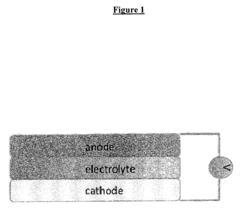
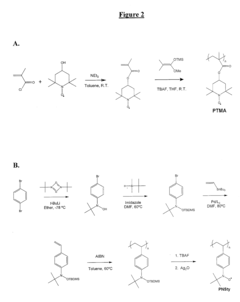
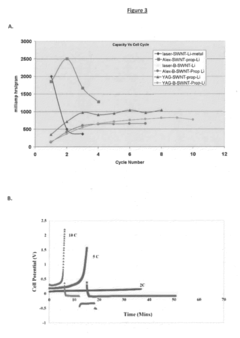
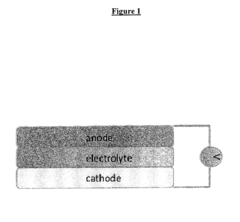
How to Characterize Rate Performance and Pulse Power of ORB Cells — Standard Tests
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ORB Cell Performance Characterization Goals
The primary goal of characterizing the rate performance and pulse power of ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells is to establish standardized testing protocols that accurately assess and quantify the unique capabilities of these innovative energy storage devices. This characterization aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ORB cell behavior under various operational conditions, enabling researchers and manufacturers to optimize cell design and performance.
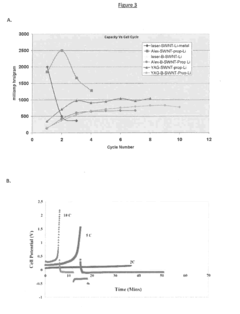
One key objective is to determine the rate capability of ORB cells across a wide range of charge and discharge rates. This involves measuring the cell's capacity retention and voltage profiles at different C-rates, typically ranging from low rates (e.g., C/10) to high rates (e.g., 10C or higher). By analyzing these data, researchers can evaluate the cell's ability to maintain its capacity and energy density under diverse usage scenarios, which is crucial for applications requiring rapid charge or discharge.
Another critical goal is to assess the pulse power performance of ORB cells. This involves subjecting the cells to short-duration, high-current pulses and measuring their voltage response. The pulse power characterization aims to quantify the cell's ability to deliver or accept sudden bursts of power, which is essential for applications such as regenerative braking in electric vehicles or grid frequency regulation.
Evaluating the cycling stability of ORB cells at different rates is also a fundamental objective. This involves conducting long-term cycling tests at various charge and discharge rates to determine capacity fade, coulombic efficiency, and overall cycle life. Understanding how rate performance evolves over extended cycling is crucial for predicting the long-term reliability and durability of ORB cells in real-world applications.
Furthermore, the characterization goals include investigating the temperature dependence of rate performance and pulse power. This involves conducting tests across a range of operating temperatures to understand how thermal conditions affect the cell's capabilities. Such information is vital for designing thermal management systems and determining the suitable operating range for ORB cells in different applications.
Lastly, the characterization aims to establish correlations between the cell's chemical composition, structure, and its rate and pulse power performance. This involves systematically varying parameters such as electrode thickness, electrolyte composition, and radical concentration to understand their impact on cell performance. By identifying these structure-property relationships, researchers can guide the development of next-generation ORB cells with enhanced rate and power capabilities.
One key objective is to determine the rate capability of ORB cells across a wide range of charge and discharge rates. This involves measuring the cell's capacity retention and voltage profiles at different C-rates, typically ranging from low rates (e.g., C/10) to high rates (e.g., 10C or higher). By analyzing these data, researchers can evaluate the cell's ability to maintain its capacity and energy density under diverse usage scenarios, which is crucial for applications requiring rapid charge or discharge.
Another critical goal is to assess the pulse power performance of ORB cells. This involves subjecting the cells to short-duration, high-current pulses and measuring their voltage response. The pulse power characterization aims to quantify the cell's ability to deliver or accept sudden bursts of power, which is essential for applications such as regenerative braking in electric vehicles or grid frequency regulation.
Evaluating the cycling stability of ORB cells at different rates is also a fundamental objective. This involves conducting long-term cycling tests at various charge and discharge rates to determine capacity fade, coulombic efficiency, and overall cycle life. Understanding how rate performance evolves over extended cycling is crucial for predicting the long-term reliability and durability of ORB cells in real-world applications.
Furthermore, the characterization goals include investigating the temperature dependence of rate performance and pulse power. This involves conducting tests across a range of operating temperatures to understand how thermal conditions affect the cell's capabilities. Such information is vital for designing thermal management systems and determining the suitable operating range for ORB cells in different applications.
Lastly, the characterization aims to establish correlations between the cell's chemical composition, structure, and its rate and pulse power performance. This involves systematically varying parameters such as electrode thickness, electrolyte composition, and radical concentration to understand their impact on cell performance. By identifying these structure-property relationships, researchers can guide the development of next-generation ORB cells with enhanced rate and power capabilities.
Market Demand for ORB Cell Testing
The market demand for ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cell testing is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of ORB technology in various applications. As the energy storage industry continues to evolve, there is a pressing need for standardized and reliable testing methods to characterize the performance of ORB cells, particularly in terms of rate performance and pulse power capabilities.
The automotive sector represents a major driver for ORB cell testing demand. With the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production, manufacturers require comprehensive testing protocols to evaluate the suitability of ORB cells for high-power applications such as regenerative braking and acceleration. The ability to accurately assess rate performance and pulse power characteristics is crucial for optimizing battery pack designs and ensuring vehicle performance meets consumer expectations.
In the consumer electronics market, the demand for ORB cell testing is also on the rise. Manufacturers of smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices are exploring ORB technology as a potential alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These companies require robust testing methodologies to evaluate the fast-charging capabilities and power delivery of ORB cells, which are critical factors in enhancing user experience and product differentiation.
The renewable energy sector presents another significant market for ORB cell testing. As grid-scale energy storage systems become more prevalent, there is a growing need to assess the performance of ORB cells in large-scale applications. Utility companies and renewable energy developers are particularly interested in understanding the pulse power characteristics of ORB cells, which can impact their ability to provide grid stabilization services and manage peak demand.
The industrial and aerospace sectors are also contributing to the demand for ORB cell testing. In industrial applications, the potential for ORB cells to provide high-power output for short durations is attracting interest from manufacturers of power tools and material handling equipment. Similarly, the aerospace industry is exploring ORB technology for its potential weight savings and high-power capabilities in aircraft systems.
As the market for ORB cells expands, there is a parallel increase in demand for testing equipment and services. Manufacturers of battery testing systems are developing specialized equipment capable of accurately measuring the unique characteristics of ORB cells. Additionally, third-party testing laboratories are expanding their capabilities to include ORB cell testing, catering to companies that lack in-house testing facilities or expertise.
The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations is further driving the need for comprehensive ORB cell testing. Stakeholders across industries are seeking detailed information on the lifecycle performance and degradation characteristics of ORB cells to assess their long-term viability and environmental impact. This trend is expected to continue, reinforcing the importance of standardized testing protocols for rate performance and pulse power in ORB cells.
The automotive sector represents a major driver for ORB cell testing demand. With the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production, manufacturers require comprehensive testing protocols to evaluate the suitability of ORB cells for high-power applications such as regenerative braking and acceleration. The ability to accurately assess rate performance and pulse power characteristics is crucial for optimizing battery pack designs and ensuring vehicle performance meets consumer expectations.
In the consumer electronics market, the demand for ORB cell testing is also on the rise. Manufacturers of smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices are exploring ORB technology as a potential alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These companies require robust testing methodologies to evaluate the fast-charging capabilities and power delivery of ORB cells, which are critical factors in enhancing user experience and product differentiation.
The renewable energy sector presents another significant market for ORB cell testing. As grid-scale energy storage systems become more prevalent, there is a growing need to assess the performance of ORB cells in large-scale applications. Utility companies and renewable energy developers are particularly interested in understanding the pulse power characteristics of ORB cells, which can impact their ability to provide grid stabilization services and manage peak demand.
The industrial and aerospace sectors are also contributing to the demand for ORB cell testing. In industrial applications, the potential for ORB cells to provide high-power output for short durations is attracting interest from manufacturers of power tools and material handling equipment. Similarly, the aerospace industry is exploring ORB technology for its potential weight savings and high-power capabilities in aircraft systems.
As the market for ORB cells expands, there is a parallel increase in demand for testing equipment and services. Manufacturers of battery testing systems are developing specialized equipment capable of accurately measuring the unique characteristics of ORB cells. Additionally, third-party testing laboratories are expanding their capabilities to include ORB cell testing, catering to companies that lack in-house testing facilities or expertise.
The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations is further driving the need for comprehensive ORB cell testing. Stakeholders across industries are seeking detailed information on the lifecycle performance and degradation characteristics of ORB cells to assess their long-term viability and environmental impact. This trend is expected to continue, reinforcing the importance of standardized testing protocols for rate performance and pulse power in ORB cells.
Current Challenges in ORB Cell Rate Testing
The characterization of rate performance and pulse power in organic radical battery (ORB) cells presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must address. One of the primary difficulties lies in the rapid charge-discharge kinetics of ORB cells, which can lead to inaccuracies in traditional testing methods designed for slower electrochemical systems. The high-speed electron transfer processes in ORB cells require advanced testing equipment capable of capturing data at much higher frequencies than conventional battery testing systems.
Another challenge is the potential for self-discharge in ORB cells, which can affect the accuracy of rate performance measurements. The organic radical species used in these cells may undergo side reactions or degradation during testing, leading to capacity fade that is not necessarily representative of the cell's true rate capabilities. This necessitates the development of testing protocols that can distinguish between capacity loss due to high-rate cycling and that caused by self-discharge or degradation.
The stability of organic radical materials under various testing conditions also poses a significant hurdle. Temperature fluctuations during high-rate cycling can impact the stability of the radical species, potentially altering the cell's performance characteristics. Consequently, precise temperature control and monitoring systems are crucial for obtaining reliable and reproducible rate performance data.
Furthermore, the pulse power testing of ORB cells is complicated by their unique charge storage mechanism. Unlike traditional batteries that rely on ion intercalation, ORB cells store charge through reversible oxidation-reduction reactions of stable radical species. This fundamental difference requires a reevaluation of standard pulse power testing methodologies to ensure they accurately reflect the capabilities of ORB cells.
The development of standardized testing protocols for ORB cells is also hindered by the diversity of organic radical materials and cell designs. Different radical species and electrolyte combinations can exhibit varying rate performance and pulse power characteristics, making it challenging to establish universally applicable testing standards. This diversity necessitates a flexible yet consistent approach to characterization that can accommodate the unique properties of different ORB cell chemistries.
Lastly, the interpretation of rate performance and pulse power data for ORB cells requires careful consideration of their distinct operating principles. Traditional metrics used for lithium-ion batteries may not fully capture the performance advantages of ORB cells, particularly in high-power applications. Developing new performance indicators and benchmarks that accurately reflect the strengths of ORB technology is essential for fair comparison and evaluation against other energy storage systems.
Another challenge is the potential for self-discharge in ORB cells, which can affect the accuracy of rate performance measurements. The organic radical species used in these cells may undergo side reactions or degradation during testing, leading to capacity fade that is not necessarily representative of the cell's true rate capabilities. This necessitates the development of testing protocols that can distinguish between capacity loss due to high-rate cycling and that caused by self-discharge or degradation.
The stability of organic radical materials under various testing conditions also poses a significant hurdle. Temperature fluctuations during high-rate cycling can impact the stability of the radical species, potentially altering the cell's performance characteristics. Consequently, precise temperature control and monitoring systems are crucial for obtaining reliable and reproducible rate performance data.
Furthermore, the pulse power testing of ORB cells is complicated by their unique charge storage mechanism. Unlike traditional batteries that rely on ion intercalation, ORB cells store charge through reversible oxidation-reduction reactions of stable radical species. This fundamental difference requires a reevaluation of standard pulse power testing methodologies to ensure they accurately reflect the capabilities of ORB cells.
The development of standardized testing protocols for ORB cells is also hindered by the diversity of organic radical materials and cell designs. Different radical species and electrolyte combinations can exhibit varying rate performance and pulse power characteristics, making it challenging to establish universally applicable testing standards. This diversity necessitates a flexible yet consistent approach to characterization that can accommodate the unique properties of different ORB cell chemistries.
Lastly, the interpretation of rate performance and pulse power data for ORB cells requires careful consideration of their distinct operating principles. Traditional metrics used for lithium-ion batteries may not fully capture the performance advantages of ORB cells, particularly in high-power applications. Developing new performance indicators and benchmarks that accurately reflect the strengths of ORB technology is essential for fair comparison and evaluation against other energy storage systems.
Standard Test Protocols for ORB Cells
01 ORB cell performance optimization
Optimization techniques for ORB (Optically Rechargeable Battery) cells focus on improving their rate performance and pulse power capabilities. This involves enhancing the cell's ability to quickly charge and discharge, as well as deliver high power in short bursts. Strategies may include advanced electrode materials, improved electrolyte formulations, and optimized cell design to reduce internal resistance and enhance energy transfer efficiency.- ORB cell performance optimization: Optimization techniques for ORB (Optically Rechargeable Battery) cells focus on improving rate performance and pulse power capabilities. This involves enhancing the cell's ability to quickly charge and discharge while maintaining efficiency. Strategies may include advanced electrode designs, electrolyte formulations, and charge control mechanisms to maximize energy storage and delivery.
- Pulse power management in battery systems: Effective pulse power management is crucial for ORB cells to handle high-current, short-duration power demands. This involves implementing sophisticated control systems and power electronics to regulate voltage and current during rapid charge/discharge cycles. Advanced algorithms and hardware solutions are employed to optimize power delivery while protecting the cell from degradation.
- Rate performance enhancement techniques: Improving the rate performance of ORB cells involves developing materials and structures that facilitate rapid ion transport and electron transfer. This may include the use of nanostructured electrodes, high-conductivity additives, and advanced separator materials. The goal is to reduce internal resistance and improve the cell's ability to maintain capacity at high charge/discharge rates.
- Thermal management for high-performance ORB cells: Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining optimal performance in ORB cells, especially during high-rate and pulse power operations. This involves implementing cooling systems, heat dissipation techniques, and temperature monitoring to prevent overheating and ensure consistent performance across various operating conditions.
- Integration of ORB cells in energy storage systems: The integration of ORB cells into larger energy storage systems requires careful consideration of their unique characteristics. This includes developing specialized charging circuits, power management units, and system-level control strategies to leverage the cells' high rate performance and pulse power capabilities effectively. The focus is on optimizing overall system efficiency and reliability.
02 Pulse power management in battery systems
Effective pulse power management is crucial for ORB cells to meet high-power demand applications. This involves implementing sophisticated control systems that can regulate the rapid charge and discharge cycles, manage thermal effects, and ensure the longevity of the battery. Advanced power electronics and intelligent battery management systems are employed to optimize the pulse power delivery while maintaining cell stability and preventing degradation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Rate performance enhancement techniques
Improving the rate performance of ORB cells involves developing strategies to increase the speed of energy storage and release. This may include the use of nanostructured materials to shorten ion diffusion paths, implementing advanced current collectors for faster electron transfer, and designing cell architectures that facilitate rapid ion movement. The goal is to achieve high charge and discharge rates without compromising the cell's capacity or cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optical charging efficiency for ORB cells
Enhancing the optical charging efficiency is key to improving the overall performance of ORB cells. This involves optimizing the photosensitive components to capture and convert light energy more effectively, developing transparent electrodes that allow for better light penetration, and engineering the cell structure to maximize the utilization of incident light. Improved optical charging efficiency contributes to faster charging rates and higher energy conversion efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of ORB cells in energy storage systems
The integration of ORB cells into larger energy storage systems requires careful consideration of their unique characteristics. This includes developing specialized charging infrastructure that can provide both electrical and optical charging capabilities, designing hybrid systems that combine ORB cells with other energy storage technologies, and creating smart grid interfaces that can leverage the rapid response capabilities of ORB cells for grid stabilization and peak shaving applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Battery Testing Industry
The characterization of rate performance and pulse power of ORB cells is a critical area in energy storage technology, currently in a growth phase. The market for advanced battery technologies is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. While the technology is evolving, it has not yet reached full maturity. Companies like A123 Systems, Fudan University, and Yale University are at the forefront of research and development in this field. Their efforts focus on improving electrode materials, cell design, and testing methodologies to enhance the performance and reliability of ORB cells. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with both established players and emerging startups vying for market share and technological breakthroughs.
A123 Systems LLC
Technical Solution: A123 Systems has developed advanced lithium-ion battery technology specifically for high-power applications, including ORB (Optimized Rate Battery) cells. Their approach to characterizing rate performance and pulse power involves standardized testing protocols. These include constant current discharge tests at various C-rates to assess capacity retention, as well as hybrid pulse power characterization (HPPC) tests to evaluate power capability[1]. A123's ORB cells undergo rigorous pulse power tests, typically involving 10-second discharge pulses at different states of charge (SOC) to determine the maximum power output and internal resistance[2]. The company also employs electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to analyze cell behavior under different frequency responses, providing insights into the electrochemical processes occurring within the cell[3].
Strengths: Highly optimized for high-power applications, excellent pulse power capabilities, and advanced testing methodologies. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to standard lithium-ion cells, and may have lower energy density due to power optimization.
Hefei Guoxuan High-Tech Power Energy Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hefei Guoxuan has developed a comprehensive testing regime for their high-performance battery cells, including ORB-type cells. Their approach to characterizing rate performance and pulse power involves a multi-step process. First, they conduct capacity tests at various discharge rates (e.g., 0.5C, 1C, 2C, 5C) to establish the rate capability curve[1]. For pulse power characterization, they employ a modified version of the HPPC test, which includes both charge and discharge pulses at different SOC levels[2]. Guoxuan also utilizes advanced diagnostic tools such as in-situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to correlate cell performance with structural changes during high-rate cycling[3]. Additionally, they have implemented machine learning algorithms to predict long-term pulse power performance based on short-term test data, enhancing the efficiency of their characterization process[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive testing methodology, advanced diagnostic techniques, and innovative predictive modeling. Weaknesses: Potentially time-consuming and resource-intensive characterization process, which may impact production costs.
Core Innovations in Pulse Power Testing
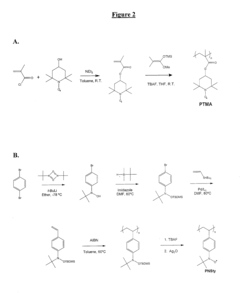
Hybrid radical energy storage device and method of making
PatentActiveUS20120295166A1
Innovation
- A hybrid solid-state electrochemical device is developed, featuring a pre-lithiated nanostructured anode, a stable polymeric organic radical-based cathode, and a high-performance solid-state polymer electrolyte, which enhances energy density and cycle stability, while minimizing flammability and temperature effects.
Hybrid radical energy storage device and method of making
PatentInactiveUS20140377648A1
Innovation
- A hybrid solid-state electrochemical device is developed, featuring a pre-lithiated nanostructured anode, a stable polymeric organic radical-based cathode, and a high-performance solid-state polymer electrolyte, which enhances energy density and cycle stability, while minimizing flammability and temperature effects.
Regulatory Standards for Battery Testing
Regulatory standards for battery testing play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of energy storage systems. These standards provide a framework for consistent evaluation and comparison of battery technologies across different manufacturers and applications. For ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cells, characterizing rate performance and pulse power requires adherence to established testing protocols.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards relevant to battery testing, including IEC 62660-1 for performance testing and IEC 62660-2 for reliability and abuse testing of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicle applications. While these standards were initially designed for lithium-ion batteries, they serve as a foundation for testing other battery chemistries, including ORB cells.
ANSI/CAN/UL 1973 is another important standard that covers batteries for use in stationary and mobile applications. This standard outlines safety requirements and test procedures for battery systems, including those used in grid energy storage and electric vehicles. It encompasses various aspects of battery performance, including capacity, efficiency, and cycle life.
For pulse power characterization, the U.S. Department of Energy's FreedomCAR Battery Test Manual provides detailed procedures for hybrid electric vehicle applications. Although not specifically designed for ORB cells, these procedures can be adapted to assess the pulse power capabilities of various battery chemistries.
The SAE J2464 standard, developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers, focuses on electric and hybrid vehicle battery systems. It includes test procedures for evaluating battery performance under various conditions, including pulse power tests that can be applicable to ORB cells with appropriate modifications.
In the European Union, the UN/ECE-R100 regulation sets safety requirements for rechargeable energy storage systems in electric vehicles. While primarily focused on safety, this regulation also influences performance testing methodologies to ensure batteries meet the necessary standards for automotive applications.
For grid energy storage applications, the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) has developed a protocol for uniformly measuring and expressing the performance of energy storage systems. This protocol, while not a regulatory standard, provides valuable guidance on testing procedures that can be applied to ORB cells in grid storage scenarios.
As ORB technology continues to evolve, it is likely that specific standards will be developed to address the unique characteristics of organic radical batteries. In the meantime, researchers and manufacturers must adapt existing standards and best practices to ensure thorough and consistent evaluation of ORB cell performance, including rate capability and pulse power characteristics.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards relevant to battery testing, including IEC 62660-1 for performance testing and IEC 62660-2 for reliability and abuse testing of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicle applications. While these standards were initially designed for lithium-ion batteries, they serve as a foundation for testing other battery chemistries, including ORB cells.
ANSI/CAN/UL 1973 is another important standard that covers batteries for use in stationary and mobile applications. This standard outlines safety requirements and test procedures for battery systems, including those used in grid energy storage and electric vehicles. It encompasses various aspects of battery performance, including capacity, efficiency, and cycle life.
For pulse power characterization, the U.S. Department of Energy's FreedomCAR Battery Test Manual provides detailed procedures for hybrid electric vehicle applications. Although not specifically designed for ORB cells, these procedures can be adapted to assess the pulse power capabilities of various battery chemistries.
The SAE J2464 standard, developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers, focuses on electric and hybrid vehicle battery systems. It includes test procedures for evaluating battery performance under various conditions, including pulse power tests that can be applicable to ORB cells with appropriate modifications.
In the European Union, the UN/ECE-R100 regulation sets safety requirements for rechargeable energy storage systems in electric vehicles. While primarily focused on safety, this regulation also influences performance testing methodologies to ensure batteries meet the necessary standards for automotive applications.
For grid energy storage applications, the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) has developed a protocol for uniformly measuring and expressing the performance of energy storage systems. This protocol, while not a regulatory standard, provides valuable guidance on testing procedures that can be applied to ORB cells in grid storage scenarios.
As ORB technology continues to evolve, it is likely that specific standards will be developed to address the unique characteristics of organic radical batteries. In the meantime, researchers and manufacturers must adapt existing standards and best practices to ensure thorough and consistent evaluation of ORB cell performance, including rate capability and pulse power characteristics.
Environmental Impact of ORB Cell Testing
The environmental impact of ORB (Organic Radical Battery) cell testing is a crucial aspect to consider in the development and implementation of these innovative energy storage devices. As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, it is essential to evaluate the ecological footprint of ORB cell testing procedures.
ORB cells, which utilize organic radical compounds as active materials, offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, the testing processes themselves may have environmental implications that need to be carefully assessed and mitigated.
One of the primary environmental concerns in ORB cell testing is the use and disposal of electrolytes. These electrolytes often contain organic solvents, which can be volatile and potentially harmful if released into the environment. Proper handling, containment, and disposal protocols must be established to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The energy consumption during testing procedures is another significant factor to consider. Rate performance and pulse power characterization often involve repeated charge-discharge cycles, which can be energy-intensive. Implementing energy-efficient testing equipment and optimizing test protocols can help reduce the overall energy footprint of ORB cell testing.
Material waste generation is an additional environmental consideration. The production of test cells, including electrode materials, separators, and packaging, may result in waste that requires proper disposal or recycling. Developing strategies to minimize waste and maximize the reuse of materials can contribute to a more sustainable testing process.
The potential for chemical emissions during testing should also be addressed. While ORB cells generally have lower toxicity compared to some conventional battery chemistries, the organic compounds used may still pose environmental risks if released. Adequate ventilation and filtration systems should be in place to capture and treat any emissions generated during testing.
Water usage and potential contamination are additional factors to evaluate. Cooling systems used in testing equipment may consume significant amounts of water, and there is a risk of water contamination from electrolyte spills or leaks. Implementing water-efficient cooling technologies and robust spill prevention measures can help mitigate these impacts.
Long-term environmental effects of ORB cell testing should also be considered. This includes the potential accumulation of organic radical compounds in the environment and their impact on ecosystems. Conducting thorough lifecycle assessments and environmental fate studies can provide valuable insights into the long-term ecological implications of ORB technology.
By comprehensively addressing these environmental aspects, researchers and industry professionals can work towards developing more sustainable testing protocols for ORB cells. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances the overall viability and acceptance of ORB technology in the renewable energy landscape.
ORB cells, which utilize organic radical compounds as active materials, offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, the testing processes themselves may have environmental implications that need to be carefully assessed and mitigated.
One of the primary environmental concerns in ORB cell testing is the use and disposal of electrolytes. These electrolytes often contain organic solvents, which can be volatile and potentially harmful if released into the environment. Proper handling, containment, and disposal protocols must be established to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The energy consumption during testing procedures is another significant factor to consider. Rate performance and pulse power characterization often involve repeated charge-discharge cycles, which can be energy-intensive. Implementing energy-efficient testing equipment and optimizing test protocols can help reduce the overall energy footprint of ORB cell testing.
Material waste generation is an additional environmental consideration. The production of test cells, including electrode materials, separators, and packaging, may result in waste that requires proper disposal or recycling. Developing strategies to minimize waste and maximize the reuse of materials can contribute to a more sustainable testing process.
The potential for chemical emissions during testing should also be addressed. While ORB cells generally have lower toxicity compared to some conventional battery chemistries, the organic compounds used may still pose environmental risks if released. Adequate ventilation and filtration systems should be in place to capture and treat any emissions generated during testing.
Water usage and potential contamination are additional factors to evaluate. Cooling systems used in testing equipment may consume significant amounts of water, and there is a risk of water contamination from electrolyte spills or leaks. Implementing water-efficient cooling technologies and robust spill prevention measures can help mitigate these impacts.
Long-term environmental effects of ORB cell testing should also be considered. This includes the potential accumulation of organic radical compounds in the environment and their impact on ecosystems. Conducting thorough lifecycle assessments and environmental fate studies can provide valuable insights into the long-term ecological implications of ORB technology.
By comprehensively addressing these environmental aspects, researchers and industry professionals can work towards developing more sustainable testing protocols for ORB cells. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances the overall viability and acceptance of ORB technology in the renewable energy landscape.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!