How to Measure Redox Stability of Radical Polymers — Electrochemical Protocols
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Radical Polymer Redox Stability Background and Objectives
Radical polymers have emerged as a promising class of materials in the field of organic electronics and energy storage due to their unique redox properties. These polymers contain stable radical moieties along their backbone or as pendant groups, enabling them to undergo reversible oxidation and reduction processes. The ability to measure and understand the redox stability of radical polymers is crucial for their successful implementation in various applications, including organic batteries, supercapacitors, and electrochromic devices.
The development of radical polymers can be traced back to the 1960s when the first stable organic radical, TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl, was synthesized. Since then, significant progress has been made in the design and synthesis of various radical polymers, with a focus on improving their stability, conductivity, and electrochemical performance. The field has seen a resurgence of interest in recent years, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and high-performance energy storage materials.
The primary objective of studying the redox stability of radical polymers is to assess their long-term performance and reliability under repeated charge-discharge cycles. This is particularly important for applications in energy storage devices, where the stability of the active material directly impacts the device's lifespan and efficiency. Electrochemical protocols play a crucial role in evaluating the redox stability of radical polymers, as they allow for precise control and measurement of the oxidation and reduction processes.
One of the key challenges in measuring redox stability is developing standardized protocols that can accurately capture the complex behavior of radical polymers under various conditions. This includes understanding the impact of factors such as electrolyte composition, temperature, and cycling rate on the stability of the radical moieties. Additionally, researchers aim to elucidate the mechanisms of degradation and develop strategies to mitigate capacity fading and loss of electrochemical activity over time.
The evolution of electrochemical techniques has significantly advanced our ability to probe the redox properties of radical polymers. From traditional cyclic voltammetry to more sophisticated methods like electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) and in situ spectroelectrochemistry, these tools provide valuable insights into the redox processes occurring within the polymer matrix. The integration of these techniques with computational modeling and advanced characterization methods has further enhanced our understanding of radical polymer behavior at the molecular level.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing more robust and reliable methods for assessing redox stability. This includes the exploration of accelerated aging techniques, the use of advanced data analysis algorithms to extract meaningful information from electrochemical measurements, and the development of in situ and operando characterization methods to monitor changes in polymer structure and composition during redox cycling.
The development of radical polymers can be traced back to the 1960s when the first stable organic radical, TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl, was synthesized. Since then, significant progress has been made in the design and synthesis of various radical polymers, with a focus on improving their stability, conductivity, and electrochemical performance. The field has seen a resurgence of interest in recent years, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and high-performance energy storage materials.
The primary objective of studying the redox stability of radical polymers is to assess their long-term performance and reliability under repeated charge-discharge cycles. This is particularly important for applications in energy storage devices, where the stability of the active material directly impacts the device's lifespan and efficiency. Electrochemical protocols play a crucial role in evaluating the redox stability of radical polymers, as they allow for precise control and measurement of the oxidation and reduction processes.
One of the key challenges in measuring redox stability is developing standardized protocols that can accurately capture the complex behavior of radical polymers under various conditions. This includes understanding the impact of factors such as electrolyte composition, temperature, and cycling rate on the stability of the radical moieties. Additionally, researchers aim to elucidate the mechanisms of degradation and develop strategies to mitigate capacity fading and loss of electrochemical activity over time.
The evolution of electrochemical techniques has significantly advanced our ability to probe the redox properties of radical polymers. From traditional cyclic voltammetry to more sophisticated methods like electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) and in situ spectroelectrochemistry, these tools provide valuable insights into the redox processes occurring within the polymer matrix. The integration of these techniques with computational modeling and advanced characterization methods has further enhanced our understanding of radical polymer behavior at the molecular level.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing more robust and reliable methods for assessing redox stability. This includes the exploration of accelerated aging techniques, the use of advanced data analysis algorithms to extract meaningful information from electrochemical measurements, and the development of in situ and operando characterization methods to monitor changes in polymer structure and composition during redox cycling.
Market Analysis for Radical Polymer Applications
The market for radical polymer applications has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced energy storage solutions and sustainable materials. Radical polymers, with their unique redox properties, have found applications in various sectors, including energy storage, electronics, and biomedical fields.
In the energy storage sector, radical polymers are being explored as potential alternatives to traditional battery materials. The global battery market is projected to reach $279 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.1% from 2020 to 2027. Radical polymers offer advantages such as high energy density, fast charge-discharge rates, and improved cycle life, making them attractive for next-generation batteries and supercapacitors.
The electronics industry is another key market for radical polymer applications. With the growing demand for flexible and wearable electronics, radical polymers are being investigated for use in organic electronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). The global flexible electronics market is expected to reach $48.5 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 7.4% from 2021 to 2026.
In the biomedical field, radical polymers show promise for applications in drug delivery systems and biosensors. The global drug delivery market is forecasted to reach $2,015 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028. Radical polymers' ability to undergo reversible redox reactions makes them suitable for controlled drug release and biosensing applications.
The market for radical polymer applications is also influenced by the growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns. As industries seek more eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials, radical polymers offer potential solutions due to their organic nature and potential for recyclability.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of radical polymers. These include the need for improved stability, scalability of production processes, and cost-effectiveness compared to existing technologies. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for expanding the market potential of radical polymer applications across various industries.
In the energy storage sector, radical polymers are being explored as potential alternatives to traditional battery materials. The global battery market is projected to reach $279 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.1% from 2020 to 2027. Radical polymers offer advantages such as high energy density, fast charge-discharge rates, and improved cycle life, making them attractive for next-generation batteries and supercapacitors.
The electronics industry is another key market for radical polymer applications. With the growing demand for flexible and wearable electronics, radical polymers are being investigated for use in organic electronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). The global flexible electronics market is expected to reach $48.5 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 7.4% from 2021 to 2026.
In the biomedical field, radical polymers show promise for applications in drug delivery systems and biosensors. The global drug delivery market is forecasted to reach $2,015 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028. Radical polymers' ability to undergo reversible redox reactions makes them suitable for controlled drug release and biosensing applications.
The market for radical polymer applications is also influenced by the growing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns. As industries seek more eco-friendly alternatives to traditional materials, radical polymers offer potential solutions due to their organic nature and potential for recyclability.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of radical polymers. These include the need for improved stability, scalability of production processes, and cost-effectiveness compared to existing technologies. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for expanding the market potential of radical polymer applications across various industries.
Current Challenges in Redox Stability Measurement
The measurement of redox stability in radical polymers presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals must address. One of the primary difficulties lies in the inherent instability of radical species, which can undergo rapid degradation or side reactions during the measurement process. This instability often leads to inaccurate or inconsistent results, making it challenging to obtain reliable data on the long-term performance of these materials.
Another major hurdle is the lack of standardized protocols for measuring redox stability. Different research groups and industries often employ varying methodologies, making it difficult to compare results across studies or establish benchmarks for material performance. This absence of standardization hampers progress in the field and complicates the development of new radical polymer materials with improved stability.
The complex nature of radical polymer systems also poses significant challenges. These materials often exhibit intricate interactions between the polymer backbone, radical centers, and surrounding environment, which can influence their redox behavior. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of impurities can dramatically affect the stability of radical polymers, necessitating careful control and monitoring of experimental conditions.
Furthermore, the selection of appropriate electrochemical techniques and parameters for stability measurements remains a critical challenge. Techniques such as cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy each have their strengths and limitations when applied to radical polymers. Determining the most suitable method for a given system and optimizing experimental parameters to obtain meaningful results requires significant expertise and often involves a process of trial and error.
The development of in situ characterization methods that can provide real-time information on the redox processes and structural changes occurring within radical polymers during electrochemical cycling is another area of ongoing challenge. Such techniques are crucial for understanding degradation mechanisms and improving material design, but their implementation often requires sophisticated instrumentation and data analysis methods.
Lastly, the translation of laboratory-scale measurements to practical applications presents its own set of challenges. The behavior of radical polymers in actual devices or under real-world operating conditions may differ significantly from that observed in controlled laboratory experiments. Bridging this gap and developing predictive models that can accurately forecast the long-term stability of radical polymers in various applications remains a significant hurdle in the field.
Another major hurdle is the lack of standardized protocols for measuring redox stability. Different research groups and industries often employ varying methodologies, making it difficult to compare results across studies or establish benchmarks for material performance. This absence of standardization hampers progress in the field and complicates the development of new radical polymer materials with improved stability.
The complex nature of radical polymer systems also poses significant challenges. These materials often exhibit intricate interactions between the polymer backbone, radical centers, and surrounding environment, which can influence their redox behavior. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of impurities can dramatically affect the stability of radical polymers, necessitating careful control and monitoring of experimental conditions.
Furthermore, the selection of appropriate electrochemical techniques and parameters for stability measurements remains a critical challenge. Techniques such as cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy each have their strengths and limitations when applied to radical polymers. Determining the most suitable method for a given system and optimizing experimental parameters to obtain meaningful results requires significant expertise and often involves a process of trial and error.
The development of in situ characterization methods that can provide real-time information on the redox processes and structural changes occurring within radical polymers during electrochemical cycling is another area of ongoing challenge. Such techniques are crucial for understanding degradation mechanisms and improving material design, but their implementation often requires sophisticated instrumentation and data analysis methods.
Lastly, the translation of laboratory-scale measurements to practical applications presents its own set of challenges. The behavior of radical polymers in actual devices or under real-world operating conditions may differ significantly from that observed in controlled laboratory experiments. Bridging this gap and developing predictive models that can accurately forecast the long-term stability of radical polymers in various applications remains a significant hurdle in the field.
Existing Electrochemical Protocols for Redox Stability
01 Redox-active polymers for energy storage
Radical polymers are being developed for use in energy storage applications due to their redox stability. These polymers can undergo reversible oxidation and reduction reactions, making them suitable for use in batteries and capacitors. The stability of these polymers under repeated redox cycles is crucial for their long-term performance in energy storage devices.- Redox-active polymers for energy storage: Radical polymers are being developed for use in energy storage applications due to their redox stability. These polymers can undergo reversible oxidation and reduction reactions, making them suitable for use in batteries and capacitors. The stability of these polymers under repeated redox cycles is crucial for their long-term performance in energy storage devices.
- Stabilization techniques for radical polymers: Various methods are employed to enhance the redox stability of radical polymers. These include the incorporation of stabilizing functional groups, optimizing the polymer structure, and using specific polymerization techniques. Such stabilization methods aim to prevent unwanted side reactions and maintain the integrity of the radical centers during redox processes.
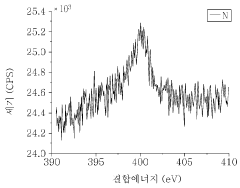
- Characterization of radical polymer redox properties: Advanced analytical techniques are used to study the redox properties and stability of radical polymers. These methods include cyclic voltammetry, spectroelectrochemistry, and in-situ spectroscopic techniques. Such characterization is essential for understanding the redox behavior and identifying factors that affect the stability of radical polymers under various conditions.
- Application of radical polymers in electrochemical devices: Radical polymers with enhanced redox stability are being incorporated into various electrochemical devices. These include organic radical batteries, electrochromic displays, and sensors. The stability of these polymers under repeated redox cycling is crucial for the long-term performance and reliability of such devices.
- Synthesis of novel radical polymers with improved stability: Research is focused on developing new synthetic routes and designing novel molecular structures to create radical polymers with improved redox stability. This includes the exploration of different polymer backbones, pendant groups, and crosslinking strategies to enhance the overall stability and performance of radical polymers in various applications.
02 Stabilization techniques for radical polymers
Various techniques are employed to enhance the redox stability of radical polymers. These include the incorporation of stabilizing functional groups, optimizing the polymer structure, and using specific polymerization methods. Such techniques aim to prevent unwanted side reactions and maintain the radical character of the polymers during redox processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Characterization methods for redox stability
Advanced characterization techniques are used to assess the redox stability of radical polymers. These methods include cyclic voltammetry, spectroelectrochemistry, and in-situ spectroscopic techniques. Such characterization is essential for understanding the behavior of radical polymers under different redox conditions and optimizing their performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application of radical polymers in electrochemical devices
Radical polymers with enhanced redox stability are being applied in various electrochemical devices. These include organic radical batteries, electrochromic displays, and sensors. The stable redox behavior of these polymers contributes to the longevity and reliability of such devices, making them attractive for practical applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synthesis of novel radical polymers with improved stability
Research is focused on synthesizing new radical polymers with improved redox stability. This involves designing monomers with specific structural features, exploring new polymerization techniques, and investigating the effects of different radical moieties on stability. The goal is to create polymers that maintain their radical character and redox properties over extended periods and under various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Radical Polymer Research
The field of measuring redox stability in radical polymers is in a developing stage, with growing market potential due to applications in energy storage and organic electronics. The technology's maturity varies across different sectors, with some areas more advanced than others. Key players like BASF Corp., 3M Innovative Properties Co., and Eastman Chemical Co. are driving innovation in this space. Universities such as MIT, Harvard, and EPFL are contributing significant research. The market is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and emerging specialized firms, indicating a competitive landscape with opportunities for both incremental improvements and disruptive innovations.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed advanced electrochemical protocols for measuring redox stability of radical polymers. Their approach involves cyclic voltammetry and rotating disk electrode techniques to assess the long-term stability of radical polymers under various conditions[1]. They utilize in-situ spectroelectrochemical methods to monitor structural changes during redox cycling[3]. BASF has also implemented accelerated aging tests combined with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to predict the lifetime of radical polymer-based devices[5]. Their protocols include precise control of temperature, electrolyte composition, and applied potentials to simulate real-world operating conditions[2].
Strengths: Comprehensive testing methods, advanced analytical techniques, and simulation of real-world conditions. Weaknesses: Potentially time-consuming and resource-intensive protocols, may require specialized equipment.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a multi-faceted approach to measure redox stability of radical polymers. Their protocol incorporates cyclic voltammetry with extended cycling periods to assess long-term stability[2]. They employ rotating ring-disk electrode techniques to detect and quantify any degradation products formed during redox processes[4]. 3M's method also includes in-situ Raman spectroscopy to monitor structural changes in real-time during electrochemical cycling[1]. Additionally, they have implemented a novel chronoamperometry technique that allows for the evaluation of charge retention capacity over extended periods, providing insights into the practical stability of radical polymers in energy storage applications[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive analysis combining multiple techniques, real-time monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Complex setup and data interpretation, potentially high equipment costs.
Core Innovations in Stability Measurement Methods
Method and apparatus for measuring degree of depolymerization of decomposable polymer by using electrochemistry
PatentWO2024063234A1
Innovation
- A method and device using electrochemical techniques involving a redox solution and electrodes to measure the intensity of current generated during the depolymerization process, allowing for quick and accurate determination of the degree of polymer depolymerization and molecular weight by varying voltage and using specific redox species and solvents.
Method for measuring the concentration or change in concentration of a redox-active substance and corresponding device
PatentInactiveUS8105478B2
Innovation
- The method involves pulsing the potential of a working electrode to alternate between measuring and relaxation phases, allowing the capacitive current to decay and the concentration gradient to relax, enabling measurements at electrodes with diameters of several hundred micrometers to centimeters using a single potentiostat and inexpensive transducer arrays, without the need for bipotentiostat.
Environmental Impact of Radical Polymer Testing
The environmental impact of radical polymer testing is a crucial consideration in the development and application of these materials. As research into radical polymers intensifies, it is essential to evaluate the potential ecological consequences of their testing protocols, particularly those involving electrochemical methods.
Electrochemical testing of radical polymers often requires the use of organic solvents and electrolytes, which can pose environmental risks if not properly managed. These chemicals may be toxic, flammable, or persistent in the environment, necessitating careful handling and disposal procedures. Additionally, the production of these solvents and electrolytes may involve energy-intensive processes, contributing to indirect environmental impacts through increased carbon emissions.
The electrodes used in electrochemical testing, typically made of materials such as platinum, gold, or carbon, also have environmental implications. Mining and processing of precious metals for electrode fabrication can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and energy consumption. Furthermore, the disposal or recycling of used electrodes must be carefully managed to prevent the release of potentially harmful materials into the environment.
Energy consumption during electrochemical testing is another significant factor to consider. Long-term cycling experiments and high-precision measurements often require continuous operation of potentiostats and other electronic equipment, contributing to electricity usage and associated carbon emissions. Implementing energy-efficient protocols and utilizing renewable energy sources for laboratory operations can help mitigate these impacts.
The generation of waste products during radical polymer testing is an additional environmental concern. Degradation products from polymer samples, used electrolytes, and contaminated solvents must be properly treated and disposed of to prevent environmental contamination. Developing closed-loop systems for solvent recycling and implementing green chemistry principles in test design can significantly reduce waste generation and minimize environmental impact.
As the field of radical polymer research advances, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly testing methods. This includes exploring aqueous electrolytes to reduce reliance on organic solvents, designing recyclable electrode materials, and optimizing test protocols to minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Additionally, the application of in silico modeling and high-throughput screening techniques can help reduce the number of physical experiments required, further decreasing the environmental footprint of radical polymer research.
Electrochemical testing of radical polymers often requires the use of organic solvents and electrolytes, which can pose environmental risks if not properly managed. These chemicals may be toxic, flammable, or persistent in the environment, necessitating careful handling and disposal procedures. Additionally, the production of these solvents and electrolytes may involve energy-intensive processes, contributing to indirect environmental impacts through increased carbon emissions.
The electrodes used in electrochemical testing, typically made of materials such as platinum, gold, or carbon, also have environmental implications. Mining and processing of precious metals for electrode fabrication can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and energy consumption. Furthermore, the disposal or recycling of used electrodes must be carefully managed to prevent the release of potentially harmful materials into the environment.
Energy consumption during electrochemical testing is another significant factor to consider. Long-term cycling experiments and high-precision measurements often require continuous operation of potentiostats and other electronic equipment, contributing to electricity usage and associated carbon emissions. Implementing energy-efficient protocols and utilizing renewable energy sources for laboratory operations can help mitigate these impacts.
The generation of waste products during radical polymer testing is an additional environmental concern. Degradation products from polymer samples, used electrolytes, and contaminated solvents must be properly treated and disposed of to prevent environmental contamination. Developing closed-loop systems for solvent recycling and implementing green chemistry principles in test design can significantly reduce waste generation and minimize environmental impact.
As the field of radical polymer research advances, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly testing methods. This includes exploring aqueous electrolytes to reduce reliance on organic solvents, designing recyclable electrode materials, and optimizing test protocols to minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Additionally, the application of in silico modeling and high-throughput screening techniques can help reduce the number of physical experiments required, further decreasing the environmental footprint of radical polymer research.
Standardization of Redox Stability Protocols
The standardization of redox stability protocols for radical polymers is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable measurements across different research groups and applications. This process involves establishing a set of agreed-upon procedures and parameters for evaluating the electrochemical stability of radical polymers. The primary goal is to create a unified approach that allows for accurate comparisons between different materials and studies.
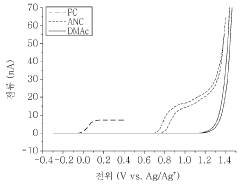
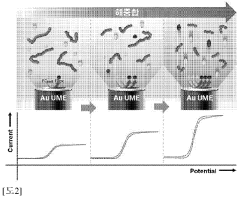
One key aspect of standardization is the selection of appropriate electrochemical techniques. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and rotating disk electrode (RDE) measurements are commonly employed methods that should be included in the standardized protocols. These techniques provide valuable information about the redox behavior and stability of radical polymers under various conditions.
The standardization process should also address the preparation of electrode materials and electrolytes. Consistent electrode surface preparation, including cleaning and polishing procedures, is essential for reproducible results. Similarly, the composition and concentration of electrolytes should be carefully defined to ensure comparability across different studies.
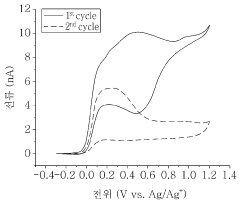
Another critical factor to consider is the cycling conditions during stability tests. Standardized protocols should specify the potential range, scan rate, and number of cycles to be used in CV experiments. For RDE measurements, rotation speeds and potential hold times should be clearly defined. These parameters significantly influence the observed stability and must be consistent for meaningful comparisons.
Environmental factors, such as temperature and atmospheric conditions, also play a crucial role in redox stability measurements. Standardized protocols should include guidelines for controlling and reporting these variables to minimize their impact on the results.
Data analysis and reporting methods are equally important in the standardization process. Clear guidelines should be established for calculating and presenting key parameters, such as redox potentials, peak currents, and capacity retention. This ensures that researchers can easily compare results from different studies and draw accurate conclusions about the relative stability of various radical polymers.
Interlaboratory studies and round-robin tests are valuable tools for validating and refining standardized protocols. These collaborative efforts help identify potential sources of variability and improve the robustness of the measurement procedures. Regular updates to the protocols may be necessary as new insights and techniques emerge in the field of radical polymer research.
One key aspect of standardization is the selection of appropriate electrochemical techniques. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and rotating disk electrode (RDE) measurements are commonly employed methods that should be included in the standardized protocols. These techniques provide valuable information about the redox behavior and stability of radical polymers under various conditions.
The standardization process should also address the preparation of electrode materials and electrolytes. Consistent electrode surface preparation, including cleaning and polishing procedures, is essential for reproducible results. Similarly, the composition and concentration of electrolytes should be carefully defined to ensure comparability across different studies.
Another critical factor to consider is the cycling conditions during stability tests. Standardized protocols should specify the potential range, scan rate, and number of cycles to be used in CV experiments. For RDE measurements, rotation speeds and potential hold times should be clearly defined. These parameters significantly influence the observed stability and must be consistent for meaningful comparisons.
Environmental factors, such as temperature and atmospheric conditions, also play a crucial role in redox stability measurements. Standardized protocols should include guidelines for controlling and reporting these variables to minimize their impact on the results.
Data analysis and reporting methods are equally important in the standardization process. Clear guidelines should be established for calculating and presenting key parameters, such as redox potentials, peak currents, and capacity retention. This ensures that researchers can easily compare results from different studies and draw accurate conclusions about the relative stability of various radical polymers.
Interlaboratory studies and round-robin tests are valuable tools for validating and refining standardized protocols. These collaborative efforts help identify potential sources of variability and improve the robustness of the measurement procedures. Regular updates to the protocols may be necessary as new insights and techniques emerge in the field of radical polymer research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!