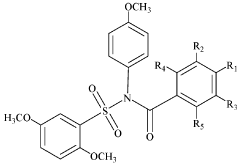
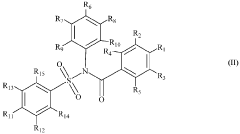
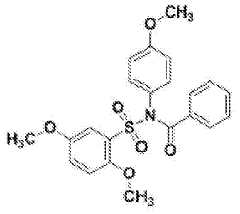
Variability of Tautomerization in Phytochemical Adaptation
JUL 29, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Background and Research Objectives
Tautomerization, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, plays a crucial role in the adaptation mechanisms of phytochemicals. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, known as tautomers, which differ only in the position of a proton and a π bond. The study of tautomerization in phytochemicals has gained significant attention due to its implications in plant defense mechanisms, metabolic processes, and potential applications in drug discovery and development.
The historical context of tautomerization research dates back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different molecular structures. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that researchers began to explore its relevance in biological systems, particularly in plant biochemistry. The advent of advanced spectroscopic techniques and computational methods in recent decades has greatly enhanced our understanding of tautomeric processes in phytochemicals.
The variability of tautomerization in phytochemical adaptation is a complex and multifaceted area of study. It encompasses the investigation of how environmental factors, such as temperature, pH, and solvent conditions, influence the tautomeric equilibrium of plant-derived compounds. This variability can significantly impact the biological activity, stability, and reactivity of phytochemicals, thus affecting their roles in plant defense, signaling, and interaction with other organisms.
The primary objectives of research in this field are manifold. Firstly, there is a need to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying tautomeric transitions in various classes of phytochemicals, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids. This involves identifying key structural features that promote or inhibit tautomerization and understanding how these processes are regulated within plant cells.
Secondly, researchers aim to explore the ecological and evolutionary significance of tautomeric variability in phytochemicals. This includes investigating how plants utilize tautomerization to adapt to changing environmental conditions, defend against pathogens and herbivores, and optimize their metabolic processes. Understanding these adaptive strategies could provide valuable insights into plant resilience and inform agricultural practices.
Another crucial objective is to develop predictive models and computational tools that can accurately simulate tautomeric behavior in complex biological systems. Such models would greatly enhance our ability to design novel plant-based compounds with desired properties for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Furthermore, the research seeks to uncover potential applications of tautomeric phytochemicals in drug discovery and development. Many plant-derived compounds exhibit different biological activities depending on their tautomeric form, offering opportunities for the creation of new pharmaceuticals with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
In conclusion, the study of tautomerization variability in phytochemical adaptation represents a frontier in plant biochemistry and organic chemistry. By addressing these research objectives, scientists aim to unlock new insights into plant biology, evolution, and the potential applications of phytochemicals in various fields, ultimately contributing to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and environmental science.
The historical context of tautomerization research dates back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different molecular structures. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that researchers began to explore its relevance in biological systems, particularly in plant biochemistry. The advent of advanced spectroscopic techniques and computational methods in recent decades has greatly enhanced our understanding of tautomeric processes in phytochemicals.
The variability of tautomerization in phytochemical adaptation is a complex and multifaceted area of study. It encompasses the investigation of how environmental factors, such as temperature, pH, and solvent conditions, influence the tautomeric equilibrium of plant-derived compounds. This variability can significantly impact the biological activity, stability, and reactivity of phytochemicals, thus affecting their roles in plant defense, signaling, and interaction with other organisms.
The primary objectives of research in this field are manifold. Firstly, there is a need to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying tautomeric transitions in various classes of phytochemicals, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids. This involves identifying key structural features that promote or inhibit tautomerization and understanding how these processes are regulated within plant cells.
Secondly, researchers aim to explore the ecological and evolutionary significance of tautomeric variability in phytochemicals. This includes investigating how plants utilize tautomerization to adapt to changing environmental conditions, defend against pathogens and herbivores, and optimize their metabolic processes. Understanding these adaptive strategies could provide valuable insights into plant resilience and inform agricultural practices.
Another crucial objective is to develop predictive models and computational tools that can accurately simulate tautomeric behavior in complex biological systems. Such models would greatly enhance our ability to design novel plant-based compounds with desired properties for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Furthermore, the research seeks to uncover potential applications of tautomeric phytochemicals in drug discovery and development. Many plant-derived compounds exhibit different biological activities depending on their tautomeric form, offering opportunities for the creation of new pharmaceuticals with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
In conclusion, the study of tautomerization variability in phytochemical adaptation represents a frontier in plant biochemistry and organic chemistry. By addressing these research objectives, scientists aim to unlock new insights into plant biology, evolution, and the potential applications of phytochemicals in various fields, ultimately contributing to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and environmental science.
Phytochemical Adaptation Market Analysis
The phytochemical adaptation market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the health benefits associated with plant-based compounds. This market encompasses a wide range of products, including nutraceuticals, functional foods, and natural pharmaceuticals. The global phytochemical market was valued at approximately $4.57 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.93 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period.
The rising demand for natural and organic products is a key factor fueling market expansion. Consumers are increasingly seeking alternatives to synthetic chemicals in food, beverages, and personal care products. This trend is particularly evident in developed regions such as North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products containing phytochemicals.
The pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries are major drivers of the phytochemical adaptation market. These sectors are investing heavily in research and development to identify and utilize novel plant-based compounds with potential therapeutic properties. The growing interest in personalized nutrition and preventive healthcare is also contributing to market growth, as phytochemicals are recognized for their role in supporting overall health and wellness.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, present significant growth opportunities for the phytochemical adaptation market. These regions have a rich biodiversity and traditional knowledge of medicinal plants, which can be leveraged for product development. Additionally, the increasing disposable income and changing lifestyle patterns in these areas are driving demand for natural health products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have become more health-conscious and are seeking natural ways to boost their immune systems. This has led to increased demand for phytochemical-rich supplements and functional foods, a trend that is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era.
However, the market faces challenges such as the variability in phytochemical content due to factors like environmental conditions, genetic variations, and post-harvest processing. This variability, including tautomerization, can affect the efficacy and consistency of phytochemical-based products. As a result, there is a growing need for advanced research and technologies to standardize and optimize phytochemical extraction and formulation processes.
In conclusion, the phytochemical adaptation market shows strong growth potential, driven by consumer preferences for natural products, advancements in research, and the expanding applications of phytochemicals across various industries. The ongoing research on tautomerization variability in phytochemical adaptation is crucial for addressing challenges and unlocking new opportunities in this dynamic market.
The rising demand for natural and organic products is a key factor fueling market expansion. Consumers are increasingly seeking alternatives to synthetic chemicals in food, beverages, and personal care products. This trend is particularly evident in developed regions such as North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay premium prices for products containing phytochemicals.
The pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries are major drivers of the phytochemical adaptation market. These sectors are investing heavily in research and development to identify and utilize novel plant-based compounds with potential therapeutic properties. The growing interest in personalized nutrition and preventive healthcare is also contributing to market growth, as phytochemicals are recognized for their role in supporting overall health and wellness.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, present significant growth opportunities for the phytochemical adaptation market. These regions have a rich biodiversity and traditional knowledge of medicinal plants, which can be leveraged for product development. Additionally, the increasing disposable income and changing lifestyle patterns in these areas are driving demand for natural health products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers have become more health-conscious and are seeking natural ways to boost their immune systems. This has led to increased demand for phytochemical-rich supplements and functional foods, a trend that is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era.
However, the market faces challenges such as the variability in phytochemical content due to factors like environmental conditions, genetic variations, and post-harvest processing. This variability, including tautomerization, can affect the efficacy and consistency of phytochemical-based products. As a result, there is a growing need for advanced research and technologies to standardize and optimize phytochemical extraction and formulation processes.
In conclusion, the phytochemical adaptation market shows strong growth potential, driven by consumer preferences for natural products, advancements in research, and the expanding applications of phytochemicals across various industries. The ongoing research on tautomerization variability in phytochemical adaptation is crucial for addressing challenges and unlocking new opportunities in this dynamic market.
Current Challenges in Tautomerization Research
The field of tautomerization research in phytochemical adaptation faces several significant challenges that hinder our comprehensive understanding and practical applications. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent complexity of tautomeric systems in plant-derived compounds. Phytochemicals often exhibit multiple tautomeric forms, each with distinct chemical properties and biological activities. This variability makes it difficult to predict and control tautomerization processes in different environmental conditions.
Another major challenge lies in the dynamic nature of tautomerization in biological systems. The interconversion between tautomers can be influenced by various factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of specific enzymes or cofactors. These dynamic changes pose significant difficulties in accurately measuring and characterizing tautomeric equilibria in real-time within living plant tissues. Consequently, researchers struggle to elucidate the precise roles of different tautomers in plant adaptation mechanisms.
The lack of standardized methodologies for studying tautomerization in complex phytochemical mixtures further complicates research efforts. Current analytical techniques often have limitations in distinguishing between closely related tautomeric forms, especially when dealing with complex plant extracts. This challenge is particularly pronounced when attempting to identify and quantify minor tautomeric species that may play crucial roles in plant adaptation processes.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of tautomerization research in phytochemical adaptation requires expertise from various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, plant physiology, and computational modeling. Integrating these diverse perspectives and methodologies remains a significant challenge, often leading to fragmented understanding and inconsistent results across different studies.
The environmental variability encountered in natural plant habitats adds another layer of complexity to tautomerization research. Factors such as soil composition, light intensity, and water availability can significantly influence tautomeric equilibria in phytochemicals. Replicating these diverse environmental conditions in laboratory settings to study tautomerization processes accurately is often challenging and resource-intensive.
Lastly, the translation of fundamental tautomerization research into practical applications for crop improvement or drug discovery faces substantial hurdles. Bridging the gap between theoretical understanding and real-world applications requires overcoming regulatory, economic, and technological barriers. Developing strategies to manipulate tautomeric equilibria in plants for enhanced stress tolerance or improved nutritional value remains a complex and long-term challenge in the field.
Another major challenge lies in the dynamic nature of tautomerization in biological systems. The interconversion between tautomers can be influenced by various factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of specific enzymes or cofactors. These dynamic changes pose significant difficulties in accurately measuring and characterizing tautomeric equilibria in real-time within living plant tissues. Consequently, researchers struggle to elucidate the precise roles of different tautomers in plant adaptation mechanisms.
The lack of standardized methodologies for studying tautomerization in complex phytochemical mixtures further complicates research efforts. Current analytical techniques often have limitations in distinguishing between closely related tautomeric forms, especially when dealing with complex plant extracts. This challenge is particularly pronounced when attempting to identify and quantify minor tautomeric species that may play crucial roles in plant adaptation processes.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of tautomerization research in phytochemical adaptation requires expertise from various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, plant physiology, and computational modeling. Integrating these diverse perspectives and methodologies remains a significant challenge, often leading to fragmented understanding and inconsistent results across different studies.
The environmental variability encountered in natural plant habitats adds another layer of complexity to tautomerization research. Factors such as soil composition, light intensity, and water availability can significantly influence tautomeric equilibria in phytochemicals. Replicating these diverse environmental conditions in laboratory settings to study tautomerization processes accurately is often challenging and resource-intensive.
Lastly, the translation of fundamental tautomerization research into practical applications for crop improvement or drug discovery faces substantial hurdles. Bridging the gap between theoretical understanding and real-world applications requires overcoming regulatory, economic, and technological barriers. Developing strategies to manipulate tautomeric equilibria in plants for enhanced stress tolerance or improved nutritional value remains a complex and long-term challenge in the field.
Current Tautomerization Analysis Methods
01 Computational methods for tautomer prediction
Advanced computational techniques are employed to predict and analyze tautomeric forms of molecules. These methods utilize algorithms and models to assess the stability and likelihood of different tautomeric structures, aiding in drug discovery and chemical analysis processes.- Tautomerization in chemical compound analysis: Tautomerization variability is a significant consideration in chemical compound analysis, particularly in drug discovery and development. It involves the structural isomerism where rapid interconversion between two or more structures occurs. This phenomenon can affect the properties, reactivity, and biological activity of compounds, necessitating careful consideration in molecular design and analysis.
- Computational methods for tautomer prediction: Advanced computational methods and algorithms are employed to predict and analyze tautomeric forms of molecules. These tools help in understanding the energetics and probabilities of different tautomeric states, aiding in the design of more effective drugs and chemical compounds. Machine learning and quantum mechanical calculations are often utilized in these predictive models.
- Impact of tautomerization on drug-target interactions: Tautomerization can significantly influence drug-target interactions by altering the binding affinity and specificity of compounds to their biological targets. Understanding and accounting for tautomeric forms is crucial in structure-based drug design and optimization of lead compounds. This knowledge helps in predicting drug efficacy and potential side effects more accurately.
- Analytical techniques for tautomer identification: Various analytical techniques are employed to identify and characterize tautomeric forms in solution and solid state. These include NMR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, and mass spectrometry. Advanced spectroscopic methods allow for the detection and quantification of different tautomeric species, providing crucial information for pharmaceutical and materials science applications.
- Tautomerization in biological systems: Tautomerization plays a significant role in biological systems, affecting processes such as enzyme catalysis, DNA base pairing, and protein-ligand interactions. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of biomolecules is essential for elucidating mechanisms of biological reactions and designing biomimetic systems. This knowledge has implications in fields ranging from genetics to drug metabolism studies.
02 Tautomerization in pharmaceutical compounds
Tautomerization plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical compounds, affecting their properties and interactions. Understanding and controlling tautomeric variability is essential for drug design, formulation, and efficacy. This includes considering tautomeric forms in structure-activity relationships and drug-target interactions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Analytical techniques for tautomer identification
Various analytical techniques are used to identify and characterize tautomeric forms. These may include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and mass spectrometry. Advanced instrumentation and data analysis methods help in distinguishing between different tautomers and quantifying their relative abundances.Expand Specific Solutions04 Tautomerization in biological systems
Tautomerization is significant in biological systems, affecting protein-ligand interactions, enzyme catalysis, and genetic processes. Understanding tautomeric variability in biomolecules is crucial for elucidating biological mechanisms and developing targeted therapies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental factors influencing tautomerization
Environmental factors such as pH, temperature, and solvent properties can significantly influence tautomeric equilibria. These factors are important considerations in various fields, including materials science, chemical engineering, and environmental chemistry, where tautomeric variability can affect product properties and reactions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Phytochemical Research
The research on tautomerization variability in phytochemical adaptation is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as the importance of plant-based compounds in various industries increases. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity across different companies. Key players like Sunshine Lake Pharma, Humanwell Healthcare, and Bayer CropScience are investing in this field, leveraging their expertise in pharmaceuticals and agriculture. Academic institutions such as the University of Southern California and China Agricultural University are also contributing significantly to the fundamental research. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established corporations and innovative startups vying for breakthroughs in understanding and applying tautomerization principles in phytochemistry.
University of Southern California
Technical Solution: USC has developed advanced computational methods to study tautomerization in phytochemicals. Their approach combines quantum mechanical calculations with machine learning algorithms to predict tautomeric equilibria in complex plant-derived compounds[1]. This method allows for rapid screening of large libraries of phytochemicals to identify compounds with desirable tautomeric properties for drug discovery and crop protection applications[2]. USC researchers have also investigated how environmental factors like pH and solvent polarity influence tautomeric ratios in key plant metabolites, providing insights into phytochemical adaptation mechanisms[3].
Strengths: Cutting-edge computational techniques, interdisciplinary approach combining chemistry and data science. Weaknesses: May require validation with experimental studies, computational cost for large-scale analyses.
Bayer CropScience LP
Technical Solution: Bayer CropScience has developed proprietary computational models to predict and optimize the tautomeric behavior of agrochemicals. Their approach integrates quantum mechanical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations, and machine learning algorithms to design crop protection compounds with tailored tautomeric properties[10]. This has led to the development of novel herbicides and fungicides with improved efficacy and reduced environmental impact[11]. Bayer researchers have also investigated how tautomerization affects the uptake and translocation of agrochemicals in plants, leading to optimized formulations for enhanced bioavailability[12]. Additionally, they have explored the role of tautomerization in the mode of action of insecticides, resulting in the discovery of new target sites for pest control.
Strengths: Extensive resources for computational and experimental studies, direct application to product development. Weaknesses: Research may be primarily focused on commercial applications rather than fundamental science.
Breakthrough Studies in Tautomeric Variability
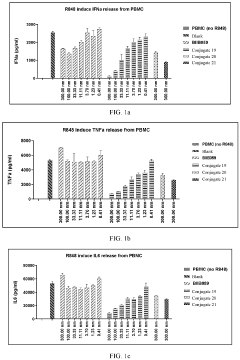
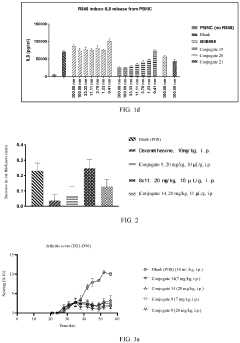
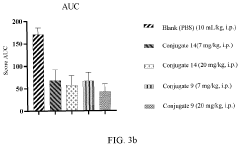
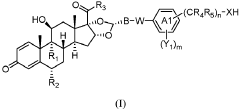
Steroid compound and conjugate thereof
PatentPendingEP4393937A1
Innovation
- A glucocorticoid receptor agonist linked to a protein, such as an antibody or antigen-binding fragment, is used to create an immunoconjugate that can target immune cells, influence cytokine release, and affect various immune-related processes, including skin fibrosis and arthritic symptoms, while maintaining biological safety and plasma stability.
Compositions and methods for treating multiple myeloma
PatentWO2017030987A1
Innovation
- The use of BRD9647 and its derivatives, which selectively inhibit the proliferation of stroma-dependent multiple myeloma cells by benzoylating cellular amines, particularly those with an AZIN1 polypeptide mutation, thereby disrupting polyamine regulation and cell growth.
Environmental Factors Affecting Tautomerization
Tautomerization in phytochemicals is significantly influenced by various environmental factors, which play a crucial role in the adaptation mechanisms of plants. Temperature is one of the primary factors affecting tautomerization rates and equilibria. Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of tautomerization, potentially altering the distribution of tautomers in plant tissues. This temperature-dependent behavior can be particularly important for plants in diverse climates, as it may contribute to their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
pH is another critical environmental factor that impacts tautomerization in phytochemicals. Many plant metabolites exhibit pH-dependent tautomerization, which can affect their biological activity and chemical properties. For instance, flavonoids, a class of plant secondary metabolites, can undergo tautomerization between their keto and enol forms depending on the pH of their environment. This pH-sensitive behavior can influence the antioxidant properties and bioavailability of these compounds in different plant tissues and cellular compartments.
Light exposure is also known to influence tautomerization processes in certain phytochemicals. Photoinduced tautomerization can occur in some plant pigments, such as anthocyanins, which are responsible for the vibrant colors in many fruits and flowers. The interconversion between different tautomeric forms under varying light conditions can contribute to the plant's ability to adapt to different light environments and protect against excessive light exposure.
Solvent polarity is another environmental factor that can affect tautomerization in phytochemicals. The polarity of the surrounding medium can influence the stability of different tautomeric forms, potentially altering the equilibrium between them. This is particularly relevant in plant cells, where the local environment can vary significantly between different cellular compartments and tissues.
Pressure, although less commonly studied, can also impact tautomerization processes in some phytochemicals. High-pressure environments may alter the equilibrium between tautomeric forms, potentially affecting the chemical and biological properties of these compounds. This factor could be particularly relevant for plants growing in extreme environments, such as deep-sea or high-altitude locations.
The presence of metal ions in the plant's environment can also influence tautomerization processes. Some phytochemicals can form complexes with metal ions, which can stabilize certain tautomeric forms or catalyze the interconversion between tautomers. This interaction between metal ions and phytochemicals can play a role in plant adaptation mechanisms, particularly in environments with varying metal ion concentrations.
Understanding these environmental factors and their effects on tautomerization is crucial for elucidating the complex adaptation mechanisms of plants. The variability in tautomerization induced by these factors can contribute to the plasticity of plant responses to environmental changes, potentially enhancing their survival and fitness in diverse ecological niches.
pH is another critical environmental factor that impacts tautomerization in phytochemicals. Many plant metabolites exhibit pH-dependent tautomerization, which can affect their biological activity and chemical properties. For instance, flavonoids, a class of plant secondary metabolites, can undergo tautomerization between their keto and enol forms depending on the pH of their environment. This pH-sensitive behavior can influence the antioxidant properties and bioavailability of these compounds in different plant tissues and cellular compartments.
Light exposure is also known to influence tautomerization processes in certain phytochemicals. Photoinduced tautomerization can occur in some plant pigments, such as anthocyanins, which are responsible for the vibrant colors in many fruits and flowers. The interconversion between different tautomeric forms under varying light conditions can contribute to the plant's ability to adapt to different light environments and protect against excessive light exposure.
Solvent polarity is another environmental factor that can affect tautomerization in phytochemicals. The polarity of the surrounding medium can influence the stability of different tautomeric forms, potentially altering the equilibrium between them. This is particularly relevant in plant cells, where the local environment can vary significantly between different cellular compartments and tissues.
Pressure, although less commonly studied, can also impact tautomerization processes in some phytochemicals. High-pressure environments may alter the equilibrium between tautomeric forms, potentially affecting the chemical and biological properties of these compounds. This factor could be particularly relevant for plants growing in extreme environments, such as deep-sea or high-altitude locations.
The presence of metal ions in the plant's environment can also influence tautomerization processes. Some phytochemicals can form complexes with metal ions, which can stabilize certain tautomeric forms or catalyze the interconversion between tautomers. This interaction between metal ions and phytochemicals can play a role in plant adaptation mechanisms, particularly in environments with varying metal ion concentrations.
Understanding these environmental factors and their effects on tautomerization is crucial for elucidating the complex adaptation mechanisms of plants. The variability in tautomerization induced by these factors can contribute to the plasticity of plant responses to environmental changes, potentially enhancing their survival and fitness in diverse ecological niches.
Computational Modeling of Tautomeric Equilibria
Computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria has become an essential tool in understanding the variability of tautomerization in phytochemical adaptation. These models provide valuable insights into the complex interplay between different tautomeric forms and their impact on biological functions.
One of the primary approaches in computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria is the use of quantum mechanical calculations. Density Functional Theory (DFT) methods have proven particularly effective in predicting the relative stabilities of different tautomers. These calculations can accurately estimate the energy differences between tautomeric forms, allowing researchers to determine the most probable structures under various environmental conditions.
Molecular dynamics simulations offer another powerful technique for modeling tautomeric equilibria. By simulating the behavior of molecules over time, these models can capture the dynamic nature of tautomerization processes. This approach is particularly useful for understanding how factors such as temperature, pH, and solvent effects influence the distribution of tautomers in phytochemical systems.
Machine learning algorithms have recently emerged as a promising tool for predicting tautomeric equilibria. By training on large datasets of known tautomeric systems, these models can rapidly estimate the likelihood of different tautomeric forms for novel compounds. This approach has the potential to significantly accelerate the screening of phytochemicals for desired properties related to tautomerization.
Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods provide a sophisticated approach to modeling tautomeric equilibria in complex biological environments. These models combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations for the tautomerizing region with the computational efficiency of molecular mechanics for the surrounding system. This allows researchers to study tautomerization processes in the context of protein-ligand interactions or within plant cell environments.
Continuum solvation models, such as the Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM), have been successfully applied to study the effects of different solvents on tautomeric equilibria. These models can predict how changes in polarity and dielectric constants influence the stability of various tautomers, providing insights into the adaptability of phytochemicals across different cellular compartments.
The integration of these computational approaches with experimental data, such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to more accurate and reliable models of tautomeric equilibria. This synergy between computational and experimental methods continues to drive advancements in our understanding of phytochemical adaptation through tautomerization.
One of the primary approaches in computational modeling of tautomeric equilibria is the use of quantum mechanical calculations. Density Functional Theory (DFT) methods have proven particularly effective in predicting the relative stabilities of different tautomers. These calculations can accurately estimate the energy differences between tautomeric forms, allowing researchers to determine the most probable structures under various environmental conditions.
Molecular dynamics simulations offer another powerful technique for modeling tautomeric equilibria. By simulating the behavior of molecules over time, these models can capture the dynamic nature of tautomerization processes. This approach is particularly useful for understanding how factors such as temperature, pH, and solvent effects influence the distribution of tautomers in phytochemical systems.
Machine learning algorithms have recently emerged as a promising tool for predicting tautomeric equilibria. By training on large datasets of known tautomeric systems, these models can rapidly estimate the likelihood of different tautomeric forms for novel compounds. This approach has the potential to significantly accelerate the screening of phytochemicals for desired properties related to tautomerization.
Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods provide a sophisticated approach to modeling tautomeric equilibria in complex biological environments. These models combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations for the tautomerizing region with the computational efficiency of molecular mechanics for the surrounding system. This allows researchers to study tautomerization processes in the context of protein-ligand interactions or within plant cell environments.
Continuum solvation models, such as the Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM), have been successfully applied to study the effects of different solvents on tautomeric equilibria. These models can predict how changes in polarity and dielectric constants influence the stability of various tautomers, providing insights into the adaptability of phytochemicals across different cellular compartments.
The integration of these computational approaches with experimental data, such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to more accurate and reliable models of tautomeric equilibria. This synergy between computational and experimental methods continues to drive advancements in our understanding of phytochemical adaptation through tautomerization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!