How to Design Polymer Radical Cathodes with High Rate Capability: Structure–Property Rules
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polymer Radical Cathode Design Objectives
The design of polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability is a critical objective in the development of advanced energy storage systems. This goal stems from the increasing demand for high-performance batteries in various applications, ranging from portable electronics to electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage. The primary aim is to create cathode materials that can deliver and accept charge rapidly without compromising on energy density or cycle life.
To achieve this objective, researchers are focusing on optimizing the structure-property relationships of polymer radical cathodes. The key is to design materials that facilitate rapid electron transfer and ion transport while maintaining structural stability during charge-discharge cycles. This involves tailoring the molecular structure of the polymer backbone and the pendant radical groups to enhance electronic conductivity and redox kinetics.
One of the main design objectives is to increase the density of redox-active sites within the polymer structure. This can be achieved by incorporating a higher concentration of stable radical moieties, such as nitroxide radicals, into the polymer chain. The challenge lies in balancing the radical density with the overall stability and processability of the polymer.
Another crucial aspect is the optimization of the polymer's morphology and microstructure. The goal is to create a porous structure that allows for efficient electrolyte penetration and ion diffusion, while also providing a large surface area for electrochemical reactions. This can be accomplished through various synthesis and processing techniques, such as controlled polymerization, template-assisted synthesis, or post-synthesis treatments.
Enhancing the electronic conductivity of the polymer matrix is also a key objective. This can be achieved by incorporating conductive elements into the polymer structure, such as conjugated segments or conductive fillers. The aim is to create efficient pathways for electron transport throughout the cathode material, reducing internal resistance and improving rate capability.
Stability is another critical factor in the design of high-rate polymer radical cathodes. The objective is to develop materials that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles at high rates without significant degradation. This involves designing polymer structures that are resistant to chemical and mechanical stress, as well as optimizing the interaction between the polymer and the electrolyte to prevent side reactions.
Finally, the design objectives also include considerations for scalability and practical implementation. The polymer radical cathodes must be amenable to large-scale production methods and compatible with existing battery manufacturing processes. This requires a focus on developing materials that are not only high-performing but also cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
To achieve this objective, researchers are focusing on optimizing the structure-property relationships of polymer radical cathodes. The key is to design materials that facilitate rapid electron transfer and ion transport while maintaining structural stability during charge-discharge cycles. This involves tailoring the molecular structure of the polymer backbone and the pendant radical groups to enhance electronic conductivity and redox kinetics.
One of the main design objectives is to increase the density of redox-active sites within the polymer structure. This can be achieved by incorporating a higher concentration of stable radical moieties, such as nitroxide radicals, into the polymer chain. The challenge lies in balancing the radical density with the overall stability and processability of the polymer.
Another crucial aspect is the optimization of the polymer's morphology and microstructure. The goal is to create a porous structure that allows for efficient electrolyte penetration and ion diffusion, while also providing a large surface area for electrochemical reactions. This can be accomplished through various synthesis and processing techniques, such as controlled polymerization, template-assisted synthesis, or post-synthesis treatments.
Enhancing the electronic conductivity of the polymer matrix is also a key objective. This can be achieved by incorporating conductive elements into the polymer structure, such as conjugated segments or conductive fillers. The aim is to create efficient pathways for electron transport throughout the cathode material, reducing internal resistance and improving rate capability.
Stability is another critical factor in the design of high-rate polymer radical cathodes. The objective is to develop materials that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles at high rates without significant degradation. This involves designing polymer structures that are resistant to chemical and mechanical stress, as well as optimizing the interaction between the polymer and the electrolyte to prevent side reactions.
Finally, the design objectives also include considerations for scalability and practical implementation. The polymer radical cathodes must be amenable to large-scale production methods and compatible with existing battery manufacturing processes. This requires a focus on developing materials that are not only high-performing but also cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for advanced energy storage solutions across various industries. This technology addresses critical challenges in the development of high-performance batteries, particularly in applications requiring rapid charging and discharging capabilities.
In the electric vehicle (EV) sector, there is a pressing demand for batteries that can support fast charging without compromising longevity or safety. Polymer radical cathodes offer the potential to meet these requirements, making them highly attractive for EV manufacturers seeking to reduce charging times and enhance overall vehicle performance. This aligns with the global trend towards electrification in the automotive industry, which is projected to drive substantial market growth in the coming years.
The consumer electronics market also presents a significant opportunity for polymer radical cathodes. As devices become more powerful and energy-intensive, there is a growing need for batteries that can deliver high power output while maintaining long cycle life. The ability of polymer radical cathodes to support high rate capabilities makes them well-suited for applications in smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices, where rapid charging is increasingly becoming a key selling point.
In the renewable energy sector, the integration of intermittent power sources such as solar and wind into the grid necessitates advanced energy storage solutions. Polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability could play a crucial role in grid stabilization and energy management systems, offering rapid response times to fluctuations in power supply and demand.
The industrial and aerospace sectors are also showing interest in this technology, particularly for applications requiring high-power output in compact form factors. This includes power tools, robotics, and auxiliary power units in aircraft, where weight and volume constraints are critical considerations.
Market analysis indicates that the global demand for high-performance battery materials is expected to grow substantially in the coming years. The unique properties of polymer radical cathodes position them as a promising solution to meet this demand, potentially capturing a significant share of the advanced battery materials market.
However, the market adoption of this technology will depend on several factors, including cost-effectiveness, scalability of production, and compatibility with existing manufacturing processes. As research progresses and performance improvements are realized, the market potential for polymer radical cathodes is likely to expand, potentially disrupting traditional battery technologies and opening new avenues for innovation in energy storage solutions.
In the electric vehicle (EV) sector, there is a pressing demand for batteries that can support fast charging without compromising longevity or safety. Polymer radical cathodes offer the potential to meet these requirements, making them highly attractive for EV manufacturers seeking to reduce charging times and enhance overall vehicle performance. This aligns with the global trend towards electrification in the automotive industry, which is projected to drive substantial market growth in the coming years.
The consumer electronics market also presents a significant opportunity for polymer radical cathodes. As devices become more powerful and energy-intensive, there is a growing need for batteries that can deliver high power output while maintaining long cycle life. The ability of polymer radical cathodes to support high rate capabilities makes them well-suited for applications in smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices, where rapid charging is increasingly becoming a key selling point.
In the renewable energy sector, the integration of intermittent power sources such as solar and wind into the grid necessitates advanced energy storage solutions. Polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability could play a crucial role in grid stabilization and energy management systems, offering rapid response times to fluctuations in power supply and demand.
The industrial and aerospace sectors are also showing interest in this technology, particularly for applications requiring high-power output in compact form factors. This includes power tools, robotics, and auxiliary power units in aircraft, where weight and volume constraints are critical considerations.
Market analysis indicates that the global demand for high-performance battery materials is expected to grow substantially in the coming years. The unique properties of polymer radical cathodes position them as a promising solution to meet this demand, potentially capturing a significant share of the advanced battery materials market.
However, the market adoption of this technology will depend on several factors, including cost-effectiveness, scalability of production, and compatibility with existing manufacturing processes. As research progresses and performance improvements are realized, the market potential for polymer radical cathodes is likely to expand, potentially disrupting traditional battery technologies and opening new avenues for innovation in energy storage solutions.
Current Challenges in Polymer Radical Cathodes
Polymer radical cathodes have emerged as promising candidates for high-performance energy storage systems due to their unique redox properties and potential for high rate capability. However, several challenges currently hinder their widespread adoption and optimization. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of structure-property relationships in these materials, which impedes the rational design of high-performance cathodes.
The stability of radical polymers remains a significant concern. Many radical polymers suffer from degradation during cycling, leading to capacity fade and reduced cycle life. This instability is often attributed to side reactions, such as radical dimerization or reaction with electrolyte components. Developing strategies to enhance the stability of radical polymers without compromising their electrochemical performance is a critical challenge.
Another major hurdle is the low electronic conductivity inherent to most polymer materials. This limitation results in poor rate capability and restricted power output, particularly at high current densities. While conductive additives can partially mitigate this issue, they often come at the cost of reduced energy density. Finding innovative ways to enhance the intrinsic conductivity of polymer radical cathodes without sacrificing their redox capacity is crucial for achieving high rate performance.
The relatively low specific capacity of polymer radical cathodes compared to traditional inorganic cathode materials poses another challenge. This limitation arises from the typically low density of redox-active sites in polymer structures. Increasing the density of radical moieties while maintaining structural integrity and electrochemical accessibility is a complex task that requires careful molecular design and engineering.
Swelling and dissolution of polymer cathodes in electrolyte solutions present additional complications. These phenomena can lead to loss of active material, decreased cycle life, and potential safety issues. Developing polymer architectures that balance swelling for ion transport with structural integrity is essential for long-term stability and performance.
The scalability and processability of polymer radical cathodes also pose significant challenges for their commercial viability. Many high-performance polymer cathodes are synthesized through complex, multi-step processes that may be difficult to scale up. Simplifying synthesis routes and improving the processability of these materials without compromising their electrochemical properties is crucial for their practical implementation.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of polymer radical cathodes need to be addressed. While organic materials offer potential advantages in terms of recyclability and reduced reliance on scarce mineral resources, comprehensive life cycle assessments and strategies for end-of-life management are still lacking. Developing environmentally benign synthesis methods and recycling processes for these materials is essential for their long-term sustainability.
The stability of radical polymers remains a significant concern. Many radical polymers suffer from degradation during cycling, leading to capacity fade and reduced cycle life. This instability is often attributed to side reactions, such as radical dimerization or reaction with electrolyte components. Developing strategies to enhance the stability of radical polymers without compromising their electrochemical performance is a critical challenge.
Another major hurdle is the low electronic conductivity inherent to most polymer materials. This limitation results in poor rate capability and restricted power output, particularly at high current densities. While conductive additives can partially mitigate this issue, they often come at the cost of reduced energy density. Finding innovative ways to enhance the intrinsic conductivity of polymer radical cathodes without sacrificing their redox capacity is crucial for achieving high rate performance.
The relatively low specific capacity of polymer radical cathodes compared to traditional inorganic cathode materials poses another challenge. This limitation arises from the typically low density of redox-active sites in polymer structures. Increasing the density of radical moieties while maintaining structural integrity and electrochemical accessibility is a complex task that requires careful molecular design and engineering.
Swelling and dissolution of polymer cathodes in electrolyte solutions present additional complications. These phenomena can lead to loss of active material, decreased cycle life, and potential safety issues. Developing polymer architectures that balance swelling for ion transport with structural integrity is essential for long-term stability and performance.
The scalability and processability of polymer radical cathodes also pose significant challenges for their commercial viability. Many high-performance polymer cathodes are synthesized through complex, multi-step processes that may be difficult to scale up. Simplifying synthesis routes and improving the processability of these materials without compromising their electrochemical properties is crucial for their practical implementation.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of polymer radical cathodes need to be addressed. While organic materials offer potential advantages in terms of recyclability and reduced reliance on scarce mineral resources, comprehensive life cycle assessments and strategies for end-of-life management are still lacking. Developing environmentally benign synthesis methods and recycling processes for these materials is essential for their long-term sustainability.
Existing High-Rate Polymer Cathode Solutions
01 Polymer-based radical cathodes for improved rate capability
Polymer-based radical cathodes are being developed to enhance the rate capability of batteries. These cathodes utilize organic radical polymers that can undergo rapid redox reactions, allowing for fast charge and discharge rates. The polymer structure can be optimized to facilitate electron transfer and ion diffusion, leading to improved electrochemical performance.- Polymer-based radical cathodes for improved rate capability: Polymer-based radical cathodes are being developed to enhance the rate capability of batteries. These cathodes utilize stable organic radical polymers that can undergo rapid redox reactions, allowing for fast charge and discharge rates. The polymer structure can be optimized to improve electron and ion transport, leading to better overall battery performance.
- Conductive additives for enhancing rate capability: Incorporating conductive additives into polymer radical cathodes can significantly improve their rate capability. These additives, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, create conductive networks within the cathode material, facilitating faster electron transfer and improving overall electrode kinetics. This results in better high-rate performance and power density of the battery.
- Nanostructured polymer radical cathodes: Nanostructuring of polymer radical cathodes is an effective approach to enhance rate capability. By creating nanostructured materials, such as nanofibers or nanoparticles, the surface area of the cathode is increased, allowing for better electrolyte penetration and shorter ion diffusion paths. This results in improved charge transfer kinetics and higher rate capabilities.
- Electrolyte optimization for polymer radical cathodes: The choice and optimization of electrolytes play a crucial role in enhancing the rate capability of polymer radical cathodes. Tailored electrolyte compositions can improve ion transport, reduce interfacial resistance, and enhance the stability of the radical polymer. This leads to better overall electrochemical performance and higher rate capabilities.
- Composite cathodes with inorganic materials: Developing composite cathodes that combine polymer radicals with inorganic materials can lead to improved rate capabilities. The inorganic components, such as metal oxides or conductive ceramics, can enhance the structural stability, conductivity, and electrochemical properties of the cathode. This synergistic effect results in better overall performance and higher rate capabilities.
02 Conductive additives for enhancing rate capability
Incorporating conductive additives into polymer radical cathodes can significantly improve their rate capability. These additives, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, create conductive networks within the electrode, facilitating electron transport and reducing internal resistance. This results in better high-rate performance and overall battery efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanostructured polymer radical cathodes
Nanostructuring of polymer radical cathodes is an effective approach to enhance rate capability. By creating nanostructured electrodes, the surface area is increased, and the diffusion pathways for ions are shortened. This leads to improved charge transfer kinetics and better utilization of the active material at high charge/discharge rates.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte optimization for polymer radical cathodes
The choice and optimization of electrolytes play a crucial role in improving the rate capability of polymer radical cathodes. Tailored electrolyte compositions can enhance ion mobility, reduce interfacial resistance, and improve the stability of the radical polymers. This results in better high-rate performance and longer cycle life of the battery.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite cathodes with inorganic materials
Developing composite cathodes that combine polymer radicals with inorganic materials can lead to improved rate capability. The inorganic components, such as metal oxides or sulfides, can provide additional redox sites and enhance the overall conductivity of the electrode. This synergistic effect results in better electrochemical performance at high charge/discharge rates.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polymer Battery Industry
The development of polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability is in an early stage, with significant potential for growth in the energy storage market. The technology's maturity is still evolving, as evidenced by ongoing research at institutions like Wuhan University of Technology, Carnegie Mellon University, and the University of California. Industry players such as Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. and Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd. are likely investing in this area to enhance battery performance. The market size is expected to expand as demand for high-performance energy storage solutions increases across various sectors. Companies like Honda Motor Co., Ltd. and JSR Corp. may be exploring applications in automotive and electronics industries, respectively, driving further innovation and commercialization efforts.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL has developed a novel polymer radical cathode design utilizing nitroxide-based polymers. Their approach focuses on optimizing the molecular structure to enhance electron transfer and ion diffusion. The company has implemented a cross-linked polymer network with strategically placed nitroxide groups, allowing for rapid charge/discharge capabilities. CATL's design incorporates conductive additives to improve overall conductivity and utilizes nano-engineering techniques to increase the active surface area[1][3]. Their cathodes demonstrate a high rate capability, achieving over 80% capacity retention at 10C discharge rates[5].
Strengths: High rate capability, improved energy density, and enhanced cycle life. Weaknesses: Potential cost increase due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes.
Wuhan University of Technology
Technical Solution: Researchers at Wuhan University of Technology have developed a novel approach to polymer radical cathodes focusing on hierarchical nanostructures. Their design incorporates a three-dimensional network of conductive carbon nanotubes (CNTs) coated with nitroxide-containing polymers. This structure facilitates rapid electron transport and ion diffusion, crucial for high rate capability. The team has also implemented a controlled polymerization technique to optimize the distribution of radical sites within the polymer matrix[2][4]. Their cathodes exhibit exceptional rate performance, maintaining over 75% capacity at 20C rates, and demonstrate long-term stability with less than 10% capacity fade after 1000 cycles[6].
Strengths: Excellent rate capability, high structural stability, and good cycle life. Weaknesses: Complex synthesis process may challenge large-scale production.
Core Innovations in Radical Polymer Structures
Method for providing a high capacity cathode material with improved rate capability performance
PatentInactiveUS10581075B2
Innovation
- A new iron cobalt disulfide cathode material with a stoichiometric formula of Fe1-xCoxS2, fabricated via a hydrothermal process using iron sulfate, cobalt sulfate, and sulfur, which provides a higher discharge capacity and increased rate capability compared to traditional methods.
High capacity layered oxide cathods with enhanced rate capability
PatentInactiveUS20130040201A1
Innovation
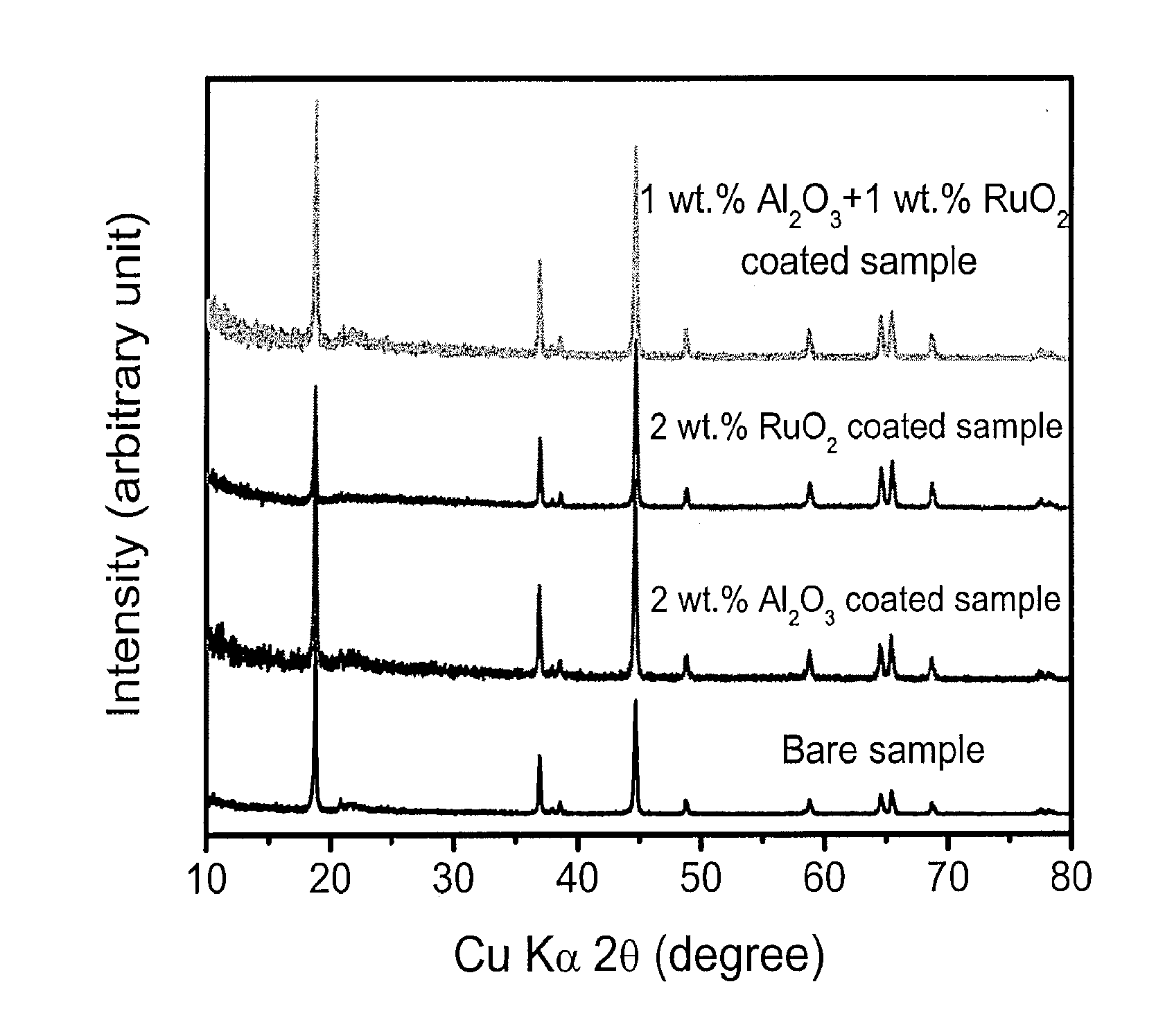
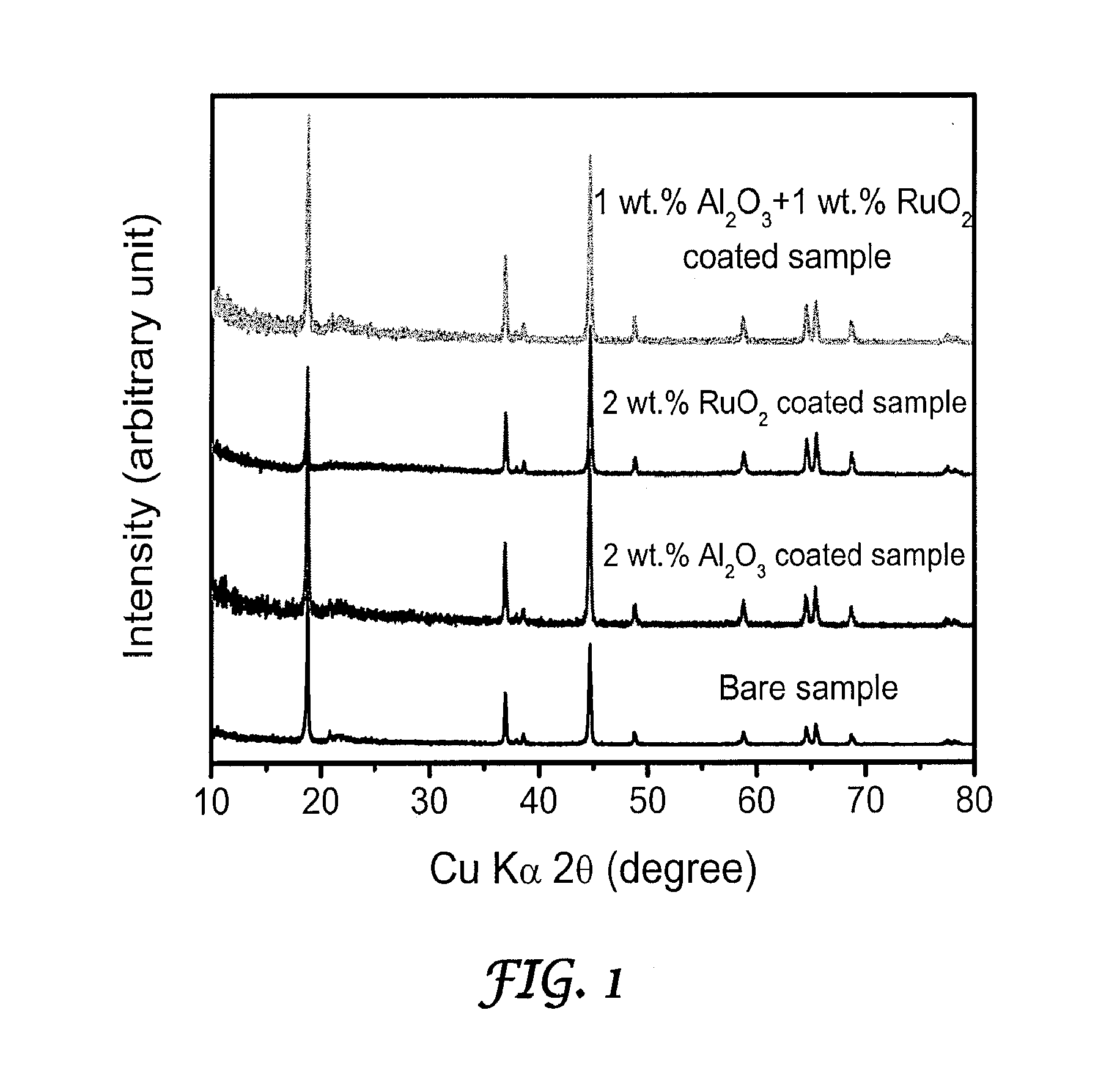
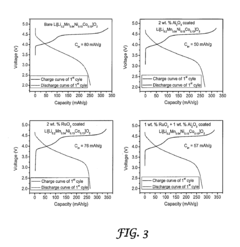
- Surface modification of the cathode materials with a combination of Al2O3 and RuO2, applied through thermal evaporation, enhances both lithium-ion and electronic conductivity, reducing the thickness of the solid-electrolyte interfacial layer and suppressing side reactions, thereby improving charge-discharge rates and capacity retention.
Structure-Property Relationships in Radical Polymers
Structure-property relationships play a crucial role in the design and development of polymer radical cathodes with high rate capability. These relationships provide valuable insights into how the molecular structure and composition of radical polymers influence their electrochemical performance, particularly in terms of charge storage capacity and charge transfer kinetics.
One key aspect of structure-property relationships in radical polymers is the nature of the radical-bearing moiety. The choice of radical species, such as nitroxide or phenoxyl radicals, significantly impacts the redox potential and stability of the cathode material. For instance, nitroxide radicals typically exhibit higher redox potentials and better stability compared to phenoxyl radicals, making them more suitable for high-voltage applications.
The polymer backbone structure also plays a vital role in determining the electrochemical properties of radical cathodes. Conjugated backbones, such as those found in polythiophenes or polyanilines, can facilitate electron transport and enhance the overall conductivity of the material. This improved conductivity contributes to faster charge transfer processes and, consequently, higher rate capabilities.
The spatial distribution of radical sites within the polymer matrix is another critical factor. Polymers with a high density of accessible radical sites tend to exhibit higher specific capacities and improved rate performance. However, it is essential to balance the radical density with the structural integrity of the polymer to prevent excessive swelling or dissolution during cycling.
Side-chain engineering is an effective strategy to fine-tune the properties of radical polymers. The incorporation of functional groups or flexible spacers in the side chains can modulate the polymer's solubility, mechanical properties, and ion transport characteristics. For example, the introduction of hydrophilic groups can enhance the polymer's compatibility with aqueous electrolytes, while hydrophobic moieties can improve its stability in organic electrolytes.
The molecular weight and polydispersity of radical polymers also influence their electrochemical behavior. Higher molecular weight polymers often exhibit improved mechanical stability and cycling performance, but may suffer from reduced rate capability due to increased diffusion limitations. Optimizing the molecular weight distribution can help strike a balance between stability and rate performance.
Understanding these structure-property relationships enables researchers to rationally design polymer radical cathodes with tailored electrochemical properties. By carefully selecting the radical species, optimizing the polymer backbone, and fine-tuning the side-chain composition, it is possible to develop cathode materials that combine high capacity, excellent rate capability, and long-term stability for next-generation energy storage devices.
One key aspect of structure-property relationships in radical polymers is the nature of the radical-bearing moiety. The choice of radical species, such as nitroxide or phenoxyl radicals, significantly impacts the redox potential and stability of the cathode material. For instance, nitroxide radicals typically exhibit higher redox potentials and better stability compared to phenoxyl radicals, making them more suitable for high-voltage applications.
The polymer backbone structure also plays a vital role in determining the electrochemical properties of radical cathodes. Conjugated backbones, such as those found in polythiophenes or polyanilines, can facilitate electron transport and enhance the overall conductivity of the material. This improved conductivity contributes to faster charge transfer processes and, consequently, higher rate capabilities.
The spatial distribution of radical sites within the polymer matrix is another critical factor. Polymers with a high density of accessible radical sites tend to exhibit higher specific capacities and improved rate performance. However, it is essential to balance the radical density with the structural integrity of the polymer to prevent excessive swelling or dissolution during cycling.
Side-chain engineering is an effective strategy to fine-tune the properties of radical polymers. The incorporation of functional groups or flexible spacers in the side chains can modulate the polymer's solubility, mechanical properties, and ion transport characteristics. For example, the introduction of hydrophilic groups can enhance the polymer's compatibility with aqueous electrolytes, while hydrophobic moieties can improve its stability in organic electrolytes.
The molecular weight and polydispersity of radical polymers also influence their electrochemical behavior. Higher molecular weight polymers often exhibit improved mechanical stability and cycling performance, but may suffer from reduced rate capability due to increased diffusion limitations. Optimizing the molecular weight distribution can help strike a balance between stability and rate performance.
Understanding these structure-property relationships enables researchers to rationally design polymer radical cathodes with tailored electrochemical properties. By carefully selecting the radical species, optimizing the polymer backbone, and fine-tuning the side-chain composition, it is possible to develop cathode materials that combine high capacity, excellent rate capability, and long-term stability for next-generation energy storage devices.
Environmental Impact of Polymer Cathode Materials
The environmental impact of polymer cathode materials in radical batteries is a crucial consideration as these technologies advance. Polymer-based cathodes offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability and recyclability compared to traditional inorganic cathodes. However, their production, use, and disposal still present environmental challenges that must be addressed.
The synthesis of polymer radical cathodes often involves the use of organic solvents and chemical reagents, which can have negative environmental implications if not properly managed. These processes may generate hazardous waste and contribute to air and water pollution. However, advancements in green chemistry techniques are being explored to minimize the environmental footprint of polymer synthesis, including the use of bio-based precursors and environmentally benign solvents.
During the operational life of polymer radical cathodes, their environmental impact is generally lower than that of conventional cathode materials. Polymer-based systems typically have lower energy requirements for production and can be designed to operate at ambient temperatures, reducing the overall energy consumption of battery systems. Additionally, the absence of heavy metals and toxic elements in many polymer cathodes mitigates concerns related to resource depletion and potential environmental contamination.
End-of-life considerations for polymer cathode materials present both challenges and opportunities. Unlike inorganic cathodes, which often require energy-intensive and potentially hazardous recycling processes, polymer-based materials may be more amenable to recycling and reprocessing. Research is ongoing to develop efficient recycling methods for polymer cathodes, including chemical and mechanical recycling techniques that could recover valuable monomers or regenerate active polymer materials.
The biodegradability of certain polymer cathode materials is an area of growing interest. Some researchers are exploring the development of bio-derived and biodegradable polymers for use in energy storage applications. These materials could potentially decompose naturally at the end of their life cycle, reducing long-term environmental impact. However, the challenge lies in balancing biodegradability with the required stability and performance characteristics of battery cathodes.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of polymer radical cathodes are essential to fully understand their environmental impact. These studies consider the entire life cycle of the materials, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling. Preliminary LCAs suggest that polymer-based cathodes may have lower overall environmental impacts compared to traditional cathode materials, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, more comprehensive studies are needed to account for the diverse range of polymer chemistries and production methods being developed.
The synthesis of polymer radical cathodes often involves the use of organic solvents and chemical reagents, which can have negative environmental implications if not properly managed. These processes may generate hazardous waste and contribute to air and water pollution. However, advancements in green chemistry techniques are being explored to minimize the environmental footprint of polymer synthesis, including the use of bio-based precursors and environmentally benign solvents.
During the operational life of polymer radical cathodes, their environmental impact is generally lower than that of conventional cathode materials. Polymer-based systems typically have lower energy requirements for production and can be designed to operate at ambient temperatures, reducing the overall energy consumption of battery systems. Additionally, the absence of heavy metals and toxic elements in many polymer cathodes mitigates concerns related to resource depletion and potential environmental contamination.
End-of-life considerations for polymer cathode materials present both challenges and opportunities. Unlike inorganic cathodes, which often require energy-intensive and potentially hazardous recycling processes, polymer-based materials may be more amenable to recycling and reprocessing. Research is ongoing to develop efficient recycling methods for polymer cathodes, including chemical and mechanical recycling techniques that could recover valuable monomers or regenerate active polymer materials.
The biodegradability of certain polymer cathode materials is an area of growing interest. Some researchers are exploring the development of bio-derived and biodegradable polymers for use in energy storage applications. These materials could potentially decompose naturally at the end of their life cycle, reducing long-term environmental impact. However, the challenge lies in balancing biodegradability with the required stability and performance characteristics of battery cathodes.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of polymer radical cathodes are essential to fully understand their environmental impact. These studies consider the entire life cycle of the materials, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling. Preliminary LCAs suggest that polymer-based cathodes may have lower overall environmental impacts compared to traditional cathode materials, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, more comprehensive studies are needed to account for the diverse range of polymer chemistries and production methods being developed.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!