Tautomerization in Carbohydrates: Implications for Energy Metabolism
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carbohydrate Tautomerization Background and Objectives
Carbohydrate tautomerization is a fundamental process in organic chemistry that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism. This phenomenon involves the interconversion between different structural isomers of carbohydrates, which can significantly impact their reactivity and biological functions. The study of tautomerization in carbohydrates has gained increasing attention due to its implications for understanding and potentially manipulating energy metabolism pathways.
The historical context of carbohydrate tautomerization research dates back to the early 20th century when Emil Fischer first proposed the concept of ring-chain tautomerism in sugars. Since then, our understanding of this process has evolved significantly, with advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods enabling more detailed investigations into the mechanisms and kinetics of tautomeric transitions.
In recent years, the field has experienced a resurgence of interest, driven by the recognition of tautomerization's importance in various biological processes, including enzyme catalysis, glycosylation reactions, and cellular energy production. This renewed focus has led to the development of novel experimental approaches and theoretical models aimed at elucidating the complex interplay between carbohydrate structure, tautomeric equilibria, and metabolic pathways.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding carbohydrate tautomerization and its implications for energy metabolism. We aim to explore the fundamental principles governing tautomeric transitions in carbohydrates, examine the latest experimental and computational techniques used to study these processes, and assess their potential impact on metabolic regulation and energy production in living systems.
Furthermore, this report seeks to identify key challenges and opportunities in the field, with a particular focus on emerging technologies and methodologies that may enable more precise control and manipulation of carbohydrate tautomerization. By doing so, we hope to lay the groundwork for future research directions that could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for metabolic disorders or innovative approaches to energy production and storage.
As we delve into this complex and rapidly evolving field, it is essential to consider the broader implications of carbohydrate tautomerization research. Advances in our understanding of these processes have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and renewable energy. By exploring the intricate relationship between carbohydrate structure, tautomerization, and energy metabolism, we aim to uncover new avenues for scientific discovery and technological innovation that could have far-reaching impacts on human health and sustainable energy solutions.
The historical context of carbohydrate tautomerization research dates back to the early 20th century when Emil Fischer first proposed the concept of ring-chain tautomerism in sugars. Since then, our understanding of this process has evolved significantly, with advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods enabling more detailed investigations into the mechanisms and kinetics of tautomeric transitions.
In recent years, the field has experienced a resurgence of interest, driven by the recognition of tautomerization's importance in various biological processes, including enzyme catalysis, glycosylation reactions, and cellular energy production. This renewed focus has led to the development of novel experimental approaches and theoretical models aimed at elucidating the complex interplay between carbohydrate structure, tautomeric equilibria, and metabolic pathways.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding carbohydrate tautomerization and its implications for energy metabolism. We aim to explore the fundamental principles governing tautomeric transitions in carbohydrates, examine the latest experimental and computational techniques used to study these processes, and assess their potential impact on metabolic regulation and energy production in living systems.
Furthermore, this report seeks to identify key challenges and opportunities in the field, with a particular focus on emerging technologies and methodologies that may enable more precise control and manipulation of carbohydrate tautomerization. By doing so, we hope to lay the groundwork for future research directions that could lead to novel therapeutic strategies for metabolic disorders or innovative approaches to energy production and storage.
As we delve into this complex and rapidly evolving field, it is essential to consider the broader implications of carbohydrate tautomerization research. Advances in our understanding of these processes have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and renewable energy. By exploring the intricate relationship between carbohydrate structure, tautomerization, and energy metabolism, we aim to uncover new avenues for scientific discovery and technological innovation that could have far-reaching impacts on human health and sustainable energy solutions.
Metabolic Relevance of Carbohydrate Tautomerization
Carbohydrate tautomerization plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, influencing various biochemical processes within living organisms. This phenomenon involves the interconversion between different structural forms of carbohydrates, particularly in the context of monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose. The tautomeric equilibrium of these sugars significantly impacts their reactivity, binding properties, and overall metabolic fate.
In the context of energy metabolism, the most relevant tautomerization occurs between the open-chain (aldehyde or ketone) and cyclic (hemiacetal or hemiketal) forms of monosaccharides. This interconversion is fundamental to the initial steps of glycolysis, where glucose undergoes phosphorylation and subsequent isomerization. The ability of glucose to exist in both open-chain and cyclic forms allows for its efficient recognition by enzymes and transporters, facilitating its entry into cells and subsequent metabolic processing.
The tautomerization of fructose-6-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate, catalyzed by phosphoglucose isomerase, represents a key step in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. This reversible reaction involves the opening of the fructose ring, followed by a series of proton transfers and ring closure to form glucose. The equilibrium between these tautomers is critical for maintaining the balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, thus regulating cellular energy production and storage.
Furthermore, carbohydrate tautomerization influences the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which are implicated in various metabolic disorders, including diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The open-chain forms of reducing sugars are more reactive and prone to non-enzymatic glycation of proteins, leading to AGE formation. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of carbohydrates is therefore essential for developing strategies to mitigate AGE-related complications in metabolic disorders.
The tautomerization of carbohydrates also affects their interaction with metabolic enzymes. Many enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism, such as aldolases and ketolases, specifically recognize and act upon either the open-chain or cyclic forms of their substrates. The dynamic equilibrium between these forms ensures that the appropriate tautomer is available for enzymatic reactions, maintaining the efficiency of metabolic pathways.
In conclusion, carbohydrate tautomerization is a fundamental aspect of energy metabolism, influencing enzymatic reactions, metabolic regulation, and the formation of potentially harmful byproducts. Its relevance extends beyond basic biochemistry, impacting our understanding of metabolic disorders and the development of therapeutic strategies targeting carbohydrate metabolism.
In the context of energy metabolism, the most relevant tautomerization occurs between the open-chain (aldehyde or ketone) and cyclic (hemiacetal or hemiketal) forms of monosaccharides. This interconversion is fundamental to the initial steps of glycolysis, where glucose undergoes phosphorylation and subsequent isomerization. The ability of glucose to exist in both open-chain and cyclic forms allows for its efficient recognition by enzymes and transporters, facilitating its entry into cells and subsequent metabolic processing.
The tautomerization of fructose-6-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate, catalyzed by phosphoglucose isomerase, represents a key step in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. This reversible reaction involves the opening of the fructose ring, followed by a series of proton transfers and ring closure to form glucose. The equilibrium between these tautomers is critical for maintaining the balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, thus regulating cellular energy production and storage.
Furthermore, carbohydrate tautomerization influences the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which are implicated in various metabolic disorders, including diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The open-chain forms of reducing sugars are more reactive and prone to non-enzymatic glycation of proteins, leading to AGE formation. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of carbohydrates is therefore essential for developing strategies to mitigate AGE-related complications in metabolic disorders.
The tautomerization of carbohydrates also affects their interaction with metabolic enzymes. Many enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism, such as aldolases and ketolases, specifically recognize and act upon either the open-chain or cyclic forms of their substrates. The dynamic equilibrium between these forms ensures that the appropriate tautomer is available for enzymatic reactions, maintaining the efficiency of metabolic pathways.
In conclusion, carbohydrate tautomerization is a fundamental aspect of energy metabolism, influencing enzymatic reactions, metabolic regulation, and the formation of potentially harmful byproducts. Its relevance extends beyond basic biochemistry, impacting our understanding of metabolic disorders and the development of therapeutic strategies targeting carbohydrate metabolism.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Tautomer Research
Tautomerization in carbohydrates represents a critical area of research with significant implications for energy metabolism. Current understanding of this phenomenon has advanced considerably, yet numerous challenges persist in tautomer research. The interconversion between different tautomeric forms of carbohydrates plays a crucial role in various biochemical processes, particularly in energy production and storage.
Recent studies have shed light on the dynamic nature of tautomerization in carbohydrates, revealing its impact on molecular recognition, enzymatic reactions, and metabolic pathways. The ability of carbohydrates to exist in multiple tautomeric forms allows for rapid adaptation to changing cellular environments, influencing their reactivity and biological functions. This flexibility is particularly relevant in the context of energy metabolism, where quick interconversion between tautomers can facilitate or hinder specific metabolic reactions.
One of the primary challenges in tautomer research lies in the accurate prediction and characterization of tautomeric equilibria in complex biological systems. While computational methods have improved significantly, discrepancies between theoretical predictions and experimental observations still exist, especially in aqueous environments that mimic physiological conditions. The development of more sophisticated models that account for solvent effects, pH variations, and intermolecular interactions remains an active area of research.
Another significant challenge is the real-time detection and quantification of tautomeric species in living systems. Current analytical techniques often struggle to capture the rapid interconversion between tautomers, leading to potential misinterpretations of metabolic processes. Advanced spectroscopic methods and high-resolution imaging techniques are being explored to address this limitation, but further refinement is necessary to fully elucidate the role of tautomerization in energy metabolism.
The impact of tautomerization on enzyme-substrate interactions presents yet another frontier in carbohydrate research. Understanding how different tautomeric forms affect binding affinities and catalytic efficiencies of metabolic enzymes is crucial for unraveling the intricacies of energy production pathways. This knowledge could potentially lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting specific tautomeric forms to modulate metabolic processes.
As research progresses, the integration of tautomerization studies with systems biology approaches is becoming increasingly important. Mapping the tautomeric landscape of carbohydrates within the broader context of cellular metabolism could provide valuable insights into the regulation of energy flux and the adaptability of metabolic networks. This holistic perspective may unlock new avenues for optimizing energy utilization in both normal and pathological states.
Recent studies have shed light on the dynamic nature of tautomerization in carbohydrates, revealing its impact on molecular recognition, enzymatic reactions, and metabolic pathways. The ability of carbohydrates to exist in multiple tautomeric forms allows for rapid adaptation to changing cellular environments, influencing their reactivity and biological functions. This flexibility is particularly relevant in the context of energy metabolism, where quick interconversion between tautomers can facilitate or hinder specific metabolic reactions.
One of the primary challenges in tautomer research lies in the accurate prediction and characterization of tautomeric equilibria in complex biological systems. While computational methods have improved significantly, discrepancies between theoretical predictions and experimental observations still exist, especially in aqueous environments that mimic physiological conditions. The development of more sophisticated models that account for solvent effects, pH variations, and intermolecular interactions remains an active area of research.
Another significant challenge is the real-time detection and quantification of tautomeric species in living systems. Current analytical techniques often struggle to capture the rapid interconversion between tautomers, leading to potential misinterpretations of metabolic processes. Advanced spectroscopic methods and high-resolution imaging techniques are being explored to address this limitation, but further refinement is necessary to fully elucidate the role of tautomerization in energy metabolism.
The impact of tautomerization on enzyme-substrate interactions presents yet another frontier in carbohydrate research. Understanding how different tautomeric forms affect binding affinities and catalytic efficiencies of metabolic enzymes is crucial for unraveling the intricacies of energy production pathways. This knowledge could potentially lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting specific tautomeric forms to modulate metabolic processes.
As research progresses, the integration of tautomerization studies with systems biology approaches is becoming increasingly important. Mapping the tautomeric landscape of carbohydrates within the broader context of cellular metabolism could provide valuable insights into the regulation of energy flux and the adaptability of metabolic networks. This holistic perspective may unlock new avenues for optimizing energy utilization in both normal and pathological states.
Analytical Methods for Tautomer Detection and Quantification
01 Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
This involves the control and modulation of carbohydrate breakdown and utilization in the body. It includes processes that regulate glucose uptake, glycolysis, and glycogen synthesis. Various enzymes, hormones, and signaling pathways play crucial roles in maintaining energy homeostasis through carbohydrate metabolism regulation.- Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism: This involves the control and modulation of carbohydrate metabolism pathways in the body. It includes mechanisms that regulate glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, and gluconeogenesis. Various enzymes, hormones, and signaling molecules play crucial roles in maintaining energy homeostasis through carbohydrate metabolism regulation.
- Carbohydrate-based energy supplements: These are formulations designed to provide readily available energy from carbohydrates. They may include simple sugars, complex carbohydrates, or a combination of both. These supplements are often used in sports nutrition to enhance performance and recovery by providing quick energy sources for metabolism.
- Metabolic pathways of carbohydrate utilization: This focuses on the biochemical processes involved in breaking down carbohydrates for energy production. It includes pathways such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Understanding these pathways is crucial for developing strategies to optimize energy metabolism and treat metabolic disorders.
- Carbohydrate metabolism in disease states: This area explores how carbohydrate metabolism is altered in various diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. It involves studying the dysregulation of glucose homeostasis and developing therapeutic approaches to correct metabolic imbalances related to carbohydrate utilization.
- Genetic factors influencing carbohydrate metabolism: This involves the study of genetic variations that affect carbohydrate metabolism and energy production. It includes identifying genes responsible for encoding enzymes involved in carbohydrate breakdown, transport proteins for glucose uptake, and regulatory factors that control metabolic pathways. This research can lead to personalized approaches for optimizing carbohydrate utilization and energy metabolism.
02 Carbohydrate-based energy supplements
These are formulations designed to provide readily available energy from carbohydrates. They may include various types of sugars, complex carbohydrates, or a combination of both. These supplements are often used in sports nutrition to enhance performance and recovery by providing quick energy sources for metabolism.Expand Specific Solutions03 Metabolic pathways of carbohydrate energy production
This focuses on the biochemical processes involved in extracting energy from carbohydrates. It includes pathways such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Understanding these pathways is crucial for developing strategies to optimize energy production and utilization in various physiological states.Expand Specific Solutions04 Carbohydrate metabolism in disease states
This area explores how carbohydrate metabolism is altered in various diseases, particularly metabolic disorders like diabetes. It involves studying the dysregulation of glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance, and other factors that affect carbohydrate utilization and energy production in pathological conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modulation of carbohydrate metabolism for therapeutic purposes
This involves developing strategies to manipulate carbohydrate metabolism for health benefits. It includes the use of drugs, dietary interventions, or other therapeutic approaches to optimize energy utilization, manage blood sugar levels, or treat metabolic disorders by targeting specific aspects of carbohydrate metabolism.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Scientists in the Field
The field of tautomerization in carbohydrates and its implications for energy metabolism is in a relatively early stage of development, with growing interest due to its potential impact on understanding metabolic processes. The market size is currently modest but expanding as more researchers and companies recognize its significance. Technologically, it's still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different aspects. Key players like Incyte Corp., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Galapagos NV are investing in research and development, while academic institutions such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology and University of Bath are contributing fundamental insights. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and research institutions, each bringing unique expertise to advance the field.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed advanced techniques to study tautomerization in carbohydrates and its impact on energy metabolism. Their approach involves high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to detect and quantify tautomeric forms of sugars in real-time[1]. They have also implemented computational modeling to predict tautomerization rates and equilibrium constants under various physiological conditions[3]. Roche's research has revealed that tautomerization can significantly affect the binding affinity of carbohydrates to enzymes involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, potentially altering metabolic flux[5].
Strengths: Cutting-edge analytical techniques, comprehensive approach combining experimental and computational methods. Weaknesses: High cost of specialized equipment, complexity in translating findings to clinical applications.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT researchers have pioneered the use of ultrafast spectroscopy techniques to study tautomerization dynamics in carbohydrates. They have developed femtosecond-resolved infrared spectroscopy methods to observe tautomerization events in real-time, providing unprecedented insights into the kinetics of these processes[2]. MIT's work has also focused on the role of tautomerization in modulating the reactivity of carbohydrates in enzymatic reactions, particularly those involved in cellular energy production[4]. Their studies have demonstrated that tautomerization can act as a regulatory mechanism in carbohydrate metabolism, influencing the rate of ATP production[6].
Strengths: World-class expertise in physical chemistry and spectroscopy, interdisciplinary approach combining biology and physics. Weaknesses: Highly specialized research may be challenging to translate into practical applications in the short term.
Significant Discoveries in Carbohydrate Tautomerization
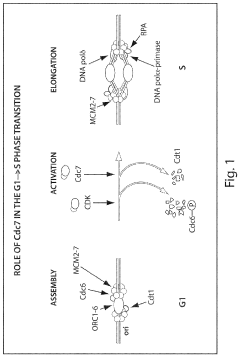
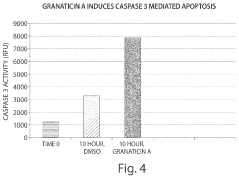
Cdc7 kinase inhibitors and uses thereof
PatentActiveUS20230255929A1
Innovation
- The use of benzoisochromanequinones, specifically granaticins, which inhibit Cdc7 kinase activity, offering a potential treatment for proliferative disorders by blocking the transition from G1 to S phase in the cell cycle.
Enzymatic synthesis of kavalactones and flavokavains
PatentActiveUS20220002768A1
Innovation
- The elucidation of the native kavalactone biosynthetic pathway from Piper methysticum allows for metabolic engineering to produce kavalactones and flavokavains through expression in heterologous hosts using enzymes at least 80% identical to naturally occurring enzymes, enabling the production of CoA esters, kavalactone backbones, and flavokavain compounds.
Biochemical Pathways Affected by Tautomerization
Tautomerization in carbohydrates plays a crucial role in various biochemical pathways, particularly those involved in energy metabolism. This process affects the structure and reactivity of sugar molecules, leading to significant implications for metabolic processes.
One of the primary pathways influenced by tautomerization is glycolysis. The interconversion between aldose and ketose forms of glucose, facilitated by tautomerization, is essential for the initial steps of glycolysis. This process allows for the phosphorylation of glucose and its subsequent breakdown into pyruvate, generating ATP and NADH in the process.
The pentose phosphate pathway is another metabolic route significantly impacted by tautomerization. The interconversion between aldose and ketose forms of pentose sugars is critical for the oxidative and non-oxidative phases of this pathway. Tautomerization enables the regeneration of ribulose-5-phosphate, a key intermediate in nucleotide synthesis and NADPH production.
Gluconeogenesis, the reverse process of glycolysis, also relies on tautomerization. The conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate involves a series of reactions where tautomerization plays a role in maintaining the correct stereochemistry of intermediates.
In the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis, tautomerization is crucial for the fixation of carbon dioxide. The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the addition of CO2 to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, a process that involves tautomeric shifts in the sugar molecule.
The urea cycle, while not directly involving carbohydrates, is indirectly affected by tautomerization in related pathways. The interconversion of amino acids and keto acids, which feed into the urea cycle, often involves tautomeric shifts that influence the overall efficiency of nitrogen metabolism.
Tautomerization also impacts the Krebs cycle, particularly in the reactions involving isocitrate dehydrogenase. The conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate involves a tautomeric shift that is essential for the oxidative decarboxylation step.
Understanding these tautomerization-dependent pathways is crucial for comprehending cellular energy metabolism and developing potential therapeutic interventions for metabolic disorders. The intricate balance of tautomeric forms in carbohydrates ensures the proper functioning of these essential biochemical pathways, highlighting the significance of this process in maintaining cellular homeostasis and energy production.
One of the primary pathways influenced by tautomerization is glycolysis. The interconversion between aldose and ketose forms of glucose, facilitated by tautomerization, is essential for the initial steps of glycolysis. This process allows for the phosphorylation of glucose and its subsequent breakdown into pyruvate, generating ATP and NADH in the process.
The pentose phosphate pathway is another metabolic route significantly impacted by tautomerization. The interconversion between aldose and ketose forms of pentose sugars is critical for the oxidative and non-oxidative phases of this pathway. Tautomerization enables the regeneration of ribulose-5-phosphate, a key intermediate in nucleotide synthesis and NADPH production.
Gluconeogenesis, the reverse process of glycolysis, also relies on tautomerization. The conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate involves a series of reactions where tautomerization plays a role in maintaining the correct stereochemistry of intermediates.
In the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis, tautomerization is crucial for the fixation of carbon dioxide. The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the addition of CO2 to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, a process that involves tautomeric shifts in the sugar molecule.
The urea cycle, while not directly involving carbohydrates, is indirectly affected by tautomerization in related pathways. The interconversion of amino acids and keto acids, which feed into the urea cycle, often involves tautomeric shifts that influence the overall efficiency of nitrogen metabolism.
Tautomerization also impacts the Krebs cycle, particularly in the reactions involving isocitrate dehydrogenase. The conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate involves a tautomeric shift that is essential for the oxidative decarboxylation step.
Understanding these tautomerization-dependent pathways is crucial for comprehending cellular energy metabolism and developing potential therapeutic interventions for metabolic disorders. The intricate balance of tautomeric forms in carbohydrates ensures the proper functioning of these essential biochemical pathways, highlighting the significance of this process in maintaining cellular homeostasis and energy production.
Computational Modeling of Tautomeric Equilibria
Computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates has become an essential tool for understanding the complex dynamics of energy metabolism. These models provide valuable insights into the structural changes and energetic landscapes associated with tautomerization processes, which are crucial for predicting and interpreting metabolic pathways.
One of the primary approaches in computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria involves the use of quantum mechanical (QM) methods. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations have proven particularly effective in accurately predicting the relative stabilities of different tautomeric forms. These calculations take into account the electronic structure of the molecules, providing a detailed picture of the energy differences between tautomers.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations offer another powerful technique for studying tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. By simulating the motion of atoms and molecules over time, MD simulations can reveal the dynamic interconversion between tautomeric forms and the influence of environmental factors such as solvent effects and temperature.
Hybrid QM/MM (Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics) methods have emerged as a sophisticated approach to modeling tautomeric equilibria in complex biological systems. These methods combine the accuracy of QM calculations for the tautomerizing region with the computational efficiency of MM simulations for the surrounding environment, allowing for more realistic modeling of tautomerization in cellular contexts.
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being applied to predict tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. By training on large datasets of experimental and computational results, these models can rapidly estimate tautomeric ratios and transition rates for novel compounds, accelerating the discovery process in metabolic research.
Continuum solvation models, such as the Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM), have been integrated into computational studies to account for the effects of solvation on tautomeric equilibria. These models provide a more accurate representation of the physiological environment in which tautomerization occurs, improving the relevance of computational predictions to in vivo metabolic processes.
Recent advancements in computational power and algorithms have enabled the application of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations to study tautomeric equilibria. These simulations combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations with the dynamic nature of molecular dynamics, offering unprecedented insights into the time-dependent behavior of tautomeric systems in carbohydrates.
The integration of these computational methods with experimental techniques, such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to a more comprehensive understanding of tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. This synergistic approach allows for the validation and refinement of computational models, enhancing their predictive power and applicability to real-world metabolic systems.
One of the primary approaches in computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria involves the use of quantum mechanical (QM) methods. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations have proven particularly effective in accurately predicting the relative stabilities of different tautomeric forms. These calculations take into account the electronic structure of the molecules, providing a detailed picture of the energy differences between tautomers.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations offer another powerful technique for studying tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. By simulating the motion of atoms and molecules over time, MD simulations can reveal the dynamic interconversion between tautomeric forms and the influence of environmental factors such as solvent effects and temperature.
Hybrid QM/MM (Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics) methods have emerged as a sophisticated approach to modeling tautomeric equilibria in complex biological systems. These methods combine the accuracy of QM calculations for the tautomerizing region with the computational efficiency of MM simulations for the surrounding environment, allowing for more realistic modeling of tautomerization in cellular contexts.
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being applied to predict tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. By training on large datasets of experimental and computational results, these models can rapidly estimate tautomeric ratios and transition rates for novel compounds, accelerating the discovery process in metabolic research.
Continuum solvation models, such as the Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM), have been integrated into computational studies to account for the effects of solvation on tautomeric equilibria. These models provide a more accurate representation of the physiological environment in which tautomerization occurs, improving the relevance of computational predictions to in vivo metabolic processes.
Recent advancements in computational power and algorithms have enabled the application of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations to study tautomeric equilibria. These simulations combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations with the dynamic nature of molecular dynamics, offering unprecedented insights into the time-dependent behavior of tautomeric systems in carbohydrates.
The integration of these computational methods with experimental techniques, such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to a more comprehensive understanding of tautomeric equilibria in carbohydrates. This synergistic approach allows for the validation and refinement of computational models, enhancing their predictive power and applicability to real-world metabolic systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!