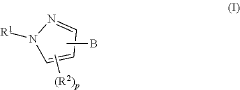
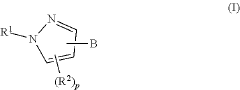
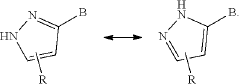
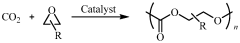
Tautomerization Impacts on Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Fundamentals and Research Objectives
Tautomerization is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding reaction mechanisms and molecular behavior. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, known as tautomers, which differ in the position of a proton and a π bond. The study of tautomerization is essential for predicting and explaining various chemical reactions, as well as understanding the properties and reactivity of organic compounds.
The historical development of tautomerization research can be traced back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different structural forms of certain compounds. Since then, significant advancements have been made in elucidating the mechanisms and factors influencing tautomeric equilibria. Modern spectroscopic techniques, computational methods, and advanced experimental approaches have greatly enhanced our understanding of tautomerization processes.
In the context of reaction mechanisms, tautomerization can have profound impacts on the course and outcome of organic reactions. It can affect the reactivity of functional groups, influence the stereochemistry of products, and even determine the feasibility of certain transformations. Understanding these impacts is crucial for designing efficient synthetic routes, developing new catalysts, and optimizing reaction conditions in both academic and industrial settings.
The primary objectives of tautomerization research in organic chemistry are multifaceted. First, there is a need to develop more accurate predictive models for tautomeric equilibria in various chemical environments. This includes understanding the effects of solvent, temperature, pH, and other external factors on tautomerization processes. Second, researchers aim to elucidate the kinetics and thermodynamics of tautomerization reactions, which are essential for understanding reaction rates and equilibrium constants.
Another key objective is to investigate the role of tautomerization in biological systems, where it can influence the structure and function of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. This has important implications for drug design and the development of new therapeutic strategies. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploiting tautomerization for the design of smart materials and molecular switches, which could have applications in nanotechnology and information storage.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of tautomerization in asymmetric synthesis and catalysis. By controlling tautomeric equilibria, it may be possible to develop new strategies for enantioselective reactions and the synthesis of complex chiral molecules. This could have significant implications for the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
The historical development of tautomerization research can be traced back to the late 19th century when chemists first observed the dynamic equilibrium between different structural forms of certain compounds. Since then, significant advancements have been made in elucidating the mechanisms and factors influencing tautomeric equilibria. Modern spectroscopic techniques, computational methods, and advanced experimental approaches have greatly enhanced our understanding of tautomerization processes.
In the context of reaction mechanisms, tautomerization can have profound impacts on the course and outcome of organic reactions. It can affect the reactivity of functional groups, influence the stereochemistry of products, and even determine the feasibility of certain transformations. Understanding these impacts is crucial for designing efficient synthetic routes, developing new catalysts, and optimizing reaction conditions in both academic and industrial settings.
The primary objectives of tautomerization research in organic chemistry are multifaceted. First, there is a need to develop more accurate predictive models for tautomeric equilibria in various chemical environments. This includes understanding the effects of solvent, temperature, pH, and other external factors on tautomerization processes. Second, researchers aim to elucidate the kinetics and thermodynamics of tautomerization reactions, which are essential for understanding reaction rates and equilibrium constants.
Another key objective is to investigate the role of tautomerization in biological systems, where it can influence the structure and function of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. This has important implications for drug design and the development of new therapeutic strategies. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploiting tautomerization for the design of smart materials and molecular switches, which could have applications in nanotechnology and information storage.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of tautomerization in asymmetric synthesis and catalysis. By controlling tautomeric equilibria, it may be possible to develop new strategies for enantioselective reactions and the synthesis of complex chiral molecules. This could have significant implications for the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
Market Analysis of Tautomerization-Related Products
The market for tautomerization-related products in organic chemistry is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced pharmaceutical compounds and fine chemicals. Tautomerization, a process where a molecule rapidly interconverts between two or more structural isomers, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and drug development processes.
In the pharmaceutical industry, tautomerization-related products are particularly valuable for drug discovery and development. These products include specialized reagents, catalysts, and analytical tools designed to study and control tautomeric equilibria. The ability to manipulate tautomeric forms can lead to improved drug efficacy, stability, and bioavailability, making these products essential for pharmaceutical research and development.
The fine chemicals sector also represents a substantial market for tautomerization-related products. Manufacturers of dyes, pigments, and other specialty chemicals utilize tautomerization principles to create products with enhanced properties. This has led to an increased demand for tautomerization-specific catalysts and process optimization tools.
Academic and research institutions form another significant market segment. The study of tautomerization mechanisms and their impact on reaction outcomes is a growing field of research, driving demand for specialized laboratory equipment and analytical instruments designed to investigate tautomeric phenomena.
The market for software and computational tools related to tautomerization is expanding rapidly. These products include molecular modeling software, quantum chemical calculation packages, and machine learning algorithms designed to predict and analyze tautomeric behavior. Such tools are becoming increasingly important in both industrial and academic settings for understanding complex reaction mechanisms and designing more efficient synthetic routes.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for tautomerization-related products, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing investments in research and development and the rapid expansion of the pharmaceutical sector in countries like China and India.
Key market players include major chemical and pharmaceutical companies, as well as specialized suppliers of research tools and analytical instruments. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative products that can better control and exploit tautomeric equilibria in various applications.
In the pharmaceutical industry, tautomerization-related products are particularly valuable for drug discovery and development. These products include specialized reagents, catalysts, and analytical tools designed to study and control tautomeric equilibria. The ability to manipulate tautomeric forms can lead to improved drug efficacy, stability, and bioavailability, making these products essential for pharmaceutical research and development.
The fine chemicals sector also represents a substantial market for tautomerization-related products. Manufacturers of dyes, pigments, and other specialty chemicals utilize tautomerization principles to create products with enhanced properties. This has led to an increased demand for tautomerization-specific catalysts and process optimization tools.
Academic and research institutions form another significant market segment. The study of tautomerization mechanisms and their impact on reaction outcomes is a growing field of research, driving demand for specialized laboratory equipment and analytical instruments designed to investigate tautomeric phenomena.
The market for software and computational tools related to tautomerization is expanding rapidly. These products include molecular modeling software, quantum chemical calculation packages, and machine learning algorithms designed to predict and analyze tautomeric behavior. Such tools are becoming increasingly important in both industrial and academic settings for understanding complex reaction mechanisms and designing more efficient synthetic routes.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for tautomerization-related products, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing investments in research and development and the rapid expansion of the pharmaceutical sector in countries like China and India.
Key market players include major chemical and pharmaceutical companies, as well as specialized suppliers of research tools and analytical instruments. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative products that can better control and exploit tautomeric equilibria in various applications.
Current Challenges in Tautomerization Research
Tautomerization presents several significant challenges in contemporary organic chemistry research, particularly in understanding and predicting reaction mechanisms. One of the primary difficulties lies in the dynamic nature of tautomeric equilibria, which can rapidly shift under varying conditions. This makes it challenging to isolate and study individual tautomers, as they may interconvert faster than they can be observed or measured.
The impact of tautomerization on reaction rates and product distributions is another area of complexity. Tautomers can exhibit different reactivity profiles, leading to unexpected outcomes in synthetic processes. Researchers struggle to accurately model these effects in silico, as current computational methods often lack the precision required to capture the subtle energetic differences between tautomeric forms.
Furthermore, the influence of solvents on tautomeric equilibria poses a significant challenge. Solvent effects can dramatically alter the relative stability of different tautomers, making it difficult to extrapolate results from one solvent system to another. This complicates the development of universal reaction models and necessitates extensive experimental validation across various solvent conditions.
The role of tautomerization in biological systems adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Many enzymes and receptors interact specifically with certain tautomeric forms of substrates or ligands. Understanding these preferences and how they affect biological processes is crucial but remains challenging due to the dynamic nature of tautomerization in physiological environments.
Analytical techniques for studying tautomerization also present limitations. While methods such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography have provided valuable insights, they often struggle to capture the full picture of tautomeric behavior, especially in rapidly equilibrating systems. Developing more sensitive and time-resolved analytical tools remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the integration of tautomerization effects into broader reaction prediction and retrosynthesis platforms represents a frontier in organic chemistry research. Current systems often treat molecules as static entities, failing to account for the dynamic equilibria that can significantly influence reaction outcomes. Overcoming this limitation requires not only improved theoretical models but also more sophisticated algorithms capable of handling the complexity introduced by tautomeric phenomena.
The impact of tautomerization on reaction rates and product distributions is another area of complexity. Tautomers can exhibit different reactivity profiles, leading to unexpected outcomes in synthetic processes. Researchers struggle to accurately model these effects in silico, as current computational methods often lack the precision required to capture the subtle energetic differences between tautomeric forms.
Furthermore, the influence of solvents on tautomeric equilibria poses a significant challenge. Solvent effects can dramatically alter the relative stability of different tautomers, making it difficult to extrapolate results from one solvent system to another. This complicates the development of universal reaction models and necessitates extensive experimental validation across various solvent conditions.
The role of tautomerization in biological systems adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Many enzymes and receptors interact specifically with certain tautomeric forms of substrates or ligands. Understanding these preferences and how they affect biological processes is crucial but remains challenging due to the dynamic nature of tautomerization in physiological environments.
Analytical techniques for studying tautomerization also present limitations. While methods such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography have provided valuable insights, they often struggle to capture the full picture of tautomeric behavior, especially in rapidly equilibrating systems. Developing more sensitive and time-resolved analytical tools remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the integration of tautomerization effects into broader reaction prediction and retrosynthesis platforms represents a frontier in organic chemistry research. Current systems often treat molecules as static entities, failing to account for the dynamic equilibria that can significantly influence reaction outcomes. Overcoming this limitation requires not only improved theoretical models but also more sophisticated algorithms capable of handling the complexity introduced by tautomeric phenomena.
Existing Methodologies for Studying Tautomerization
01 Keto-enol tautomerization mechanisms
Keto-enol tautomerization is a common type of tautomerization reaction involving the interconversion between a ketone and an enol form. This mechanism often involves proton transfer and can be influenced by factors such as solvent, temperature, and catalysts. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for predicting chemical behavior and designing synthetic strategies.- Computational methods for studying tautomerization: Advanced computational techniques are employed to study tautomerization reaction mechanisms. These methods involve quantum mechanical calculations and molecular modeling to predict tautomeric equilibria, transition states, and reaction pathways. Such computational approaches help in understanding the energetics and kinetics of tautomerization processes, providing valuable insights for various chemical and biological applications.
- Tautomerization in pharmaceutical compounds: Tautomerization plays a crucial role in the behavior and properties of pharmaceutical compounds. The study of tautomeric forms is essential for drug design and development, as different tautomers can exhibit varying biological activities, solubilities, and stability profiles. Understanding tautomerization mechanisms helps in predicting drug-target interactions and optimizing drug formulations.
- Catalytic tautomerization processes: Catalysts can significantly influence tautomerization reaction mechanisms. Various catalytic systems, including metal complexes, enzymes, and acid-base catalysts, can facilitate tautomerization by lowering activation energies and stabilizing transition states. The study of catalytic tautomerization is important for developing efficient synthetic methodologies and understanding biological processes involving tautomeric transformations.
- Tautomerization in material science applications: Tautomerization mechanisms are relevant in various material science applications. The interconversion between tautomeric forms can be exploited in the design of smart materials, sensors, and molecular switches. Understanding tautomerization processes helps in developing materials with tunable properties, such as color-changing indicators and responsive polymers.
- Environmental factors affecting tautomerization: Environmental factors, such as solvent effects, temperature, and pH, can significantly influence tautomerization reaction mechanisms. The study of these factors is crucial for predicting tautomeric equilibria and understanding the behavior of tautomeric systems under different conditions. This knowledge is valuable for optimizing reaction conditions and controlling tautomerization processes in various chemical and biological systems.
02 Computational methods for studying tautomerization
Advanced computational techniques are employed to study tautomerization reaction mechanisms. These methods include quantum mechanical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations, and machine learning approaches. They help in predicting tautomeric equilibria, transition states, and energetics of tautomerization processes, providing valuable insights for both theoretical and practical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Catalytic effects on tautomerization
Catalysts play a significant role in tautomerization reactions by lowering activation energies and altering reaction pathways. Various types of catalysts, including acids, bases, and metal complexes, can influence tautomerization mechanisms. Understanding catalytic effects is essential for controlling tautomeric equilibria and developing efficient synthetic processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Tautomerization in biological systems
Tautomerization mechanisms are crucial in biological systems, particularly in the context of DNA and RNA base pairing, enzyme catalysis, and drug-target interactions. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing new therapeutic approaches and explaining biological phenomena at the molecular level.Expand Specific Solutions05 Solvent effects on tautomerization
The solvent environment significantly influences tautomerization reaction mechanisms. Factors such as solvent polarity, hydrogen bonding capacity, and dielectric constant can affect the stability of different tautomeric forms and the kinetics of interconversion. Studying solvent effects is crucial for predicting and controlling tautomerization in various chemical and biological processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Tautomerization Research
The field of tautomerization in organic chemistry reaction mechanisms is in a mature stage of development, with ongoing research focused on refining understanding and applications. The market size for this specialized area is relatively small but significant within the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Technologically, the field is well-established, with companies like Sunshine Lake Pharma, The Broad Institute, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Harvard, MIT, and the University of Delaware also contribute significantly to advancing knowledge in this area. The competitive landscape is characterized by collaboration between industry and academia, with a focus on applying tautomerization insights to drug discovery and development processes.
The Broad Institute, Inc.
Technical Solution: The Broad Institute has developed advanced computational methods to study tautomerization in organic chemistry reactions. Their approach combines quantum mechanical calculations with machine learning algorithms to predict tautomeric equilibria and their impact on reaction mechanisms. They have created a large database of tautomeric structures and their relative energies, which is used to train predictive models. These models can rapidly assess the likelihood of tautomerization occurring during a reaction and its potential effects on reaction pathways and product distributions[1][3]. The institute has also developed experimental techniques using high-resolution mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy to validate their computational predictions and study tautomerization dynamics in real-time[2].
Strengths: Cutting-edge computational methods, large tautomer database, and integrated experimental validation. Weaknesses: High computational cost for complex systems and potential limitations in accurately modeling solvent effects on tautomerization.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard researchers have pioneered the use of ultrafast spectroscopy techniques to study tautomerization dynamics in organic reactions. They have developed femtosecond-resolved infrared spectroscopy methods that can directly observe tautomeric interconversions on picosecond timescales[4]. This has provided unprecedented insights into the kinetics and mechanisms of tautomerization processes. Additionally, Harvard chemists have explored the use of designer solvents and catalysts to control tautomeric equilibria and selectively stabilize specific tautomers during reactions[5]. They have demonstrated how this approach can be used to influence reaction outcomes and improve selectivity in organic syntheses involving tautomerizable compounds.
Strengths: Cutting-edge spectroscopic techniques for studying fast dynamics, innovative approaches for controlling tautomerization. Weaknesses: Specialized equipment requirements, potential challenges in translating fundamental insights to practical applications.
Breakthrough Discoveries in Tautomerization Mechanisms
Methods and compositions of small molecule modulators of hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor) activity
PatentInactiveUS20190375739A1
Innovation
- Development of novel compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that modulate HGF/SF activity, including specific structures and tautomers, which mimic the activity of HGF/SF, and are administered at optimal times post-onset of disease or condition to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Polycarbonate polyol compositions and methods
PatentWO2010028362A1
Innovation
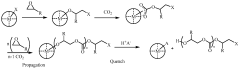
- A polymerization system comprising a metal complex with a permanent ligand set and a chain transfer agent having multiple initiation sites, along with a co-catalyst, to produce polycarbonate polyols with a high percentage of hydroxyl end groups and controlled molecular weight, achieving a carbonate-to-ether linkage ratio and polydispersity index suitable for specific applications.
Computational Approaches in Tautomerization Studies
Computational approaches have become indispensable tools in studying tautomerization phenomena and their impacts on reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry. These methods offer powerful insights into the complex interplay between molecular structures, energetics, and reaction pathways.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly density functional theory (DFT), have emerged as the cornerstone of computational tautomerization studies. DFT methods provide an excellent balance between accuracy and computational cost, allowing researchers to investigate the relative stabilities of different tautomeric forms and the energy barriers associated with their interconversion. Advanced functionals, such as M06-2X and ωB97X-D, have shown remarkable performance in capturing the subtle electronic effects that govern tautomeric equilibria.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations complement static quantum mechanical calculations by incorporating the effects of temperature and solvent interactions. These simulations can reveal the dynamic nature of tautomerization processes, including the timescales of interconversion and the influence of environmental factors. Enhanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, have proven particularly valuable in exploring the free energy landscapes of tautomeric systems.
Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to tautomerization studies, offering new avenues for predicting tautomeric preferences and reaction outcomes. Neural networks trained on extensive datasets of known tautomeric pairs can rapidly estimate equilibrium constants and identify potential tautomeric forms for novel compounds. These methods show promise in high-throughput virtual screening applications and in guiding the design of new organic molecules with desired tautomeric properties.
Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods provide a powerful framework for studying tautomerization in complex environments, such as enzyme active sites or heterogeneous catalysts. By treating the tautomerizing molecule and its immediate surroundings with high-level quantum mechanical methods while representing the broader environment with classical force fields, QM/MM approaches offer a balanced description of both electronic and steric effects on tautomeric equilibria.
The integration of these computational techniques with experimental data, particularly from NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to a more comprehensive understanding of tautomerization phenomena. This synergistic approach allows researchers to validate computational predictions, refine theoretical models, and uncover the subtle factors that influence tautomeric preferences in real-world systems.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly density functional theory (DFT), have emerged as the cornerstone of computational tautomerization studies. DFT methods provide an excellent balance between accuracy and computational cost, allowing researchers to investigate the relative stabilities of different tautomeric forms and the energy barriers associated with their interconversion. Advanced functionals, such as M06-2X and ωB97X-D, have shown remarkable performance in capturing the subtle electronic effects that govern tautomeric equilibria.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations complement static quantum mechanical calculations by incorporating the effects of temperature and solvent interactions. These simulations can reveal the dynamic nature of tautomerization processes, including the timescales of interconversion and the influence of environmental factors. Enhanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, have proven particularly valuable in exploring the free energy landscapes of tautomeric systems.
Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to tautomerization studies, offering new avenues for predicting tautomeric preferences and reaction outcomes. Neural networks trained on extensive datasets of known tautomeric pairs can rapidly estimate equilibrium constants and identify potential tautomeric forms for novel compounds. These methods show promise in high-throughput virtual screening applications and in guiding the design of new organic molecules with desired tautomeric properties.
Hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods provide a powerful framework for studying tautomerization in complex environments, such as enzyme active sites or heterogeneous catalysts. By treating the tautomerizing molecule and its immediate surroundings with high-level quantum mechanical methods while representing the broader environment with classical force fields, QM/MM approaches offer a balanced description of both electronic and steric effects on tautomeric equilibria.
The integration of these computational techniques with experimental data, particularly from NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, has led to a more comprehensive understanding of tautomerization phenomena. This synergistic approach allows researchers to validate computational predictions, refine theoretical models, and uncover the subtle factors that influence tautomeric preferences in real-world systems.
Environmental Factors Affecting Tautomerization
Tautomerization, a dynamic equilibrium between structural isomers, is significantly influenced by various environmental factors. These factors play a crucial role in determining the predominant tautomeric form and the rate of interconversion between tautomers, ultimately affecting reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry.
Temperature is one of the most critical environmental factors impacting tautomerization. Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of tautomerization, as they provide the necessary energy for molecules to overcome the activation barrier between tautomeric forms. This can lead to a shift in the equilibrium position and alter the distribution of tautomers present in a reaction mixture.
Solvent polarity and hydrogen bonding capabilities also exert a substantial influence on tautomerization processes. Polar solvents can stabilize charged or highly polar tautomeric forms through solvation effects, potentially shifting the equilibrium towards these species. Additionally, solvents with strong hydrogen bonding abilities may interact differently with various tautomers, affecting their relative stabilities and the overall tautomeric equilibrium.
pH plays a pivotal role in tautomerization, particularly for compounds containing acidic or basic functional groups. Changes in pH can alter the protonation state of molecules, directly impacting the stability and prevalence of different tautomeric forms. This is especially relevant in biological systems, where subtle pH changes can significantly affect the behavior of biomolecules and their interactions.
Pressure, although less commonly considered, can also influence tautomerization. High-pressure conditions may favor tautomeric forms with smaller molecular volumes, potentially altering reaction pathways and product distributions in organic syntheses conducted under extreme conditions.
The presence of catalysts or specific ions in the reaction environment can dramatically affect tautomerization processes. Certain metal ions or enzymes can selectively stabilize particular tautomeric forms or lower the activation energy for tautomerization, effectively catalyzing the interconversion between tautomers.
Light exposure is another environmental factor that can impact tautomerization, particularly for photosensitive compounds. UV or visible light can provide the energy required for certain tautomeric transitions, leading to photo-induced tautomerization processes that may not occur under standard conditions.
Understanding these environmental factors and their effects on tautomerization is crucial for predicting and controlling reaction outcomes in organic chemistry. By manipulating these factors, chemists can potentially steer reactions towards desired products, optimize yields, and develop more efficient synthetic strategies. This knowledge is particularly valuable in the design of new catalysts, the development of pharmaceuticals with improved bioavailability, and the creation of responsive materials that exploit tautomeric transitions.
Temperature is one of the most critical environmental factors impacting tautomerization. Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of tautomerization, as they provide the necessary energy for molecules to overcome the activation barrier between tautomeric forms. This can lead to a shift in the equilibrium position and alter the distribution of tautomers present in a reaction mixture.
Solvent polarity and hydrogen bonding capabilities also exert a substantial influence on tautomerization processes. Polar solvents can stabilize charged or highly polar tautomeric forms through solvation effects, potentially shifting the equilibrium towards these species. Additionally, solvents with strong hydrogen bonding abilities may interact differently with various tautomers, affecting their relative stabilities and the overall tautomeric equilibrium.
pH plays a pivotal role in tautomerization, particularly for compounds containing acidic or basic functional groups. Changes in pH can alter the protonation state of molecules, directly impacting the stability and prevalence of different tautomeric forms. This is especially relevant in biological systems, where subtle pH changes can significantly affect the behavior of biomolecules and their interactions.
Pressure, although less commonly considered, can also influence tautomerization. High-pressure conditions may favor tautomeric forms with smaller molecular volumes, potentially altering reaction pathways and product distributions in organic syntheses conducted under extreme conditions.
The presence of catalysts or specific ions in the reaction environment can dramatically affect tautomerization processes. Certain metal ions or enzymes can selectively stabilize particular tautomeric forms or lower the activation energy for tautomerization, effectively catalyzing the interconversion between tautomers.
Light exposure is another environmental factor that can impact tautomerization, particularly for photosensitive compounds. UV or visible light can provide the energy required for certain tautomeric transitions, leading to photo-induced tautomerization processes that may not occur under standard conditions.
Understanding these environmental factors and their effects on tautomerization is crucial for predicting and controlling reaction outcomes in organic chemistry. By manipulating these factors, chemists can potentially steer reactions towards desired products, optimize yields, and develop more efficient synthetic strategies. This knowledge is particularly valuable in the design of new catalysts, the development of pharmaceuticals with improved bioavailability, and the creation of responsive materials that exploit tautomeric transitions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!