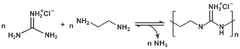Enhancing Polymer Membranes for CO2 Capture Efficiency
OCT 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CO2 Capture Membrane Technology Background and Objectives
Carbon dioxide capture and separation technologies have evolved significantly over the past several decades, driven by increasing global concerns about climate change and greenhouse gas emissions. Polymer membrane technology for CO2 capture represents one of the most promising approaches due to its energy efficiency, operational simplicity, and scalability compared to traditional absorption or adsorption methods. The historical development of this field began in the 1980s with rudimentary gas separation membranes, progressing through significant breakthroughs in material science during the 1990s and 2000s.
The evolution of polymer membrane technology has been characterized by continuous improvements in selectivity, permeability, and stability. Early membranes suffered from the well-documented "permeability-selectivity trade-off," where increasing one property typically resulted in decreasing the other. Recent advances in polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, and computational modeling have begun to overcome these limitations, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in membrane performance.
Current technological trends point toward the development of mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs), thermally rearranged polymers, and facilitated transport membranes. These advanced materials incorporate various fillers, functional groups, or carrier molecules to enhance CO2 capture efficiency while maintaining structural integrity under industrial operating conditions. The integration of molecular simulation techniques with experimental approaches has accelerated innovation in this field, allowing for more targeted design of membrane materials.
The primary technical objective in this domain is to develop polymer membranes with significantly enhanced CO2/N2 selectivity (>100) and CO2 permeability (>1000 Barrer) that can maintain performance under realistic flue gas conditions. These conditions include the presence of contaminants such as SOx, NOx, water vapor, and particulate matter, as well as elevated temperatures and pressures. Additionally, membranes must demonstrate long-term stability (>3-5 years) to be economically viable for industrial implementation.
Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing costs to make membrane technology competitive with established carbon capture technologies, developing scalable production methods for large-area membranes, and creating modular designs that can be retrofitted to existing power plants and industrial facilities. The ultimate goal is to achieve a CO2 capture cost below $30 per ton, which would represent a significant improvement over current technologies that typically operate at $40-100 per ton.
Research efforts are increasingly focused on bio-inspired and biomimetic approaches, learning from natural CO2 transport mechanisms such as those found in respiratory systems. Simultaneously, there is growing interest in developing dual-function membranes that not only capture CO2 but also facilitate its conversion into valuable products, creating economic incentives for carbon capture beyond regulatory compliance.
The evolution of polymer membrane technology has been characterized by continuous improvements in selectivity, permeability, and stability. Early membranes suffered from the well-documented "permeability-selectivity trade-off," where increasing one property typically resulted in decreasing the other. Recent advances in polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, and computational modeling have begun to overcome these limitations, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in membrane performance.
Current technological trends point toward the development of mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs), thermally rearranged polymers, and facilitated transport membranes. These advanced materials incorporate various fillers, functional groups, or carrier molecules to enhance CO2 capture efficiency while maintaining structural integrity under industrial operating conditions. The integration of molecular simulation techniques with experimental approaches has accelerated innovation in this field, allowing for more targeted design of membrane materials.
The primary technical objective in this domain is to develop polymer membranes with significantly enhanced CO2/N2 selectivity (>100) and CO2 permeability (>1000 Barrer) that can maintain performance under realistic flue gas conditions. These conditions include the presence of contaminants such as SOx, NOx, water vapor, and particulate matter, as well as elevated temperatures and pressures. Additionally, membranes must demonstrate long-term stability (>3-5 years) to be economically viable for industrial implementation.
Secondary objectives include reducing manufacturing costs to make membrane technology competitive with established carbon capture technologies, developing scalable production methods for large-area membranes, and creating modular designs that can be retrofitted to existing power plants and industrial facilities. The ultimate goal is to achieve a CO2 capture cost below $30 per ton, which would represent a significant improvement over current technologies that typically operate at $40-100 per ton.
Research efforts are increasingly focused on bio-inspired and biomimetic approaches, learning from natural CO2 transport mechanisms such as those found in respiratory systems. Simultaneously, there is growing interest in developing dual-function membranes that not only capture CO2 but also facilitate its conversion into valuable products, creating economic incentives for carbon capture beyond regulatory compliance.
Market Analysis for Carbon Capture Solutions
The global carbon capture market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability commitments. As of 2023, the carbon capture and storage (CCS) market is valued at approximately $7.5 billion, with projections indicating growth to reach $15.3 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 10.7%. This expansion is particularly evident in regions with stringent carbon emission policies, such as the European Union, North America, and increasingly, parts of Asia.
Polymer membrane technology for CO2 capture represents a rapidly growing segment within this broader market. The membrane-based gas separation market specifically for carbon capture applications currently accounts for about 18% of the total carbon capture technology market, with expectations to increase to 25% by 2028 due to its cost-effectiveness and operational advantages compared to traditional methods.
Industrial sectors constitute the primary demand drivers, with power generation, cement production, and chemical manufacturing collectively accounting for over 65% of the current market for carbon capture solutions. The power generation sector alone represents 38% of the market share, as coal and natural gas plants seek efficient retrofitting options to comply with emission standards.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. China and India are emerging as particularly significant growth markets, with annual growth rates exceeding 15% as these nations balance industrial expansion with climate commitments.
From a competitive standpoint, the polymer membrane market for CO2 capture features both established industrial gas companies and specialized technology startups. Major industrial players control about 60% of the market, while innovative startups focusing exclusively on advanced membrane technologies have captured roughly 25% market share through technological differentiation.
Customer adoption patterns reveal increasing preference for solutions offering lower energy penalties and operational flexibility. End-users are willing to pay premium prices for membrane technologies that demonstrate capture efficiency above 90% while maintaining energy consumption below 1.5 GJ/ton CO2 captured. This price sensitivity varies significantly by region, with European customers demonstrating willingness to pay 15-20% more for higher performance solutions compared to their North American counterparts.
Regulatory frameworks continue to shape market dynamics, with carbon pricing mechanisms in 45 countries directly influencing return-on-investment calculations for carbon capture projects. Regions with carbon prices exceeding $50/ton CO2 show adoption rates three times higher than unregulated markets, creating geographic disparities in technology deployment.
Polymer membrane technology for CO2 capture represents a rapidly growing segment within this broader market. The membrane-based gas separation market specifically for carbon capture applications currently accounts for about 18% of the total carbon capture technology market, with expectations to increase to 25% by 2028 due to its cost-effectiveness and operational advantages compared to traditional methods.
Industrial sectors constitute the primary demand drivers, with power generation, cement production, and chemical manufacturing collectively accounting for over 65% of the current market for carbon capture solutions. The power generation sector alone represents 38% of the market share, as coal and natural gas plants seek efficient retrofitting options to comply with emission standards.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. China and India are emerging as particularly significant growth markets, with annual growth rates exceeding 15% as these nations balance industrial expansion with climate commitments.
From a competitive standpoint, the polymer membrane market for CO2 capture features both established industrial gas companies and specialized technology startups. Major industrial players control about 60% of the market, while innovative startups focusing exclusively on advanced membrane technologies have captured roughly 25% market share through technological differentiation.
Customer adoption patterns reveal increasing preference for solutions offering lower energy penalties and operational flexibility. End-users are willing to pay premium prices for membrane technologies that demonstrate capture efficiency above 90% while maintaining energy consumption below 1.5 GJ/ton CO2 captured. This price sensitivity varies significantly by region, with European customers demonstrating willingness to pay 15-20% more for higher performance solutions compared to their North American counterparts.
Regulatory frameworks continue to shape market dynamics, with carbon pricing mechanisms in 45 countries directly influencing return-on-investment calculations for carbon capture projects. Regions with carbon prices exceeding $50/ton CO2 show adoption rates three times higher than unregulated markets, creating geographic disparities in technology deployment.
Current Polymer Membrane Limitations and Challenges
Despite significant advancements in polymer membrane technology for CO2 capture, several critical limitations continue to impede their widespread industrial implementation. The fundamental challenge lies in the inherent trade-off between permeability and selectivity, known as the Robeson upper bound. As membranes become more permeable to CO2, they typically sacrifice selectivity over other gases such as N2, CH4, and H2, reducing overall separation efficiency.
Material stability presents another significant hurdle, particularly in harsh industrial environments. Polymer membranes often experience plasticization when exposed to high CO2 partial pressures, causing swelling that compromises the membrane's structural integrity and separation performance. This effect becomes more pronounced in mixed gas scenarios typical of industrial flue gases or natural gas streams.
Physical aging of polymer membranes constitutes a long-term reliability concern. Over time, the free volume within glassy polymers decreases, leading to reduced permeability and altered separation characteristics. This aging process accelerates under elevated temperatures and pressures, conditions common in industrial carbon capture applications.
Fouling and chemical degradation further compromise membrane performance in real-world applications. Contaminants in flue gas streams, including particulate matter, SOx, NOx, and water vapor, can irreversibly damage membrane surfaces or block transport pathways. Acidic components may catalyze chemical degradation of the polymer matrix, shortening operational lifetimes.
Scalability and manufacturing consistency remain significant barriers to commercialization. Current fabrication techniques struggle to produce defect-free membranes at industrial scales while maintaining uniform thickness and performance characteristics. The development of cost-effective, reproducible manufacturing processes lags behind laboratory-scale innovations.
Energy efficiency represents another critical limitation. While membranes generally require less energy than absorption-based capture systems, the compression energy needed to create sufficient driving force for gas separation remains substantial. This energy penalty significantly impacts the economic viability of membrane-based carbon capture systems.
Cost considerations further complicate widespread adoption. High-performance polymers with enhanced CO2 separation capabilities often involve expensive monomers or complex synthesis procedures. The balance between material cost, performance, and durability has not yet reached the threshold needed for broad commercial implementation.
Mechanical strength under pressure differentials poses additional engineering challenges. Thin membranes that maximize gas flux often lack the structural integrity to withstand the pressure gradients required for efficient separation, necessitating complex support structures that add cost and may introduce additional mass transfer resistance.
Material stability presents another significant hurdle, particularly in harsh industrial environments. Polymer membranes often experience plasticization when exposed to high CO2 partial pressures, causing swelling that compromises the membrane's structural integrity and separation performance. This effect becomes more pronounced in mixed gas scenarios typical of industrial flue gases or natural gas streams.
Physical aging of polymer membranes constitutes a long-term reliability concern. Over time, the free volume within glassy polymers decreases, leading to reduced permeability and altered separation characteristics. This aging process accelerates under elevated temperatures and pressures, conditions common in industrial carbon capture applications.
Fouling and chemical degradation further compromise membrane performance in real-world applications. Contaminants in flue gas streams, including particulate matter, SOx, NOx, and water vapor, can irreversibly damage membrane surfaces or block transport pathways. Acidic components may catalyze chemical degradation of the polymer matrix, shortening operational lifetimes.
Scalability and manufacturing consistency remain significant barriers to commercialization. Current fabrication techniques struggle to produce defect-free membranes at industrial scales while maintaining uniform thickness and performance characteristics. The development of cost-effective, reproducible manufacturing processes lags behind laboratory-scale innovations.
Energy efficiency represents another critical limitation. While membranes generally require less energy than absorption-based capture systems, the compression energy needed to create sufficient driving force for gas separation remains substantial. This energy penalty significantly impacts the economic viability of membrane-based carbon capture systems.
Cost considerations further complicate widespread adoption. High-performance polymers with enhanced CO2 separation capabilities often involve expensive monomers or complex synthesis procedures. The balance between material cost, performance, and durability has not yet reached the threshold needed for broad commercial implementation.
Mechanical strength under pressure differentials poses additional engineering challenges. Thin membranes that maximize gas flux often lack the structural integrity to withstand the pressure gradients required for efficient separation, necessitating complex support structures that add cost and may introduce additional mass transfer resistance.
Current Polymer Membrane Enhancement Approaches
01 Polymer membrane composition for enhanced efficiency
The composition of polymer membranes significantly affects their efficiency. By incorporating specific polymers and additives, the performance characteristics such as selectivity, permeability, and durability can be optimized. Various polymer types including polyamides, polyimides, and fluoropolymers offer different advantages in terms of chemical resistance and separation capabilities. The addition of nanoparticles or functional groups can further enhance the membrane's efficiency by improving its structural integrity and separation properties.- Membrane composition for enhanced efficiency: The composition of polymer membranes significantly affects their efficiency. Various polymeric materials can be used to create membranes with specific properties such as improved permeability, selectivity, and durability. Incorporating specific additives or modifying the polymer structure can enhance separation performance. Advanced polymer blends and composite materials can be engineered to achieve optimal filtration characteristics while maintaining structural integrity under operational conditions.
- Membrane structure and morphology optimization: The structural design and morphology of polymer membranes play crucial roles in determining their efficiency. Controlling pore size, distribution, and interconnectivity can significantly enhance separation performance. Various fabrication techniques can be employed to create membranes with tailored structures, including asymmetric membranes, thin-film composite membranes, and hollow fiber configurations. Optimizing the membrane thickness and surface characteristics can improve flux rates while maintaining selectivity.
- Surface modification techniques: Surface modification of polymer membranes can significantly improve their efficiency by enhancing specific properties such as hydrophilicity, fouling resistance, or chemical stability. Techniques include plasma treatment, chemical grafting, coating with functional materials, and incorporation of nanoparticles. These modifications can reduce membrane fouling, increase flux, improve selectivity, and extend membrane lifespan under challenging operational conditions.
- Gas separation and filtration applications: Polymer membranes designed specifically for gas separation and filtration demonstrate enhanced efficiency through specialized formulations and structures. These membranes can selectively separate gas mixtures based on differences in molecular size, shape, or interaction with the membrane material. Applications include carbon dioxide capture, hydrogen purification, natural gas sweetening, and air separation. The efficiency of these membranes depends on their permeability, selectivity, and stability under various operating conditions.
- Water treatment and purification systems: Polymer membranes for water treatment and purification are designed to efficiently remove contaminants while maintaining high water flux. These membranes can be tailored for specific applications such as desalination, wastewater treatment, and ultrapure water production. The efficiency of these systems depends on membrane properties such as hydrophilicity, charge, pore size, and fouling resistance. Advanced membrane configurations and module designs can optimize flow patterns and reduce concentration polarization, further enhancing system efficiency.
02 Membrane structure and morphology optimization
The structural design and morphology of polymer membranes play crucial roles in determining their efficiency. Techniques such as phase inversion, electrospinning, and interfacial polymerization can be used to create membranes with controlled pore size, distribution, and interconnectivity. Asymmetric and composite membrane structures can provide improved flux while maintaining selectivity. The thickness, surface roughness, and cross-sectional morphology can be tailored to specific separation applications, enhancing overall membrane efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification techniques for polymer membranes
Surface modification of polymer membranes can significantly improve their efficiency by altering surface properties without affecting bulk characteristics. Techniques such as plasma treatment, UV irradiation, chemical grafting, and coating can be employed to introduce functional groups that enhance hydrophilicity, reduce fouling, or improve selectivity. These modifications can lead to increased flux, better antifouling properties, and extended membrane lifetime, ultimately improving the overall efficiency of separation processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fouling reduction strategies for membrane systems
Fouling is a major challenge affecting polymer membrane efficiency in various applications. Strategies to reduce fouling include incorporating hydrophilic additives, zwitterionic polymers, or antimicrobial agents into the membrane matrix. Physical modifications such as creating patterned surfaces or introducing charged groups can also minimize foulant adhesion. Additionally, operational techniques like backwashing, air scouring, and optimized flow dynamics can be implemented to maintain membrane performance over time and reduce the frequency of cleaning cycles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel polymer membrane materials for specific applications
Development of novel polymer membrane materials tailored for specific applications has led to significant improvements in efficiency. These include mixed matrix membranes incorporating inorganic fillers, thermally rearranged polymers for gas separation, biomimetic membranes for water purification, and stimuli-responsive membranes that can adapt to changing conditions. Emerging materials such as metal-organic frameworks, covalent organic frameworks, and graphene-based composites are being integrated into polymer matrices to create next-generation membranes with unprecedented separation performance and energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in CO2 Capture Membrane Development
The polymer membrane CO2 capture technology market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing R&D investments and expanding commercial applications. The global market size is projected to reach significant scale as carbon capture becomes critical for climate goals. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovations to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Leading players include established industrial gas companies like Air Liquide and Chevron, alongside specialized membrane technology developers such as Membrane Technology & Research. Research institutions including Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Rice University, and King Abdullah University of Science & Technology are driving fundamental advancements. Chinese entities like CNPC and Sinopec are increasingly active, reflecting the technology's global strategic importance. Collaboration between industry and academia remains essential for overcoming technical barriers to widespread adoption.
Air Liquide SA
Technical Solution: Air Liquide has developed advanced polymer membrane technology for CO2 capture utilizing proprietary hollow fiber membrane configurations. Their MEDAL™ membrane system employs specially engineered polymers with high CO2/N2 selectivity ratios exceeding 50:1. The technology incorporates perfluoropolymers and polyimides modified with specific functional groups that enhance CO2 solubility while maintaining mechanical stability. Air Liquide's approach includes multi-layer composite membranes with an ultrathin selective layer (< 100 nm) supported by porous substrates, optimizing both permeability and selectivity. Their membranes operate under moderate pressure differentials (10-40 bar) and can achieve CO2 recovery rates of 90%+ with purities suitable for geological storage or utilization. The company has successfully deployed these systems at industrial scale, with installations processing up to 40 million standard cubic feet per day of flue gas.
Strengths: Extensive industrial deployment experience with proven scalability; proprietary hollow fiber manufacturing capabilities allowing cost-effective production; integrated system approach combining membrane technology with complementary capture methods. Weaknesses: Performance degradation in the presence of certain contaminants like SOx and NOx; requires significant pressure differential which increases operational costs; membrane lifetime limitations in harsh industrial environments.
Lawrence Livermore National Security LLC
Technical Solution: Lawrence Livermore National Security has pioneered the development of Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) that combine polymer matrices with engineered nanomaterials for enhanced CO2 capture. Their proprietary technology incorporates metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with tailored pore structures specifically designed for CO2 affinity. The membranes utilize poly(ethylene oxide)-based polymers functionalized with amine groups that selectively interact with CO2 molecules. LLNS has developed a patented manufacturing process that ensures uniform dispersion of nanomaterials throughout the polymer matrix, preventing agglomeration that typically plagues MMMs. Their latest generation membranes demonstrate CO2 permeability exceeding 1000 Barrers while maintaining CO2/N2 selectivity above 40, representing a significant advancement beyond the traditional permeability-selectivity trade-off. The technology operates effectively at temperatures ranging from ambient to 100°C, making it suitable for various industrial flue gas conditions.
Strengths: Exceptional performance metrics that surpass Robeson's upper bound for polymer membranes; robust operation across varying temperature and humidity conditions; potential for significant cost reduction compared to conventional amine scrubbing. Weaknesses: Challenges in scaling up production from laboratory to industrial scale; potential for nanomaterial leaching during extended operation; higher initial manufacturing costs compared to conventional polymer membranes.
Key Innovations in CO2-Selective Membrane Materials
Method for manufacturing carbon dioxide separation membrane, and carbon dioxide separation membrane
PatentWO2013024594A1
Innovation
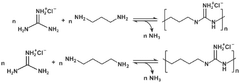
- A method involving radiation graft polymerization of a polymer film with a quaternary ammonium group-containing monomer, followed by treatment with a fluoride salt to form a salt with fluoride ions, enhancing the membrane's affinity for CO2 and durability.
Enhancing membrane stability through utilization of high molecular weight fixed carriers
PatentWO2025193866A1
Innovation
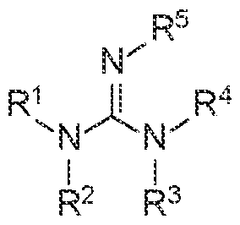
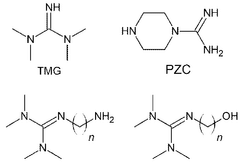
- Development of membranes comprising a support layer with a selective polymer layer containing high molecular weight polymeric fixed carriers, such as polyguanidine polymers, which enhance stability and selectivity for CO2 separation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of polymer membrane technologies for CO2 capture extends far beyond their immediate application in emissions reduction. When evaluating these membranes from a lifecycle perspective, several critical factors emerge. The production phase of polymer membranes typically involves petrochemical feedstocks and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, contributing to their initial carbon footprint. However, this environmental investment must be weighed against the significant CO2 emissions prevented throughout the operational lifespan of these membranes.
Advanced polymer membranes demonstrate promising sustainability metrics compared to conventional carbon capture technologies such as amine scrubbing. The latter requires substantial thermal energy for solvent regeneration, whereas membrane-based systems operate with significantly lower energy penalties. Quantitative assessments indicate that polymer membrane systems can reduce the energy requirement for CO2 capture by 20-40%, translating to proportional reductions in the overall carbon footprint of the capture process.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental parameter. Traditional solvent-based capture technologies consume 1-2 tons of water per ton of CO2 captured, while polymer membrane systems require negligible water inputs during operation. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where industrial water usage faces increasing scrutiny and regulation.
The end-of-life management of polymer membranes presents both challenges and opportunities. Current disposal practices often involve landfilling or incineration, neither of which is optimal from an environmental perspective. Research into biodegradable polymer formulations and membrane recycling protocols shows promise for reducing waste impacts. Some innovative approaches involve repurposing spent membranes for lower-grade separation applications, extending their functional lifecycle.
Raw material sourcing for next-generation membranes is shifting toward bio-based polymers and sustainable additives. These materials can reduce dependence on fossil resources while potentially enhancing membrane performance. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing traditional petroleum-based polymers with bio-derived alternatives indicate potential reductions in global warming potential by 30-60%, depending on feedstock and processing methods.
The scalability of membrane technologies also contributes to their environmental profile. Their modular nature allows for distributed implementation, potentially reducing transportation emissions associated with centralized capture facilities. Additionally, the relatively small physical footprint of membrane systems minimizes land use impacts compared to alternative technologies requiring extensive infrastructure.
Advanced polymer membranes demonstrate promising sustainability metrics compared to conventional carbon capture technologies such as amine scrubbing. The latter requires substantial thermal energy for solvent regeneration, whereas membrane-based systems operate with significantly lower energy penalties. Quantitative assessments indicate that polymer membrane systems can reduce the energy requirement for CO2 capture by 20-40%, translating to proportional reductions in the overall carbon footprint of the capture process.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental parameter. Traditional solvent-based capture technologies consume 1-2 tons of water per ton of CO2 captured, while polymer membrane systems require negligible water inputs during operation. This advantage becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where industrial water usage faces increasing scrutiny and regulation.
The end-of-life management of polymer membranes presents both challenges and opportunities. Current disposal practices often involve landfilling or incineration, neither of which is optimal from an environmental perspective. Research into biodegradable polymer formulations and membrane recycling protocols shows promise for reducing waste impacts. Some innovative approaches involve repurposing spent membranes for lower-grade separation applications, extending their functional lifecycle.
Raw material sourcing for next-generation membranes is shifting toward bio-based polymers and sustainable additives. These materials can reduce dependence on fossil resources while potentially enhancing membrane performance. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing traditional petroleum-based polymers with bio-derived alternatives indicate potential reductions in global warming potential by 30-60%, depending on feedstock and processing methods.
The scalability of membrane technologies also contributes to their environmental profile. Their modular nature allows for distributed implementation, potentially reducing transportation emissions associated with centralized capture facilities. Additionally, the relatively small physical footprint of membrane systems minimizes land use impacts compared to alternative technologies requiring extensive infrastructure.
Techno-Economic Analysis of Enhanced Membrane Systems
The techno-economic analysis of enhanced membrane systems for CO2 capture reveals significant potential for cost reduction and performance improvement. Current economic assessments indicate that polymer membrane systems can achieve CO2 capture costs between $40-60 per ton, compared to conventional amine scrubbing technologies at $50-70 per ton. This cost advantage stems primarily from lower energy requirements and reduced capital expenditure.
When evaluating membrane systems at industrial scale, the capital costs typically represent 30-40% of total capture costs, while operational expenses account for 60-70%. Energy consumption—particularly for compression and vacuum generation—constitutes the largest operational cost factor. Enhanced polymer membranes with improved CO2/N2 selectivity above 50 and CO2 permeability exceeding 1000 Barrer could potentially reduce energy requirements by 15-25%, translating to operational cost savings of approximately $8-12 per ton of CO2 captured.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that membrane performance parameters significantly impact economic viability. A 10% improvement in selectivity can reduce capture costs by 3-5%, while equivalent permeability enhancements yield 2-3% cost reductions. However, membrane durability presents a critical economic factor, as replacement costs can substantially affect long-term economics. Current membranes requiring replacement every 3-5 years add approximately $5-8 per ton to overall capture costs.
Scale-up considerations reveal favorable economics at larger installations, with costs decreasing by 15-20% when scaling from pilot (10 tons CO2/day) to commercial scale (500+ tons CO2/day). This economy of scale primarily results from more efficient energy integration and reduced specific capital costs for auxiliary equipment.
Comparative analysis with alternative capture technologies shows that enhanced polymer membranes become particularly competitive in retrofit applications where space constraints exist and in scenarios with moderate CO2 concentrations (8-15%). Under these conditions, membrane systems demonstrate 10-15% lower levelized costs compared to amine-based systems, primarily due to reduced footprint requirements and lower parasitic energy loads.
Future economic projections suggest that continued advances in membrane materials could reduce capture costs to $30-40 per ton by 2030, making carbon capture economically viable for a broader range of industrial applications. This projection assumes improvements in both membrane performance and manufacturing processes, with production costs decreasing by 25-30% through economies of scale and advanced fabrication techniques.
When evaluating membrane systems at industrial scale, the capital costs typically represent 30-40% of total capture costs, while operational expenses account for 60-70%. Energy consumption—particularly for compression and vacuum generation—constitutes the largest operational cost factor. Enhanced polymer membranes with improved CO2/N2 selectivity above 50 and CO2 permeability exceeding 1000 Barrer could potentially reduce energy requirements by 15-25%, translating to operational cost savings of approximately $8-12 per ton of CO2 captured.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that membrane performance parameters significantly impact economic viability. A 10% improvement in selectivity can reduce capture costs by 3-5%, while equivalent permeability enhancements yield 2-3% cost reductions. However, membrane durability presents a critical economic factor, as replacement costs can substantially affect long-term economics. Current membranes requiring replacement every 3-5 years add approximately $5-8 per ton to overall capture costs.
Scale-up considerations reveal favorable economics at larger installations, with costs decreasing by 15-20% when scaling from pilot (10 tons CO2/day) to commercial scale (500+ tons CO2/day). This economy of scale primarily results from more efficient energy integration and reduced specific capital costs for auxiliary equipment.
Comparative analysis with alternative capture technologies shows that enhanced polymer membranes become particularly competitive in retrofit applications where space constraints exist and in scenarios with moderate CO2 concentrations (8-15%). Under these conditions, membrane systems demonstrate 10-15% lower levelized costs compared to amine-based systems, primarily due to reduced footprint requirements and lower parasitic energy loads.
Future economic projections suggest that continued advances in membrane materials could reduce capture costs to $30-40 per ton by 2030, making carbon capture economically viable for a broader range of industrial applications. This projection assumes improvements in both membrane performance and manufacturing processes, with production costs decreasing by 25-30% through economies of scale and advanced fabrication techniques.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!