Tautomerization in Protic Ionic Liquids: Acid-Base Equilibrium Effects
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Background and Objectives
Tautomerization, a fundamental process in organic chemistry, involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers. This phenomenon has gained significant attention in the context of protic ionic liquids (PILs), where the acid-base equilibrium effects play a crucial role. The study of tautomerization in PILs has evolved over the past few decades, driven by the unique properties of these solvents and their potential applications in various fields.
The historical development of tautomerization research can be traced back to the early 20th century, with pioneering work on keto-enol tautomerism. However, the exploration of tautomerization in PILs is a more recent endeavor, emerging in the late 1990s and early 2000s as the field of ionic liquids expanded. This intersection of tautomerization and PILs has opened up new avenues for understanding molecular behavior in these complex systems.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in spectroscopic techniques, computational methods, and the synthesis of novel PILs. These developments have enabled researchers to probe the intricacies of tautomeric equilibria with unprecedented precision and to design PILs with tailored properties for specific applications.
Current trends in tautomerization research within PILs focus on elucidating the mechanisms of proton transfer, understanding the influence of PIL composition on tautomeric equilibria, and exploring the potential of these systems in catalysis, separations, and materials science. The interplay between tautomerization and the unique solvation environment provided by PILs continues to be a subject of intense investigation.
The primary objectives of studying tautomerization in PILs are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to develop a comprehensive understanding of how the acid-base properties of PILs influence tautomeric equilibria. This knowledge is crucial for predicting and controlling molecular behavior in these systems. Secondly, there is a drive to exploit tautomerization in PILs for practical applications, such as enhancing reaction rates, improving selectivity in organic syntheses, and developing novel separation processes.
Another key goal is to establish predictive models that can accurately describe tautomeric equilibria in PILs across a wide range of conditions. This objective requires integrating experimental data with advanced computational techniques to capture the complex interplay between solvent properties and molecular dynamics.
Furthermore, researchers are working towards designing PILs that can selectively stabilize specific tautomeric forms, opening up possibilities for molecular switches and responsive materials. The long-term vision is to harness the unique properties of PILs to manipulate tautomerization processes with unprecedented control, potentially revolutionizing fields such as drug delivery, energy storage, and smart materials.
The historical development of tautomerization research can be traced back to the early 20th century, with pioneering work on keto-enol tautomerism. However, the exploration of tautomerization in PILs is a more recent endeavor, emerging in the late 1990s and early 2000s as the field of ionic liquids expanded. This intersection of tautomerization and PILs has opened up new avenues for understanding molecular behavior in these complex systems.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in spectroscopic techniques, computational methods, and the synthesis of novel PILs. These developments have enabled researchers to probe the intricacies of tautomeric equilibria with unprecedented precision and to design PILs with tailored properties for specific applications.
Current trends in tautomerization research within PILs focus on elucidating the mechanisms of proton transfer, understanding the influence of PIL composition on tautomeric equilibria, and exploring the potential of these systems in catalysis, separations, and materials science. The interplay between tautomerization and the unique solvation environment provided by PILs continues to be a subject of intense investigation.
The primary objectives of studying tautomerization in PILs are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to develop a comprehensive understanding of how the acid-base properties of PILs influence tautomeric equilibria. This knowledge is crucial for predicting and controlling molecular behavior in these systems. Secondly, there is a drive to exploit tautomerization in PILs for practical applications, such as enhancing reaction rates, improving selectivity in organic syntheses, and developing novel separation processes.
Another key goal is to establish predictive models that can accurately describe tautomeric equilibria in PILs across a wide range of conditions. This objective requires integrating experimental data with advanced computational techniques to capture the complex interplay between solvent properties and molecular dynamics.
Furthermore, researchers are working towards designing PILs that can selectively stabilize specific tautomeric forms, opening up possibilities for molecular switches and responsive materials. The long-term vision is to harness the unique properties of PILs to manipulate tautomerization processes with unprecedented control, potentially revolutionizing fields such as drug delivery, energy storage, and smart materials.
Market Analysis for Protic Ionic Liquids
The market for protic ionic liquids (PILs) has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by their unique properties and diverse applications across various industries. PILs, characterized by their ability to undergo tautomerization and exhibit acid-base equilibrium effects, have garnered substantial interest in both academic research and industrial sectors.
The global market for PILs is primarily segmented into regions such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World. Among these, North America and Europe currently dominate the market share due to their advanced research infrastructure and strong presence of key industry players. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, attributed to increasing investments in research and development activities and growing industrial applications.
Key application areas for PILs include catalysis, electrochemistry, separation processes, and biomass processing. The catalysis segment holds a significant market share, as PILs offer enhanced reaction rates and selectivity compared to conventional solvents. In electrochemistry, PILs are increasingly being used in energy storage devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors, due to their high ionic conductivity and wide electrochemical window.
The separation processes segment is also showing promising growth, with PILs being employed in gas separation, liquid-liquid extraction, and desulfurization processes. Additionally, the use of PILs in biomass processing for the production of biofuels and value-added chemicals is gaining traction, driven by the growing focus on sustainable and renewable energy sources.
Market trends indicate a rising demand for task-specific PILs tailored for specific applications. This has led to increased research and development efforts to design PILs with optimized properties, such as improved thermal stability, conductivity, and selectivity. Furthermore, the integration of PILs with other emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology and biotechnology, is opening up new avenues for market growth.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and limited commercial availability of some PILs continue to hinder market growth. However, ongoing efforts to develop cost-effective synthesis methods and scale-up production processes are expected to address these challenges in the near future.
In conclusion, the market for PILs demonstrates strong growth potential, driven by their versatile applications and unique properties. As research in tautomerization and acid-base equilibrium effects in PILs advances, it is anticipated that new applications and improved formulations will further expand the market opportunities in the coming years.
The global market for PILs is primarily segmented into regions such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World. Among these, North America and Europe currently dominate the market share due to their advanced research infrastructure and strong presence of key industry players. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, attributed to increasing investments in research and development activities and growing industrial applications.
Key application areas for PILs include catalysis, electrochemistry, separation processes, and biomass processing. The catalysis segment holds a significant market share, as PILs offer enhanced reaction rates and selectivity compared to conventional solvents. In electrochemistry, PILs are increasingly being used in energy storage devices, such as batteries and supercapacitors, due to their high ionic conductivity and wide electrochemical window.
The separation processes segment is also showing promising growth, with PILs being employed in gas separation, liquid-liquid extraction, and desulfurization processes. Additionally, the use of PILs in biomass processing for the production of biofuels and value-added chemicals is gaining traction, driven by the growing focus on sustainable and renewable energy sources.
Market trends indicate a rising demand for task-specific PILs tailored for specific applications. This has led to increased research and development efforts to design PILs with optimized properties, such as improved thermal stability, conductivity, and selectivity. Furthermore, the integration of PILs with other emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology and biotechnology, is opening up new avenues for market growth.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and limited commercial availability of some PILs continue to hinder market growth. However, ongoing efforts to develop cost-effective synthesis methods and scale-up production processes are expected to address these challenges in the near future.
In conclusion, the market for PILs demonstrates strong growth potential, driven by their versatile applications and unique properties. As research in tautomerization and acid-base equilibrium effects in PILs advances, it is anticipated that new applications and improved formulations will further expand the market opportunities in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Tautomerization Studies
The field of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids faces several significant challenges that hinder our comprehensive understanding and practical applications. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of the acid-base equilibrium effects in these systems. Protic ionic liquids, by their nature, involve proton transfer processes, which can significantly influence tautomeric equilibria. This interplay between acid-base chemistry and tautomerization creates a multifaceted system that is difficult to predict and control.
A major challenge lies in the accurate measurement and quantification of tautomeric species in protic ionic liquids. Traditional spectroscopic techniques often struggle to distinguish between rapidly interconverting tautomers, especially in the presence of the ionic liquid's own spectral signatures. This limitation makes it challenging to determine precise equilibrium constants and kinetic parameters, which are crucial for understanding the tautomerization process.
The dynamic nature of protic ionic liquids adds another layer of complexity. The constant exchange of protons between the ionic liquid components and the tautomeric species creates a highly fluctuating environment. This dynamism makes it difficult to isolate and study individual tautomeric forms, as they are constantly influenced by their surroundings. Consequently, researchers face significant hurdles in developing reliable models to predict tautomeric behavior in these systems.
Furthermore, the influence of the ionic liquid's structure on tautomerization is not fully understood. The unique solvation environment provided by protic ionic liquids can dramatically alter tautomeric equilibria compared to conventional solvents. Factors such as hydrogen bonding networks, ion pair formation, and local charge distributions all play roles that are not yet fully elucidated. This lack of understanding impedes the rational design of ionic liquids for specific tautomer-dependent applications.
Another significant challenge is the temperature dependence of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids. Many ionic liquids exhibit a wide liquid range, and tautomeric equilibria can shift dramatically with temperature changes. This temperature sensitivity complicates the study of these systems and makes it difficult to extrapolate results from one temperature regime to another. It also poses challenges for applications where temperature control is crucial.
Lastly, the field faces a computational challenge. Accurate modeling of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids requires sophisticated computational methods that can handle both the quantum mechanical aspects of tautomerization and the complex, dynamic environment of the ionic liquid. Current computational approaches often struggle to capture all relevant interactions simultaneously, limiting our ability to predict and design systems with desired tautomeric properties.
A major challenge lies in the accurate measurement and quantification of tautomeric species in protic ionic liquids. Traditional spectroscopic techniques often struggle to distinguish between rapidly interconverting tautomers, especially in the presence of the ionic liquid's own spectral signatures. This limitation makes it challenging to determine precise equilibrium constants and kinetic parameters, which are crucial for understanding the tautomerization process.
The dynamic nature of protic ionic liquids adds another layer of complexity. The constant exchange of protons between the ionic liquid components and the tautomeric species creates a highly fluctuating environment. This dynamism makes it difficult to isolate and study individual tautomeric forms, as they are constantly influenced by their surroundings. Consequently, researchers face significant hurdles in developing reliable models to predict tautomeric behavior in these systems.
Furthermore, the influence of the ionic liquid's structure on tautomerization is not fully understood. The unique solvation environment provided by protic ionic liquids can dramatically alter tautomeric equilibria compared to conventional solvents. Factors such as hydrogen bonding networks, ion pair formation, and local charge distributions all play roles that are not yet fully elucidated. This lack of understanding impedes the rational design of ionic liquids for specific tautomer-dependent applications.
Another significant challenge is the temperature dependence of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids. Many ionic liquids exhibit a wide liquid range, and tautomeric equilibria can shift dramatically with temperature changes. This temperature sensitivity complicates the study of these systems and makes it difficult to extrapolate results from one temperature regime to another. It also poses challenges for applications where temperature control is crucial.
Lastly, the field faces a computational challenge. Accurate modeling of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids requires sophisticated computational methods that can handle both the quantum mechanical aspects of tautomerization and the complex, dynamic environment of the ionic liquid. Current computational approaches often struggle to capture all relevant interactions simultaneously, limiting our ability to predict and design systems with desired tautomeric properties.
Existing Methodologies for Tautomerization Analysis
01 Acid-base equilibrium in protic ionic liquids
Protic ionic liquids exhibit unique acid-base equilibrium properties due to their ability to transfer protons. This equilibrium is influenced by the strength of the acid and base components, as well as environmental factors such as temperature and concentration. Understanding these equilibria is crucial for optimizing the performance of protic ionic liquids in various applications.- Acid-base equilibrium in protic ionic liquids: Protic ionic liquids exhibit unique acid-base equilibrium properties due to their ability to transfer protons. This equilibrium is influenced by the strength of the acid and base components, as well as environmental factors such as temperature and concentration. Understanding these equilibria is crucial for optimizing the performance of protic ionic liquids in various applications.
- Synthesis and characterization of protic ionic liquids: The synthesis of protic ionic liquids involves the combination of a Brønsted acid and a Brønsted base. Various methods are employed to prepare these ionic liquids, including direct neutralization and ion exchange. Characterization techniques such as NMR spectroscopy, conductivity measurements, and thermal analysis are used to study their properties and acid-base behavior.
- Applications of protic ionic liquids in electrochemistry: Protic ionic liquids find extensive use in electrochemical applications due to their unique acid-base properties. They serve as electrolytes in fuel cells, batteries, and capacitors, offering advantages such as high conductivity and wide electrochemical windows. The acid-base equilibrium of these ionic liquids plays a crucial role in determining their electrochemical performance.
- Influence of structural features on acid-base properties: The acid-base equilibrium in protic ionic liquids is significantly affected by their structural features. Factors such as the nature of the cation and anion, alkyl chain length, and functional groups impact the proton transfer process and overall acidity or basicity. Understanding these structure-property relationships is essential for designing protic ionic liquids with tailored acid-base characteristics.
- Protic ionic liquids as solvents and catalysts: The acid-base properties of protic ionic liquids make them excellent solvents and catalysts for various chemical reactions. They can act as both proton donors and acceptors, facilitating acid-catalyzed reactions and influencing reaction kinetics. Their tunable acidity and basicity allow for the optimization of reaction conditions in organic synthesis, biocatalysis, and other chemical processes.
02 Synthesis and characterization of protic ionic liquids
The synthesis of protic ionic liquids involves the combination of a Brønsted acid and a Brønsted base. Various methods are employed to prepare these ionic liquids, including direct neutralization and ion exchange. Characterization techniques such as NMR spectroscopy, conductivity measurements, and thermal analysis are used to study their properties and acid-base behavior.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of protic ionic liquids in electrochemistry
Protic ionic liquids find extensive use in electrochemical applications due to their unique acid-base properties. They serve as electrolytes in fuel cells, batteries, and supercapacitors, where their proton conductivity and wide electrochemical window are advantageous. The acid-base equilibrium of these ionic liquids plays a crucial role in determining their performance in such applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Influence of structural factors on acid-base equilibrium
The structure of the cation and anion in protic ionic liquids significantly affects their acid-base equilibrium. Factors such as alkyl chain length, functional groups, and steric hindrance can alter the proton transfer dynamics and overall acidity or basicity of the ionic liquid. Understanding these structure-property relationships is essential for designing protic ionic liquids with desired acid-base characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Protic ionic liquids as solvents and catalysts
The acid-base properties of protic ionic liquids make them excellent solvents and catalysts for various chemical reactions. They can act as both proton donors and acceptors, facilitating acid-catalyzed reactions and influencing reaction equilibria. Their tunable acidity and ability to stabilize reaction intermediates make them valuable in organic synthesis, biocatalysis, and other chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Protic Ionic Liquids Research
The field of tautomerization in protic ionic liquids is in an early developmental stage, characterized by growing research interest but limited commercial applications. The market size remains relatively small, primarily driven by academic and industrial research activities. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with ongoing efforts to understand and control acid-base equilibrium effects. Companies like Sunshine Lake Pharma, The Broad Institute, and Wuhan Createrna Science and Technology are at the forefront of research, exploring potential applications in drug discovery and chemical processes. However, the technology's maturity is still low, with significant challenges in predicting and manipulating tautomeric equilibria in these complex systems.
Technische Universität Darmstadt
Technical Solution: Technische Universität Darmstadt has developed a comprehensive approach to studying tautomerization in protic ionic liquids, focusing on the interplay between acid-base equilibria and solvent effects. Their research combines advanced experimental techniques, including time-resolved spectroscopy and electrochemical methods, with theoretical modeling to elucidate the mechanisms of proton transfer in PILs[10]. They have pioneered the use of ultrafast laser spectroscopy to directly observe proton transfer events in real-time, providing unprecedented insights into the dynamics of tautomerization[11]. Additionally, they have developed novel PIL systems with tunable acid-base properties, allowing for systematic investigation of how ionic liquid composition affects tautomeric equilibria[12].
Strengths: Cutting-edge spectroscopic techniques, strong integration of experiment and theory, development of novel PIL systems. Weaknesses: Highly specialized equipment required, may be challenging to scale up for industrial applications.
Max Planck Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften eV
Technical Solution: Max Planck Society has developed advanced spectroscopic techniques to study tautomerization in protic ionic liquids (PILs). They utilize a combination of NMR spectroscopy and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the acid-base equilibria and proton transfer mechanisms in PILs[1]. Their approach involves synthesizing deuterated PILs to track proton exchange processes and employing 2D NMR experiments to map out the hydrogen-bonding networks[2]. This method allows for the quantification of tautomeric ratios and the determination of rate constants for proton transfer, providing insights into how the ionic liquid environment affects acid-base behavior[3].
Strengths: Cutting-edge spectroscopic techniques, combined experimental and computational approach. Weaknesses: Potentially limited to specific types of PILs, may require specialized equipment.
Innovative Approaches in Acid-Base Equilibrium Studies
Compositions and methods for treating multiple myeloma
PatentActiveUS20190010120A1
Innovation
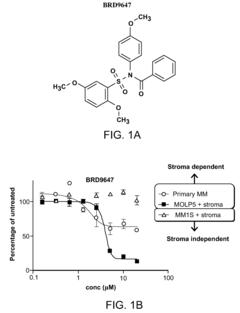
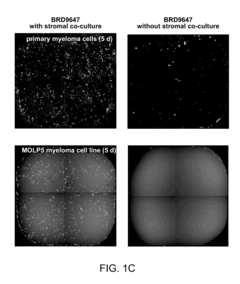
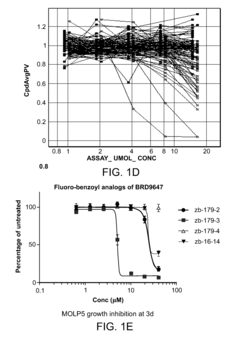
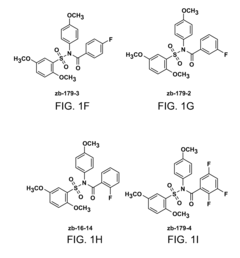
- The development of derivatives or analogs of BRD9647, which inhibit the proliferation of multiple myeloma cells by covalently modifying residues of polypeptides with a benzoyl group, specifically targeting stroma-dependent multiple myeloma cells through benzoylation of cellular amines.
Inhibitors of RNA guided nucleases and uses thereof
PatentActiveUS20190263807A1
Innovation
- Development of specific compounds and methods to inhibit RNA-guided endonuclease activity, including small molecules that can rapidly and reversibly control the activity of Cas9 and Cpf1, using high-throughput biochemical and cellular assays to detect and screen for inhibitory agents.
Environmental Impact of Protic Ionic Liquids
Protic ionic liquids (PILs) have gained significant attention in recent years due to their unique properties and potential applications in various fields. However, their environmental impact is a crucial aspect that requires thorough examination. The environmental effects of PILs are multifaceted and depend on factors such as their chemical structure, physical properties, and intended use.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with PILs is their potential for bioaccumulation and persistence in ecosystems. Unlike conventional organic solvents, PILs often exhibit low volatility and high stability, which can lead to their accumulation in soil and water systems. This persistence may have long-term effects on aquatic and terrestrial organisms, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem balance.
The toxicity of PILs to various organisms is another critical environmental consideration. Studies have shown that the toxicity of PILs can vary widely depending on their specific composition and the target organisms. Some PILs have demonstrated relatively low toxicity to certain aquatic species, while others have shown more significant adverse effects. The ionic nature of these compounds can also influence their interaction with biological membranes, potentially leading to cellular disruption in exposed organisms.
Biodegradability is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of PILs. While some PILs have shown promising biodegradation rates, others may be resistant to natural breakdown processes. The persistence of non-biodegradable PILs in the environment can lead to long-term contamination issues. Research into designing more biodegradable PILs is ongoing, with a focus on incorporating easily cleavable bonds or using bio-based precursors.
The production and disposal of PILs also contribute to their overall environmental footprint. The synthesis of PILs often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful precursors. Proper disposal methods for used PILs are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Recycling and regeneration techniques for PILs are areas of active research, aiming to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact.
Water solubility is another important aspect of PILs' environmental behavior. Highly water-soluble PILs can easily disperse in aquatic environments, potentially affecting a wide range of organisms. Conversely, PILs with low water solubility may accumulate in sediments or biological tissues, leading to localized environmental impacts. Understanding the partitioning behavior of PILs in different environmental compartments is essential for predicting their fate and effects.
In conclusion, while PILs offer many advantages in various applications, their environmental impact must be carefully considered and mitigated. Ongoing research focuses on developing greener PILs with reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and minimized environmental persistence. Comprehensive life cycle assessments and environmental risk evaluations are necessary to fully understand and manage the environmental implications of PILs in different applications and ecosystems.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with PILs is their potential for bioaccumulation and persistence in ecosystems. Unlike conventional organic solvents, PILs often exhibit low volatility and high stability, which can lead to their accumulation in soil and water systems. This persistence may have long-term effects on aquatic and terrestrial organisms, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystem balance.
The toxicity of PILs to various organisms is another critical environmental consideration. Studies have shown that the toxicity of PILs can vary widely depending on their specific composition and the target organisms. Some PILs have demonstrated relatively low toxicity to certain aquatic species, while others have shown more significant adverse effects. The ionic nature of these compounds can also influence their interaction with biological membranes, potentially leading to cellular disruption in exposed organisms.
Biodegradability is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of PILs. While some PILs have shown promising biodegradation rates, others may be resistant to natural breakdown processes. The persistence of non-biodegradable PILs in the environment can lead to long-term contamination issues. Research into designing more biodegradable PILs is ongoing, with a focus on incorporating easily cleavable bonds or using bio-based precursors.
The production and disposal of PILs also contribute to their overall environmental footprint. The synthesis of PILs often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful precursors. Proper disposal methods for used PILs are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Recycling and regeneration techniques for PILs are areas of active research, aiming to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact.
Water solubility is another important aspect of PILs' environmental behavior. Highly water-soluble PILs can easily disperse in aquatic environments, potentially affecting a wide range of organisms. Conversely, PILs with low water solubility may accumulate in sediments or biological tissues, leading to localized environmental impacts. Understanding the partitioning behavior of PILs in different environmental compartments is essential for predicting their fate and effects.
In conclusion, while PILs offer many advantages in various applications, their environmental impact must be carefully considered and mitigated. Ongoing research focuses on developing greener PILs with reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and minimized environmental persistence. Comprehensive life cycle assessments and environmental risk evaluations are necessary to fully understand and manage the environmental implications of PILs in different applications and ecosystems.
Computational Modeling of Tautomerization Processes
Computational modeling of tautomerization processes in protic ionic liquids (PILs) has become an essential tool for understanding the complex acid-base equilibrium effects in these systems. The development of accurate and efficient computational methods has significantly advanced our ability to predict and analyze tautomeric behavior in PILs, providing valuable insights for both fundamental research and practical applications.
One of the primary challenges in modeling tautomerization in PILs is accurately representing the dynamic nature of proton transfer processes. Quantum mechanical methods, such as density functional theory (DFT), have been widely employed to calculate the relative energies of different tautomeric forms and the transition states between them. These calculations provide crucial information about the thermodynamic stability and kinetic barriers associated with tautomerization.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations have also played a vital role in elucidating the time-dependent behavior of tautomeric systems in PILs. By incorporating appropriate force fields that can describe the breaking and formation of covalent bonds, MD simulations can capture the dynamic interconversion between tautomers and their interactions with the ionic liquid environment. This approach has been particularly useful in understanding how the unique properties of PILs, such as their high ionic strength and hydrogen-bonding capabilities, influence tautomeric equilibria.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, have been employed to overcome the limitations of traditional MD simulations in exploring rare events like tautomerization. These methods allow for the efficient calculation of free energy surfaces and reaction pathways, providing a more complete picture of the tautomerization landscape in PILs.
The integration of quantum mechanical and molecular mechanical (QM/MM) methods has emerged as a powerful approach for modeling tautomerization in complex PIL systems. This hybrid methodology allows for the accurate treatment of the tautomerizing molecule and its immediate environment using quantum mechanics, while the bulk of the system is described by more computationally efficient molecular mechanics. QM/MM simulations have been particularly valuable in capturing the influence of specific PIL ion pairs on tautomeric equilibria.
Recent advancements in machine learning techniques have also begun to impact the field of tautomerization modeling. Neural network potentials trained on high-level quantum mechanical data are being developed to achieve quantum-level accuracy at a fraction of the computational cost. These methods show promise for enabling large-scale simulations of tautomerization processes in PILs while maintaining high accuracy.
As computational power continues to increase and methodologies evolve, we can expect further refinements in the modeling of tautomerization in PILs. Future developments may include more accurate description of long-range electrostatic interactions, improved treatment of nuclear quantum effects, and the incorporation of machine learning techniques for predicting tautomeric behavior in novel PIL systems.
One of the primary challenges in modeling tautomerization in PILs is accurately representing the dynamic nature of proton transfer processes. Quantum mechanical methods, such as density functional theory (DFT), have been widely employed to calculate the relative energies of different tautomeric forms and the transition states between them. These calculations provide crucial information about the thermodynamic stability and kinetic barriers associated with tautomerization.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations have also played a vital role in elucidating the time-dependent behavior of tautomeric systems in PILs. By incorporating appropriate force fields that can describe the breaking and formation of covalent bonds, MD simulations can capture the dynamic interconversion between tautomers and their interactions with the ionic liquid environment. This approach has been particularly useful in understanding how the unique properties of PILs, such as their high ionic strength and hydrogen-bonding capabilities, influence tautomeric equilibria.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, have been employed to overcome the limitations of traditional MD simulations in exploring rare events like tautomerization. These methods allow for the efficient calculation of free energy surfaces and reaction pathways, providing a more complete picture of the tautomerization landscape in PILs.
The integration of quantum mechanical and molecular mechanical (QM/MM) methods has emerged as a powerful approach for modeling tautomerization in complex PIL systems. This hybrid methodology allows for the accurate treatment of the tautomerizing molecule and its immediate environment using quantum mechanics, while the bulk of the system is described by more computationally efficient molecular mechanics. QM/MM simulations have been particularly valuable in capturing the influence of specific PIL ion pairs on tautomeric equilibria.
Recent advancements in machine learning techniques have also begun to impact the field of tautomerization modeling. Neural network potentials trained on high-level quantum mechanical data are being developed to achieve quantum-level accuracy at a fraction of the computational cost. These methods show promise for enabling large-scale simulations of tautomerization processes in PILs while maintaining high accuracy.
As computational power continues to increase and methodologies evolve, we can expect further refinements in the modeling of tautomerization in PILs. Future developments may include more accurate description of long-range electrostatic interactions, improved treatment of nuclear quantum effects, and the incorporation of machine learning techniques for predicting tautomeric behavior in novel PIL systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!