The significance of V16 engines in the evolution of supercars
AUG 15, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V16 Engine Evolution
The evolution of V16 engines in supercars represents a significant chapter in automotive engineering history. These powerplants, characterized by their 16-cylinder configuration, have played a crucial role in pushing the boundaries of performance and prestige in high-end vehicles.
The journey of V16 engines in supercars began in the early 20th century, with luxury marques like Cadillac and Marmon introducing these massive powerplants. These early V16s were primarily designed for smoothness and refinement rather than outright performance, setting a precedent for their association with luxury and exclusivity.
As automotive technology progressed, the focus of V16 engines shifted towards performance. The 1930s saw the emergence of V16-powered racing cars, most notably the Auto Union Type C, which dominated Grand Prix racing. This period marked the transition of V16 engines from symbols of luxury to icons of speed and power.
The post-war era witnessed a decline in V16 usage due to practical constraints and changing market demands. However, the allure of these engines persisted in the realm of concept cars and limited-edition supercars. Manufacturers occasionally revisited the V16 configuration to showcase their engineering prowess and create halo vehicles.
In the modern era, V16 engines have made sporadic appearances in supercars, each time pushing the envelope of what's possible in automotive engineering. The Cizeta V16T of the early 1990s and the Bugatti Veyron of the 2000s are prime examples of how V16 engines continued to captivate enthusiasts and engineers alike.
The significance of V16 engines in supercar evolution extends beyond mere performance metrics. These engines have consistently represented the pinnacle of automotive engineering, serving as testbeds for cutting-edge technologies and manufacturing techniques. Their development has driven advancements in areas such as materials science, fuel efficiency, and power density.
Moreover, V16 engines have played a crucial role in shaping the image and aspirations of supercar brands. The complexity, rarity, and sheer audacity of producing a V16 engine have made them powerful marketing tools, elevating the status of the vehicles they power and the brands that create them.
As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, the role of V16 engines in supercars is evolving. While their future in production vehicles may be limited, the legacy of V16 engines continues to influence the design philosophy and engineering ambitions of modern supercars, inspiring manufacturers to push the boundaries of performance and innovation in new and exciting ways.
The journey of V16 engines in supercars began in the early 20th century, with luxury marques like Cadillac and Marmon introducing these massive powerplants. These early V16s were primarily designed for smoothness and refinement rather than outright performance, setting a precedent for their association with luxury and exclusivity.
As automotive technology progressed, the focus of V16 engines shifted towards performance. The 1930s saw the emergence of V16-powered racing cars, most notably the Auto Union Type C, which dominated Grand Prix racing. This period marked the transition of V16 engines from symbols of luxury to icons of speed and power.
The post-war era witnessed a decline in V16 usage due to practical constraints and changing market demands. However, the allure of these engines persisted in the realm of concept cars and limited-edition supercars. Manufacturers occasionally revisited the V16 configuration to showcase their engineering prowess and create halo vehicles.
In the modern era, V16 engines have made sporadic appearances in supercars, each time pushing the envelope of what's possible in automotive engineering. The Cizeta V16T of the early 1990s and the Bugatti Veyron of the 2000s are prime examples of how V16 engines continued to captivate enthusiasts and engineers alike.
The significance of V16 engines in supercar evolution extends beyond mere performance metrics. These engines have consistently represented the pinnacle of automotive engineering, serving as testbeds for cutting-edge technologies and manufacturing techniques. Their development has driven advancements in areas such as materials science, fuel efficiency, and power density.
Moreover, V16 engines have played a crucial role in shaping the image and aspirations of supercar brands. The complexity, rarity, and sheer audacity of producing a V16 engine have made them powerful marketing tools, elevating the status of the vehicles they power and the brands that create them.
As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, the role of V16 engines in supercars is evolving. While their future in production vehicles may be limited, the legacy of V16 engines continues to influence the design philosophy and engineering ambitions of modern supercars, inspiring manufacturers to push the boundaries of performance and innovation in new and exciting ways.
Supercar Market Trends
The supercar market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. The global supercar market size was valued at approximately $13.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $28.7 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period.
One of the key trends shaping the supercar market is the increasing demand for high-performance vehicles with advanced powertrain technologies. While traditional V8 and V12 engines have long been the staple of supercars, there is a growing interest in more exotic configurations, including V16 engines. These powerplants offer unparalleled performance and exclusivity, appealing to ultra-high-net-worth individuals seeking the pinnacle of automotive engineering.
The shift towards electrification is also having a profound impact on the supercar market. Many established manufacturers and new entrants are developing hybrid and all-electric supercars, combining cutting-edge battery technology with high-performance electric motors. This trend is driven by both environmental concerns and the potential for even greater performance capabilities offered by electric powertrains.
Geographical diversification is another notable trend in the supercar market. While traditional markets like Europe and North America remain strong, emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are becoming increasingly important. China, in particular, has seen a surge in demand for supercars, with sales growing at double-digit rates in recent years.
Customization and personalization have become crucial differentiators in the supercar market. Manufacturers are offering extensive bespoke options, allowing customers to create truly unique vehicles. This trend extends beyond aesthetics to include performance upgrades and limited-edition models, further driving up average transaction prices and profit margins.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and autonomous driving features, is also shaping the future of supercars. These innovations are not only enhancing performance and safety but also redefining the driving experience for supercar enthusiasts.
Despite the overall growth trajectory, the supercar market faces challenges, including stricter emissions regulations and the need for sustainable manufacturing practices. Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to address these issues while maintaining the high-performance characteristics that define the supercar segment.
One of the key trends shaping the supercar market is the increasing demand for high-performance vehicles with advanced powertrain technologies. While traditional V8 and V12 engines have long been the staple of supercars, there is a growing interest in more exotic configurations, including V16 engines. These powerplants offer unparalleled performance and exclusivity, appealing to ultra-high-net-worth individuals seeking the pinnacle of automotive engineering.
The shift towards electrification is also having a profound impact on the supercar market. Many established manufacturers and new entrants are developing hybrid and all-electric supercars, combining cutting-edge battery technology with high-performance electric motors. This trend is driven by both environmental concerns and the potential for even greater performance capabilities offered by electric powertrains.
Geographical diversification is another notable trend in the supercar market. While traditional markets like Europe and North America remain strong, emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are becoming increasingly important. China, in particular, has seen a surge in demand for supercars, with sales growing at double-digit rates in recent years.
Customization and personalization have become crucial differentiators in the supercar market. Manufacturers are offering extensive bespoke options, allowing customers to create truly unique vehicles. This trend extends beyond aesthetics to include performance upgrades and limited-edition models, further driving up average transaction prices and profit margins.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and autonomous driving features, is also shaping the future of supercars. These innovations are not only enhancing performance and safety but also redefining the driving experience for supercar enthusiasts.
Despite the overall growth trajectory, the supercar market faces challenges, including stricter emissions regulations and the need for sustainable manufacturing practices. Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to address these issues while maintaining the high-performance characteristics that define the supercar segment.
V16 Tech Challenges
The development of V16 engines for supercars has presented numerous technical challenges that have pushed the boundaries of automotive engineering. One of the primary obstacles has been the sheer size and weight of these engines, which can significantly impact vehicle dynamics and performance. Engineers have had to devise innovative solutions to integrate these massive powerplants into sleek, aerodynamic chassis designs without compromising handling or stability.
Thermal management has been another critical challenge in V16 engine development. The immense heat generated by 16 cylinders operating at high revolutions requires sophisticated cooling systems. This has led to the development of advanced radiator designs, oil coolers, and even active aerodynamic elements to manage airflow and heat dissipation effectively.
Fuel efficiency and emissions control have posed significant hurdles for V16 engines. The inherent thirst of these large-displacement powerplants has required the implementation of cutting-edge fuel injection systems and engine management technologies to optimize combustion and reduce fuel consumption. Additionally, meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations has necessitated the development of complex exhaust aftertreatment systems.
Balancing and vibration control have been ongoing challenges in V16 engine design. The long crankshaft and multiple firing events create substantial vibrations that can affect both engine longevity and passenger comfort. Engineers have had to employ advanced materials, precision manufacturing techniques, and innovative damping systems to mitigate these issues.
The complexity of V16 engines has also presented challenges in terms of reliability and maintenance. With a higher number of moving parts compared to smaller engines, ensuring long-term durability and ease of servicing has required meticulous engineering and the use of advanced materials and manufacturing processes.
Power delivery and drivability have been areas of focus in V16 engine development. Harnessing the immense power output of these engines while maintaining tractable performance across a wide range of operating conditions has necessitated the development of sophisticated transmission systems and electronic control units.
Lastly, the cost and complexity of manufacturing V16 engines have posed significant challenges for automakers. The specialized tooling, extensive research and development, and low production volumes associated with these engines have made them economically viable only for the most exclusive and high-end supercars.
Thermal management has been another critical challenge in V16 engine development. The immense heat generated by 16 cylinders operating at high revolutions requires sophisticated cooling systems. This has led to the development of advanced radiator designs, oil coolers, and even active aerodynamic elements to manage airflow and heat dissipation effectively.
Fuel efficiency and emissions control have posed significant hurdles for V16 engines. The inherent thirst of these large-displacement powerplants has required the implementation of cutting-edge fuel injection systems and engine management technologies to optimize combustion and reduce fuel consumption. Additionally, meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations has necessitated the development of complex exhaust aftertreatment systems.
Balancing and vibration control have been ongoing challenges in V16 engine design. The long crankshaft and multiple firing events create substantial vibrations that can affect both engine longevity and passenger comfort. Engineers have had to employ advanced materials, precision manufacturing techniques, and innovative damping systems to mitigate these issues.
The complexity of V16 engines has also presented challenges in terms of reliability and maintenance. With a higher number of moving parts compared to smaller engines, ensuring long-term durability and ease of servicing has required meticulous engineering and the use of advanced materials and manufacturing processes.
Power delivery and drivability have been areas of focus in V16 engine development. Harnessing the immense power output of these engines while maintaining tractable performance across a wide range of operating conditions has necessitated the development of sophisticated transmission systems and electronic control units.
Lastly, the cost and complexity of manufacturing V16 engines have posed significant challenges for automakers. The specialized tooling, extensive research and development, and low production volumes associated with these engines have made them economically viable only for the most exclusive and high-end supercars.
Current V16 Solutions
01 V16 engine design and configuration
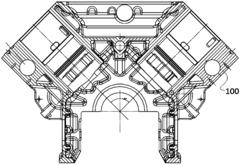
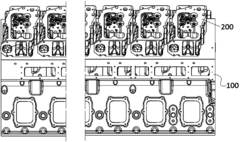
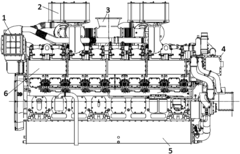
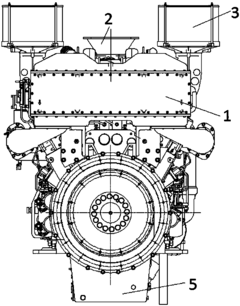
V16 engines are large, powerful internal combustion engines with 16 cylinders arranged in a V-shape. These engines are typically used in high-performance vehicles, marine applications, and industrial machinery. The V-configuration allows for a more compact design compared to inline engines with the same number of cylinders, while still providing significant power output.- V16 engine design and configuration: V16 engines are large, powerful internal combustion engines with 16 cylinders arranged in a V-shape. These engines are typically used in high-performance vehicles, marine applications, and industrial machinery. The V-configuration allows for a more compact design compared to inline engines, while still providing significant power output.
- V16 engine applications in vehicles: V16 engines are often utilized in luxury and high-performance automobiles, as well as in some specialized vehicles such as racing cars and concept vehicles. These engines provide exceptional power and torque, making them suitable for vehicles that require outstanding performance characteristics.
- Historical development of V16 engines: The development of V16 engines dates back to the early 20th century, with various designs and improvements made over time. These engines have been used in a range of applications, from aircraft to automobiles, and have played a significant role in the evolution of high-performance internal combustion engines.
- V16 engine control systems and optimization: Modern V16 engines incorporate advanced control systems and optimization techniques to improve performance, efficiency, and emissions. These may include electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and sophisticated engine management systems to ensure optimal operation across various operating conditions.
- V16 engine manufacturing and assembly: The production of V16 engines involves complex manufacturing and assembly processes due to their size and intricate design. Specialized tooling, precision machining, and quality control measures are essential to ensure the reliability and performance of these large engines.
02 V16 engine applications in vehicles
V16 engines are often employed in luxury and high-performance automobiles, as well as in some specialized vehicles such as military tanks and large trucks. These engines provide exceptional power and torque, making them suitable for applications requiring significant output and performance capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions03 V16 engine control systems
Modern V16 engines incorporate advanced control systems to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. These systems may include electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and sophisticated engine management computers to ensure smooth operation and maximum power output across various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Historical development of V16 engines
V16 engines have a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. They were initially developed for use in luxury automobiles and racing cars, with various manufacturers experimenting with different designs and configurations. Over time, V16 engines have evolved to incorporate new technologies and materials, improving their performance and reliability.Expand Specific Solutions05 V16 engine cooling and lubrication systems
Due to their large size and high power output, V16 engines require sophisticated cooling and lubrication systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent wear. These systems may include advanced oil pumps, multiple radiators, and carefully designed coolant passages to ensure efficient heat dissipation and proper lubrication of all moving parts.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V16 Manufacturers
The V16 engine's role in supercar evolution represents a niche but significant technological advancement in the automotive industry. Currently, the market for V16-powered supercars is limited, with only a few manufacturers exploring this technology. The development stage is still relatively early, with companies like Bugatti leading the way. The market size remains small due to the high costs and complexity associated with V16 engines. Technologically, V16 engines are at an advanced stage, offering exceptional power and performance. However, their practical application is limited by factors such as fuel efficiency and emissions regulations. Companies like Mitsubishi Motors, Honda, Toyota, and Renault are focusing on more mainstream engine configurations, while specialized manufacturers continue to push the boundaries of V16 technology in ultra-high-end supercars.
Renault SA
Technical Solution: While Renault has not been directly involved in V16 engine development for supercars, the company has made significant contributions to high-performance engine technology. Renault's expertise in Formula 1 racing, where they have used V6 turbo-hybrid engines, has provided valuable insights into creating powerful, efficient engines for road cars[3]. This knowledge has indirectly influenced the evolution of supercar engines. Renault's performance division, Renault Sport, has focused on developing high-output four-cylinder and V6 engines for their sports cars and hot hatches, emphasizing efficiency and power-to-weight ratio over cylinder count[4].
Strengths: Strong presence in motorsports, particularly Formula 1, which drives innovation in engine technology. Weaknesses: Limited direct experience with V16 engines or ultra-high-end supercars.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Technical Solution: Mercedes-Benz has been at the forefront of V16 engine development for supercars. Their most notable contribution is the Mercedes-Benz U80, a 7.7-liter V16 engine developed in the 1930s for the Auto Union racing cars[1]. This engine was capable of producing up to 520 horsepower, an extraordinary figure for its time. In modern times, Mercedes-Benz has continued to push the boundaries of engine technology, although they have focused more on V8 and V12 configurations for their high-performance models. The company's experience with V16 engines has informed their approach to developing powerful, efficient engines for their current lineup of supercars and high-performance vehicles[2].
Strengths: Extensive experience in high-performance engine development, strong brand recognition in the luxury and supercar markets. Weaknesses: Limited recent focus on V16 engines, as market trends have shifted towards smaller, more efficient powertrains.
V16 Innovations
V-engine for vehicle
PatentWO2003074852A1
Innovation
- The V-type engine design incorporates auxiliary machines and transmission means on both sides of the crankshaft, with a dry sump lubrication system and strategically positioned output shafts and valve drive shafts to adjust the engine's center of gravity closer to the vehicle's center, allowing for improved power transmission and reduced height, while balancing weights for enhanced stability.
High-power V16 diesel engine
PatentActiveCN108194198A
Innovation
- A high-power V-shaped 16-cylinder diesel engine is designed, which uses a V-shaped cylinder block, 16 single cylinder heads, four turbochargers and an intercooler, combined with a cooling system of high and low temperature water circulation loops, to achieve turbocharging through Technology and classified cooling systems increase air density and lower temperatures to meet the needs of high power and torque.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations have played a significant role in shaping the evolution of supercars, particularly in relation to V16 engines. As environmental concerns have grown over the past few decades, governments worldwide have implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards, directly impacting the development and use of high-performance engines like the V16.
The V16 engine, known for its impressive power output and smooth operation, has faced considerable challenges in meeting modern emissions requirements. These regulations typically focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as limiting the release of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter.
In the European Union, the introduction of Euro emissions standards has progressively tightened restrictions on vehicle emissions. The latest Euro 6 standard, implemented in 2014, has set particularly challenging targets for manufacturers. These regulations have forced supercar makers to reconsider their engine designs, often leading to a shift away from larger displacement engines like the V16 towards smaller, more efficient powerplants.
Similarly, in the United States, the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards have put pressure on automakers to improve fuel efficiency across their vehicle lineups. This has indirectly affected the viability of V16 engines in supercars, as manufacturers must balance the performance of their high-end models with the overall efficiency of their product range.
The impact of these regulations on V16 engines has been profound. Many supercar manufacturers have opted to downsize their engines, moving towards turbocharged V8 or even V6 configurations to meet emissions targets while maintaining high performance levels. This trend has led to the virtual disappearance of V16 engines from modern supercars, with only a handful of limited-production models featuring this engine configuration in recent years.
However, the push for cleaner emissions has also driven innovation in engine technology. Some manufacturers have explored hybrid powertrains as a way to combine high performance with improved efficiency. This approach allows for the potential retention of larger displacement engines, including V16s, by offsetting their emissions with electric power assistance.
Looking forward, the future of V16 engines in supercars remains uncertain. As emissions regulations continue to tighten, particularly with the growing focus on electric vehicles, the challenges facing large displacement engines will only increase. However, advancements in materials science and engine management systems may yet provide opportunities for V16 engines to comply with future emissions standards, potentially preserving their place in the supercar landscape.
The V16 engine, known for its impressive power output and smooth operation, has faced considerable challenges in meeting modern emissions requirements. These regulations typically focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as limiting the release of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter.
In the European Union, the introduction of Euro emissions standards has progressively tightened restrictions on vehicle emissions. The latest Euro 6 standard, implemented in 2014, has set particularly challenging targets for manufacturers. These regulations have forced supercar makers to reconsider their engine designs, often leading to a shift away from larger displacement engines like the V16 towards smaller, more efficient powerplants.
Similarly, in the United States, the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards have put pressure on automakers to improve fuel efficiency across their vehicle lineups. This has indirectly affected the viability of V16 engines in supercars, as manufacturers must balance the performance of their high-end models with the overall efficiency of their product range.
The impact of these regulations on V16 engines has been profound. Many supercar manufacturers have opted to downsize their engines, moving towards turbocharged V8 or even V6 configurations to meet emissions targets while maintaining high performance levels. This trend has led to the virtual disappearance of V16 engines from modern supercars, with only a handful of limited-production models featuring this engine configuration in recent years.
However, the push for cleaner emissions has also driven innovation in engine technology. Some manufacturers have explored hybrid powertrains as a way to combine high performance with improved efficiency. This approach allows for the potential retention of larger displacement engines, including V16s, by offsetting their emissions with electric power assistance.
Looking forward, the future of V16 engines in supercars remains uncertain. As emissions regulations continue to tighten, particularly with the growing focus on electric vehicles, the challenges facing large displacement engines will only increase. However, advancements in materials science and engine management systems may yet provide opportunities for V16 engines to comply with future emissions standards, potentially preserving their place in the supercar landscape.
V16 vs Alternatives
The V16 engine represents a pinnacle of automotive engineering, offering unparalleled power and prestige in the world of supercars. However, its significance can be best understood when compared to alternative engine configurations commonly used in high-performance vehicles.
V16 engines, with their 16 cylinders arranged in a V-formation, provide exceptional power output and smooth operation. They typically produce higher horsepower and torque figures than their smaller counterparts, making them ideal for supercars where performance is paramount. The V16 configuration also allows for a more balanced engine design, reducing vibration and enhancing overall refinement.
In contrast, V8 engines are more commonly found in supercars due to their balance of power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. While they may not match the raw power output of a V16, V8 engines offer excellent performance characteristics and are easier to package within a vehicle's chassis. Their widespread use has led to extensive development and optimization, making them a reliable choice for many manufacturers.
V10 engines occupy a middle ground between V8s and V12s, offering a unique combination of power and compact size. They have found favor in some supercar designs, providing a distinctive exhaust note and impressive performance figures. However, their relative rarity compared to V8s and V12s has limited their widespread adoption.
V12 engines are often considered the closest rivals to V16s in terms of prestige and performance. They offer a smoother power delivery than V8s and can produce substantial horsepower figures. V12s have been a staple in many iconic supercars, valued for their refined character and impressive output. However, they still fall short of the V16's ultimate power potential and exclusivity.
Alternatively, some supercar manufacturers have explored unconventional engine layouts, such as W12 or quad-turbo W16 configurations. These designs aim to combine high power output with more compact packaging, addressing some of the size and weight concerns associated with traditional V12 and V16 engines.
In recent years, hybrid and electric powertrains have emerged as significant alternatives in the supercar market. These technologies offer instant torque delivery and impressive acceleration figures, challenging traditional combustion engines in performance metrics. However, they currently lack the emotional appeal and distinctive character that V16 and other high-cylinder count engines provide.
While V16 engines undoubtedly offer unmatched power and prestige, their complexity, cost, and packaging challenges have limited their widespread adoption in supercars. As a result, manufacturers often opt for more practical alternatives that still deliver exceptional performance while meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations and efficiency requirements.
V16 engines, with their 16 cylinders arranged in a V-formation, provide exceptional power output and smooth operation. They typically produce higher horsepower and torque figures than their smaller counterparts, making them ideal for supercars where performance is paramount. The V16 configuration also allows for a more balanced engine design, reducing vibration and enhancing overall refinement.
In contrast, V8 engines are more commonly found in supercars due to their balance of power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. While they may not match the raw power output of a V16, V8 engines offer excellent performance characteristics and are easier to package within a vehicle's chassis. Their widespread use has led to extensive development and optimization, making them a reliable choice for many manufacturers.
V10 engines occupy a middle ground between V8s and V12s, offering a unique combination of power and compact size. They have found favor in some supercar designs, providing a distinctive exhaust note and impressive performance figures. However, their relative rarity compared to V8s and V12s has limited their widespread adoption.
V12 engines are often considered the closest rivals to V16s in terms of prestige and performance. They offer a smoother power delivery than V8s and can produce substantial horsepower figures. V12s have been a staple in many iconic supercars, valued for their refined character and impressive output. However, they still fall short of the V16's ultimate power potential and exclusivity.
Alternatively, some supercar manufacturers have explored unconventional engine layouts, such as W12 or quad-turbo W16 configurations. These designs aim to combine high power output with more compact packaging, addressing some of the size and weight concerns associated with traditional V12 and V16 engines.
In recent years, hybrid and electric powertrains have emerged as significant alternatives in the supercar market. These technologies offer instant torque delivery and impressive acceleration figures, challenging traditional combustion engines in performance metrics. However, they currently lack the emotional appeal and distinctive character that V16 and other high-cylinder count engines provide.
While V16 engines undoubtedly offer unmatched power and prestige, their complexity, cost, and packaging challenges have limited their widespread adoption in supercars. As a result, manufacturers often opt for more practical alternatives that still deliver exceptional performance while meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations and efficiency requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!