How To Automate Electroporation Parameter Tuning For New Cell Types
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Automation Goals
Electroporation automation for new cell types aims to streamline and optimize the process of introducing genetic material or molecules into cells through electrical pulses. The primary goal is to develop a system that can automatically determine and adjust the optimal electroporation parameters for various cell types without extensive manual intervention.
One key objective is to create a robust and adaptable platform capable of handling a wide range of cell types, from commonly used lines to rare or difficult-to-transfect cells. This system should be able to rapidly assess the characteristics of new cell types and propose suitable initial electroporation parameters based on existing data and machine learning algorithms.
Another crucial goal is to minimize cell damage and maximize transfection efficiency simultaneously. The automated system should be able to fine-tune parameters such as voltage, pulse duration, and number of pulses in real-time, based on feedback from cell viability and transfection success rates. This adaptive approach would significantly reduce the time and resources required for optimizing electroporation protocols for new cell types.
Improving reproducibility and standardization across different laboratories and experiments is also a major aim of electroporation automation. By reducing human error and subjective decision-making, the automated system should provide consistent and reliable results, facilitating easier comparison of data between research groups and accelerating scientific progress in fields relying on cell manipulation.
Cost-effectiveness and resource optimization are additional objectives of electroporation automation. The system should aim to minimize reagent consumption and reduce the number of cells required for successful transfection, making the process more economical and sustainable, especially when working with rare or expensive cell types.
Lastly, the automation of electroporation parameter tuning should strive for user-friendliness and accessibility. The goal is to develop an intuitive interface that allows researchers of varying expertise levels to easily input cell characteristics, monitor the optimization process, and obtain detailed reports on the optimized parameters and transfection outcomes. This would democratize access to advanced cell manipulation techniques and accelerate research across various fields of biology and medicine.
One key objective is to create a robust and adaptable platform capable of handling a wide range of cell types, from commonly used lines to rare or difficult-to-transfect cells. This system should be able to rapidly assess the characteristics of new cell types and propose suitable initial electroporation parameters based on existing data and machine learning algorithms.
Another crucial goal is to minimize cell damage and maximize transfection efficiency simultaneously. The automated system should be able to fine-tune parameters such as voltage, pulse duration, and number of pulses in real-time, based on feedback from cell viability and transfection success rates. This adaptive approach would significantly reduce the time and resources required for optimizing electroporation protocols for new cell types.
Improving reproducibility and standardization across different laboratories and experiments is also a major aim of electroporation automation. By reducing human error and subjective decision-making, the automated system should provide consistent and reliable results, facilitating easier comparison of data between research groups and accelerating scientific progress in fields relying on cell manipulation.
Cost-effectiveness and resource optimization are additional objectives of electroporation automation. The system should aim to minimize reagent consumption and reduce the number of cells required for successful transfection, making the process more economical and sustainable, especially when working with rare or expensive cell types.
Lastly, the automation of electroporation parameter tuning should strive for user-friendliness and accessibility. The goal is to develop an intuitive interface that allows researchers of varying expertise levels to easily input cell characteristics, monitor the optimization process, and obtain detailed reports on the optimized parameters and transfection outcomes. This would democratize access to advanced cell manipulation techniques and accelerate research across various fields of biology and medicine.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for automated electroporation parameter tuning for new cell types is driven by the growing need for efficient and reproducible cell transfection methods across various research and industrial applications. As the field of cell biology and genetic engineering continues to expand, researchers and biotechnology companies are constantly working with new cell types, each requiring optimized electroporation parameters for successful transfection.
The global electroporation market is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of electroporation techniques in gene therapy, cancer treatment, and vaccine development. The automation of parameter tuning addresses a critical pain point in this market, as manual optimization is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often leads to inconsistent results.
In academic research, there is a rising demand for high-throughput screening and gene editing technologies, which require efficient transfection of diverse cell types. Automated parameter tuning can significantly accelerate research timelines and improve experimental reproducibility, making it an attractive solution for research institutions and pharmaceutical companies engaged in drug discovery and development.
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are major drivers of market demand for automated electroporation solutions. These sectors require robust and scalable transfection methods for the production of recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and gene therapies. Automated parameter tuning can enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality, making it a valuable tool for large-scale biomanufacturing processes.
Emerging applications in personalized medicine and cell-based therapies are creating new opportunities for automated electroporation technologies. As these fields advance, there is an increasing need for efficient and reliable methods to genetically modify patient-derived cells, such as T cells for CAR-T therapy. Automated parameter tuning can help streamline the manufacturing process for these personalized treatments, potentially reducing costs and improving patient outcomes.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing emphasis on precision medicine and the development of CRISPR-based gene editing technologies. These applications often involve working with primary cells and hard-to-transfect cell lines, which require carefully optimized electroporation parameters. Automated tuning systems can significantly reduce the time and resources needed to establish effective protocols for these challenging cell types.
In conclusion, the market demand for automated electroporation parameter tuning is driven by the need for increased efficiency, reproducibility, and scalability in cell transfection across various research and industrial applications. As the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries continue to expand and new cell-based therapies emerge, the demand for automated solutions is expected to grow, offering significant opportunities for innovation and market expansion in this field.
The global electroporation market is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of electroporation techniques in gene therapy, cancer treatment, and vaccine development. The automation of parameter tuning addresses a critical pain point in this market, as manual optimization is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often leads to inconsistent results.
In academic research, there is a rising demand for high-throughput screening and gene editing technologies, which require efficient transfection of diverse cell types. Automated parameter tuning can significantly accelerate research timelines and improve experimental reproducibility, making it an attractive solution for research institutions and pharmaceutical companies engaged in drug discovery and development.
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are major drivers of market demand for automated electroporation solutions. These sectors require robust and scalable transfection methods for the production of recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and gene therapies. Automated parameter tuning can enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality, making it a valuable tool for large-scale biomanufacturing processes.
Emerging applications in personalized medicine and cell-based therapies are creating new opportunities for automated electroporation technologies. As these fields advance, there is an increasing need for efficient and reliable methods to genetically modify patient-derived cells, such as T cells for CAR-T therapy. Automated parameter tuning can help streamline the manufacturing process for these personalized treatments, potentially reducing costs and improving patient outcomes.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing emphasis on precision medicine and the development of CRISPR-based gene editing technologies. These applications often involve working with primary cells and hard-to-transfect cell lines, which require carefully optimized electroporation parameters. Automated tuning systems can significantly reduce the time and resources needed to establish effective protocols for these challenging cell types.
In conclusion, the market demand for automated electroporation parameter tuning is driven by the need for increased efficiency, reproducibility, and scalability in cell transfection across various research and industrial applications. As the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries continue to expand and new cell-based therapies emerge, the demand for automated solutions is expected to grow, offering significant opportunities for innovation and market expansion in this field.
Current Challenges
Electroporation parameter tuning for new cell types presents several significant challenges in the current technological landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization across different cell types and electroporation devices. Each cell type has unique characteristics, including membrane composition, size, and susceptibility to electrical fields, making it difficult to establish universal parameters.
The time-consuming nature of manual parameter optimization poses another major challenge. Researchers often rely on trial-and-error approaches, which can be labor-intensive and inefficient. This process typically involves testing multiple combinations of voltage, pulse duration, and frequency, leading to extended experimental timelines and increased resource consumption.
Furthermore, the complexity of cellular responses to electroporation adds another layer of difficulty. The optimal balance between transfection efficiency and cell viability varies widely among cell types, necessitating fine-tuning of parameters for each specific application. This complexity is compounded by the fact that even slight variations in experimental conditions can significantly impact results.
The limited availability of real-time feedback mechanisms during the electroporation process hinders rapid optimization. Current technologies often rely on post-electroporation analysis, which delays the iterative improvement of parameters and extends the overall optimization timeline.
Another challenge lies in the scalability of parameter tuning methods. As research expands to include a wider variety of cell types and genetic modifications, the demand for efficient parameter optimization grows. However, current manual methods struggle to keep pace with this increasing demand, creating a bottleneck in cellular engineering and transfection studies.
The variability in cell preparation and handling procedures also contributes to the challenges in parameter tuning. Factors such as cell density, growth phase, and buffer composition can all influence electroporation outcomes, making it difficult to isolate the effects of electrical parameters alone.
Lastly, the integration of parameter tuning with other aspects of cellular engineering workflows remains a significant hurdle. Automating this process requires seamless coordination with cell culture systems, analysis tools, and data management platforms, which is often hindered by compatibility issues and the lack of standardized interfaces between different components of the experimental setup.
The time-consuming nature of manual parameter optimization poses another major challenge. Researchers often rely on trial-and-error approaches, which can be labor-intensive and inefficient. This process typically involves testing multiple combinations of voltage, pulse duration, and frequency, leading to extended experimental timelines and increased resource consumption.
Furthermore, the complexity of cellular responses to electroporation adds another layer of difficulty. The optimal balance between transfection efficiency and cell viability varies widely among cell types, necessitating fine-tuning of parameters for each specific application. This complexity is compounded by the fact that even slight variations in experimental conditions can significantly impact results.
The limited availability of real-time feedback mechanisms during the electroporation process hinders rapid optimization. Current technologies often rely on post-electroporation analysis, which delays the iterative improvement of parameters and extends the overall optimization timeline.
Another challenge lies in the scalability of parameter tuning methods. As research expands to include a wider variety of cell types and genetic modifications, the demand for efficient parameter optimization grows. However, current manual methods struggle to keep pace with this increasing demand, creating a bottleneck in cellular engineering and transfection studies.
The variability in cell preparation and handling procedures also contributes to the challenges in parameter tuning. Factors such as cell density, growth phase, and buffer composition can all influence electroporation outcomes, making it difficult to isolate the effects of electrical parameters alone.
Lastly, the integration of parameter tuning with other aspects of cellular engineering workflows remains a significant hurdle. Automating this process requires seamless coordination with cell culture systems, analysis tools, and data management platforms, which is often hindered by compatibility issues and the lack of standardized interfaces between different components of the experimental setup.
Existing Automation Solutions
01 Voltage and pulse duration optimization
Optimizing voltage levels and pulse durations is crucial for effective electroporation. This involves adjusting the electric field strength and the duration of applied pulses to achieve optimal cell membrane permeabilization while minimizing cell damage. The process may include gradual increases in voltage or pulse duration to find the ideal parameters for specific cell types or applications.- Voltage and pulse duration optimization: Optimizing voltage levels and pulse durations is crucial for effective electroporation. This involves adjusting the electric field strength and the duration of pulses to achieve optimal cell membrane permeability without causing excessive damage. The process may include gradual increases in voltage or pulse duration to find the most effective parameters for specific cell types or applications.
- Electrode configuration and design: The design and configuration of electrodes play a significant role in electroporation efficiency. This includes optimizing electrode spacing, shape, and material to ensure uniform electric field distribution. Advanced electrode designs may incorporate multiple electrodes or adjustable configurations to adapt to different sample sizes or cell types.
- Temperature control and monitoring: Maintaining and monitoring optimal temperature during electroporation is essential for preserving cell viability and enhancing transfection efficiency. This may involve integrating cooling systems or temperature sensors into the electroporation device, as well as developing protocols for pre-cooling or post-treatment temperature management.
- Pulse sequence and waveform optimization: Developing optimal pulse sequences and waveforms can significantly improve electroporation outcomes. This includes experimenting with different pulse patterns, such as single vs. multiple pulses, alternating polarity, or varying waveform shapes (e.g., square, exponential decay). The goal is to find the most effective combination for specific applications while minimizing cell damage.
- Adaptive parameter tuning using machine learning: Implementing machine learning algorithms to dynamically adjust electroporation parameters based on real-time feedback can enhance the efficiency and reproducibility of the process. This approach involves collecting data on cell responses to various parameter combinations and using this information to predict and adjust optimal settings for different cell types or experimental conditions.
02 Electrode configuration and design
The design and configuration of electrodes play a significant role in electroporation efficiency. This includes optimizing electrode shape, size, spacing, and arrangement to ensure uniform electric field distribution across the target area. Advanced electrode designs may incorporate multiple electrodes or adjustable configurations to adapt to different sample sizes or tissue types.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pulse sequence and waveform modulation
Developing optimal pulse sequences and waveforms can enhance electroporation outcomes. This involves experimenting with various pulse patterns, such as single vs. multiple pulses, alternating polarity, or complex waveforms. The goal is to find sequences that maximize membrane permeability while minimizing cellular stress and improving overall transfection efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Real-time monitoring and feedback systems
Implementing real-time monitoring and feedback systems allows for dynamic adjustment of electroporation parameters. This may include measuring electrical impedance, temperature, or other cellular responses during the process. Such systems can automatically adjust parameters to maintain optimal conditions throughout the electroporation procedure, improving consistency and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cell-specific parameter optimization
Tailoring electroporation parameters to specific cell types or tissues is essential for maximizing efficiency. This involves conducting systematic studies to determine the optimal combination of voltage, pulse duration, and other parameters for different cell lines or tissue types. The approach may include developing databases or algorithms to predict optimal parameters based on cell characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The automation of electroporation parameter tuning for new cell types is a rapidly evolving field in the biotechnology sector. The market is in its growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding applications of cell engineering in research and therapeutics. Key players like Bio-Rad Laboratories, MaxCyte, and Life Technologies are at the forefront, offering advanced electroporation systems. Emerging companies such as CyteQuest and Cellares are introducing innovative solutions, focusing on continuous flow and automated cell therapy manufacturing. The technology is maturing, with established academic institutions like Tsinghua University and the University of California contributing to research advancements. However, there's still room for improvement in automation and optimization for diverse cell types, indicating ongoing opportunities for innovation and market growth.
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Technical Solution: Bio-Rad has developed the Gene Pulser Xcell Electroporation System, which features an intuitive software interface for parameter optimization. The system allows users to create and store custom protocols for different cell types. While not fully automated, the Gene Pulser Xcell system incorporates a Protocol Library with pre-optimized settings for various cell types, which can serve as starting points for new cell lines[9]. The system also includes an Optimization Module that can test multiple electroporation conditions in a single experiment, streamlining the parameter tuning process. Bio-Rad's approach focuses on user flexibility and ease of use, allowing researchers to quickly adapt protocols for new cell types based on similar existing protocols[10].
Strengths: User-friendly interface and extensive protocol library. Weaknesses: Less automated compared to some newer systems, requiring more user input for optimization.
MaxCyte, Inc.
Technical Solution: MaxCyte has developed an automated electroporation platform called ExPERT that utilizes a proprietary Flow Electroporation technology. This system employs a continuous flow process and pre-optimized electroporation protocols for various cell types. The platform incorporates machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time feedback on cell viability and transfection efficiency, allowing for automated adjustment of electroporation parameters[1]. The system can process up to 2 x 10^11 cells in less than 30 minutes, significantly reducing the time required for parameter optimization[2]. MaxCyte's technology also includes a library of cell-specific protocols that can be used as starting points for new cell types, further streamlining the optimization process[3].
Strengths: High-throughput capability, real-time parameter adjustment, and extensive pre-optimized protocol library. Weaknesses: High initial cost and potential complexity for smaller research labs.
Core Innovations
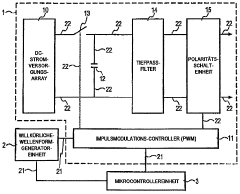
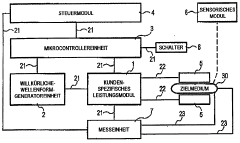
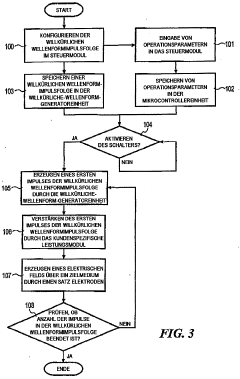
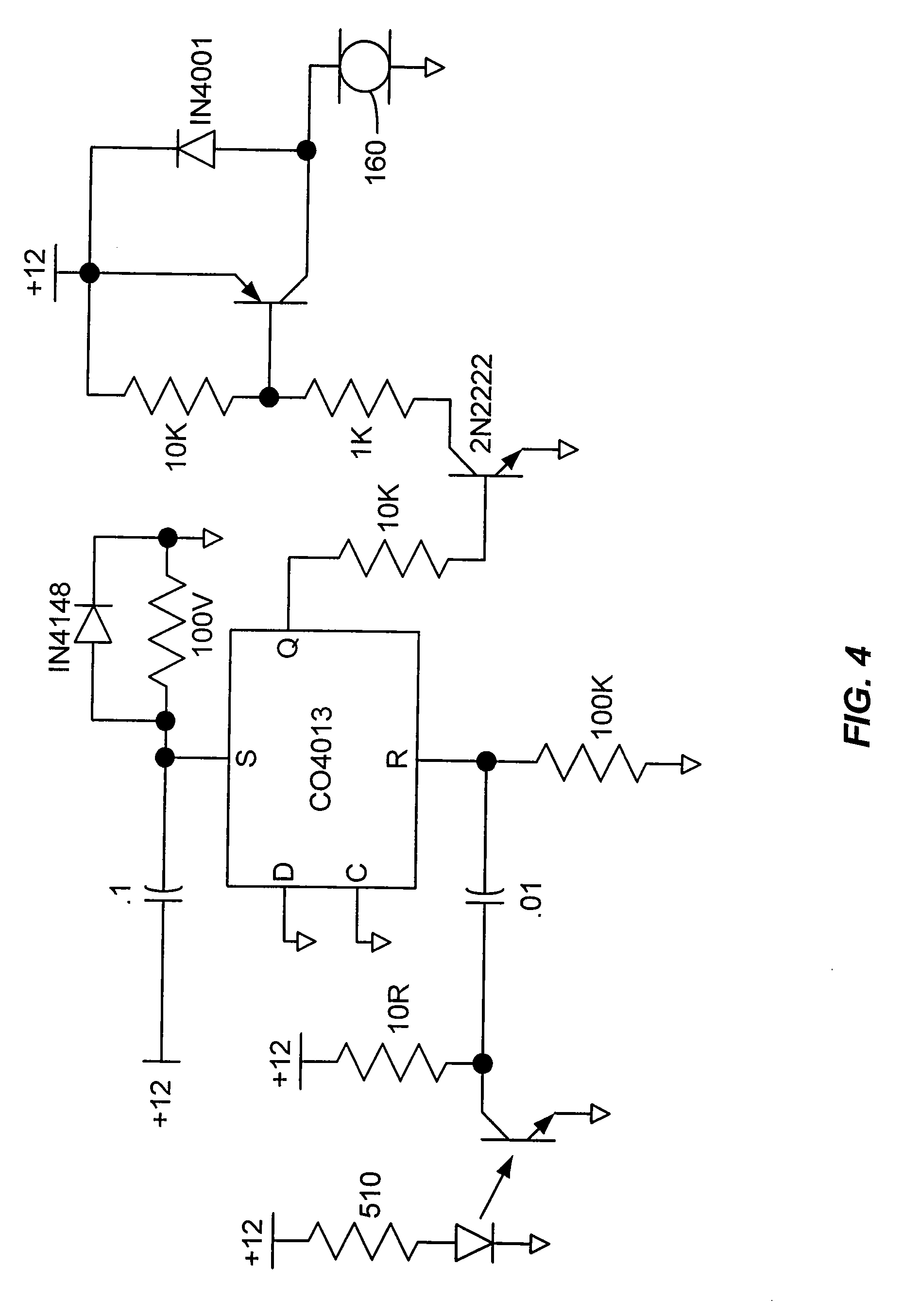
programmable apparatus and method for optimizing and real-time monitoring of gene transfection based on a user-configured arbitrary waveform pulse sequence
PatentInactiveDE102005031427A1
Innovation
- An apparatus and method for generating and applying an optimized electric field using user-configured arbitrary waveform pulse trains, incorporating a custom power module, microcontroller, and sensors to monitor and adjust parameters like pulse shape, duration, and frequency, ensuring minimal tissue damage.
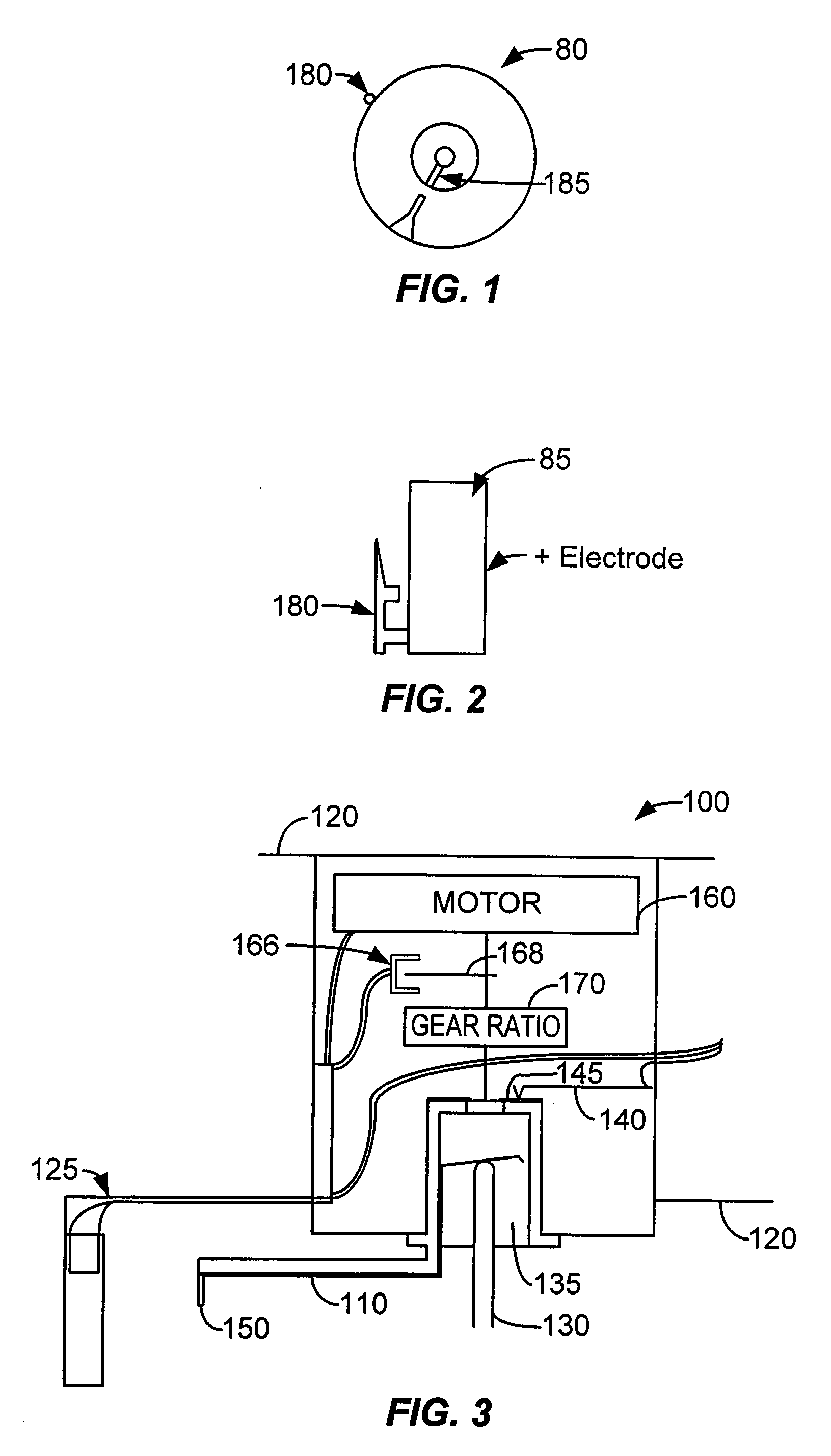
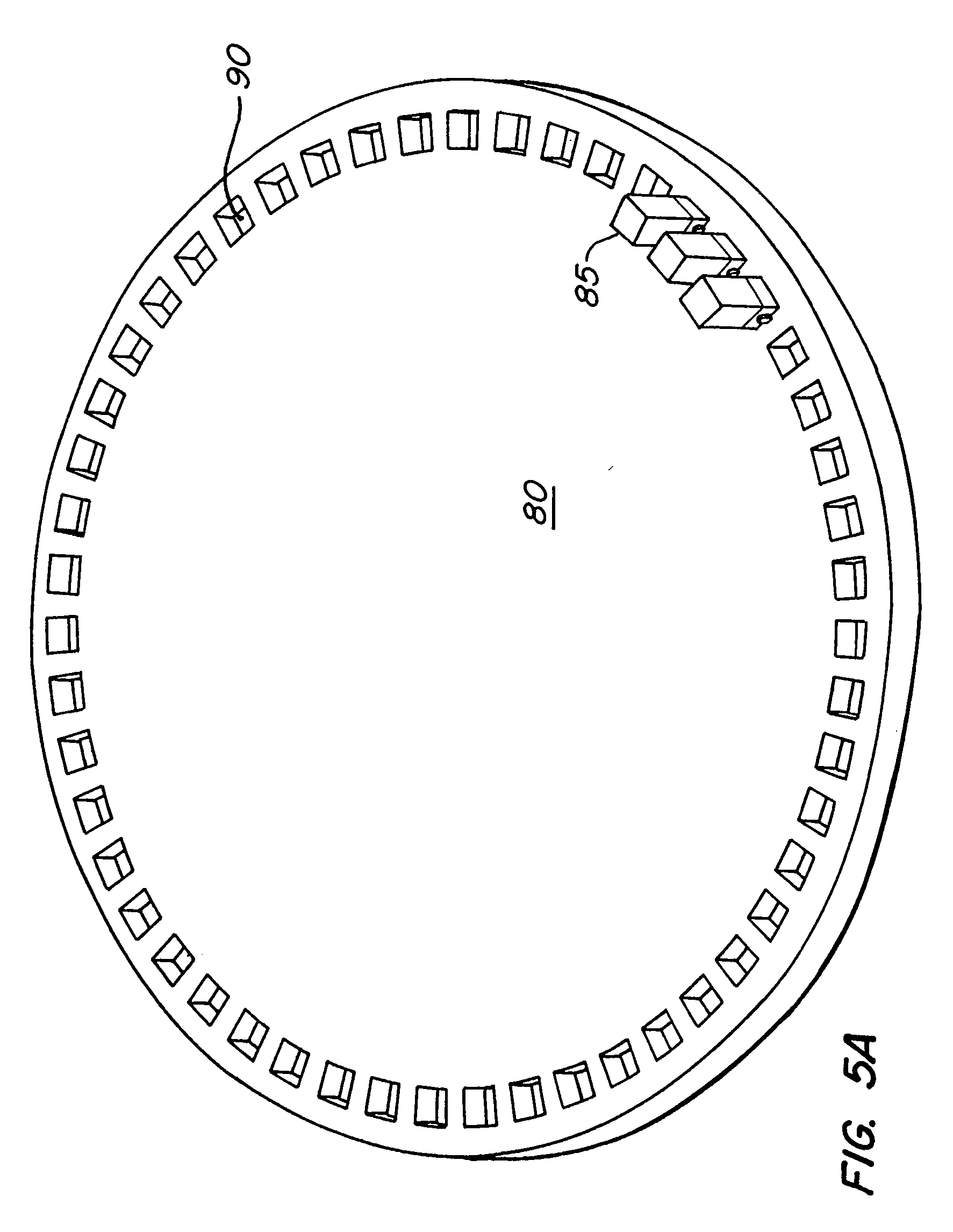
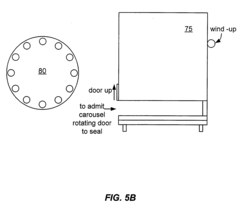
Automatic electroporation optimization system
PatentInactiveUS20060246572A1
Innovation
- An automatic electroporation system that allows operators to select optimization modes, control system parameters such as waveform, pulse width, and voltage, and perform multiple experiments with a cuvette carousel and commutator assembly, enabling automated delivery of pulses and data transfer using a hand-held device.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the development and implementation of automated electroporation parameter tuning systems for new cell types. As this technology advances, it is essential to navigate the complex landscape of regulatory requirements to ensure compliance and safety.
The primary regulatory bodies overseeing this field include the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, and similar organizations in other regions. These agencies have established guidelines and regulations that govern the use of automated systems in cell manipulation and genetic modification processes.
One of the key regulatory challenges is ensuring the safety and efficacy of the automated electroporation process. Regulatory bodies require extensive documentation and validation of the automated system's performance, including its ability to consistently produce desired results across various cell types. This involves demonstrating the system's accuracy, precision, and reproducibility in parameter selection and application.
Data integrity and traceability are also critical regulatory considerations. Automated systems must maintain comprehensive records of all parameters used, cell types processed, and outcomes achieved. This data must be securely stored and easily retrievable for auditing purposes, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the process.
Furthermore, regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of quality control measures. Manufacturers of automated electroporation systems must implement robust quality management systems that cover all aspects of the device's lifecycle, from design and development to production and post-market surveillance. This includes regular calibration, maintenance, and performance verification protocols.
Risk management is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. Developers must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with the automated system and implement appropriate mitigation strategies. This includes safeguards against system failures, parameter errors, and potential biological contamination.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to keep pace with innovations in automated electroporation. This could lead to the development of new guidelines specifically addressing the unique challenges posed by AI-driven parameter tuning systems. Companies working in this field should maintain open communication channels with regulatory bodies to stay informed about evolving requirements and contribute to the development of appropriate regulatory standards.
In conclusion, navigating the regulatory landscape for automated electroporation parameter tuning systems requires a comprehensive approach that addresses safety, efficacy, data integrity, quality control, and risk management. Compliance with these regulatory considerations is essential for the successful development and implementation of this technology in clinical and research settings.
The primary regulatory bodies overseeing this field include the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, and similar organizations in other regions. These agencies have established guidelines and regulations that govern the use of automated systems in cell manipulation and genetic modification processes.
One of the key regulatory challenges is ensuring the safety and efficacy of the automated electroporation process. Regulatory bodies require extensive documentation and validation of the automated system's performance, including its ability to consistently produce desired results across various cell types. This involves demonstrating the system's accuracy, precision, and reproducibility in parameter selection and application.
Data integrity and traceability are also critical regulatory considerations. Automated systems must maintain comprehensive records of all parameters used, cell types processed, and outcomes achieved. This data must be securely stored and easily retrievable for auditing purposes, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the process.
Furthermore, regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of quality control measures. Manufacturers of automated electroporation systems must implement robust quality management systems that cover all aspects of the device's lifecycle, from design and development to production and post-market surveillance. This includes regular calibration, maintenance, and performance verification protocols.
Risk management is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. Developers must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with the automated system and implement appropriate mitigation strategies. This includes safeguards against system failures, parameter errors, and potential biological contamination.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt to keep pace with innovations in automated electroporation. This could lead to the development of new guidelines specifically addressing the unique challenges posed by AI-driven parameter tuning systems. Companies working in this field should maintain open communication channels with regulatory bodies to stay informed about evolving requirements and contribute to the development of appropriate regulatory standards.
In conclusion, navigating the regulatory landscape for automated electroporation parameter tuning systems requires a comprehensive approach that addresses safety, efficacy, data integrity, quality control, and risk management. Compliance with these regulatory considerations is essential for the successful development and implementation of this technology in clinical and research settings.
Cell Viability Optimization
Cell viability optimization is a critical aspect of automating electroporation parameter tuning for new cell types. The process involves maximizing the number of viable cells post-electroporation while maintaining high transfection efficiency. This optimization is essential because different cell types have varying sensitivities to electrical pulses, and finding the right balance is crucial for successful gene delivery.
One of the primary approaches to cell viability optimization is the systematic adjustment of electroporation parameters. These parameters include voltage, pulse duration, number of pulses, and interval between pulses. By fine-tuning these variables, researchers can minimize cell damage while ensuring efficient DNA or RNA uptake. Advanced automation systems can employ machine learning algorithms to predict optimal parameter combinations based on cell type characteristics and historical data.
Another key factor in optimizing cell viability is the composition of the electroporation buffer. The buffer's ionic strength, pH, and osmolarity can significantly impact cell survival rates. Automated systems can be programmed to test various buffer formulations, adjusting components such as potassium and magnesium ion concentrations to enhance cell membrane stability during electroporation.
Temperature control during the electroporation process also plays a crucial role in maintaining cell viability. Automated systems can incorporate precise temperature regulation mechanisms to prevent heat-induced cellular stress. This may involve rapid cooling immediately after pulse delivery or maintaining a constant optimal temperature throughout the procedure.
Post-electroporation recovery strategies are equally important for cell viability optimization. Automated systems can be designed to implement tailored recovery protocols, such as the immediate addition of growth factors or antioxidants to the cell suspension. These compounds can help mitigate cellular stress and promote rapid recovery, thereby increasing overall viability rates.
Real-time monitoring of cell health during the electroporation process is another avenue for optimization. Advanced automated systems can integrate live-cell imaging technologies or impedance-based cell analysis to assess cell viability in real-time. This allows for immediate adjustments to electroporation parameters if cell stress indicators are detected, ensuring optimal outcomes for each specific cell type.
By combining these various approaches and leveraging the power of automation and machine learning, researchers can significantly enhance cell viability optimization in electroporation processes. This not only improves the efficiency of gene delivery but also expands the range of cell types that can be successfully transfected, opening new possibilities in fields such as gene therapy and cellular reprogramming.
One of the primary approaches to cell viability optimization is the systematic adjustment of electroporation parameters. These parameters include voltage, pulse duration, number of pulses, and interval between pulses. By fine-tuning these variables, researchers can minimize cell damage while ensuring efficient DNA or RNA uptake. Advanced automation systems can employ machine learning algorithms to predict optimal parameter combinations based on cell type characteristics and historical data.
Another key factor in optimizing cell viability is the composition of the electroporation buffer. The buffer's ionic strength, pH, and osmolarity can significantly impact cell survival rates. Automated systems can be programmed to test various buffer formulations, adjusting components such as potassium and magnesium ion concentrations to enhance cell membrane stability during electroporation.
Temperature control during the electroporation process also plays a crucial role in maintaining cell viability. Automated systems can incorporate precise temperature regulation mechanisms to prevent heat-induced cellular stress. This may involve rapid cooling immediately after pulse delivery or maintaining a constant optimal temperature throughout the procedure.
Post-electroporation recovery strategies are equally important for cell viability optimization. Automated systems can be designed to implement tailored recovery protocols, such as the immediate addition of growth factors or antioxidants to the cell suspension. These compounds can help mitigate cellular stress and promote rapid recovery, thereby increasing overall viability rates.
Real-time monitoring of cell health during the electroporation process is another avenue for optimization. Advanced automated systems can integrate live-cell imaging technologies or impedance-based cell analysis to assess cell viability in real-time. This allows for immediate adjustments to electroporation parameters if cell stress indicators are detected, ensuring optimal outcomes for each specific cell type.
By combining these various approaches and leveraging the power of automation and machine learning, researchers can significantly enhance cell viability optimization in electroporation processes. This not only improves the efficiency of gene delivery but also expands the range of cell types that can be successfully transfected, opening new possibilities in fields such as gene therapy and cellular reprogramming.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!