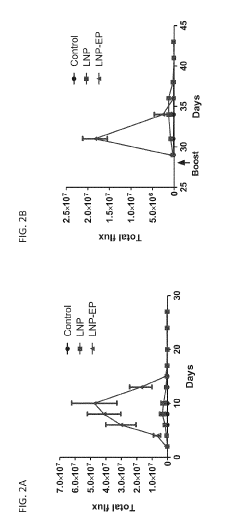
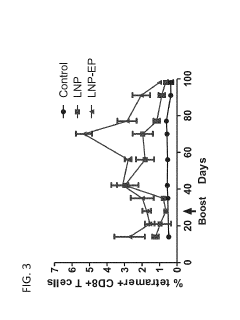
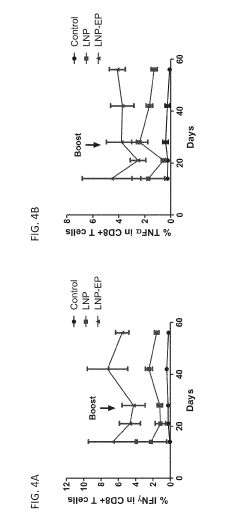
Electroporation Assisted Vaccination: Delivery Metrics And Trials
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Vaccination Background and Objectives
Electroporation-assisted vaccination represents a significant advancement in the field of immunization, combining the principles of electroporation with traditional vaccine delivery methods. This innovative approach has emerged as a promising technique to enhance the efficacy of vaccines by improving the cellular uptake of antigens. The technology has evolved over the past few decades, with initial research focusing on in vitro applications before progressing to in vivo studies and clinical trials.
The development of electroporation-assisted vaccination can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers first discovered that electric pulses could temporarily increase cell membrane permeability. This phenomenon, known as electroporation, was initially used for gene transfer in laboratory settings. As the potential for medical applications became apparent, scientists began exploring its use in vaccine delivery.
The primary objective of electroporation-assisted vaccination is to overcome the limitations of conventional vaccination methods, particularly in terms of immune response generation and antigen delivery efficiency. By applying controlled electric pulses to the vaccination site, the technique aims to create transient pores in cell membranes, facilitating the entry of vaccine components into cells. This enhanced cellular uptake is expected to result in a more robust and long-lasting immune response.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of sophisticated electroporation devices that can deliver precise electrical pulses while minimizing discomfort and tissue damage. These devices have been designed to be portable, user-friendly, and suitable for various clinical settings, from large-scale vaccination programs to personalized medicine applications.
The potential applications of electroporation-assisted vaccination extend beyond traditional preventive vaccines. Researchers are exploring its use in therapeutic vaccines for cancer treatment, DNA vaccines for infectious diseases, and even in the delivery of gene therapies. The versatility of this technology has attracted significant interest from both academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies, driving further research and development efforts.
As the field progresses, key objectives include optimizing electroporation parameters for different types of vaccines, improving the design of electroporation devices for enhanced safety and efficacy, and conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate the technology's effectiveness across various populations and disease targets. Additionally, researchers aim to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which electroporation enhances immune responses, potentially leading to new insights in immunology and vaccine design.
The development of electroporation-assisted vaccination can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers first discovered that electric pulses could temporarily increase cell membrane permeability. This phenomenon, known as electroporation, was initially used for gene transfer in laboratory settings. As the potential for medical applications became apparent, scientists began exploring its use in vaccine delivery.
The primary objective of electroporation-assisted vaccination is to overcome the limitations of conventional vaccination methods, particularly in terms of immune response generation and antigen delivery efficiency. By applying controlled electric pulses to the vaccination site, the technique aims to create transient pores in cell membranes, facilitating the entry of vaccine components into cells. This enhanced cellular uptake is expected to result in a more robust and long-lasting immune response.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of sophisticated electroporation devices that can deliver precise electrical pulses while minimizing discomfort and tissue damage. These devices have been designed to be portable, user-friendly, and suitable for various clinical settings, from large-scale vaccination programs to personalized medicine applications.
The potential applications of electroporation-assisted vaccination extend beyond traditional preventive vaccines. Researchers are exploring its use in therapeutic vaccines for cancer treatment, DNA vaccines for infectious diseases, and even in the delivery of gene therapies. The versatility of this technology has attracted significant interest from both academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies, driving further research and development efforts.
As the field progresses, key objectives include optimizing electroporation parameters for different types of vaccines, improving the design of electroporation devices for enhanced safety and efficacy, and conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate the technology's effectiveness across various populations and disease targets. Additionally, researchers aim to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which electroporation enhances immune responses, potentially leading to new insights in immunology and vaccine design.
Market Analysis for Electroporation Vaccine Delivery
The market for electroporation-assisted vaccine delivery is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for more effective and efficient vaccination methods. This technology offers several advantages over traditional vaccine delivery methods, including enhanced immune responses, reduced dosage requirements, and improved cellular uptake of antigens.
The global electroporation market, which includes vaccine delivery applications, was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period. The vaccine delivery segment is expected to be a major contributor to this growth, particularly in light of the ongoing global focus on vaccination campaigns.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising prevalence of infectious diseases, the need for more effective vaccine delivery systems, and increasing investments in research and development of novel vaccination technologies. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in electroporation-assisted vaccination, as researchers explore ways to enhance the efficacy of potential vaccines against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Geographically, North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, is a major market for electroporation technology, with several leading companies and research institutions based in the country. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced vaccination techniques.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key companies in the electroporation-assisted vaccine delivery market include Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Ichor Medical Systems, and Genetronics Biomedical. These companies are actively engaged in clinical trials and collaborations with pharmaceutical firms to develop and commercialize electroporation-based vaccine delivery systems.
Despite the promising growth prospects, the market faces certain challenges. These include the high cost of electroporation devices, regulatory hurdles in obtaining approvals for novel vaccine delivery methods, and the need for skilled personnel to administer electroporation-assisted vaccines. Additionally, there is ongoing research to optimize electroporation parameters and reduce any potential side effects associated with the technique.
In conclusion, the market for electroporation-assisted vaccine delivery shows strong growth potential, driven by technological advancements, increasing research activities, and the global focus on improving vaccination efficacy. As the technology continues to mature and demonstrate its benefits in clinical trials, it is expected to gain wider acceptance and adoption in the coming years, potentially revolutionizing the field of vaccine delivery.
The global electroporation market, which includes vaccine delivery applications, was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period. The vaccine delivery segment is expected to be a major contributor to this growth, particularly in light of the ongoing global focus on vaccination campaigns.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising prevalence of infectious diseases, the need for more effective vaccine delivery systems, and increasing investments in research and development of novel vaccination technologies. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in electroporation-assisted vaccination, as researchers explore ways to enhance the efficacy of potential vaccines against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Geographically, North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, is a major market for electroporation technology, with several leading companies and research institutions based in the country. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced vaccination techniques.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Key companies in the electroporation-assisted vaccine delivery market include Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Ichor Medical Systems, and Genetronics Biomedical. These companies are actively engaged in clinical trials and collaborations with pharmaceutical firms to develop and commercialize electroporation-based vaccine delivery systems.
Despite the promising growth prospects, the market faces certain challenges. These include the high cost of electroporation devices, regulatory hurdles in obtaining approvals for novel vaccine delivery methods, and the need for skilled personnel to administer electroporation-assisted vaccines. Additionally, there is ongoing research to optimize electroporation parameters and reduce any potential side effects associated with the technique.
In conclusion, the market for electroporation-assisted vaccine delivery shows strong growth potential, driven by technological advancements, increasing research activities, and the global focus on improving vaccination efficacy. As the technology continues to mature and demonstrate its benefits in clinical trials, it is expected to gain wider acceptance and adoption in the coming years, potentially revolutionizing the field of vaccine delivery.
Technical Challenges in Electroporation Assisted Vaccination
Electroporation-assisted vaccination faces several technical challenges that researchers and developers must overcome to enhance its efficacy and widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of electrical parameters for different vaccine types and target tissues. The voltage, pulse duration, and frequency of electrical pulses need to be carefully calibrated to achieve optimal cell membrane permeabilization without causing excessive tissue damage or pain.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of suitable electrode designs and delivery devices. These must ensure uniform electric field distribution across the target tissue while minimizing invasiveness and patient discomfort. Current electrode configurations often struggle to achieve consistent results across different anatomical sites and tissue types, necessitating further innovation in this area.
The stability and integrity of vaccine formulations during the electroporation process present additional hurdles. The intense electrical fields generated during electroporation can potentially damage sensitive biomolecules, such as DNA or protein-based vaccines. Researchers must develop robust formulations and delivery strategies that protect the vaccine components from degradation while still allowing for effective cellular uptake.
Scaling up electroporation-assisted vaccination for mass immunization campaigns poses logistical and technical difficulties. The need for specialized equipment and trained personnel to administer the treatment limits its applicability in resource-constrained settings. Developing portable, user-friendly devices that can be operated with minimal training is crucial for broader implementation.
Safety concerns and potential side effects associated with electroporation remain significant challenges. While generally well-tolerated, the procedure can cause local tissue damage, pain, and inflammation. Minimizing these adverse effects while maintaining vaccine efficacy is a delicate balance that researchers continue to investigate. Long-term safety studies are also needed to address any potential risks associated with repeated electroporation treatments.
The heterogeneity of immune responses among individuals presents another obstacle in optimizing electroporation-assisted vaccination. Factors such as age, genetics, and pre-existing immunity can influence the effectiveness of the technique. Developing personalized approaches or identifying biomarkers to predict and enhance individual responses to electroporation-assisted vaccination is an ongoing area of research.
Regulatory hurdles and standardization issues also pose challenges to the widespread adoption of this technology. Establishing clear guidelines for the safe and effective use of electroporation in vaccine delivery, as well as harmonizing protocols across different regulatory jurisdictions, is essential for its integration into mainstream vaccination programs.
Another significant challenge lies in the development of suitable electrode designs and delivery devices. These must ensure uniform electric field distribution across the target tissue while minimizing invasiveness and patient discomfort. Current electrode configurations often struggle to achieve consistent results across different anatomical sites and tissue types, necessitating further innovation in this area.
The stability and integrity of vaccine formulations during the electroporation process present additional hurdles. The intense electrical fields generated during electroporation can potentially damage sensitive biomolecules, such as DNA or protein-based vaccines. Researchers must develop robust formulations and delivery strategies that protect the vaccine components from degradation while still allowing for effective cellular uptake.
Scaling up electroporation-assisted vaccination for mass immunization campaigns poses logistical and technical difficulties. The need for specialized equipment and trained personnel to administer the treatment limits its applicability in resource-constrained settings. Developing portable, user-friendly devices that can be operated with minimal training is crucial for broader implementation.
Safety concerns and potential side effects associated with electroporation remain significant challenges. While generally well-tolerated, the procedure can cause local tissue damage, pain, and inflammation. Minimizing these adverse effects while maintaining vaccine efficacy is a delicate balance that researchers continue to investigate. Long-term safety studies are also needed to address any potential risks associated with repeated electroporation treatments.
The heterogeneity of immune responses among individuals presents another obstacle in optimizing electroporation-assisted vaccination. Factors such as age, genetics, and pre-existing immunity can influence the effectiveness of the technique. Developing personalized approaches or identifying biomarkers to predict and enhance individual responses to electroporation-assisted vaccination is an ongoing area of research.
Regulatory hurdles and standardization issues also pose challenges to the widespread adoption of this technology. Establishing clear guidelines for the safe and effective use of electroporation in vaccine delivery, as well as harmonizing protocols across different regulatory jurisdictions, is essential for its integration into mainstream vaccination programs.
Current Electroporation Assisted Vaccination Methods
01 Electroporation device design for vaccine delivery
Specialized electroporation devices are designed for efficient vaccine delivery. These devices incorporate features such as electrode configurations, pulse generators, and control systems to optimize the electroporation process for vaccination. The designs focus on improving the effectiveness of vaccine delivery while minimizing discomfort and tissue damage.- Electroporation device design for vaccine delivery: Specialized electroporation devices are designed for efficient vaccine delivery. These devices incorporate features such as electrode configurations, pulse generators, and control systems to optimize the electroporation process for vaccination. The design focuses on enhancing the effectiveness of vaccine delivery while minimizing discomfort and tissue damage.
- Optimization of electroporation parameters: Research focuses on optimizing electroporation parameters for vaccine delivery. This includes determining the ideal voltage, pulse duration, and frequency to achieve maximum vaccine uptake and immune response. Studies aim to balance efficacy with patient comfort and safety, considering factors such as tissue type and vaccine formulation.
- Combination of electroporation with other delivery methods: Electroporation is combined with other delivery methods to enhance vaccine efficacy. This may include the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, or other carriers in conjunction with electroporation. The synergistic effect of these combined approaches aims to improve vaccine uptake, distribution, and overall immunogenicity.
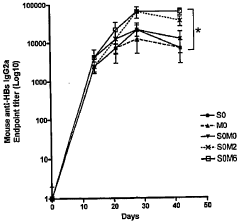
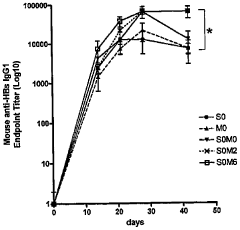
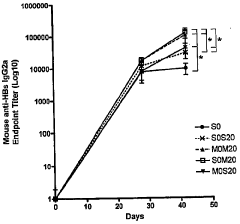
- Assessment of immune response and vaccine efficacy: Metrics are developed to assess the immune response and overall efficacy of electroporation-assisted vaccination. These may include measurements of antibody titers, T-cell responses, and long-term protection. Advanced techniques such as immunoassays, flow cytometry, and challenge studies are employed to evaluate vaccine performance.
- Safety and tolerability evaluation: Studies focus on evaluating the safety and tolerability of electroporation-assisted vaccination. This includes assessing local and systemic adverse events, pain levels, and tissue damage. Long-term follow-up studies are conducted to ensure the safety profile of this delivery method, with particular attention to different patient populations and vaccine types.
02 Optimization of electroporation parameters
Research focuses on optimizing electroporation parameters for vaccine delivery. This includes studying the effects of pulse duration, voltage, frequency, and electrode spacing on vaccine uptake and immune response. The goal is to determine the most effective combination of parameters for different types of vaccines and target tissues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Immune response assessment and vaccination efficacy
Methods and systems are developed to assess the immune response and overall efficacy of electroporation-assisted vaccination. This involves measuring antibody titers, T-cell responses, and other immunological markers to evaluate the effectiveness of the vaccine delivery method. Long-term studies are conducted to compare the durability of immune responses between electroporation-assisted and traditional vaccination methods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination of electroporation with other delivery enhancers
Research explores the combination of electroporation with other delivery enhancers to improve vaccine efficacy. This includes the use of nanoparticles, adjuvants, or other physical methods like ultrasound to synergistically enhance vaccine uptake and immune response. The goal is to develop multi-modal approaches that maximize vaccination effectiveness while minimizing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and tolerability assessment
Studies focus on evaluating the safety and tolerability of electroporation-assisted vaccination. This includes assessing local and systemic adverse events, pain levels, and tissue damage. Long-term follow-up studies are conducted to ensure the safety of this delivery method, particularly in different patient populations and for various vaccine types.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electroporation Vaccine Delivery
The electroporation-assisted vaccination field is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for this technology is expanding, driven by the need for more effective vaccine delivery methods. Key players like Inovio Pharmaceuticals and ModernaTX are leading innovation, with significant contributions from academic institutions such as the University of California and Rutgers University. The technology's maturity is progressing, evidenced by ongoing clinical trials and collaborations between industry and academia. Companies like Medtronic and Boston Scientific are also entering the space, indicating growing commercial interest. While still evolving, electroporation-assisted vaccination shows promise in enhancing vaccine efficacy and delivery, attracting diverse players from biotech, medical device, and pharmaceutical sectors.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Inovio Pharmaceuticals has developed a proprietary electroporation-assisted DNA vaccine delivery platform called CELLECTRA®. This technology uses controlled electrical pulses to create temporary pores in cell membranes, enhancing the uptake of DNA plasmids. The CELLECTRA® device is designed to deliver the company's DNA medicines directly into cells in the body. In clinical trials, this approach has shown to significantly increase immune responses to the vaccine, with up to 100-fold improvement in T cell and antibody responses compared to conventional injection methods[1][3]. Inovio has applied this technology to develop vaccines for various diseases, including COVID-19, HPV-related cancers, and HIV, demonstrating its versatility and potential for addressing multiple health challenges[2].
Strengths: Enhanced vaccine efficacy, versatile platform applicable to multiple diseases, non-invasive delivery method. Weaknesses: Requires specialized device for administration, potential for local discomfort at injection site, higher cost compared to traditional vaccination methods.
MaxCyte, Inc.
Technical Solution: MaxCyte has developed the ExPERT™ platform, a scalable electroporation technology for cell engineering and transfection. This platform utilizes Flow Electroporation® technology to deliver molecules into cells with high efficiency and low cell mortality. The ExPERT™ platform is designed for both clinical and commercial applications, allowing for the engineering of various cell types, including T cells, NK cells, and stem cells. MaxCyte's technology has been validated in over 75 partnered program licenses in cell therapy, with more than 15 licensed for clinical use[4]. The company's electroporation devices are capable of processing up to 200 billion cells in less than 30 minutes, making them suitable for large-scale manufacturing of cell therapies[5].
Strengths: High-throughput capability, versatility in cell types and molecules, proven track record in clinical applications. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on ex vivo applications, may require specialized training for operation, potential for high initial investment costs.
Core Innovations in Electroporation Delivery Metrics
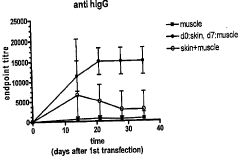
Methods of enhancing immune response using electroporation-assisted vaccination and boosting
PatentActiveAU2013206520B2
Innovation
- The method involves administering a vaccine composition via electroporation in a first tissue followed by a boost administration in a second tissue, utilizing electroporation devices to enhance immune response, with the initial administration often in skin tissue and subsequent boosts in muscle tissue, spaced over specific intervals to optimize immune processing.
Method for enhanced delivery of gene based therapy and vaccination using electroporation
PatentInactiveUS20190307704A1
Innovation
- A method combining lipid-based nanoparticles formulated to carry RNA replicons with an electroporation regimen, applying high-voltage electrical pulses to temporarily permeabilize cell membranes and enhance the delivery of nucleic acids in vivo, improving transfection efficiency and immune responses.
Clinical Trial Design for Electroporation Vaccines
Clinical trial design for electroporation vaccines requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure the safety, efficacy, and reliability of the study results. The design typically begins with a clear definition of the study objectives, which may include evaluating the immune response, assessing safety profiles, or comparing the effectiveness of electroporation-assisted vaccination to traditional methods.
A crucial aspect of the trial design is the selection of appropriate study populations. This involves determining inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure a representative sample while minimizing confounding factors. Considerations may include age ranges, health status, and prior vaccination history. The sample size calculation is another critical element, as it must be sufficiently large to detect statistically significant differences between treatment groups.
The choice of control groups is essential in electroporation vaccine trials. Depending on the study objectives, controls may include placebo groups, groups receiving standard vaccination methods, or groups receiving the vaccine without electroporation. Randomization and blinding procedures are implemented to minimize bias and ensure the validity of results.
Endpoint selection is a key component of the trial design. Primary endpoints often focus on immunogenicity measures, such as antibody titers or T-cell responses. Secondary endpoints may include safety assessments, tolerability, and long-term efficacy. The timing and frequency of endpoint measurements must be carefully planned to capture the dynamics of the immune response.
Safety monitoring is paramount in electroporation vaccine trials. This includes establishing clear protocols for adverse event reporting, defining safety endpoints, and implementing independent safety monitoring committees. Special attention is given to local reactions at the electroporation site and systemic effects.
The trial design must also account for the unique aspects of electroporation-assisted vaccination. This includes standardizing the electroporation protocol, specifying the device settings, and ensuring consistency in the administration technique across study sites. Training of study personnel in the use of electroporation devices is crucial to maintain protocol adherence.
Statistical analysis plans are developed as an integral part of the trial design. These plans outline the methods for data analysis, handling of missing data, and criteria for interim analyses. Adaptive trial designs may be considered to allow for modifications based on interim results, potentially optimizing the study efficiency.
Ethical considerations play a significant role in the design of electroporation vaccine trials. This includes obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and addressing potential risks associated with the electroporation procedure. Regulatory compliance is also a key factor, with trial designs adhering to guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or EMA.
A crucial aspect of the trial design is the selection of appropriate study populations. This involves determining inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure a representative sample while minimizing confounding factors. Considerations may include age ranges, health status, and prior vaccination history. The sample size calculation is another critical element, as it must be sufficiently large to detect statistically significant differences between treatment groups.
The choice of control groups is essential in electroporation vaccine trials. Depending on the study objectives, controls may include placebo groups, groups receiving standard vaccination methods, or groups receiving the vaccine without electroporation. Randomization and blinding procedures are implemented to minimize bias and ensure the validity of results.
Endpoint selection is a key component of the trial design. Primary endpoints often focus on immunogenicity measures, such as antibody titers or T-cell responses. Secondary endpoints may include safety assessments, tolerability, and long-term efficacy. The timing and frequency of endpoint measurements must be carefully planned to capture the dynamics of the immune response.
Safety monitoring is paramount in electroporation vaccine trials. This includes establishing clear protocols for adverse event reporting, defining safety endpoints, and implementing independent safety monitoring committees. Special attention is given to local reactions at the electroporation site and systemic effects.
The trial design must also account for the unique aspects of electroporation-assisted vaccination. This includes standardizing the electroporation protocol, specifying the device settings, and ensuring consistency in the administration technique across study sites. Training of study personnel in the use of electroporation devices is crucial to maintain protocol adherence.
Statistical analysis plans are developed as an integral part of the trial design. These plans outline the methods for data analysis, handling of missing data, and criteria for interim analyses. Adaptive trial designs may be considered to allow for modifications based on interim results, potentially optimizing the study efficiency.
Ethical considerations play a significant role in the design of electroporation vaccine trials. This includes obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and addressing potential risks associated with the electroporation procedure. Regulatory compliance is also a key factor, with trial designs adhering to guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or EMA.
Regulatory Considerations for Electroporation Vaccines
Regulatory considerations for electroporation-assisted vaccines are crucial for ensuring safety, efficacy, and compliance with established guidelines. The development and approval process for these innovative vaccines involves multiple regulatory bodies, including the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe.
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the safety profile of electroporation devices used in vaccine delivery. Regulatory agencies require extensive preclinical and clinical data to demonstrate that the electroporation process does not cause undue tissue damage or adverse effects. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive documentation on the design, manufacturing, and quality control processes of both the vaccine and the electroporation device.
Efficacy is another key regulatory consideration. Regulatory bodies demand robust clinical trial data that demonstrate the superior immunogenicity of electroporation-assisted vaccines compared to traditional delivery methods. This includes data on antibody titers, T-cell responses, and long-term protection against target pathogens.
The regulatory pathway for electroporation vaccines often involves a combination product approach, as it includes both a biological product (the vaccine) and a medical device (the electroporation apparatus). This necessitates a coordinated review process that evaluates both components simultaneously, adding complexity to the regulatory submission.
Standardization of electroporation protocols is a critical regulatory concern. Agencies require clear, reproducible procedures for vaccine administration, including specific parameters for electrical pulse delivery. This ensures consistency in clinical trials and eventual real-world use, which is essential for regulatory approval and post-market surveillance.
Data integrity and patient privacy are also significant regulatory considerations. Clinical trials for electroporation vaccines must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, ensuring proper data collection, management, and reporting. Additionally, as these vaccines may involve the collection of genetic information, compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR in Europe is essential.
Post-market surveillance is a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for electroporation vaccines. Manufacturers must have robust systems in place to monitor and report adverse events, as well as to conduct long-term safety and efficacy studies. This ongoing vigilance is critical for maintaining regulatory approval and ensuring public trust in the technology.
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the safety profile of electroporation devices used in vaccine delivery. Regulatory agencies require extensive preclinical and clinical data to demonstrate that the electroporation process does not cause undue tissue damage or adverse effects. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive documentation on the design, manufacturing, and quality control processes of both the vaccine and the electroporation device.
Efficacy is another key regulatory consideration. Regulatory bodies demand robust clinical trial data that demonstrate the superior immunogenicity of electroporation-assisted vaccines compared to traditional delivery methods. This includes data on antibody titers, T-cell responses, and long-term protection against target pathogens.
The regulatory pathway for electroporation vaccines often involves a combination product approach, as it includes both a biological product (the vaccine) and a medical device (the electroporation apparatus). This necessitates a coordinated review process that evaluates both components simultaneously, adding complexity to the regulatory submission.
Standardization of electroporation protocols is a critical regulatory concern. Agencies require clear, reproducible procedures for vaccine administration, including specific parameters for electrical pulse delivery. This ensures consistency in clinical trials and eventual real-world use, which is essential for regulatory approval and post-market surveillance.
Data integrity and patient privacy are also significant regulatory considerations. Clinical trials for electroporation vaccines must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, ensuring proper data collection, management, and reporting. Additionally, as these vaccines may involve the collection of genetic information, compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR in Europe is essential.
Post-market surveillance is a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for electroporation vaccines. Manufacturers must have robust systems in place to monitor and report adverse events, as well as to conduct long-term safety and efficacy studies. This ongoing vigilance is critical for maintaining regulatory approval and ensuring public trust in the technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!