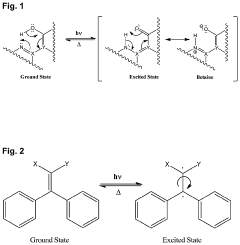
Tautomerization in Luminescent Materials: Brightness Optimization
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Tautomerization Background and Objectives
Tautomerization, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, has gained significant attention in the field of luminescent materials due to its potential for optimizing brightness. This phenomenon involves the rapid interconversion between structural isomers, known as tautomers, which can profoundly impact the photophysical properties of luminescent compounds. The study of tautomerization in luminescent materials has evolved over the past few decades, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance light-emitting devices and fluorescent probes.
The primary objective of research in this area is to harness tautomerization to enhance the brightness of luminescent materials. This goal is motivated by the need for more efficient and brighter materials in various applications, including organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), fluorescence microscopy, and chemical sensing. By understanding and controlling tautomerization processes, researchers aim to develop novel materials with improved quantum yields and reduced non-radiative decay pathways.
The evolution of tautomerization research in luminescent materials has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies focused on identifying tautomeric systems and elucidating their basic photophysical properties. As analytical techniques advanced, researchers gained deeper insights into the dynamics of tautomerization and its impact on excited-state processes. More recently, the field has shifted towards rational design strategies that exploit tautomerization to achieve desired luminescent properties.
Current technological trends in this area include the development of stimuli-responsive luminescent materials that utilize tautomerization for sensing applications, the exploration of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) processes for highly efficient emitters, and the integration of tautomeric systems into host-guest complexes for tunable emission properties. Additionally, computational methods have become increasingly important in predicting and optimizing tautomerization-based luminescent systems.
The anticipated technological goals in this field encompass several key areas. Researchers aim to develop luminescent materials with near-unity quantum yields by leveraging tautomerization to minimize non-radiative decay pathways. Another objective is to create smart materials that can modulate their emission properties through controlled tautomerization in response to external stimuli. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in utilizing tautomerization for the design of multi-color emissive systems and the development of novel photoswitchable materials for advanced optical applications.
The primary objective of research in this area is to harness tautomerization to enhance the brightness of luminescent materials. This goal is motivated by the need for more efficient and brighter materials in various applications, including organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), fluorescence microscopy, and chemical sensing. By understanding and controlling tautomerization processes, researchers aim to develop novel materials with improved quantum yields and reduced non-radiative decay pathways.
The evolution of tautomerization research in luminescent materials has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies focused on identifying tautomeric systems and elucidating their basic photophysical properties. As analytical techniques advanced, researchers gained deeper insights into the dynamics of tautomerization and its impact on excited-state processes. More recently, the field has shifted towards rational design strategies that exploit tautomerization to achieve desired luminescent properties.
Current technological trends in this area include the development of stimuli-responsive luminescent materials that utilize tautomerization for sensing applications, the exploration of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) processes for highly efficient emitters, and the integration of tautomeric systems into host-guest complexes for tunable emission properties. Additionally, computational methods have become increasingly important in predicting and optimizing tautomerization-based luminescent systems.
The anticipated technological goals in this field encompass several key areas. Researchers aim to develop luminescent materials with near-unity quantum yields by leveraging tautomerization to minimize non-radiative decay pathways. Another objective is to create smart materials that can modulate their emission properties through controlled tautomerization in response to external stimuli. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in utilizing tautomerization for the design of multi-color emissive systems and the development of novel photoswitchable materials for advanced optical applications.
Market Analysis for Luminescent Materials
The luminescent materials market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global market for luminescent materials is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that reflects the expanding applications and technological advancements in this field.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the widespread adoption of luminescent materials in display technologies. The rise of OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays in smartphones, televisions, and other consumer electronics has created a surge in demand for high-performance luminescent materials. This trend is expected to continue as manufacturers seek to improve display quality, energy efficiency, and product lifespan.
The lighting industry represents another significant market segment for luminescent materials. With the global shift towards energy-efficient lighting solutions, LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology has gained prominence. Luminescent materials play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and color quality of LED lighting, contributing to the market's expansion in both residential and commercial applications.
In the automotive sector, luminescent materials are increasingly being utilized for interior and exterior lighting, as well as in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The growing emphasis on vehicle safety and aesthetics is driving the demand for innovative lighting solutions, further boosting the market for luminescent materials in this industry.
The healthcare and life sciences sectors also present substantial opportunities for luminescent materials. Fluorescent probes and markers are widely used in medical imaging, diagnostics, and research applications. As these fields continue to advance, the demand for high-performance luminescent materials is expected to grow, particularly in areas such as bioimaging and drug discovery.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for luminescent materials, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with strong demand from established industries and ongoing research and development activities.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialized manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the performance and efficiency of luminescent materials, with a particular focus on enhancing brightness and color purity.
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the widespread adoption of luminescent materials in display technologies. The rise of OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays in smartphones, televisions, and other consumer electronics has created a surge in demand for high-performance luminescent materials. This trend is expected to continue as manufacturers seek to improve display quality, energy efficiency, and product lifespan.
The lighting industry represents another significant market segment for luminescent materials. With the global shift towards energy-efficient lighting solutions, LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology has gained prominence. Luminescent materials play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and color quality of LED lighting, contributing to the market's expansion in both residential and commercial applications.
In the automotive sector, luminescent materials are increasingly being utilized for interior and exterior lighting, as well as in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The growing emphasis on vehicle safety and aesthetics is driving the demand for innovative lighting solutions, further boosting the market for luminescent materials in this industry.
The healthcare and life sciences sectors also present substantial opportunities for luminescent materials. Fluorescent probes and markers are widely used in medical imaging, diagnostics, and research applications. As these fields continue to advance, the demand for high-performance luminescent materials is expected to grow, particularly in areas such as bioimaging and drug discovery.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for luminescent materials, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with strong demand from established industries and ongoing research and development activities.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialized manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the performance and efficiency of luminescent materials, with a particular focus on enhancing brightness and color purity.
Current Challenges in Brightness Optimization
The optimization of brightness in luminescent materials through tautomerization presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the precise control of tautomeric equilibrium. Tautomerization, being a dynamic process, can lead to unpredictable shifts in molecular structure, which directly impacts the luminescent properties of the material. Achieving a stable and controllable tautomeric state that maximizes brightness remains a complex task.
Another major challenge lies in the design of molecular structures that can effectively harness tautomerization for enhanced luminescence. While tautomerization can potentially increase brightness, it can also lead to undesired energy dissipation pathways, reducing overall luminescent efficiency. Balancing these competing effects requires intricate molecular engineering and a deep understanding of structure-property relationships.
The environmental sensitivity of tautomeric systems poses yet another hurdle. Factors such as temperature, pH, and solvent polarity can significantly influence tautomeric equilibrium, leading to inconsistent luminescent performance across different conditions. Developing materials that maintain optimal brightness across a wide range of environmental parameters is crucial for practical applications but remains technically challenging.
Furthermore, the scalability of tautomerization-based brightness optimization techniques presents a significant industrial challenge. While promising results may be achieved in laboratory settings, translating these findings into large-scale production processes while maintaining consistent performance is often problematic. This scaling issue is particularly acute when considering the potential applications in areas such as display technologies or biomedical imaging.
The long-term stability of tautomeric luminescent materials is another area of concern. Many materials that exhibit impressive initial brightness may suffer from degradation over time due to repeated tautomeric switching or exposure to ambient conditions. Enhancing the durability and longevity of these materials without compromising their luminescent properties is a key focus of current research efforts.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating tautomerization-optimized luminescent materials into existing technological frameworks cannot be overlooked. Many current applications are designed around conventional luminescent materials, and the unique properties of tautomeric systems may require significant adaptations in device architecture and manufacturing processes. Overcoming these integration challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of these advanced materials in real-world applications.
Another major challenge lies in the design of molecular structures that can effectively harness tautomerization for enhanced luminescence. While tautomerization can potentially increase brightness, it can also lead to undesired energy dissipation pathways, reducing overall luminescent efficiency. Balancing these competing effects requires intricate molecular engineering and a deep understanding of structure-property relationships.
The environmental sensitivity of tautomeric systems poses yet another hurdle. Factors such as temperature, pH, and solvent polarity can significantly influence tautomeric equilibrium, leading to inconsistent luminescent performance across different conditions. Developing materials that maintain optimal brightness across a wide range of environmental parameters is crucial for practical applications but remains technically challenging.
Furthermore, the scalability of tautomerization-based brightness optimization techniques presents a significant industrial challenge. While promising results may be achieved in laboratory settings, translating these findings into large-scale production processes while maintaining consistent performance is often problematic. This scaling issue is particularly acute when considering the potential applications in areas such as display technologies or biomedical imaging.
The long-term stability of tautomeric luminescent materials is another area of concern. Many materials that exhibit impressive initial brightness may suffer from degradation over time due to repeated tautomeric switching or exposure to ambient conditions. Enhancing the durability and longevity of these materials without compromising their luminescent properties is a key focus of current research efforts.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating tautomerization-optimized luminescent materials into existing technological frameworks cannot be overlooked. Many current applications are designed around conventional luminescent materials, and the unique properties of tautomeric systems may require significant adaptations in device architecture and manufacturing processes. Overcoming these integration challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of these advanced materials in real-world applications.
Existing Brightness Enhancement Strategies
01 Composition of luminescent materials
The brightness of luminescent materials can be enhanced by carefully selecting and combining different chemical compounds. This may involve using rare earth elements, phosphors, or other luminescent substances to create materials with improved light emission properties. The composition can be optimized to achieve higher quantum efficiency and better color rendering.- Composition of luminescent materials: The brightness of luminescent materials can be enhanced by carefully selecting and combining different chemical compounds. This includes the use of rare earth elements, phosphors, and other luminescent substances. The composition and ratio of these materials significantly affect the overall brightness and efficiency of the luminescent material.
- Structural design for improved light emission: The structural design of luminescent materials plays a crucial role in their brightness. This includes optimizing particle size, crystal structure, and surface morphology. Nanostructured materials and layered designs can enhance light emission and reduce energy loss, resulting in brighter luminescent materials.
- Doping techniques for brightness enhancement: Doping luminescent materials with specific elements or compounds can significantly improve their brightness. This technique involves introducing controlled impurities into the host material to modify its electronic structure and optical properties. Proper doping can lead to increased quantum efficiency and higher luminescence intensity.
- Surface treatment and coating methods: Various surface treatment and coating methods can be employed to enhance the brightness of luminescent materials. These techniques include applying protective coatings, surface passivation, and creating anti-reflective layers. Such treatments can reduce surface defects, prevent degradation, and improve light extraction efficiency.
- Excitation and energy transfer optimization: Optimizing the excitation process and energy transfer mechanisms within luminescent materials can lead to increased brightness. This involves designing materials with efficient absorption of excitation energy, minimizing non-radiative energy losses, and enhancing energy transfer between different luminescent centers. Techniques such as sensitization and up-conversion can be utilized to achieve higher brightness levels.
02 Structural modifications for improved brightness
Altering the physical structure of luminescent materials can significantly impact their brightness. This may include creating nanostructures, layered compositions, or specific crystal structures that enhance light emission and reduce energy loss. Such modifications can improve light extraction efficiency and overall luminous output.Expand Specific Solutions03 Doping techniques for enhanced luminescence
Introducing specific dopants or activators into the host material can greatly enhance the brightness of luminescent materials. This technique involves carefully selecting and controlling the concentration of dopants to optimize energy transfer and light emission processes. Proper doping can lead to increased quantum yield and improved luminous efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surface treatment and coating methods
Applying various surface treatments or coatings to luminescent materials can enhance their brightness. These methods may include passivation techniques, anti-reflection coatings, or plasmonic structures that improve light extraction and reduce surface defects. Such treatments can significantly increase the overall light output and efficiency of the luminescent material.Expand Specific Solutions05 Optimization of excitation and emission processes
Improving the brightness of luminescent materials can be achieved by optimizing the excitation and emission processes. This may involve developing novel excitation sources, enhancing energy transfer mechanisms, or reducing non-radiative decay pathways. By fine-tuning these processes, the overall quantum efficiency and brightness of the luminescent material can be significantly increased.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminescent Materials Industry
The field of tautomerization in luminescent materials for brightness optimization is in a dynamic growth phase, with increasing market size driven by demand for high-performance lighting solutions. The technology is approaching maturity, but significant advancements are still being pursued. Key players like 3M Innovative Properties, Merck Patent GmbH, and Koninklijke Philips NV are leading research efforts, leveraging their expertise in materials science and optoelectronics. Companies such as Sumitomo Chemical and Nichia Corp. are also making notable contributions, particularly in developing novel luminescent compounds. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established multinational corporations and specialized research institutions, all vying to enhance luminescent material efficiency and brightness through innovative tautomeric designs.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M Innovative Properties Co. has developed novel approaches to optimize brightness in luminescent materials through tautomerization, particularly in the field of optical films and coatings. Their research focuses on creating advanced materials that exploit tautomeric equilibria to enhance light emission and management. 3M has patented several fluorescent dye compositions that undergo controlled tautomeric interconversion, resulting in improved quantum yield and color stability[13]. The company has also explored the use of tautomeric compounds in light-converting layers for display applications, achieving enhanced brightness and viewing angle performance[14]. Additionally, 3M has developed tautomeric additives for optical adhesives and encapsulants, which contribute to improved light extraction efficiency in LED packages and displays[15].
Strengths: Versatile application across multiple industries, excellent optical properties, and potential for integration with existing manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Challenges in achieving long-term environmental stability and potential for color shift under extreme conditions.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Koninklijke Philips NV has made significant advancements in brightness optimization through tautomerization in luminescent materials, particularly in the field of solid-state lighting. Their approach involves developing phosphor materials that exhibit controlled tautomeric behavior, allowing for improved energy conversion and enhanced luminous output. Philips has patented several compositions incorporating rare-earth doped aluminate and silicate phosphors that demonstrate tautomeric shifts, resulting in broader emission spectra and higher luminous efficacy[10]. The company has also explored the use of organic-inorganic hybrid materials that leverage intramolecular proton transfer to achieve tunable emission properties and improved thermal stability[11]. Additionally, Philips has invested in research on quantum dot materials with tautomeric ligands, enabling precise control over the emission wavelength and color rendering properties[12].
Strengths: High luminous efficacy, excellent color quality, and compatibility with various lighting applications. Weaknesses: Potential for thermal degradation and challenges in maintaining consistent performance across different operating conditions.
Core Innovations in Tautomeric Luminescence
UV and high energy visible absorbing ophthalmic lenses
PatentActiveUS12007629B2
Innovation
- The development of ophthalmic articles with a light-absorbing layer containing a weight percent of light-absorbing compounds in the range of 0.1 to 10, with a transmittance of no more than 50% for light wavelengths up to 443 nm, incorporated into various forms such as monolithic films, adhesive layers, or composite lenses, using compounds that absorb energy through mechanisms like hydrogen atom transfer or double bond breaking, allowing for effective UV and HEV light blocking while minimizing coloration.
A method of improving the luminescence of luminescent materials and luminescent materials when improved by the method
PatentInactiveGB788451A
Innovation
- Milling luminescent materials in a substantially non-acidic liquid medium, followed by acid and alkaline washing, and optionally drying before acid washing, to break down particles and enhance the effectiveness of subsequent chemical treatments, thereby increasing luminescent brightness.
Environmental Impact of Luminescent Materials
The environmental impact of luminescent materials used in tautomerization-based brightness optimization is a critical consideration in the development and application of these technologies. These materials, while offering significant advancements in lighting efficiency and performance, also pose potential risks to ecosystems and human health if not properly managed throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminescent materials is their production process. The synthesis of these compounds often involves the use of rare earth elements and heavy metals, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental contamination if not sourced and processed responsibly. Mining and refining these elements can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution, particularly in regions with less stringent environmental regulations.
During the use phase, luminescent materials generally contribute positively to environmental sustainability by improving energy efficiency in lighting applications. Tautomerization-optimized luminescent materials can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional lighting technologies, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. However, the potential for light pollution, especially in outdoor applications, remains a concern that needs to be addressed through proper design and implementation.
End-of-life management of luminescent materials presents another set of environmental challenges. Improper disposal can lead to the release of toxic substances into soil and water systems. Recycling these materials is complex due to their composition, often requiring specialized processes to recover valuable components while safely disposing of hazardous elements. The development of efficient recycling technologies and the implementation of robust waste management systems are crucial for mitigating the long-term environmental impact of these materials.
The potential for bioaccumulation of certain components of luminescent materials in ecosystems is an area that requires ongoing research and monitoring. Some rare earth elements and heavy metals used in these materials can persist in the environment and accumulate in food chains, potentially affecting wildlife and human health over time. This necessitates careful consideration of material selection and design to minimize the use of potentially harmful substances without compromising performance.
Efforts to address these environmental concerns are driving innovation in the field of luminescent materials. Research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, exploring bio-based alternatives, and improving the recyclability and biodegradability of these materials. Additionally, life cycle assessments are increasingly being employed to evaluate the overall environmental footprint of luminescent materials from production to disposal, guiding more sustainable practices in their development and use.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminescent materials is their production process. The synthesis of these compounds often involves the use of rare earth elements and heavy metals, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental contamination if not sourced and processed responsibly. Mining and refining these elements can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution, particularly in regions with less stringent environmental regulations.
During the use phase, luminescent materials generally contribute positively to environmental sustainability by improving energy efficiency in lighting applications. Tautomerization-optimized luminescent materials can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional lighting technologies, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. However, the potential for light pollution, especially in outdoor applications, remains a concern that needs to be addressed through proper design and implementation.
End-of-life management of luminescent materials presents another set of environmental challenges. Improper disposal can lead to the release of toxic substances into soil and water systems. Recycling these materials is complex due to their composition, often requiring specialized processes to recover valuable components while safely disposing of hazardous elements. The development of efficient recycling technologies and the implementation of robust waste management systems are crucial for mitigating the long-term environmental impact of these materials.
The potential for bioaccumulation of certain components of luminescent materials in ecosystems is an area that requires ongoing research and monitoring. Some rare earth elements and heavy metals used in these materials can persist in the environment and accumulate in food chains, potentially affecting wildlife and human health over time. This necessitates careful consideration of material selection and design to minimize the use of potentially harmful substances without compromising performance.
Efforts to address these environmental concerns are driving innovation in the field of luminescent materials. Research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, exploring bio-based alternatives, and improving the recyclability and biodegradability of these materials. Additionally, life cycle assessments are increasingly being employed to evaluate the overall environmental footprint of luminescent materials from production to disposal, guiding more sustainable practices in their development and use.
Quantum Yield Measurement Techniques
Quantum yield measurement techniques are crucial for evaluating the brightness optimization of luminescent materials undergoing tautomerization. These methods provide quantitative data on the efficiency of light emission, enabling researchers to assess the impact of tautomeric forms on luminescence performance.
One widely used technique is the integrating sphere method. This approach involves placing the sample inside a highly reflective sphere, which collects all emitted light. By comparing the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed, researchers can accurately determine the quantum yield. This method is particularly valuable for materials with complex tautomeric equilibria, as it accounts for all emission pathways.
Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy offers another powerful tool for quantum yield measurements. By analyzing the decay of luminescence over time, scientists can distinguish between different tautomeric species and their respective contributions to overall brightness. This technique is especially useful for materials where tautomerization occurs on timescales comparable to the luminescence lifetime.
Comparative methods represent a simpler approach, wherein the quantum yield of an unknown sample is determined by comparison to a well-characterized standard. While less absolute than integrating sphere measurements, this technique can provide rapid screening of multiple tautomeric forms, facilitating the optimization process.
Photoacoustic spectroscopy has emerged as a complementary technique for quantum yield determination. By measuring the heat generated from non-radiative relaxation processes, researchers can indirectly quantify the quantum yield. This method is particularly valuable for materials where tautomerization significantly affects non-radiative pathways.
Advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM), enable spatially resolved quantum yield measurements. This approach is invaluable for materials where tautomerization rates vary across different regions or under different local environments, providing insights into the spatial distribution of brightness optimization.
Computational methods have also gained prominence in quantum yield predictions. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations, coupled with time-dependent DFT, allow researchers to model the electronic structures of different tautomeric forms and estimate their relative quantum yields. These theoretical approaches guide experimental efforts by identifying promising tautomeric structures for brightness optimization.
The choice of quantum yield measurement technique depends on various factors, including the specific properties of the luminescent material, the nature of the tautomerization process, and the desired precision of the measurements. Often, a combination of techniques is employed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the brightness optimization process in tautomeric luminescent materials.
One widely used technique is the integrating sphere method. This approach involves placing the sample inside a highly reflective sphere, which collects all emitted light. By comparing the number of photons emitted to the number absorbed, researchers can accurately determine the quantum yield. This method is particularly valuable for materials with complex tautomeric equilibria, as it accounts for all emission pathways.
Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy offers another powerful tool for quantum yield measurements. By analyzing the decay of luminescence over time, scientists can distinguish between different tautomeric species and their respective contributions to overall brightness. This technique is especially useful for materials where tautomerization occurs on timescales comparable to the luminescence lifetime.
Comparative methods represent a simpler approach, wherein the quantum yield of an unknown sample is determined by comparison to a well-characterized standard. While less absolute than integrating sphere measurements, this technique can provide rapid screening of multiple tautomeric forms, facilitating the optimization process.
Photoacoustic spectroscopy has emerged as a complementary technique for quantum yield determination. By measuring the heat generated from non-radiative relaxation processes, researchers can indirectly quantify the quantum yield. This method is particularly valuable for materials where tautomerization significantly affects non-radiative pathways.
Advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM), enable spatially resolved quantum yield measurements. This approach is invaluable for materials where tautomerization rates vary across different regions or under different local environments, providing insights into the spatial distribution of brightness optimization.
Computational methods have also gained prominence in quantum yield predictions. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations, coupled with time-dependent DFT, allow researchers to model the electronic structures of different tautomeric forms and estimate their relative quantum yields. These theoretical approaches guide experimental efforts by identifying promising tautomeric structures for brightness optimization.
The choice of quantum yield measurement technique depends on various factors, including the specific properties of the luminescent material, the nature of the tautomerization process, and the desired precision of the measurements. Often, a combination of techniques is employed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the brightness optimization process in tautomeric luminescent materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!