Tautomerization in Cosmetic Chemistry: Stabilizing Ingredients
JUL 29, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization in Cosmetics: Background and Objectives
Tautomerization, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, has gained significant attention in the cosmetic industry due to its profound impact on the stability and efficacy of various ingredients. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, where a hydrogen atom shifts from one atom to another within the same molecule. In the context of cosmetic chemistry, understanding and controlling tautomerization is crucial for developing stable, effective, and long-lasting products.
The historical background of tautomerization research in cosmetics can be traced back to the mid-20th century when chemists began to recognize its relevance in formulation stability. As the cosmetic industry evolved, the need for more sophisticated and multifunctional ingredients grew, leading to increased focus on molecular behavior under various conditions. Tautomerization emerged as a critical factor influencing the performance of active ingredients, preservatives, and colorants in cosmetic formulations.
Over the past few decades, the cosmetic industry has witnessed a paradigm shift towards "clean" and "natural" products, further emphasizing the importance of understanding tautomerization. This shift has driven research into plant-based ingredients and bio-inspired molecules, many of which exhibit tautomeric behavior. Consequently, the ability to predict and control tautomerization has become a key competitive advantage for cosmetic companies striving to develop innovative and stable natural formulations.
The primary objective of research on tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry is to enhance the stability of ingredients and, by extension, the overall product. This encompasses several key goals: firstly, to develop a comprehensive understanding of tautomeric equilibria in various cosmetic ingredients under different formulation conditions. Secondly, to identify and characterize the factors that influence tautomeric shifts, such as pH, temperature, and the presence of other ingredients in the formulation.
Another crucial objective is to design novel molecules or modify existing ones to exploit favorable tautomeric properties. This includes creating ingredients that maintain a specific tautomeric form for improved efficacy or developing "smart" molecules that can switch between tautomers in response to environmental triggers, potentially leading to adaptive cosmetic formulations.
Furthermore, researchers aim to establish reliable methods for predicting tautomeric behavior in complex cosmetic matrices. This involves developing advanced computational models and experimental techniques to accurately assess tautomerization in real-world formulations. Such tools would significantly streamline the product development process and reduce the time and resources required for stability testing.
Ultimately, the overarching goal of tautomerization research in cosmetic chemistry is to translate scientific insights into practical applications. This includes developing guidelines for formulators to optimize ingredient stability, creating new preservation systems based on tautomeric principles, and innovating color-changing or pH-responsive cosmetic products that leverage controlled tautomeric shifts.
The historical background of tautomerization research in cosmetics can be traced back to the mid-20th century when chemists began to recognize its relevance in formulation stability. As the cosmetic industry evolved, the need for more sophisticated and multifunctional ingredients grew, leading to increased focus on molecular behavior under various conditions. Tautomerization emerged as a critical factor influencing the performance of active ingredients, preservatives, and colorants in cosmetic formulations.
Over the past few decades, the cosmetic industry has witnessed a paradigm shift towards "clean" and "natural" products, further emphasizing the importance of understanding tautomerization. This shift has driven research into plant-based ingredients and bio-inspired molecules, many of which exhibit tautomeric behavior. Consequently, the ability to predict and control tautomerization has become a key competitive advantage for cosmetic companies striving to develop innovative and stable natural formulations.
The primary objective of research on tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry is to enhance the stability of ingredients and, by extension, the overall product. This encompasses several key goals: firstly, to develop a comprehensive understanding of tautomeric equilibria in various cosmetic ingredients under different formulation conditions. Secondly, to identify and characterize the factors that influence tautomeric shifts, such as pH, temperature, and the presence of other ingredients in the formulation.
Another crucial objective is to design novel molecules or modify existing ones to exploit favorable tautomeric properties. This includes creating ingredients that maintain a specific tautomeric form for improved efficacy or developing "smart" molecules that can switch between tautomers in response to environmental triggers, potentially leading to adaptive cosmetic formulations.
Furthermore, researchers aim to establish reliable methods for predicting tautomeric behavior in complex cosmetic matrices. This involves developing advanced computational models and experimental techniques to accurately assess tautomerization in real-world formulations. Such tools would significantly streamline the product development process and reduce the time and resources required for stability testing.
Ultimately, the overarching goal of tautomerization research in cosmetic chemistry is to translate scientific insights into practical applications. This includes developing guidelines for formulators to optimize ingredient stability, creating new preservation systems based on tautomeric principles, and innovating color-changing or pH-responsive cosmetic products that leverage controlled tautomeric shifts.
Market Analysis for Stable Cosmetic Ingredients
The global cosmetics market has been experiencing steady growth, with an increasing demand for stable and effective ingredients. The market for stable cosmetic ingredients is driven by consumer preferences for long-lasting, high-performance products that maintain their efficacy throughout their shelf life. This demand has led to a surge in research and development efforts focused on ingredient stabilization techniques, including tautomerization.
Tautomerization, a process where certain compounds can exist in two or more structural forms that readily interconvert, has gained significant attention in cosmetic chemistry. This phenomenon is particularly relevant for stabilizing ingredients that are prone to degradation or loss of efficacy over time. The market for such stabilized ingredients is expected to grow as cosmetic manufacturers seek to improve product longevity and performance.
Consumer awareness regarding product safety and efficacy has also contributed to the increased demand for stable cosmetic ingredients. Customers are becoming more informed about the importance of product stability and are willing to pay premium prices for cosmetics that maintain their quality over extended periods. This trend has created a lucrative market segment for cosmetic companies that can deliver products with enhanced stability profiles.
The skincare segment, in particular, has shown substantial growth potential for stable ingredients. Anti-aging products, serums, and moisturizers that incorporate stabilized active ingredients have gained popularity among consumers looking for long-term benefits. The hair care sector has also seen an uptick in demand for stable ingredients, especially in leave-in treatments and color protection products.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for stable cosmetic ingredients, owing to stringent regulatory standards and high consumer awareness. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing middle-class population with a penchant for premium cosmetic products.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major cosmetic ingredient suppliers and specialty chemical companies. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative stabilization technologies, with a focus on natural and sustainable solutions. Collaborations between ingredient manufacturers and cosmetic brands are becoming more common, as they work together to develop customized stable formulations.
In conclusion, the market for stable cosmetic ingredients, particularly those benefiting from tautomerization research, presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. As the cosmetics industry continues to evolve, the demand for ingredients that can maintain their stability and efficacy is expected to drive further advancements in formulation technologies and product development strategies.
Tautomerization, a process where certain compounds can exist in two or more structural forms that readily interconvert, has gained significant attention in cosmetic chemistry. This phenomenon is particularly relevant for stabilizing ingredients that are prone to degradation or loss of efficacy over time. The market for such stabilized ingredients is expected to grow as cosmetic manufacturers seek to improve product longevity and performance.
Consumer awareness regarding product safety and efficacy has also contributed to the increased demand for stable cosmetic ingredients. Customers are becoming more informed about the importance of product stability and are willing to pay premium prices for cosmetics that maintain their quality over extended periods. This trend has created a lucrative market segment for cosmetic companies that can deliver products with enhanced stability profiles.
The skincare segment, in particular, has shown substantial growth potential for stable ingredients. Anti-aging products, serums, and moisturizers that incorporate stabilized active ingredients have gained popularity among consumers looking for long-term benefits. The hair care sector has also seen an uptick in demand for stable ingredients, especially in leave-in treatments and color protection products.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for stable cosmetic ingredients, owing to stringent regulatory standards and high consumer awareness. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing middle-class population with a penchant for premium cosmetic products.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major cosmetic ingredient suppliers and specialty chemical companies. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative stabilization technologies, with a focus on natural and sustainable solutions. Collaborations between ingredient manufacturers and cosmetic brands are becoming more common, as they work together to develop customized stable formulations.
In conclusion, the market for stable cosmetic ingredients, particularly those benefiting from tautomerization research, presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. As the cosmetics industry continues to evolve, the demand for ingredients that can maintain their stability and efficacy is expected to drive further advancements in formulation technologies and product development strategies.
Current Challenges in Ingredient Stabilization
The stabilization of cosmetic ingredients remains a significant challenge in the industry, particularly when dealing with compounds prone to tautomerization. Tautomerization, a form of structural isomerism where rapid interconversion between isomers occurs, can lead to instability in formulations, affecting product efficacy and shelf life. One of the primary challenges is maintaining the desired tautomeric form of an ingredient throughout the product's lifecycle.
Many active ingredients in cosmetics, such as antioxidants and UV filters, exhibit tautomerism. The interconversion between tautomers can result in changes to the ingredient's physical and chemical properties, potentially altering its effectiveness or safety profile. For instance, some UV filters may lose their protective capabilities if they shift to a less active tautomeric form. This instability can compromise the product's performance and may even lead to unexpected skin reactions.
pH fluctuations in cosmetic formulations present another significant hurdle. Tautomerization is often pH-dependent, and even slight changes in acidity or alkalinity can trigger unwanted tautomeric shifts. Formulators must carefully balance pH levels to maintain ingredient stability while ensuring product safety and efficacy. This balancing act becomes increasingly complex when multiple pH-sensitive ingredients are present in a single formulation.
Temperature variations during manufacturing, storage, and use can also induce tautomerization. Many cosmetic products are exposed to a wide range of temperatures throughout their lifecycle, from production to consumer use. Ensuring that ingredients remain in their desired tautomeric form across this temperature spectrum is a considerable challenge. Some compounds may require specialized storage conditions or packaging to maintain stability, adding complexity and cost to the production process.
Interactions between different ingredients in a formulation can further complicate stabilization efforts. Certain combinations may catalyze tautomerization or create an environment that favors an undesired tautomeric form. Formulators must carefully consider potential interactions and their impact on ingredient stability when developing new products. This often requires extensive compatibility testing and may limit the range of ingredients that can be effectively combined.
The cosmetics industry also faces increasing pressure to use natural and sustainable ingredients, many of which are more prone to instability and tautomerization than their synthetic counterparts. Stabilizing these natural compounds without resorting to artificial preservatives or stabilizers presents a significant technical challenge. Researchers must develop innovative approaches to harness the benefits of natural ingredients while ensuring their stability and efficacy in various formulations.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining advanced analytical techniques, innovative formulation strategies, and a deep understanding of molecular behavior. As the demand for more sophisticated and effective cosmetic products continues to grow, overcoming the hurdles associated with ingredient stabilization, particularly in the context of tautomerization, remains a critical focus for research and development in cosmetic chemistry.
Many active ingredients in cosmetics, such as antioxidants and UV filters, exhibit tautomerism. The interconversion between tautomers can result in changes to the ingredient's physical and chemical properties, potentially altering its effectiveness or safety profile. For instance, some UV filters may lose their protective capabilities if they shift to a less active tautomeric form. This instability can compromise the product's performance and may even lead to unexpected skin reactions.
pH fluctuations in cosmetic formulations present another significant hurdle. Tautomerization is often pH-dependent, and even slight changes in acidity or alkalinity can trigger unwanted tautomeric shifts. Formulators must carefully balance pH levels to maintain ingredient stability while ensuring product safety and efficacy. This balancing act becomes increasingly complex when multiple pH-sensitive ingredients are present in a single formulation.
Temperature variations during manufacturing, storage, and use can also induce tautomerization. Many cosmetic products are exposed to a wide range of temperatures throughout their lifecycle, from production to consumer use. Ensuring that ingredients remain in their desired tautomeric form across this temperature spectrum is a considerable challenge. Some compounds may require specialized storage conditions or packaging to maintain stability, adding complexity and cost to the production process.
Interactions between different ingredients in a formulation can further complicate stabilization efforts. Certain combinations may catalyze tautomerization or create an environment that favors an undesired tautomeric form. Formulators must carefully consider potential interactions and their impact on ingredient stability when developing new products. This often requires extensive compatibility testing and may limit the range of ingredients that can be effectively combined.
The cosmetics industry also faces increasing pressure to use natural and sustainable ingredients, many of which are more prone to instability and tautomerization than their synthetic counterparts. Stabilizing these natural compounds without resorting to artificial preservatives or stabilizers presents a significant technical challenge. Researchers must develop innovative approaches to harness the benefits of natural ingredients while ensuring their stability and efficacy in various formulations.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining advanced analytical techniques, innovative formulation strategies, and a deep understanding of molecular behavior. As the demand for more sophisticated and effective cosmetic products continues to grow, overcoming the hurdles associated with ingredient stabilization, particularly in the context of tautomerization, remains a critical focus for research and development in cosmetic chemistry.
Existing Tautomerization Control Methods
01 Chemical structure stabilization
Tautomerization stability can be enhanced by modifying the chemical structure of compounds. This involves introducing specific functional groups or substituents that favor one tautomeric form over others, thereby reducing the likelihood of interconversion between different tautomers. Such modifications can lead to improved stability and predictability in pharmaceutical and chemical applications.- Chemical structure stabilization: Tautomerization stability can be enhanced by modifying the chemical structure of compounds. This involves introducing specific functional groups or altering molecular geometry to favor one tautomeric form over others. Such modifications can reduce the energy barrier between tautomers, leading to a more stable predominant form.
- Environmental factor control: Controlling environmental factors such as pH, temperature, and solvent polarity can significantly impact tautomerization stability. By optimizing these conditions, it's possible to shift the equilibrium towards a more stable tautomeric form, thereby enhancing overall stability and reducing unwanted interconversions.
- Computational modeling and prediction: Advanced computational methods and molecular modeling techniques are employed to predict and analyze tautomerization stability. These tools help in understanding the energetics of tautomeric transitions, allowing for the design of more stable compounds and the optimization of reaction conditions to favor desired tautomeric forms.
- Stabilization through complexation: Forming complexes with metal ions or other stabilizing agents can enhance tautomerization stability. This approach involves creating coordination compounds or supramolecular structures that lock the molecule in a specific tautomeric form, thereby preventing unwanted interconversions and increasing overall stability.
- Kinetic and thermodynamic control: Manipulating reaction kinetics and thermodynamics can be used to control tautomerization stability. This involves designing reaction pathways that favor the formation of more stable tautomers or creating energy barriers that prevent rapid interconversion between tautomeric forms, thus enhancing the stability of desired tautomeric structures.
02 Environmental factor control
Controlling environmental factors such as pH, temperature, and solvent composition can significantly impact tautomerization stability. By optimizing these conditions, it's possible to stabilize specific tautomeric forms and prevent unwanted interconversions. This approach is particularly useful in formulation development and storage of sensitive compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Computational modeling and prediction
Advanced computational methods and molecular modeling techniques are employed to predict and analyze tautomerization stability. These tools help in understanding the energetics of different tautomeric forms, allowing for better design of stable compounds and optimization of existing molecules. Such approaches can significantly reduce experimental time and costs in drug discovery and development processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Formulation strategies
Developing specific formulation strategies can enhance tautomerization stability in various products. This includes the use of stabilizing excipients, encapsulation techniques, or creating specialized delivery systems that protect compounds from conditions that promote tautomerization. Such strategies are crucial in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and agrochemical industries to maintain product efficacy and shelf-life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical techniques for stability assessment
Advanced analytical techniques are utilized to assess and monitor tautomerization stability. These include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and real-time analysis tools that can detect and quantify different tautomeric forms. Such techniques are essential for quality control, stability testing, and optimization of compounds prone to tautomerization in various industrial and research applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cosmetic Chemistry and Stabilization
The research on tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry for stabilizing ingredients is in a developing stage, with the market showing significant growth potential. The global cosmetics industry, valued at over $500 billion, is driving demand for innovative stabilization techniques. Major players like L'Oréal, Unilever, and Shiseido are investing heavily in R&D to enhance product stability and efficacy. While the technology is not yet fully mature, companies such as BASF and Merck are making strides in developing advanced tautomerization-based stabilization methods. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established cosmetic giants and specialized chemical firms, with increasing collaborations between academia and industry to accelerate technological advancements.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed advanced tautomerization control techniques for cosmetic ingredients. Their approach involves using specific pH-controlled environments and stabilizing agents to manipulate tautomeric equilibria. They have implemented a novel microemulsion system that encapsulates tautomeric compounds, preventing unwanted shifts between tautomers[1]. Additionally, L'Oréal has pioneered the use of cyclodextrins to form inclusion complexes with tautomeric molecules, effectively "locking" them in the desired form[3]. This technology has been particularly successful in stabilizing retinoids and certain plant extracts in their skincare formulations.
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, extensive patent portfolio, and strong market presence. Weaknesses: High R&D costs and potential regulatory challenges with novel stabilization techniques.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has focused on developing synthetic strategies to control tautomerization in cosmetic ingredients. They have created a series of novel molecules with "locked" tautomeric forms, achieved through strategic molecular design and synthesis[2]. Their approach includes the introduction of specific functional groups that favor one tautomer over others. BASF has also developed a range of stabilizing excipients that can be added to formulations to maintain the desired tautomeric form of active ingredients. Their research has led to the creation of more stable versions of popular cosmetic ingredients like salicylic acid derivatives and certain UV filters[4].
Strengths: Strong chemical synthesis capabilities, broad product portfolio, and global research network. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs for synthesized ingredients and longer development timelines.
Innovative Approaches to Tautomer Stabilization
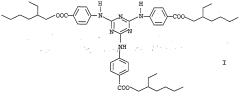
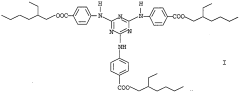
Method for producing the tautomeric form (i) of 2, 4, 6-trianilino-p- (carbo-2'-ethylhexyl-1'-oxy)-1, 3, 5-triazine
PatentWO2003074499A1
Innovation
- A process involving crystallization from a tautomeric mixture using specific solvents such as aliphatic alcohols, aliphatic carboxylic acid alkyl esters, aromatic carboxylic acid alkyl esters, and dialkyl ketones, with up to 30% hydrocarbon as a cosolvent, to isolate the tautomeric form I, which is stable and does not convert back into a mixture, enhancing chemical uniformity and storage stability.
Method for producing the tautomeric form (i) of 2, 4, 6-trianilino-p- (carbo-2'-ethylhexyl-1'-oxy)-1, 3, 5-triazine
PatentInactiveEP1483250A1
Innovation
- A process involving crystallization from a mixture of tautomers in the presence of specific solvents such as aliphatic alcohols, aliphatic carboxylic acid alkyl esters, aromatic carboxylic acid alkyl esters, and dialkyl ketones, with up to 30% hydrocarbon as a cosolvent, to isolate the tautomeric form I, which is stable and does not convert back to the tautomeric mixture.
Regulatory Framework for Cosmetic Ingredients
The regulatory framework for cosmetic ingredients plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of products containing tautomeric compounds. In the context of tautomerization research for stabilizing ingredients in cosmetic chemistry, regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards to address the unique challenges posed by these dynamic molecular structures.
The European Union's Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 serves as a cornerstone for cosmetic ingredient regulation, emphasizing the importance of safety assessments for all substances used in cosmetic formulations. This regulation specifically addresses the need for manufacturers to consider the potential impact of tautomerization on ingredient stability and safety. Under this framework, companies must provide comprehensive data on the tautomeric behavior of ingredients, including their potential to form different structural isomers under varying conditions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees cosmetic ingredient regulation through the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not require pre-market approval for most cosmetic ingredients, it mandates that manufacturers ensure the safety of their products, including those containing tautomeric compounds. The agency has issued guidance documents that specifically address the need for stability testing of cosmetic ingredients, which is particularly relevant for tautomeric substances prone to structural changes.
The International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) has also recognized the importance of tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry. This multilateral group, comprising regulatory authorities from various countries, has developed harmonized approaches for assessing the safety of cosmetic ingredients. Their guidelines emphasize the need for thorough characterization of tautomeric compounds, including their potential for interconversion and the impact on product stability and efficacy.
Japan's regulatory framework, overseen by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, includes specific provisions for the evaluation of quasi-drug ingredients, many of which are subject to tautomerization. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Codex (JCIC) provides detailed standards for the quality and purity of cosmetic ingredients, including methods for assessing the stability of tautomeric compounds.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the development of advanced analytical methods to detect and characterize tautomeric forms in cosmetic products. This includes the use of sophisticated spectroscopic techniques and computational modeling to predict tautomeric behavior under various conditions. Such advancements in regulatory science are essential for ensuring the accurate assessment of ingredient safety and stability in the context of tautomerization.
The European Union's Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 serves as a cornerstone for cosmetic ingredient regulation, emphasizing the importance of safety assessments for all substances used in cosmetic formulations. This regulation specifically addresses the need for manufacturers to consider the potential impact of tautomerization on ingredient stability and safety. Under this framework, companies must provide comprehensive data on the tautomeric behavior of ingredients, including their potential to form different structural isomers under varying conditions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees cosmetic ingredient regulation through the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. While the FDA does not require pre-market approval for most cosmetic ingredients, it mandates that manufacturers ensure the safety of their products, including those containing tautomeric compounds. The agency has issued guidance documents that specifically address the need for stability testing of cosmetic ingredients, which is particularly relevant for tautomeric substances prone to structural changes.
The International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) has also recognized the importance of tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry. This multilateral group, comprising regulatory authorities from various countries, has developed harmonized approaches for assessing the safety of cosmetic ingredients. Their guidelines emphasize the need for thorough characterization of tautomeric compounds, including their potential for interconversion and the impact on product stability and efficacy.
Japan's regulatory framework, overseen by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, includes specific provisions for the evaluation of quasi-drug ingredients, many of which are subject to tautomerization. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Codex (JCIC) provides detailed standards for the quality and purity of cosmetic ingredients, including methods for assessing the stability of tautomeric compounds.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the development of advanced analytical methods to detect and characterize tautomeric forms in cosmetic products. This includes the use of sophisticated spectroscopic techniques and computational modeling to predict tautomeric behavior under various conditions. Such advancements in regulatory science are essential for ensuring the accurate assessment of ingredient safety and stability in the context of tautomerization.
Environmental Impact of Stabilization Techniques
The environmental impact of stabilization techniques in cosmetic chemistry, particularly those involving tautomerization, is a critical consideration in the development and production of sustainable beauty products. Tautomerization, a process where molecules rapidly interconvert between structural isomers, plays a significant role in stabilizing cosmetic ingredients. However, the methods used to control and exploit this phenomenon can have varying effects on the environment.
Traditional stabilization techniques often rely on synthetic additives and preservatives, which may contribute to water pollution when washed off during use. These compounds can persist in aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting marine life and accumulating in the food chain. In contrast, tautomerization-based stabilization methods may offer more environmentally friendly alternatives by reducing the need for such additives.
The energy consumption associated with stabilization processes is another environmental concern. Conventional methods may require energy-intensive manufacturing processes or temperature-controlled storage conditions. Tautomerization-based approaches could potentially lower energy requirements by leveraging natural molecular behavior, thus reducing the carbon footprint of cosmetic production.
Waste generation is a significant issue in the cosmetics industry. Stabilization techniques that extend product shelf life can help reduce waste by preventing premature spoilage. Tautomerization research aims to achieve this goal while minimizing the use of synthetic stabilizers, potentially leading to a decrease in packaging waste and overall environmental impact.
The sourcing of raw materials for stabilization compounds is also an important environmental consideration. Some traditional stabilizers may be derived from non-renewable resources or require extensive processing. Tautomerization research focuses on utilizing naturally occurring molecular structures, which could promote the use of more sustainable, plant-based ingredients in cosmetic formulations.
Biodegradability is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients. Tautomerization-based stabilization techniques have the potential to improve the biodegradability of products by relying on inherent molecular properties rather than persistent synthetic additives. This could lead to reduced accumulation of harmful substances in soil and water systems.
As the cosmetics industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the environmental benefits of tautomerization-based stabilization techniques are becoming increasingly apparent. By reducing reliance on synthetic additives, lowering energy consumption, minimizing waste, and improving biodegradability, these methods align with the growing demand for eco-friendly beauty products. However, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand and optimize the environmental advantages of tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry.
Traditional stabilization techniques often rely on synthetic additives and preservatives, which may contribute to water pollution when washed off during use. These compounds can persist in aquatic ecosystems, potentially disrupting marine life and accumulating in the food chain. In contrast, tautomerization-based stabilization methods may offer more environmentally friendly alternatives by reducing the need for such additives.
The energy consumption associated with stabilization processes is another environmental concern. Conventional methods may require energy-intensive manufacturing processes or temperature-controlled storage conditions. Tautomerization-based approaches could potentially lower energy requirements by leveraging natural molecular behavior, thus reducing the carbon footprint of cosmetic production.
Waste generation is a significant issue in the cosmetics industry. Stabilization techniques that extend product shelf life can help reduce waste by preventing premature spoilage. Tautomerization research aims to achieve this goal while minimizing the use of synthetic stabilizers, potentially leading to a decrease in packaging waste and overall environmental impact.
The sourcing of raw materials for stabilization compounds is also an important environmental consideration. Some traditional stabilizers may be derived from non-renewable resources or require extensive processing. Tautomerization research focuses on utilizing naturally occurring molecular structures, which could promote the use of more sustainable, plant-based ingredients in cosmetic formulations.
Biodegradability is a key factor in assessing the environmental impact of cosmetic ingredients. Tautomerization-based stabilization techniques have the potential to improve the biodegradability of products by relying on inherent molecular properties rather than persistent synthetic additives. This could lead to reduced accumulation of harmful substances in soil and water systems.
As the cosmetics industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the environmental benefits of tautomerization-based stabilization techniques are becoming increasingly apparent. By reducing reliance on synthetic additives, lowering energy consumption, minimizing waste, and improving biodegradability, these methods align with the growing demand for eco-friendly beauty products. However, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand and optimize the environmental advantages of tautomerization in cosmetic chemistry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!