Future Trends in Butyrate Supplementation for Health Benefits
Butyrate Supplementation Background and Objectives
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut bacteria during the fermentation of dietary fiber, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. The evolution of butyrate supplementation can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began to uncover the importance of gut microbiota in human health. As our understanding of the gut-brain axis and the role of the microbiome in various physiological processes has expanded, so too has the interest in butyrate as a therapeutic agent.
The primary objective of butyrate supplementation is to harness its diverse health-promoting properties, which include anti-inflammatory effects, improved gut barrier function, and potential benefits for metabolic health. Research has shown that butyrate may play a crucial role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis, regulating immune responses, and even influencing cognitive function. These findings have led to a surge in studies exploring the potential applications of butyrate supplementation across various health conditions.
One of the key drivers behind the growing interest in butyrate supplementation is the recognition of the "Western diet" problem. The typical Western diet, characterized by high consumption of processed foods and low fiber intake, has been associated with a reduction in butyrate-producing bacteria in the gut. This dietary shift has potentially contributed to the rise in inflammatory and metabolic disorders, creating a need for interventions that can restore butyrate levels and promote gut health.
The technological evolution of butyrate supplementation has focused on addressing the challenges associated with its delivery and bioavailability. Early forms of butyrate supplements were often limited by their strong odor and poor stability. However, recent advancements have led to the development of more palatable and effective formulations, such as microencapsulated butyrate and prodrug forms that can target specific areas of the gastrointestinal tract.
Looking ahead, the future trends in butyrate supplementation are likely to be shaped by several factors. These include the ongoing research into the microbiome and its impact on health, the development of personalized nutrition approaches, and the integration of butyrate supplementation with other therapeutic strategies. There is also growing interest in exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining butyrate with other bioactive compounds or probiotics to enhance its health benefits.
As we move forward, the objectives of butyrate supplementation research and development are expected to expand beyond gut health. Emerging areas of investigation include the role of butyrate in neurological disorders, cancer prevention, and metabolic syndrome management. Additionally, there is a push towards developing more targeted delivery systems that can enhance the efficacy of butyrate supplementation while minimizing potential side effects.
Market Analysis for Butyrate Health Products
The global market for butyrate health products has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of gut health and its impact on overall well-being. The market encompasses a wide range of products, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages fortified with butyrate or its precursors. As consumers become more health-conscious and seek natural solutions for digestive issues, the demand for butyrate-based products is expected to continue its upward trajectory.
Market research indicates that the butyrate supplement market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising prevalence of digestive disorders, increasing adoption of preventive healthcare approaches, and growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of butyrate supplementation. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific regions.
The market is segmented based on product type, with oral supplements dominating the landscape. However, there is a growing trend towards incorporating butyrate into functional foods and beverages, offering consumers more convenient and palatable options for supplementation. This diversification is expected to open up new opportunities for market players and drive further growth in the coming years.
Key consumer demographics driving market growth include health-conscious millennials, aging populations seeking digestive health solutions, and individuals with specific health conditions such as inflammatory bowel diseases. The increasing focus on personalized nutrition and microbiome health is also contributing to the market expansion, as consumers seek tailored solutions for their gut health needs.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as limited consumer awareness in some regions, regulatory hurdles for product claims, and the need for more extensive clinical research to support efficacy claims. Additionally, the market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups vying for market share.
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the future of the butyrate health products market. These include the development of novel delivery systems to improve bioavailability, the integration of butyrate with other synergistic ingredients for enhanced health benefits, and the expansion of product offerings to target specific health conditions beyond gut health. As research continues to uncover new potential applications for butyrate supplementation, the market is poised for further diversification and growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Supplementation
Despite the growing interest in butyrate supplementation for its potential health benefits, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the poor bioavailability of oral butyrate supplements. The human digestive system rapidly absorbs butyrate in the upper gastrointestinal tract, limiting its delivery to the colon where it exerts most of its beneficial effects. This absorption issue significantly reduces the effectiveness of traditional butyrate supplements.
Another challenge lies in the unpleasant taste and odor of butyrate, which can lead to poor patient compliance. The strong, rancid smell of butyrate makes it difficult for many individuals to consistently consume the supplement, potentially limiting its long-term health benefits. This sensory issue has prompted researchers to explore various encapsulation and delivery methods to mask the undesirable organoleptic properties of butyrate.
The optimal dosage and formulation of butyrate supplements remain unclear, presenting a significant challenge for both researchers and healthcare providers. The lack of standardized dosing guidelines makes it difficult to determine the most effective and safe amount of butyrate for different health conditions and patient populations. This uncertainty can lead to inconsistent results in clinical studies and suboptimal outcomes in therapeutic applications.
Furthermore, the stability of butyrate supplements during storage and transit poses a considerable challenge. Butyrate is highly susceptible to degradation when exposed to heat, light, and moisture, which can compromise its potency and shelf life. This instability necessitates careful packaging and storage solutions, potentially increasing production costs and limiting distribution options.
The regulatory landscape surrounding butyrate supplementation also presents challenges. As a naturally occurring compound, butyrate falls into a gray area between food supplements and pharmaceuticals in many jurisdictions. This ambiguity can lead to inconsistent quality control standards and regulatory oversight, potentially affecting product safety and efficacy.
Lastly, while the potential health benefits of butyrate are promising, there is still a need for more comprehensive, long-term clinical studies to fully elucidate its effects on various health conditions. The current body of evidence, while growing, is still limited in scope and duration, making it challenging to definitively establish the long-term safety and efficacy of butyrate supplementation across diverse patient populations.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Methods
01 Gut health improvement
Butyrate supplementation can enhance gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, reducing inflammation in the intestinal lining, and improving overall digestive function. This can lead to better nutrient absorption and a stronger immune system.- Gut health improvement: Butyrate supplementation has been shown to improve gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing intestinal barrier function, and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. This can lead to better nutrient absorption and overall digestive wellness.
- Metabolic health enhancement: Butyrate supplementation may help improve metabolic health by regulating glucose metabolism, increasing insulin sensitivity, and supporting weight management. These effects can contribute to better overall metabolic function and potentially reduce the risk of metabolic disorders.
- Immune system support: Butyrate has been found to have immunomodulatory effects, potentially enhancing the body's immune response and reducing chronic inflammation. This can lead to improved overall immune function and may help in managing inflammatory conditions.
- Cognitive function improvement: Some studies suggest that butyrate supplementation may have neuroprotective effects and could potentially improve cognitive function. This includes supporting brain health, enhancing memory, and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
- Cardiovascular health support: Butyrate supplementation may contribute to cardiovascular health by helping to regulate blood pressure, improve lipid profiles, and reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular system. These effects could potentially lower the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
02 Metabolic health benefits
Butyrate supplementation may help regulate metabolism, potentially aiding in weight management and improving insulin sensitivity. It can also support the body's energy production processes, particularly in the colon cells.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cognitive function enhancement
Studies suggest that butyrate supplementation may have neuroprotective effects, potentially improving cognitive function and memory. It may also help in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases by supporting brain health.Expand Specific Solutions04 Anti-inflammatory properties
Butyrate has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can benefit various systems in the body. This may help in reducing the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation and support overall health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Immune system modulation
Butyrate supplementation may help modulate the immune system, potentially enhancing its function and reducing the risk of autoimmune disorders. It can also support the body's natural defense mechanisms against pathogens.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Supplement Industry
The future of butyrate supplementation for health benefits is entering a dynamic phase, with increasing market potential and technological advancements. The industry is in a growth stage, driven by rising consumer awareness of gut health and microbiome research. Market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Nestlé, DSM IP Assets BV, and Evonik Operations GmbH leading innovation. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and The University of Chicago are contributing to research advancements. The involvement of pharmaceutical companies like Baxter International and nutraceutical firms such as Pharmavite LLC suggests a maturing industry with diverse applications and delivery methods for butyrate supplementation.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Baxter International, Inc.
Innovative Butyrate Formulation Technologies
- The composition promotes increased butyrate production in the gut, which has potential health benefits including maintaining immune homeostasis, regulating inflammation, and providing energy for enterocyte regeneration.
- The composition can be used as a medicament for treating or managing allergic diseases, immune hypersensitivities, and cancer by leveraging the beneficial effects of increased butyrate production.
- The composition may help re-establish normal gut microbiota after antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or gut surgery by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
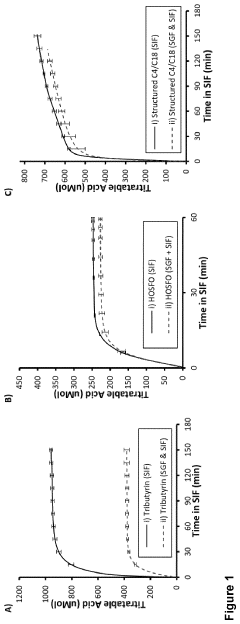
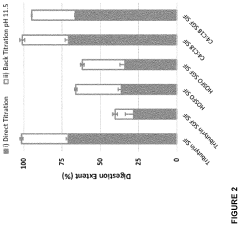
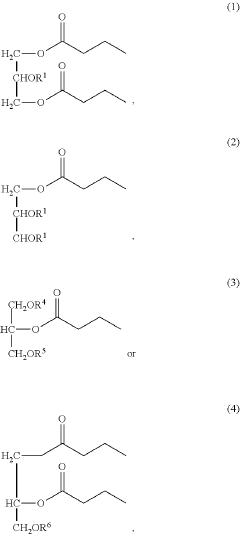
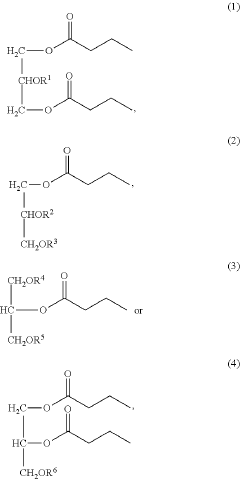
- Development of butyrate moiety containing triglycerides with improved organoleptic properties, specifically designed to have reduced gastric lipolysis and enhanced delivery of butyric acid, using compounds like 1,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol and combinations thereof, for use in nutritional compositions and dietary supplements.
Regulatory Framework for Butyrate Supplements
The regulatory framework for butyrate supplements is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies butyrate supplements as dietary supplements, which fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification means that manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them, but they do not need FDA approval before selling them.
However, the FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded products after they reach the market. Manufacturers must also comply with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) to ensure the quality and safety of their products. Additionally, any claims made about the health benefits of butyrate supplements must be substantiated by scientific evidence and cannot claim to treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
In the European Union, butyrate supplements are regulated under the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC). This directive sets out harmonized rules for the labeling of food supplements and introduces specific rules on vitamins and minerals in food supplements. However, it does not cover other substances used in food supplements, such as butyrate. Member states may have additional national regulations governing these products.
In Japan, butyrate supplements would likely fall under the category of Foods with Function Claims (FFC), which was introduced in 2015. This system allows food business operators to make function claims for foods without government evaluation of the evidence, provided they notify the Consumer Affairs Agency and assume responsibility for the safety and effectiveness of their products.
As research into the health benefits of butyrate continues to grow, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address this specific supplement more directly. Future trends may include more stringent quality control measures, standardized dosage recommendations, and clearer guidelines on permissible health claims. There may also be a push for more comprehensive safety assessments, particularly for long-term use of butyrate supplements.
Given the increasing interest in the gut microbiome and its impact on overall health, regulatory bodies may also begin to develop more specific guidelines for microbiome-modulating supplements like butyrate. This could include requirements for more detailed labeling of the specific forms of butyrate used in supplements and their bioavailability.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
As butyrate supplementation gains traction in the health and wellness industry, safety and efficacy considerations become paramount. The long-term effects of butyrate supplementation on human health are still being studied, necessitating careful monitoring and ongoing research. One primary safety concern is the potential for gastrointestinal distress, particularly in individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Dosage optimization is crucial to minimize adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
Efficacy considerations revolve around the bioavailability and targeted delivery of butyrate supplements. The volatile nature of butyrate poses challenges in ensuring its stability and absorption in the gut. Future trends may focus on developing advanced delivery systems, such as encapsulation technologies or prodrug formulations, to enhance butyrate's bioavailability and targeted release in the colon.
The interaction of butyrate supplements with the existing gut microbiome is another critical factor. While butyrate is known to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, excessive supplementation may disrupt the delicate balance of the gut ecosystem. Research into personalized supplementation strategies based on individual microbiome profiles could lead to more effective and safer interventions.
Quality control and standardization of butyrate supplements are essential for ensuring consistent efficacy and safety across different products. As the market expands, regulatory bodies may implement stricter guidelines for manufacturing and labeling of butyrate supplements. This could include standardized testing methods for potency and purity, as well as clear dosage recommendations based on scientific evidence.
The potential for drug interactions and contraindications with butyrate supplements warrants careful consideration. As butyrate's effects on various physiological processes become better understood, healthcare providers will need to be vigilant about potential interactions with medications, particularly those affecting gut health or metabolism. Comprehensive clinical trials and post-market surveillance will be crucial in identifying and mitigating any unforeseen risks associated with long-term butyrate supplementation.