How To Validate Electroporation Efficiency With Flow Cytometry
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electroporation Validation Goals
Electroporation validation using flow cytometry aims to quantitatively assess the efficiency of cell membrane permeabilization and subsequent molecular uptake. This process is crucial for optimizing electroporation protocols and ensuring consistent results in various applications, including gene transfer, drug delivery, and cell-based therapies.
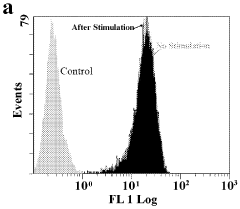
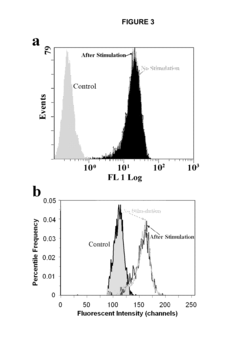
The primary goal of electroporation validation is to determine the percentage of cells successfully electroporated while maintaining cell viability. Flow cytometry offers a powerful tool for this purpose, allowing rapid analysis of large cell populations at the single-cell level. By measuring fluorescence intensity, researchers can distinguish between electroporated and non-electroporated cells, providing a clear metric for electroporation efficiency.
Another key objective is to optimize electroporation parameters, such as voltage, pulse duration, and number of pulses. Flow cytometry enables researchers to systematically evaluate these parameters by comparing the efficiency and cell viability across different conditions. This data-driven approach facilitates the development of protocols tailored to specific cell types and applications.
Assessing the uniformity of electroporation across the cell population is also a critical goal. Flow cytometry's ability to analyze individual cells allows researchers to identify subpopulations with varying degrees of electroporation, providing insights into the consistency and reproducibility of the process.
Furthermore, validating electroporation efficiency aims to correlate the degree of membrane permeabilization with the uptake of specific molecules of interest. This is particularly important for applications involving the delivery of DNA, RNA, or proteins into cells. By using fluorescently labeled molecules, researchers can simultaneously measure electroporation efficiency and the quantity of internalized molecules.
Minimizing cell damage and maintaining high viability is another crucial objective in electroporation validation. Flow cytometry enables the concurrent assessment of cell viability through the use of viability dyes, allowing researchers to strike a balance between efficient electroporation and cell survival.
Lastly, electroporation validation seeks to establish standardized protocols and quality control measures. By leveraging flow cytometry's quantitative capabilities, researchers can define acceptance criteria for successful electroporation, ensuring consistency across experiments and facilitating the translation of electroporation techniques to clinical applications.
The primary goal of electroporation validation is to determine the percentage of cells successfully electroporated while maintaining cell viability. Flow cytometry offers a powerful tool for this purpose, allowing rapid analysis of large cell populations at the single-cell level. By measuring fluorescence intensity, researchers can distinguish between electroporated and non-electroporated cells, providing a clear metric for electroporation efficiency.
Another key objective is to optimize electroporation parameters, such as voltage, pulse duration, and number of pulses. Flow cytometry enables researchers to systematically evaluate these parameters by comparing the efficiency and cell viability across different conditions. This data-driven approach facilitates the development of protocols tailored to specific cell types and applications.
Assessing the uniformity of electroporation across the cell population is also a critical goal. Flow cytometry's ability to analyze individual cells allows researchers to identify subpopulations with varying degrees of electroporation, providing insights into the consistency and reproducibility of the process.
Furthermore, validating electroporation efficiency aims to correlate the degree of membrane permeabilization with the uptake of specific molecules of interest. This is particularly important for applications involving the delivery of DNA, RNA, or proteins into cells. By using fluorescently labeled molecules, researchers can simultaneously measure electroporation efficiency and the quantity of internalized molecules.
Minimizing cell damage and maintaining high viability is another crucial objective in electroporation validation. Flow cytometry enables the concurrent assessment of cell viability through the use of viability dyes, allowing researchers to strike a balance between efficient electroporation and cell survival.
Lastly, electroporation validation seeks to establish standardized protocols and quality control measures. By leveraging flow cytometry's quantitative capabilities, researchers can define acceptance criteria for successful electroporation, ensuring consistency across experiments and facilitating the translation of electroporation techniques to clinical applications.
Flow Cytometry Market Analysis
The flow cytometry market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications in various fields, including cell biology, immunology, and clinical diagnostics. The global flow cytometry market size was valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period.
The market is segmented based on technology, products, applications, and end-users. Among these, the cell-based flow cytometry segment holds the largest market share due to its widespread use in research and clinical applications. The bead-based flow cytometry segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by its increasing adoption in multiplex protein and nucleic acid detection assays.
In terms of products, instruments dominate the market, followed by reagents and software. The instruments segment is further categorized into cell analyzers and cell sorters, with cell analyzers holding a larger market share. The reagents segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR, fueled by the increasing demand for high-quality reagents and the development of application-specific reagents.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is the largest end-user of flow cytometry, followed by academic and research institutions, and hospitals and clinical testing laboratories. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the increasing use of flow cytometry in drug discovery and development processes.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, attributed to increasing research activities, rising healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness about advanced diagnostic technologies.
Key players in the flow cytometry market include Becton, Dickinson and Company, Danaher Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bio-Rad Laboratories, and Sysmex Corporation. These companies are focusing on product innovations, strategic collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
The market for flow cytometry in electroporation efficiency validation is expected to grow as researchers increasingly adopt this technique for various applications, including gene therapy, cell-based therapies, and genetic engineering. The ability of flow cytometry to provide rapid and accurate quantification of transfection efficiency makes it an invaluable tool in optimizing electroporation protocols and assessing the success of gene delivery methods.
The market is segmented based on technology, products, applications, and end-users. Among these, the cell-based flow cytometry segment holds the largest market share due to its widespread use in research and clinical applications. The bead-based flow cytometry segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by its increasing adoption in multiplex protein and nucleic acid detection assays.
In terms of products, instruments dominate the market, followed by reagents and software. The instruments segment is further categorized into cell analyzers and cell sorters, with cell analyzers holding a larger market share. The reagents segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR, fueled by the increasing demand for high-quality reagents and the development of application-specific reagents.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is the largest end-user of flow cytometry, followed by academic and research institutions, and hospitals and clinical testing laboratories. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the increasing use of flow cytometry in drug discovery and development processes.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, attributed to increasing research activities, rising healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness about advanced diagnostic technologies.
Key players in the flow cytometry market include Becton, Dickinson and Company, Danaher Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bio-Rad Laboratories, and Sysmex Corporation. These companies are focusing on product innovations, strategic collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
The market for flow cytometry in electroporation efficiency validation is expected to grow as researchers increasingly adopt this technique for various applications, including gene therapy, cell-based therapies, and genetic engineering. The ability of flow cytometry to provide rapid and accurate quantification of transfection efficiency makes it an invaluable tool in optimizing electroporation protocols and assessing the success of gene delivery methods.
Electroporation Challenges
Electroporation, while a powerful technique for introducing molecules into cells, faces several significant challenges that can impact its efficiency and reproducibility. One of the primary obstacles is the delicate balance between achieving successful membrane permeabilization and maintaining cell viability. Excessive electrical pulses can lead to irreversible cell damage or death, while insufficient voltage may result in inadequate molecule uptake.
The heterogeneity of cell populations presents another hurdle. Different cell types, sizes, and physiological states within a sample can respond variably to the same electroporation conditions. This variability makes it challenging to optimize parameters that work uniformly across the entire population, potentially leading to inconsistent results.
Another critical challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms governing electroporation at the molecular level. While the general principle of transient pore formation in the cell membrane is well-established, the exact dynamics of pore opening, closure, and molecular transport remain areas of active research. This knowledge gap hampers the development of more refined and targeted electroporation strategies.
The choice of buffer composition and electrode material can significantly influence electroporation outcomes. Ionic strength, pH, and the presence of specific molecules in the buffer can affect membrane stability and recovery. Similarly, electrode material and design impact the uniformity and efficiency of the electric field applied to the cell suspension.
Scaling up electroporation for large-volume or high-throughput applications poses additional challenges. Maintaining consistent field strength and temperature across larger volumes or multiple samples simultaneously can be technically demanding and may require specialized equipment.
Post-electroporation cell recovery is another critical aspect that can affect overall efficiency. The stress induced by membrane permeabilization can trigger various cellular responses, including temporary growth arrest or altered gene expression patterns. Optimizing recovery conditions to minimize these effects while maximizing the retention of introduced molecules is crucial but often complex.
Lastly, the validation of electroporation efficiency itself presents a challenge, particularly when working with diverse molecular cargoes or cell types. While flow cytometry offers a powerful tool for assessing uptake at the single-cell level, developing appropriate controls and distinguishing between membrane-bound and internalized molecules can be intricate, requiring careful experimental design and data interpretation.
The heterogeneity of cell populations presents another hurdle. Different cell types, sizes, and physiological states within a sample can respond variably to the same electroporation conditions. This variability makes it challenging to optimize parameters that work uniformly across the entire population, potentially leading to inconsistent results.
Another critical challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms governing electroporation at the molecular level. While the general principle of transient pore formation in the cell membrane is well-established, the exact dynamics of pore opening, closure, and molecular transport remain areas of active research. This knowledge gap hampers the development of more refined and targeted electroporation strategies.
The choice of buffer composition and electrode material can significantly influence electroporation outcomes. Ionic strength, pH, and the presence of specific molecules in the buffer can affect membrane stability and recovery. Similarly, electrode material and design impact the uniformity and efficiency of the electric field applied to the cell suspension.
Scaling up electroporation for large-volume or high-throughput applications poses additional challenges. Maintaining consistent field strength and temperature across larger volumes or multiple samples simultaneously can be technically demanding and may require specialized equipment.
Post-electroporation cell recovery is another critical aspect that can affect overall efficiency. The stress induced by membrane permeabilization can trigger various cellular responses, including temporary growth arrest or altered gene expression patterns. Optimizing recovery conditions to minimize these effects while maximizing the retention of introduced molecules is crucial but often complex.
Lastly, the validation of electroporation efficiency itself presents a challenge, particularly when working with diverse molecular cargoes or cell types. While flow cytometry offers a powerful tool for assessing uptake at the single-cell level, developing appropriate controls and distinguishing between membrane-bound and internalized molecules can be intricate, requiring careful experimental design and data interpretation.
Current Validation Methods
01 Optimization of electric field parameters
Improving electroporation efficiency by optimizing electric field parameters such as pulse duration, voltage, and frequency. This involves adjusting the electrical conditions to enhance cell membrane permeability while minimizing cell damage, leading to more effective delivery of molecules into cells.- Optimization of electric field parameters: Improving electroporation efficiency by optimizing electric field parameters such as pulse duration, voltage, and frequency. This involves adjusting the electrical conditions to enhance cell membrane permeability while minimizing cellular damage.
- Cell-specific electroporation techniques: Developing cell-specific electroporation methods to increase efficiency for different cell types. This includes tailoring protocols for various cell sizes, shapes, and membrane compositions to achieve optimal gene transfer or molecule uptake.
- Electrode design and configuration: Enhancing electroporation efficiency through innovative electrode designs and configurations. This involves creating electrodes that provide more uniform electric field distribution and better contact with target cells or tissues.
- Combination with other techniques: Improving electroporation efficiency by combining it with other techniques such as sonoporation, chemical enhancers, or nanoparticles. This synergistic approach aims to increase membrane permeability and transfection rates.
- Real-time monitoring and feedback systems: Implementing real-time monitoring and feedback systems to optimize electroporation efficiency. This includes using sensors and algorithms to adjust parameters during the process, ensuring optimal conditions for each specific application.
02 Cell-specific electroporation techniques
Developing electroporation methods tailored to specific cell types or tissues. This approach considers the unique characteristics of different cell membranes and optimizes the electroporation process accordingly, resulting in improved efficiency for various biological applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanostructure-assisted electroporation
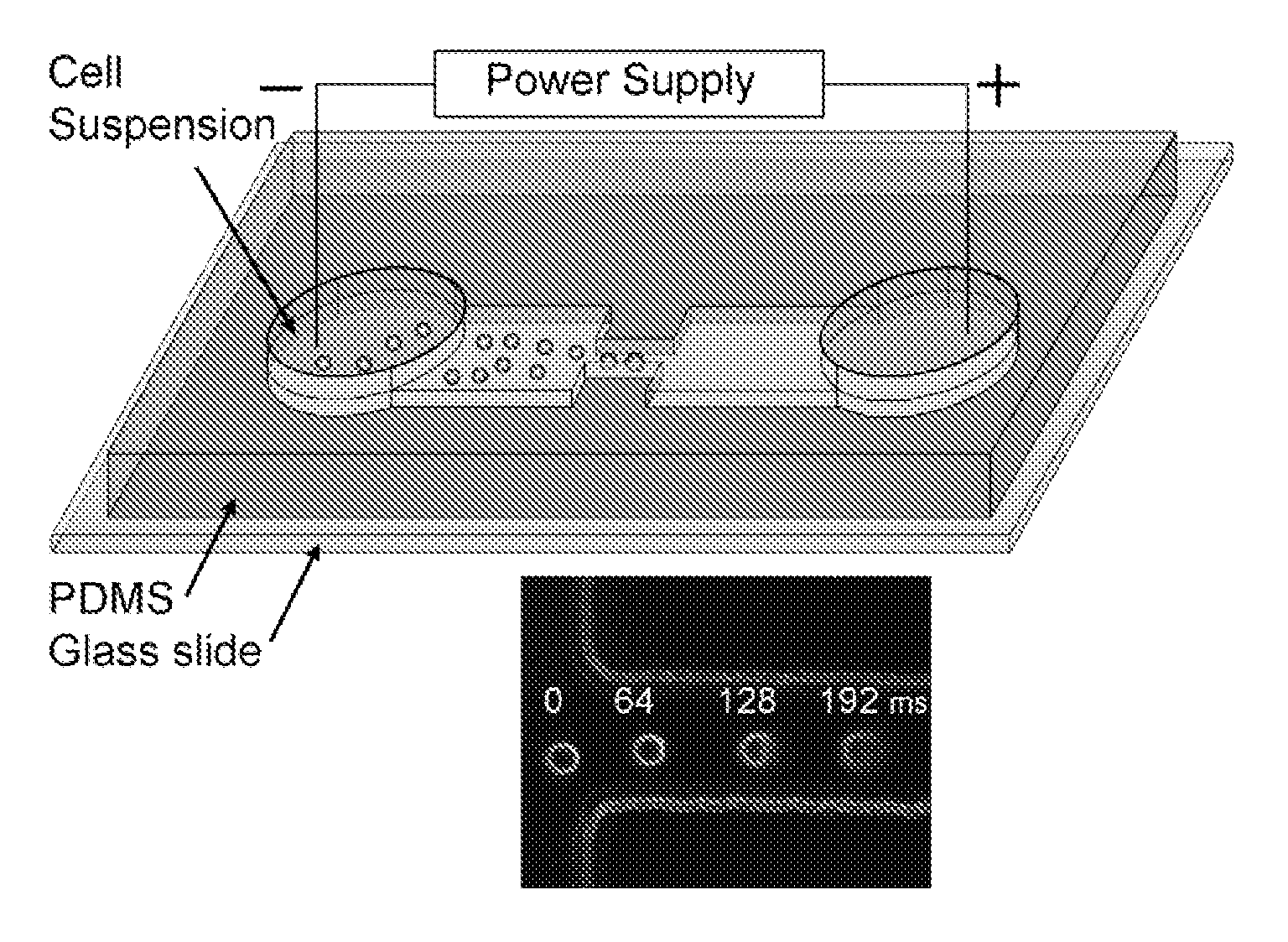
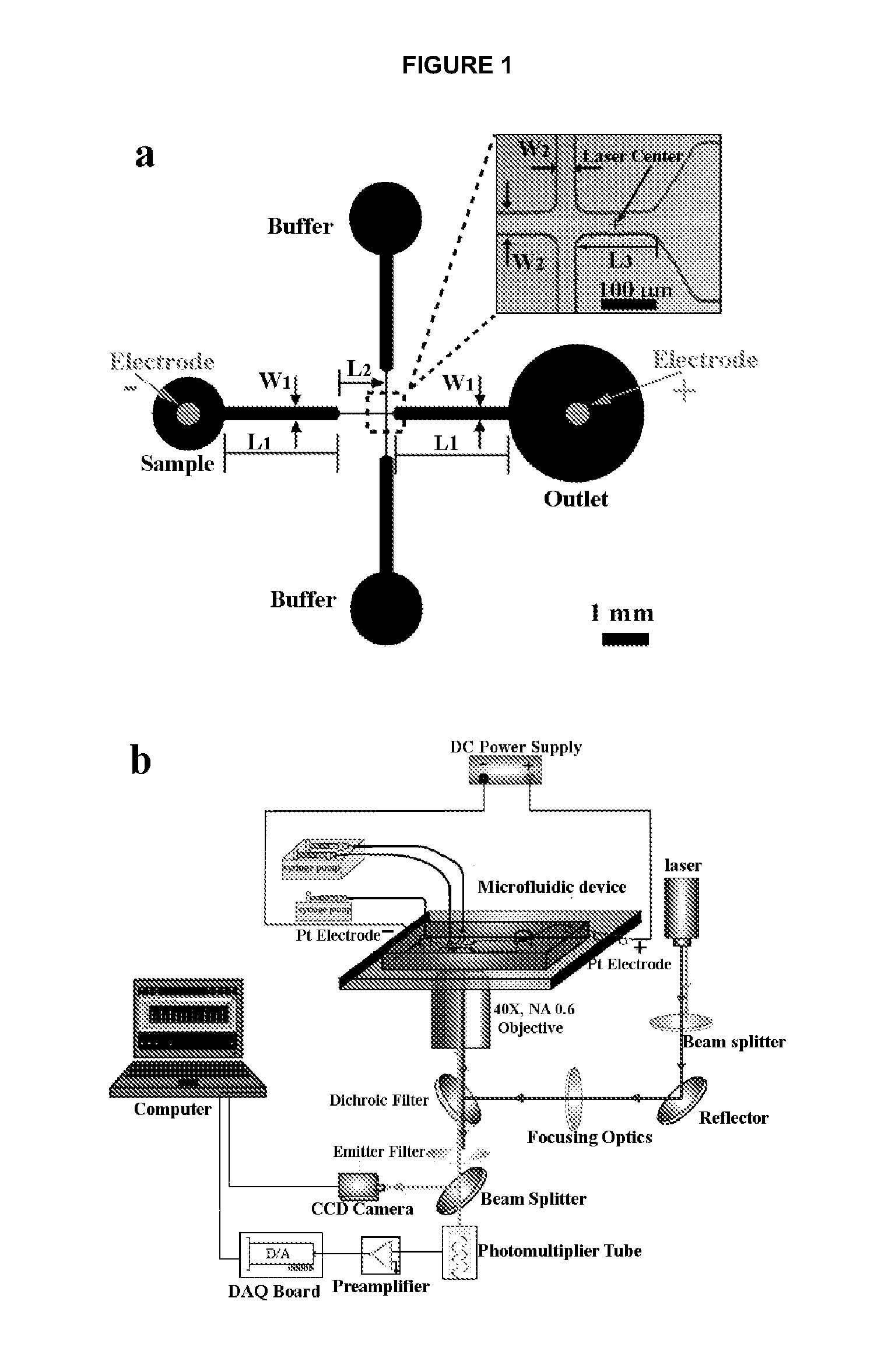
Incorporating nanostructures or nanomaterials to enhance electroporation efficiency. These materials can help concentrate the electric field, reduce the required voltage, and improve the uniformity of pore formation in cell membranes, leading to more consistent and effective electroporation results.Expand Specific Solutions04 Microfluidic electroporation systems
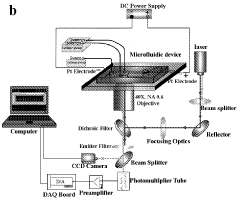
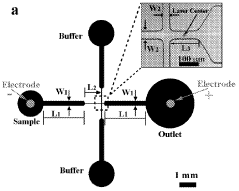
Utilizing microfluidic devices for electroporation to improve efficiency and control. These systems allow for precise manipulation of cells and electric fields, enabling high-throughput electroporation with reduced sample volumes and enhanced reproducibility.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of electroporation with other techniques
Enhancing electroporation efficiency by combining it with other methods such as sonoporation, chemical permeabilization, or optical techniques. This synergistic approach can overcome limitations of individual methods and improve overall transfection or molecule delivery efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electroporation
The electroporation efficiency validation market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for cell engineering and gene therapy applications. The market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 8-10% over the next five years. Technologically, flow cytometry-based validation is becoming more sophisticated, with companies like Cytek Biosciences and Becton, Dickinson & Co. leading innovation in high-parameter analysis. Emerging players such as ThinkCyte and Aqsens Health are introducing novel single-cell analysis platforms, while established firms like Life Technologies and Sartorius BioAnalytical Instruments continue to dominate with comprehensive solution offerings. The integration of AI and automation is expected to further advance the field, improving accuracy and throughput in electroporation efficiency assessment.
Cytek Biosciences, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cytek Biosciences has pioneered the use of full spectrum flow cytometry for electroporation efficiency validation. Their Aurora and Northern Lights systems employ innovative optical design and unmixing algorithms to separate overlapping spectra, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple fluorescent proteins and viability markers in electroporated samples[4]. This technology enables researchers to use a wider range of fluorophores, including those with similar emission spectra, providing more detailed information about transfection efficiency and cell health. Cytek's SpectroFlo software incorporates machine learning algorithms to optimize signal separation and quantification, enhancing the accuracy of electroporation efficiency measurements[5]. The company has also developed standardized protocols for assessing electroporation outcomes across different cell types and conditions.
Strengths: Full spectrum analysis allows for more comprehensive data collection. Advanced software improves accuracy of measurements. Weaknesses: May require adjustment of existing protocols to fully utilize spectral capabilities. Initial setup and optimization can be time-consuming.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. has developed a comprehensive approach to validating electroporation efficiency using flow cytometry. Their Attune NxT Flow Cytometer, designed for high-throughput analysis, incorporates acoustic-assisted hydrodynamic focusing to improve sample throughput and data quality when analyzing electroporated cells[6]. The company's electroporation validation strategy involves multi-color flow cytometry, combining fluorescent protein expression analysis with membrane integrity dyes and cell cycle markers. This allows for simultaneous assessment of transfection efficiency, cell viability, and proliferation status post-electroporation. Life Technologies has also introduced novel fluorescent proteins optimized for rapid expression and detection in electroporated cells, enhancing the sensitivity of flow cytometric analysis[7]. Their integrated workflow solutions include optimized electroporation buffers and protocols designed to work seamlessly with their flow cytometry systems.
Strengths: High-throughput capabilities suitable for large-scale electroporation experiments. Integrated solutions from electroporation to analysis streamline workflow. Weaknesses: Proprietary reagents and systems may increase operational costs. May require investment in specific Life Technologies products for optimal performance.
Flow Cytometry Innovations
Electroporative flow cytometry
PatentWO2009032827A2
Innovation
- Electroporative flow cytometry, which combines electroporation with flow cytometry, allows for the detection of protein translocation and biomechanical properties at the single cell level by subjecting cells to an electrical field that opens membrane pores, enabling the release of intracellular materials and subsequent analysis using flow cytometry techniques.
Electroporative flow cytometry
PatentInactiveUS20100221769A1
Innovation
- The development of electroporative flow cytometry, which combines electroporation with flow cytometry to detect protein translocation and biomechanical changes in cells at the single cell level, allowing for high-throughput analysis of cellular features such as protein translocation and cytoskeleton deformability.
Regulatory Considerations
When validating electroporation efficiency using flow cytometry, it is crucial to consider the regulatory landscape governing this process. Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have established guidelines for the use of flow cytometry in research and clinical applications. These regulations aim to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and reproducibility of flow cytometry data.
One key regulatory consideration is the validation of flow cytometry instruments and protocols. This includes regular calibration and performance checks to maintain instrument accuracy. Standardized beads and controls should be used to ensure consistent results across different experiments and laboratories. Documentation of these validation procedures is essential for regulatory compliance and may be subject to inspection during audits.
The selection and validation of fluorochromes and antibodies used in flow cytometry experiments are also subject to regulatory scrutiny. Researchers must demonstrate that the chosen reagents are specific, sensitive, and suitable for the intended application. This may involve providing data on antibody specificity, titration experiments, and appropriate controls to account for non-specific binding and autofluorescence.
Data analysis and interpretation in flow cytometry experiments are another area of regulatory focus. Gating strategies and analysis algorithms should be well-documented and validated. The use of automated analysis tools must be justified and their performance verified against manual analysis methods. Regulatory bodies may require the submission of raw data and analysis workflows to ensure transparency and reproducibility.
Quality control measures are paramount in meeting regulatory requirements. This includes the implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation, instrument operation, and data analysis. Regular proficiency testing and participation in external quality assessment programs may be necessary to demonstrate ongoing competence and compliance with industry standards.
Biosafety considerations are also an important aspect of regulatory compliance when working with electroporated cells. Proper containment measures and waste disposal protocols must be in place to prevent potential biohazards. This is particularly critical when working with genetically modified organisms or potentially infectious materials.
For clinical applications, such as cell therapy products involving electroporated cells, additional regulatory requirements come into play. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed, which encompass stringent quality control measures, documentation practices, and validation of all processes involved in product manufacturing and testing.
Lastly, data management and record-keeping are crucial for regulatory compliance. All experimental data, including raw flow cytometry files, analysis reports, and validation documentation, must be securely stored and readily accessible for regulatory inspections. Electronic data management systems should comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or similar regulations to ensure data integrity and traceability.
One key regulatory consideration is the validation of flow cytometry instruments and protocols. This includes regular calibration and performance checks to maintain instrument accuracy. Standardized beads and controls should be used to ensure consistent results across different experiments and laboratories. Documentation of these validation procedures is essential for regulatory compliance and may be subject to inspection during audits.
The selection and validation of fluorochromes and antibodies used in flow cytometry experiments are also subject to regulatory scrutiny. Researchers must demonstrate that the chosen reagents are specific, sensitive, and suitable for the intended application. This may involve providing data on antibody specificity, titration experiments, and appropriate controls to account for non-specific binding and autofluorescence.
Data analysis and interpretation in flow cytometry experiments are another area of regulatory focus. Gating strategies and analysis algorithms should be well-documented and validated. The use of automated analysis tools must be justified and their performance verified against manual analysis methods. Regulatory bodies may require the submission of raw data and analysis workflows to ensure transparency and reproducibility.
Quality control measures are paramount in meeting regulatory requirements. This includes the implementation of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation, instrument operation, and data analysis. Regular proficiency testing and participation in external quality assessment programs may be necessary to demonstrate ongoing competence and compliance with industry standards.
Biosafety considerations are also an important aspect of regulatory compliance when working with electroporated cells. Proper containment measures and waste disposal protocols must be in place to prevent potential biohazards. This is particularly critical when working with genetically modified organisms or potentially infectious materials.
For clinical applications, such as cell therapy products involving electroporated cells, additional regulatory requirements come into play. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed, which encompass stringent quality control measures, documentation practices, and validation of all processes involved in product manufacturing and testing.
Lastly, data management and record-keeping are crucial for regulatory compliance. All experimental data, including raw flow cytometry files, analysis reports, and validation documentation, must be securely stored and readily accessible for regulatory inspections. Electronic data management systems should comply with 21 CFR Part 11 or similar regulations to ensure data integrity and traceability.
Standardization Efforts
Standardization efforts in validating electroporation efficiency with flow cytometry have become increasingly important as the technique gains widespread adoption in various fields of research and clinical applications. These efforts aim to establish consistent protocols, reference materials, and quality control measures to ensure reproducibility and comparability of results across different laboratories and experimental setups.
One of the primary focuses of standardization has been the development of universal calibration particles for flow cytometry. These particles, with known fluorescence intensities and sizes, serve as reference standards for instrument calibration and data normalization. By using these standardized particles, researchers can more accurately compare electroporation efficiency results between different flow cytometers and experimental conditions.
Another key aspect of standardization involves the establishment of guidelines for sample preparation and staining protocols. Organizations such as the International Society for Advancement of Cytometry (ISAC) have been working on developing best practices for cell handling, fixation, and fluorescent labeling specific to electroporation efficiency assessment. These guidelines aim to minimize variability introduced by sample preparation techniques and ensure consistent staining of electroporated cells.
Efforts have also been made to standardize data analysis and reporting methods. Flow cytometry software developers have been collaborating with researchers to create standardized gating strategies and analysis templates specifically designed for electroporation efficiency assessment. These tools help reduce inter-operator variability and facilitate the comparison of results across different studies.
The development of reference cell lines with known electroporation characteristics has been another important standardization initiative. These cell lines serve as positive and negative controls, allowing researchers to validate their experimental setup and compare their results to established benchmarks. Efforts are underway to create a panel of such reference cell lines representing various cell types and electroporation conditions.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have played a crucial role in identifying sources of variability and establishing consensus protocols. These studies involve multiple laboratories performing standardized electroporation experiments and analyzing the results using flow cytometry. The findings from these studies have led to refinements in protocols and the identification of critical parameters that need to be controlled for reliable efficiency measurements.
Regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders have also been involved in standardization efforts, particularly for clinical applications of electroporation. Guidelines for good manufacturing practices (GMP) and quality control measures specific to electroporation-based therapies are being developed to ensure consistency and safety in clinical settings.
One of the primary focuses of standardization has been the development of universal calibration particles for flow cytometry. These particles, with known fluorescence intensities and sizes, serve as reference standards for instrument calibration and data normalization. By using these standardized particles, researchers can more accurately compare electroporation efficiency results between different flow cytometers and experimental conditions.
Another key aspect of standardization involves the establishment of guidelines for sample preparation and staining protocols. Organizations such as the International Society for Advancement of Cytometry (ISAC) have been working on developing best practices for cell handling, fixation, and fluorescent labeling specific to electroporation efficiency assessment. These guidelines aim to minimize variability introduced by sample preparation techniques and ensure consistent staining of electroporated cells.
Efforts have also been made to standardize data analysis and reporting methods. Flow cytometry software developers have been collaborating with researchers to create standardized gating strategies and analysis templates specifically designed for electroporation efficiency assessment. These tools help reduce inter-operator variability and facilitate the comparison of results across different studies.
The development of reference cell lines with known electroporation characteristics has been another important standardization initiative. These cell lines serve as positive and negative controls, allowing researchers to validate their experimental setup and compare their results to established benchmarks. Efforts are underway to create a panel of such reference cell lines representing various cell types and electroporation conditions.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have played a crucial role in identifying sources of variability and establishing consensus protocols. These studies involve multiple laboratories performing standardized electroporation experiments and analyzing the results using flow cytometry. The findings from these studies have led to refinements in protocols and the identification of critical parameters that need to be controlled for reliable efficiency measurements.
Regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders have also been involved in standardization efforts, particularly for clinical applications of electroporation. Guidelines for good manufacturing practices (GMP) and quality control measures specific to electroporation-based therapies are being developed to ensure consistency and safety in clinical settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!