Domestic vs. international production scales for V16 engines
AUG 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V16 Engine Background
The V16 engine represents a pinnacle of automotive engineering, characterized by its 16-cylinder configuration arranged in a V-shape. This unique design emerged in the early 20th century as a solution for applications requiring immense power output and smooth operation. The V16 layout allows for a compact engine design relative to its displacement, making it suitable for high-performance vehicles and marine applications.
Historically, V16 engines gained prominence in the 1930s, with luxury automobile manufacturers such as Cadillac and Marmon introducing them in their flagship models. These engines were known for their exceptional smoothness and power delivery, setting new standards in the automotive industry. However, their complexity and high production costs limited widespread adoption.
In the realm of marine and industrial applications, V16 engines have found more sustained use. Large ships, submarines, and stationary power generation systems have utilized V16 configurations to meet demanding power requirements. The ability to produce substantial horsepower and torque while maintaining relatively compact dimensions has made V16 engines particularly valuable in these sectors.
The production of V16 engines has always been a niche market, with limited manufacturers specializing in their design and construction. Internationally, companies like MTU Friedrichshafen in Germany and Wärtsilä in Finland have been at the forefront of V16 engine production for marine and power generation applications. These manufacturers have continuously refined their designs to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase power output.
Domestically, the production of V16 engines has been even more limited, with few manufacturers possessing the capability to design and produce these complex powerplants. The specialized nature of V16 engines, combined with their high development and production costs, has resulted in a concentrated market with only a handful of players globally.
The comparison of domestic and international production scales for V16 engines reveals significant disparities. International manufacturers, particularly those in Europe, have established a more robust production infrastructure for V16 engines, driven by demand from the marine and power generation sectors. These companies benefit from economies of scale and long-standing expertise in large engine manufacturing.
In contrast, domestic production of V16 engines has been more limited in scale, often focusing on specific applications or custom-built solutions. The smaller domestic market for such specialized engines has resulted in lower production volumes and higher per-unit costs compared to international counterparts.
Historically, V16 engines gained prominence in the 1930s, with luxury automobile manufacturers such as Cadillac and Marmon introducing them in their flagship models. These engines were known for their exceptional smoothness and power delivery, setting new standards in the automotive industry. However, their complexity and high production costs limited widespread adoption.
In the realm of marine and industrial applications, V16 engines have found more sustained use. Large ships, submarines, and stationary power generation systems have utilized V16 configurations to meet demanding power requirements. The ability to produce substantial horsepower and torque while maintaining relatively compact dimensions has made V16 engines particularly valuable in these sectors.
The production of V16 engines has always been a niche market, with limited manufacturers specializing in their design and construction. Internationally, companies like MTU Friedrichshafen in Germany and Wärtsilä in Finland have been at the forefront of V16 engine production for marine and power generation applications. These manufacturers have continuously refined their designs to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase power output.
Domestically, the production of V16 engines has been even more limited, with few manufacturers possessing the capability to design and produce these complex powerplants. The specialized nature of V16 engines, combined with their high development and production costs, has resulted in a concentrated market with only a handful of players globally.
The comparison of domestic and international production scales for V16 engines reveals significant disparities. International manufacturers, particularly those in Europe, have established a more robust production infrastructure for V16 engines, driven by demand from the marine and power generation sectors. These companies benefit from economies of scale and long-standing expertise in large engine manufacturing.
In contrast, domestic production of V16 engines has been more limited in scale, often focusing on specific applications or custom-built solutions. The smaller domestic market for such specialized engines has resulted in lower production volumes and higher per-unit costs compared to international counterparts.
Market Analysis
The global market for V16 engines has experienced significant shifts in recent years, with production scales varying considerably between domestic and international manufacturers. Traditionally, V16 engines have been associated with high-performance luxury vehicles and marine applications, but their market presence has been relatively niche due to their complexity and high production costs.
In the international market, production scales for V16 engines have remained limited, with only a handful of manufacturers maintaining active production lines. These engines are primarily found in ultra-luxury vehicles and specialized industrial applications. The production volumes are typically in the low hundreds per year, reflecting the exclusive nature of these powerplants.
Domestic production of V16 engines, particularly in emerging markets, has seen some growth in recent years. This increase is partly driven by the rising demand for high-performance engines in developing economies and the desire to establish domestic capabilities in advanced engine manufacturing. However, the production scales still lag behind those of international manufacturers in terms of volume and technological sophistication.
The market demand for V16 engines is heavily influenced by factors such as environmental regulations, fuel efficiency standards, and the shift towards electrification in the automotive industry. These factors have led to a gradual decline in the overall market size for large displacement engines, including V16s, in many international markets.
Despite these challenges, there remains a niche market for V16 engines, particularly in the marine sector and specialized industrial applications. In these areas, the demand for high-power, high-torque engines continues to support limited production scales both domestically and internationally.
The comparison of production scales reveals that international manufacturers generally have more established production processes and higher output capabilities for V16 engines. This is due to their longer history in producing these engines and their ability to leverage economies of scale across multiple high-end brands or applications.
Domestic production, while growing, often faces challenges in achieving comparable scales. These challenges include limited access to advanced manufacturing technologies, smaller domestic markets for ultra-luxury vehicles, and the high costs associated with developing and producing such complex engines.
Looking ahead, the market for V16 engines is likely to remain specialized and limited in scale. Both domestic and international production will need to adapt to changing market demands, potentially focusing on hybrid or more efficient V16 designs to maintain relevance in an increasingly environmentally conscious market landscape.
In the international market, production scales for V16 engines have remained limited, with only a handful of manufacturers maintaining active production lines. These engines are primarily found in ultra-luxury vehicles and specialized industrial applications. The production volumes are typically in the low hundreds per year, reflecting the exclusive nature of these powerplants.
Domestic production of V16 engines, particularly in emerging markets, has seen some growth in recent years. This increase is partly driven by the rising demand for high-performance engines in developing economies and the desire to establish domestic capabilities in advanced engine manufacturing. However, the production scales still lag behind those of international manufacturers in terms of volume and technological sophistication.
The market demand for V16 engines is heavily influenced by factors such as environmental regulations, fuel efficiency standards, and the shift towards electrification in the automotive industry. These factors have led to a gradual decline in the overall market size for large displacement engines, including V16s, in many international markets.
Despite these challenges, there remains a niche market for V16 engines, particularly in the marine sector and specialized industrial applications. In these areas, the demand for high-power, high-torque engines continues to support limited production scales both domestically and internationally.
The comparison of production scales reveals that international manufacturers generally have more established production processes and higher output capabilities for V16 engines. This is due to their longer history in producing these engines and their ability to leverage economies of scale across multiple high-end brands or applications.
Domestic production, while growing, often faces challenges in achieving comparable scales. These challenges include limited access to advanced manufacturing technologies, smaller domestic markets for ultra-luxury vehicles, and the high costs associated with developing and producing such complex engines.
Looking ahead, the market for V16 engines is likely to remain specialized and limited in scale. Both domestic and international production will need to adapt to changing market demands, potentially focusing on hybrid or more efficient V16 designs to maintain relevance in an increasingly environmentally conscious market landscape.
Production Challenges
The production of V16 engines presents significant challenges due to their complexity and limited market demand. One of the primary hurdles is the high cost associated with manufacturing these large, specialized engines. The intricate design and precision required in the production process contribute to increased expenses, making it difficult for manufacturers to achieve economies of scale.
Domestic production of V16 engines often faces additional challenges compared to international counterparts. Limited access to advanced manufacturing technologies and specialized tooling can hinder the production efficiency and quality of domestically produced V16 engines. This technological gap may result in longer production times and potentially lower output volumes, impacting overall competitiveness in the global market.
Skilled labor shortages pose another significant challenge in V16 engine production. The assembly of these complex engines requires highly trained technicians with specialized knowledge. Domestic manufacturers may struggle to find and retain qualified personnel, particularly in regions with less developed automotive industries. This shortage can lead to production bottlenecks and increased labor costs.
Quality control and consistency present ongoing challenges in V16 engine production. The intricate nature of these engines demands stringent quality assurance processes to ensure reliability and performance. Domestic manufacturers may face difficulties in implementing and maintaining the same level of quality control measures as their international counterparts, potentially affecting the reputation and market acceptance of their products.
Supply chain management is a critical aspect of V16 engine production that can pose significant challenges. The procurement of specialized components and materials may be more challenging for domestic manufacturers, especially if they rely heavily on imported parts. This dependency can lead to longer lead times, increased costs, and potential disruptions in the production process.
Environmental regulations and emissions standards also impact V16 engine production. As global emissions standards become increasingly stringent, manufacturers must invest in research and development to ensure compliance. Domestic producers may face additional hurdles in meeting these standards, particularly if they lack access to the latest emissions control technologies or have limited resources for extensive testing and certification processes.
The limited market demand for V16 engines further complicates production challenges. With a relatively small customer base, manufacturers struggle to justify large-scale production investments. This constraint often results in smaller production runs, which can lead to higher per-unit costs and reduced profitability. Domestic producers may find it particularly challenging to compete in this niche market, especially when facing established international competitors with greater resources and brand recognition.
Domestic production of V16 engines often faces additional challenges compared to international counterparts. Limited access to advanced manufacturing technologies and specialized tooling can hinder the production efficiency and quality of domestically produced V16 engines. This technological gap may result in longer production times and potentially lower output volumes, impacting overall competitiveness in the global market.
Skilled labor shortages pose another significant challenge in V16 engine production. The assembly of these complex engines requires highly trained technicians with specialized knowledge. Domestic manufacturers may struggle to find and retain qualified personnel, particularly in regions with less developed automotive industries. This shortage can lead to production bottlenecks and increased labor costs.
Quality control and consistency present ongoing challenges in V16 engine production. The intricate nature of these engines demands stringent quality assurance processes to ensure reliability and performance. Domestic manufacturers may face difficulties in implementing and maintaining the same level of quality control measures as their international counterparts, potentially affecting the reputation and market acceptance of their products.
Supply chain management is a critical aspect of V16 engine production that can pose significant challenges. The procurement of specialized components and materials may be more challenging for domestic manufacturers, especially if they rely heavily on imported parts. This dependency can lead to longer lead times, increased costs, and potential disruptions in the production process.
Environmental regulations and emissions standards also impact V16 engine production. As global emissions standards become increasingly stringent, manufacturers must invest in research and development to ensure compliance. Domestic producers may face additional hurdles in meeting these standards, particularly if they lack access to the latest emissions control technologies or have limited resources for extensive testing and certification processes.
The limited market demand for V16 engines further complicates production challenges. With a relatively small customer base, manufacturers struggle to justify large-scale production investments. This constraint often results in smaller production runs, which can lead to higher per-unit costs and reduced profitability. Domestic producers may find it particularly challenging to compete in this niche market, especially when facing established international competitors with greater resources and brand recognition.
Current Production Methods
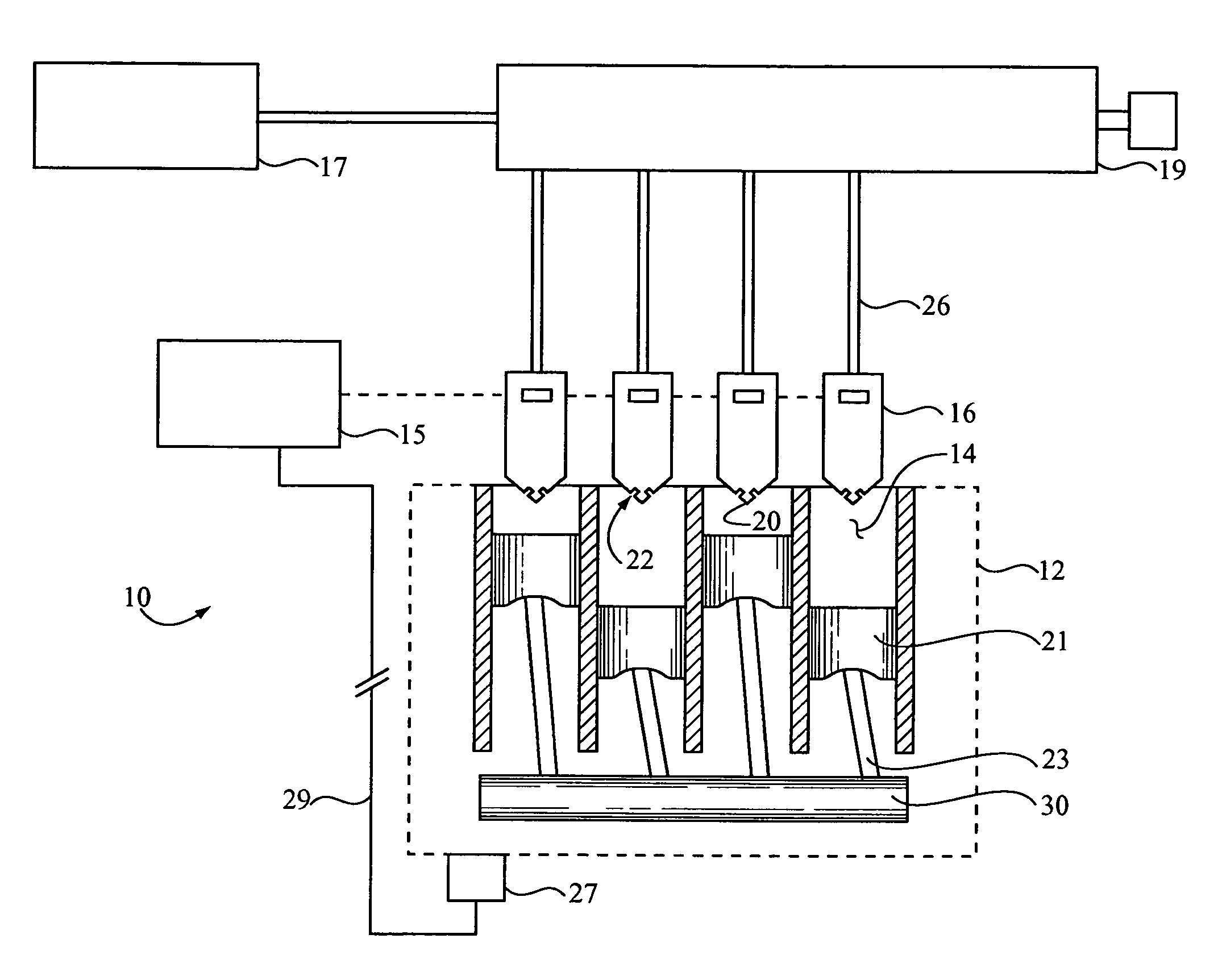
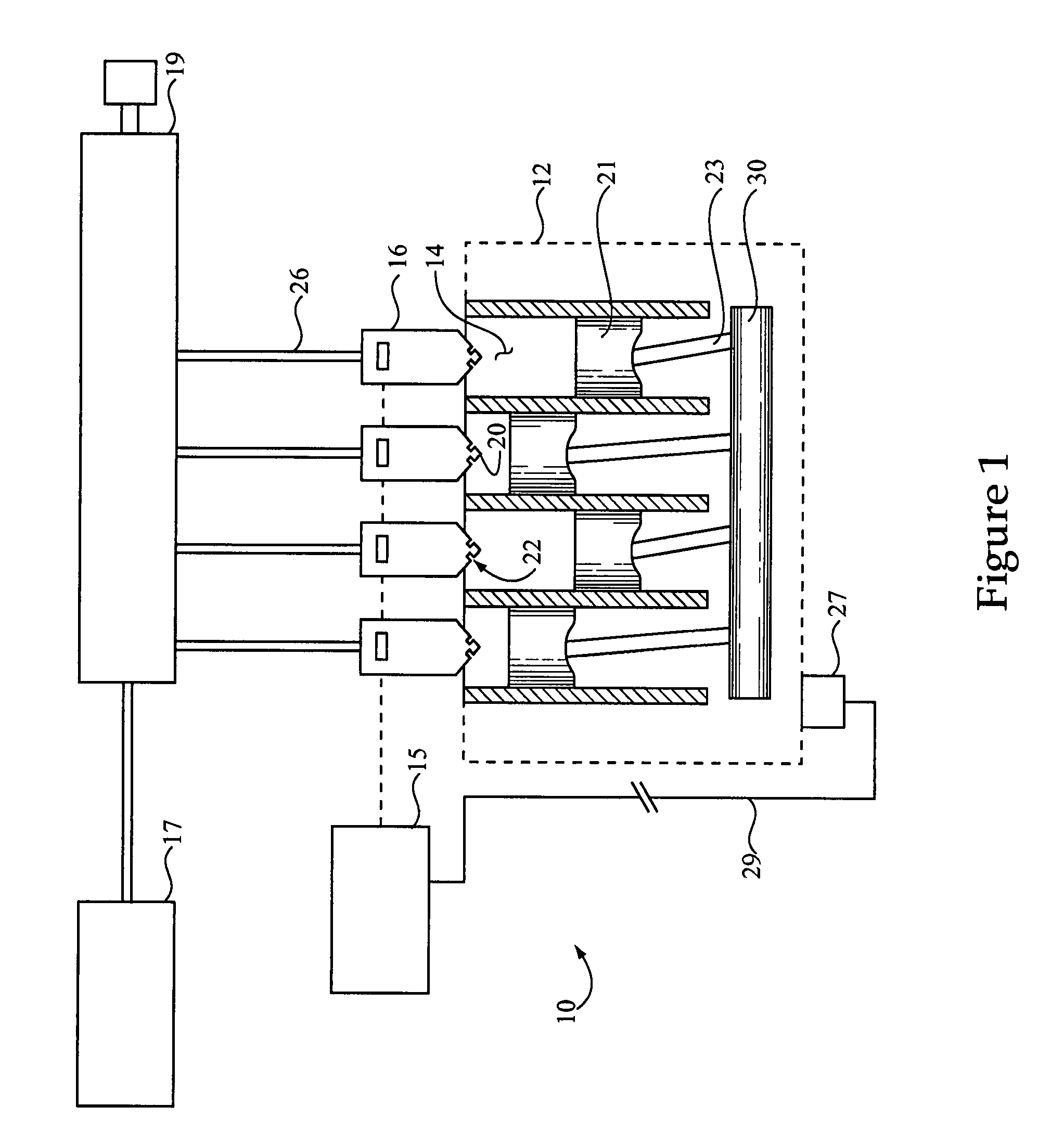
01 V16 engine design and manufacturing
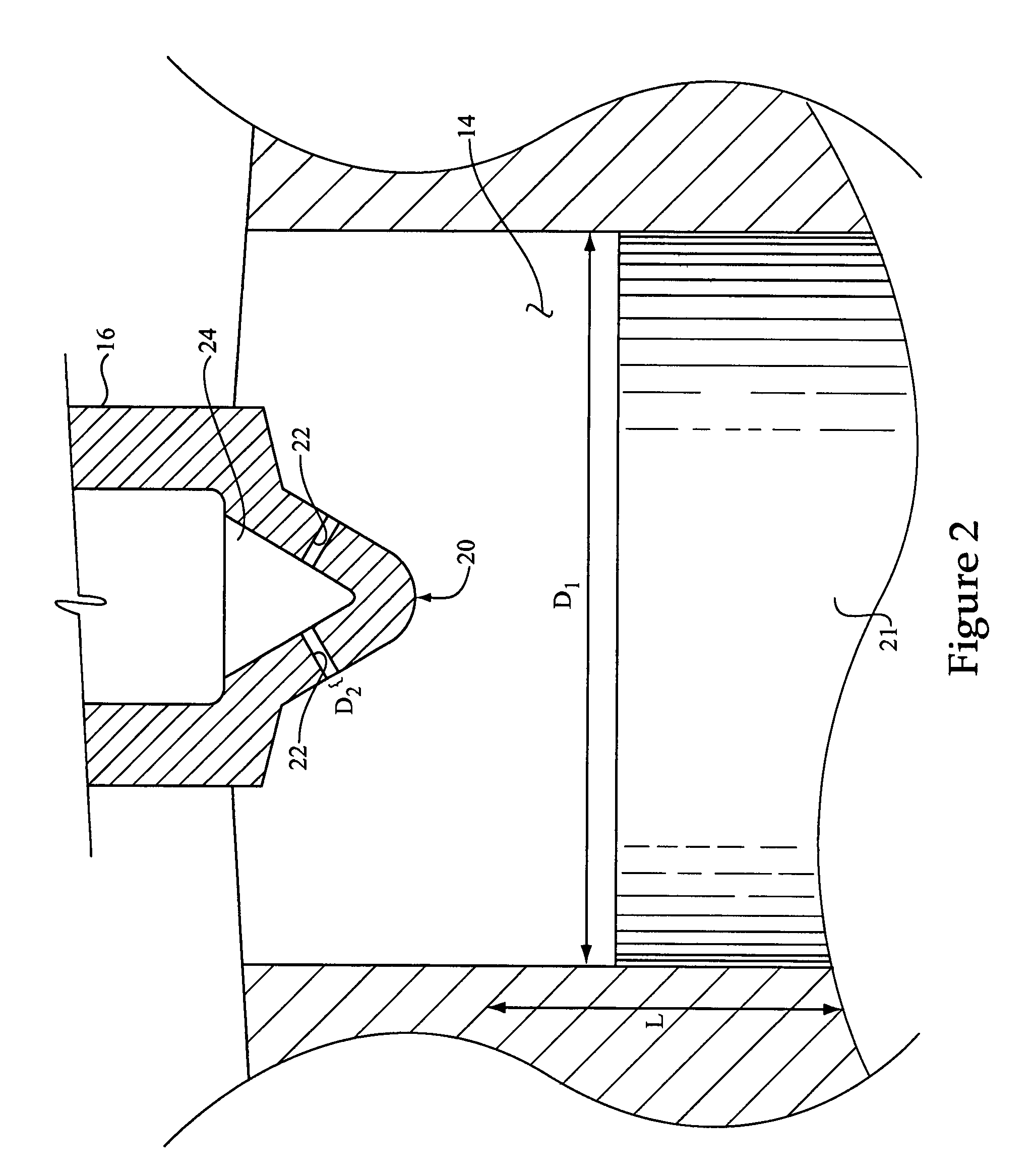
V16 engines are complex powerplants that require specialized design and manufacturing processes. These engines feature 16 cylinders arranged in a V configuration, offering high power output and smooth operation. The production of V16 engines involves advanced engineering techniques, precision machining, and careful assembly to ensure optimal performance and reliability.- V16 engine design and configuration: V16 engines are designed with 16 cylinders arranged in a V-shape configuration. This layout allows for increased power output and smoother operation compared to smaller engines. The design often includes advanced cooling systems, fuel injection, and exhaust systems to optimize performance and efficiency.
- Manufacturing processes for V16 engines: Production of V16 engines involves specialized manufacturing processes, including precision machining, assembly line techniques, and quality control measures. Advanced manufacturing technologies such as CNC machining and robotics are often employed to ensure consistent production quality and efficiency at scale.
- Materials and components for V16 engines: V16 engines require high-performance materials and components to withstand the extreme conditions of operation. This includes the use of lightweight alloys, advanced lubricants, and specialized parts such as high-strength pistons, crankshafts, and valves. The selection and sourcing of these materials play a crucial role in production scaling.
- Production scaling and efficiency improvements: Scaling up V16 engine production involves optimizing manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and logistics. This may include implementing lean manufacturing principles, just-in-time inventory systems, and automated production lines to increase efficiency and reduce costs while maintaining quality standards.
- Testing and quality control for V16 engines: Large-scale production of V16 engines requires robust testing and quality control measures. This includes the use of advanced diagnostic equipment, dynamometer testing, and computerized analysis to ensure each engine meets performance and reliability standards. Implementing efficient testing protocols is crucial for maintaining production quality at scale.
02 Production scale optimization for V16 engines
Optimizing production scales for V16 engines involves implementing efficient manufacturing processes, automation technologies, and lean production principles. This includes streamlining assembly lines, utilizing advanced robotics, and implementing just-in-time inventory systems to reduce costs and improve productivity while maintaining high quality standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quality control and testing in V16 engine production
Ensuring the quality of V16 engines during production requires rigorous testing and quality control measures. This includes implementing advanced inspection techniques, performance testing, and durability assessments throughout the manufacturing process. Specialized equipment and protocols are used to verify engine specifications, emissions compliance, and overall reliability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Supply chain management for V16 engine production
Effective supply chain management is crucial for V16 engine production at scale. This involves coordinating with suppliers for specialized components, managing inventory levels, and ensuring timely delivery of materials. Implementing advanced logistics systems and fostering strong relationships with suppliers can help optimize production efficiency and reduce costs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental considerations in V16 engine manufacturing
As environmental regulations become more stringent, V16 engine manufacturers must consider sustainability in their production processes. This includes implementing cleaner manufacturing techniques, reducing waste and emissions, and exploring more environmentally friendly materials. Additionally, manufacturers may need to adapt their production lines to accommodate evolving engine technologies that meet stricter emissions standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers
The competition landscape for V16 engine production scales reveals a mature market dominated by established automotive and heavy machinery manufacturers. The industry is in a consolidation phase, with major players like Toyota, BMW, Honda, and Mercedes-Benz leading in technological advancements and production capabilities. Market size is relatively small due to the niche nature of V16 engines, primarily used in luxury vehicles and specialized industrial applications. Technological maturity is high, with companies like Cummins, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and Guangxi Yuchai Machinery Co. contributing to ongoing refinements in efficiency and performance. The comparison between domestic and international production scales likely favors international manufacturers due to their longer history and broader market reach.
Guangxi Yuchai Machinery Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Guangxi Yuchai Machinery Co., Ltd. is a major player in the Chinese engine market, with capabilities extending to large displacement engines including V16 configurations. The company has been expanding its production capabilities to compete on an international scale. Yuchai's V16 engines are primarily targeted at power generation and marine applications. The company has invested in modernizing its production facilities, incorporating automation and advanced quality control systems to improve manufacturing efficiency and product reliability[5]. Yuchai has also focused on developing engines that meet stringent emission standards, positioning itself to compete in both domestic and international markets. The company's production scale for V16 engines has been growing, supported by China's increasing demand for large power generation units and marine propulsion systems[6].
Strengths: Competitive pricing, growing domestic market, and improving manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Less established international reputation compared to Western manufacturers, and potential challenges in meeting the most stringent international emissions standards.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Technical Solution: Mercedes-Benz Group AG, through its subsidiary MTU Friedrichshafen (now part of Rolls-Royce Power Systems), has been a significant player in the V16 engine market, particularly for marine and power generation applications. The MTU Series 8000 engines, which include V16 configurations, are known for their high power density and efficiency. These engines can produce up to 10,000 kW of power. Mercedes-Benz's production of V16 engines is characterized by a focus on precision engineering and advanced materials. The company utilizes state-of-the-art manufacturing techniques, including computerized machining centers and rigorous testing procedures, to ensure high quality and reliability[7]. Production is primarily centered in Germany, with additional facilities in the United States to serve the North American market. The company has invested in flexible manufacturing systems that allow for efficient production scaling to meet varying demand levels[8].
Strengths: High-quality engineering, strong brand reputation, and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to some competitors, and potential challenges in adapting to rapidly changing environmental regulations.
Core Technologies
Internal combustion engine and operating method therefor
PatentInactiveUS7597084B2
Innovation
- The design includes a high-pressure fuel injection system with multiple small outlet orifices in fuel injectors and a turbocharger configuration to facilitate efficient fuel-air mixing, allowing for higher power density operation at elevated RPM and BMEP while minimizing smoke output and fuel consumption.
Internal combustion engine and operating method therefor
PatentWO2008121202A1
Innovation
- The design includes a high-pressure fuel injection system with multiple small outlet orifices in fuel injectors and a turbocharger configuration to facilitate efficient fuel-air mixing, allowing for higher BMEP and RPM while minimizing smoke output and fuel consumption, resulting in engines that can produce at least 150 horsepower per liter of displacement with low smoke emissions.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the production scales of V16 engines both domestically and internationally. These regulations have become increasingly stringent over the years, significantly impacting the manufacturing processes and market demand for high-displacement engines like the V16.
In many countries, particularly in Europe and North America, strict emissions standards have been implemented to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. These regulations often set limits on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. As a result, manufacturers of V16 engines have had to invest heavily in advanced technologies to meet these standards, which has led to increased production costs and, in some cases, reduced production scales.
The European Union, for instance, has implemented Euro 6 standards for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, which set stringent limits on emissions. These standards have made it challenging for manufacturers to produce large-displacement engines like V16s in high volumes, as they struggle to meet the required emissions targets without compromising performance.
In contrast, some countries with less stringent environmental regulations may still allow for larger production scales of V16 engines. However, the global trend towards stricter emissions standards is gradually affecting these markets as well. For example, China has been implementing increasingly stringent emissions standards, which has led to a reduction in the production of large-displacement engines, including V16s.
The impact of environmental regulations on V16 engine production scales is not limited to emissions standards alone. Fuel efficiency requirements, such as the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States, also play a significant role. These standards incentivize manufacturers to produce more fuel-efficient vehicles, which often leads to a shift away from large-displacement engines like V16s.
Furthermore, some countries have implemented tax policies that discourage the production and sale of high-displacement engines. For instance, in many European countries, vehicle taxes are based on engine size or CO2 emissions, making V16 engines less attractive to consumers and, consequently, reducing their production scales.
The disparity in environmental regulations between different countries and regions has led to variations in V16 engine production scales internationally. While some markets may still support larger production volumes, the overall trend is towards smaller, more efficient engines that can meet increasingly stringent environmental standards.
In many countries, particularly in Europe and North America, strict emissions standards have been implemented to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. These regulations often set limits on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. As a result, manufacturers of V16 engines have had to invest heavily in advanced technologies to meet these standards, which has led to increased production costs and, in some cases, reduced production scales.
The European Union, for instance, has implemented Euro 6 standards for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, which set stringent limits on emissions. These standards have made it challenging for manufacturers to produce large-displacement engines like V16s in high volumes, as they struggle to meet the required emissions targets without compromising performance.
In contrast, some countries with less stringent environmental regulations may still allow for larger production scales of V16 engines. However, the global trend towards stricter emissions standards is gradually affecting these markets as well. For example, China has been implementing increasingly stringent emissions standards, which has led to a reduction in the production of large-displacement engines, including V16s.
The impact of environmental regulations on V16 engine production scales is not limited to emissions standards alone. Fuel efficiency requirements, such as the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States, also play a significant role. These standards incentivize manufacturers to produce more fuel-efficient vehicles, which often leads to a shift away from large-displacement engines like V16s.
Furthermore, some countries have implemented tax policies that discourage the production and sale of high-displacement engines. For instance, in many European countries, vehicle taxes are based on engine size or CO2 emissions, making V16 engines less attractive to consumers and, consequently, reducing their production scales.
The disparity in environmental regulations between different countries and regions has led to variations in V16 engine production scales internationally. While some markets may still support larger production volumes, the overall trend is towards smaller, more efficient engines that can meet increasingly stringent environmental standards.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of V16 engine production scales varies significantly between domestic and international markets. In the global context, V16 engines are primarily manufactured by a select few high-end automotive and marine engine producers, with limited production volumes due to their specialized nature and high costs. This niche market structure has led to concentrated economic benefits in specific regions, particularly in countries with established luxury vehicle industries.
Domestically, the production of V16 engines often represents a showcase of technological prowess and manufacturing capabilities. While the direct economic impact may be limited due to low production volumes, the indirect effects can be substantial. These engines serve as halo products, enhancing brand prestige and potentially driving sales of other, more mainstream products within a manufacturer's lineup. This can lead to increased revenue streams and job creation in related sectors such as research and development, advanced materials, and precision manufacturing.
Internationally, the production of V16 engines contributes to a country's export potential in the high-value automotive sector. Nations with established V16 engine production capabilities can leverage this expertise to attract foreign investment and foster international collaborations. This can result in technology transfer, skill development, and the creation of high-paying jobs in the advanced manufacturing sector.
The economic multiplier effect of V16 engine production is significant, particularly in the supply chain. Specialized component manufacturers, tooling companies, and engineering service providers all benefit from the high-precision requirements of V16 engine production. This creates a network of supporting industries that can contribute substantially to local and regional economies.
However, the limited production scales of V16 engines also present economic challenges. The high development and production costs associated with these engines require significant capital investment, which can be difficult to recoup given the small market size. This economic reality has led to a consolidation of V16 engine production among a few key players globally, potentially limiting broader economic benefits across multiple regions.
In conclusion, while the direct economic impact of V16 engine production may be constrained by limited production scales, the indirect and long-term economic benefits can be substantial, particularly in fostering innovation, enhancing manufacturing capabilities, and supporting high-value job creation in both domestic and international markets.
Domestically, the production of V16 engines often represents a showcase of technological prowess and manufacturing capabilities. While the direct economic impact may be limited due to low production volumes, the indirect effects can be substantial. These engines serve as halo products, enhancing brand prestige and potentially driving sales of other, more mainstream products within a manufacturer's lineup. This can lead to increased revenue streams and job creation in related sectors such as research and development, advanced materials, and precision manufacturing.
Internationally, the production of V16 engines contributes to a country's export potential in the high-value automotive sector. Nations with established V16 engine production capabilities can leverage this expertise to attract foreign investment and foster international collaborations. This can result in technology transfer, skill development, and the creation of high-paying jobs in the advanced manufacturing sector.
The economic multiplier effect of V16 engine production is significant, particularly in the supply chain. Specialized component manufacturers, tooling companies, and engineering service providers all benefit from the high-precision requirements of V16 engine production. This creates a network of supporting industries that can contribute substantially to local and regional economies.
However, the limited production scales of V16 engines also present economic challenges. The high development and production costs associated with these engines require significant capital investment, which can be difficult to recoup given the small market size. This economic reality has led to a consolidation of V16 engine production among a few key players globally, potentially limiting broader economic benefits across multiple regions.
In conclusion, while the direct economic impact of V16 engine production may be constrained by limited production scales, the indirect and long-term economic benefits can be substantial, particularly in fostering innovation, enhancing manufacturing capabilities, and supporting high-value job creation in both domestic and international markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!