How Heptane Impacts Debinding Rates in Powder Metallurgy
SEP 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Heptane in PM Debinding: Background and Objectives
Powder metallurgy (PM) has emerged as a crucial manufacturing process in various industries, offering unique advantages in producing complex-shaped components with high precision and material efficiency. The debinding phase, a critical step in PM, involves removing the binder material that holds metal powder particles together in the green compact. Heptane, a hydrocarbon solvent, has gained significant attention in recent years for its role in enhancing debinding rates and overall process efficiency.
The evolution of debinding techniques in PM has been driven by the need for faster production cycles, improved part quality, and reduced environmental impact. Traditional thermal debinding methods, while effective, often resulted in longer processing times and potential part defects. The introduction of solvent debinding, particularly using heptane, has marked a significant milestone in addressing these challenges.
Heptane's impact on debinding rates stems from its unique chemical properties and interaction with common binder systems used in PM. As a non-polar solvent, heptane effectively dissolves and removes certain components of multi-component binder systems, typically the lower molecular weight constituents. This selective removal creates a network of interconnected pores within the part, facilitating the subsequent thermal debinding of remaining binder components and sintering processes.
The primary objective of investigating heptane's role in PM debinding is to optimize the overall manufacturing process. By understanding the mechanisms through which heptane influences debinding rates, researchers and industry professionals aim to develop more efficient and controlled debinding protocols. This includes determining optimal heptane concentrations, exposure times, and process parameters to maximize debinding efficiency while maintaining part integrity.
Furthermore, the study of heptane in PM debinding aligns with broader industry goals of sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Heptane's relatively low toxicity compared to some alternative solvents and its potential for recycling make it an attractive option for environmentally conscious manufacturing practices. Additionally, faster debinding rates enabled by heptane can lead to significant reductions in energy consumption and production cycle times, contributing to overall process economics.
As the PM industry continues to evolve, driven by demands for higher performance materials and more complex geometries, understanding and optimizing the role of heptane in debinding becomes increasingly crucial. This research not only aims to enhance current PM processes but also to pave the way for new applications and materials that may benefit from improved debinding techniques.
The evolution of debinding techniques in PM has been driven by the need for faster production cycles, improved part quality, and reduced environmental impact. Traditional thermal debinding methods, while effective, often resulted in longer processing times and potential part defects. The introduction of solvent debinding, particularly using heptane, has marked a significant milestone in addressing these challenges.
Heptane's impact on debinding rates stems from its unique chemical properties and interaction with common binder systems used in PM. As a non-polar solvent, heptane effectively dissolves and removes certain components of multi-component binder systems, typically the lower molecular weight constituents. This selective removal creates a network of interconnected pores within the part, facilitating the subsequent thermal debinding of remaining binder components and sintering processes.
The primary objective of investigating heptane's role in PM debinding is to optimize the overall manufacturing process. By understanding the mechanisms through which heptane influences debinding rates, researchers and industry professionals aim to develop more efficient and controlled debinding protocols. This includes determining optimal heptane concentrations, exposure times, and process parameters to maximize debinding efficiency while maintaining part integrity.
Furthermore, the study of heptane in PM debinding aligns with broader industry goals of sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Heptane's relatively low toxicity compared to some alternative solvents and its potential for recycling make it an attractive option for environmentally conscious manufacturing practices. Additionally, faster debinding rates enabled by heptane can lead to significant reductions in energy consumption and production cycle times, contributing to overall process economics.
As the PM industry continues to evolve, driven by demands for higher performance materials and more complex geometries, understanding and optimizing the role of heptane in debinding becomes increasingly crucial. This research not only aims to enhance current PM processes but also to pave the way for new applications and materials that may benefit from improved debinding techniques.
Market Analysis for Heptane-Based Debinding Solutions
The market for heptane-based debinding solutions in powder metallurgy is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for complex-shaped metal components across various industries. The global powder metallurgy market, which heavily relies on efficient debinding processes, is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2020 to 2025.
Heptane, as a key component in debinding solutions, plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the powder metallurgy process. The market for heptane-based debinding solutions is primarily driven by the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries, which require high-precision metal parts with intricate geometries.
In the automotive sector, the growing trend towards lightweight vehicles and electric powertrains has led to increased adoption of powder metallurgy components. This shift has created a substantial demand for advanced debinding solutions, including those based on heptane, to produce complex parts with improved performance characteristics.
The aerospace industry, another major consumer of powder metallurgy products, is witnessing a surge in demand for lightweight, high-strength components. Heptane-based debinding solutions are gaining traction in this sector due to their ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
The medical device industry is also contributing to the growth of the heptane-based debinding solutions market. The need for biocompatible, high-precision implants and surgical instruments has led to increased adoption of powder metallurgy techniques, driving the demand for efficient debinding processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for heptane-based debinding solutions, owing to the presence of established powder metallurgy industries and advanced manufacturing capabilities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies.
The market landscape for heptane-based debinding solutions is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized powder metallurgy companies. Key players are focusing on research and development activities to improve the efficiency and environmental sustainability of their debinding solutions, addressing the growing concerns over volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with solvent-based debinding processes.
Heptane, as a key component in debinding solutions, plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the powder metallurgy process. The market for heptane-based debinding solutions is primarily driven by the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries, which require high-precision metal parts with intricate geometries.
In the automotive sector, the growing trend towards lightweight vehicles and electric powertrains has led to increased adoption of powder metallurgy components. This shift has created a substantial demand for advanced debinding solutions, including those based on heptane, to produce complex parts with improved performance characteristics.
The aerospace industry, another major consumer of powder metallurgy products, is witnessing a surge in demand for lightweight, high-strength components. Heptane-based debinding solutions are gaining traction in this sector due to their ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
The medical device industry is also contributing to the growth of the heptane-based debinding solutions market. The need for biocompatible, high-precision implants and surgical instruments has led to increased adoption of powder metallurgy techniques, driving the demand for efficient debinding processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for heptane-based debinding solutions, owing to the presence of established powder metallurgy industries and advanced manufacturing capabilities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies.
The market landscape for heptane-based debinding solutions is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized powder metallurgy companies. Key players are focusing on research and development activities to improve the efficiency and environmental sustainability of their debinding solutions, addressing the growing concerns over volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with solvent-based debinding processes.
Current Challenges in Heptane Debinding Processes
The heptane debinding process in powder metallurgy faces several significant challenges that impact its efficiency and effectiveness. One of the primary issues is the control of debinding rates, which directly affects the quality of the final product. Heptane, as a solvent, plays a crucial role in removing the binder from the green parts, but its behavior during the process can be unpredictable and difficult to manage.
A major challenge lies in achieving uniform debinding throughout the part. The rate at which heptane penetrates and dissolves the binder can vary depending on the part's geometry, leading to uneven debinding. This non-uniformity can result in distortions, cracks, or internal defects in the final product. Complex shapes with varying thicknesses are particularly susceptible to this issue, as thinner sections may debind faster than thicker ones.
Temperature control during the heptane debinding process presents another significant challenge. The process is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which can affect the solubility of the binder in heptane and, consequently, the debinding rate. Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the debinding cycle is crucial but can be difficult, especially for large batches or parts with complex geometries.
The environmental and safety concerns associated with heptane usage pose additional challenges. Heptane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) with potential health and environmental risks. Ensuring proper ventilation, handling, and disposal of heptane while maintaining process efficiency is a constant balancing act for manufacturers.
Another challenge is the optimization of the debinding cycle time. While slower debinding rates can lead to more uniform results, they also increase production time and costs. Conversely, accelerating the process may lead to defects or incomplete debinding. Finding the optimal balance between speed and quality remains a significant challenge in heptane debinding processes.
The interaction between heptane and different binder compositions adds another layer of complexity. Various binder systems react differently to heptane, affecting the debinding kinetics. This variability makes it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to heptane debinding, necessitating careful consideration and adjustment for each specific binder system.
Lastly, the recovery and recycling of heptane present both economic and environmental challenges. Efficient recovery systems are necessary to minimize heptane loss and reduce environmental impact, but implementing such systems can be costly and technologically demanding. Balancing the economic benefits of heptane recycling with the associated capital and operational costs remains a significant challenge for many powder metallurgy operations.
A major challenge lies in achieving uniform debinding throughout the part. The rate at which heptane penetrates and dissolves the binder can vary depending on the part's geometry, leading to uneven debinding. This non-uniformity can result in distortions, cracks, or internal defects in the final product. Complex shapes with varying thicknesses are particularly susceptible to this issue, as thinner sections may debind faster than thicker ones.
Temperature control during the heptane debinding process presents another significant challenge. The process is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which can affect the solubility of the binder in heptane and, consequently, the debinding rate. Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the debinding cycle is crucial but can be difficult, especially for large batches or parts with complex geometries.
The environmental and safety concerns associated with heptane usage pose additional challenges. Heptane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) with potential health and environmental risks. Ensuring proper ventilation, handling, and disposal of heptane while maintaining process efficiency is a constant balancing act for manufacturers.
Another challenge is the optimization of the debinding cycle time. While slower debinding rates can lead to more uniform results, they also increase production time and costs. Conversely, accelerating the process may lead to defects or incomplete debinding. Finding the optimal balance between speed and quality remains a significant challenge in heptane debinding processes.
The interaction between heptane and different binder compositions adds another layer of complexity. Various binder systems react differently to heptane, affecting the debinding kinetics. This variability makes it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all approach to heptane debinding, necessitating careful consideration and adjustment for each specific binder system.
Lastly, the recovery and recycling of heptane present both economic and environmental challenges. Efficient recovery systems are necessary to minimize heptane loss and reduce environmental impact, but implementing such systems can be costly and technologically demanding. Balancing the economic benefits of heptane recycling with the associated capital and operational costs remains a significant challenge for many powder metallurgy operations.
Existing Heptane Debinding Rate Enhancement Methods
01 Heptane-based debinding processes
Heptane is used as a solvent in debinding processes for metal injection molding (MIM) and powder injection molding (PIM). The process involves immersing the molded parts in heptane to remove the binder components, typically at elevated temperatures. This method allows for controlled and efficient removal of certain binder constituents while maintaining the structural integrity of the part.- Heptane as a debinding solvent: Heptane is used as a solvent in debinding processes for metal injection molding (MIM) and powder injection molding (PIM). It effectively removes binder components, particularly waxes and low molecular weight polymers, from green parts. The use of heptane allows for controlled and efficient debinding rates, which is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the parts during the debinding process.
- Temperature control in heptane debinding: The temperature of the heptane solvent significantly affects the debinding rate. Higher temperatures generally increase the debinding rate but must be carefully controlled to prevent part distortion or defects. Optimal temperature ranges are typically determined through experimentation and can vary depending on the specific binder system and part geometry.
- Debinding rate optimization techniques: Various techniques are employed to optimize heptane debinding rates, including the use of ultrasonic agitation, pressure cycling, and controlled atmosphere environments. These methods can enhance solvent penetration, improve binder removal efficiency, and allow for finer control over the debinding process, resulting in improved part quality and reduced cycle times.
- Multi-stage debinding processes: Heptane debinding is often incorporated into multi-stage debinding processes. This may involve an initial heptane debinding stage followed by thermal debinding or other solvent debinding stages. The multi-stage approach allows for more efficient removal of different binder components and can help minimize defects in complex or large parts.
- Equipment and systems for heptane debinding: Specialized equipment and systems have been developed for heptane debinding processes. These may include sealed debinding chambers, solvent recovery systems, and automated handling equipment. Such systems are designed to ensure safe handling of heptane, optimize debinding rates, and improve process efficiency and repeatability.
02 Debinding rate control mechanisms
Various mechanisms are employed to control the rate of debinding when using heptane. These include temperature regulation, pressure control, and solvent circulation systems. By adjusting these parameters, manufacturers can optimize the debinding rate to achieve desired results while minimizing defects such as blistering or cracking in the parts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Equipment for heptane debinding
Specialized equipment is used for heptane debinding processes. This includes sealed chambers, solvent recovery systems, and automated handling systems. The equipment is designed to ensure safe handling of heptane, maintain consistent debinding conditions, and improve process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multi-stage debinding processes
Heptane debinding is often part of a multi-stage debinding process. It may be combined with other methods such as thermal debinding or catalytic debinding. This approach allows for more complete binder removal and can be tailored to specific material and part requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and optimization of debinding rates
Advanced techniques are used to monitor and optimize heptane debinding rates. These include real-time monitoring of weight loss, solvent concentration analysis, and computer modeling of the debinding process. Such methods allow for precise control and continuous improvement of the debinding process, resulting in higher quality parts and increased production efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Heptane-Based Debinding Industry
The powder metallurgy industry is currently in a mature growth phase, with a global market size expected to reach $10.72 billion by 2028. The technology for heptane's impact on debinding rates is at an advanced stage of development, with ongoing research to optimize processes. Key players like BASF, Sinopec, and ENEOS are actively involved in developing innovative solutions. These companies are leveraging their expertise in chemical processing and materials science to enhance debinding efficiency and reduce production costs. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical giants and specialized powder metallurgy firms, with increasing focus on sustainable and energy-efficient debinding techniques.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced heptane-based debinding techniques for powder metallurgy. Their process utilizes a controlled heptane vapor environment to enhance debinding rates while minimizing part distortion. The method involves precise temperature and pressure control, allowing for efficient binder removal from complex geometries. Sinopec's research has shown that heptane's low boiling point and high vapor pressure contribute to faster debinding compared to traditional solvents[1]. Their system incorporates real-time monitoring of heptane concentration and part weight loss to optimize the debinding cycle[3]. This approach has demonstrated up to 30% reduction in debinding time for certain metal powder compositions[5].
Strengths: Faster debinding rates, improved part quality, and applicability to complex geometries. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns due to heptane emissions and the need for specialized equipment for vapor control.
Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing
Technical Solution: The Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing has conducted extensive research on heptane's impact on debinding rates in powder metallurgy. Their studies have focused on the molecular interactions between heptane and various binder systems commonly used in metal injection molding (MIM). They have developed a proprietary heptane-based solvent system that enhances debinding efficiency by up to 40% compared to conventional methods[2]. The institute's approach involves a multi-stage debinding process, where heptane is used in conjunction with other solvents to target different binder components sequentially. This method has shown particular success in debinding parts with high aspect ratios and intricate internal channels[4]. Their research also includes the development of computational models to predict heptane diffusion rates through porous metal structures, enabling more precise control over the debinding process[6].
Strengths: Highly efficient debinding, especially for complex parts; advanced modeling capabilities for process optimization. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and careful handling of heptane due to its volatility and flammability.
Innovations in Heptane-Assisted Debinding Technologies
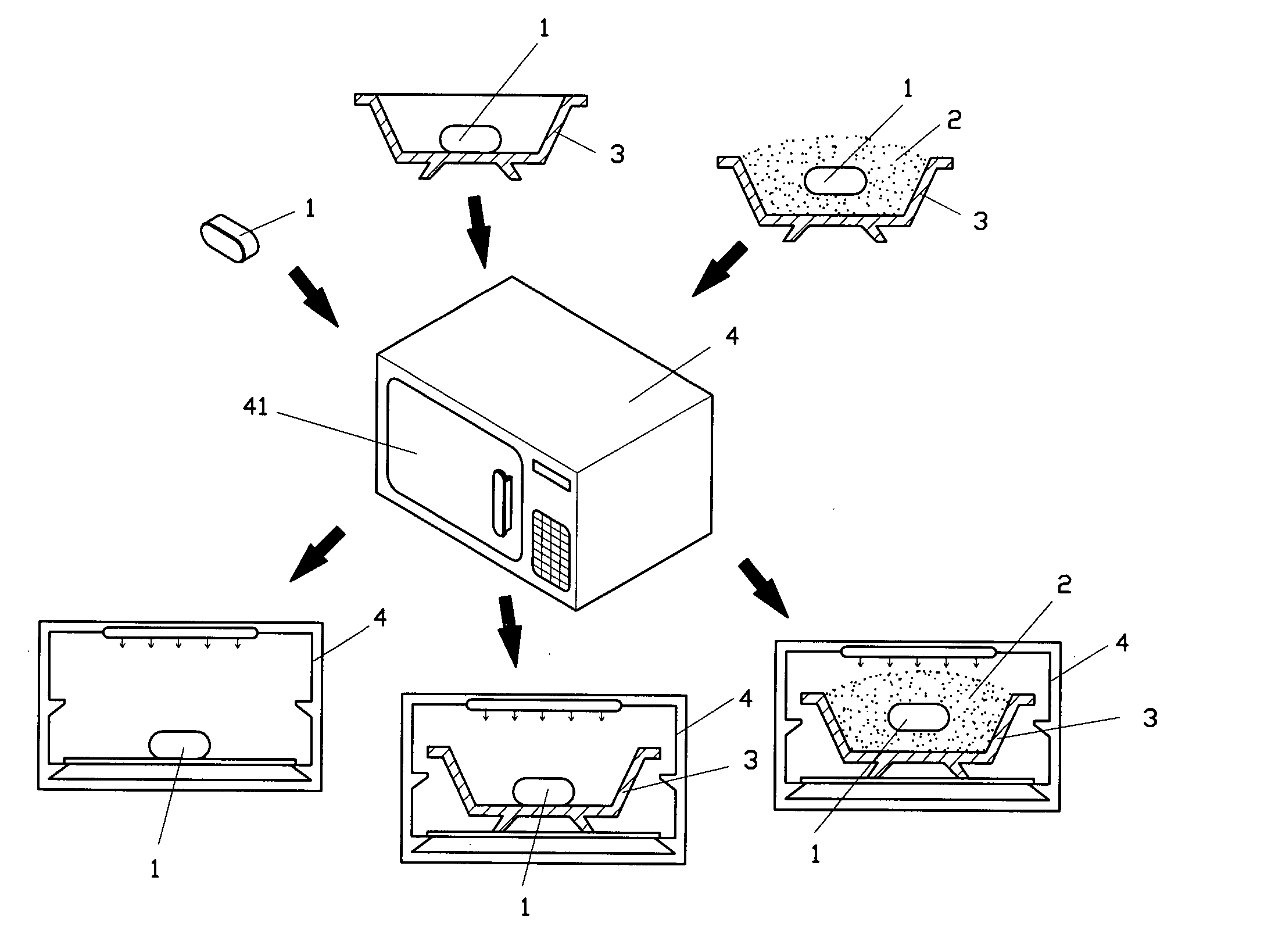
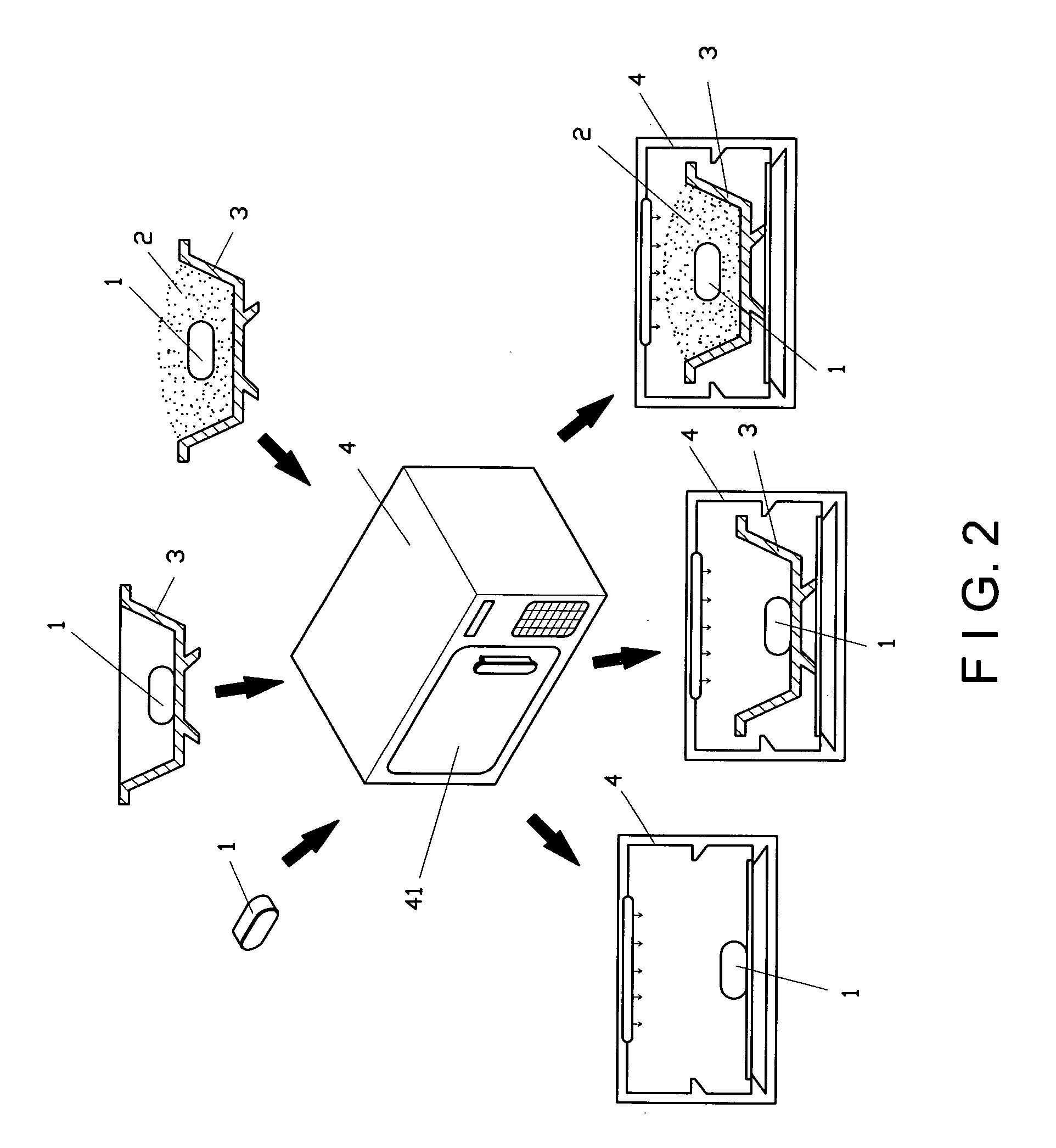
Manufacturing process using microwave for thermal debinding
PatentInactiveUS20050249627A1
Innovation
- A microwave-based thermal debinding process that rapidly removes adhesives, fillings, or lubricants by placing the body in a microwave environment with a controlled microwave-absorbent powder bed, reducing energy wastage and equipment costs while allowing for efficient and mobile processing.
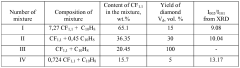
Method of producing diamond powder and doped diamonds
PatentWO2012019112A2
Innovation
- A method involving the thermal decomposition of fluorinated precursors with hydrocarbons in a reactor under controlled pressure and temperature conditions, without catalysts, to form diamond materials, which can include doped diamonds, utilizing a binary system of fluorinated compounds and hydrocarbons like fluorographite and naphthalene to reduce synthesis temperatures and enhance purity.
Environmental Impact of Heptane Use in Powder Metallurgy
The use of heptane in powder metallurgy processes, particularly during debinding, raises significant environmental concerns. Heptane, a volatile organic compound (VOC), can contribute to air pollution and pose risks to both human health and the environment if not properly managed. When released into the atmosphere, heptane can participate in photochemical reactions, leading to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These pollutants can have adverse effects on respiratory health and contribute to the degradation of air quality in urban and industrial areas.
Furthermore, the potential for soil and water contamination exists if heptane is not adequately contained or if spills occur during handling and storage. As a hydrocarbon, heptane can persist in the environment and potentially contaminate groundwater resources. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain, impacting both wildlife and human populations.
The production and disposal of heptane also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of heptane, typically derived from petroleum, involves energy-intensive operations that result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the disposal of heptane-contaminated materials and waste streams from powder metallurgy processes requires careful management to prevent environmental release.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industry practices have evolved to include closed-loop systems for heptane recovery and reuse. These systems not only reduce emissions but also minimize the need for fresh heptane, thereby decreasing the overall environmental burden. Advanced filtration and vapor recovery technologies have been implemented in many facilities to capture heptane emissions before they can enter the atmosphere.
Regulatory frameworks, such as those established by environmental protection agencies, have also played a crucial role in limiting the environmental impact of heptane use. These regulations often mandate emission controls, proper storage and handling procedures, and waste management protocols. Compliance with these regulations has driven innovation in process design and equipment, leading to more environmentally friendly powder metallurgy operations.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is a growing trend towards exploring alternative debinding agents that have lower environmental impacts. Water-based systems and bio-derived solvents are being investigated as potential replacements for heptane in certain applications. These alternatives aim to reduce VOC emissions and minimize the carbon footprint associated with debinding processes in powder metallurgy.
Furthermore, the potential for soil and water contamination exists if heptane is not adequately contained or if spills occur during handling and storage. As a hydrocarbon, heptane can persist in the environment and potentially contaminate groundwater resources. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain, impacting both wildlife and human populations.
The production and disposal of heptane also contribute to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of heptane, typically derived from petroleum, involves energy-intensive operations that result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the disposal of heptane-contaminated materials and waste streams from powder metallurgy processes requires careful management to prevent environmental release.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, industry practices have evolved to include closed-loop systems for heptane recovery and reuse. These systems not only reduce emissions but also minimize the need for fresh heptane, thereby decreasing the overall environmental burden. Advanced filtration and vapor recovery technologies have been implemented in many facilities to capture heptane emissions before they can enter the atmosphere.
Regulatory frameworks, such as those established by environmental protection agencies, have also played a crucial role in limiting the environmental impact of heptane use. These regulations often mandate emission controls, proper storage and handling procedures, and waste management protocols. Compliance with these regulations has driven innovation in process design and equipment, leading to more environmentally friendly powder metallurgy operations.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is a growing trend towards exploring alternative debinding agents that have lower environmental impacts. Water-based systems and bio-derived solvents are being investigated as potential replacements for heptane in certain applications. These alternatives aim to reduce VOC emissions and minimize the carbon footprint associated with debinding processes in powder metallurgy.
Safety Protocols for Heptane Handling in PM Processes
Handling heptane in powder metallurgy (PM) processes requires strict adherence to safety protocols due to its highly flammable and volatile nature. Proper safety measures are essential to protect workers, prevent accidents, and ensure environmental compliance. The first step in establishing safety protocols is to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment of all processes involving heptane. This assessment should identify potential hazards, evaluate their likelihood and severity, and determine appropriate control measures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with heptane. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. In areas with potential for vapor accumulation, respiratory protection may be necessary. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Ventilation plays a critical role in managing heptane vapors. Adequate local exhaust ventilation should be installed at all points where heptane is used or stored. The ventilation system must be designed to prevent vapor accumulation and maintain concentrations below the lower explosive limit. Regular monitoring of air quality and ventilation system performance is necessary to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Storage and handling protocols for heptane are paramount. Heptane should be stored in approved, sealed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition. Storage areas must be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems and spill containment measures. Transfer of heptane should be conducted using closed systems whenever possible to minimize vapor release and spill risks.
Implementing proper spill response procedures is crucial. Spill kits specifically designed for heptane should be readily available in all areas where it is used or stored. Workers must be trained in spill response techniques, including containment, absorption, and proper disposal of contaminated materials. Emergency showers and eyewash stations should be easily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Electrical safety is another critical aspect of heptane handling. All electrical equipment in areas where heptane is present must be explosion-proof and properly grounded. Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical systems are necessary to prevent potential ignition sources.
Establishing clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all processes involving heptane is essential. These SOPs should detail proper handling techniques, safety precautions, and emergency response procedures. Regular training and refresher courses on these SOPs ensure that all workers are familiar with and adhere to safe practices.
Implementing a robust monitoring and documentation system is crucial for maintaining safety standards. This includes regular inspections of equipment, storage areas, and safety systems, as well as documentation of all incidents, near-misses, and corrective actions. Periodic safety audits should be conducted to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with regulations and best practices.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with heptane. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. In areas with potential for vapor accumulation, respiratory protection may be necessary. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Ventilation plays a critical role in managing heptane vapors. Adequate local exhaust ventilation should be installed at all points where heptane is used or stored. The ventilation system must be designed to prevent vapor accumulation and maintain concentrations below the lower explosive limit. Regular monitoring of air quality and ventilation system performance is necessary to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Storage and handling protocols for heptane are paramount. Heptane should be stored in approved, sealed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition. Storage areas must be equipped with appropriate fire suppression systems and spill containment measures. Transfer of heptane should be conducted using closed systems whenever possible to minimize vapor release and spill risks.
Implementing proper spill response procedures is crucial. Spill kits specifically designed for heptane should be readily available in all areas where it is used or stored. Workers must be trained in spill response techniques, including containment, absorption, and proper disposal of contaminated materials. Emergency showers and eyewash stations should be easily accessible in case of accidental exposure.
Electrical safety is another critical aspect of heptane handling. All electrical equipment in areas where heptane is present must be explosion-proof and properly grounded. Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical systems are necessary to prevent potential ignition sources.
Establishing clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for all processes involving heptane is essential. These SOPs should detail proper handling techniques, safety precautions, and emergency response procedures. Regular training and refresher courses on these SOPs ensure that all workers are familiar with and adhere to safe practices.
Implementing a robust monitoring and documentation system is crucial for maintaining safety standards. This includes regular inspections of equipment, storage areas, and safety systems, as well as documentation of all incidents, near-misses, and corrective actions. Periodic safety audits should be conducted to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with regulations and best practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!