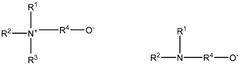Lithium Mine Reagent Alternatives vs Extraction Selectivity: Efficiency Comparison
OCT 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Extraction Background and Objectives
Lithium has emerged as a critical element in the global transition towards renewable energy and electrification, primarily due to its essential role in lithium-ion batteries. The historical development of lithium extraction techniques dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1990s when lithium-ion batteries began commercial production. Traditional extraction methods have predominantly relied on evaporative processes in salt flats or hard rock mining, both presenting considerable environmental and efficiency challenges.
The technological evolution in lithium extraction has accelerated dramatically in the past decade, driven by exponential growth in demand from electric vehicle manufacturers and energy storage systems. This surge has exposed limitations in conventional extraction methodologies, particularly regarding water consumption, land use, and extraction efficiency. The industry is now at a critical juncture where innovation in extraction reagents and processes is essential to meet projected demand growth of 40% annually through 2030.
Current extraction technologies demonstrate varying degrees of selectivity efficiency, with traditional methods achieving only 30-50% recovery rates. The primary technical objective in this field is to develop reagents that can selectively extract lithium from complex brines and mineral sources with minimal co-extraction of contaminants such as magnesium, calcium, and sodium. This selectivity challenge represents the fundamental bottleneck in scaling lithium production to meet global demand projections.
Alternative reagents under investigation include novel sorbents, ion-exchange materials, solvent extraction systems, and membrane technologies. Each approach offers distinct advantages in terms of selectivity, efficiency, environmental impact, and economic viability. The comparative analysis of these reagents against traditional methods reveals significant potential for breakthrough technologies that could revolutionize the lithium supply chain.
The strategic importance of lithium extraction innovation extends beyond mere production capacity. As geopolitical considerations increasingly influence critical mineral supply chains, developing diverse and efficient extraction technologies becomes a matter of national security for many countries. This has accelerated research funding and commercial interest in alternative reagent development.
Our technical objectives in this analysis include: quantifying the selectivity efficiency of various reagent classes across different lithium sources; evaluating environmental footprints of alternative extraction processes; assessing scalability challenges for promising technologies; and identifying potential disruptive innovations that could fundamentally alter the economics of lithium production within the next five years.
The technological evolution in lithium extraction has accelerated dramatically in the past decade, driven by exponential growth in demand from electric vehicle manufacturers and energy storage systems. This surge has exposed limitations in conventional extraction methodologies, particularly regarding water consumption, land use, and extraction efficiency. The industry is now at a critical juncture where innovation in extraction reagents and processes is essential to meet projected demand growth of 40% annually through 2030.
Current extraction technologies demonstrate varying degrees of selectivity efficiency, with traditional methods achieving only 30-50% recovery rates. The primary technical objective in this field is to develop reagents that can selectively extract lithium from complex brines and mineral sources with minimal co-extraction of contaminants such as magnesium, calcium, and sodium. This selectivity challenge represents the fundamental bottleneck in scaling lithium production to meet global demand projections.
Alternative reagents under investigation include novel sorbents, ion-exchange materials, solvent extraction systems, and membrane technologies. Each approach offers distinct advantages in terms of selectivity, efficiency, environmental impact, and economic viability. The comparative analysis of these reagents against traditional methods reveals significant potential for breakthrough technologies that could revolutionize the lithium supply chain.
The strategic importance of lithium extraction innovation extends beyond mere production capacity. As geopolitical considerations increasingly influence critical mineral supply chains, developing diverse and efficient extraction technologies becomes a matter of national security for many countries. This has accelerated research funding and commercial interest in alternative reagent development.
Our technical objectives in this analysis include: quantifying the selectivity efficiency of various reagent classes across different lithium sources; evaluating environmental footprints of alternative extraction processes; assessing scalability challenges for promising technologies; and identifying potential disruptive innovations that could fundamentally alter the economics of lithium production within the next five years.
Market Analysis for Lithium Extraction Technologies
The global lithium market has experienced unprecedented growth, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production and renewable energy storage systems. Market valuations indicate the lithium extraction industry reached approximately $4.1 billion in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 8.9% through 2030. This accelerated demand trajectory has fundamentally altered market dynamics, creating both opportunities and challenges for extraction technology providers.
Traditional lithium extraction methods, particularly evaporation ponds, continue to dominate market share at roughly 58% of global production. However, alternative extraction technologies utilizing novel reagents are gaining significant traction due to their improved efficiency profiles and reduced environmental footprint. Direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies, which employ specialized sorbents and solvents, currently represent about 10% of the market but are experiencing the fastest growth rate among all extraction methodologies.
Regional market analysis reveals distinct patterns in technology adoption. South American operations in the "Lithium Triangle" (Argentina, Bolivia, Chile) remain heavily invested in traditional brine evaporation, while North American and Australian producers are more aggressively pursuing alternative reagent technologies. Chinese manufacturers have established dominance in lithium processing, controlling approximately 60% of global refining capacity, which has significant implications for reagent selection and extraction methodology.
Demand-side analysis indicates that battery manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing high-purity lithium compounds (99.5%+ purity), which directly influences extraction technology selection. The premium for battery-grade lithium has widened to 15-20% above technical-grade material, creating strong economic incentives for extraction methods offering superior selectivity.
Market segmentation by reagent type shows emerging preference for ion-exchange materials, particularly engineered sorbents that demonstrate high lithium selectivity in the presence of competing ions such as sodium, magnesium, and calcium. These advanced materials command premium pricing but deliver significantly improved extraction efficiency, with some systems reporting lithium recovery rates exceeding 90% compared to 40-60% for traditional methods.
Investment patterns reveal accelerating capital flows into alternative reagent development, with venture funding in this sector reaching $780 million in 2022, representing a 215% increase over 2020 levels. Major mining corporations are strategically diversifying their extraction technology portfolios through acquisitions and research partnerships, indicating strong confidence in the commercial viability of next-generation extraction reagents.
Traditional lithium extraction methods, particularly evaporation ponds, continue to dominate market share at roughly 58% of global production. However, alternative extraction technologies utilizing novel reagents are gaining significant traction due to their improved efficiency profiles and reduced environmental footprint. Direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies, which employ specialized sorbents and solvents, currently represent about 10% of the market but are experiencing the fastest growth rate among all extraction methodologies.
Regional market analysis reveals distinct patterns in technology adoption. South American operations in the "Lithium Triangle" (Argentina, Bolivia, Chile) remain heavily invested in traditional brine evaporation, while North American and Australian producers are more aggressively pursuing alternative reagent technologies. Chinese manufacturers have established dominance in lithium processing, controlling approximately 60% of global refining capacity, which has significant implications for reagent selection and extraction methodology.
Demand-side analysis indicates that battery manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing high-purity lithium compounds (99.5%+ purity), which directly influences extraction technology selection. The premium for battery-grade lithium has widened to 15-20% above technical-grade material, creating strong economic incentives for extraction methods offering superior selectivity.
Market segmentation by reagent type shows emerging preference for ion-exchange materials, particularly engineered sorbents that demonstrate high lithium selectivity in the presence of competing ions such as sodium, magnesium, and calcium. These advanced materials command premium pricing but deliver significantly improved extraction efficiency, with some systems reporting lithium recovery rates exceeding 90% compared to 40-60% for traditional methods.
Investment patterns reveal accelerating capital flows into alternative reagent development, with venture funding in this sector reaching $780 million in 2022, representing a 215% increase over 2020 levels. Major mining corporations are strategically diversifying their extraction technology portfolios through acquisitions and research partnerships, indicating strong confidence in the commercial viability of next-generation extraction reagents.
Current Challenges in Reagent-Based Lithium Extraction
The current landscape of reagent-based lithium extraction faces significant challenges that impede efficiency and sustainability. Traditional extraction methods predominantly rely on sulfuric acid leaching, which while effective, presents environmental concerns due to high water consumption and potential acid contamination of surrounding ecosystems. This has prompted regulatory scrutiny and increased operational costs for mining companies worldwide.
Selectivity remains a primary technical hurdle in reagent-based extraction processes. Lithium-rich brines and ores typically contain numerous competing ions including sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which interfere with extraction efficiency. Current reagents often demonstrate insufficient discrimination between lithium and these competing elements, necessitating additional purification steps that increase production costs and energy consumption.
The stability of extraction reagents under varying operational conditions presents another significant challenge. Temperature fluctuations, pH variations, and brine composition heterogeneity can dramatically affect reagent performance. Many existing reagents exhibit degradation or reduced selectivity when exposed to extreme conditions common in mining operations, limiting their practical application across diverse lithium resources.
Reagent recovery and recycling capabilities remain underdeveloped, creating economic and environmental inefficiencies. The inability to effectively recover and reuse extraction reagents not only increases operational costs but also generates additional waste streams requiring management. This challenge is particularly acute for proprietary or specialized reagents with higher production costs.
Scaling laboratory-proven reagent technologies to commercial operations introduces additional complexities. Promising reagents that demonstrate excellent selectivity in controlled laboratory environments often fail to maintain performance when scaled to industrial volumes. Factors including mixing dynamics, contact time, and reagent distribution uniformity become critical at commercial scales.
The economic viability of alternative reagents faces scrutiny against established methods. Novel reagents may offer improved selectivity or environmental profiles but frequently at higher procurement costs. This creates a significant barrier to adoption, particularly for smaller mining operations with limited capital for process innovation.
Standardization challenges further complicate reagent evaluation and selection. The lithium industry lacks universally accepted protocols for assessing reagent performance across different lithium sources, making direct comparisons between alternative solutions difficult and impeding informed decision-making by mining operators.
Selectivity remains a primary technical hurdle in reagent-based extraction processes. Lithium-rich brines and ores typically contain numerous competing ions including sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which interfere with extraction efficiency. Current reagents often demonstrate insufficient discrimination between lithium and these competing elements, necessitating additional purification steps that increase production costs and energy consumption.
The stability of extraction reagents under varying operational conditions presents another significant challenge. Temperature fluctuations, pH variations, and brine composition heterogeneity can dramatically affect reagent performance. Many existing reagents exhibit degradation or reduced selectivity when exposed to extreme conditions common in mining operations, limiting their practical application across diverse lithium resources.
Reagent recovery and recycling capabilities remain underdeveloped, creating economic and environmental inefficiencies. The inability to effectively recover and reuse extraction reagents not only increases operational costs but also generates additional waste streams requiring management. This challenge is particularly acute for proprietary or specialized reagents with higher production costs.
Scaling laboratory-proven reagent technologies to commercial operations introduces additional complexities. Promising reagents that demonstrate excellent selectivity in controlled laboratory environments often fail to maintain performance when scaled to industrial volumes. Factors including mixing dynamics, contact time, and reagent distribution uniformity become critical at commercial scales.
The economic viability of alternative reagents faces scrutiny against established methods. Novel reagents may offer improved selectivity or environmental profiles but frequently at higher procurement costs. This creates a significant barrier to adoption, particularly for smaller mining operations with limited capital for process innovation.
Standardization challenges further complicate reagent evaluation and selection. The lithium industry lacks universally accepted protocols for assessing reagent performance across different lithium sources, making direct comparisons between alternative solutions difficult and impeding informed decision-making by mining operators.
Comparative Analysis of Current Extraction Reagents
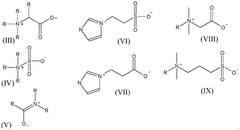
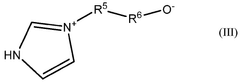
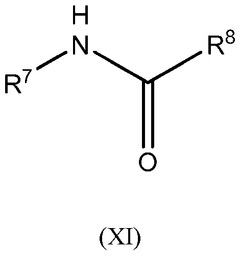
01 Selective extraction reagents for lithium mining
Various chemical reagents can be used to selectively extract lithium from brine or ore sources. These reagents are designed to preferentially bind with lithium ions while minimizing interactions with competing ions such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. The selectivity of these reagents is crucial for efficient lithium extraction processes, as it directly impacts the purity of the final product and reduces the need for additional purification steps. Advanced extraction reagents include specialized sorbents, ion exchange materials, and chelating agents that can significantly improve lithium recovery rates.- Selective extraction reagents for lithium: Various chemical reagents can be used to selectively extract lithium from brine or ore sources. These reagents are designed to preferentially bind with lithium ions while minimizing interactions with competing ions such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. The selectivity of these reagents is crucial for efficient lithium extraction processes, as it directly impacts the purity of the final product and reduces processing costs. Advanced extraction reagents include specialized sorbents, ion exchange materials, and chelating agents that can significantly improve lithium recovery rates.
- Membrane-based lithium extraction technologies: Membrane-based technologies offer innovative approaches for lithium extraction with enhanced selectivity and efficiency. These systems utilize specialized membranes that allow lithium ions to pass through while blocking other elements. The membrane technologies include electrodialysis, nanofiltration, and other separation techniques that can be applied to various lithium sources including brines and geothermal waters. These methods typically consume less energy and chemicals compared to traditional extraction processes, making them more environmentally friendly while maintaining high lithium recovery rates.
- Direct lithium extraction (DLE) methods: Direct lithium extraction methods represent cutting-edge approaches that can extract lithium directly from brines without the need for large evaporation ponds. These methods utilize advanced materials such as lithium-selective adsorbents, ion-sieves, and specialized extraction media that can capture lithium ions with high selectivity. DLE technologies significantly reduce water consumption and processing time compared to traditional methods, while offering higher recovery rates. These processes can be optimized for different brine compositions and can be operated continuously, improving overall extraction efficiency.
- Bioleaching and bio-assisted extraction processes: Bioleaching and bio-assisted extraction processes utilize microorganisms or their metabolic products to facilitate lithium extraction from various sources. These biological approaches can enhance the dissolution of lithium-bearing minerals or improve the selectivity of lithium separation from other elements. Microorganisms can produce organic acids or other compounds that selectively complex with lithium ions. These environmentally friendly methods typically operate under mild conditions, reducing energy requirements and environmental impact while maintaining extraction efficiency.
- Process optimization and integrated extraction systems: Integrated extraction systems combine multiple technologies and process optimizations to maximize lithium recovery efficiency. These systems often incorporate sequential extraction stages, recycling of reagents, and real-time monitoring to enhance overall performance. Advanced process control strategies, including automated adjustment of extraction parameters based on feed composition, can significantly improve selectivity and efficiency. These integrated approaches also focus on minimizing waste generation and energy consumption while maximizing lithium yield and purity, making the entire extraction process more economically viable and sustainable.
02 Membrane-based lithium extraction technologies
Membrane-based technologies offer innovative approaches for selective lithium extraction from various sources. These technologies utilize specialized membranes that allow lithium ions to pass through while blocking other elements, thereby increasing extraction efficiency and selectivity. The membranes can be modified with functional groups that enhance lithium selectivity or combined with electrochemical systems to drive ion transport. This approach reduces chemical consumption and can operate continuously, making it particularly suitable for processing lithium-rich brines with varying compositions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrochemical methods for lithium extraction
Electrochemical methods employ electrical potential differences to selectively extract lithium from solutions. These techniques include electrochemical adsorption, electrodialysis, and capacitive deionization, which can achieve high lithium selectivity by controlling electrode potentials and surface chemistry. Electrochemical approaches often consume less energy than traditional evaporation methods and can operate effectively at ambient temperatures. The efficiency of these methods can be enhanced by optimizing electrode materials, cell design, and operating parameters to maximize lithium recovery while minimizing energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Direct lithium extraction (DLE) processes
Direct lithium extraction processes represent a category of advanced techniques designed to extract lithium directly from brines without extensive evaporation ponds. These processes typically combine selective adsorption materials with innovative process designs to achieve high recovery rates and reduced environmental footprint. DLE technologies can significantly reduce water consumption and processing time compared to traditional methods. The efficiency of DLE processes depends on the selectivity of the extraction media, regeneration capabilities, and process integration with downstream purification steps.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization for enhanced lithium recovery
Various process optimization strategies can significantly improve the efficiency and selectivity of lithium extraction operations. These include multi-stage extraction processes, counter-current flow arrangements, and precise control of operating parameters such as pH, temperature, and contact time. Advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring can help maintain optimal conditions throughout the extraction process. Additionally, innovative pre-treatment methods can remove interfering elements before the main extraction step, thereby enhancing overall process efficiency and extending the lifespan of extraction media.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Lithium Mining Technology
The lithium extraction technology market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for efficient and environmentally sustainable extraction methods. The global market size is expanding rapidly, driven by the electric vehicle revolution and energy storage needs, with projections exceeding $10 billion by 2030. Technologically, direct lithium extraction (DLE) methods are gaining momentum but remain at varying maturity levels. Companies like Lilac Solutions and EnergyX are pioneering innovative ion-exchange technologies, while established players such as CATL and its subsidiary Guangdong Bangpu focus on recycling approaches. Academic institutions including Huazhong University of Science & Technology and Central South University are advancing fundamental research, collaborating with industry leaders like Koch Technology Solutions and Samsung Electronics to bridge the gap between theoretical selectivity improvements and commercial-scale implementation.
Lilac Solutions, Inc.
Technical Solution: Lilac Solutions has developed an innovative ion exchange technology for lithium extraction from brine resources. Their approach uses engineered ion exchange beads with high selectivity for lithium over competing ions like sodium, magnesium, and calcium. The process involves flowing brine through columns containing these beads, which selectively absorb lithium while rejecting other elements. The lithium is then eluted using a small volume of fresh water, producing a concentrated lithium solution. This technology significantly reduces the physical footprint compared to traditional evaporation ponds, with extraction taking hours instead of months[1]. Lilac's system is modular and can be scaled according to project requirements, making it adaptable to various brine compositions and production targets. The company has demonstrated lithium recovery rates exceeding 90% in field pilots, compared to 40-50% for conventional methods, while maintaining high purity levels suitable for battery-grade lithium production[2].
Strengths: High selectivity for lithium (>90% recovery rates); Rapid extraction (hours vs months); Minimal environmental footprint; Water-efficient process; Adaptable to various brine chemistries. Weaknesses: Requires specialized ion exchange materials that may have limited lifespan; Higher upfront capital costs compared to traditional methods; Potential scaling challenges for very large operations.
Energy Exploration Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Energy Exploration Technologies (EnergyX) has pioneered a lithium extraction technology based on mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) incorporating metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Their LiTAS™ (Lithium Ion Transport and Separation) platform utilizes these advanced membranes to selectively filter lithium ions from brine solutions while blocking larger ions like sodium, magnesium, and calcium. The technology operates through a direct lithium extraction (DLE) process that can work with various brine concentrations and compositions. EnergyX's approach reduces water consumption by over 90% compared to evaporation ponds and can operate continuously in a flow-through system[3]. The company has reported lithium recovery rates of up to 90% in pilot tests, with processing times measured in days rather than months. Their system is modular and scalable, allowing for deployment across different sized operations. EnergyX has also developed a complementary electrodialysis technology that can further concentrate lithium solutions to battery-grade levels without additional chemical inputs[4].
Strengths: Highly selective membrane technology; Significantly reduced water consumption; Faster extraction timeframes; Modular and scalable design; Lower chemical reagent requirements. Weaknesses: Membrane fouling may occur with certain brine compositions; Technology is relatively new with limited long-term operational data; Higher energy requirements compared to traditional methods; Potential challenges with membrane durability in harsh brine environments.
Technical Review of Selective Extraction Patents
Reagent compositions, apparatus and methods for extracting lithium from mixed salts
PatentWO2024249270A1
Innovation
- The use of lithium selective zwitterionic extractants and modifiers in a solvent extraction process to selectively extract lithium from aqueous solutions containing mixed salts, such as carnallite and lithium sulfate, by forming stable complexes and maximizing lithium recovery while minimizing magnesium removal.
Methods and systems for selectively extracting lithium from lithium-ion battery materials
PatentWO2025188884A1
Innovation
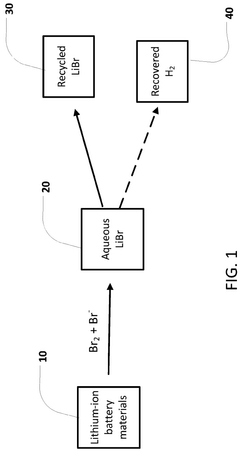
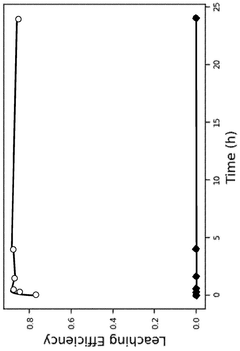
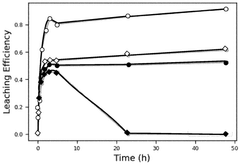
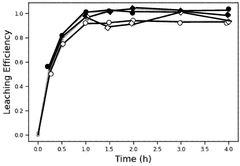
- The use of a bromine reactant, such as an aqueous mixture of Br2 and a bromide salt, to selectively leach lithium from lithium-ion battery materials, particularly lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC811) and lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP), forming an aqueous LiBr solution that can be electrolytically processed to recover lithium metal, hydrogen gas, and bromine gas.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Extraction Reagents
The environmental impact of extraction reagents in lithium mining represents a critical consideration in the industry's sustainability profile. Traditional lithium extraction methods, particularly those using sulfuric acid leaching, have demonstrated significant ecological consequences including soil acidification, groundwater contamination, and disruption of local ecosystems. These impacts extend beyond the immediate mining area, affecting downstream water bodies and agricultural lands.
Alternative reagents show varying degrees of environmental improvement. Ionic liquids, while offering enhanced selectivity for lithium over competing ions, present concerns regarding their biodegradability and potential bioaccumulation in aquatic environments. Studies indicate that certain ionic liquids may persist in the environment for extended periods, though their contained use in closed-loop systems can mitigate these risks.
Bioleaching approaches utilizing microorganisms demonstrate promising environmental profiles with significantly reduced chemical footprints. These biological agents naturally degrade after use, minimizing long-term environmental persistence. However, the introduction of non-native microbial species into mining environments requires careful ecological risk assessment to prevent unintended consequences in local ecosystems.
Supercritical CO2 extraction methods offer notable environmental advantages through reduced water consumption and minimal chemical waste generation. The carbon dioxide utilized can be recycled within the process, creating a near-closed system with limited emissions. This approach substantially reduces the water footprint compared to conventional brine evaporation techniques, a critical consideration in the water-scarce regions where many lithium operations are located.
Comparative lifecycle assessments reveal that membrane-based extraction technologies generally exhibit lower environmental impact scores across multiple categories including global warming potential, acidification, and ecotoxicity. These systems operate with minimal chemical inputs and generate significantly less hazardous waste than conventional methods, though their manufacturing and disposal present separate environmental considerations.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence reagent selection, with jurisdictions implementing stricter controls on mining effluents and waste management. Companies adopting more environmentally benign extraction reagents often gain competitive advantages through expedited permitting processes and improved stakeholder relations, particularly in environmentally sensitive regions.
The environmental impact assessment must also consider reagent production and transportation factors. Some novel extraction compounds require energy-intensive manufacturing processes that may offset their operational environmental benefits when evaluated from a holistic perspective. This underscores the importance of comprehensive cradle-to-grave environmental analysis when comparing extraction reagent alternatives.
Alternative reagents show varying degrees of environmental improvement. Ionic liquids, while offering enhanced selectivity for lithium over competing ions, present concerns regarding their biodegradability and potential bioaccumulation in aquatic environments. Studies indicate that certain ionic liquids may persist in the environment for extended periods, though their contained use in closed-loop systems can mitigate these risks.
Bioleaching approaches utilizing microorganisms demonstrate promising environmental profiles with significantly reduced chemical footprints. These biological agents naturally degrade after use, minimizing long-term environmental persistence. However, the introduction of non-native microbial species into mining environments requires careful ecological risk assessment to prevent unintended consequences in local ecosystems.
Supercritical CO2 extraction methods offer notable environmental advantages through reduced water consumption and minimal chemical waste generation. The carbon dioxide utilized can be recycled within the process, creating a near-closed system with limited emissions. This approach substantially reduces the water footprint compared to conventional brine evaporation techniques, a critical consideration in the water-scarce regions where many lithium operations are located.
Comparative lifecycle assessments reveal that membrane-based extraction technologies generally exhibit lower environmental impact scores across multiple categories including global warming potential, acidification, and ecotoxicity. These systems operate with minimal chemical inputs and generate significantly less hazardous waste than conventional methods, though their manufacturing and disposal present separate environmental considerations.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence reagent selection, with jurisdictions implementing stricter controls on mining effluents and waste management. Companies adopting more environmentally benign extraction reagents often gain competitive advantages through expedited permitting processes and improved stakeholder relations, particularly in environmentally sensitive regions.
The environmental impact assessment must also consider reagent production and transportation factors. Some novel extraction compounds require energy-intensive manufacturing processes that may offset their operational environmental benefits when evaluated from a holistic perspective. This underscores the importance of comprehensive cradle-to-grave environmental analysis when comparing extraction reagent alternatives.
Economic Feasibility of Alternative Reagent Implementation
The implementation of alternative reagents in lithium mining operations requires thorough economic analysis to determine viability beyond technical performance. Initial capital expenditure for transitioning from traditional acid leaching to alternative reagents such as ionic liquids or bio-leaching agents represents a significant investment barrier. Equipment modifications, process redesign, and staff retraining collectively contribute to implementation costs that can range from $5-20 million depending on operation scale.
Operational expenditure comparisons reveal nuanced economic considerations. While conventional sulfuric acid remains cost-effective at $100-200 per ton, newer selective chelating agents may cost $1,500-3,000 per ton. However, this price differential must be evaluated against recovery efficiency improvements, which can increase lithium yield by 15-30% with selective reagents, potentially offsetting higher reagent costs through improved resource utilization.
Reagent recycling capabilities significantly impact long-term economics. Advanced solvents and ionic liquids demonstrate 85-95% recovery rates across multiple extraction cycles, substantially reducing replacement costs compared to conventional acids with 40-60% recovery rates. This recyclability factor becomes increasingly important as operations scale, creating economic advantages for operations exceeding 10,000 tons annual production.
Environmental compliance costs represent another critical economic factor. Traditional acid-based extraction methods incur substantial neutralization and waste management expenses, estimated at 15-25% of operational costs. Alternative reagents that reduce environmental impact can decrease these compliance costs by 30-50%, providing significant economic benefits in jurisdictions with stringent environmental regulations.
Market volatility considerations cannot be overlooked in economic feasibility assessments. The price stability of alternative reagents versus conventional acids impacts long-term planning. While sulfuric acid prices have fluctuated between $70-300 per ton over the past decade, specialized extraction agents demonstrate more stable pricing structures, allowing for more predictable operational budgeting despite higher initial costs.
Return on investment timelines vary significantly between reagent technologies. Conventional acid-based systems typically achieve ROI within 2-3 years, while alternative reagent implementations may require 3-5 years to reach profitability. However, operations with longer projected lifespans benefit disproportionately from alternative reagents due to cumulative efficiency gains and reduced environmental remediation requirements over time.
Operational expenditure comparisons reveal nuanced economic considerations. While conventional sulfuric acid remains cost-effective at $100-200 per ton, newer selective chelating agents may cost $1,500-3,000 per ton. However, this price differential must be evaluated against recovery efficiency improvements, which can increase lithium yield by 15-30% with selective reagents, potentially offsetting higher reagent costs through improved resource utilization.
Reagent recycling capabilities significantly impact long-term economics. Advanced solvents and ionic liquids demonstrate 85-95% recovery rates across multiple extraction cycles, substantially reducing replacement costs compared to conventional acids with 40-60% recovery rates. This recyclability factor becomes increasingly important as operations scale, creating economic advantages for operations exceeding 10,000 tons annual production.
Environmental compliance costs represent another critical economic factor. Traditional acid-based extraction methods incur substantial neutralization and waste management expenses, estimated at 15-25% of operational costs. Alternative reagents that reduce environmental impact can decrease these compliance costs by 30-50%, providing significant economic benefits in jurisdictions with stringent environmental regulations.
Market volatility considerations cannot be overlooked in economic feasibility assessments. The price stability of alternative reagents versus conventional acids impacts long-term planning. While sulfuric acid prices have fluctuated between $70-300 per ton over the past decade, specialized extraction agents demonstrate more stable pricing structures, allowing for more predictable operational budgeting despite higher initial costs.
Return on investment timelines vary significantly between reagent technologies. Conventional acid-based systems typically achieve ROI within 2-3 years, while alternative reagent implementations may require 3-5 years to reach profitability. However, operations with longer projected lifespans benefit disproportionately from alternative reagents due to cumulative efficiency gains and reduced environmental remediation requirements over time.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!