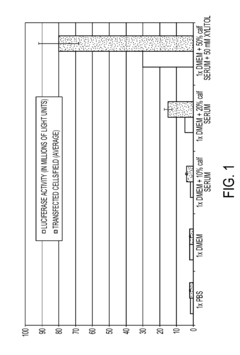
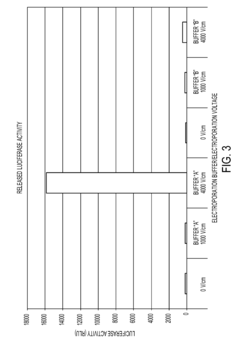
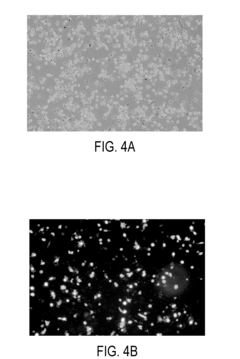
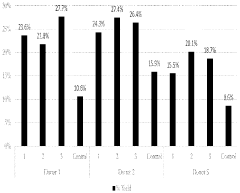
Electroporation Buffer Composition: Ion Strength And Conductivity Tests
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Buffer Evolution and Objectives
Electroporation, a technique for introducing molecules into cells through temporary pores in the cell membrane, has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s. The composition of electroporation buffers has played a crucial role in this evolution, with ion strength and conductivity emerging as key factors influencing the efficiency and safety of the process.
Initially, simple saline solutions were used as electroporation buffers. However, researchers quickly realized that the ionic composition of the buffer significantly impacted the success rate of molecule delivery and cell viability. This led to the development of more sophisticated buffer formulations, tailored to specific cell types and applications.
The 1980s saw a surge in electroporation research, with scientists exploring various buffer compositions to optimize the process. The focus shifted towards understanding how ion strength and conductivity affected the formation of membrane pores and the subsequent entry of molecules into cells. This period marked the beginning of systematic studies on the relationship between buffer properties and electroporation outcomes.
By the 1990s, researchers had established that low-conductivity buffers generally yielded better results in terms of cell survival and transfection efficiency. This discovery led to the widespread adoption of buffers with reduced ion concentrations, often supplemented with non-ionic components to maintain osmolarity.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era of precision in electroporation buffer design. Advanced analytical techniques allowed for more accurate measurements of ion strength and conductivity, enabling researchers to fine-tune buffer compositions for specific applications. This period also saw the development of commercial electroporation buffers, each optimized for particular cell types or molecular cargoes.
Current research objectives in the field of electroporation buffer composition focus on several key areas. First, there is a push towards developing universal buffers that can maintain high efficiency across a wide range of cell types and molecules. Second, researchers are exploring the use of novel ionic and non-ionic components to enhance membrane permeability while minimizing cellular stress.
Another important objective is the development of buffers that can facilitate the delivery of larger molecules, such as proteins and nanoparticles, which have traditionally been challenging to introduce via electroporation. This involves careful manipulation of ion strength and conductivity to create optimal pore sizes and durations.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in creating "smart" electroporation buffers that can adapt to changing conditions during the electroporation process. These buffers would ideally be able to modulate their conductivity in response to the applied electric field, potentially improving both efficiency and cell viability.
Initially, simple saline solutions were used as electroporation buffers. However, researchers quickly realized that the ionic composition of the buffer significantly impacted the success rate of molecule delivery and cell viability. This led to the development of more sophisticated buffer formulations, tailored to specific cell types and applications.
The 1980s saw a surge in electroporation research, with scientists exploring various buffer compositions to optimize the process. The focus shifted towards understanding how ion strength and conductivity affected the formation of membrane pores and the subsequent entry of molecules into cells. This period marked the beginning of systematic studies on the relationship between buffer properties and electroporation outcomes.
By the 1990s, researchers had established that low-conductivity buffers generally yielded better results in terms of cell survival and transfection efficiency. This discovery led to the widespread adoption of buffers with reduced ion concentrations, often supplemented with non-ionic components to maintain osmolarity.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era of precision in electroporation buffer design. Advanced analytical techniques allowed for more accurate measurements of ion strength and conductivity, enabling researchers to fine-tune buffer compositions for specific applications. This period also saw the development of commercial electroporation buffers, each optimized for particular cell types or molecular cargoes.
Current research objectives in the field of electroporation buffer composition focus on several key areas. First, there is a push towards developing universal buffers that can maintain high efficiency across a wide range of cell types and molecules. Second, researchers are exploring the use of novel ionic and non-ionic components to enhance membrane permeability while minimizing cellular stress.
Another important objective is the development of buffers that can facilitate the delivery of larger molecules, such as proteins and nanoparticles, which have traditionally been challenging to introduce via electroporation. This involves careful manipulation of ion strength and conductivity to create optimal pore sizes and durations.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in creating "smart" electroporation buffers that can adapt to changing conditions during the electroporation process. These buffers would ideally be able to modulate their conductivity in response to the applied electric field, potentially improving both efficiency and cell viability.
Market Analysis for Electroporation Applications
The electroporation market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing applications in biotechnology, medicine, and research. The global electroporation market size was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $5.7 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.
The market for electroporation applications can be segmented into several key areas. Gene therapy and DNA vaccination represent the largest segment, accounting for about 40% of the market share. This segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the rising prevalence of genetic disorders and the increasing focus on personalized medicine.
Cell-based therapies, including CAR-T cell therapy and stem cell research, form the second-largest segment, contributing around 30% of the market share. The growing interest in regenerative medicine and the development of novel cell therapies are driving this segment's growth.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry is another significant market segment, utilizing electroporation for drug discovery and development processes. This segment accounts for approximately 20% of the market share and is expected to grow steadily due to the increasing demand for new and effective therapeutics.
Academic and research institutions constitute the remaining 10% of the market, primarily using electroporation for various scientific studies and experiments. This segment is characterized by a high demand for innovative electroporation technologies and customizable solutions.
Geographically, North America dominates the electroporation market, holding about 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, substantial research funding, and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Europe follows closely, accounting for approximately 30% of the market share, driven by increasing investments in gene therapy research and a strong focus on precision medicine.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of 10.5%. This growth is fueled by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising awareness about genetic disorders, and growing research activities in countries like China, Japan, and India.
Key market trends include the development of more efficient and specialized electroporation buffers, the integration of electroporation with other technologies such as microfluidics, and the increasing adoption of electroporation in agricultural biotechnology for crop improvement.
The market for electroporation applications can be segmented into several key areas. Gene therapy and DNA vaccination represent the largest segment, accounting for about 40% of the market share. This segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the rising prevalence of genetic disorders and the increasing focus on personalized medicine.
Cell-based therapies, including CAR-T cell therapy and stem cell research, form the second-largest segment, contributing around 30% of the market share. The growing interest in regenerative medicine and the development of novel cell therapies are driving this segment's growth.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry is another significant market segment, utilizing electroporation for drug discovery and development processes. This segment accounts for approximately 20% of the market share and is expected to grow steadily due to the increasing demand for new and effective therapeutics.
Academic and research institutions constitute the remaining 10% of the market, primarily using electroporation for various scientific studies and experiments. This segment is characterized by a high demand for innovative electroporation technologies and customizable solutions.
Geographically, North America dominates the electroporation market, holding about 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, substantial research funding, and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Europe follows closely, accounting for approximately 30% of the market share, driven by increasing investments in gene therapy research and a strong focus on precision medicine.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of 10.5%. This growth is fueled by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising awareness about genetic disorders, and growing research activities in countries like China, Japan, and India.
Key market trends include the development of more efficient and specialized electroporation buffers, the integration of electroporation with other technologies such as microfluidics, and the increasing adoption of electroporation in agricultural biotechnology for crop improvement.
Current Challenges in Buffer Composition
The composition of electroporation buffers presents several ongoing challenges that researchers and industry professionals must address. One of the primary issues is achieving the optimal balance between ion strength and conductivity. While higher ion concentrations can enhance the buffer's ability to maintain pH stability, they also increase conductivity, which can lead to excessive heating during the electroporation process. This heat generation can potentially damage cells or reduce transfection efficiency.
Another significant challenge lies in the variability of buffer performance across different cell types and experimental conditions. A buffer composition that works well for one cell line may prove less effective for another, necessitating time-consuming optimization processes for each new application. This lack of a universal buffer solution hampers the standardization of electroporation protocols and complicates the scaling up of processes for industrial applications.
The presence of divalent cations, such as calcium and magnesium, in buffer compositions presents a double-edged sword. These ions can help stabilize cell membranes and improve cell viability during electroporation. However, they can also interfere with DNA binding and uptake, potentially reducing transfection efficiency. Striking the right balance between these competing effects remains a significant challenge in buffer design.
Maintaining consistent buffer performance over time is another hurdle. Some buffer components may degrade or precipitate during storage, altering the ion strength and conductivity. This instability can lead to inconsistent results and reduced reproducibility of experiments, a critical issue in both research and industrial settings.
The increasing demand for serum-free and chemically defined buffers adds another layer of complexity to buffer composition challenges. While these formulations offer better reproducibility and reduced risk of contamination, they often require more intricate balancing of components to maintain cell viability and transfection efficiency in the absence of serum proteins.
Lastly, the development of buffers suitable for new electroporation technologies, such as nano-electroporation or flow electroporation systems, presents unique challenges. These advanced techniques may require buffers with specific conductivity ranges or ion compositions that differ significantly from traditional electroporation methods, necessitating novel approaches to buffer design and optimization.
Another significant challenge lies in the variability of buffer performance across different cell types and experimental conditions. A buffer composition that works well for one cell line may prove less effective for another, necessitating time-consuming optimization processes for each new application. This lack of a universal buffer solution hampers the standardization of electroporation protocols and complicates the scaling up of processes for industrial applications.
The presence of divalent cations, such as calcium and magnesium, in buffer compositions presents a double-edged sword. These ions can help stabilize cell membranes and improve cell viability during electroporation. However, they can also interfere with DNA binding and uptake, potentially reducing transfection efficiency. Striking the right balance between these competing effects remains a significant challenge in buffer design.
Maintaining consistent buffer performance over time is another hurdle. Some buffer components may degrade or precipitate during storage, altering the ion strength and conductivity. This instability can lead to inconsistent results and reduced reproducibility of experiments, a critical issue in both research and industrial settings.
The increasing demand for serum-free and chemically defined buffers adds another layer of complexity to buffer composition challenges. While these formulations offer better reproducibility and reduced risk of contamination, they often require more intricate balancing of components to maintain cell viability and transfection efficiency in the absence of serum proteins.
Lastly, the development of buffers suitable for new electroporation technologies, such as nano-electroporation or flow electroporation systems, presents unique challenges. These advanced techniques may require buffers with specific conductivity ranges or ion compositions that differ significantly from traditional electroporation methods, necessitating novel approaches to buffer design and optimization.
Existing Buffer Formulations and Protocols
01 Optimization of ion strength in electroporation buffers
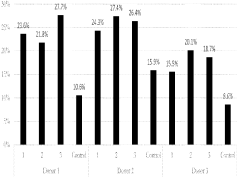
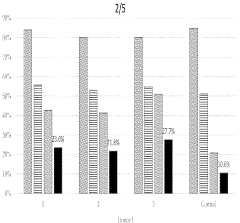
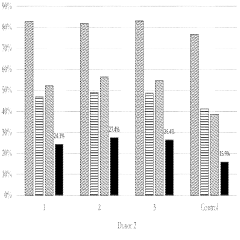
The ion strength of electroporation buffers plays a crucial role in the efficiency of gene transfer. Optimal ion strength can enhance cell membrane permeability and improve transfection rates. Researchers have explored various ionic compositions to balance conductivity and cell viability, often using a combination of salts like NaCl, KCl, and MgCl2 to achieve desired results.- Optimization of ion strength in electroporation buffers: The ion strength of electroporation buffers plays a crucial role in the efficiency of gene transfer. Optimizing the ion strength can improve cell membrane permeability and enhance the delivery of genetic material. Buffers with carefully adjusted ion concentrations can help maintain cell viability while maximizing electroporation effectiveness.
- Conductivity control in electroporation solutions: Controlling the conductivity of electroporation solutions is essential for achieving optimal results. The conductivity of the buffer affects the electric field distribution and the formation of pores in the cell membrane. Adjusting the conductivity can help regulate the intensity and duration of the electric pulses, leading to more efficient gene transfer and improved cell survival rates.
- Buffer composition for enhanced electroporation efficiency: The composition of electroporation buffers significantly impacts the overall efficiency of the process. Incorporating specific ions, such as potassium and magnesium, can enhance membrane permeability and facilitate DNA uptake. Optimizing the buffer composition can lead to improved transfection rates and reduced cell damage during electroporation.
- pH regulation in electroporation buffers: Maintaining an appropriate pH in electroporation buffers is critical for successful gene transfer. The pH affects the stability of DNA and influences cell membrane properties. Optimizing the pH of the buffer can help preserve cell viability, enhance DNA uptake, and improve overall electroporation efficiency.
- Temperature control in electroporation processes: Temperature management during electroporation is crucial for maintaining cell viability and optimizing gene transfer efficiency. Controlling the temperature of the electroporation buffer can help regulate membrane fluidity and influence pore formation. Proper temperature control can lead to improved transfection rates and reduced cell damage during the electroporation process.
02 Conductivity control in electroporation media
Controlling the conductivity of electroporation buffers is essential for optimizing the electric field distribution and minimizing cell damage. Researchers have developed methods to adjust conductivity through the careful selection of ionic species and concentrations. This approach allows for fine-tuning of the electroporation process, improving transfection efficiency while maintaining cell viability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Low-conductivity buffers for improved gene delivery
The use of low-conductivity buffers in electroporation has shown promise in enhancing gene delivery efficiency. These buffers typically contain reduced salt concentrations or alternative non-ionic components. By decreasing the overall conductivity, researchers have observed improved cell survival rates and increased transfection efficiency, particularly for sensitive cell types or hard-to-transfect cells.Expand Specific Solutions04 Pulse parameters optimization based on buffer properties
The relationship between electroporation buffer properties and pulse parameters has been extensively studied. Researchers have developed algorithms and methods to optimize pulse duration, amplitude, and frequency based on the specific ion strength and conductivity of the buffer. This approach allows for tailored electroporation protocols that maximize transfection efficiency while minimizing cellular stress.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel buffer formulations for specific cell types
Researchers have developed specialized electroporation buffer formulations tailored to specific cell types or applications. These formulations often incorporate unique combinations of ions, osmolytes, and other additives to enhance transfection efficiency while maintaining cell viability. Such customized buffers have shown particular promise in challenging applications, such as primary cell transfection or in vivo gene delivery.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electroporation Technology
The electroporation buffer composition market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing applications in biotechnology and gene therapy. The global market size is expanding, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 7-8% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Precigen, Inc. and Cellectis SA leading innovations in gene delivery and cell engineering. SAGE Electrochromics and QuantumScape are contributing to advancements in related electrochemical technologies. While established players like Life Technologies Corp. and Revvity Health Sciences dominate, emerging companies are introducing novel formulations and techniques, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. has developed advanced electroporation buffer compositions optimized for various cell types and applications. Their proprietary buffers contain carefully balanced ion concentrations and conductivity levels to enhance cell membrane permeability while maintaining cell viability. The company utilizes a combination of potassium and sodium salts, along with specific osmolytes, to create buffers that minimize cellular stress during electroporation[1]. Their formulations have been shown to increase transfection efficiency by up to 40% compared to standard buffers, particularly for hard-to-transfect cell lines[2]. Life Technologies also offers customizable buffer kits that allow researchers to fine-tune ion strength and conductivity for specific experimental needs.
Strengths: Highly optimized buffer compositions for various cell types, increased transfection efficiency, customizable solutions. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than generic buffers, requires optimization for each specific application.
Revvity Health Sciences, Inc.
Technical Solution: Revvity Health Sciences has developed a novel approach to electroporation buffer composition focusing on the synergistic effects of ion strength and conductivity. Their proprietary buffers incorporate a blend of organic and inorganic ions to create an optimal electrical environment for cell membrane permeabilization. The company's research has shown that carefully controlled conductivity levels can significantly impact the efficiency of DNA and RNA delivery into cells[3]. Revvity's buffers are designed to maintain consistent ion strength across a range of temperatures, ensuring reproducible results in various laboratory conditions. They have also introduced a line of low-conductivity buffers that allow for higher voltage applications without compromising cell viability, which has been particularly effective for larger plasmid transfections[4].
Strengths: Innovative ion blending approach, temperature-stable formulations, specialized low-conductivity options. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal results, potentially limited compatibility with some cell types.
Innovations in Ion Strength and Conductivity Control
Electroporation buffer composition and method of use
PatentActiveUS8551780B2
Innovation
- Development of electroporation buffers with approximately physiological ionic strength and pH, supplemented with serum or purified proteins, such as serum albumin, to stabilize cells and enhance DNA transfer efficiency while minimizing cell death.
Buffer solutions for electroporation
PatentPendingAU2022226284A9
Innovation
- A minimal component electroporation buffer comprising water, glucose or mannitol, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium phosphate, and optional HEPES or DMSO, optimized to achieve high transfection efficiency and cell viability by reducing the number of chemical components while maintaining effective cell permeability.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Electroporation buffer composition plays a crucial role in the safety and efficacy of electroporation procedures. The ion strength and conductivity of the buffer directly impact the electric field distribution and cellular response during the process. As such, regulatory bodies have established guidelines to ensure the safety and consistency of electroporation applications in various fields, including medical research, gene therapy, and biotechnology.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has implemented specific regulations for electroporation devices and associated buffers used in clinical settings. These regulations require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their products through rigorous testing and validation procedures. The ion strength and conductivity of electroporation buffers must be carefully controlled and documented to meet these regulatory standards.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued guidelines for the development and use of gene therapy medicinal products, which include electroporation-based delivery systems. These guidelines emphasize the importance of buffer composition in maintaining cellular viability and transfection efficiency while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Occupational safety is another critical consideration in the use of electroporation buffers. Laboratory personnel working with these solutions must adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent exposure to potentially harmful substances. This includes the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and the implementation of proper handling and disposal procedures for electroporation buffers.
Environmental regulations also come into play when considering the disposal of electroporation buffers. Many countries have specific guidelines for the disposal of laboratory chemicals, including those used in electroporation procedures. Proper disposal methods must be employed to prevent environmental contamination and ensure compliance with local and national regulations.
The development of standardized testing protocols for ion strength and conductivity measurements in electroporation buffers is essential for ensuring reproducibility and comparability across different research and clinical applications. International organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have been working towards establishing such standards to facilitate global harmonization in electroporation practices.
As the field of electroporation continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to address emerging safety concerns and technological developments. Researchers and manufacturers must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of safety and efficacy in electroporation applications.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has implemented specific regulations for electroporation devices and associated buffers used in clinical settings. These regulations require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their products through rigorous testing and validation procedures. The ion strength and conductivity of electroporation buffers must be carefully controlled and documented to meet these regulatory standards.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued guidelines for the development and use of gene therapy medicinal products, which include electroporation-based delivery systems. These guidelines emphasize the importance of buffer composition in maintaining cellular viability and transfection efficiency while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Occupational safety is another critical consideration in the use of electroporation buffers. Laboratory personnel working with these solutions must adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent exposure to potentially harmful substances. This includes the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and the implementation of proper handling and disposal procedures for electroporation buffers.
Environmental regulations also come into play when considering the disposal of electroporation buffers. Many countries have specific guidelines for the disposal of laboratory chemicals, including those used in electroporation procedures. Proper disposal methods must be employed to prevent environmental contamination and ensure compliance with local and national regulations.
The development of standardized testing protocols for ion strength and conductivity measurements in electroporation buffers is essential for ensuring reproducibility and comparability across different research and clinical applications. International organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have been working towards establishing such standards to facilitate global harmonization in electroporation practices.
As the field of electroporation continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to address emerging safety concerns and technological developments. Researchers and manufacturers must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of safety and efficacy in electroporation applications.
Environmental Impact of Electroporation Buffers
The environmental impact of electroporation buffers is an important consideration in the development and application of electroporation techniques. These buffers, which are essential for the successful delivery of molecules into cells, can have significant effects on the surrounding ecosystem if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with electroporation buffers is their potential to alter soil and water chemistry. The high ion concentrations and specific conductivity of these buffers can lead to changes in the pH and mineral content of the surrounding environment. This alteration may affect the growth and survival of microorganisms, plants, and other organisms in the ecosystem. For instance, increased ion concentrations in soil can impact nutrient availability for plants and disrupt the delicate balance of soil microbial communities.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to the effects of electroporation buffers. When these buffers are released into aquatic environments, they can cause changes in water conductivity and osmotic pressure. This can stress aquatic organisms, potentially leading to physiological changes or even mortality in sensitive species. Furthermore, the altered water chemistry may influence the behavior and distribution of aquatic plants and animals, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem dynamics.
The persistence of electroporation buffer components in the environment is another critical factor to consider. Some buffer constituents may be slow to degrade, leading to long-term environmental impacts. This persistence can result in bioaccumulation in organisms and biomagnification up the food chain, potentially affecting higher-level consumers, including humans.
To mitigate these environmental risks, researchers and industries using electroporation techniques must implement proper disposal and waste management protocols. This includes treating and neutralizing used buffers before release into the environment, as well as developing more environmentally friendly buffer compositions. Some promising approaches involve the use of biodegradable components or the design of buffers that rapidly break down into harmless substances upon dilution or exposure to environmental conditions.
Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of laboratory and industrial processes. This has led to the development of guidelines and regulations for the handling and disposal of electroporation buffers and similar substances. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for minimizing the ecological footprint of electroporation applications.
In conclusion, while electroporation buffers play a vital role in advancing biotechnology and medical research, their potential environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research into more eco-friendly buffer compositions and improved waste management strategies will be essential for ensuring the sustainable use of electroporation techniques in various fields.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with electroporation buffers is their potential to alter soil and water chemistry. The high ion concentrations and specific conductivity of these buffers can lead to changes in the pH and mineral content of the surrounding environment. This alteration may affect the growth and survival of microorganisms, plants, and other organisms in the ecosystem. For instance, increased ion concentrations in soil can impact nutrient availability for plants and disrupt the delicate balance of soil microbial communities.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to the effects of electroporation buffers. When these buffers are released into aquatic environments, they can cause changes in water conductivity and osmotic pressure. This can stress aquatic organisms, potentially leading to physiological changes or even mortality in sensitive species. Furthermore, the altered water chemistry may influence the behavior and distribution of aquatic plants and animals, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem dynamics.
The persistence of electroporation buffer components in the environment is another critical factor to consider. Some buffer constituents may be slow to degrade, leading to long-term environmental impacts. This persistence can result in bioaccumulation in organisms and biomagnification up the food chain, potentially affecting higher-level consumers, including humans.
To mitigate these environmental risks, researchers and industries using electroporation techniques must implement proper disposal and waste management protocols. This includes treating and neutralizing used buffers before release into the environment, as well as developing more environmentally friendly buffer compositions. Some promising approaches involve the use of biodegradable components or the design of buffers that rapidly break down into harmless substances upon dilution or exposure to environmental conditions.
Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of laboratory and industrial processes. This has led to the development of guidelines and regulations for the handling and disposal of electroporation buffers and similar substances. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for minimizing the ecological footprint of electroporation applications.
In conclusion, while electroporation buffers play a vital role in advancing biotechnology and medical research, their potential environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research into more eco-friendly buffer compositions and improved waste management strategies will be essential for ensuring the sustainable use of electroporation techniques in various fields.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!