ORB Thermal Behavior: Testing Protocols and Thermal Runaway Risk Analysis
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ORB Thermal Background and Objectives
The thermal behavior of Orbital Replaceable Units (ORUs) has become a critical concern in the aerospace industry, particularly in the context of satellite and spacecraft operations. ORUs are modular components designed for easy replacement in space systems, and their thermal management is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of space missions.
The evolution of ORU thermal management techniques has been closely tied to the advancement of space exploration. Early space missions relied on passive thermal control systems, which were simple but limited in their ability to regulate temperature in extreme space environments. As space missions became more complex and long-duration, active thermal control systems were developed to provide more precise temperature regulation for sensitive electronic components within ORUs.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated thermal management solutions for ORUs. These include phase change materials, advanced heat pipes, and miniaturized pumped fluid loops. These innovations have significantly improved the thermal performance of ORUs, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation and temperature control in the harsh space environment.
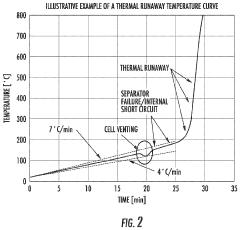
The primary objective of studying ORU thermal behavior is to develop comprehensive testing protocols and risk analysis methodologies for thermal runaway events. Thermal runaway, a process where an increase in temperature causes a further increase in temperature, can lead to catastrophic failures in space systems. Understanding and mitigating this risk is paramount for ensuring the safety and success of space missions.
Current research aims to establish standardized testing procedures that can accurately simulate the thermal conditions ORUs may encounter during their operational lifetime. These protocols must account for various factors, including vacuum conditions, radiation exposure, and thermal cycling. Additionally, researchers are working on developing advanced thermal modeling techniques to predict the behavior of ORUs under different thermal loads and environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to enhance the accuracy of thermal runaway risk analysis. This involves developing sophisticated algorithms and simulation tools that can predict the likelihood and severity of thermal runaway events based on ORU design, materials, and operational parameters. By improving risk assessment capabilities, engineers can design more robust ORUs and implement effective preventive measures.
The ultimate goal of this research is to establish a comprehensive framework for ORU thermal management that encompasses design guidelines, testing protocols, and risk mitigation strategies. This framework will enable the development of more reliable and efficient ORUs, contributing to the advancement of space exploration and satellite technology.
The evolution of ORU thermal management techniques has been closely tied to the advancement of space exploration. Early space missions relied on passive thermal control systems, which were simple but limited in their ability to regulate temperature in extreme space environments. As space missions became more complex and long-duration, active thermal control systems were developed to provide more precise temperature regulation for sensitive electronic components within ORUs.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated thermal management solutions for ORUs. These include phase change materials, advanced heat pipes, and miniaturized pumped fluid loops. These innovations have significantly improved the thermal performance of ORUs, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation and temperature control in the harsh space environment.
The primary objective of studying ORU thermal behavior is to develop comprehensive testing protocols and risk analysis methodologies for thermal runaway events. Thermal runaway, a process where an increase in temperature causes a further increase in temperature, can lead to catastrophic failures in space systems. Understanding and mitigating this risk is paramount for ensuring the safety and success of space missions.
Current research aims to establish standardized testing procedures that can accurately simulate the thermal conditions ORUs may encounter during their operational lifetime. These protocols must account for various factors, including vacuum conditions, radiation exposure, and thermal cycling. Additionally, researchers are working on developing advanced thermal modeling techniques to predict the behavior of ORUs under different thermal loads and environmental conditions.
Another key objective is to enhance the accuracy of thermal runaway risk analysis. This involves developing sophisticated algorithms and simulation tools that can predict the likelihood and severity of thermal runaway events based on ORU design, materials, and operational parameters. By improving risk assessment capabilities, engineers can design more robust ORUs and implement effective preventive measures.
The ultimate goal of this research is to establish a comprehensive framework for ORU thermal management that encompasses design guidelines, testing protocols, and risk mitigation strategies. This framework will enable the development of more reliable and efficient ORUs, contributing to the advancement of space exploration and satellite technology.
Market Demand for ORB Thermal Management
The market demand for ORB (Optical Resonance Breathing) thermal management has been steadily increasing due to the growing concerns over thermal runaway risks in various industries. As energy storage technologies advance and the use of high-capacity batteries becomes more widespread, the need for effective thermal management solutions has become paramount.
In the automotive sector, the electric vehicle (EV) market has been a significant driver for ORB thermal management systems. With the global EV market expanding rapidly, manufacturers are seeking robust thermal management solutions to ensure battery safety and longevity. The aerospace industry has also shown increasing interest in ORB thermal management, particularly for satellite and spacecraft applications where thermal control is critical for mission success.
The consumer electronics market represents another substantial segment demanding advanced thermal management solutions. As devices become more powerful and compact, the risk of thermal runaway in smartphones, laptops, and wearables has escalated. This has led to a surge in demand for innovative thermal management technologies like ORB systems.
Industrial applications, including large-scale energy storage systems and data centers, have emerged as key markets for ORB thermal management. The push for renewable energy integration and the exponential growth of data processing requirements have intensified the need for reliable thermal control solutions in these sectors.
Market analysts project that the global thermal management market, including ORB technologies, will experience significant growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the expansion of 5G networks, and the ongoing digital transformation across industries.
The demand for ORB thermal management is also being driven by stringent safety regulations and standards imposed by governments and industry bodies. These regulations aim to mitigate the risks associated with thermal runaway in various applications, thereby creating a favorable environment for the adoption of advanced thermal management solutions.
Research and development efforts in ORB thermal management are focusing on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing integration capabilities. This is expected to further boost market demand as more cost-effective and high-performance solutions become available.
As awareness of thermal runaway risks grows and the importance of thermal management in ensuring product safety and performance becomes more widely recognized, the market for ORB thermal management solutions is poised for continued expansion across multiple industries and applications.
In the automotive sector, the electric vehicle (EV) market has been a significant driver for ORB thermal management systems. With the global EV market expanding rapidly, manufacturers are seeking robust thermal management solutions to ensure battery safety and longevity. The aerospace industry has also shown increasing interest in ORB thermal management, particularly for satellite and spacecraft applications where thermal control is critical for mission success.
The consumer electronics market represents another substantial segment demanding advanced thermal management solutions. As devices become more powerful and compact, the risk of thermal runaway in smartphones, laptops, and wearables has escalated. This has led to a surge in demand for innovative thermal management technologies like ORB systems.
Industrial applications, including large-scale energy storage systems and data centers, have emerged as key markets for ORB thermal management. The push for renewable energy integration and the exponential growth of data processing requirements have intensified the need for reliable thermal control solutions in these sectors.
Market analysts project that the global thermal management market, including ORB technologies, will experience significant growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the expansion of 5G networks, and the ongoing digital transformation across industries.
The demand for ORB thermal management is also being driven by stringent safety regulations and standards imposed by governments and industry bodies. These regulations aim to mitigate the risks associated with thermal runaway in various applications, thereby creating a favorable environment for the adoption of advanced thermal management solutions.
Research and development efforts in ORB thermal management are focusing on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing integration capabilities. This is expected to further boost market demand as more cost-effective and high-performance solutions become available.
As awareness of thermal runaway risks grows and the importance of thermal management in ensuring product safety and performance becomes more widely recognized, the market for ORB thermal management solutions is poised for continued expansion across multiple industries and applications.
Current Challenges in ORB Thermal Testing
The current landscape of ORB (Oxygen-Releasing Battery) thermal testing presents several significant challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address to ensure the safety and reliability of these innovative energy storage systems. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically tailored for ORB technologies. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, ORBs have unique thermal characteristics due to their oxygen-releasing mechanism, which requires specialized testing methodologies.
The complexity of ORB thermal behavior poses another major challenge. The interaction between the oxygen-releasing components and other battery materials during thermal events is not yet fully understood, making it difficult to predict and model thermal runaway scenarios accurately. This knowledge gap hampers the development of effective safety measures and risk mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, the current testing equipment and facilities may not be adequately equipped to handle the specific requirements of ORB thermal testing. The potential release of oxygen during thermal events necessitates specialized containment and monitoring systems that are not typically found in standard battery testing laboratories. This limitation often results in incomplete or potentially hazardous testing procedures.
Another significant challenge lies in the time-consuming nature of comprehensive thermal testing for ORBs. The need for long-duration tests to assess thermal stability and performance under various conditions can delay product development cycles and increase costs for manufacturers. This challenge is particularly acute given the rapid pace of innovation in the energy storage sector.
The interpretation of thermal test results for ORBs also presents difficulties. The unique thermal signatures of these batteries require new analytical frameworks and expertise to accurately assess safety margins and failure modes. Many existing thermal runaway risk analysis models may not be directly applicable to ORB systems, necessitating the development of new predictive tools and risk assessment methodologies.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for ORB thermal testing remains uncertain. The absence of specific guidelines and standards from regulatory bodies creates ambiguity for manufacturers and testing facilities. This regulatory gap not only complicates compliance efforts but also potentially hinders the widespread adoption of ORB technologies in various applications.
Addressing these challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies to develop comprehensive and standardized thermal testing protocols for ORBs. Such efforts will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of this promising energy storage technology while ensuring its safe integration into various applications.
The complexity of ORB thermal behavior poses another major challenge. The interaction between the oxygen-releasing components and other battery materials during thermal events is not yet fully understood, making it difficult to predict and model thermal runaway scenarios accurately. This knowledge gap hampers the development of effective safety measures and risk mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, the current testing equipment and facilities may not be adequately equipped to handle the specific requirements of ORB thermal testing. The potential release of oxygen during thermal events necessitates specialized containment and monitoring systems that are not typically found in standard battery testing laboratories. This limitation often results in incomplete or potentially hazardous testing procedures.
Another significant challenge lies in the time-consuming nature of comprehensive thermal testing for ORBs. The need for long-duration tests to assess thermal stability and performance under various conditions can delay product development cycles and increase costs for manufacturers. This challenge is particularly acute given the rapid pace of innovation in the energy storage sector.
The interpretation of thermal test results for ORBs also presents difficulties. The unique thermal signatures of these batteries require new analytical frameworks and expertise to accurately assess safety margins and failure modes. Many existing thermal runaway risk analysis models may not be directly applicable to ORB systems, necessitating the development of new predictive tools and risk assessment methodologies.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for ORB thermal testing remains uncertain. The absence of specific guidelines and standards from regulatory bodies creates ambiguity for manufacturers and testing facilities. This regulatory gap not only complicates compliance efforts but also potentially hinders the widespread adoption of ORB technologies in various applications.
Addressing these challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies to develop comprehensive and standardized thermal testing protocols for ORBs. Such efforts will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of this promising energy storage technology while ensuring its safe integration into various applications.
Existing ORB Thermal Testing Solutions
01 Thermal management systems for ORBs
Oxygen-Rich Batteries (ORBs) require effective thermal management systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating. These systems may include cooling mechanisms, heat dissipation techniques, and temperature monitoring devices to ensure safe and efficient battery operation.- Thermal management systems for ORBs: Oxygen-Rich Batteries (ORBs) require efficient thermal management systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating. These systems may include cooling mechanisms, heat dissipation techniques, and temperature monitoring devices to ensure safe and efficient battery operation.
- Electrode design for improved thermal behavior: Innovative electrode designs can enhance the thermal behavior of ORBs. This may involve using materials with high thermal conductivity, optimizing electrode thickness and porosity, or incorporating heat-resistant coatings to improve heat dissipation and prevent thermal runaway.
- Electrolyte composition for thermal stability: The composition of electrolytes in ORBs plays a crucial role in their thermal behavior. Developing electrolytes with high thermal stability, low flammability, and improved heat transfer properties can enhance the overall thermal performance and safety of the battery.
- Thermal insulation and containment strategies: Implementing effective thermal insulation and containment strategies can help manage the thermal behavior of ORBs. This may include using advanced insulation materials, designing battery casings with improved heat dissipation properties, and incorporating safety features to prevent thermal propagation between cells.
- Thermal modeling and simulation for ORBs: Developing accurate thermal models and simulation techniques for ORBs can help predict and optimize their thermal behavior. These models can assist in designing more efficient cooling systems, identifying potential hotspots, and improving overall battery performance and safety.
02 Electrode design for improved thermal behavior
Innovative electrode designs can enhance the thermal behavior of ORBs. This may involve using materials with high thermal conductivity, optimizing electrode thickness, or incorporating heat-dissipating structures to reduce hotspots and improve overall thermal stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte composition for thermal stability
The composition of the electrolyte in ORBs plays a crucial role in their thermal behavior. Developing electrolytes with high thermal stability, low flammability, and good ionic conductivity can improve the overall safety and performance of the battery under various temperature conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal runaway prevention and mitigation
Implementing safety features to prevent and mitigate thermal runaway in ORBs is essential. This may include the use of thermal fuses, pressure relief mechanisms, or advanced battery management systems that can detect and respond to abnormal temperature increases.Expand Specific Solutions05 Thermal modeling and simulation for ORBs
Developing accurate thermal models and simulation techniques for ORBs can help predict and optimize their thermal behavior. These models can account for various factors such as heat generation, dissipation, and transfer within the battery, enabling better design and performance optimization.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ORB Thermal Management
The ORB thermal behavior testing and thermal runaway risk analysis market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for safer and more efficient energy storage solutions. The market size is expanding rapidly, fueled by the growing electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing but still evolving, with companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology, Samsung SDI, and Tesla leading innovation. These firms, along with others such as BYD and LG Energy Solution, are investing heavily in research and development to improve battery safety and performance. Universities like Tsinghua and Nanjing Tech are contributing valuable research, while specialized companies like Fluence Energy and Corvus Energy are developing advanced thermal management systems. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established battery manufacturers and emerging technology firms, all striving to address the critical challenges of thermal stability in energy storage systems.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL has developed advanced thermal management systems for their ORBs (Outdoor Rechargeable Batteries). Their approach includes a multi-layer protection strategy, incorporating phase change materials (PCMs) and intelligent battery management systems (BMS). The PCMs absorb excess heat during high-load operations, while the BMS continuously monitors cell temperatures and adjusts charging/discharging rates accordingly[1]. CATL's testing protocols involve accelerated aging tests under various temperature conditions, simulating extreme outdoor environments. They've also implemented a novel thermal runaway propagation prevention design, using fire-resistant materials between cells to isolate potential thermal events[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive thermal management approach, advanced testing protocols, and innovative safety features. Weaknesses: Potential increased production costs due to complex thermal management systems, and the need for continuous R&D to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving field.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has focused on developing high-performance ORBs with enhanced thermal stability. Their approach includes the use of advanced cathode materials with higher thermal stability, such as nickel-rich NCM (Nickel Cobalt Manganese) cathodes[2]. They've also implemented a unique cooling system that utilizes a combination of liquid and air cooling, allowing for efficient heat dissipation in outdoor environments. Samsung's testing protocols include extensive thermal cycling tests and abuse tests to simulate extreme conditions. They've developed a proprietary algorithm for their BMS that can predict and prevent thermal runaway events based on real-time data analysis[4].
Strengths: Advanced materials science, efficient cooling systems, and predictive thermal management. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs associated with premium materials and complex cooling systems.
Core Innovations in Thermal Runaway Prevention
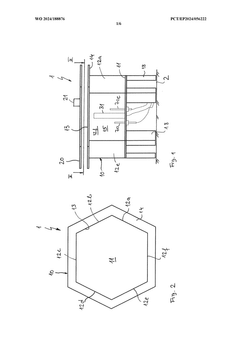
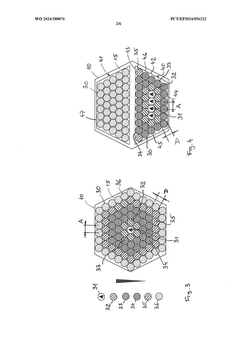
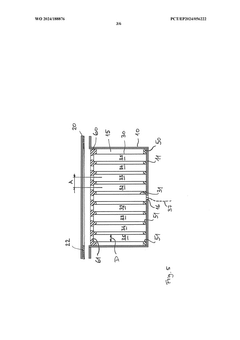
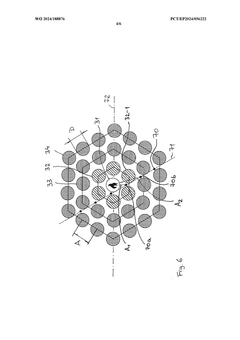
Test stand with temperature sensors for evaluating a material intended for use in a battery and test method using the test stand
PatentWO2024188876A1
Innovation
- A test stand equipped with multiple temperature sensors arranged at different distances from an initiation cell, allowing for the measurement of temperature changes and analysis of thermal propagation in a controlled environment that mimics real battery conditions, including a honeycomb pattern or linear arrangement of battery cells, and optional pressure limitation means to simulate realistic thermal runaway scenarios.
System and method for early-stage detection of thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries
PatentPendingUS20240154203A1
Innovation
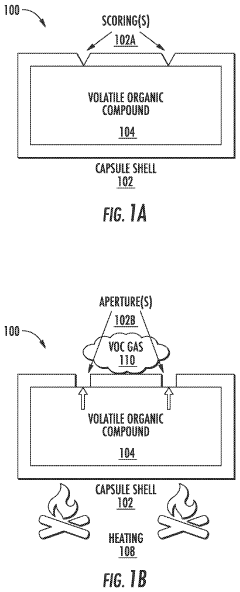
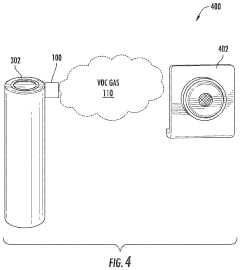
- A thermally reactive capsule coupled to a battery cell, containing a volatile organic compound (VOC) that vaporizes and generates pressure when the cell reaches a critical temperature, triggering a pressure relief mechanism and releasing gas detectable by a sensor, providing an early warning of thermal runaway.
Regulatory Framework for ORB Thermal Testing
The regulatory framework for ORB (Oxygen-Reducing Battery) thermal testing is a critical component in ensuring the safety and reliability of these advanced energy storage systems. As ORB technology continues to evolve, regulatory bodies worldwide are developing and refining guidelines to address the unique thermal characteristics and potential risks associated with these batteries.
At the forefront of ORB thermal testing regulations is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The IEC has established specific standards, such as IEC 62619, which outlines safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries in industrial applications. While not exclusively focused on ORBs, these standards provide a foundation for thermal testing protocols that can be adapted to address the specific needs of oxygen-reducing batteries.
In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) play crucial roles in shaping the regulatory landscape for battery thermal testing. The DOE's Battery500 Consortium, aimed at developing next-generation battery technologies, has been instrumental in identifying key thermal safety considerations for advanced battery systems, including ORBs.
The European Union, through its Battery Directive and REACH regulations, has also been proactive in addressing the thermal safety aspects of emerging battery technologies. These regulations emphasize the importance of comprehensive thermal runaway risk analysis and mandate specific testing protocols to ensure battery safety throughout the product lifecycle.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented stringent thermal testing requirements for battery manufacturers. The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) have developed specific guidelines for thermal runaway prevention and mitigation in advanced battery systems.
A key focus of the regulatory framework is the standardization of thermal runaway testing protocols. These protocols typically include abuse tests such as overcharging, external short circuit, and thermal shock to evaluate the battery's response under extreme conditions. Regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing the need for real-time monitoring and early detection systems to prevent thermal runaway incidents.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the importance of supply chain transparency and traceability in thermal safety. Manufacturers are required to provide detailed documentation on thermal management systems, safety features, and quality control measures implemented during the production process.
As ORB technology advances, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve, incorporating more specific guidelines for oxygen-reducing chemistries. This may include specialized thermal testing protocols that account for the unique oxygen management mechanisms in ORBs and their potential impact on thermal behavior.
At the forefront of ORB thermal testing regulations is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The IEC has established specific standards, such as IEC 62619, which outlines safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries in industrial applications. While not exclusively focused on ORBs, these standards provide a foundation for thermal testing protocols that can be adapted to address the specific needs of oxygen-reducing batteries.
In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) play crucial roles in shaping the regulatory landscape for battery thermal testing. The DOE's Battery500 Consortium, aimed at developing next-generation battery technologies, has been instrumental in identifying key thermal safety considerations for advanced battery systems, including ORBs.
The European Union, through its Battery Directive and REACH regulations, has also been proactive in addressing the thermal safety aspects of emerging battery technologies. These regulations emphasize the importance of comprehensive thermal runaway risk analysis and mandate specific testing protocols to ensure battery safety throughout the product lifecycle.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented stringent thermal testing requirements for battery manufacturers. The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) have developed specific guidelines for thermal runaway prevention and mitigation in advanced battery systems.
A key focus of the regulatory framework is the standardization of thermal runaway testing protocols. These protocols typically include abuse tests such as overcharging, external short circuit, and thermal shock to evaluate the battery's response under extreme conditions. Regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing the need for real-time monitoring and early detection systems to prevent thermal runaway incidents.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the importance of supply chain transparency and traceability in thermal safety. Manufacturers are required to provide detailed documentation on thermal management systems, safety features, and quality control measures implemented during the production process.
As ORB technology advances, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve, incorporating more specific guidelines for oxygen-reducing chemistries. This may include specialized thermal testing protocols that account for the unique oxygen management mechanisms in ORBs and their potential impact on thermal behavior.
Environmental Impact of ORB Thermal Management
The environmental impact of ORB (Optical Reflecting Balloon) thermal management is a critical aspect to consider in the development and deployment of these advanced space technologies. As ORBs play an increasingly important role in various space missions, their thermal behavior and management strategies have significant implications for the space environment.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to ORB thermal management is the potential release of thermal energy into the surrounding space. The thermal control systems employed in ORBs must be designed to minimize heat dissipation into the space environment, as excessive thermal emissions can contribute to space debris heating and potentially affect the thermal balance of nearby spacecraft or satellites.
Furthermore, the materials used in ORB thermal management systems must be carefully selected to ensure minimal environmental impact throughout the lifecycle of the device. This includes considerations for the production, deployment, operation, and eventual decommissioning of ORBs. The use of environmentally friendly and recyclable materials in thermal management components can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of these space technologies.
The thermal runaway risk associated with ORBs also presents potential environmental hazards. In the event of a thermal runaway incident, the release of high-temperature gases or particles could contribute to the growing problem of space debris. This not only poses risks to other space assets but also has long-term implications for the sustainability of space activities.
Another important aspect to consider is the impact of ORB thermal management on the Earth's atmosphere during re-entry scenarios. The thermal protection systems designed to withstand the extreme temperatures of atmospheric re-entry must also be engineered to minimize the release of harmful substances or particulates into the upper atmosphere.
The testing protocols for ORB thermal behavior must incorporate environmental impact assessments to ensure that the thermal management strategies employed do not adversely affect the space environment. This may include simulations and analyses of various operational scenarios to predict and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with thermal management systems.
As the number of ORBs and other space assets increases, the cumulative environmental impact of their thermal management systems becomes more significant. Therefore, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on innovative thermal control technologies that not only enhance the performance and reliability of ORBs but also minimize their environmental footprint in space.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to ORB thermal management is the potential release of thermal energy into the surrounding space. The thermal control systems employed in ORBs must be designed to minimize heat dissipation into the space environment, as excessive thermal emissions can contribute to space debris heating and potentially affect the thermal balance of nearby spacecraft or satellites.
Furthermore, the materials used in ORB thermal management systems must be carefully selected to ensure minimal environmental impact throughout the lifecycle of the device. This includes considerations for the production, deployment, operation, and eventual decommissioning of ORBs. The use of environmentally friendly and recyclable materials in thermal management components can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of these space technologies.
The thermal runaway risk associated with ORBs also presents potential environmental hazards. In the event of a thermal runaway incident, the release of high-temperature gases or particles could contribute to the growing problem of space debris. This not only poses risks to other space assets but also has long-term implications for the sustainability of space activities.
Another important aspect to consider is the impact of ORB thermal management on the Earth's atmosphere during re-entry scenarios. The thermal protection systems designed to withstand the extreme temperatures of atmospheric re-entry must also be engineered to minimize the release of harmful substances or particulates into the upper atmosphere.
The testing protocols for ORB thermal behavior must incorporate environmental impact assessments to ensure that the thermal management strategies employed do not adversely affect the space environment. This may include simulations and analyses of various operational scenarios to predict and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with thermal management systems.
As the number of ORBs and other space assets increases, the cumulative environmental impact of their thermal management systems becomes more significant. Therefore, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on innovative thermal control technologies that not only enhance the performance and reliability of ORBs but also minimize their environmental footprint in space.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!