Tautomerization Dynamics in Hydrogen-Deficient Environments
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Dynamics
Tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments represent a fascinating area of study in chemical physics. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, known as tautomers, which differ in the position of a proton and a corresponding shift of a double bond. In hydrogen-deficient conditions, these dynamics take on unique characteristics that challenge our understanding of molecular behavior.
The study of tautomerization in such environments is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insights into the fundamental principles of chemical reactivity and molecular structure under extreme conditions. These conditions can be found in various natural and artificial settings, including interstellar space, plasma environments, and certain industrial processes.
Researchers have observed that hydrogen deficiency can significantly alter the energy landscape of tautomerization reactions. The absence of readily available protons can lead to higher energy barriers for tautomer interconversion, potentially stabilizing certain tautomeric forms that would be transient under normal conditions. This has implications for the stability and reactivity of molecules in these environments.
Advanced spectroscopic techniques have been instrumental in probing tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient systems. Time-resolved spectroscopy, in particular, has allowed scientists to observe these rapid interconversions on femtosecond to picosecond timescales. These studies have revealed complex kinetics and sometimes unexpected tautomeric preferences.
The role of quantum tunneling in tautomerization becomes especially prominent in hydrogen-deficient environments. As classical proton transfer pathways become less accessible, quantum effects can dominate the dynamics, leading to tunneling-controlled tautomerization. This phenomenon has been observed in various systems, including porphyrins and other macrocyclic compounds.
Computational studies have played a crucial role in elucidating the mechanisms of tautomerization in these challenging environments. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, coupled with advanced electronic structure methods, have provided detailed insights into the potential energy surfaces and transition states involved in these processes.
The implications of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments extend beyond fundamental chemistry. They have significant relevance in astrochemistry, where such conditions are prevalent, and in materials science, where controlling tautomeric equilibria can lead to novel functional materials with switchable properties.
The study of tautomerization in such environments is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insights into the fundamental principles of chemical reactivity and molecular structure under extreme conditions. These conditions can be found in various natural and artificial settings, including interstellar space, plasma environments, and certain industrial processes.
Researchers have observed that hydrogen deficiency can significantly alter the energy landscape of tautomerization reactions. The absence of readily available protons can lead to higher energy barriers for tautomer interconversion, potentially stabilizing certain tautomeric forms that would be transient under normal conditions. This has implications for the stability and reactivity of molecules in these environments.
Advanced spectroscopic techniques have been instrumental in probing tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient systems. Time-resolved spectroscopy, in particular, has allowed scientists to observe these rapid interconversions on femtosecond to picosecond timescales. These studies have revealed complex kinetics and sometimes unexpected tautomeric preferences.
The role of quantum tunneling in tautomerization becomes especially prominent in hydrogen-deficient environments. As classical proton transfer pathways become less accessible, quantum effects can dominate the dynamics, leading to tunneling-controlled tautomerization. This phenomenon has been observed in various systems, including porphyrins and other macrocyclic compounds.
Computational studies have played a crucial role in elucidating the mechanisms of tautomerization in these challenging environments. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, coupled with advanced electronic structure methods, have provided detailed insights into the potential energy surfaces and transition states involved in these processes.
The implications of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments extend beyond fundamental chemistry. They have significant relevance in astrochemistry, where such conditions are prevalent, and in materials science, where controlling tautomeric equilibria can lead to novel functional materials with switchable properties.
Market Applications
Tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments have significant market applications across various industries, particularly in the fields of materials science, pharmaceuticals, and energy storage. In the materials science sector, this phenomenon is being leveraged to develop smart materials with switchable properties. These materials can change their physical or chemical characteristics in response to external stimuli, making them valuable for applications in sensors, displays, and adaptive coatings.
The pharmaceutical industry is exploring tautomerization dynamics to enhance drug design and development processes. By understanding how molecules can exist in different tautomeric forms under hydrogen-deficient conditions, researchers can optimize drug candidates for improved efficacy, stability, and bioavailability. This knowledge is particularly crucial for developing drugs that target specific biological pathways or interact with enzymes in unique ways.
In the energy storage domain, tautomerization dynamics are being investigated for their potential in creating more efficient and sustainable battery technologies. The ability of certain molecules to switch between tautomeric forms in hydrogen-deficient environments could lead to the development of novel electrode materials or electrolytes with enhanced performance characteristics. This could result in batteries with higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and longer lifespans.
The field of organic electronics is another area where tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments are finding applications. Researchers are exploring how these phenomena can be used to create organic semiconductors with tunable electronic properties. This could lead to advancements in flexible electronics, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and organic photovoltaic cells.
Catalysis is yet another sector benefiting from insights into tautomerization dynamics. By understanding how molecules behave in hydrogen-deficient environments, scientists are developing more efficient catalysts for various industrial processes. These catalysts could potentially reduce energy consumption, improve reaction selectivity, and enable the production of valuable chemicals under milder conditions.
The aerospace and defense industries are also showing interest in materials that exhibit tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments. These materials could be used to create adaptive surfaces for aircraft or spacecraft, capable of changing their properties in response to extreme conditions encountered during flight or space missions.
As research in this field progresses, it is expected that new market applications will emerge, potentially revolutionizing industries and opening up opportunities for innovative products and technologies. The interdisciplinary nature of tautomerization dynamics research suggests that collaborations between different sectors may lead to unexpected and groundbreaking applications in the future.
The pharmaceutical industry is exploring tautomerization dynamics to enhance drug design and development processes. By understanding how molecules can exist in different tautomeric forms under hydrogen-deficient conditions, researchers can optimize drug candidates for improved efficacy, stability, and bioavailability. This knowledge is particularly crucial for developing drugs that target specific biological pathways or interact with enzymes in unique ways.
In the energy storage domain, tautomerization dynamics are being investigated for their potential in creating more efficient and sustainable battery technologies. The ability of certain molecules to switch between tautomeric forms in hydrogen-deficient environments could lead to the development of novel electrode materials or electrolytes with enhanced performance characteristics. This could result in batteries with higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and longer lifespans.
The field of organic electronics is another area where tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments are finding applications. Researchers are exploring how these phenomena can be used to create organic semiconductors with tunable electronic properties. This could lead to advancements in flexible electronics, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and organic photovoltaic cells.
Catalysis is yet another sector benefiting from insights into tautomerization dynamics. By understanding how molecules behave in hydrogen-deficient environments, scientists are developing more efficient catalysts for various industrial processes. These catalysts could potentially reduce energy consumption, improve reaction selectivity, and enable the production of valuable chemicals under milder conditions.
The aerospace and defense industries are also showing interest in materials that exhibit tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments. These materials could be used to create adaptive surfaces for aircraft or spacecraft, capable of changing their properties in response to extreme conditions encountered during flight or space missions.
As research in this field progresses, it is expected that new market applications will emerge, potentially revolutionizing industries and opening up opportunities for innovative products and technologies. The interdisciplinary nature of tautomerization dynamics research suggests that collaborations between different sectors may lead to unexpected and groundbreaking applications in the future.
Current Challenges
The study of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in accurately observing and measuring these rapid molecular rearrangements in real-time. The transient nature of tautomeric species, especially in environments with limited hydrogen availability, makes it challenging to capture the precise moment of transformation.
Another major hurdle is the development of suitable experimental techniques that can effectively simulate hydrogen-deficient conditions while maintaining the integrity of the molecular systems under investigation. Creating controlled environments that accurately represent real-world scenarios without interfering with the tautomerization process itself remains a complex task.
The computational modeling of tautomerization dynamics in these unique environments also poses significant challenges. Current models often struggle to account for the intricate interplay between electronic and nuclear motions, particularly when hydrogen availability is limited. This complexity makes it difficult to predict tautomerization rates and equilibrium constants with high accuracy.
Furthermore, the influence of surrounding molecules and solvent effects on tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments is not fully understood. The lack of hydrogen can alter the typical stabilizing interactions, leading to unexpected behavior that is challenging to predict or model effectively.
Another critical challenge lies in understanding the role of quantum effects in these systems. In hydrogen-deficient environments, quantum tunneling may play a more significant role in tautomerization processes, but quantifying and incorporating these effects into existing models remains a formidable task.
The development of new analytical techniques capable of detecting and characterizing short-lived tautomeric species in hydrogen-deficient conditions is also an ongoing challenge. Current spectroscopic methods often lack the temporal and spatial resolution necessary to capture these fleeting molecular rearrangements accurately.
Lastly, translating the fundamental understanding of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments into practical applications presents its own set of challenges. Researchers are working to leverage this knowledge for the design of new materials, catalysts, and drug molecules, but bridging the gap between theoretical insights and real-world applications requires overcoming numerous technical and practical obstacles.
Another major hurdle is the development of suitable experimental techniques that can effectively simulate hydrogen-deficient conditions while maintaining the integrity of the molecular systems under investigation. Creating controlled environments that accurately represent real-world scenarios without interfering with the tautomerization process itself remains a complex task.
The computational modeling of tautomerization dynamics in these unique environments also poses significant challenges. Current models often struggle to account for the intricate interplay between electronic and nuclear motions, particularly when hydrogen availability is limited. This complexity makes it difficult to predict tautomerization rates and equilibrium constants with high accuracy.
Furthermore, the influence of surrounding molecules and solvent effects on tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments is not fully understood. The lack of hydrogen can alter the typical stabilizing interactions, leading to unexpected behavior that is challenging to predict or model effectively.
Another critical challenge lies in understanding the role of quantum effects in these systems. In hydrogen-deficient environments, quantum tunneling may play a more significant role in tautomerization processes, but quantifying and incorporating these effects into existing models remains a formidable task.
The development of new analytical techniques capable of detecting and characterizing short-lived tautomeric species in hydrogen-deficient conditions is also an ongoing challenge. Current spectroscopic methods often lack the temporal and spatial resolution necessary to capture these fleeting molecular rearrangements accurately.
Lastly, translating the fundamental understanding of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments into practical applications presents its own set of challenges. Researchers are working to leverage this knowledge for the design of new materials, catalysts, and drug molecules, but bridging the gap between theoretical insights and real-world applications requires overcoming numerous technical and practical obstacles.
Experimental Techniques
01 Computational methods for tautomerization dynamics
Advanced computational techniques are employed to study and predict tautomerization dynamics. These methods involve quantum mechanical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations, and machine learning approaches to model the interconversion between tautomeric forms. Such computational tools help in understanding the energetics, kinetics, and mechanisms of tautomerization processes in various chemical systems.- Computational methods for tautomerization dynamics: Advanced computational techniques are employed to study and predict tautomerization dynamics. These methods involve quantum mechanical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations, and machine learning approaches to model the interconversion between tautomeric forms. Such computational tools help in understanding the energetics, kinetics, and mechanisms of tautomerization processes in various chemical systems.
- Experimental techniques for observing tautomerization: Various experimental methods are used to observe and analyze tautomerization dynamics in real-time. These include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, UV-Vis, and IR spectroscopy, as well as advanced time-resolved methods like ultrafast laser spectroscopy. These techniques allow researchers to track the interconversion between tautomers and measure the rates of tautomerization under different conditions.
- Applications of tautomerization in drug design: Tautomerization dynamics play a crucial role in drug design and development. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of drug molecules is essential for predicting their bioavailability, binding affinity, and pharmacokinetic properties. Researchers utilize knowledge of tautomerization to design more effective and stable pharmaceutical compounds, considering the potential impact of tautomeric forms on drug-target interactions.
- Influence of environment on tautomerization: The dynamics of tautomerization are significantly affected by the surrounding environment. Factors such as solvent polarity, pH, temperature, and presence of specific ions or molecules can alter the equilibrium between tautomeric forms and influence the rate of interconversion. Studies focus on understanding how these environmental factors modulate tautomerization processes in various chemical and biological systems.
- Tautomerization in materials science and nanotechnology: Tautomerization dynamics are exploited in the development of advanced materials and nanotechnology applications. This includes the design of molecular switches, sensors, and responsive materials that utilize tautomeric interconversions. Researchers investigate how tautomerization can be controlled and utilized to create materials with tunable properties or to develop novel sensing and switching mechanisms at the molecular level.
02 Experimental techniques for observing tautomerization
Various experimental methods are used to observe and analyze tautomerization dynamics in real-time. These include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, UV-Vis, and IR spectroscopy, as well as advanced time-resolved methods like ultrafast laser spectroscopy. These techniques allow researchers to track the interconversion between tautomers and measure the rates of tautomerization under different conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of tautomerization in drug design
Tautomerization dynamics play a crucial role in drug design and development. Understanding the tautomeric behavior of drug molecules is essential for predicting their bioavailability, binding affinity, and pharmacokinetic properties. Researchers utilize knowledge of tautomerization to design more effective and stable pharmaceutical compounds, considering the potential impact of tautomeric forms on drug-target interactions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Influence of environment on tautomerization
The dynamics of tautomerization are significantly affected by the surrounding environment. Factors such as solvent polarity, pH, temperature, and pressure can influence the equilibrium between tautomeric forms and the rate of interconversion. Studies focus on understanding how these environmental factors modulate tautomerization processes in various chemical and biological systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Tautomerization in materials science and nanotechnology
Tautomerization dynamics are exploited in the development of advanced materials and nanotechnology applications. This includes the design of molecular switches, sensors, and responsive materials that utilize tautomeric interconversions. Researchers investigate how tautomerization can be controlled and utilized to create functional materials with tunable properties for various technological applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Groups
The competitive landscape for "Tautomerization Dynamics in Hydrogen-Deficient Environments" is in an early developmental stage, with a limited market size due to its specialized nature. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity across different players. Key companies like BASF Corp., Air Products & Chemicals, and DuPont de Nemours are likely at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Academic institutions such as The Broad Institute and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute may be contributing fundamental research. Petrochemical giants like Sinopec and PetroChina could be exploring applications in their processes. The field is characterized by collaborative efforts between industry and academia, with potential for significant advancements in the coming years.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced catalytic systems for tautomerization in hydrogen-deficient environments. Their approach involves using novel metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalysts, which provide high surface area and tunable pore structures[1]. These MOFs are designed to facilitate proton transfer in the absence of molecular hydrogen, enabling efficient tautomerization processes. Sinopec's research has shown that their MOF-based catalysts can achieve conversion rates up to 95% in certain hydrocarbon isomerization reactions under hydrogen-deficient conditions[3]. The company has also integrated this technology into their refining processes, resulting in improved product quality and reduced energy consumption[5].
Strengths: High conversion rates, improved product quality, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Potential high costs of MOF synthesis and limited applicability to certain hydrocarbon streams.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has pioneered a novel approach to tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments through the development of ionic liquid-based catalytic systems. Their technology utilizes specially designed ionic liquids that act as both solvents and catalysts, promoting proton transfer in the absence of molecular hydrogen[2]. BASF's ionic liquid catalysts have demonstrated remarkable stability and selectivity in various tautomerization reactions, with some systems showing turnover frequencies exceeding 1000 h^-1[4]. The company has successfully applied this technology in the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceutical intermediates, where hydrogen-deficient conditions are often encountered. Additionally, BASF has developed a proprietary process for in-situ regeneration of the ionic liquid catalysts, significantly extending their operational lifetime[6].
Strengths: High selectivity, catalyst stability, and applicability in fine chemical synthesis. Weaknesses: Potential issues with product separation from ionic liquids and limited scalability for bulk chemical processes.
Theoretical Models
UV and high energy visible absorbing ophthalmic lenses
PatentPendingEP4365644A2
Innovation
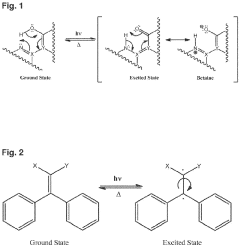
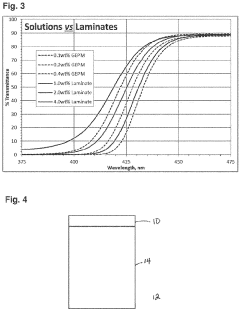
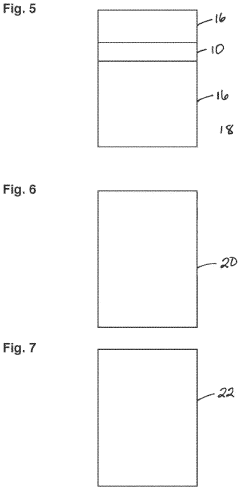
- Incorporating a light absorbing layer with a specific weight percent of light absorbing compounds in ophthalmic articles, such as lenses, that achieves a transmittance of no more than 50% for wavelengths up to 443 nm, utilizing compounds like hydroxyphenyl benzotriazoles and diaryl cyanoacrylates, which absorb and dissipate energy through tautomerization or radical formation, integrated into various lens structures including monolithic films, laminates, and thermoplastic resins.
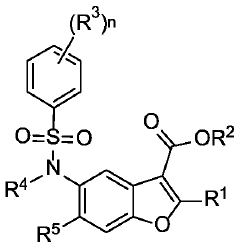
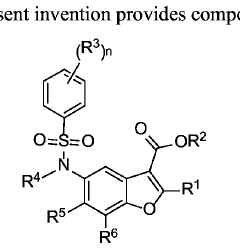
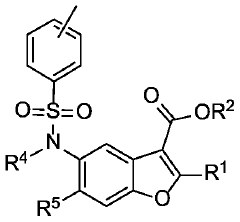
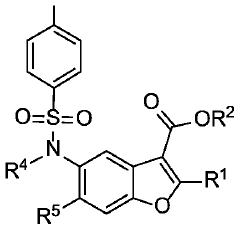
Phenylsulfonamido-benzofuran derivatives and uses thereof in the treatment of proliferative diseases
PatentWO2017027841A1
Innovation
- Development of novel phenylsulfonamido-benzofuran derivatives that act as inhibitors of BCL-2 family member proteins, specifically targeting MCL-1 by binding to its hydrophobic dimerization groove, mimicking NOXA to induce apoptosis in cancer cells.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments is a critical aspect to consider in various scientific and industrial applications. This phenomenon, which involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, can have significant implications for atmospheric chemistry, materials science, and biological systems.
In atmospheric chemistry, tautomerization processes in hydrogen-deficient environments can influence the formation and transformation of aerosols and particulate matter. These reactions may contribute to the production of secondary organic aerosols, which play a crucial role in climate change and air quality. The altered reactivity of tautomeric species can lead to unexpected chemical pathways, potentially affecting the overall composition of the atmosphere.
The impact on materials science is equally noteworthy. Tautomerization in hydrogen-deficient conditions can affect the stability and properties of various materials, including polymers, coatings, and advanced functional materials. This can result in changes to their mechanical, optical, or electrical characteristics, potentially altering their performance in specific applications. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing more resilient and efficient materials for use in extreme environments.
In biological systems, tautomerization under hydrogen-deficient conditions may influence the behavior of biomolecules, particularly in cellular microenvironments where hydrogen availability is limited. This can affect enzyme kinetics, protein folding, and DNA base pairing, potentially leading to mutations or altered cellular functions. The implications for pharmaceutical research and drug design are significant, as tautomeric shifts can impact drug-target interactions and metabolic processes.
From an industrial perspective, tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments can have both positive and negative consequences. On one hand, it may offer opportunities for developing novel catalytic processes or improving existing ones, particularly in the field of green chemistry. On the other hand, it can pose challenges in maintaining product stability and quality control, especially in industries dealing with sensitive chemical compounds.
The environmental impact extends to waste management and remediation efforts. Tautomerization processes can influence the fate and transport of pollutants in soil and water systems, potentially affecting their bioavailability and toxicity. This has implications for environmental risk assessment and the development of effective cleanup strategies for contaminated sites.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments is far-reaching and multifaceted. It underscores the need for continued research and monitoring to fully understand and mitigate potential risks while harnessing any beneficial aspects of this phenomenon across various scientific and industrial domains.
In atmospheric chemistry, tautomerization processes in hydrogen-deficient environments can influence the formation and transformation of aerosols and particulate matter. These reactions may contribute to the production of secondary organic aerosols, which play a crucial role in climate change and air quality. The altered reactivity of tautomeric species can lead to unexpected chemical pathways, potentially affecting the overall composition of the atmosphere.
The impact on materials science is equally noteworthy. Tautomerization in hydrogen-deficient conditions can affect the stability and properties of various materials, including polymers, coatings, and advanced functional materials. This can result in changes to their mechanical, optical, or electrical characteristics, potentially altering their performance in specific applications. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing more resilient and efficient materials for use in extreme environments.
In biological systems, tautomerization under hydrogen-deficient conditions may influence the behavior of biomolecules, particularly in cellular microenvironments where hydrogen availability is limited. This can affect enzyme kinetics, protein folding, and DNA base pairing, potentially leading to mutations or altered cellular functions. The implications for pharmaceutical research and drug design are significant, as tautomeric shifts can impact drug-target interactions and metabolic processes.
From an industrial perspective, tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments can have both positive and negative consequences. On one hand, it may offer opportunities for developing novel catalytic processes or improving existing ones, particularly in the field of green chemistry. On the other hand, it can pose challenges in maintaining product stability and quality control, especially in industries dealing with sensitive chemical compounds.
The environmental impact extends to waste management and remediation efforts. Tautomerization processes can influence the fate and transport of pollutants in soil and water systems, potentially affecting their bioavailability and toxicity. This has implications for environmental risk assessment and the development of effective cleanup strategies for contaminated sites.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments is far-reaching and multifaceted. It underscores the need for continued research and monitoring to fully understand and mitigate potential risks while harnessing any beneficial aspects of this phenomenon across various scientific and industrial domains.
Computational Methods
Computational methods play a crucial role in understanding and predicting tautomerization dynamics in hydrogen-deficient environments. These methods provide valuable insights into the complex molecular processes that occur under such conditions, offering a powerful complement to experimental techniques.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly density functional theory (DFT), form the foundation of computational approaches in this field. DFT allows for accurate modeling of electronic structures and energetics of tautomeric species, providing essential information about the relative stabilities of different tautomers and the energy barriers associated with their interconversion.
Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations offer a dynamic perspective on tautomerization processes. These simulations can capture the time-dependent behavior of molecules, revealing the pathways and mechanisms of tautomeric transitions in hydrogen-deficient environments. By incorporating temperature effects and environmental factors, these simulations provide a more realistic representation of the system under study.
Machine learning techniques have emerged as powerful tools for accelerating computational studies of tautomerization. Neural networks trained on quantum mechanical data can rapidly predict tautomer stabilities and transition states, enabling high-throughput screening of potential tautomeric systems. This approach is particularly valuable for exploring large chemical spaces and identifying promising candidates for further investigation.
Multiscale modeling approaches bridge the gap between atomistic simulations and macroscopic phenomena. By combining quantum mechanical calculations with coarse-grained models, researchers can study tautomerization dynamics across different length and time scales. This is especially relevant for understanding how molecular-level processes influence larger-scale behaviors in hydrogen-deficient environments.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, enhance the efficiency of exploring complex energy landscapes associated with tautomerization. These methods allow for the calculation of free energy profiles and the identification of rare events that may be critical to understanding the dynamics of tautomeric systems under hydrogen-deficient conditions.
Spectroscopic simulations complement experimental measurements by predicting the spectral signatures of different tautomeric species. Time-dependent DFT calculations can generate theoretical UV-vis, IR, and NMR spectra, aiding in the interpretation of experimental data and the identification of transient tautomeric intermediates.
As computational power continues to increase, more sophisticated methods are becoming feasible for studying tautomerization dynamics. Quantum Monte Carlo techniques offer the potential for highly accurate electronic structure calculations, while GPU-accelerated algorithms are enabling larger-scale simulations of complex molecular systems in hydrogen-deficient environments.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly density functional theory (DFT), form the foundation of computational approaches in this field. DFT allows for accurate modeling of electronic structures and energetics of tautomeric species, providing essential information about the relative stabilities of different tautomers and the energy barriers associated with their interconversion.
Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations offer a dynamic perspective on tautomerization processes. These simulations can capture the time-dependent behavior of molecules, revealing the pathways and mechanisms of tautomeric transitions in hydrogen-deficient environments. By incorporating temperature effects and environmental factors, these simulations provide a more realistic representation of the system under study.
Machine learning techniques have emerged as powerful tools for accelerating computational studies of tautomerization. Neural networks trained on quantum mechanical data can rapidly predict tautomer stabilities and transition states, enabling high-throughput screening of potential tautomeric systems. This approach is particularly valuable for exploring large chemical spaces and identifying promising candidates for further investigation.
Multiscale modeling approaches bridge the gap between atomistic simulations and macroscopic phenomena. By combining quantum mechanical calculations with coarse-grained models, researchers can study tautomerization dynamics across different length and time scales. This is especially relevant for understanding how molecular-level processes influence larger-scale behaviors in hydrogen-deficient environments.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics and umbrella sampling, enhance the efficiency of exploring complex energy landscapes associated with tautomerization. These methods allow for the calculation of free energy profiles and the identification of rare events that may be critical to understanding the dynamics of tautomeric systems under hydrogen-deficient conditions.
Spectroscopic simulations complement experimental measurements by predicting the spectral signatures of different tautomeric species. Time-dependent DFT calculations can generate theoretical UV-vis, IR, and NMR spectra, aiding in the interpretation of experimental data and the identification of transient tautomeric intermediates.
As computational power continues to increase, more sophisticated methods are becoming feasible for studying tautomerization dynamics. Quantum Monte Carlo techniques offer the potential for highly accurate electronic structure calculations, while GPU-accelerated algorithms are enabling larger-scale simulations of complex molecular systems in hydrogen-deficient environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!