger surface areas. The speed of the coating process and its impact on the final electrode properties are critical parameters that need to be optimized for high-volume production.
Material availability and cost implications also play a significant role in scalability assessment. The supply chain for radical polymers and other electrode components must be evaluated to ensure a steady and economically viable source for large-scale manufacturing. Any rare or specialized materials that may pose supply constraints should be identified and alternatives explored.
Environmental and safety considerations become more pronounced at industrial scales. The assessment should include an analysis of waste management, emissions control, and worker safety protocols associated with handling larger quantities of materials and increased production volumes.
Equipment and infrastructure requirements for scaled-up production need thorough evaluation. This includes assessing the need for specialized machinery, clean room facilities, and quality control systems capable of handling increased throughput while maintaining product specifications.
Lastly, the scalability assessment should consider the flexibility of the manufacturing process to accommodate potential future modifications or improvements in electrode design. The ability to integrate new materials or adjust formulations without significant disruption to the production line is valuable for long-term scalability.
By comprehensively addressing these aspects, the scalability assessment provides crucial insights into the feasibility and challenges of transitioning radical polymer electrode fabrication from laboratory-scale to industrial-scale production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!