Electroporation In Vivo: Safety Protocols And Regulatory Considerations
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Background
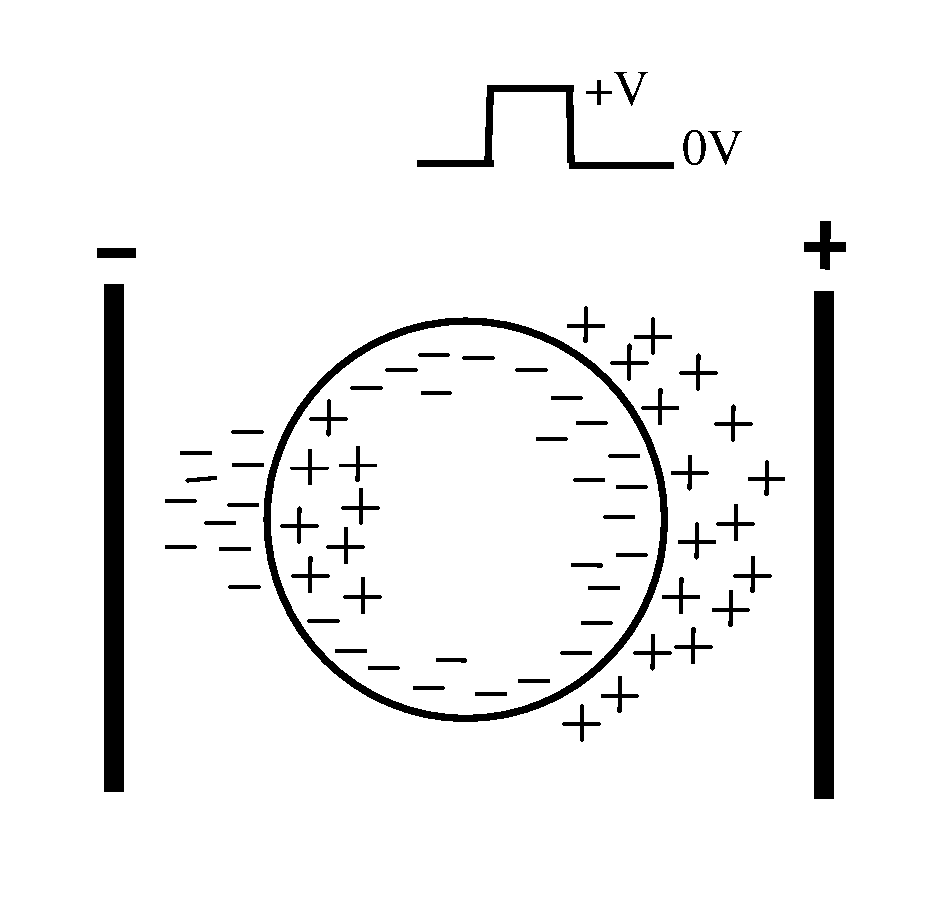
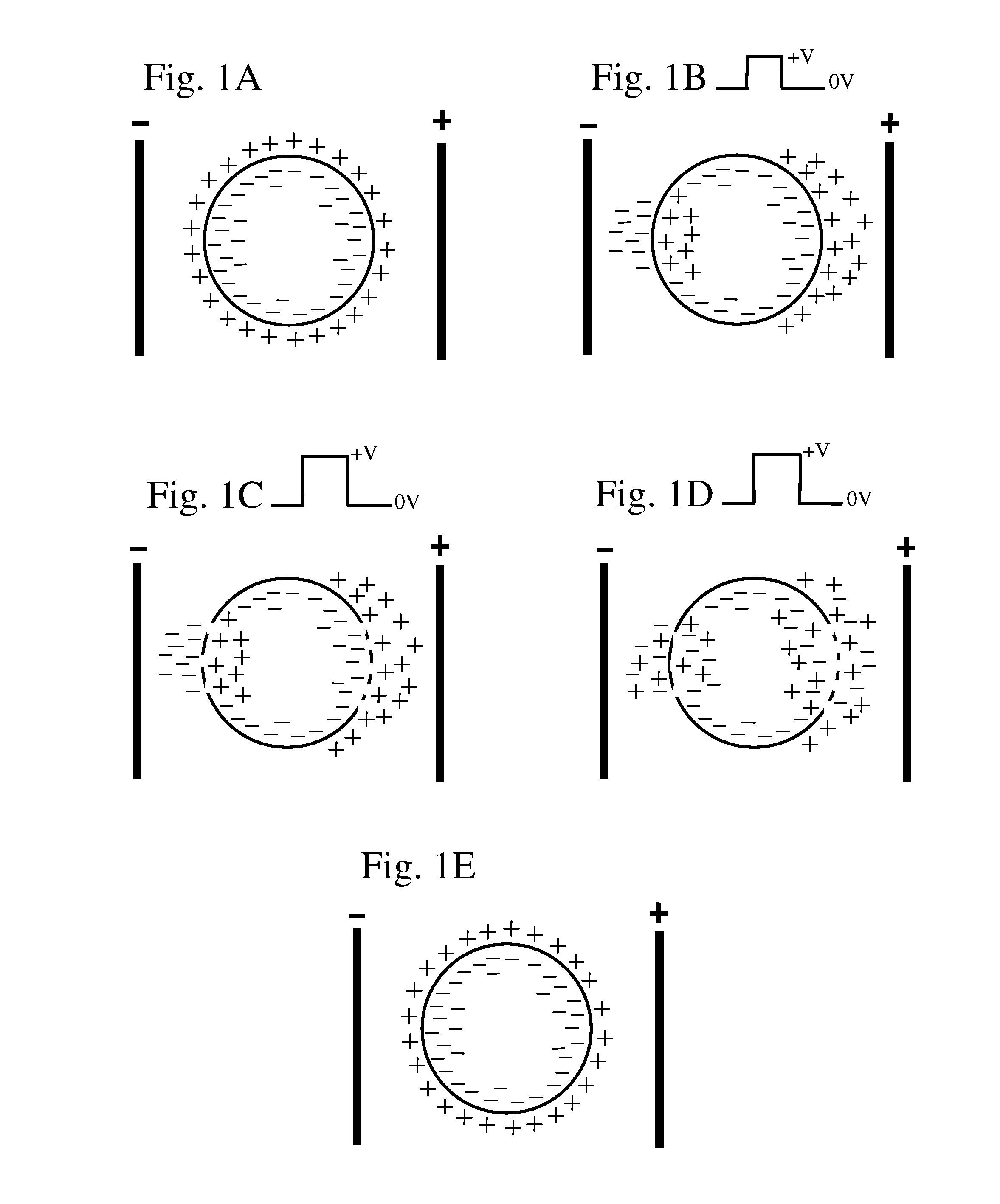
Electroporation is a powerful technique that has revolutionized the field of molecular biology and medicine. This method involves the application of electrical pulses to temporarily increase the permeability of cell membranes, allowing for the introduction of foreign molecules such as DNA, RNA, or drugs into cells. The concept of electroporation was first discovered in the 1960s, but it wasn't until the 1980s that it gained significant attention in scientific research.
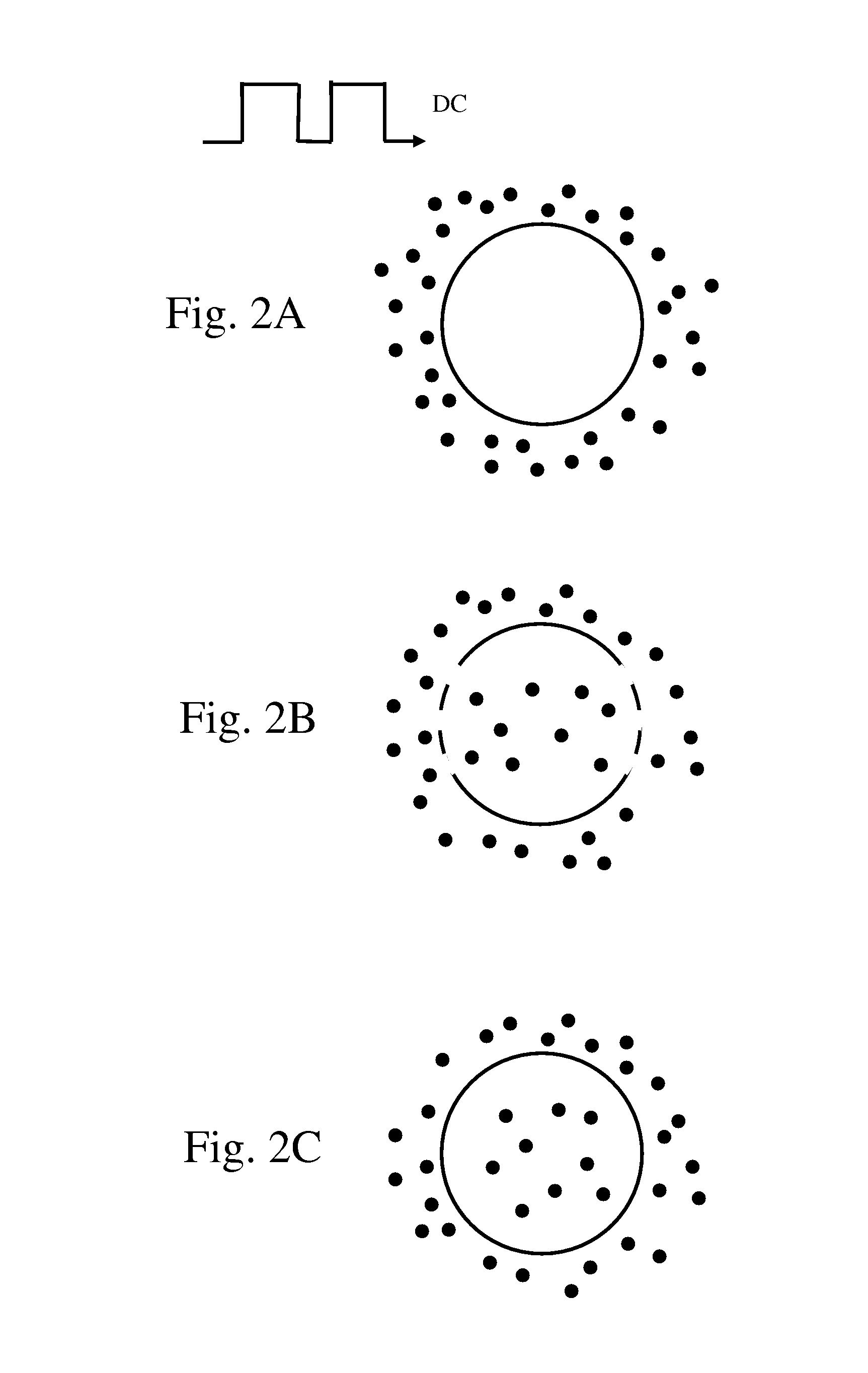
The fundamental principle behind electroporation is based on the creation of transient pores in the cell membrane when exposed to an electric field. These pores allow molecules to pass through the membrane barrier, which is normally impermeable to large molecules. The duration and intensity of the electric pulses are critical factors in determining the efficiency and safety of the electroporation process.
In vivo electroporation, specifically, refers to the application of this technique directly in living organisms. This approach has gained considerable interest in recent years due to its potential for gene therapy, DNA vaccination, and targeted drug delivery. The ability to deliver genetic material or therapeutic agents directly to specific tissues or organs in a living subject offers numerous advantages over traditional methods.
The development of in vivo electroporation has been driven by advancements in electrode design, pulse generators, and delivery systems. Early studies focused on simple needle electrodes, but more sophisticated designs have emerged, including plate electrodes, multi-needle arrays, and non-invasive electrodes. These innovations have improved the efficiency and safety of the technique, allowing for more precise and targeted delivery of molecules to specific tissues.
As the field has progressed, researchers have explored various applications of in vivo electroporation across different organ systems and species. Notable successes have been achieved in areas such as cancer treatment, where electroporation has been used to enhance the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to tumors. Additionally, the technique has shown promise in DNA vaccination, offering a potential alternative to traditional vaccine delivery methods.
However, the use of electroporation in living organisms also presents unique challenges and safety considerations. The application of electric fields to living tissues can potentially cause tissue damage, inflammation, or unwanted physiological responses. As a result, extensive research has been conducted to optimize electroporation parameters and develop safety protocols that minimize these risks while maximizing the efficiency of molecule delivery.
The fundamental principle behind electroporation is based on the creation of transient pores in the cell membrane when exposed to an electric field. These pores allow molecules to pass through the membrane barrier, which is normally impermeable to large molecules. The duration and intensity of the electric pulses are critical factors in determining the efficiency and safety of the electroporation process.
In vivo electroporation, specifically, refers to the application of this technique directly in living organisms. This approach has gained considerable interest in recent years due to its potential for gene therapy, DNA vaccination, and targeted drug delivery. The ability to deliver genetic material or therapeutic agents directly to specific tissues or organs in a living subject offers numerous advantages over traditional methods.
The development of in vivo electroporation has been driven by advancements in electrode design, pulse generators, and delivery systems. Early studies focused on simple needle electrodes, but more sophisticated designs have emerged, including plate electrodes, multi-needle arrays, and non-invasive electrodes. These innovations have improved the efficiency and safety of the technique, allowing for more precise and targeted delivery of molecules to specific tissues.
As the field has progressed, researchers have explored various applications of in vivo electroporation across different organ systems and species. Notable successes have been achieved in areas such as cancer treatment, where electroporation has been used to enhance the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to tumors. Additionally, the technique has shown promise in DNA vaccination, offering a potential alternative to traditional vaccine delivery methods.
However, the use of electroporation in living organisms also presents unique challenges and safety considerations. The application of electric fields to living tissues can potentially cause tissue damage, inflammation, or unwanted physiological responses. As a result, extensive research has been conducted to optimize electroporation parameters and develop safety protocols that minimize these risks while maximizing the efficiency of molecule delivery.
Market Analysis
The market for in vivo electroporation technologies has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient gene delivery methods in various biomedical applications. This technique has gained traction in fields such as gene therapy, cancer treatment, and vaccine development, owing to its ability to enhance the uptake of therapeutic molecules into cells.
The global electroporation market, which includes both in vitro and in vivo applications, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% in the coming years. In vivo electroporation, specifically, is expected to witness faster growth due to its potential in clinical applications and personalized medicine.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the rising prevalence of cancer and genetic disorders. In vivo electroporation has shown promise in delivering cancer immunotherapies and gene-based treatments, making it an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. Additionally, the technique's potential in DNA vaccination has garnered attention, especially in light of recent global health crises.
The market for in vivo electroporation is segmented based on application areas, including oncology, gene therapy, and vaccine delivery. Oncology currently holds the largest market share, with numerous clinical trials exploring electroporation-based cancer treatments. However, the vaccine delivery segment is expected to grow rapidly, fueled by the need for more effective vaccine administration methods.
Geographically, North America dominates the in vivo electroporation market, followed by Europe. This is primarily due to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, substantial research funding, and favorable regulatory environments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key companies are focusing on developing more sophisticated electroporation devices and expanding their product portfolios. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry players are also on the rise, aiming to accelerate the translation of research findings into clinical applications.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of in vivo electroporation. These include concerns about safety, the need for standardized protocols, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of this technology. As research progresses and regulatory frameworks evolve, the market for in vivo electroporation is expected to continue its upward trajectory, offering significant opportunities for stakeholders in the biotechnology and healthcare sectors.
The global electroporation market, which includes both in vitro and in vivo applications, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% in the coming years. In vivo electroporation, specifically, is expected to witness faster growth due to its potential in clinical applications and personalized medicine.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the rising prevalence of cancer and genetic disorders. In vivo electroporation has shown promise in delivering cancer immunotherapies and gene-based treatments, making it an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. Additionally, the technique's potential in DNA vaccination has garnered attention, especially in light of recent global health crises.
The market for in vivo electroporation is segmented based on application areas, including oncology, gene therapy, and vaccine delivery. Oncology currently holds the largest market share, with numerous clinical trials exploring electroporation-based cancer treatments. However, the vaccine delivery segment is expected to grow rapidly, fueled by the need for more effective vaccine administration methods.
Geographically, North America dominates the in vivo electroporation market, followed by Europe. This is primarily due to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, substantial research funding, and favorable regulatory environments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key companies are focusing on developing more sophisticated electroporation devices and expanding their product portfolios. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry players are also on the rise, aiming to accelerate the translation of research findings into clinical applications.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of in vivo electroporation. These include concerns about safety, the need for standardized protocols, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of this technology. As research progresses and regulatory frameworks evolve, the market for in vivo electroporation is expected to continue its upward trajectory, offering significant opportunities for stakeholders in the biotechnology and healthcare sectors.
Technical Challenges
Electroporation in vivo presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and clinicians must address to ensure safety and efficacy. One of the primary concerns is the precise control of electric field distribution within target tissues. The heterogeneous nature of biological structures can lead to unpredictable field patterns, potentially causing uneven gene transfer or cellular damage in non-target areas. This issue is particularly pronounced in complex organ systems, where achieving uniform electroporation across the entire target region remains difficult.
Another critical challenge lies in minimizing tissue damage and inflammatory responses. The application of electric pulses can cause localized heating, pH changes, and electrochemical reactions, all of which may lead to cellular stress or necrosis. Balancing the need for effective membrane permeabilization with the preservation of tissue integrity requires careful optimization of pulse parameters, including voltage, duration, and frequency. This balance becomes even more delicate when dealing with sensitive organs or in the presence of pre-existing medical conditions.
The development of suitable electrode designs for in vivo applications poses another significant hurdle. Electrodes must be biocompatible, minimally invasive, and capable of delivering uniform electric fields to the target area. For deep-seated tissues, the challenge of accessing the target site without causing collateral damage to surrounding structures is particularly acute. Innovative electrode configurations, such as needle arrays or flexible, conformable designs, are being explored to address these issues, but each comes with its own set of technical and practical limitations.
Monitoring and real-time control of the electroporation process in vivo represent ongoing technical challenges. Current methods often rely on indirect measurements or post-treatment analysis, making it difficult to adjust parameters during the procedure. The development of advanced imaging techniques and biosensors that can provide immediate feedback on membrane permeability and tissue status could significantly enhance the precision and safety of in vivo electroporation.
Lastly, the scalability of electroporation protocols from small animal models to human subjects presents considerable technical obstacles. Differences in tissue composition, organ size, and physiological parameters necessitate careful translation and adaptation of electroporation parameters. This scaling process is further complicated by the need to ensure consistent and reproducible results across diverse patient populations, considering factors such as age, body composition, and health status.
Another critical challenge lies in minimizing tissue damage and inflammatory responses. The application of electric pulses can cause localized heating, pH changes, and electrochemical reactions, all of which may lead to cellular stress or necrosis. Balancing the need for effective membrane permeabilization with the preservation of tissue integrity requires careful optimization of pulse parameters, including voltage, duration, and frequency. This balance becomes even more delicate when dealing with sensitive organs or in the presence of pre-existing medical conditions.
The development of suitable electrode designs for in vivo applications poses another significant hurdle. Electrodes must be biocompatible, minimally invasive, and capable of delivering uniform electric fields to the target area. For deep-seated tissues, the challenge of accessing the target site without causing collateral damage to surrounding structures is particularly acute. Innovative electrode configurations, such as needle arrays or flexible, conformable designs, are being explored to address these issues, but each comes with its own set of technical and practical limitations.
Monitoring and real-time control of the electroporation process in vivo represent ongoing technical challenges. Current methods often rely on indirect measurements or post-treatment analysis, making it difficult to adjust parameters during the procedure. The development of advanced imaging techniques and biosensors that can provide immediate feedback on membrane permeability and tissue status could significantly enhance the precision and safety of in vivo electroporation.
Lastly, the scalability of electroporation protocols from small animal models to human subjects presents considerable technical obstacles. Differences in tissue composition, organ size, and physiological parameters necessitate careful translation and adaptation of electroporation parameters. This scaling process is further complicated by the need to ensure consistent and reproducible results across diverse patient populations, considering factors such as age, body composition, and health status.
Current Protocols
01 Safety mechanisms in electroporation devices
Electroporation devices incorporate various safety mechanisms to prevent accidental discharge and ensure proper electrode placement. These may include safety interlocks, automatic shut-off systems, and real-time monitoring of electrical parameters to maintain safe voltage levels during treatment.- Safety mechanisms in electroporation devices: Electroporation devices incorporate various safety mechanisms to prevent accidental discharge and ensure user protection. These may include automatic shut-off systems, voltage limiters, and insulated components. Such features help minimize the risk of electrical injuries during the electroporation process.
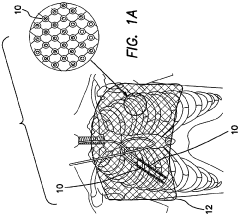
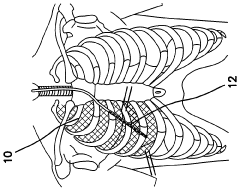
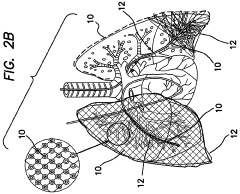
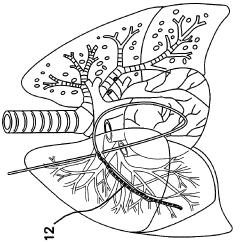
- Electrode design for improved safety: Advanced electrode designs are implemented to enhance safety during electroporation. These may include rounded edges, biocompatible materials, and precise spacing to control the electric field distribution. Improved electrode configurations help reduce the risk of tissue damage and increase overall procedure safety.
- Monitoring and control systems: Electroporation devices integrate sophisticated monitoring and control systems to ensure safe operation. These systems may include real-time impedance measurement, temperature monitoring, and feedback loops to adjust pulse parameters. Such features help maintain optimal conditions and prevent potential adverse effects during the procedure.
- Pulse optimization for safety: Researchers focus on optimizing pulse parameters to enhance electroporation safety. This includes adjusting pulse duration, amplitude, and frequency to achieve effective results while minimizing cellular damage. Advanced algorithms and modeling techniques are employed to determine the safest and most efficient pulse protocols for various applications.
- Training and safety protocols: Comprehensive training programs and safety protocols are developed to ensure proper use of electroporation devices. These may include user manuals, instructional videos, and hands-on training sessions. Establishing standardized safety guidelines and best practices helps minimize the risk of accidents and improves overall procedure safety.
02 Electrode design for minimizing tissue damage
Advanced electrode designs are developed to minimize tissue damage during electroporation. These include specialized shapes, materials, and coatings that optimize electric field distribution and reduce the risk of burns or excessive cell death in the treated area.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pulse parameters optimization for safety
Researchers focus on optimizing pulse parameters such as duration, frequency, and amplitude to enhance safety while maintaining efficacy. This involves developing algorithms and control systems that adjust these parameters in real-time based on tissue impedance and other factors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of imaging technologies for precise targeting
Advanced imaging technologies are integrated into electroporation systems to ensure precise targeting of the treatment area. This includes real-time ultrasound guidance, MRI compatibility, and computer-assisted planning tools to minimize the risk of affecting non-target tissues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-treatment care and monitoring protocols
Comprehensive post-treatment care and monitoring protocols are developed to ensure patient safety after electroporation procedures. These include guidelines for managing potential side effects, follow-up examinations, and long-term safety assessments to detect and address any delayed complications.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The electroporation in vivo market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing applications in gene therapy and cancer treatment. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like MaxCyte, Inovio Pharmaceuticals, and Bio-Rad Laboratories leading innovation. These firms are developing more sophisticated and safer electroporation devices, addressing key challenges such as precise targeting and minimizing tissue damage. Regulatory considerations are becoming more stringent, reflecting the technology's growing clinical relevance. While established players dominate, emerging companies like Cellares Corp. are introducing novel approaches, potentially disrupting the market landscape.
MaxCyte, Inc.
Technical Solution: MaxCyte has developed a proprietary Flow Electroporation® technology for in vivo applications. Their platform utilizes a controlled electric field to temporarily create pores in cell membranes, allowing for the efficient delivery of therapeutic molecules. The company has implemented advanced safety protocols, including real-time monitoring of electrical parameters and automated shut-off mechanisms to prevent tissue damage[1]. MaxCyte's system also incorporates disposable processing assemblies to minimize contamination risks. They have conducted extensive preclinical studies to optimize electroporation parameters for various tissue types, ensuring efficient gene delivery while maintaining cell viability[2]. MaxCyte has also developed specialized electrodes designed for specific in vivo applications, such as intramuscular or intratumoral delivery, to enhance targeting and reduce off-target effects[3].
Strengths: Highly efficient gene delivery, customizable for different tissue types, and advanced safety features. Weaknesses: May require specialized training for operators and potential for localized tissue damage if parameters are not optimized.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Inovio has pioneered the CELLECTRA® electroporation device for in vivo DNA vaccine delivery. Their technology uses a proprietary pulse sequence that creates transient pores in cell membranes while minimizing tissue damage. The CELLECTRA® system incorporates a smart applicator that adjusts electrical parameters based on tissue resistance, ensuring consistent delivery across different subjects[4]. Inovio has implemented rigorous safety protocols, including pre-pulse tissue measurements and real-time monitoring of electrical current. They have conducted extensive clinical trials, demonstrating the safety and efficacy of their electroporation technology in humans for various indications, including infectious diseases and cancer[5]. Inovio has also developed minimally invasive electrode designs for intradermal delivery, which have shown improved patient comfort and compliance in clinical settings[6].
Strengths: Extensive clinical data supporting safety and efficacy, adaptive pulse technology, and minimally invasive designs. Weaknesses: Limited to DNA-based therapeutics and may require multiple treatments for optimal efficacy.
Key Innovations
Method and apparatus of low strength electric field network-mediated delivery of therapeutics in solid organs
PatentWO2008112787A2
Innovation
- A low strength electric field network (LSEN) is used to permeabilize cell membranes for targeted delivery of therapeutic molecules like genes, proteins, and drugs in solid organs, employing customized electrode arrays and configurations for each organ type, allowing for ex vivo and in vivo applications with reduced voltage and increased efficiency.
Electroporation and Electrophoresis System and Method for Achieving Molecular Penetration into Cells In Vivo
PatentInactiveUS20080033340A1
Innovation
- A system and method that combine high-intensity pulses for inducing electroporation with low-intensity pulses for electrophoretic molecule movement and adherence, allowing for efficient delivery of molecules into cells while reducing intensity and duration of pulses, thereby minimizing discomfort and tissue damage.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for in vivo electroporation is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful navigation to ensure both safety and compliance. At the international level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provide overarching guidelines that influence national regulatory bodies.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory authority overseeing in vivo electroporation. The FDA categorizes electroporation devices as medical devices, subject to the regulatory pathways outlined in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Depending on the intended use and risk profile, these devices may fall under Class II or Class III classifications, requiring either a 510(k) clearance or a more rigorous Premarket Approval (PMA) process.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), which came into full effect in May 2021 and May 2022, respectively. These regulations have significant implications for electroporation devices and associated therapies, particularly in terms of clinical evidence requirements and post-market surveillance.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has its own regulatory framework, which includes specific guidelines for novel therapies and medical devices. The PMDA's approach often emphasizes the importance of early consultation and stepwise development strategies for innovative technologies like in vivo electroporation.
Regulatory considerations for in vivo electroporation extend beyond device approval to encompass the entire treatment protocol. This includes the regulation of any genetic material or drugs delivered via electroporation, which may fall under separate regulatory pathways for biologics or pharmaceuticals. The combination of device and drug delivery adds complexity to the regulatory process, often requiring a coordinated review across different divisions within regulatory agencies.
Safety protocols are a critical component of the regulatory framework. These typically include requirements for preclinical studies demonstrating safety in animal models, followed by carefully designed clinical trials with robust safety monitoring. Regulatory bodies often require long-term follow-up studies to assess potential delayed effects of electroporation and any associated genetic modifications.
As the field of in vivo electroporation advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging areas of focus include the development of standards for electroporation protocols, harmonization of international regulations to facilitate global research and commercialization, and the adaptation of existing frameworks to accommodate novel applications of the technology, such as in cancer immunotherapy or gene editing.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory authority overseeing in vivo electroporation. The FDA categorizes electroporation devices as medical devices, subject to the regulatory pathways outlined in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Depending on the intended use and risk profile, these devices may fall under Class II or Class III classifications, requiring either a 510(k) clearance or a more rigorous Premarket Approval (PMA) process.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), which came into full effect in May 2021 and May 2022, respectively. These regulations have significant implications for electroporation devices and associated therapies, particularly in terms of clinical evidence requirements and post-market surveillance.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has its own regulatory framework, which includes specific guidelines for novel therapies and medical devices. The PMDA's approach often emphasizes the importance of early consultation and stepwise development strategies for innovative technologies like in vivo electroporation.
Regulatory considerations for in vivo electroporation extend beyond device approval to encompass the entire treatment protocol. This includes the regulation of any genetic material or drugs delivered via electroporation, which may fall under separate regulatory pathways for biologics or pharmaceuticals. The combination of device and drug delivery adds complexity to the regulatory process, often requiring a coordinated review across different divisions within regulatory agencies.
Safety protocols are a critical component of the regulatory framework. These typically include requirements for preclinical studies demonstrating safety in animal models, followed by carefully designed clinical trials with robust safety monitoring. Regulatory bodies often require long-term follow-up studies to assess potential delayed effects of electroporation and any associated genetic modifications.
As the field of in vivo electroporation advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging areas of focus include the development of standards for electroporation protocols, harmonization of international regulations to facilitate global research and commercialization, and the adaptation of existing frameworks to accommodate novel applications of the technology, such as in cancer immunotherapy or gene editing.
Ethical Considerations
Electroporation in vivo raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible research and clinical applications. The primary ethical concern revolves around the potential risks to human and animal subjects involved in electroporation procedures. As this technique involves the application of electrical pulses to living tissues, there is a need to balance the potential benefits with the risks of tissue damage, pain, or unintended physiological effects.
One key ethical consideration is the principle of non-maleficence, which requires researchers and clinicians to minimize harm to subjects. This necessitates rigorous safety protocols and thorough pre-clinical testing to assess potential adverse effects before progressing to human trials. Additionally, the principle of beneficence must be upheld, ensuring that the potential benefits of electroporation outweigh the risks for the subjects involved.
Informed consent is another critical ethical aspect of in vivo electroporation research and applications. Subjects must be fully informed about the procedure, its potential risks, and expected outcomes. This is particularly important given the novel nature of electroporation techniques and the potential for unforeseen long-term effects. Special considerations must be given to vulnerable populations, such as children or individuals with compromised decision-making capacity.
Animal welfare is a significant ethical concern in pre-clinical electroporation studies. Researchers must adhere to the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) to minimize animal suffering and use alternative methods where possible. This includes optimizing experimental designs to reduce the number of animals required and implementing refined techniques to minimize pain and distress.
The ethical use of genetic manipulation through electroporation also warrants careful consideration. While electroporation offers promising avenues for gene therapy and genetic research, it raises questions about the limits of genetic intervention and the potential for unintended consequences. Ethical guidelines must be established to govern the appropriate use of electroporation for genetic modifications, particularly in germline cells.
Privacy and data protection are additional ethical concerns, especially as electroporation techniques generate large amounts of biological and genetic data. Researchers and clinicians must ensure the confidentiality and security of subject information, adhering to data protection regulations and ethical guidelines for handling sensitive medical information.
Lastly, the equitable distribution of electroporation technology and its potential benefits is an important ethical consideration. As this technology advances, efforts should be made to ensure that it does not exacerbate existing healthcare disparities and that its benefits are accessible to diverse populations.
One key ethical consideration is the principle of non-maleficence, which requires researchers and clinicians to minimize harm to subjects. This necessitates rigorous safety protocols and thorough pre-clinical testing to assess potential adverse effects before progressing to human trials. Additionally, the principle of beneficence must be upheld, ensuring that the potential benefits of electroporation outweigh the risks for the subjects involved.
Informed consent is another critical ethical aspect of in vivo electroporation research and applications. Subjects must be fully informed about the procedure, its potential risks, and expected outcomes. This is particularly important given the novel nature of electroporation techniques and the potential for unforeseen long-term effects. Special considerations must be given to vulnerable populations, such as children or individuals with compromised decision-making capacity.
Animal welfare is a significant ethical concern in pre-clinical electroporation studies. Researchers must adhere to the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) to minimize animal suffering and use alternative methods where possible. This includes optimizing experimental designs to reduce the number of animals required and implementing refined techniques to minimize pain and distress.
The ethical use of genetic manipulation through electroporation also warrants careful consideration. While electroporation offers promising avenues for gene therapy and genetic research, it raises questions about the limits of genetic intervention and the potential for unintended consequences. Ethical guidelines must be established to govern the appropriate use of electroporation for genetic modifications, particularly in germline cells.
Privacy and data protection are additional ethical concerns, especially as electroporation techniques generate large amounts of biological and genetic data. Researchers and clinicians must ensure the confidentiality and security of subject information, adhering to data protection regulations and ethical guidelines for handling sensitive medical information.
Lastly, the equitable distribution of electroporation technology and its potential benefits is an important ethical consideration. As this technology advances, efforts should be made to ensure that it does not exacerbate existing healthcare disparities and that its benefits are accessible to diverse populations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!