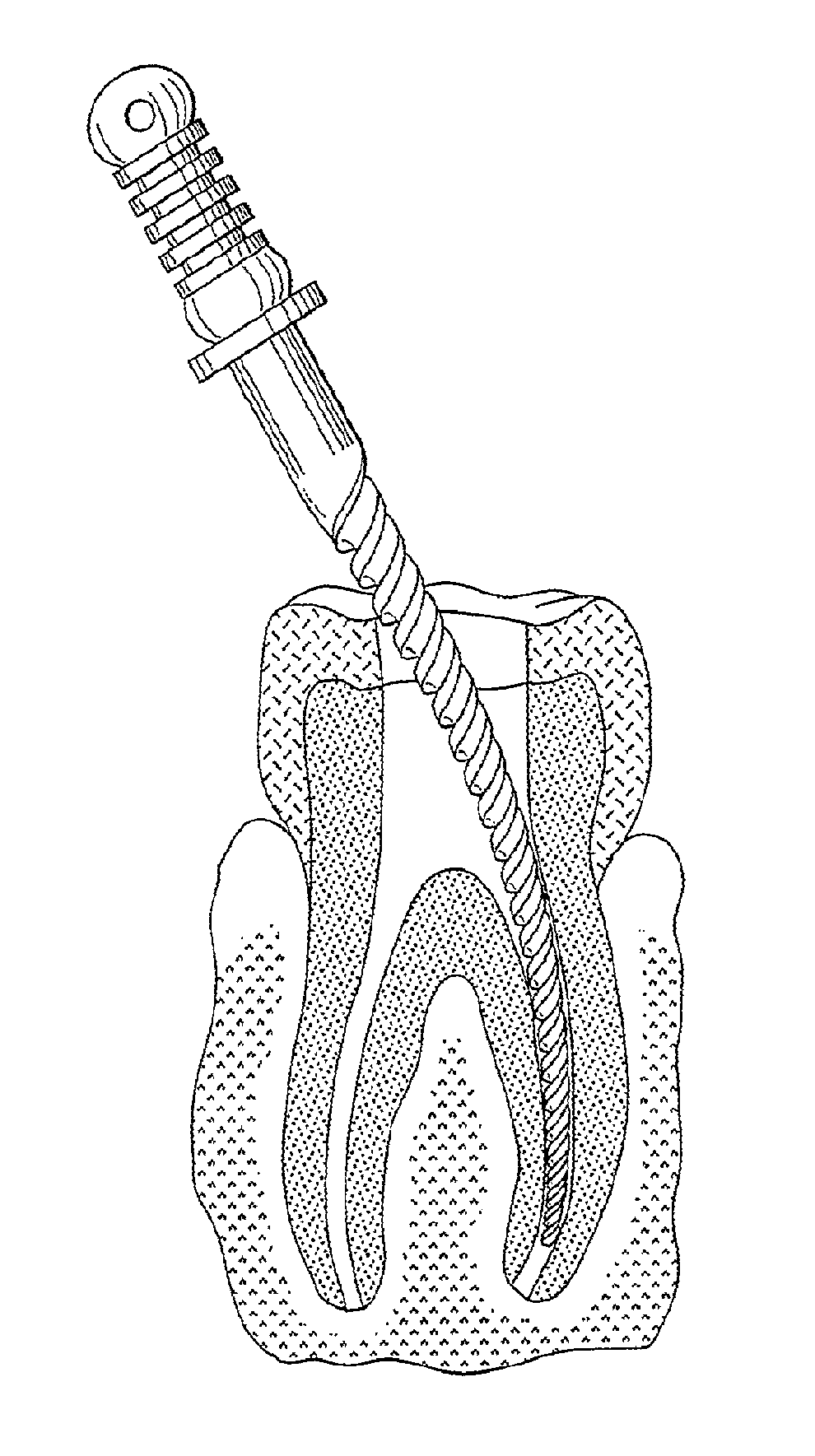
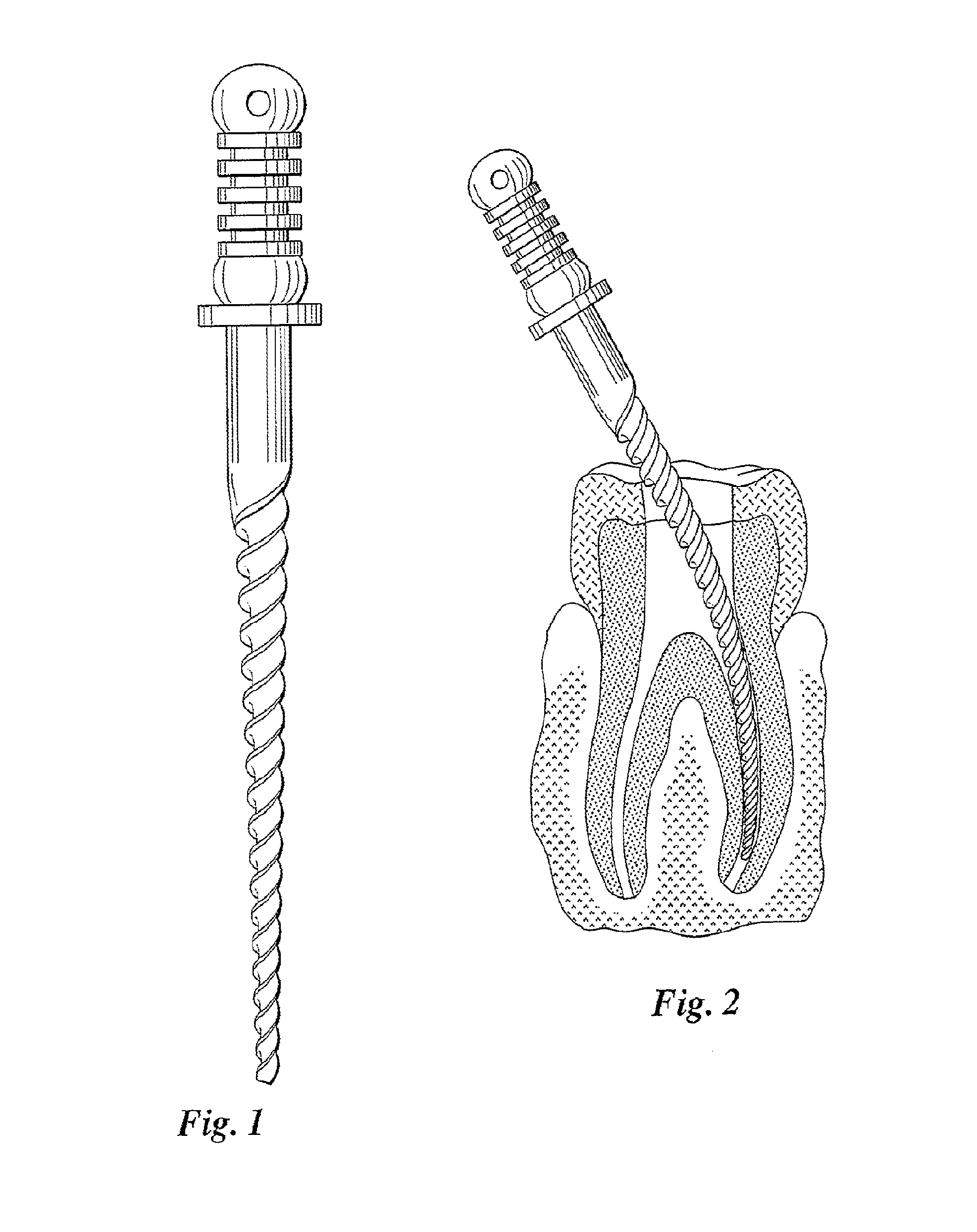
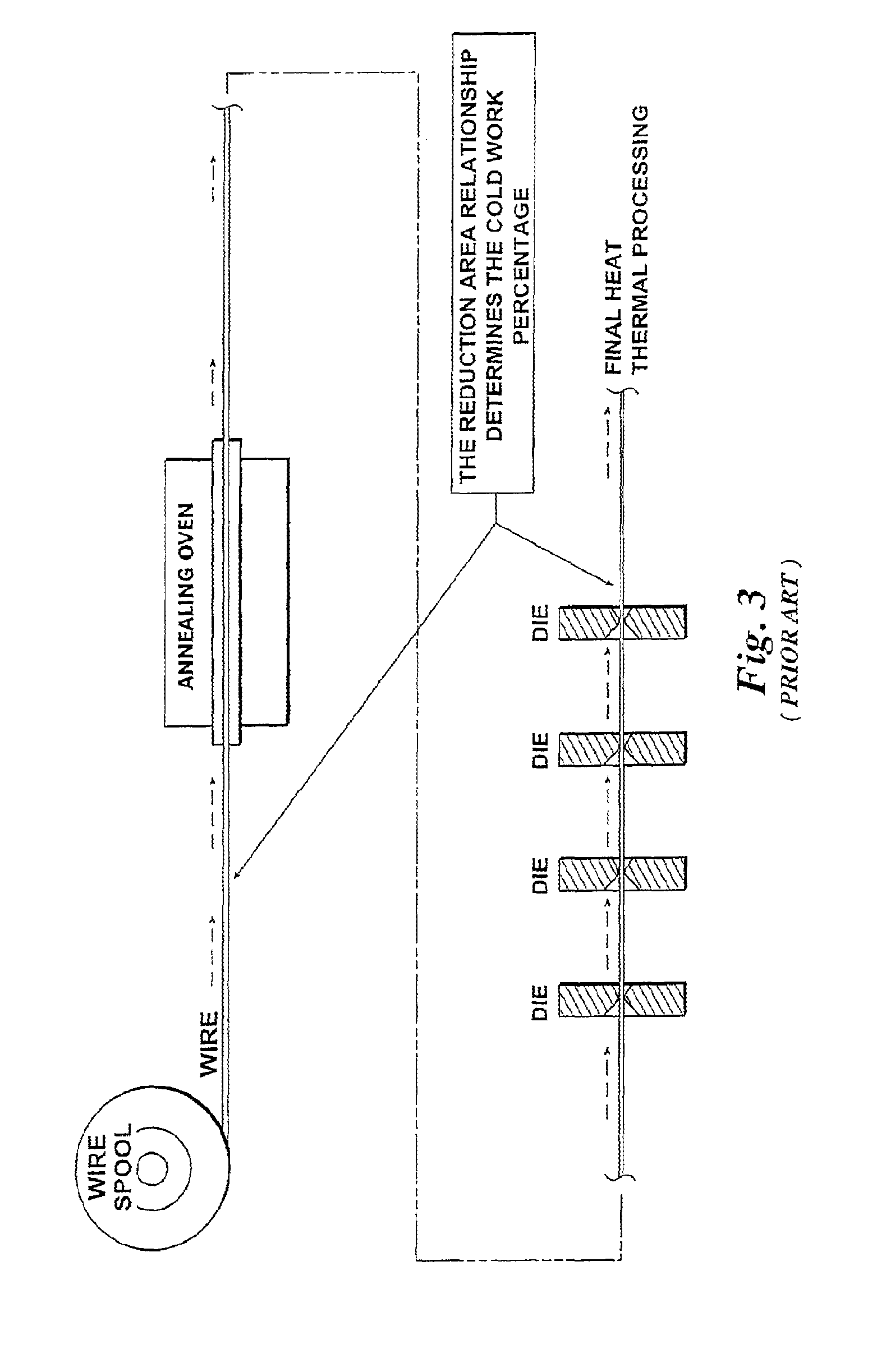
Effect of Annealing Temperature on Nitinol’s Recovery Stress
AUG 6, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol Annealing Background and Objectives
Nitinol, a remarkable shape memory alloy composed of nickel and titanium, has revolutionized various industries since its discovery in the 1960s. This unique material possesses the ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated, a property known as the shape memory effect. The annealing process plays a crucial role in determining the performance characteristics of Nitinol, particularly its recovery stress.
The evolution of Nitinol technology has been marked by continuous advancements in understanding and controlling its properties. Initially, the focus was on exploring the basic shape memory effect. However, as research progressed, the importance of heat treatment, especially annealing, in tailoring Nitinol's behavior became increasingly apparent.
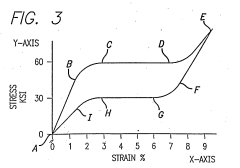
Annealing temperature has emerged as a critical parameter in optimizing Nitinol's recovery stress. This aspect of Nitinol processing has gained significant attention in recent years due to its profound impact on the material's functional properties. The relationship between annealing temperature and recovery stress is complex, involving intricate changes in the material's microstructure and phase transformation characteristics.
The primary objective of investigating the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is to enhance the material's performance in various applications. This research aims to establish a comprehensive understanding of how different annealing temperatures influence the recovery stress, thereby enabling more precise control over Nitinol's behavior in specific use cases.
Furthermore, this study seeks to identify optimal annealing conditions that maximize recovery stress for different Nitinol compositions and applications. By doing so, it addresses the growing demand for Nitinol-based devices with improved reliability and functionality in fields such as medical devices, aerospace, and robotics.
Another key goal is to develop predictive models that correlate annealing temperature with recovery stress. Such models would significantly streamline the design and manufacturing processes for Nitinol components, reducing development time and costs while improving product performance.
The research also aims to explore the potential for expanding Nitinol's application range by fine-tuning its recovery stress through annealing. This could open up new possibilities in emerging technologies and industries where precise control of shape memory properties is crucial.
Ultimately, this investigation into the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is expected to contribute to the broader understanding of shape memory alloys and their processing. The insights gained from this research will not only advance Nitinol technology but also potentially inspire innovations in the development of other smart materials.
The evolution of Nitinol technology has been marked by continuous advancements in understanding and controlling its properties. Initially, the focus was on exploring the basic shape memory effect. However, as research progressed, the importance of heat treatment, especially annealing, in tailoring Nitinol's behavior became increasingly apparent.
Annealing temperature has emerged as a critical parameter in optimizing Nitinol's recovery stress. This aspect of Nitinol processing has gained significant attention in recent years due to its profound impact on the material's functional properties. The relationship between annealing temperature and recovery stress is complex, involving intricate changes in the material's microstructure and phase transformation characteristics.
The primary objective of investigating the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is to enhance the material's performance in various applications. This research aims to establish a comprehensive understanding of how different annealing temperatures influence the recovery stress, thereby enabling more precise control over Nitinol's behavior in specific use cases.
Furthermore, this study seeks to identify optimal annealing conditions that maximize recovery stress for different Nitinol compositions and applications. By doing so, it addresses the growing demand for Nitinol-based devices with improved reliability and functionality in fields such as medical devices, aerospace, and robotics.
Another key goal is to develop predictive models that correlate annealing temperature with recovery stress. Such models would significantly streamline the design and manufacturing processes for Nitinol components, reducing development time and costs while improving product performance.
The research also aims to explore the potential for expanding Nitinol's application range by fine-tuning its recovery stress through annealing. This could open up new possibilities in emerging technologies and industries where precise control of shape memory properties is crucial.
Ultimately, this investigation into the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is expected to contribute to the broader understanding of shape memory alloys and their processing. The insights gained from this research will not only advance Nitinol technology but also potentially inspire innovations in the development of other smart materials.
Market Demand for Nitinol Shape Memory Alloys
The market demand for Nitinol shape memory alloys has been steadily growing across various industries due to their unique properties, particularly their shape memory effect and superelasticity. These characteristics make Nitinol an attractive material for a wide range of applications, from medical devices to aerospace components.
In the medical field, Nitinol has seen significant adoption in the production of stents, guidewires, and orthodontic archwires. The biocompatibility and ability to conform to body temperature have made it a preferred choice for minimally invasive surgical procedures. The global market for Nitinol medical devices is experiencing robust growth, driven by an aging population and increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases.
The aerospace industry has also recognized the potential of Nitinol alloys. Their high fatigue resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make them suitable for aircraft components and actuators. As the demand for more fuel-efficient and lightweight aircraft increases, the market for Nitinol in aerospace applications is expected to expand.
Consumer electronics represent another growing market for Nitinol. The material's flexibility and durability make it ideal for smartphone antennas, eyeglass frames, and other wearable devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, the demand for Nitinol in smart devices is likely to surge.
The automotive sector is exploring Nitinol for applications such as self-repairing car bodies and adaptive headlight systems. While still in early stages, this market segment shows promise for future growth as automakers seek innovative materials to enhance vehicle performance and safety.
Industrial applications of Nitinol, including pipe couplings, seals, and actuators, are also on the rise. The material's resistance to corrosion and ability to operate in harsh environments make it valuable in oil and gas, chemical processing, and robotics industries.
The global Nitinol market is influenced by factors such as raw material availability, manufacturing costs, and regulatory approvals, particularly in medical applications. As research continues to optimize Nitinol's properties, including its recovery stress characteristics, new market opportunities are likely to emerge.
Understanding the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is crucial for expanding its applications and meeting specific market demands. Improved control over recovery stress could lead to more precise and efficient devices across various industries, potentially opening up new market segments and driving further demand for Nitinol shape memory alloys.
In the medical field, Nitinol has seen significant adoption in the production of stents, guidewires, and orthodontic archwires. The biocompatibility and ability to conform to body temperature have made it a preferred choice for minimally invasive surgical procedures. The global market for Nitinol medical devices is experiencing robust growth, driven by an aging population and increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases.
The aerospace industry has also recognized the potential of Nitinol alloys. Their high fatigue resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make them suitable for aircraft components and actuators. As the demand for more fuel-efficient and lightweight aircraft increases, the market for Nitinol in aerospace applications is expected to expand.
Consumer electronics represent another growing market for Nitinol. The material's flexibility and durability make it ideal for smartphone antennas, eyeglass frames, and other wearable devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, the demand for Nitinol in smart devices is likely to surge.
The automotive sector is exploring Nitinol for applications such as self-repairing car bodies and adaptive headlight systems. While still in early stages, this market segment shows promise for future growth as automakers seek innovative materials to enhance vehicle performance and safety.
Industrial applications of Nitinol, including pipe couplings, seals, and actuators, are also on the rise. The material's resistance to corrosion and ability to operate in harsh environments make it valuable in oil and gas, chemical processing, and robotics industries.
The global Nitinol market is influenced by factors such as raw material availability, manufacturing costs, and regulatory approvals, particularly in medical applications. As research continues to optimize Nitinol's properties, including its recovery stress characteristics, new market opportunities are likely to emerge.
Understanding the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is crucial for expanding its applications and meeting specific market demands. Improved control over recovery stress could lead to more precise and efficient devices across various industries, potentially opening up new market segments and driving further demand for Nitinol shape memory alloys.
Current Challenges in Nitinol Annealing Processes
The annealing process of Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, plays a crucial role in determining its recovery stress properties. However, several challenges persist in optimizing this process, particularly in relation to temperature control and its effects on the material's performance.
One of the primary challenges is achieving precise and uniform temperature distribution during the annealing process. Nitinol's shape memory and superelastic properties are highly sensitive to temperature variations, and even small fluctuations can lead to inconsistent recovery stress across the material. This non-uniformity can result in unpredictable behavior and reduced reliability in applications where precise control of recovery stress is essential.
Another significant challenge lies in determining the optimal annealing temperature for specific Nitinol compositions. The relationship between annealing temperature and recovery stress is complex and can vary depending on factors such as the alloy's composition, prior processing history, and intended application. Finding the ideal temperature range that maximizes recovery stress while maintaining other desirable properties requires extensive experimentation and characterization.
The time-temperature relationship during annealing also presents challenges. The duration of exposure to elevated temperatures can significantly impact the material's microstructure and, consequently, its recovery stress. Balancing the annealing time with the desired temperature to achieve optimal results is a delicate process that requires careful control and monitoring.
Furthermore, the cooling rate following the annealing process can greatly influence the final properties of Nitinol. Rapid cooling may lead to residual stresses and undesired phase transformations, while slow cooling might result in excessive grain growth. Both scenarios can adversely affect the recovery stress characteristics of the material.
The scalability of annealing processes from laboratory to industrial production levels poses another challenge. Maintaining consistent temperature profiles and uniform heat distribution in larger batches or continuous production settings is technically demanding and often requires specialized equipment and process controls.
Lastly, the environmental impact and energy efficiency of high-temperature annealing processes are growing concerns. Developing more sustainable annealing methods that reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving the recovery stress properties of Nitinol is an ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining materials science, process engineering, and advanced characterization techniques. Innovations in temperature control systems, in-situ monitoring technologies, and computational modeling of annealing processes are some of the areas where advancements could lead to significant improvements in Nitinol's recovery stress optimization through annealing.
One of the primary challenges is achieving precise and uniform temperature distribution during the annealing process. Nitinol's shape memory and superelastic properties are highly sensitive to temperature variations, and even small fluctuations can lead to inconsistent recovery stress across the material. This non-uniformity can result in unpredictable behavior and reduced reliability in applications where precise control of recovery stress is essential.
Another significant challenge lies in determining the optimal annealing temperature for specific Nitinol compositions. The relationship between annealing temperature and recovery stress is complex and can vary depending on factors such as the alloy's composition, prior processing history, and intended application. Finding the ideal temperature range that maximizes recovery stress while maintaining other desirable properties requires extensive experimentation and characterization.
The time-temperature relationship during annealing also presents challenges. The duration of exposure to elevated temperatures can significantly impact the material's microstructure and, consequently, its recovery stress. Balancing the annealing time with the desired temperature to achieve optimal results is a delicate process that requires careful control and monitoring.
Furthermore, the cooling rate following the annealing process can greatly influence the final properties of Nitinol. Rapid cooling may lead to residual stresses and undesired phase transformations, while slow cooling might result in excessive grain growth. Both scenarios can adversely affect the recovery stress characteristics of the material.
The scalability of annealing processes from laboratory to industrial production levels poses another challenge. Maintaining consistent temperature profiles and uniform heat distribution in larger batches or continuous production settings is technically demanding and often requires specialized equipment and process controls.
Lastly, the environmental impact and energy efficiency of high-temperature annealing processes are growing concerns. Developing more sustainable annealing methods that reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving the recovery stress properties of Nitinol is an ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining materials science, process engineering, and advanced characterization techniques. Innovations in temperature control systems, in-situ monitoring technologies, and computational modeling of annealing processes are some of the areas where advancements could lead to significant improvements in Nitinol's recovery stress optimization through annealing.
Existing Annealing Methods for Nitinol
01 Nitinol recovery stress in medical devices
Nitinol's recovery stress is utilized in various medical devices, particularly in stents and implants. The shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol allow these devices to be compressed for insertion and then expand to their predetermined shape when deployed in the body. This recovery stress enables the devices to maintain their position and function effectively.- Nitinol shape memory and superelasticity: Nitinol exhibits unique shape memory and superelastic properties, allowing it to recover its original shape after deformation. This recovery stress is utilized in various applications, including medical devices and actuators. The material's ability to generate significant forces during shape recovery makes it valuable for creating compact and efficient mechanisms.
- Temperature-induced phase transformation: The recovery stress in Nitinol is closely related to its temperature-induced phase transformation. As the material transitions between its martensite and austenite phases, it generates substantial forces. This phenomenon is exploited in applications such as thermal actuators and temperature-responsive devices, where precise control of the transformation temperature is crucial.
- Stress-induced martensite formation: Nitinol's recovery stress can also be induced through mechanical loading, leading to stress-induced martensite formation. This property is particularly useful in applications requiring reversible deformation and energy absorption, such as in vibration damping systems and impact-resistant structures. The material's ability to undergo large deformations and return to its original shape makes it ideal for these purposes.
- Optimization of Nitinol properties: Researchers and engineers focus on optimizing Nitinol's properties to enhance its recovery stress characteristics. This includes adjusting the alloy composition, heat treatment processes, and microstructure to tailor the material's behavior for specific applications. Advanced manufacturing techniques and surface treatments are also employed to improve the material's performance and durability.
- Applications in medical devices: Nitinol's recovery stress is extensively utilized in medical devices, particularly in minimally invasive procedures. The material's ability to change shape and exert controlled forces within the body makes it ideal for stents, guidewires, and other implantable devices. Its biocompatibility and fatigue resistance further contribute to its widespread use in the medical field.
02 Actuators and mechanical systems using Nitinol recovery stress
The recovery stress of Nitinol is harnessed in actuators and mechanical systems. These applications utilize the material's ability to generate significant force upon shape recovery, enabling the creation of compact and efficient actuators for various industrial and robotic applications. The stress generated during the shape memory effect can be used to perform mechanical work.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management and energy harvesting applications
Nitinol's recovery stress is exploited in thermal management systems and energy harvesting devices. The material's ability to undergo stress changes in response to temperature variations allows for the development of thermally activated switches, heat engines, and energy conversion systems that can capture and utilize waste heat.Expand Specific Solutions04 Structural applications and civil engineering
The recovery stress of Nitinol is utilized in structural applications and civil engineering projects. The material's ability to generate significant forces upon activation makes it suitable for use in vibration damping systems, seismic protection devices, and self-repairing structures. These applications leverage Nitinol's unique properties to enhance the resilience and adaptability of built structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Characterization and modeling of Nitinol recovery stress
Research focuses on characterizing and modeling the recovery stress behavior of Nitinol. This includes developing methods to measure and predict the stress-strain relationships, phase transformation characteristics, and fatigue properties of Nitinol under various conditions. Advanced modeling techniques are employed to simulate and optimize the performance of Nitinol-based devices and systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol Manufacturing Industry
The competitive landscape for research on the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's recovery stress is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing innovation. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for shape memory alloys in various sectors, including medical devices, aerospace, and automotive. Key players like W. L. Gore & Associates, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic are leading the research efforts, leveraging their extensive experience in materials science and medical applications. Smaller companies and research institutions, such as EndoSpan and the University of Connecticut, are also contributing to advancements in this field. The technology's maturity level is moderate, with ongoing research focused on optimizing Nitinol's properties for specific applications.
W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.
Technical Solution: W. L. Gore & Associates has developed a unique approach to annealing Nitinol that focuses on creating a gradient of properties within a single component. Their process involves selective annealing of different regions of a Nitinol wire or sheet at varying temperatures, typically ranging from 400°C to 600°C[7]. This technique allows for the creation of Nitinol components with different recovery stress levels in different areas, which is particularly useful in complex medical devices such as endovascular grafts. Gore has also explored the use of rapid thermal annealing techniques to reduce processing time while maintaining precise control over the material's properties[8]. Their research has shown that annealing temperatures around 500°C for short durations (1-5 minutes) can produce Nitinol with high recovery stress without compromising its superelastic properties[9].
Strengths: Ability to create components with varying properties, potential for faster processing times. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for precise temperature control across different regions.
Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials
Technical Solution: The Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials has developed a novel approach to annealing Nitinol that focuses on optimizing both recovery stress and fatigue resistance. Their method involves a two-step annealing process: an initial high-temperature anneal (700-800°C) followed by a lower temperature anneal (400-450°C)[13]. This process is designed to create a fine distribution of Ti3Ni4 precipitates while maintaining a relatively low dislocation density. The institute has applied this technique to develop Nitinol-based actuators for aerospace applications, where high recovery stress and long-term stability are crucial. Their research has shown that this annealing process can increase the recovery stress by up to 20% compared to conventional single-step annealing methods[14]. Additionally, they have explored the use of magnetic field-assisted annealing to further enhance the uniformity of precipitate distribution and improve the material's overall performance[15].
Strengths: High recovery stress achieved, potential applications in demanding aerospace environments. Weaknesses: Two-step process may be more time-consuming and energy-intensive than single-step methods.
Core Innovations in Nitinol Heat Treatment
Fatigue-Resistant Nitinol Instrument
PatentActiveUS20140242543A1
Innovation
- A nickel-titanium alloy is processed to achieve an austenite finish temperature of 40° to 60° C by subjecting it to a final thermal heat treat in the range of 410 to 440° C under constant strain, eliminating the need for thermal cycling and reducing shape memory properties, thus maintaining the martensitic state during use and enhancing fatigue resistance.
Nitinol alloy for with good mechanical stability and a good superelastic operating window
PatentWO2006081011A2
Innovation
- A nickel-titanium alloy with a ternary element such as platinum or palladium is used to enhance radiopacity while maintaining superelastic properties, allowing for a thinner strut design that maintains flexibility and mechanical stability.
Regulatory Standards for Nitinol Medical Devices
Regulatory standards for Nitinol medical devices are crucial in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these innovative products. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in establishing and enforcing these standards. For Nitinol-based devices, the FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and long-term stability of the material.
One of the key regulatory considerations is the fatigue resistance of Nitinol components. Given the unique shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol, which are influenced by annealing temperature, manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the material's fatigue behavior under various loading conditions. This includes cyclic loading tests that simulate physiological conditions and accelerated aging studies to predict long-term performance.
The FDA also mandates stringent testing for nickel ion release, as Nitinol contains a significant amount of nickel. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their devices do not release harmful levels of nickel ions over time, which could potentially cause allergic reactions or other adverse effects in patients. This requirement is particularly relevant when considering the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's surface properties and corrosion resistance.
Another critical regulatory aspect is the control and validation of the manufacturing process. The FDA requires detailed documentation of the heat treatment procedures, including precise control of annealing temperatures. This is essential because the annealing temperature directly affects Nitinol's recovery stress and, consequently, its performance in medical applications. Manufacturers must establish and validate process parameters that consistently produce Nitinol components with the desired mechanical properties and transformation temperatures.
Furthermore, regulatory standards address the need for non-destructive testing methods to ensure the quality and consistency of Nitinol components. These may include techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to verify transformation temperatures, and X-ray diffraction to assess material composition and crystalline structure. Such methods are crucial for detecting any variations in material properties that may result from inconsistencies in the annealing process.
The FDA also requires manufacturers to implement robust quality management systems that encompass all aspects of Nitinol device production, from raw material sourcing to final product testing. This includes maintaining detailed records of material processing parameters, including annealing temperatures, and establishing traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
In addition to FDA regulations, international standards such as ISO 13485 for medical device quality management systems and ASTM F2063 for wrought Nickel-Titanium shape memory alloys for medical devices and surgical implants provide further guidance for manufacturers. These standards help ensure global consistency in the quality and performance of Nitinol medical devices, facilitating international market access and regulatory compliance.
One of the key regulatory considerations is the fatigue resistance of Nitinol components. Given the unique shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol, which are influenced by annealing temperature, manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on the material's fatigue behavior under various loading conditions. This includes cyclic loading tests that simulate physiological conditions and accelerated aging studies to predict long-term performance.
The FDA also mandates stringent testing for nickel ion release, as Nitinol contains a significant amount of nickel. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their devices do not release harmful levels of nickel ions over time, which could potentially cause allergic reactions or other adverse effects in patients. This requirement is particularly relevant when considering the effect of annealing temperature on Nitinol's surface properties and corrosion resistance.
Another critical regulatory aspect is the control and validation of the manufacturing process. The FDA requires detailed documentation of the heat treatment procedures, including precise control of annealing temperatures. This is essential because the annealing temperature directly affects Nitinol's recovery stress and, consequently, its performance in medical applications. Manufacturers must establish and validate process parameters that consistently produce Nitinol components with the desired mechanical properties and transformation temperatures.
Furthermore, regulatory standards address the need for non-destructive testing methods to ensure the quality and consistency of Nitinol components. These may include techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to verify transformation temperatures, and X-ray diffraction to assess material composition and crystalline structure. Such methods are crucial for detecting any variations in material properties that may result from inconsistencies in the annealing process.
The FDA also requires manufacturers to implement robust quality management systems that encompass all aspects of Nitinol device production, from raw material sourcing to final product testing. This includes maintaining detailed records of material processing parameters, including annealing temperatures, and establishing traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
In addition to FDA regulations, international standards such as ISO 13485 for medical device quality management systems and ASTM F2063 for wrought Nickel-Titanium shape memory alloys for medical devices and surgical implants provide further guidance for manufacturers. These standards help ensure global consistency in the quality and performance of Nitinol medical devices, facilitating international market access and regulatory compliance.
Environmental Impact of Nitinol Production
The production of Nitinol, a shape memory alloy composed of nickel and titanium, has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive steps and the use of potentially hazardous materials, which can contribute to various environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental impacts of Nitinol production is the high energy consumption required for its manufacture. The melting and alloying of nickel and titanium typically occur in vacuum arc remelting furnaces, which demand substantial electrical power. This energy-intensive process contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly in regions where electricity generation relies heavily on fossil fuels.
The extraction and processing of raw materials, namely nickel and titanium, also pose environmental challenges. Mining operations for these metals can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The refining processes for both metals involve chemical treatments and high-temperature operations, further adding to the environmental footprint through emissions and waste generation.
Water usage is another significant factor in Nitinol production. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of water for cooling and cleaning purposes. This can strain local water resources, especially in water-scarce regions. Additionally, the wastewater generated during production may contain metal particles and chemical residues, necessitating proper treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution.
The use of chemicals in various stages of Nitinol production, including surface treatments and etching processes, introduces potential risks of chemical spills and emissions. These substances, if not properly managed, can contaminate soil and water sources, posing threats to local ecosystems and human health.
Waste management is a critical aspect of Nitinol production's environmental impact. Metal scraps, slag, and other byproducts generated during manufacturing require proper disposal or recycling. Improper handling of these wastes can lead to soil contamination and potential leaching of heavy metals into groundwater.
On a positive note, the unique properties of Nitinol, particularly its shape memory and superelasticity, contribute to its longevity and potential for reuse in various applications. This durability can offset some of the environmental costs associated with its production by reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing overall material consumption in certain industries.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of Nitinol production. These include developing more energy-efficient manufacturing processes, implementing closed-loop water systems to reduce water consumption, and improving waste recycling techniques. Additionally, research into alternative production methods and more environmentally friendly alloy compositions is ongoing, aiming to create a more sustainable future for shape memory alloys.
One of the primary environmental impacts of Nitinol production is the high energy consumption required for its manufacture. The melting and alloying of nickel and titanium typically occur in vacuum arc remelting furnaces, which demand substantial electrical power. This energy-intensive process contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly in regions where electricity generation relies heavily on fossil fuels.
The extraction and processing of raw materials, namely nickel and titanium, also pose environmental challenges. Mining operations for these metals can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The refining processes for both metals involve chemical treatments and high-temperature operations, further adding to the environmental footprint through emissions and waste generation.
Water usage is another significant factor in Nitinol production. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of water for cooling and cleaning purposes. This can strain local water resources, especially in water-scarce regions. Additionally, the wastewater generated during production may contain metal particles and chemical residues, necessitating proper treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution.
The use of chemicals in various stages of Nitinol production, including surface treatments and etching processes, introduces potential risks of chemical spills and emissions. These substances, if not properly managed, can contaminate soil and water sources, posing threats to local ecosystems and human health.
Waste management is a critical aspect of Nitinol production's environmental impact. Metal scraps, slag, and other byproducts generated during manufacturing require proper disposal or recycling. Improper handling of these wastes can lead to soil contamination and potential leaching of heavy metals into groundwater.
On a positive note, the unique properties of Nitinol, particularly its shape memory and superelasticity, contribute to its longevity and potential for reuse in various applications. This durability can offset some of the environmental costs associated with its production by reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing overall material consumption in certain industries.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impact of Nitinol production. These include developing more energy-efficient manufacturing processes, implementing closed-loop water systems to reduce water consumption, and improving waste recycling techniques. Additionally, research into alternative production methods and more environmentally friendly alloy compositions is ongoing, aiming to create a more sustainable future for shape memory alloys.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!