Cellulose Acetate's Innovative Use in Futuristic Material Design
Cellulose Acetate Evolution and Objectives
Cellulose acetate, a versatile biopolymer, has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the late 19th century. Initially developed as a substitute for celluloid in photographic films, its applications have expanded dramatically over the decades. The journey of cellulose acetate from a simple plastic material to a key component in futuristic material design is marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to changing technological needs.
The early 20th century saw cellulose acetate primarily used in textiles and films. However, as manufacturing processes improved, its potential in various industries became apparent. The mid-20th century witnessed a surge in its use for consumer goods, particularly in the production of eyeglass frames and other molded plastic products. This period also marked the beginning of research into its potential for advanced applications.
In recent years, the focus on sustainable and biodegradable materials has reignited interest in cellulose acetate. Its natural origin and potential for modification have positioned it as a promising candidate for eco-friendly material solutions. The current technological landscape is driving research towards enhancing the properties of cellulose acetate, exploring its nanostructure, and developing novel composites.
The primary objective in the innovative use of cellulose acetate in futuristic material design is to leverage its unique properties while addressing its limitations. Researchers aim to improve its mechanical strength, thermal stability, and barrier properties. There is a particular emphasis on developing cellulose acetate-based materials with advanced functionalities such as self-healing capabilities, smart responsiveness to environmental stimuli, and enhanced biodegradability.
Another key goal is to explore the integration of cellulose acetate with other advanced materials and technologies. This includes its potential use in 3D printing, nanocomposites, and smart textiles. The development of cellulose acetate-based materials for biomedical applications, such as drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds, is also a significant area of focus.
The evolution of cellulose acetate and the objectives for its future development are closely aligned with broader trends in material science. These include the push for sustainability, the demand for multifunctional materials, and the need for materials compatible with emerging manufacturing technologies. As research progresses, cellulose acetate is poised to play a crucial role in the development of next-generation materials that combine performance with environmental responsibility.
Market Demand Analysis for Sustainable Materials
The market demand for sustainable materials has been experiencing a significant surge in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations. Cellulose acetate, a biodegradable and renewable material derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers, is positioned to capitalize on this growing trend in futuristic material design.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards eco-friendly products, with a particular emphasis on reducing plastic waste. This shift has created a substantial market opportunity for cellulose acetate, especially in industries such as packaging, textiles, and consumer goods. The global cellulose acetate market is expected to grow steadily, propelled by its versatile applications and sustainable characteristics.
In the packaging sector, cellulose acetate films are gaining traction as an alternative to traditional plastic packaging. Food and beverage companies are increasingly adopting these materials to meet consumer demands for environmentally responsible packaging solutions. The textile industry is also embracing cellulose acetate fibers for their biodegradability and comfort properties, particularly in the production of sustainable fashion items.
The automotive industry presents another promising market for cellulose acetate. As automakers strive to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, cellulose acetate composites are being explored for interior components and structural elements. This application aligns with the industry's push towards more sustainable and recyclable materials in vehicle manufacturing.
Electronics manufacturers are also showing interest in cellulose acetate for its potential in creating biodegradable casings and components. This trend is driven by the growing concern over electronic waste and the need for more environmentally friendly product lifecycles.
The construction industry is another sector where cellulose acetate is finding innovative applications. Its use in insulation materials and as a component in sustainable building products is gaining attention, driven by the increasing focus on green building practices and energy efficiency.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain in scaling up production and reducing costs to compete with traditional materials. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the properties of cellulose acetate and optimizing production processes, which are expected to address these challenges and further expand market opportunities.
As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and sustainability targets, the demand for cellulose acetate is projected to increase across various industries. This regulatory push, combined with growing consumer awareness and corporate sustainability initiatives, is likely to drive significant market growth for cellulose acetate in futuristic material design applications.
Current Challenges in Cellulose Acetate Applications
Despite the numerous advantages of cellulose acetate in material design, several challenges persist in its applications, hindering its full potential in futuristic material development. One of the primary obstacles is the material's inherent moisture sensitivity. Cellulose acetate tends to absorb water from the environment, leading to dimensional instability and potential degradation of mechanical properties over time. This hygroscopic nature limits its use in applications requiring long-term stability or exposure to humid conditions.
Another significant challenge lies in the biodegradability of cellulose acetate. While its biodegradable nature is often touted as an environmental benefit, it can be a double-edged sword in certain applications. The rate of biodegradation can be unpredictable and varies greatly depending on environmental conditions, making it difficult to control the lifespan of cellulose acetate-based products. This uncertainty poses challenges in designing materials for specific durability requirements.
The processing of cellulose acetate also presents technical hurdles. The material's thermal sensitivity limits the range of processing temperatures, potentially restricting the manufacturing techniques that can be employed. This constraint can impact the ability to create complex shapes or integrate cellulose acetate with other materials in advanced composite structures.
Furthermore, the mechanical properties of cellulose acetate, while suitable for many applications, fall short in comparison to some synthetic polymers. Its relatively low tensile strength and impact resistance limit its use in high-performance applications where durability and strength are paramount. Enhancing these properties without compromising other beneficial characteristics remains a significant challenge for material scientists.
The cost-effectiveness of cellulose acetate production is another area of concern. While the raw material (cellulose) is abundant and renewable, the acetylation process can be energy-intensive and requires the use of acetic acid and other chemicals. Developing more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods is crucial for expanding the material's use in large-scale applications.
Lastly, there are challenges related to the end-of-life management of cellulose acetate products. While the material is biodegradable, the additives and plasticizers used in its formulation may not be. This complicates recycling efforts and can lead to incomplete degradation, potentially contributing to microplastic pollution. Addressing these end-of-life issues is essential for positioning cellulose acetate as a truly sustainable material option in futuristic designs.
Existing Cellulose Acetate Material Solutions
01 Cellulose acetate production methods
Various methods for producing cellulose acetate are described, including improvements in acetylation processes, solvent systems, and reaction conditions. These methods aim to enhance the efficiency and quality of cellulose acetate production for different applications.- Cellulose acetate production methods: Various methods for producing cellulose acetate are described, including improvements in acetylation processes, solvent systems, and reaction conditions. These methods aim to enhance the efficiency and quality of cellulose acetate production, potentially leading to better material properties for diverse applications.
- Cellulose acetate fiber applications: Cellulose acetate fibers find applications in textiles, filters, and other products. Innovations focus on improving fiber properties such as strength, durability, and processability. New techniques for fiber formation and treatment are explored to expand the range of potential uses.
- Cellulose acetate film and membrane technology: Advancements in cellulose acetate film and membrane technology are reported, including improvements in film casting, membrane formation, and surface modification. These developments aim to enhance the performance of cellulose acetate in applications such as separation processes, packaging, and optical films.
- Cellulose acetate composites and blends: Research into cellulose acetate composites and blends with other materials is ongoing. These efforts aim to create new materials with enhanced properties, such as improved mechanical strength, thermal stability, or biodegradability. Various additives and processing techniques are explored to achieve desired material characteristics.
- Cellulose acetate modification and derivatives: Chemical modifications of cellulose acetate and the development of new derivatives are investigated. These modifications aim to impart new functionalities, improve compatibility with other materials, or enhance specific properties for targeted applications. Novel synthesis routes and characterization methods are also explored.
02 Cellulose acetate fiber applications
Cellulose acetate fibers are utilized in diverse applications, including textiles, filters, and composite materials. The properties of these fibers can be tailored for specific uses through modifications in the production process or post-treatment methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cellulose acetate film and membrane technology
Advancements in cellulose acetate film and membrane technology are presented, focusing on improved formulations and manufacturing techniques. These developments enhance the performance of cellulose acetate in applications such as separation processes and packaging materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cellulose acetate biodegradability and environmental impact
Research on improving the biodegradability of cellulose acetate and reducing its environmental impact is discussed. This includes modifications to the material structure, additives to enhance degradation, and sustainable production methods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cellulose acetate blends and composites
The development of cellulose acetate blends and composites with other materials is explored. These combinations aim to enhance specific properties such as strength, flexibility, or functionality for various industrial and consumer applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellulose Acetate Industry
The innovative use of cellulose acetate in futuristic material design is gaining momentum in a rapidly evolving market. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for sustainable and versatile materials. Market size is expanding as companies like Daicel Corp., Eastman Chemical Co., and Cerdia International GmbH lead technological advancements. The technology's maturity varies, with established players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Toray Industries, Inc. driving innovation alongside emerging contributors such as Guilin University of Technology and the Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This diverse landscape suggests a dynamic field with significant potential for breakthroughs in material science and applications across multiple sectors.
Daicel Corp.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Innovative Cellulose Acetate Modifications
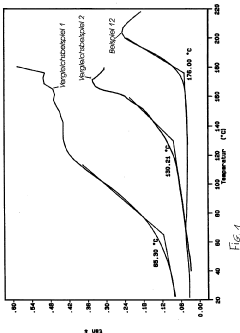
- Development of a molded composite material using cellulose acetate as a binder with natural cellulose fibers, achieving a degree of substitution (DS) of 1.2 to 2.7 and a mass ratio of 10:90 to 90:10, allowing for biodegradability and high Vicat temperatures without the need for external plasticizers, utilizing processing conditions such as moisture content, temperature, and pressure to enhance mechanical and thermal properties.
- A composite material using cellulose acetate as a binder with a degree of substitution between 1.2 and 2.7, combined with natural cellulose fibers, processed without external plasticizers, achieving a Vicat temperature of at least 160°C and improved mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of cellulose acetate's innovative use in futuristic material design reveals both promising benefits and potential concerns. Cellulose acetate, derived from natural cellulose sources, offers a more sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. Its biodegradability and renewable sourcing contribute to reduced carbon footprint and waste accumulation, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and plastic pollution.
In the production phase, cellulose acetate manufacturing generally requires less energy compared to traditional synthetic polymers. This energy efficiency translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions throughout the material's lifecycle. Additionally, the use of cellulose acetate in various applications can lead to lighter-weight products, potentially reducing transportation-related emissions in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
However, the environmental impact of cellulose acetate is not without challenges. The acetylation process, which converts cellulose into cellulose acetate, involves the use of acetic anhydride and other chemicals. Proper management and treatment of these chemicals are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Furthermore, while cellulose acetate is biodegradable, the rate of degradation can vary significantly depending on environmental conditions, potentially leading to temporary accumulation in ecosystems.
Water usage in cellulose acetate production is another consideration. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of water, which may strain local water resources in areas of production. Implementing water recycling and efficient purification systems is essential to mitigate this impact.
The end-of-life management of cellulose acetate products presents both opportunities and challenges. While the material's biodegradability offers advantages over conventional plastics, improper disposal can still lead to environmental issues. Developing and implementing effective recycling and composting infrastructure is crucial to fully realize the environmental benefits of cellulose acetate.
In terms of land use, the sourcing of cellulose for acetate production raises questions about sustainable forestry practices and potential competition with food crops. Responsible sourcing and certification programs are vital to ensure that the increased demand for cellulose does not lead to deforestation or disrupt food security.
Overall, the environmental impact of cellulose acetate in futuristic material design is largely positive when compared to traditional synthetic materials. However, ongoing research and development are necessary to optimize production processes, enhance biodegradability, and establish robust recycling systems. By addressing these challenges, cellulose acetate can play a significant role in creating more sustainable and environmentally friendly materials for the future.
Cellulose Acetate Manufacturing Processes
Cellulose acetate manufacturing processes have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating innovative techniques to enhance efficiency and product quality. The primary method involves the acetylation of cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters. This process begins with the activation of cellulose fibers using acetic acid, followed by the addition of acetic anhydride and a catalyst, usually sulfuric acid.
The reaction mixture is carefully controlled to achieve the desired degree of substitution, which determines the properties of the final product. After acetylation, the cellulose acetate is precipitated, washed, and neutralized to remove excess acids and impurities. The resulting material is then dried and processed into various forms, such as flakes, pellets, or fibers, depending on the intended application.
Advanced manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the sustainability and efficiency of cellulose acetate production. One such innovation is the use of ionic liquids as solvents, which allows for a more environmentally friendly process with reduced chemical consumption and waste generation. Additionally, microwave-assisted acetylation has shown promise in reducing reaction times and energy consumption.
Continuous flow reactors have also been implemented in some manufacturing facilities, enabling better control over reaction conditions and improving product consistency. These reactors allow for precise temperature and pressure regulation, resulting in higher-quality cellulose acetate with more uniform properties.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing bio-based alternatives to traditional acetylation agents. Research into the use of vinegar and other naturally derived acetic acid sources has shown potential for creating more sustainable cellulose acetate products. Furthermore, efforts to optimize the recovery and recycling of solvents and reagents have led to more closed-loop manufacturing processes, reducing environmental impact and production costs.
The integration of advanced analytics and process control systems has revolutionized cellulose acetate manufacturing. Real-time monitoring of reaction parameters, coupled with machine learning algorithms, allows for predictive maintenance and quality control, minimizing downtime and product variability. These technological advancements have not only improved the efficiency of cellulose acetate production but also opened up new possibilities for tailoring material properties to meet specific application requirements in futuristic material design.