Evaluating Tautomerization as a Parameter in Chemical Kinetics
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Fundamentals and Research Objectives
Tautomerization is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, involving the rapid interconversion between structural isomers. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes, making it an essential parameter in chemical kinetics. The study of tautomerization has evolved significantly over the past century, with advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods enabling deeper insights into its mechanisms and effects.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the impact of tautomerization on chemical kinetics and explore its implications in diverse fields such as drug design, materials science, and biochemistry. By understanding the dynamics of tautomeric equilibria, we aim to develop more accurate models for predicting reaction rates and outcomes in complex chemical systems.
Tautomerization can significantly influence reaction rates and equilibria, often leading to unexpected results in chemical processes. For instance, in drug development, the tautomeric form of a molecule can affect its binding affinity to target proteins, potentially altering its efficacy or toxicity profile. In materials science, tautomerization can impact the electronic properties of organic semiconductors, influencing their performance in devices such as solar cells and light-emitting diodes.
Recent technological advancements have enabled researchers to study tautomerization with unprecedented precision. High-resolution spectroscopic techniques, such as ultrafast laser spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, allow for real-time observation of tautomeric transitions. Computational methods, including density functional theory (DFT) and molecular dynamics simulations, provide valuable insights into the energetics and kinetics of tautomerization processes.
The research objectives of this study encompass several key areas. Firstly, we aim to develop improved methodologies for accurately measuring and predicting tautomerization rates in various chemical environments. This includes investigating the effects of solvent polarity, pH, and temperature on tautomeric equilibria. Secondly, we seek to elucidate the relationship between molecular structure and tautomerization propensity, with the goal of establishing predictive models for rational molecular design.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore the role of tautomerization in catalysis and enzyme-mediated reactions. By understanding how tautomeric shifts influence transition states and reaction pathways, we can potentially design more efficient catalysts and optimize enzymatic processes. Additionally, we will investigate the implications of tautomerization in the context of drug-target interactions, aiming to improve structure-based drug design strategies.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the impact of tautomerization on chemical kinetics and explore its implications in diverse fields such as drug design, materials science, and biochemistry. By understanding the dynamics of tautomeric equilibria, we aim to develop more accurate models for predicting reaction rates and outcomes in complex chemical systems.
Tautomerization can significantly influence reaction rates and equilibria, often leading to unexpected results in chemical processes. For instance, in drug development, the tautomeric form of a molecule can affect its binding affinity to target proteins, potentially altering its efficacy or toxicity profile. In materials science, tautomerization can impact the electronic properties of organic semiconductors, influencing their performance in devices such as solar cells and light-emitting diodes.
Recent technological advancements have enabled researchers to study tautomerization with unprecedented precision. High-resolution spectroscopic techniques, such as ultrafast laser spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, allow for real-time observation of tautomeric transitions. Computational methods, including density functional theory (DFT) and molecular dynamics simulations, provide valuable insights into the energetics and kinetics of tautomerization processes.
The research objectives of this study encompass several key areas. Firstly, we aim to develop improved methodologies for accurately measuring and predicting tautomerization rates in various chemical environments. This includes investigating the effects of solvent polarity, pH, and temperature on tautomeric equilibria. Secondly, we seek to elucidate the relationship between molecular structure and tautomerization propensity, with the goal of establishing predictive models for rational molecular design.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore the role of tautomerization in catalysis and enzyme-mediated reactions. By understanding how tautomeric shifts influence transition states and reaction pathways, we can potentially design more efficient catalysts and optimize enzymatic processes. Additionally, we will investigate the implications of tautomerization in the context of drug-target interactions, aiming to improve structure-based drug design strategies.
Industrial Applications of Tautomerization Kinetics
Tautomerization kinetics has found significant applications across various industrial sectors, revolutionizing processes and product development. In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding tautomerization kinetics is crucial for drug design and formulation. It aids in predicting drug stability, bioavailability, and efficacy. Pharmaceutical companies leverage this knowledge to optimize drug candidates, enhance shelf life, and improve drug delivery systems. For instance, tautomerization kinetics has been instrumental in developing pH-responsive drug release mechanisms, allowing for targeted delivery in specific physiological environments.
The chemical manufacturing sector extensively utilizes tautomerization kinetics in process optimization. It plays a vital role in designing more efficient catalysts, improving reaction yields, and reducing unwanted side products. By understanding the tautomerization behavior of reactants and intermediates, chemical engineers can fine-tune reaction conditions, leading to cost-effective and environmentally friendly production processes. This application has been particularly impactful in the synthesis of specialty chemicals and advanced materials.
In the field of materials science, tautomerization kinetics has enabled the development of smart materials with switchable properties. These materials can change their physical or chemical characteristics in response to external stimuli, such as light, temperature, or pH. Applications range from self-healing polymers to responsive coatings used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
The food and beverage industry has also benefited from insights into tautomerization kinetics. It has been applied to enhance flavor stability, control color changes, and improve the shelf life of food products. Understanding tautomerization processes in food components has led to the development of novel preservation techniques and the creation of functional foods with specific nutritional profiles.
In the energy sector, tautomerization kinetics has contributed to the advancement of fuel cell technology and energy storage systems. It has been utilized in the design of more efficient electrolytes and in optimizing the performance of redox flow batteries. Additionally, tautomerization kinetics plays a role in improving the efficiency of solar energy conversion in certain types of photovoltaic cells.
The application of tautomerization kinetics in industrial processes has led to significant improvements in product quality, process efficiency, and environmental sustainability across multiple sectors. As research in this field continues to advance, it is expected to open up new possibilities for innovation and technological breakthroughs in various industries.
The chemical manufacturing sector extensively utilizes tautomerization kinetics in process optimization. It plays a vital role in designing more efficient catalysts, improving reaction yields, and reducing unwanted side products. By understanding the tautomerization behavior of reactants and intermediates, chemical engineers can fine-tune reaction conditions, leading to cost-effective and environmentally friendly production processes. This application has been particularly impactful in the synthesis of specialty chemicals and advanced materials.
In the field of materials science, tautomerization kinetics has enabled the development of smart materials with switchable properties. These materials can change their physical or chemical characteristics in response to external stimuli, such as light, temperature, or pH. Applications range from self-healing polymers to responsive coatings used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
The food and beverage industry has also benefited from insights into tautomerization kinetics. It has been applied to enhance flavor stability, control color changes, and improve the shelf life of food products. Understanding tautomerization processes in food components has led to the development of novel preservation techniques and the creation of functional foods with specific nutritional profiles.
In the energy sector, tautomerization kinetics has contributed to the advancement of fuel cell technology and energy storage systems. It has been utilized in the design of more efficient electrolytes and in optimizing the performance of redox flow batteries. Additionally, tautomerization kinetics plays a role in improving the efficiency of solar energy conversion in certain types of photovoltaic cells.
The application of tautomerization kinetics in industrial processes has led to significant improvements in product quality, process efficiency, and environmental sustainability across multiple sectors. As research in this field continues to advance, it is expected to open up new possibilities for innovation and technological breakthroughs in various industries.
Current Challenges in Tautomerization Analysis
Tautomerization analysis in chemical kinetics presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary difficulties lies in accurately measuring and predicting tautomerization rates in complex chemical systems. The rapid interconversion between tautomers often occurs on timescales that are challenging to capture with conventional analytical techniques, leading to potential inaccuracies in kinetic models.
Another major hurdle is the environmental sensitivity of tautomerization processes. Factors such as temperature, pH, solvent polarity, and the presence of catalysts can dramatically influence tautomeric equilibria and interconversion rates. This sensitivity makes it difficult to extrapolate laboratory results to real-world applications, particularly in biological systems or industrial processes where conditions may be highly variable.
The computational modeling of tautomerization presents its own set of challenges. While quantum mechanical calculations can provide insights into tautomeric structures and energetics, accurately simulating the dynamics of tautomerization, especially in solution, remains computationally intensive and often requires simplifying assumptions that may limit the model's applicability to real-world scenarios.
Furthermore, the impact of tautomerization on other chemical processes, such as reaction mechanisms, catalysis, and molecular recognition, is not always straightforward to predict or quantify. This complexity can lead to unexpected results in chemical synthesis, drug design, and materials development, where tautomeric effects may significantly alter the properties and behavior of target molecules.
In the pharmaceutical industry, tautomerization poses particular challenges for drug discovery and development. The different tautomeric forms of a drug molecule can exhibit varying physicochemical properties, affecting solubility, bioavailability, and binding affinity to target proteins. Predicting which tautomer will predominate under physiological conditions and how this may impact drug efficacy and safety is a critical yet often difficult task.
Analytical techniques for identifying and quantifying tautomers in complex mixtures also face limitations. Spectroscopic methods may struggle to distinguish between rapidly interconverting tautomers, while separation techniques can potentially alter the tautomeric equilibrium during analysis. Developing robust, non-invasive methods for real-time monitoring of tautomerization in situ remains an active area of research.
Lastly, the integration of tautomerization parameters into broader chemical kinetics models and reaction engineering frameworks is an ongoing challenge. Balancing the need for accurate representation of tautomeric effects with the practical constraints of computational efficiency and model simplicity is a delicate task that requires careful consideration in both academic research and industrial applications.
Another major hurdle is the environmental sensitivity of tautomerization processes. Factors such as temperature, pH, solvent polarity, and the presence of catalysts can dramatically influence tautomeric equilibria and interconversion rates. This sensitivity makes it difficult to extrapolate laboratory results to real-world applications, particularly in biological systems or industrial processes where conditions may be highly variable.
The computational modeling of tautomerization presents its own set of challenges. While quantum mechanical calculations can provide insights into tautomeric structures and energetics, accurately simulating the dynamics of tautomerization, especially in solution, remains computationally intensive and often requires simplifying assumptions that may limit the model's applicability to real-world scenarios.
Furthermore, the impact of tautomerization on other chemical processes, such as reaction mechanisms, catalysis, and molecular recognition, is not always straightforward to predict or quantify. This complexity can lead to unexpected results in chemical synthesis, drug design, and materials development, where tautomeric effects may significantly alter the properties and behavior of target molecules.
In the pharmaceutical industry, tautomerization poses particular challenges for drug discovery and development. The different tautomeric forms of a drug molecule can exhibit varying physicochemical properties, affecting solubility, bioavailability, and binding affinity to target proteins. Predicting which tautomer will predominate under physiological conditions and how this may impact drug efficacy and safety is a critical yet often difficult task.
Analytical techniques for identifying and quantifying tautomers in complex mixtures also face limitations. Spectroscopic methods may struggle to distinguish between rapidly interconverting tautomers, while separation techniques can potentially alter the tautomeric equilibrium during analysis. Developing robust, non-invasive methods for real-time monitoring of tautomerization in situ remains an active area of research.
Lastly, the integration of tautomerization parameters into broader chemical kinetics models and reaction engineering frameworks is an ongoing challenge. Balancing the need for accurate representation of tautomeric effects with the practical constraints of computational efficiency and model simplicity is a delicate task that requires careful consideration in both academic research and industrial applications.
Experimental Methods for Tautomerization Evaluation
01 Computational methods for tautomerization kinetics
Advanced computational techniques are employed to study the kinetics of tautomerization reactions. These methods involve quantum mechanical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations to predict reaction rates, energy barriers, and equilibrium constants for various tautomeric systems. Such computational approaches aid in understanding the mechanisms and factors influencing tautomerization processes.- Computational methods for tautomerization kinetics: Advanced computational techniques are employed to study the kinetics of tautomerization reactions. These methods involve quantum mechanical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations to predict reaction rates, transition states, and energy barriers associated with tautomeric interconversions. Such computational approaches provide valuable insights into the mechanisms and factors influencing tautomerization processes.
- Experimental techniques for measuring tautomerization rates: Various experimental methods are used to measure tautomerization kinetics in real-time. These include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, UV-Vis, and IR spectroscopy, as well as fast kinetic methods like stopped-flow and temperature-jump techniques. These approaches allow researchers to determine rate constants, activation energies, and other kinetic parameters for tautomeric equilibria in different chemical environments.
- Influence of solvent effects on tautomerization kinetics: The kinetics of tautomerization reactions are significantly affected by solvent properties. Studies focus on how different solvents impact the rate of tautomeric interconversions, stabilization of transition states, and the overall equilibrium between tautomers. Understanding these solvent effects is crucial for predicting and controlling tautomerization processes in various applications.
- Catalytic effects on tautomerization kinetics: Catalysts play a significant role in modulating tautomerization kinetics. Research in this area explores how different catalysts, including acids, bases, and metal complexes, can accelerate or inhibit tautomeric interconversions. The development of novel catalytic systems aims to control tautomerization processes for specific applications in organic synthesis and materials science.
- Applications of tautomerization kinetics in drug design: Understanding tautomerization kinetics is crucial in pharmaceutical research and drug design. Studies focus on how tautomeric equilibria affect drug-target interactions, bioavailability, and metabolic stability. Researchers utilize kinetic data to optimize drug candidates, predict their behavior in biological systems, and improve their efficacy and safety profiles.
02 Experimental techniques for measuring tautomerization rates
Various experimental methods are used to measure tautomerization kinetics in real-time. These include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, UV-Vis, and IR spectroscopy, as well as fast kinetic methods like stopped-flow and temperature-jump techniques. These approaches allow researchers to determine rate constants and activation energies for tautomerization reactions in different chemical environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Influence of solvent effects on tautomerization kinetics
The kinetics of tautomerization reactions are significantly affected by solvent properties. Studies focus on how different solvents impact the rate and equilibrium of tautomerization processes. Factors such as solvent polarity, hydrogen bonding capability, and dielectric constant are investigated to understand their role in stabilizing different tautomeric forms and influencing the energy barriers of tautomerization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic effects on tautomerization kinetics
Research explores the use of catalysts to modify tautomerization kinetics. Both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts are investigated for their ability to lower activation energies and alter reaction pathways in tautomerization processes. This includes studies on acid-base catalysis, metal-ion catalysis, and enzyme-catalyzed tautomerization reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of tautomerization kinetics in material science
The understanding and control of tautomerization kinetics find applications in various fields of material science. This includes the development of molecular switches, sensors, and smart materials that utilize controlled tautomerization processes. Research focuses on designing systems where tautomerization can be triggered by external stimuli such as light, pH, or temperature changes, leading to materials with tunable properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Groups and Institutions
The field of tautomerization in chemical kinetics is in a mature stage of development, with ongoing research focusing on refining understanding and applications. The market size is moderate, primarily driven by pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Technological maturity is high, with established players like Pfizer, Bayer Pharma AG, and Novomer leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as MIT, Harvard, and the Broad Institute contribute significantly to advancing knowledge in this area. Emerging companies like Sunshine Lake Pharma and Duality Biologics are also making strides, indicating a competitive landscape that balances established expertise with innovative approaches. The field continues to evolve, with potential for new breakthroughs in drug discovery and chemical process optimization.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard researchers have developed advanced methodologies for evaluating tautomerization in chemical kinetics, focusing on both fundamental understanding and practical applications. Their approach combines experimental techniques like ultrafast spectroscopy with sophisticated computational modeling. Harvard's method utilizes time-resolved spectroscopy to directly observe tautomer interconversion on picosecond to nanosecond timescales[8]. This is complemented by ab initio quantum chemistry calculations to predict tautomer energetics and transition states. The Harvard team has also developed novel machine learning algorithms to predict tautomerization rates and equilibria for large datasets of organic compounds[10]. Their research has provided insights into the role of tautomerization in catalysis, atmospheric chemistry, and biochemical processes.
Strengths: Cutting-edge experimental techniques, fundamental research with broad applications. Weaknesses: May be less directly applicable to industrial processes compared to more applied approaches.
The Broad Institute, Inc.
Technical Solution: The Broad Institute has developed a comprehensive platform for evaluating tautomerization in chemical and biological systems. Their approach integrates high-throughput experimental techniques with advanced computational modeling and machine learning. The Broad's method utilizes automated liquid handling and mass spectrometry to rapidly measure tautomer ratios in diverse chemical environments[11]. This is complemented by quantum mechanical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations to predict tautomeric behavior. The institute has also implemented deep learning algorithms to predict tautomerization effects on protein-ligand interactions and enzymatic reactions[13]. Their platform has been applied to understand the role of tautomerization in drug metabolism, chemical library design, and the interpretation of genome-wide association studies.
Strengths: Interdisciplinary approach combining chemistry, biology, and data science; high-throughput capabilities. Weaknesses: May require significant resources and expertise to implement fully.
Computational Approaches to Tautomerization Kinetics
Apparatus and method to measure the kinetics parameters of a porous powder catalyst
PatentInactiveUS7867766B2
Innovation
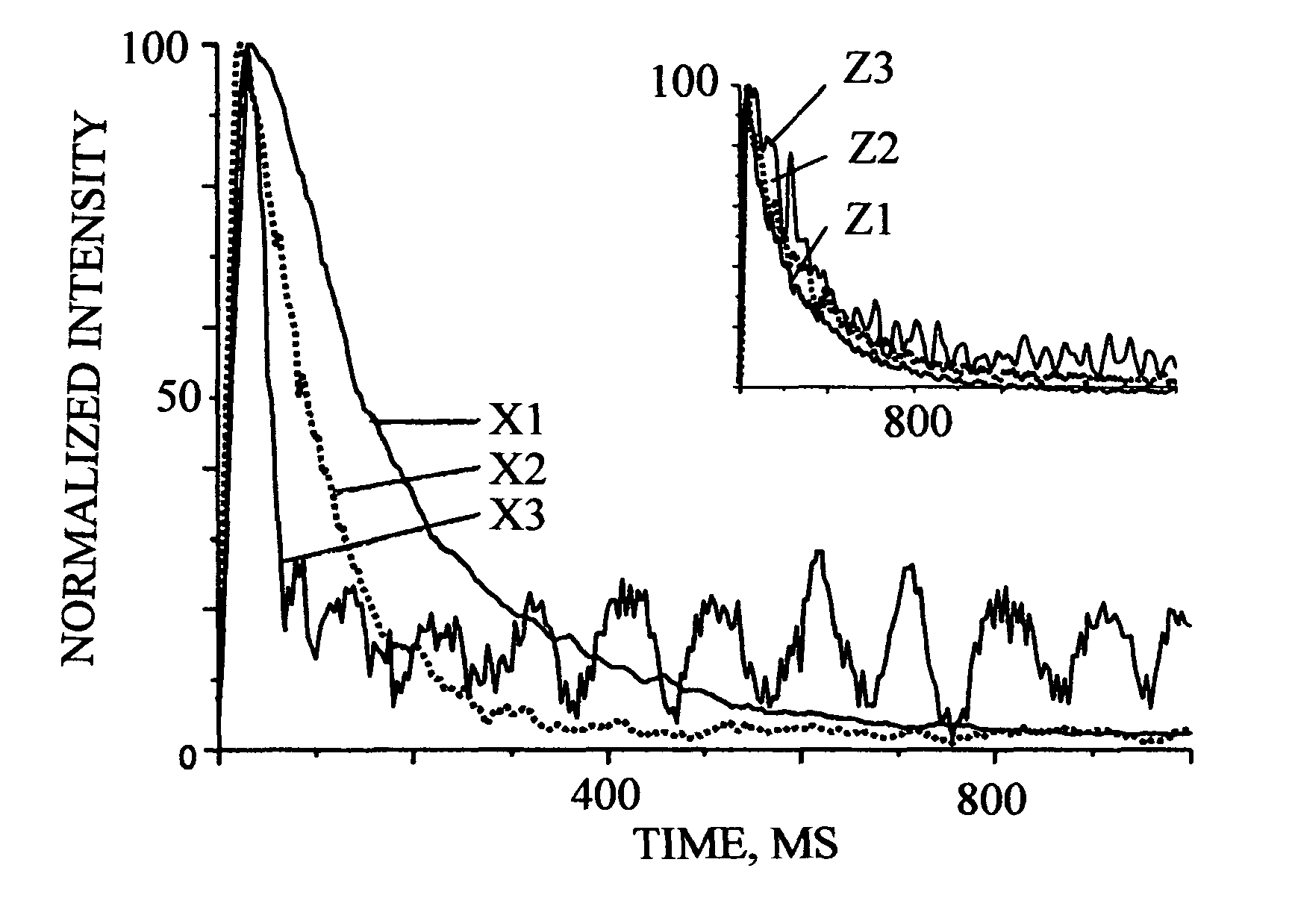
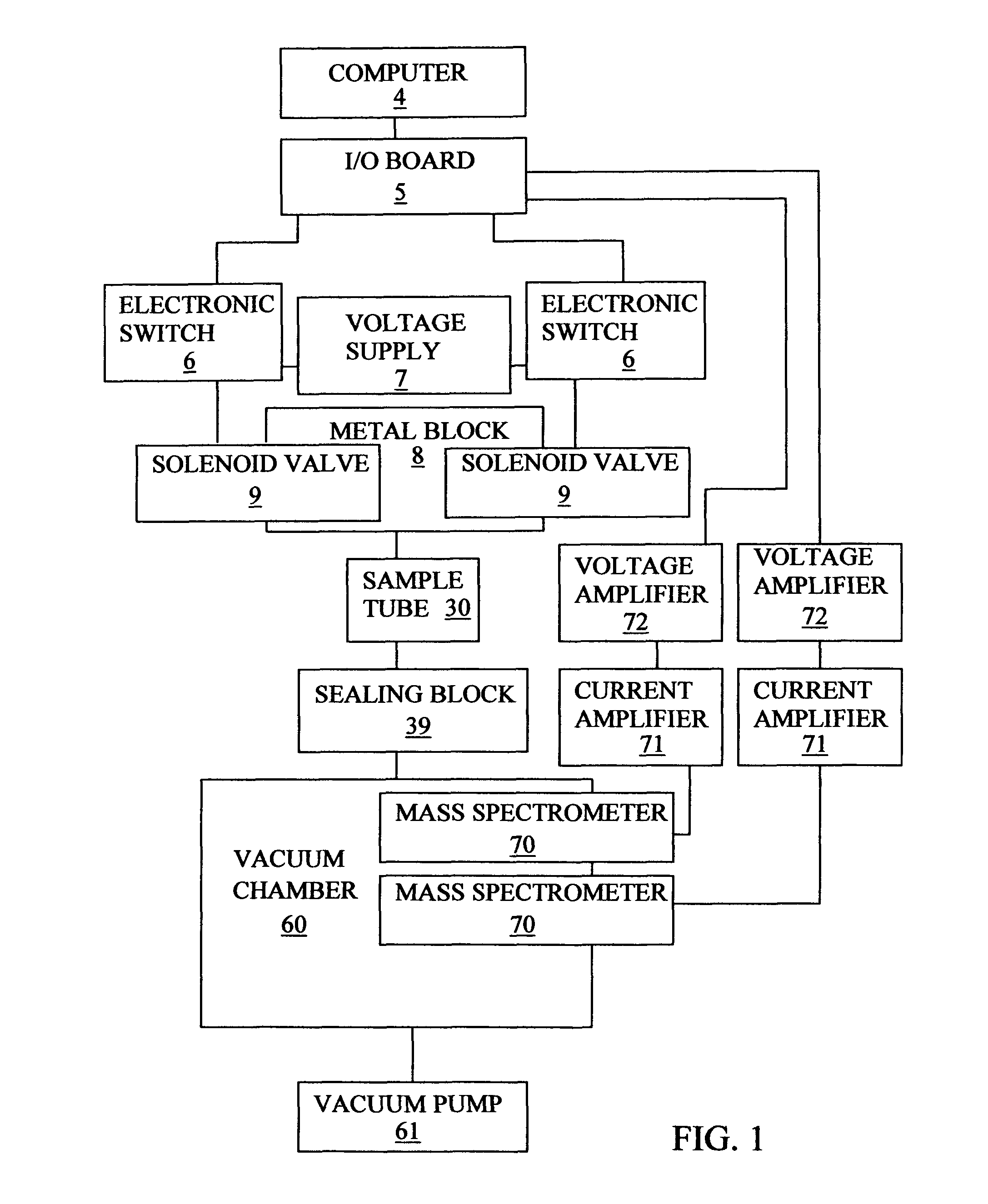
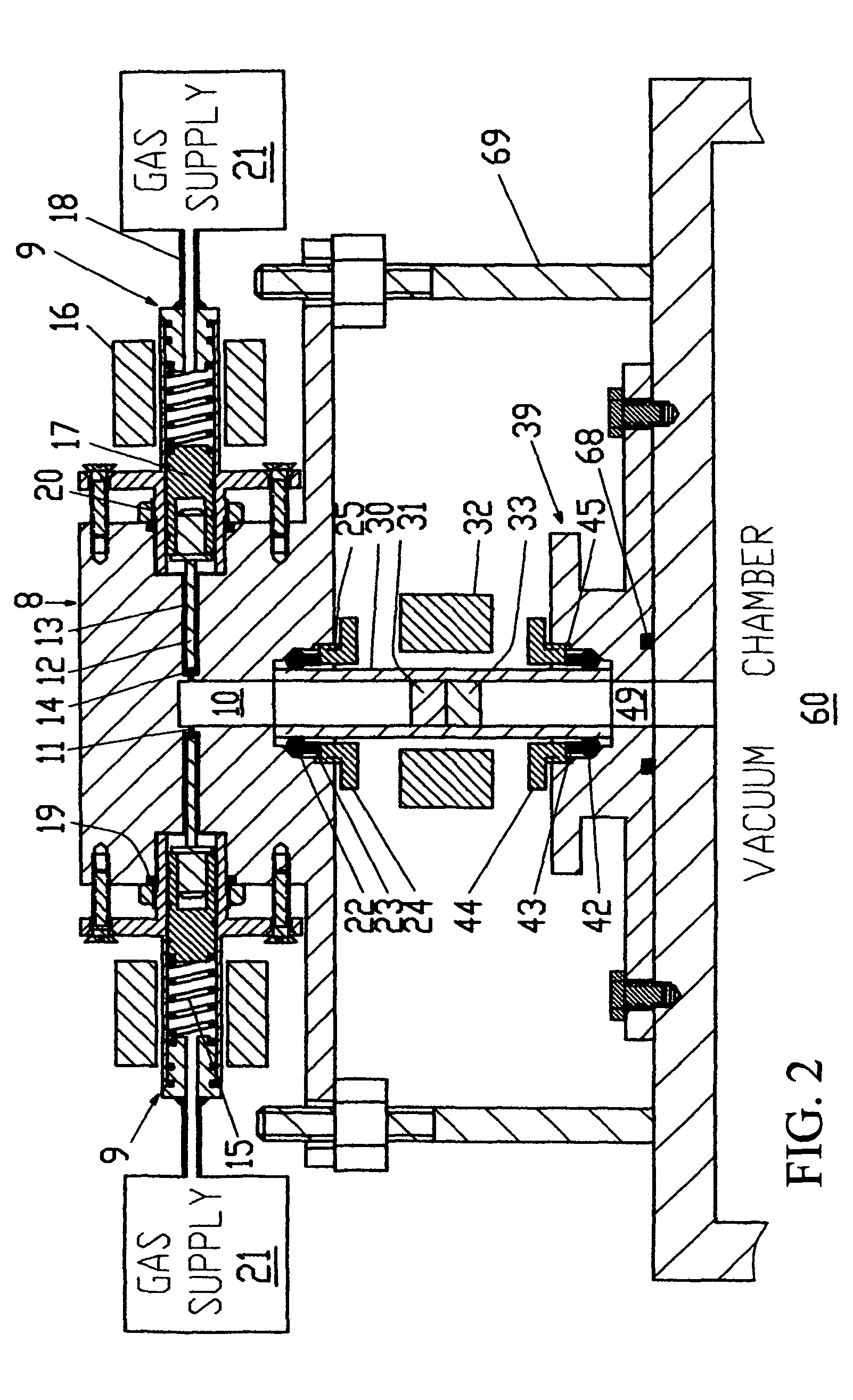
- A device and method for measuring kinetics parameters, including active site concentration and gas diffusivity, using a cylindrical sample tube and metal block with valved openings for precise gas delivery and measurement, allowing for transient adsorption and reactant molecules at near reaction temperatures, which selectively measures active sites pertinent to catalysis.
Polymers of ethylene oxide and carbon dioxide
PatentActiveEP2285864A1
Innovation
- The use of N,N'-bis(salicydene)-1,2-cyclohexyldiamine metal complexes, specifically those with metals like zinc, cobalt, chromium, aluminum, titanium, ruthenium, or manganese, to catalyze the polymerization reaction, ensuring low ether content and high carbonate percentages in the resulting polymers.
Impact on Drug Discovery and Design
Tautomerization plays a crucial role in drug discovery and design, significantly impacting the development of new pharmaceuticals. This phenomenon, which involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, can profoundly affect a compound's physicochemical properties, binding affinity, and overall efficacy as a potential drug candidate.
In the early stages of drug discovery, understanding tautomerization is essential for accurate virtual screening and molecular docking simulations. The ability of a molecule to exist in multiple tautomeric forms can lead to discrepancies between predicted and observed binding affinities if not properly accounted for. Consequently, incorporating tautomerization into computational models has become a standard practice in many drug discovery pipelines, enhancing the reliability of in silico predictions and reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives during lead compound identification.
Furthermore, tautomerization can influence a drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties. Different tautomers may exhibit varying solubility, lipophilicity, and permeability characteristics, which are critical factors in determining a drug's bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profile. As such, considering tautomerization during lead optimization can help researchers fine-tune these properties to improve a drug's overall performance and reduce potential side effects.
The impact of tautomerization extends to drug formulation and stability as well. Certain tautomeric forms may be more prone to degradation or have different crystallization behaviors, affecting the shelf life and manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical products. Understanding these dynamics allows formulators to develop more stable and effective drug formulations, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced production costs.
In the realm of structure-based drug design, tautomerization can significantly affect protein-ligand interactions. The binding pocket of a target protein may preferentially accommodate one tautomeric form over another, influencing the drug's potency and selectivity. By considering tautomerization during the design process, medicinal chemists can optimize ligand structures to maximize favorable interactions and minimize undesired binding to off-target proteins, potentially reducing side effects and improving therapeutic efficacy.
Moreover, tautomerization can impact the intellectual property landscape in pharmaceutical research. The ability to patent specific tautomeric forms of a drug compound can provide additional protection for pharmaceutical companies, potentially extending the lifecycle of their products. This consideration has led to increased attention to tautomerization in both drug discovery and patent strategy, highlighting its importance in the broader context of pharmaceutical development and commercialization.
In the early stages of drug discovery, understanding tautomerization is essential for accurate virtual screening and molecular docking simulations. The ability of a molecule to exist in multiple tautomeric forms can lead to discrepancies between predicted and observed binding affinities if not properly accounted for. Consequently, incorporating tautomerization into computational models has become a standard practice in many drug discovery pipelines, enhancing the reliability of in silico predictions and reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives during lead compound identification.
Furthermore, tautomerization can influence a drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties. Different tautomers may exhibit varying solubility, lipophilicity, and permeability characteristics, which are critical factors in determining a drug's bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profile. As such, considering tautomerization during lead optimization can help researchers fine-tune these properties to improve a drug's overall performance and reduce potential side effects.
The impact of tautomerization extends to drug formulation and stability as well. Certain tautomeric forms may be more prone to degradation or have different crystallization behaviors, affecting the shelf life and manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical products. Understanding these dynamics allows formulators to develop more stable and effective drug formulations, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced production costs.
In the realm of structure-based drug design, tautomerization can significantly affect protein-ligand interactions. The binding pocket of a target protein may preferentially accommodate one tautomeric form over another, influencing the drug's potency and selectivity. By considering tautomerization during the design process, medicinal chemists can optimize ligand structures to maximize favorable interactions and minimize undesired binding to off-target proteins, potentially reducing side effects and improving therapeutic efficacy.
Moreover, tautomerization can impact the intellectual property landscape in pharmaceutical research. The ability to patent specific tautomeric forms of a drug compound can provide additional protection for pharmaceutical companies, potentially extending the lifecycle of their products. This consideration has led to increased attention to tautomerization in both drug discovery and patent strategy, highlighting its importance in the broader context of pharmaceutical development and commercialization.
Tautomerization in Catalysis and Green Chemistry
Tautomerization plays a crucial role in catalysis and green chemistry, offering innovative pathways for sustainable chemical processes. This phenomenon, involving the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential to enhance reaction efficiency and selectivity.
In catalytic systems, tautomerization can significantly influence reaction mechanisms and outcomes. By facilitating the formation of reactive intermediates, it can lower activation barriers and accelerate reaction rates. This is particularly evident in organocatalysis, where tautomeric shifts in catalysts can modulate their activity and stereoselectivity.
The application of tautomerization in green chemistry aligns with the principles of atom economy and energy efficiency. By harnessing tautomeric equilibria, chemists can design reactions that proceed under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. This approach has been successfully employed in the development of environmentally benign synthetic methodologies.
One notable example is the use of tautomerization in the design of switchable solvents. These systems can reversibly change their properties through tautomeric shifts, allowing for facile product separation and solvent recycling. Such innovations contribute to the reduction of solvent waste, a significant environmental concern in chemical industries.
Tautomerization also plays a vital role in asymmetric catalysis. The dynamic nature of tautomeric equilibria can be exploited to create chiral environments, leading to the preferential formation of specific enantiomers. This has profound implications for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other high-value chiral compounds.
In the context of biocatalysis, understanding and controlling tautomerization can lead to improved enzyme performance. By engineering enzymes to stabilize specific tautomeric forms of substrates or intermediates, researchers can enhance catalytic efficiency and expand the scope of biocatalytic transformations.
The integration of tautomerization concepts in flow chemistry represents another frontier in green chemistry. Continuous-flow systems can be designed to exploit rapid tautomeric interconversions, enabling precise control over reaction conditions and facilitating the scale-up of sustainable processes.
As research in this field progresses, the development of computational tools for predicting and modeling tautomeric behavior in complex chemical systems will be crucial. These advancements will enable more rational design of catalytic systems and green chemical processes, further cementing the role of tautomerization as a key parameter in sustainable chemistry.
In catalytic systems, tautomerization can significantly influence reaction mechanisms and outcomes. By facilitating the formation of reactive intermediates, it can lower activation barriers and accelerate reaction rates. This is particularly evident in organocatalysis, where tautomeric shifts in catalysts can modulate their activity and stereoselectivity.
The application of tautomerization in green chemistry aligns with the principles of atom economy and energy efficiency. By harnessing tautomeric equilibria, chemists can design reactions that proceed under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. This approach has been successfully employed in the development of environmentally benign synthetic methodologies.
One notable example is the use of tautomerization in the design of switchable solvents. These systems can reversibly change their properties through tautomeric shifts, allowing for facile product separation and solvent recycling. Such innovations contribute to the reduction of solvent waste, a significant environmental concern in chemical industries.
Tautomerization also plays a vital role in asymmetric catalysis. The dynamic nature of tautomeric equilibria can be exploited to create chiral environments, leading to the preferential formation of specific enantiomers. This has profound implications for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other high-value chiral compounds.
In the context of biocatalysis, understanding and controlling tautomerization can lead to improved enzyme performance. By engineering enzymes to stabilize specific tautomeric forms of substrates or intermediates, researchers can enhance catalytic efficiency and expand the scope of biocatalytic transformations.
The integration of tautomerization concepts in flow chemistry represents another frontier in green chemistry. Continuous-flow systems can be designed to exploit rapid tautomeric interconversions, enabling precise control over reaction conditions and facilitating the scale-up of sustainable processes.
As research in this field progresses, the development of computational tools for predicting and modeling tautomeric behavior in complex chemical systems will be crucial. These advancements will enable more rational design of catalytic systems and green chemical processes, further cementing the role of tautomerization as a key parameter in sustainable chemistry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!