How to Implement High-Power ORB Cells for Grid Services: Module Design & BMS Considerations
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ORB Cell Technology Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cell technology represents a significant advancement in the field of energy storage, particularly for grid services. This innovative technology has emerged as a promising solution to address the growing demand for high-power, fast-charging, and long-lasting energy storage systems.
ORB cells have their roots in the broader field of organic electronics, which began to gain traction in the early 2000s. The concept of using organic radical compounds as active materials in batteries was first proposed in the mid-2000s, with early research focusing on nitroxide radical polymers. These initial studies demonstrated the potential for rapid charge-discharge capabilities and high power density.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing more stable and efficient organic radical compounds. By the early 2010s, scientists had made significant strides in synthesizing novel organic radical materials with improved electrochemical properties. This period saw the emergence of various radical polymer families, including TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxy) derivatives, which showed exceptional promise for high-power applications.
The primary objective of ORB cell technology development has been to create a high-power energy storage solution that can meet the demanding requirements of grid services. These objectives include rapid charge and discharge capabilities, high cycle life, improved safety, and scalability. Additionally, researchers have aimed to address the limitations of traditional lithium-ion batteries, such as thermal runaway risks and resource scarcity.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing ORB cells for practical implementation in grid-scale applications. This has involved addressing challenges related to cell design, electrode formulation, and electrolyte composition. Researchers have been working on enhancing the energy density of ORB cells while maintaining their high-power characteristics, a crucial factor for their adoption in grid services.
The development of advanced battery management systems (BMS) has become a critical aspect of ORB cell technology evolution. These systems are essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of ORB cells, particularly in high-power applications. BMS considerations include precise state-of-charge estimation, thermal management, and cell balancing techniques tailored to the unique properties of organic radical materials.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ORB cell technology in grid services are multifaceted. Researchers aim to further increase power density, improve long-term stability, and reduce production costs to make ORB cells more competitive with established technologies. Additionally, there is a strong focus on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable manufacturing processes, aligning with the growing emphasis on green energy solutions.
ORB cells have their roots in the broader field of organic electronics, which began to gain traction in the early 2000s. The concept of using organic radical compounds as active materials in batteries was first proposed in the mid-2000s, with early research focusing on nitroxide radical polymers. These initial studies demonstrated the potential for rapid charge-discharge capabilities and high power density.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing more stable and efficient organic radical compounds. By the early 2010s, scientists had made significant strides in synthesizing novel organic radical materials with improved electrochemical properties. This period saw the emergence of various radical polymer families, including TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxy) derivatives, which showed exceptional promise for high-power applications.
The primary objective of ORB cell technology development has been to create a high-power energy storage solution that can meet the demanding requirements of grid services. These objectives include rapid charge and discharge capabilities, high cycle life, improved safety, and scalability. Additionally, researchers have aimed to address the limitations of traditional lithium-ion batteries, such as thermal runaway risks and resource scarcity.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing ORB cells for practical implementation in grid-scale applications. This has involved addressing challenges related to cell design, electrode formulation, and electrolyte composition. Researchers have been working on enhancing the energy density of ORB cells while maintaining their high-power characteristics, a crucial factor for their adoption in grid services.
The development of advanced battery management systems (BMS) has become a critical aspect of ORB cell technology evolution. These systems are essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of ORB cells, particularly in high-power applications. BMS considerations include precise state-of-charge estimation, thermal management, and cell balancing techniques tailored to the unique properties of organic radical materials.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ORB cell technology in grid services are multifaceted. Researchers aim to further increase power density, improve long-term stability, and reduce production costs to make ORB cells more competitive with established technologies. Additionally, there is a strong focus on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable manufacturing processes, aligning with the growing emphasis on green energy solutions.
Grid Services Market Demand Analysis
The demand for high-power ORB (Oxygen-Redox Battery) cells in grid services is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for large-scale energy storage solutions to support renewable energy integration and grid stability. As power grids worldwide transition towards cleaner energy sources, the requirement for efficient and reliable energy storage systems has become paramount.
The grid services market is witnessing a surge in demand for advanced battery technologies that can provide multiple grid support functions. ORB cells, with their high power density and long cycle life, are well-positioned to meet these evolving needs. The market for grid-scale energy storage is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with ORB technology poised to capture a substantial share.
One of the primary drivers for ORB cell adoption in grid services is the growing penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. These sources require robust energy storage solutions to smooth out supply fluctuations and ensure grid stability. ORB cells offer the ability to rapidly charge and discharge, making them ideal for frequency regulation and load balancing applications.
Another significant market demand stems from the need for peak shaving and load shifting capabilities. As electricity demand patterns become more dynamic, utilities and grid operators are seeking flexible storage solutions that can efficiently manage peak loads and optimize energy distribution. ORB cells, with their high power output and fast response times, are well-suited to address these requirements.
The increasing focus on grid resilience and reliability is also driving demand for ORB technology. As extreme weather events and cybersecurity threats pose risks to power infrastructure, grid operators are investing in distributed energy storage systems to enhance grid stability and provide backup power during outages. ORB cells' ability to deliver high power output for extended periods makes them attractive for such applications.
Furthermore, the electrification of transportation and the growth of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure are creating new opportunities for grid-scale energy storage. ORB cells can play a crucial role in managing the increased load on the grid from EV charging stations and potentially enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications.
The market demand for ORB cells in grid services is not limited to developed economies. Emerging markets with rapidly growing energy needs and evolving grid infrastructure are also showing interest in advanced energy storage technologies. These regions present significant opportunities for ORB cell deployment, particularly in areas with weak or unreliable grid connections.
The grid services market is witnessing a surge in demand for advanced battery technologies that can provide multiple grid support functions. ORB cells, with their high power density and long cycle life, are well-positioned to meet these evolving needs. The market for grid-scale energy storage is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with ORB technology poised to capture a substantial share.
One of the primary drivers for ORB cell adoption in grid services is the growing penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. These sources require robust energy storage solutions to smooth out supply fluctuations and ensure grid stability. ORB cells offer the ability to rapidly charge and discharge, making them ideal for frequency regulation and load balancing applications.
Another significant market demand stems from the need for peak shaving and load shifting capabilities. As electricity demand patterns become more dynamic, utilities and grid operators are seeking flexible storage solutions that can efficiently manage peak loads and optimize energy distribution. ORB cells, with their high power output and fast response times, are well-suited to address these requirements.
The increasing focus on grid resilience and reliability is also driving demand for ORB technology. As extreme weather events and cybersecurity threats pose risks to power infrastructure, grid operators are investing in distributed energy storage systems to enhance grid stability and provide backup power during outages. ORB cells' ability to deliver high power output for extended periods makes them attractive for such applications.
Furthermore, the electrification of transportation and the growth of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure are creating new opportunities for grid-scale energy storage. ORB cells can play a crucial role in managing the increased load on the grid from EV charging stations and potentially enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications.
The market demand for ORB cells in grid services is not limited to developed economies. Emerging markets with rapidly growing energy needs and evolving grid infrastructure are also showing interest in advanced energy storage technologies. These regions present significant opportunities for ORB cell deployment, particularly in areas with weak or unreliable grid connections.
ORB Cell Technical Challenges and Limitations
The implementation of high-power ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells for grid services faces several technical challenges and limitations. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent instability of organic radical compounds, which can lead to self-discharge and reduced cycle life. This instability is particularly pronounced at elevated temperatures, limiting the operational range of ORB cells in grid applications where thermal management may be challenging.
Another significant challenge lies in the power density of ORB cells. While they offer high energy density, achieving the necessary power output for grid services requires careful electrode design and optimization. The electron transfer kinetics at the electrode-electrolyte interface can be a limiting factor, necessitating the development of advanced electrode materials and structures to enhance charge transfer rates.
The scalability of ORB cell production presents additional hurdles. Current manufacturing processes for organic radical compounds are often complex and costly, making large-scale production for grid-scale applications economically challenging. Developing more efficient and cost-effective synthesis methods for organic radical materials is crucial for the widespread adoption of this technology.
Electrolyte compatibility is another critical issue in ORB cell development. Finding an electrolyte that maintains stability with the organic radical compounds while providing adequate ionic conductivity and safety characteristics is essential. Many conventional electrolytes used in other battery technologies may not be suitable for ORB cells due to potential reactions with the active materials.
The long-term stability of ORB cells under various operational conditions remains a concern. Grid services often require batteries to undergo frequent charge-discharge cycles and operate in diverse environmental conditions. Ensuring that ORB cells can maintain their performance over extended periods and under varying loads is crucial for their viability in grid applications.
Module design for high-power ORB cells presents its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform temperature distribution and effective heat dissipation within large-scale modules is critical to prevent localized degradation and ensure consistent performance across all cells. Additionally, the integration of ORB cells into existing grid infrastructure may require the development of specialized power electronics and control systems.
Battery Management System (BMS) considerations for ORB cells are also complex. The unique characteristics of organic radical compounds necessitate the development of tailored algorithms for state-of-charge estimation, cell balancing, and safety monitoring. Conventional BMS solutions may not be directly applicable, requiring significant research and development efforts to create ORB-specific management systems.
Another significant challenge lies in the power density of ORB cells. While they offer high energy density, achieving the necessary power output for grid services requires careful electrode design and optimization. The electron transfer kinetics at the electrode-electrolyte interface can be a limiting factor, necessitating the development of advanced electrode materials and structures to enhance charge transfer rates.
The scalability of ORB cell production presents additional hurdles. Current manufacturing processes for organic radical compounds are often complex and costly, making large-scale production for grid-scale applications economically challenging. Developing more efficient and cost-effective synthesis methods for organic radical materials is crucial for the widespread adoption of this technology.
Electrolyte compatibility is another critical issue in ORB cell development. Finding an electrolyte that maintains stability with the organic radical compounds while providing adequate ionic conductivity and safety characteristics is essential. Many conventional electrolytes used in other battery technologies may not be suitable for ORB cells due to potential reactions with the active materials.
The long-term stability of ORB cells under various operational conditions remains a concern. Grid services often require batteries to undergo frequent charge-discharge cycles and operate in diverse environmental conditions. Ensuring that ORB cells can maintain their performance over extended periods and under varying loads is crucial for their viability in grid applications.
Module design for high-power ORB cells presents its own set of challenges. Achieving uniform temperature distribution and effective heat dissipation within large-scale modules is critical to prevent localized degradation and ensure consistent performance across all cells. Additionally, the integration of ORB cells into existing grid infrastructure may require the development of specialized power electronics and control systems.
Battery Management System (BMS) considerations for ORB cells are also complex. The unique characteristics of organic radical compounds necessitate the development of tailored algorithms for state-of-charge estimation, cell balancing, and safety monitoring. Conventional BMS solutions may not be directly applicable, requiring significant research and development efforts to create ORB-specific management systems.
Current High-Power ORB Cell Module Designs
01 ORB cell technology for power generation
ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells utilize organic radical compounds for energy storage and power generation. This technology offers advantages in terms of high energy density, rapid charging capabilities, and environmental friendliness compared to traditional battery systems.- ORB cell technology for power generation: ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells utilize organic radical compounds for energy storage and power generation. This technology offers advantages such as high power density, rapid charging capabilities, and environmental friendliness compared to traditional battery systems.
- Genetic engineering of cells for enhanced power production: Genetic modification techniques are applied to cells to improve their energy production capabilities. This involves altering genes related to metabolic pathways, enhancing mitochondrial function, or introducing novel energy-generating mechanisms to increase cellular power output.
- Microbial fuel cells for sustainable power generation: Microbial fuel cells harness the metabolic activities of microorganisms to generate electricity. This technology utilizes specialized bacteria or other microbes to convert organic matter into electrical energy, offering a sustainable approach to power generation.
- Nanotechnology-enhanced cellular power systems: Integration of nanotechnology with cellular systems to boost power generation. This approach involves using nanoparticles or nanostructures to enhance energy transfer, improve electron transport, or catalyze energy-producing reactions at the cellular level.
- Biohybrid power cells combining biological and artificial components: Development of biohybrid systems that merge biological cells with artificial components to create novel power generation units. These systems aim to leverage the advantages of both biological processes and synthetic materials for improved energy production and efficiency.
02 Genetic engineering of ORB cells for enhanced power output
Genetic modification techniques are applied to ORB cells to improve their power generation capabilities. This involves altering specific genes or introducing new genetic material to enhance the cells' energy production efficiency and overall performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 ORB cell cultivation and scaling methods
Specialized cultivation techniques and scaling methods are developed for ORB cells to optimize their growth and power generation potential. These methods focus on creating ideal conditions for cell proliferation and maintaining their energy-producing capabilities at larger scales.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of ORB cells in energy storage systems
ORB cells are incorporated into advanced energy storage systems, combining their unique properties with other technologies to create more efficient and sustainable power solutions. This integration aims to enhance overall system performance and address various energy storage challenges.Expand Specific Solutions05 ORB cell power applications in biotechnology
The power generation capabilities of ORB cells are harnessed for various biotechnology applications. This includes powering biosensors, microfluidic devices, and other small-scale biological systems, offering new possibilities in fields such as medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ORB Cell and Grid Services Industry
The implementation of high-power ORB cells for grid services is in a nascent stage, with the market poised for significant growth as energy storage solutions become increasingly critical for grid stability. The technology's maturity varies among key players, with companies like Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and Huawei Technologies leading in research and development. These firms are investing heavily in module design and Battery Management System (BMS) considerations to enhance efficiency and reliability. The competitive landscape is intensifying as telecommunications giants like Ericsson and Deutsche Telekom enter the market, leveraging their expertise in network infrastructure to develop integrated grid service solutions. As the technology evolves, we can expect rapid advancements in cell design, power density, and grid integration capabilities.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced High-Power ORB (Optimized Rechargeable Battery) Cells specifically designed for grid services. Their module design incorporates high-capacity prismatic cells with improved energy density, utilizing nickel-rich cathodes and silicon-based anodes[1]. The company's BMS (Battery Management System) employs AI-driven predictive analytics for real-time monitoring and optimization of cell performance[2]. Samsung's ORB cells feature a unique thermal management system that uses phase-change materials to maintain optimal operating temperatures, enhancing both safety and longevity[3]. The modular design allows for scalability, making it suitable for various grid applications from small-scale energy storage to utility-scale projects.
Strengths: Advanced thermal management, AI-driven BMS, and scalable modular design. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to some competitors, and potential supply chain dependencies for specialized materials.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has engineered High-Power ORB Cells tailored for grid services, focusing on longevity and rapid response capabilities. Their module design incorporates large-format pouch cells with advanced electrode materials, including proprietary nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathodes and graphite anodes with silicon additives[4]. The company's BMS utilizes machine learning algorithms to optimize charging and discharging cycles, effectively reducing capacity fade over time[5]. LG's ORB cells feature a novel electrolyte formulation that enhances power density and cycle life, crucial for grid stabilization applications[6]. The module design includes an integrated cooling system with liquid coolant channels, ensuring uniform temperature distribution across the cell stack.
Strengths: High cycle life, advanced electrolyte technology, and intelligent BMS for optimized performance. Weaknesses: Potentially higher manufacturing complexity and cost due to specialized materials and cooling system.
Core Innovations in ORB Cell Technology
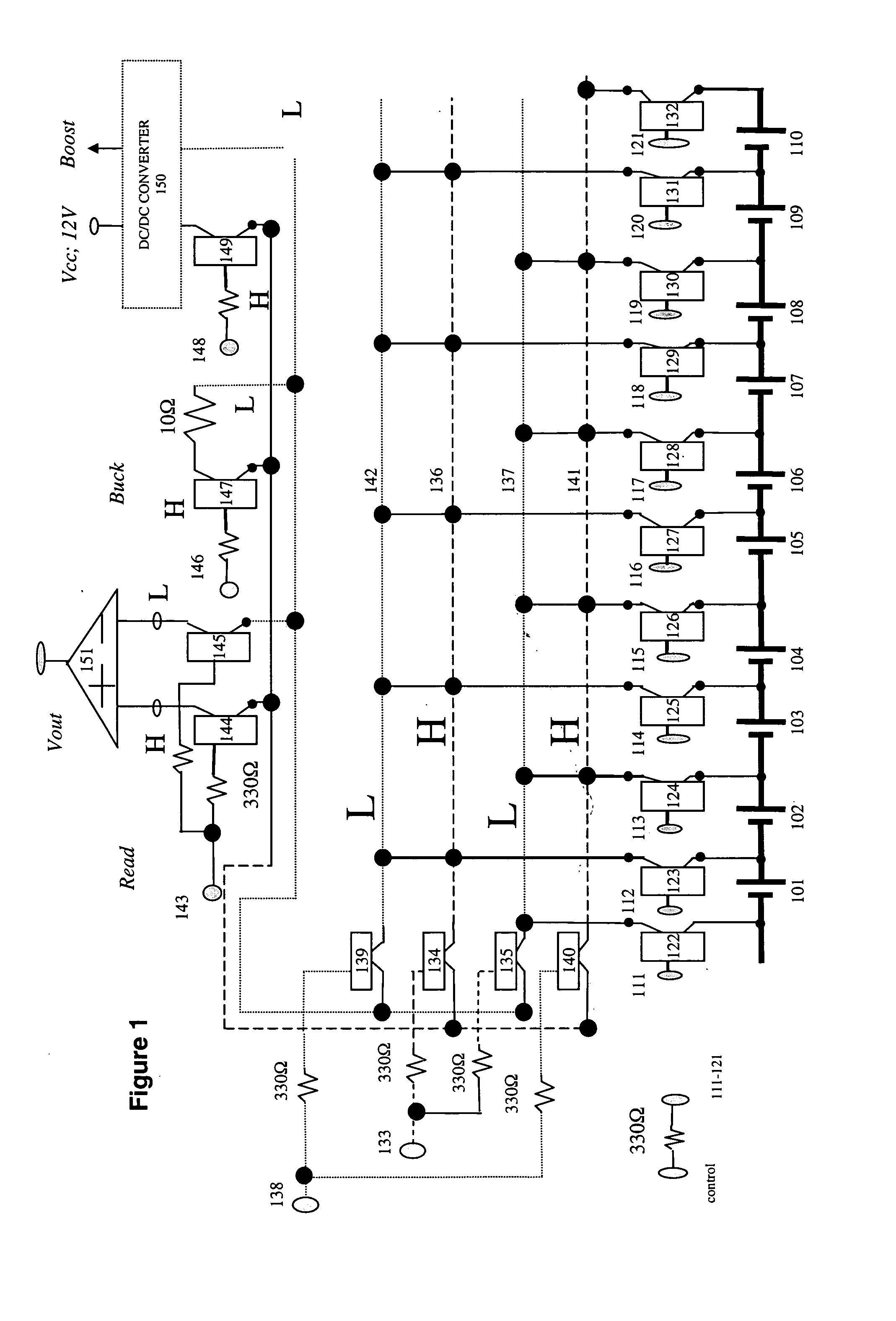
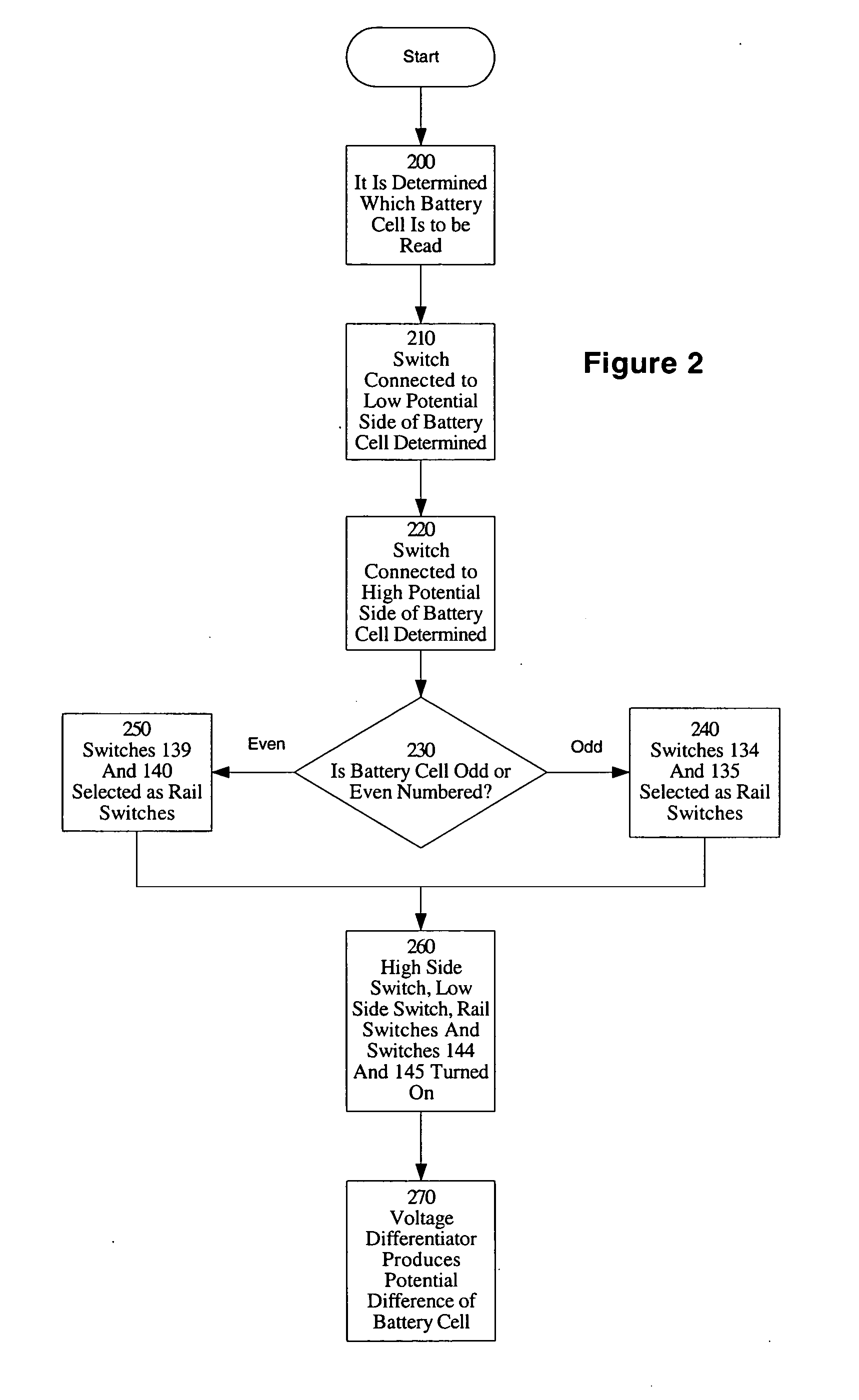
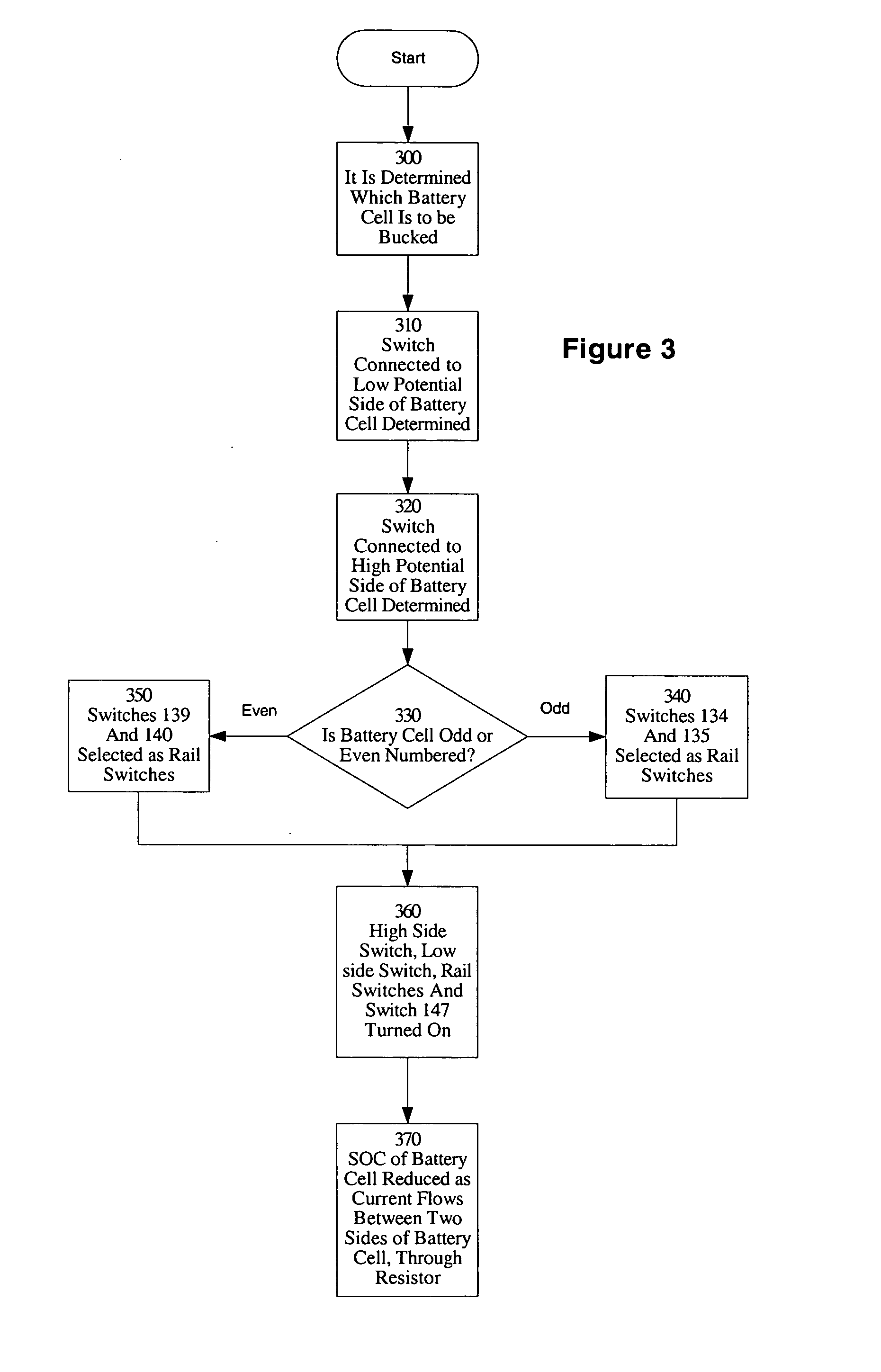
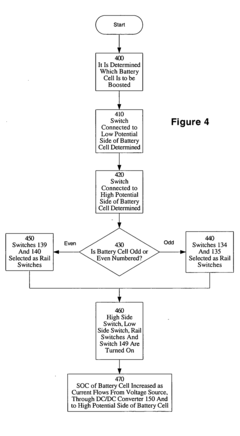
Method and apparatus for multiple battery cell management
PatentInactiveUS20050127874A1
Innovation
- The implementation of solid-state relays (SSRs) in the BMS, which are smaller and faster than mechanical relays, allowing for more efficient and safe management of battery cell charge, and the use of a modular design with four SSRs to control access to battery cells, enabling quicker response times and more efficient scaling.
Battery system having varying cell types
PatentInactiveEP2499689A1
Innovation
- A battery module design combining a high-energy-content energy store and a high-power store with a diode, where the high-energy store supplies power at low loads and the high-power store activates at increased loads, and a DC/DC converter stabilizes output voltage and charges the energy store, allowing for efficient power distribution and recharging.
Regulatory Framework for Grid-Scale Energy Storage
The regulatory framework for grid-scale energy storage plays a crucial role in the implementation of high-power ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells for grid services. As these technologies advance, policymakers and regulatory bodies are adapting to ensure safe, efficient, and sustainable integration of energy storage systems into the grid infrastructure.
At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has issued several orders to remove barriers for energy storage participation in wholesale markets. Order 841, in particular, requires grid operators to establish market rules that recognize the unique characteristics of energy storage resources, including their ability to both inject and withdraw electricity from the grid. This regulatory shift has created new opportunities for ORB cell deployment in grid services.
State-level policies also significantly impact the adoption of grid-scale energy storage technologies. Many states have implemented energy storage targets and incentives to promote the integration of storage systems into their electrical grids. For instance, California's AB 2514 mandated utilities to procure 1.3 GW of energy storage by 2020, while New York set a target of 3 GW by 2030. These policies create a favorable environment for the development and deployment of advanced storage technologies like ORB cells.
Safety regulations and standards are paramount in the implementation of high-power ORB cells. Organizations such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) have developed specific standards for energy storage systems, addressing issues like thermal runaway, fire suppression, and electrical safety. Compliance with these standards is essential for the successful deployment of ORB cells in grid applications.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the energy storage landscape. The increasing focus on sustainability and carbon reduction has led to stricter regulations on the environmental impact of energy storage technologies. ORB cells, with their potential for improved recyclability and reduced environmental footprint compared to some traditional battery technologies, may find a more favorable regulatory environment in this context.
Interconnection standards and grid codes are critical aspects of the regulatory framework that directly impact the implementation of ORB cells for grid services. These standards define the technical requirements for connecting energy storage systems to the grid, ensuring system stability, power quality, and reliability. As ORB cell technology evolves, it must adapt to meet these interconnection requirements to facilitate seamless integration with existing grid infrastructure.
In conclusion, the regulatory framework for grid-scale energy storage is dynamic and multifaceted, encompassing federal and state policies, safety standards, environmental regulations, and technical requirements. As ORB cell technology advances, navigating this complex regulatory landscape will be crucial for successful implementation in grid services. Ongoing collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and regulatory bodies will be essential to create a supportive environment for the growth and adoption of innovative energy storage solutions like high-power ORB cells.
At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has issued several orders to remove barriers for energy storage participation in wholesale markets. Order 841, in particular, requires grid operators to establish market rules that recognize the unique characteristics of energy storage resources, including their ability to both inject and withdraw electricity from the grid. This regulatory shift has created new opportunities for ORB cell deployment in grid services.
State-level policies also significantly impact the adoption of grid-scale energy storage technologies. Many states have implemented energy storage targets and incentives to promote the integration of storage systems into their electrical grids. For instance, California's AB 2514 mandated utilities to procure 1.3 GW of energy storage by 2020, while New York set a target of 3 GW by 2030. These policies create a favorable environment for the development and deployment of advanced storage technologies like ORB cells.
Safety regulations and standards are paramount in the implementation of high-power ORB cells. Organizations such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) have developed specific standards for energy storage systems, addressing issues like thermal runaway, fire suppression, and electrical safety. Compliance with these standards is essential for the successful deployment of ORB cells in grid applications.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the energy storage landscape. The increasing focus on sustainability and carbon reduction has led to stricter regulations on the environmental impact of energy storage technologies. ORB cells, with their potential for improved recyclability and reduced environmental footprint compared to some traditional battery technologies, may find a more favorable regulatory environment in this context.
Interconnection standards and grid codes are critical aspects of the regulatory framework that directly impact the implementation of ORB cells for grid services. These standards define the technical requirements for connecting energy storage systems to the grid, ensuring system stability, power quality, and reliability. As ORB cell technology evolves, it must adapt to meet these interconnection requirements to facilitate seamless integration with existing grid infrastructure.
In conclusion, the regulatory framework for grid-scale energy storage is dynamic and multifaceted, encompassing federal and state policies, safety standards, environmental regulations, and technical requirements. As ORB cell technology advances, navigating this complex regulatory landscape will be crucial for successful implementation in grid services. Ongoing collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and regulatory bodies will be essential to create a supportive environment for the growth and adoption of innovative energy storage solutions like high-power ORB cells.
Environmental Impact of High-Power ORB Cells
The implementation of high-power ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells for grid services presents significant environmental considerations that must be carefully evaluated. These advanced energy storage systems, while offering promising solutions for grid stability and renewable energy integration, also carry potential environmental impacts throughout their lifecycle.
The production phase of high-power ORB cells involves the use of organic materials and specialized manufacturing processes. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, ORB cells rely on organic radical polymers, which can be derived from more sustainable sources. This shift towards organic materials potentially reduces the environmental burden associated with mining and processing of metal-based battery components. However, the synthesis of these organic compounds may still involve energy-intensive processes and the use of chemical solvents, which require proper management to minimize environmental pollution.
During the operational phase, high-power ORB cells demonstrate several environmental advantages. Their high charge-discharge efficiency and long cycle life contribute to reduced energy waste and extended service periods, potentially lowering the overall environmental footprint of grid energy storage systems. Additionally, the absence of heavy metals and toxic materials in ORB cells mitigates concerns related to soil and water contamination in case of accidental leakage or improper disposal.
The end-of-life management of high-power ORB cells presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. The organic nature of the cell components offers the potential for more environmentally friendly recycling processes compared to conventional battery technologies. However, the development of efficient recycling methods for these novel materials is still in its early stages and requires further research and infrastructure development to maximize resource recovery and minimize waste.
The scalability of high-power ORB cells for grid services also has broader environmental implications. As these systems are deployed at larger scales, they can facilitate greater integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based power generation and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This indirect environmental benefit must be weighed against the cumulative impact of large-scale ORB cell production and deployment.
Safety considerations related to high-power ORB cells also have environmental ramifications. While these cells generally pose lower fire and explosion risks compared to some other battery technologies, ensuring proper safety measures and containment strategies is crucial to prevent any potential environmental contamination in case of system failures or accidents.
The production phase of high-power ORB cells involves the use of organic materials and specialized manufacturing processes. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, ORB cells rely on organic radical polymers, which can be derived from more sustainable sources. This shift towards organic materials potentially reduces the environmental burden associated with mining and processing of metal-based battery components. However, the synthesis of these organic compounds may still involve energy-intensive processes and the use of chemical solvents, which require proper management to minimize environmental pollution.
During the operational phase, high-power ORB cells demonstrate several environmental advantages. Their high charge-discharge efficiency and long cycle life contribute to reduced energy waste and extended service periods, potentially lowering the overall environmental footprint of grid energy storage systems. Additionally, the absence of heavy metals and toxic materials in ORB cells mitigates concerns related to soil and water contamination in case of accidental leakage or improper disposal.
The end-of-life management of high-power ORB cells presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. The organic nature of the cell components offers the potential for more environmentally friendly recycling processes compared to conventional battery technologies. However, the development of efficient recycling methods for these novel materials is still in its early stages and requires further research and infrastructure development to maximize resource recovery and minimize waste.
The scalability of high-power ORB cells for grid services also has broader environmental implications. As these systems are deployed at larger scales, they can facilitate greater integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based power generation and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This indirect environmental benefit must be weighed against the cumulative impact of large-scale ORB cell production and deployment.
Safety considerations related to high-power ORB cells also have environmental ramifications. While these cells generally pose lower fire and explosion risks compared to some other battery technologies, ensuring proper safety measures and containment strategies is crucial to prevent any potential environmental contamination in case of system failures or accidents.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!