How To Standardize Electroporation Buffers For Reproducible Results
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Buffer Standardization Goals
Electroporation buffer standardization is a critical goal in the field of cell biology and genetic engineering. The primary objective is to develop a set of universally applicable buffer compositions that can consistently produce high-efficiency transfection results across various cell types and experimental conditions. This standardization aims to address the current challenges of reproducibility and comparability in electroporation experiments.
One of the key goals is to establish a range of buffer formulations that can be optimized for different cell types, including mammalian, bacterial, and plant cells. These standardized buffers should maintain cell viability while maximizing transfection efficiency. The formulations need to consider factors such as ionic strength, pH, and osmolarity, which significantly impact the electroporation process.
Another important aspect of buffer standardization is to ensure consistency in the quality and purity of buffer components. This involves defining specific grades of chemicals to be used and establishing protocols for buffer preparation and storage. By minimizing variability in buffer composition, researchers can more easily replicate experiments and compare results across different laboratories.
The standardization process also aims to develop guidelines for buffer selection based on specific experimental parameters. This includes recommendations for adjusting buffer composition according to the size and type of genetic material being introduced, the voltage and duration of electric pulses, and the target cell characteristics. Such guidelines would enable researchers to make informed decisions about buffer choice, leading to more predictable and reproducible outcomes.
Furthermore, the standardization goals encompass the creation of quality control measures for electroporation buffers. This involves developing assays to verify buffer performance and stability over time, as well as establishing benchmarks for acceptable variation in transfection efficiency. These quality control standards would help ensure the reliability of electroporation experiments and facilitate troubleshooting when unexpected results occur.
An additional objective is to integrate buffer standardization with emerging electroporation technologies. As new electroporation devices and methods are developed, standardized buffers should be adaptable to these innovations while maintaining their core performance characteristics. This flexibility will be crucial for the long-term relevance and applicability of standardized buffer systems in evolving research environments.
One of the key goals is to establish a range of buffer formulations that can be optimized for different cell types, including mammalian, bacterial, and plant cells. These standardized buffers should maintain cell viability while maximizing transfection efficiency. The formulations need to consider factors such as ionic strength, pH, and osmolarity, which significantly impact the electroporation process.
Another important aspect of buffer standardization is to ensure consistency in the quality and purity of buffer components. This involves defining specific grades of chemicals to be used and establishing protocols for buffer preparation and storage. By minimizing variability in buffer composition, researchers can more easily replicate experiments and compare results across different laboratories.
The standardization process also aims to develop guidelines for buffer selection based on specific experimental parameters. This includes recommendations for adjusting buffer composition according to the size and type of genetic material being introduced, the voltage and duration of electric pulses, and the target cell characteristics. Such guidelines would enable researchers to make informed decisions about buffer choice, leading to more predictable and reproducible outcomes.
Furthermore, the standardization goals encompass the creation of quality control measures for electroporation buffers. This involves developing assays to verify buffer performance and stability over time, as well as establishing benchmarks for acceptable variation in transfection efficiency. These quality control standards would help ensure the reliability of electroporation experiments and facilitate troubleshooting when unexpected results occur.
An additional objective is to integrate buffer standardization with emerging electroporation technologies. As new electroporation devices and methods are developed, standardized buffers should be adaptable to these innovations while maintaining their core performance characteristics. This flexibility will be crucial for the long-term relevance and applicability of standardized buffer systems in evolving research environments.
Market Demand for Reproducible Electroporation
The market demand for reproducible electroporation has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing applications of this technique in various fields such as gene therapy, cell-based therapies, and genetic engineering. Researchers and biotechnology companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of standardized electroporation buffers to ensure consistent and reliable results across different experiments and laboratories.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the rapid expansion of the cell and gene therapy market. As these therapies move from research to clinical trials and commercialization, there is a critical need for reproducible and scalable electroporation processes. Standardized buffers play a crucial role in achieving this reproducibility, making them essential components in the development and manufacturing of advanced therapies.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are also significant contributors to the market demand for reproducible electroporation. These sectors rely heavily on electroporation for drug discovery, target validation, and the development of new therapeutic approaches. The ability to consistently deliver molecules into cells with high efficiency and low toxicity is paramount for these applications, driving the need for standardized electroporation buffers.
Academic research institutions represent another substantial market segment. As electroporation becomes a routine technique in molecular biology and genetics laboratories, there is an increasing emphasis on reproducibility and comparability of results across different research groups. Standardized buffers help address the challenges of inter-laboratory variability, enhancing the reliability and impact of scientific findings.
The agricultural biotechnology sector is emerging as a new driver of demand for reproducible electroporation. As genetic modification techniques become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for efficient and consistent methods to introduce genetic material into plant cells. Standardized electroporation buffers can significantly improve the success rates of plant transformation experiments, accelerating crop improvement efforts.
Market analysis indicates that the global electroporation market, including buffers and related products, is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of electroporation in various applications and the rising demand for more reliable and reproducible results.
However, challenges remain in fully addressing this market demand. The diversity of cell types and experimental conditions used in electroporation creates a need for versatile buffer solutions that can maintain performance across different scenarios. Additionally, there is a growing call for more transparent and comprehensive reporting of electroporation protocols, including buffer compositions, to facilitate reproducibility efforts.
In response to these market trends, several biotechnology companies are developing and commercializing standardized electroporation buffer systems. These products aim to offer researchers and industry professionals ready-to-use solutions that ensure consistent results across different cell types and experimental setups. The market is also seeing an increase in customized buffer formulations tailored to specific cell lines or applications, addressing the need for both standardization and flexibility.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the rapid expansion of the cell and gene therapy market. As these therapies move from research to clinical trials and commercialization, there is a critical need for reproducible and scalable electroporation processes. Standardized buffers play a crucial role in achieving this reproducibility, making them essential components in the development and manufacturing of advanced therapies.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are also significant contributors to the market demand for reproducible electroporation. These sectors rely heavily on electroporation for drug discovery, target validation, and the development of new therapeutic approaches. The ability to consistently deliver molecules into cells with high efficiency and low toxicity is paramount for these applications, driving the need for standardized electroporation buffers.
Academic research institutions represent another substantial market segment. As electroporation becomes a routine technique in molecular biology and genetics laboratories, there is an increasing emphasis on reproducibility and comparability of results across different research groups. Standardized buffers help address the challenges of inter-laboratory variability, enhancing the reliability and impact of scientific findings.
The agricultural biotechnology sector is emerging as a new driver of demand for reproducible electroporation. As genetic modification techniques become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for efficient and consistent methods to introduce genetic material into plant cells. Standardized electroporation buffers can significantly improve the success rates of plant transformation experiments, accelerating crop improvement efforts.
Market analysis indicates that the global electroporation market, including buffers and related products, is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of electroporation in various applications and the rising demand for more reliable and reproducible results.
However, challenges remain in fully addressing this market demand. The diversity of cell types and experimental conditions used in electroporation creates a need for versatile buffer solutions that can maintain performance across different scenarios. Additionally, there is a growing call for more transparent and comprehensive reporting of electroporation protocols, including buffer compositions, to facilitate reproducibility efforts.
In response to these market trends, several biotechnology companies are developing and commercializing standardized electroporation buffer systems. These products aim to offer researchers and industry professionals ready-to-use solutions that ensure consistent results across different cell types and experimental setups. The market is also seeing an increase in customized buffer formulations tailored to specific cell lines or applications, addressing the need for both standardization and flexibility.
Current Challenges in Electroporation Buffer Consistency
Electroporation buffer consistency remains a significant challenge in achieving reproducible results across various electroporation experiments. The lack of standardization in buffer composition and preparation methods leads to variability in transfection efficiency and cell viability. One of the primary issues is the diverse range of buffer formulations used by different research groups, making it difficult to compare and replicate results across laboratories.
The composition of electroporation buffers can significantly impact the efficiency of gene transfer and the overall success of the procedure. Factors such as ionic strength, pH, and the presence of specific additives can greatly influence the formation and stability of membrane pores during electroporation. However, there is currently no universally accepted standard for buffer composition, leading to inconsistencies in experimental outcomes.
Another challenge is the variability in buffer preparation methods. Even when using similar formulations, differences in the quality of reagents, measurement accuracy, and storage conditions can lead to discrepancies in buffer performance. This variability is further compounded by the lack of detailed reporting of buffer preparation protocols in many published studies, making it difficult for other researchers to replicate the exact conditions.
The sensitivity of cells to buffer composition adds another layer of complexity to the standardization process. Different cell types may respond optimally to different buffer formulations, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all solution. This cell-specific requirement often leads researchers to develop custom buffers for their particular experimental systems, further contributing to the lack of standardization across the field.
The absence of robust quality control measures for electroporation buffers is also a significant concern. Unlike many other laboratory reagents, there are no widely accepted standards for assessing the quality and consistency of electroporation buffers. This lack of quality assurance makes it difficult to identify and mitigate sources of variability in experimental outcomes.
Furthermore, the impact of buffer aging and storage conditions on electroporation efficiency is often overlooked. Buffers may degrade over time or become contaminated, leading to reduced performance. However, there is limited guidance on best practices for buffer storage and shelf-life determination, contributing to inconsistencies in experimental results.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from the scientific community to establish standardized protocols for buffer composition, preparation, and quality control. The development of reference standards and benchmarking tools could significantly improve the reproducibility of electroporation experiments across different laboratories and cell types.
The composition of electroporation buffers can significantly impact the efficiency of gene transfer and the overall success of the procedure. Factors such as ionic strength, pH, and the presence of specific additives can greatly influence the formation and stability of membrane pores during electroporation. However, there is currently no universally accepted standard for buffer composition, leading to inconsistencies in experimental outcomes.
Another challenge is the variability in buffer preparation methods. Even when using similar formulations, differences in the quality of reagents, measurement accuracy, and storage conditions can lead to discrepancies in buffer performance. This variability is further compounded by the lack of detailed reporting of buffer preparation protocols in many published studies, making it difficult for other researchers to replicate the exact conditions.
The sensitivity of cells to buffer composition adds another layer of complexity to the standardization process. Different cell types may respond optimally to different buffer formulations, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all solution. This cell-specific requirement often leads researchers to develop custom buffers for their particular experimental systems, further contributing to the lack of standardization across the field.
The absence of robust quality control measures for electroporation buffers is also a significant concern. Unlike many other laboratory reagents, there are no widely accepted standards for assessing the quality and consistency of electroporation buffers. This lack of quality assurance makes it difficult to identify and mitigate sources of variability in experimental outcomes.
Furthermore, the impact of buffer aging and storage conditions on electroporation efficiency is often overlooked. Buffers may degrade over time or become contaminated, leading to reduced performance. However, there is limited guidance on best practices for buffer storage and shelf-life determination, contributing to inconsistencies in experimental results.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from the scientific community to establish standardized protocols for buffer composition, preparation, and quality control. The development of reference standards and benchmarking tools could significantly improve the reproducibility of electroporation experiments across different laboratories and cell types.
Existing Buffer Standardization Approaches
01 Optimization of electroporation buffer composition
The composition of electroporation buffers plays a crucial role in ensuring reproducibility. Factors such as pH, ionic strength, and osmolarity need to be carefully optimized to maintain cell viability and transfection efficiency. Specific additives like antioxidants or membrane stabilizers may be included to enhance reproducibility across different cell types and experimental conditions.- Optimization of electroporation buffer composition: The composition of electroporation buffers plays a crucial role in ensuring reproducibility. Key factors include pH, ionic strength, and osmolarity. Optimizing these parameters can enhance cell viability and transfection efficiency, leading to more consistent results across experiments.
- Standardization of electroporation protocols: Developing and adhering to standardized protocols for electroporation can significantly improve reproducibility. This includes consistent preparation of cells, precise timing of buffer exposure, and controlled application of electric pulses. Standardization helps minimize variability between experiments and operators.
- Use of quality control measures: Implementing rigorous quality control measures for electroporation buffers and reagents is essential for reproducibility. This may involve regular testing of buffer components, monitoring of storage conditions, and validation of buffer performance across different batches and experimental setups.
- Integration of automation and robotics: Incorporating automation and robotics into electroporation processes can enhance reproducibility by reducing human error and ensuring consistent handling. Automated systems can precisely control buffer dispensing, cell manipulation, and pulse application, leading to more uniform results across experiments.
- Development of novel buffer formulations: Research into novel buffer formulations aims to improve the reproducibility of electroporation. This includes the exploration of new additives, stabilizers, and protective agents that can enhance cell survival and transfection efficiency while maintaining consistent performance across different cell types and experimental conditions.
02 Standardization of electroporation protocols
Developing standardized protocols for electroporation procedures is essential for improving reproducibility. This includes consistent methods for cell preparation, buffer handling, and post-electroporation recovery. Detailed documentation of parameters such as voltage, pulse duration, and number of pulses helps in achieving consistent results across different laboratories and experiments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quality control of electroporation reagents
Implementing rigorous quality control measures for electroporation reagents is crucial for reproducibility. This includes regular testing of buffer components, verifying the purity and stability of DNA or RNA samples, and ensuring consistent performance of electroporation devices. Proper storage and handling of reagents also contribute to reproducible results.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cell-specific optimization of electroporation conditions
Different cell types may require specific electroporation conditions for optimal results. Tailoring buffer compositions and electroporation parameters to suit particular cell lines or primary cells can significantly improve reproducibility. This may involve adjusting factors such as buffer osmolarity, temperature, or the addition of cell-specific protective agents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use of automation and high-throughput systems
Incorporating automation and high-throughput systems in electroporation processes can enhance reproducibility by minimizing human error and standardizing procedures. Automated liquid handling, precise control of electroporation parameters, and integrated data analysis can lead to more consistent and reliable results across multiple experiments and different operators.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electroporation Technology
The electroporation buffer standardization market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for reproducible results in genetic engineering and cell therapy applications. The global market size for electroporation technologies is projected to reach several hundred million dollars by 2025. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing research focuses on optimizing buffer compositions for specific cell types and applications. Key players like Thermo Fisher Scientific (Applied Biosystems), Lonza, and Panasonic are leading innovation in this space, developing proprietary buffer formulations and electroporation systems. Emerging companies such as Precigen and NanoEntek are also contributing to market expansion with novel approaches to buffer design and electroporation protocols.
Precigen, Inc.
Technical Solution: Precigen has developed a standardized electroporation buffer system called UltraVector® for reproducible gene delivery. This system utilizes a proprietary combination of ionic and non-ionic components to maintain consistent osmolarity and pH across different cell types[1]. The buffer is optimized to protect cell viability while maximizing transfection efficiency. Precigen's approach includes pre-formulated, ready-to-use buffers for specific cell types, eliminating variability in buffer preparation[2]. They have also implemented automated quality control measures to ensure batch-to-batch consistency, including conductivity and osmolarity testing[3].
Strengths: Tailored for specific cell types, ready-to-use formulations, automated quality control. Weaknesses: May be less flexible for novel cell types or unique experimental conditions.
Lonza Cologne AG
Technical Solution: Lonza has introduced the Nucleofector™ Technology, which includes optimized cell-type specific Nucleofector™ Solutions for standardized electroporation. Their approach focuses on developing buffer compositions that are tailored to specific cell types and electroporation devices[4]. Lonza's buffers are designed to maintain cell viability and ensure high transfection efficiency across a wide range of cell types, including hard-to-transfect primary cells and stem cells[5]. The company provides detailed protocols and optimization guidelines to ensure reproducibility, including recommendations for buffer storage, handling, and use with their Nucleofector™ devices[6].
Strengths: Wide range of cell-type specific buffers, comprehensive protocols for reproducibility. Weaknesses: May require specific Nucleofector™ devices for optimal results.
Innovations in Buffer Composition and Stability
Microchip electrophoretic method and device
PatentActiveJP2011185714A
Innovation
- A microchip electrophoresis method involving buffer liquid dispensing, filling, removal, cleaning, and sample dispensing steps, with optional buffer redispensing and multiple washing steps to ensure complete removal of buffer solution before sample dispensing.
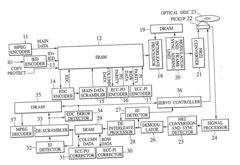
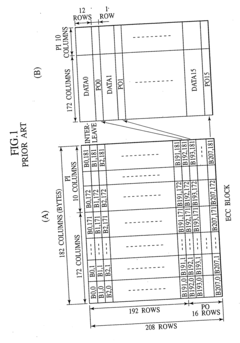
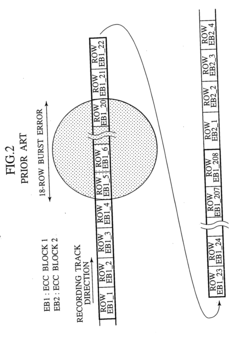
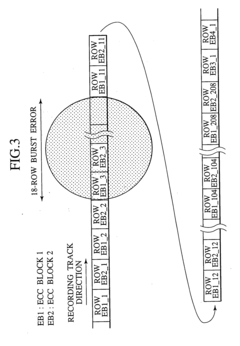
Digital signal processing method, data recording and reproducing apparatus, and data recording medium that are resistant to burst errors
PatentInactiveUS20070055920A1
Innovation
- A digital signal processing method that alternately switches data units between consecutive ECC blocks during recording and reproduction, distributing errors across multiple blocks to increase the correctable burst-error length without increasing redundancy, using a product-coding method to generate ECC blocks and interleaving data in a specific sequence to enhance error correction capabilities.
Quality Control Measures for Electroporation Buffers
Quality control measures are essential for ensuring the reproducibility and reliability of electroporation experiments. Standardization of electroporation buffers is a critical aspect of this process. To achieve consistent results, several key quality control measures should be implemented.
Firstly, the composition of electroporation buffers must be precisely defined and rigorously maintained. This includes specifying the exact concentrations of all components, such as salts, sugars, and other additives. A standardized recipe should be established and followed meticulously for each batch of buffer prepared.
pH control is another crucial factor in buffer standardization. The pH of the electroporation buffer can significantly impact the efficiency of cell membrane permeabilization and subsequent DNA uptake. Regular pH measurements and adjustments should be performed to ensure consistency across batches. Calibrated pH meters and standardized protocols for pH adjustment are necessary tools in this process.
Osmolality is an often-overlooked parameter that can greatly influence electroporation outcomes. Maintaining a consistent osmolality is vital for cell viability and transfection efficiency. Implementing routine osmolality checks using an osmometer can help detect any deviations from the established standard.
Sterility is paramount in electroporation experiments to prevent contamination and ensure reproducible results. All buffers should be prepared under aseptic conditions and subjected to sterility testing. This may involve filtration through 0.2 μm filters and periodic microbiological testing to confirm the absence of bacterial or fungal contaminants.
The storage and handling of electroporation buffers also require standardization. Proper storage conditions, including temperature and light exposure, should be defined and strictly adhered to. Expiration dates must be established based on stability studies, and buffers should be discarded after their expiration to maintain quality.
Batch-to-batch consistency is crucial for reproducible results. Implementing a system of batch numbering and record-keeping allows for traceability and easier troubleshooting if inconsistencies arise. Each batch should undergo a series of quality control tests before release for use in experiments.
Regular validation of buffer performance is essential. This can be achieved through standardized electroporation experiments using control cell lines and plasmids. Monitoring transfection efficiency and cell viability across multiple batches can help identify any deviations in buffer quality.
Lastly, the implementation of a robust documentation system is vital for maintaining quality control standards. Detailed records of buffer preparation, testing, and usage should be kept, including any deviations from established protocols. This documentation aids in troubleshooting and ensures compliance with good laboratory practices.
Firstly, the composition of electroporation buffers must be precisely defined and rigorously maintained. This includes specifying the exact concentrations of all components, such as salts, sugars, and other additives. A standardized recipe should be established and followed meticulously for each batch of buffer prepared.
pH control is another crucial factor in buffer standardization. The pH of the electroporation buffer can significantly impact the efficiency of cell membrane permeabilization and subsequent DNA uptake. Regular pH measurements and adjustments should be performed to ensure consistency across batches. Calibrated pH meters and standardized protocols for pH adjustment are necessary tools in this process.
Osmolality is an often-overlooked parameter that can greatly influence electroporation outcomes. Maintaining a consistent osmolality is vital for cell viability and transfection efficiency. Implementing routine osmolality checks using an osmometer can help detect any deviations from the established standard.
Sterility is paramount in electroporation experiments to prevent contamination and ensure reproducible results. All buffers should be prepared under aseptic conditions and subjected to sterility testing. This may involve filtration through 0.2 μm filters and periodic microbiological testing to confirm the absence of bacterial or fungal contaminants.
The storage and handling of electroporation buffers also require standardization. Proper storage conditions, including temperature and light exposure, should be defined and strictly adhered to. Expiration dates must be established based on stability studies, and buffers should be discarded after their expiration to maintain quality.
Batch-to-batch consistency is crucial for reproducible results. Implementing a system of batch numbering and record-keeping allows for traceability and easier troubleshooting if inconsistencies arise. Each batch should undergo a series of quality control tests before release for use in experiments.
Regular validation of buffer performance is essential. This can be achieved through standardized electroporation experiments using control cell lines and plasmids. Monitoring transfection efficiency and cell viability across multiple batches can help identify any deviations in buffer quality.
Lastly, the implementation of a robust documentation system is vital for maintaining quality control standards. Detailed records of buffer preparation, testing, and usage should be kept, including any deviations from established protocols. This documentation aids in troubleshooting and ensures compliance with good laboratory practices.
Regulatory Considerations for Standardized Buffers
The standardization of electroporation buffers for reproducible results must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines to ensure safety, efficacy, and consistency in both research and clinical applications. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and other national health authorities play a crucial role in overseeing the development and use of standardized buffers.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of electroporation buffers. Depending on their intended use, these buffers may be categorized as medical devices, biologics, or combination products. This classification determines the specific regulatory pathway and requirements for approval and market authorization.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential for the production of standardized electroporation buffers. Manufacturers must implement robust quality control systems to ensure consistent composition, purity, and sterility of the buffers. This includes validated production processes, rigorous testing protocols, and comprehensive documentation.
Regulatory agencies require extensive safety and efficacy data for standardized electroporation buffers. This typically involves preclinical studies to assess biocompatibility, toxicity, and potential interactions with various cell types and biomolecules. Clinical trials may also be necessary to demonstrate the reproducibility and effectiveness of the buffers in human applications.
Labeling and packaging regulations are another critical aspect of standardized electroporation buffers. Clear and accurate labeling must include composition, storage conditions, expiration dates, and intended use. Any claims regarding performance or compatibility with specific electroporation devices must be substantiated with scientific evidence.
Traceability and lot control are crucial regulatory requirements for standardized buffers. Manufacturers must implement systems to track each batch of buffer from raw materials to final product, enabling rapid identification and recall of any potentially compromised lots.
Post-market surveillance is an ongoing regulatory obligation for standardized electroporation buffers. Manufacturers must monitor and report any adverse events or quality issues, and implement corrective actions as necessary. This ensures the continued safety and efficacy of the buffers in real-world applications.
Regulatory harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline the approval process for standardized buffers across different regions. This can facilitate global adoption and reduce regulatory burdens for manufacturers.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of electroporation buffers. Depending on their intended use, these buffers may be categorized as medical devices, biologics, or combination products. This classification determines the specific regulatory pathway and requirements for approval and market authorization.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential for the production of standardized electroporation buffers. Manufacturers must implement robust quality control systems to ensure consistent composition, purity, and sterility of the buffers. This includes validated production processes, rigorous testing protocols, and comprehensive documentation.
Regulatory agencies require extensive safety and efficacy data for standardized electroporation buffers. This typically involves preclinical studies to assess biocompatibility, toxicity, and potential interactions with various cell types and biomolecules. Clinical trials may also be necessary to demonstrate the reproducibility and effectiveness of the buffers in human applications.
Labeling and packaging regulations are another critical aspect of standardized electroporation buffers. Clear and accurate labeling must include composition, storage conditions, expiration dates, and intended use. Any claims regarding performance or compatibility with specific electroporation devices must be substantiated with scientific evidence.
Traceability and lot control are crucial regulatory requirements for standardized buffers. Manufacturers must implement systems to track each batch of buffer from raw materials to final product, enabling rapid identification and recall of any potentially compromised lots.
Post-market surveillance is an ongoing regulatory obligation for standardized electroporation buffers. Manufacturers must monitor and report any adverse events or quality issues, and implement corrective actions as necessary. This ensures the continued safety and efficacy of the buffers in real-world applications.
Regulatory harmonization efforts, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), aim to streamline the approval process for standardized buffers across different regions. This can facilitate global adoption and reduce regulatory burdens for manufacturers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!