How to Evaluate Long-Term Self-discharge in Organic Radical Batteries
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ORB Self-discharge Background and Objectives
Organic Radical Batteries (ORBs) have emerged as a promising energy storage technology, offering high power density, rapid charge-discharge capabilities, and environmental friendliness. The development of ORBs can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first explored the potential of stable organic radicals as active materials in electrochemical cells. Since then, significant progress has been made in improving the performance and stability of these batteries.
The evolution of ORB technology has been driven by the need for sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources and electric mobility, the demand for high-performance batteries continues to grow. ORBs present a unique opportunity to address these needs, offering advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries in terms of resource availability, safety, and recyclability.
However, one of the critical challenges facing ORB technology is self-discharge, which refers to the gradual loss of stored energy over time when the battery is not in use. This phenomenon is particularly problematic for long-term energy storage applications and can significantly impact the overall efficiency and reliability of ORB systems. Understanding and mitigating self-discharge is crucial for the widespread adoption of ORBs in various sectors, including grid energy storage, electric vehicles, and portable electronics.
The primary objective of evaluating long-term self-discharge in ORBs is to develop accurate and reliable methods for assessing capacity loss over extended periods. This involves investigating the underlying mechanisms of self-discharge, identifying key factors that influence the rate of energy loss, and establishing standardized testing protocols. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of self-discharge behavior, researchers and engineers can work towards developing strategies to minimize this issue and improve the overall performance of ORBs.
Furthermore, the evaluation of long-term self-discharge aims to provide valuable insights for battery management systems, enabling more accurate state-of-charge estimation and predictive maintenance. This, in turn, can lead to optimized battery utilization, extended cycle life, and improved safety in various applications. As ORB technology continues to mature, addressing the challenge of self-discharge will play a crucial role in realizing its full potential as a sustainable and efficient energy storage solution for the future.
The evolution of ORB technology has been driven by the need for sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources and electric mobility, the demand for high-performance batteries continues to grow. ORBs present a unique opportunity to address these needs, offering advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries in terms of resource availability, safety, and recyclability.
However, one of the critical challenges facing ORB technology is self-discharge, which refers to the gradual loss of stored energy over time when the battery is not in use. This phenomenon is particularly problematic for long-term energy storage applications and can significantly impact the overall efficiency and reliability of ORB systems. Understanding and mitigating self-discharge is crucial for the widespread adoption of ORBs in various sectors, including grid energy storage, electric vehicles, and portable electronics.
The primary objective of evaluating long-term self-discharge in ORBs is to develop accurate and reliable methods for assessing capacity loss over extended periods. This involves investigating the underlying mechanisms of self-discharge, identifying key factors that influence the rate of energy loss, and establishing standardized testing protocols. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of self-discharge behavior, researchers and engineers can work towards developing strategies to minimize this issue and improve the overall performance of ORBs.
Furthermore, the evaluation of long-term self-discharge aims to provide valuable insights for battery management systems, enabling more accurate state-of-charge estimation and predictive maintenance. This, in turn, can lead to optimized battery utilization, extended cycle life, and improved safety in various applications. As ORB technology continues to mature, addressing the challenge of self-discharge will play a crucial role in realizing its full potential as a sustainable and efficient energy storage solution for the future.
Market Demand for Long-lasting ORBs
The market demand for long-lasting Organic Radical Batteries (ORBs) is driven by the increasing need for sustainable and high-performance energy storage solutions across various industries. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources and electrification, the demand for efficient and durable batteries continues to grow. ORBs, with their potential for long-term stability and high energy density, are positioned to address this market need.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a strong demand for batteries that can maintain their capacity over extended periods. Smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices require power sources that can withstand numerous charge cycles without significant degradation. ORBs, with their potential for reduced self-discharge rates, could significantly extend the lifespan of these devices, meeting consumer expectations for longer-lasting products.
The automotive industry, particularly the electric vehicle (EV) segment, represents a substantial market opportunity for long-lasting ORBs. As EVs become more mainstream, there is a growing demand for batteries that can maintain their performance over the vehicle's lifetime. ORBs' potential for improved cycle life and reduced capacity fade could address concerns about battery longevity in EVs, potentially reducing replacement costs and enhancing overall vehicle value.
In the renewable energy sector, grid-scale energy storage systems require batteries with extended lifespans to balance supply and demand effectively. ORBs' potential for long-term stability makes them attractive for large-scale energy storage applications, where frequent battery replacements would be cost-prohibitive and logistically challenging.
The industrial and medical sectors also present significant market opportunities for long-lasting ORBs. In industrial settings, batteries that can operate reliably for extended periods without maintenance are highly valued. Similarly, in medical devices, particularly implantable ones, long-lasting batteries are crucial to minimize the need for invasive replacement procedures.
The market demand for ORBs is further bolstered by the global push for sustainability and environmental responsibility. As organizations and governments worldwide set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions, there is a growing interest in battery technologies that offer improved environmental profiles. ORBs, with their potential for using organic materials and reduced reliance on rare earth elements, align well with these sustainability goals.
However, the market adoption of long-lasting ORBs faces challenges. The technology must demonstrate its ability to outperform existing battery solutions in terms of longevity, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance. Additionally, the market demand will be influenced by the ability of ORB manufacturers to scale production and establish reliable supply chains.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a strong demand for batteries that can maintain their capacity over extended periods. Smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices require power sources that can withstand numerous charge cycles without significant degradation. ORBs, with their potential for reduced self-discharge rates, could significantly extend the lifespan of these devices, meeting consumer expectations for longer-lasting products.
The automotive industry, particularly the electric vehicle (EV) segment, represents a substantial market opportunity for long-lasting ORBs. As EVs become more mainstream, there is a growing demand for batteries that can maintain their performance over the vehicle's lifetime. ORBs' potential for improved cycle life and reduced capacity fade could address concerns about battery longevity in EVs, potentially reducing replacement costs and enhancing overall vehicle value.
In the renewable energy sector, grid-scale energy storage systems require batteries with extended lifespans to balance supply and demand effectively. ORBs' potential for long-term stability makes them attractive for large-scale energy storage applications, where frequent battery replacements would be cost-prohibitive and logistically challenging.
The industrial and medical sectors also present significant market opportunities for long-lasting ORBs. In industrial settings, batteries that can operate reliably for extended periods without maintenance are highly valued. Similarly, in medical devices, particularly implantable ones, long-lasting batteries are crucial to minimize the need for invasive replacement procedures.
The market demand for ORBs is further bolstered by the global push for sustainability and environmental responsibility. As organizations and governments worldwide set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions, there is a growing interest in battery technologies that offer improved environmental profiles. ORBs, with their potential for using organic materials and reduced reliance on rare earth elements, align well with these sustainability goals.
However, the market adoption of long-lasting ORBs faces challenges. The technology must demonstrate its ability to outperform existing battery solutions in terms of longevity, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance. Additionally, the market demand will be influenced by the ability of ORB manufacturers to scale production and establish reliable supply chains.
Current Challenges in ORB Self-discharge Evaluation
Evaluating long-term self-discharge in Organic Radical Batteries (ORBs) presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must overcome. One of the primary difficulties lies in the inherent instability of organic radical compounds, which are prone to degradation over time. This instability can lead to accelerated self-discharge rates, making it challenging to accurately predict and measure the long-term performance of ORBs.
Another major challenge is the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for ORBs. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which have well-established testing procedures, ORBs require unique approaches to assess their self-discharge characteristics accurately. The absence of standardized methods makes it difficult to compare results across different studies and hinders the development of reliable evaluation techniques.
The complex interplay between various factors affecting self-discharge in ORBs further complicates the evaluation process. Temperature, state of charge, electrolyte composition, and electrode materials all play crucial roles in determining the self-discharge rate. Isolating and quantifying the impact of each factor requires sophisticated experimental setups and advanced analytical techniques, which may not be readily available or easily implemented.
Time-dependent phenomena pose another significant challenge in evaluating long-term self-discharge. ORBs may exhibit different self-discharge behaviors over various time scales, from hours to months or even years. Conducting experiments over extended periods is resource-intensive and may not be practical for rapid technology development cycles. Consequently, researchers must develop accelerated testing methods that can accurately predict long-term performance without compromising the validity of results.
The sensitivity of ORBs to environmental conditions adds another layer of complexity to the evaluation process. Factors such as humidity, atmospheric oxygen, and light exposure can significantly impact the self-discharge rate. Controlling these variables in laboratory settings and extrapolating the results to real-world applications requires careful consideration and advanced experimental design.
Furthermore, the diversity of organic radical compounds used in ORBs presents a challenge in developing universal evaluation methods. Different radical species may exhibit varying self-discharge mechanisms and rates, necessitating tailored approaches for each type of ORB. This diversity hampers the development of generalized evaluation techniques and requires researchers to adapt their methods for specific battery chemistries.
Lastly, the limited availability of long-term performance data for ORBs makes it difficult to validate and refine evaluation methods. As a relatively new technology, ORBs lack the extensive historical data available for traditional battery systems. This scarcity of information hinders the development of accurate predictive models and benchmarks for long-term self-discharge evaluation.
Another major challenge is the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for ORBs. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which have well-established testing procedures, ORBs require unique approaches to assess their self-discharge characteristics accurately. The absence of standardized methods makes it difficult to compare results across different studies and hinders the development of reliable evaluation techniques.
The complex interplay between various factors affecting self-discharge in ORBs further complicates the evaluation process. Temperature, state of charge, electrolyte composition, and electrode materials all play crucial roles in determining the self-discharge rate. Isolating and quantifying the impact of each factor requires sophisticated experimental setups and advanced analytical techniques, which may not be readily available or easily implemented.
Time-dependent phenomena pose another significant challenge in evaluating long-term self-discharge. ORBs may exhibit different self-discharge behaviors over various time scales, from hours to months or even years. Conducting experiments over extended periods is resource-intensive and may not be practical for rapid technology development cycles. Consequently, researchers must develop accelerated testing methods that can accurately predict long-term performance without compromising the validity of results.
The sensitivity of ORBs to environmental conditions adds another layer of complexity to the evaluation process. Factors such as humidity, atmospheric oxygen, and light exposure can significantly impact the self-discharge rate. Controlling these variables in laboratory settings and extrapolating the results to real-world applications requires careful consideration and advanced experimental design.
Furthermore, the diversity of organic radical compounds used in ORBs presents a challenge in developing universal evaluation methods. Different radical species may exhibit varying self-discharge mechanisms and rates, necessitating tailored approaches for each type of ORB. This diversity hampers the development of generalized evaluation techniques and requires researchers to adapt their methods for specific battery chemistries.
Lastly, the limited availability of long-term performance data for ORBs makes it difficult to validate and refine evaluation methods. As a relatively new technology, ORBs lack the extensive historical data available for traditional battery systems. This scarcity of information hinders the development of accurate predictive models and benchmarks for long-term self-discharge evaluation.
Existing Self-discharge Evaluation Techniques
01 Electrolyte composition to reduce self-discharge
Specific electrolyte compositions can be used to reduce self-discharge in organic radical batteries. These compositions may include additives or modified solvents that stabilize the radical species, preventing unwanted reactions that lead to capacity loss over time. The improved electrolyte formulations can significantly extend the shelf life and usability of organic radical batteries.- Electrolyte composition to reduce self-discharge: Modifying the electrolyte composition in organic radical batteries can help reduce self-discharge rates. This may involve using specific solvents, additives, or electrolyte salts that minimize side reactions and improve the stability of the organic radical species.
- Electrode material modifications: Improving the stability of electrode materials in organic radical batteries can reduce self-discharge. This may include surface modifications, doping, or using composite materials to enhance the retention of the organic radical species and prevent unwanted reactions.
- Separator design and materials: Developing advanced separator materials and designs can help mitigate self-discharge in organic radical batteries. This may involve using ion-selective membranes or composite separators that prevent the migration of reactive species between electrodes.
- Battery management systems: Implementing sophisticated battery management systems can help control and reduce self-discharge in organic radical batteries. This may include advanced monitoring, charge control algorithms, and temperature management to optimize battery performance and longevity.
- Novel organic radical structures: Developing new organic radical structures with improved stability and redox properties can inherently reduce self-discharge rates. This may involve designing molecules with specific functional groups or utilizing supramolecular assemblies to enhance the overall performance of the battery.
02 Electrode material modifications
Modifications to the electrode materials can help mitigate self-discharge in organic radical batteries. This may involve surface treatments, doping, or the use of composite materials that enhance the stability of the radical species. These modifications can improve the overall performance and longevity of the battery by reducing unwanted side reactions and maintaining the active radical state.Expand Specific Solutions03 Encapsulation techniques
Encapsulation of the organic radical materials within protective structures can significantly reduce self-discharge. This may involve using polymer coatings, nanostructures, or other encapsulating materials that isolate the active species from potential side reactions. These techniques can effectively improve the stability and cycle life of organic radical batteries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Temperature control and management
Implementing effective temperature control and management systems can help reduce self-discharge in organic radical batteries. This may include the use of thermal management materials, heat dissipation structures, or intelligent temperature regulation systems. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures can significantly enhance the stability of the radical species and reduce unwanted side reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Charge state optimization
Optimizing the charge state and developing advanced charging protocols can minimize self-discharge in organic radical batteries. This may involve implementing specific charging algorithms, partial state of charge operation, or periodic refreshing cycles. These strategies can help maintain the stability of the radical species and extend the overall battery life by reducing the rate of capacity loss during storage or idle periods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ORB Development and Testing
The evaluation of long-term self-discharge in organic radical batteries represents an emerging field within the broader context of energy storage technology. This sector is currently in its early development stage, with significant potential for growth as the demand for sustainable energy solutions increases. The market size for organic radical batteries is still relatively small compared to conventional lithium-ion technologies, but it is expected to expand as research progresses. Companies like Toyota Motor Corp., Volkswagen AG, and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. are investing in this area, leveraging their expertise in battery technology. The technical maturity of organic radical batteries is still evolving, with ongoing research focused on improving stability, capacity, and self-discharge characteristics.
Commissariat à l´énergie atomique et aux énergies Alternatives
Technical Solution: CEA's approach to evaluating long-term self-discharge in ORBs combines advanced electrochemical techniques with computational modeling. They utilize electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to monitor changes in internal resistance and charge transfer kinetics over time. CEA has developed a novel in-situ nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy method to track the evolution of radical species and electrolyte decomposition products[10]. Their evaluation process includes the use of isothermal microcalorimetry to measure heat generation associated with self-discharge reactions. Additionally, CEA employs physics-based models to simulate long-term degradation processes, which are continuously refined using experimental data[11].
Strengths: Advanced in-situ characterization techniques, integration of experimental and computational methods. Weaknesses: High equipment costs, complexity in data interpretation and model validation.
Battelle Energy Alliance LLC
Technical Solution: Battelle's approach to evaluating long-term self-discharge in ORBs focuses on a combination of electrochemical and materials characterization techniques. They employ long-term float charge tests with periodic capacity checks to quantify self-discharge rates. Battelle has developed a custom-built test platform that allows for simultaneous evaluation of multiple cells under various environmental conditions[8]. Their methodology includes post-mortem analysis using techniques such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy to identify chemical changes associated with self-discharge. Additionally, they utilize electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) measurements to detect minute changes in electrode mass related to side reactions[9].
Strengths: Comprehensive materials characterization, ability to test under various environmental conditions. Weaknesses: Destructive post-mortem analysis, potential scalability issues for large-scale evaluations.
Innovations in Long-term ORB Stability Assessment
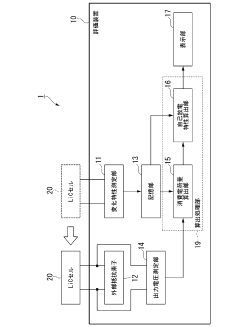
Secondary battery evaluation method, secondary battery manufacturing method, and secondary battery evaluation device
PatentPendingJP2023137582A
Innovation
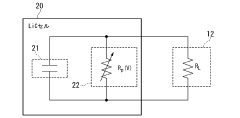
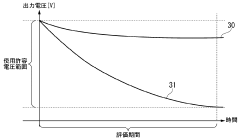
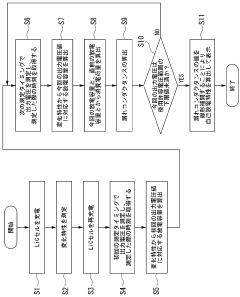
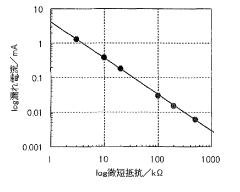
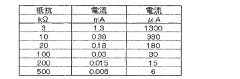
- A method involving connecting an external load with a known resistance to the LiC cell, measuring output voltage at regular intervals, calculating discharge capacity, and using a device to determine self-discharge characteristics based on these measurements, thereby shortening the evaluation time.
Inspection method for battery
PatentInactiveJP2014222603A
Innovation
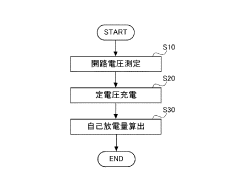
- A battery inspection method based on open circuit voltage measurement, followed by constant voltage charging to maintain the measured open circuit voltage, and calculating self-discharge from the current required during this charging process.
Environmental Impact of ORB Technologies
The environmental impact of Organic Radical Battery (ORB) technologies is a crucial aspect to consider in their development and implementation. These batteries offer several potential environmental benefits compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Firstly, ORBs utilize organic materials as their active components, which are generally more abundant and environmentally friendly than the metal-based materials used in conventional batteries. This reduces the reliance on rare earth metals and minimizes the environmental damage associated with mining and processing these resources.
ORBs also have the potential for improved recyclability and biodegradability. The organic nature of their components makes them more compatible with existing recycling processes and potentially easier to break down at the end of their life cycle. This could significantly reduce the environmental burden of battery disposal and contribute to a more circular economy in the energy storage sector.
Furthermore, the production of ORBs typically requires less energy and generates fewer emissions compared to the manufacturing of traditional batteries. This lower carbon footprint in the production phase contributes to the overall environmental sustainability of the technology. The use of organic materials also reduces the risk of toxic metal leaching into the environment in case of improper disposal or accidents.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of ORBs is not entirely benign. The production and disposal of organic materials used in these batteries still have some environmental consequences. For instance, the synthesis of organic radical compounds may involve the use of solvents or other chemicals that could have negative environmental effects if not properly managed.
Additionally, the long-term stability and performance of ORBs in real-world applications are still being studied. If these batteries require more frequent replacement due to faster degradation or self-discharge compared to traditional batteries, it could offset some of their environmental benefits. Therefore, ongoing research into improving the longevity and stability of ORBs is crucial for maximizing their positive environmental impact.
The scalability of ORB production is another factor that could influence their environmental impact. As the technology moves towards large-scale manufacturing, it will be essential to ensure that the production processes remain environmentally friendly and resource-efficient. This includes optimizing material sourcing, minimizing waste generation, and implementing sustainable manufacturing practices.
In conclusion, while ORB technologies show promising environmental advantages, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is necessary to fully understand their environmental impact compared to existing battery technologies. This assessment should consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, energy efficiency during use, and end-of-life management. As research and development in this field progress, it will be crucial to continually evaluate and improve the environmental performance of ORBs to ensure they contribute positively to sustainable energy storage solutions.
ORBs also have the potential for improved recyclability and biodegradability. The organic nature of their components makes them more compatible with existing recycling processes and potentially easier to break down at the end of their life cycle. This could significantly reduce the environmental burden of battery disposal and contribute to a more circular economy in the energy storage sector.
Furthermore, the production of ORBs typically requires less energy and generates fewer emissions compared to the manufacturing of traditional batteries. This lower carbon footprint in the production phase contributes to the overall environmental sustainability of the technology. The use of organic materials also reduces the risk of toxic metal leaching into the environment in case of improper disposal or accidents.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of ORBs is not entirely benign. The production and disposal of organic materials used in these batteries still have some environmental consequences. For instance, the synthesis of organic radical compounds may involve the use of solvents or other chemicals that could have negative environmental effects if not properly managed.
Additionally, the long-term stability and performance of ORBs in real-world applications are still being studied. If these batteries require more frequent replacement due to faster degradation or self-discharge compared to traditional batteries, it could offset some of their environmental benefits. Therefore, ongoing research into improving the longevity and stability of ORBs is crucial for maximizing their positive environmental impact.
The scalability of ORB production is another factor that could influence their environmental impact. As the technology moves towards large-scale manufacturing, it will be essential to ensure that the production processes remain environmentally friendly and resource-efficient. This includes optimizing material sourcing, minimizing waste generation, and implementing sustainable manufacturing practices.
In conclusion, while ORB technologies show promising environmental advantages, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is necessary to fully understand their environmental impact compared to existing battery technologies. This assessment should consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, energy efficiency during use, and end-of-life management. As research and development in this field progress, it will be crucial to continually evaluate and improve the environmental performance of ORBs to ensure they contribute positively to sustainable energy storage solutions.
Standardization of ORB Performance Metrics
The standardization of performance metrics for Organic Radical Batteries (ORBs) is crucial for accurately evaluating their long-term self-discharge characteristics. This process involves establishing consistent methods and parameters to measure and compare the performance of different ORB systems across various research groups and manufacturers.
One key aspect of standardization is the development of uniform testing protocols for self-discharge evaluation. These protocols should specify the precise conditions under which measurements are taken, including temperature, humidity, and storage duration. By adhering to these standardized conditions, researchers can ensure that their results are comparable and reproducible.
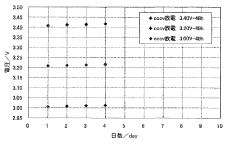
Another important element is the definition of specific performance indicators for self-discharge. These may include metrics such as capacity retention rate over time, voltage decay rate, and coulombic efficiency. Standardizing these indicators allows for a more objective comparison of different ORB technologies and helps identify the most promising approaches for minimizing self-discharge.
The establishment of reference materials and calibration standards is also essential for accurate performance evaluation. These standards can serve as benchmarks against which new ORB systems can be measured, ensuring consistency across different laboratories and research institutions.
Standardization efforts should also address the reporting of results. This includes specifying the format and units in which data should be presented, as well as the statistical methods used for data analysis. Clear guidelines on how to report uncertainty and variability in measurements will enhance the reliability and comparability of published results.
Collaboration between academic institutions, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is crucial for developing and implementing these standardized metrics. International organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) can play a vital role in coordinating these efforts and ensuring global acceptance of the established standards.
Regular review and updating of these standardized metrics are necessary to keep pace with advancements in ORB technology. As new materials and designs emerge, the performance metrics may need to be adjusted or expanded to accurately capture the characteristics of these innovative systems.
By implementing standardized performance metrics, the ORB research community can accelerate progress in addressing long-term self-discharge issues. This standardization will facilitate more effective communication of research findings, enable fair comparisons between different ORB technologies, and ultimately contribute to the development of more reliable and efficient organic radical battery systems.
One key aspect of standardization is the development of uniform testing protocols for self-discharge evaluation. These protocols should specify the precise conditions under which measurements are taken, including temperature, humidity, and storage duration. By adhering to these standardized conditions, researchers can ensure that their results are comparable and reproducible.
Another important element is the definition of specific performance indicators for self-discharge. These may include metrics such as capacity retention rate over time, voltage decay rate, and coulombic efficiency. Standardizing these indicators allows for a more objective comparison of different ORB technologies and helps identify the most promising approaches for minimizing self-discharge.
The establishment of reference materials and calibration standards is also essential for accurate performance evaluation. These standards can serve as benchmarks against which new ORB systems can be measured, ensuring consistency across different laboratories and research institutions.
Standardization efforts should also address the reporting of results. This includes specifying the format and units in which data should be presented, as well as the statistical methods used for data analysis. Clear guidelines on how to report uncertainty and variability in measurements will enhance the reliability and comparability of published results.
Collaboration between academic institutions, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is crucial for developing and implementing these standardized metrics. International organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) can play a vital role in coordinating these efforts and ensuring global acceptance of the established standards.
Regular review and updating of these standardized metrics are necessary to keep pace with advancements in ORB technology. As new materials and designs emerge, the performance metrics may need to be adjusted or expanded to accurately capture the characteristics of these innovative systems.
By implementing standardized performance metrics, the ORB research community can accelerate progress in addressing long-term self-discharge issues. This standardization will facilitate more effective communication of research findings, enable fair comparisons between different ORB technologies, and ultimately contribute to the development of more reliable and efficient organic radical battery systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!