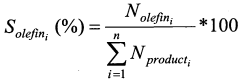How Propyne Contributes to Green Chemistry Initiatives
JUL 30, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propyne in Green Chemistry: Background and Objectives
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has emerged as a significant player in the field of green chemistry, offering innovative solutions to environmental challenges. The evolution of propyne's role in sustainable practices can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring its potential as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical processes. This aliphatic hydrocarbon, with its unique triple bond structure, has since garnered attention for its versatility and reactivity, making it an attractive candidate for various green chemistry applications.
The primary objective of incorporating propyne into green chemistry initiatives is to develop more sustainable and efficient chemical processes that reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving product quality. This aligns with the core principles of green chemistry, which emphasize the design of chemical products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances. Propyne's contribution to these goals is multifaceted, ranging from its use as a building block for pharmaceuticals to its role in developing new materials with enhanced properties.
One of the key trends in propyne's technological evolution is its increasing use in catalytic processes. Researchers have made significant strides in developing catalysts that can efficiently utilize propyne in various reactions, leading to more atom-economical and energy-efficient syntheses. This trend is expected to continue, with ongoing efforts to discover novel catalytic systems that can further optimize propyne-based reactions and expand their applicability across different industries.
The environmental benefits of propyne-based processes are becoming increasingly evident as the technology matures. Compared to traditional methods, propyne-enabled reactions often require milder conditions, consume less energy, and produce fewer by-products. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of chemical manufacturing but also aligns with the growing demand for cleaner production methods in industries such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
Looking ahead, the future of propyne in green chemistry appears promising, with several emerging areas of research and development. Scientists are exploring its potential in the synthesis of biodegradable polymers, the development of more efficient fuel additives, and the creation of novel organic electronic materials. These applications highlight the versatility of propyne and its potential to contribute to sustainability across diverse sectors.
As the field progresses, researchers aim to overcome existing challenges, such as improving the scalability of propyne-based processes and enhancing their economic viability. Addressing these issues will be crucial for the widespread adoption of propyne in industrial applications and for realizing its full potential as a key player in green chemistry initiatives.
The primary objective of incorporating propyne into green chemistry initiatives is to develop more sustainable and efficient chemical processes that reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving product quality. This aligns with the core principles of green chemistry, which emphasize the design of chemical products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances. Propyne's contribution to these goals is multifaceted, ranging from its use as a building block for pharmaceuticals to its role in developing new materials with enhanced properties.
One of the key trends in propyne's technological evolution is its increasing use in catalytic processes. Researchers have made significant strides in developing catalysts that can efficiently utilize propyne in various reactions, leading to more atom-economical and energy-efficient syntheses. This trend is expected to continue, with ongoing efforts to discover novel catalytic systems that can further optimize propyne-based reactions and expand their applicability across different industries.
The environmental benefits of propyne-based processes are becoming increasingly evident as the technology matures. Compared to traditional methods, propyne-enabled reactions often require milder conditions, consume less energy, and produce fewer by-products. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of chemical manufacturing but also aligns with the growing demand for cleaner production methods in industries such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
Looking ahead, the future of propyne in green chemistry appears promising, with several emerging areas of research and development. Scientists are exploring its potential in the synthesis of biodegradable polymers, the development of more efficient fuel additives, and the creation of novel organic electronic materials. These applications highlight the versatility of propyne and its potential to contribute to sustainability across diverse sectors.
As the field progresses, researchers aim to overcome existing challenges, such as improving the scalability of propyne-based processes and enhancing their economic viability. Addressing these issues will be crucial for the widespread adoption of propyne in industrial applications and for realizing its full potential as a key player in green chemistry initiatives.
Market Demand for Sustainable Chemical Processes
The market demand for sustainable chemical processes has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns, stricter regulations, and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has emerged as a promising candidate in green chemistry initiatives due to its potential to contribute to more sustainable chemical processes.
The global chemical industry has been under pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, with a particular focus on minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and developing safer alternatives to traditional chemical processes. This shift towards sustainability has created a significant market opportunity for innovative solutions that align with green chemistry principles.
Propyne's unique chemical properties make it an attractive option for various sustainable chemical processes. Its high reactivity and versatility allow for efficient synthesis of a wide range of valuable chemical products, often under milder conditions compared to traditional methods. This can lead to reduced energy consumption and fewer byproducts, addressing key sustainability goals in the chemical industry.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for propyne-based sustainable processes is the pharmaceutical industry. As pharmaceutical companies seek to improve their environmental performance and reduce production costs, propyne offers a pathway to more efficient and environmentally friendly drug synthesis. The ability to conduct reactions at lower temperatures and with higher selectivity can result in significant energy savings and reduced waste generation.
The polymer industry is another sector showing increasing interest in propyne-based sustainable processes. Propyne can be used as a building block for various specialty polymers, offering improved performance characteristics while potentially reducing the environmental impact of polymer production. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable materials in industries such as automotive, packaging, and consumer goods.
Furthermore, the fine chemicals sector is exploring propyne's potential in developing more sustainable routes for producing high-value chemicals. The ability to conduct selective transformations and create complex molecules with fewer steps can lead to more efficient and less resource-intensive production processes. This is particularly relevant in the context of increasing demand for specialty chemicals in electronics, agrochemicals, and other advanced applications.
The market demand for sustainable chemical processes using propyne is also influenced by regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability initiatives. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and companies set ambitious sustainability targets, there is a growing need for innovative solutions that can help meet these goals. Propyne-based processes offer a potential avenue for companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability while potentially gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
However, it is important to note that the adoption of propyne in sustainable chemical processes is still in its early stages. The market demand is currently driven primarily by research and development efforts and pilot-scale applications. As the technology matures and more commercial-scale implementations are realized, the market demand is expected to grow significantly, potentially reshaping various segments of the chemical industry.
The global chemical industry has been under pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, with a particular focus on minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and developing safer alternatives to traditional chemical processes. This shift towards sustainability has created a significant market opportunity for innovative solutions that align with green chemistry principles.
Propyne's unique chemical properties make it an attractive option for various sustainable chemical processes. Its high reactivity and versatility allow for efficient synthesis of a wide range of valuable chemical products, often under milder conditions compared to traditional methods. This can lead to reduced energy consumption and fewer byproducts, addressing key sustainability goals in the chemical industry.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for propyne-based sustainable processes is the pharmaceutical industry. As pharmaceutical companies seek to improve their environmental performance and reduce production costs, propyne offers a pathway to more efficient and environmentally friendly drug synthesis. The ability to conduct reactions at lower temperatures and with higher selectivity can result in significant energy savings and reduced waste generation.
The polymer industry is another sector showing increasing interest in propyne-based sustainable processes. Propyne can be used as a building block for various specialty polymers, offering improved performance characteristics while potentially reducing the environmental impact of polymer production. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable materials in industries such as automotive, packaging, and consumer goods.
Furthermore, the fine chemicals sector is exploring propyne's potential in developing more sustainable routes for producing high-value chemicals. The ability to conduct selective transformations and create complex molecules with fewer steps can lead to more efficient and less resource-intensive production processes. This is particularly relevant in the context of increasing demand for specialty chemicals in electronics, agrochemicals, and other advanced applications.
The market demand for sustainable chemical processes using propyne is also influenced by regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability initiatives. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and companies set ambitious sustainability targets, there is a growing need for innovative solutions that can help meet these goals. Propyne-based processes offer a potential avenue for companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability while potentially gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
However, it is important to note that the adoption of propyne in sustainable chemical processes is still in its early stages. The market demand is currently driven primarily by research and development efforts and pilot-scale applications. As the technology matures and more commercial-scale implementations are realized, the market demand is expected to grow significantly, potentially reshaping various segments of the chemical industry.
Current State and Challenges in Propyne Utilization
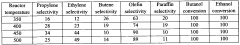
Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential contributor to green chemistry initiatives. However, its current utilization faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. The global production of propyne is primarily as a byproduct of ethylene manufacturing, with an estimated annual production of around 150,000 tons.
One of the main challenges in propyne utilization is its limited availability and high production costs. The current production methods are not optimized for large-scale propyne synthesis, making it less economically viable compared to other widely used hydrocarbons. This scarcity has hindered its broader application in various chemical processes and industrial sectors.
Another significant challenge is the lack of efficient and selective catalytic systems for propyne transformations. While propyne shows promise as a versatile building block in organic synthesis, the development of highly selective catalysts that can effectively activate and functionalize propyne remains a key area of research. Current catalytic systems often suffer from poor selectivity, leading to unwanted side products and reduced overall efficiency.
The storage and handling of propyne also present technical difficulties due to its high reactivity and flammability. Special safety measures and equipment are required for its transportation and storage, which adds to the overall cost and complexity of its utilization. This aspect has limited its adoption in smaller-scale applications and research laboratories.
From an environmental perspective, the current methods of propyne production and utilization still have room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency and carbon footprint. While propyne itself has the potential to contribute to greener chemical processes, the overall life cycle assessment of its production and use needs further optimization to align with sustainability goals.
In the academic and industrial research landscape, propyne has garnered interest for its potential in C3 chemistry and as a precursor for various valuable chemicals. However, the translation of laboratory-scale successes to industrial applications remains a challenge. The development of scalable and economically viable processes for propyne-based chemistry is an ongoing area of focus.
Geographically, the research and development efforts in propyne utilization are primarily concentrated in regions with strong petrochemical industries, such as North America, Europe, and East Asia. This distribution reflects the current state of propyne production and the existing infrastructure for its handling and processing.
Despite these challenges, recent advancements in catalysis, process engineering, and green chemistry principles have opened new avenues for propyne utilization. Innovative approaches to its production, such as biomass-derived routes and improved separation technologies, are being explored to address the supply and cost issues. Additionally, the development of novel reaction pathways and catalytic systems tailored for propyne chemistry continues to expand its potential applications in sustainable chemical manufacturing.
One of the main challenges in propyne utilization is its limited availability and high production costs. The current production methods are not optimized for large-scale propyne synthesis, making it less economically viable compared to other widely used hydrocarbons. This scarcity has hindered its broader application in various chemical processes and industrial sectors.
Another significant challenge is the lack of efficient and selective catalytic systems for propyne transformations. While propyne shows promise as a versatile building block in organic synthesis, the development of highly selective catalysts that can effectively activate and functionalize propyne remains a key area of research. Current catalytic systems often suffer from poor selectivity, leading to unwanted side products and reduced overall efficiency.
The storage and handling of propyne also present technical difficulties due to its high reactivity and flammability. Special safety measures and equipment are required for its transportation and storage, which adds to the overall cost and complexity of its utilization. This aspect has limited its adoption in smaller-scale applications and research laboratories.
From an environmental perspective, the current methods of propyne production and utilization still have room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency and carbon footprint. While propyne itself has the potential to contribute to greener chemical processes, the overall life cycle assessment of its production and use needs further optimization to align with sustainability goals.
In the academic and industrial research landscape, propyne has garnered interest for its potential in C3 chemistry and as a precursor for various valuable chemicals. However, the translation of laboratory-scale successes to industrial applications remains a challenge. The development of scalable and economically viable processes for propyne-based chemistry is an ongoing area of focus.
Geographically, the research and development efforts in propyne utilization are primarily concentrated in regions with strong petrochemical industries, such as North America, Europe, and East Asia. This distribution reflects the current state of propyne production and the existing infrastructure for its handling and processing.
Despite these challenges, recent advancements in catalysis, process engineering, and green chemistry principles have opened new avenues for propyne utilization. Innovative approaches to its production, such as biomass-derived routes and improved separation technologies, are being explored to address the supply and cost issues. Additionally, the development of novel reaction pathways and catalytic systems tailored for propyne chemistry continues to expand its potential applications in sustainable chemical manufacturing.
Existing Green Chemistry Solutions Utilizing Propyne
01 Synthesis and production methods of propyne
Various methods for synthesizing and producing propyne are described, including catalytic processes, thermal cracking, and dehydrogenation reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, selectivity, and efficiency in propyne production.- Synthesis and production of propyne: Various methods for synthesizing and producing propyne are described. These include catalytic processes, thermal decomposition, and chemical reactions involving precursor compounds. The production methods aim to improve yield, selectivity, and efficiency in obtaining propyne.
- Purification and separation of propyne: Techniques for purifying and separating propyne from mixtures or reaction products are outlined. These may involve distillation, adsorption, membrane separation, or other physical and chemical separation methods to obtain high-purity propyne.
- Applications of propyne in chemical synthesis: Propyne is used as a starting material or intermediate in various chemical syntheses. It can be employed in the production of polymers, fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other organic compounds through reactions such as cycloadditions, hydrogenations, and carbonylations.
- Propyne in fuel and energy applications: The use of propyne in fuel compositions and energy-related applications is explored. This includes its potential as a fuel additive, its role in combustion processes, and its use in the development of alternative energy sources or storage systems.
- Safety and handling of propyne: Methods and systems for the safe handling, storage, and transportation of propyne are described. This includes techniques for preventing or mitigating risks associated with its flammability and reactivity, as well as equipment designs for its safe use in industrial settings.
02 Purification and separation of propyne
Techniques for purifying and separating propyne from other hydrocarbons or reaction mixtures are outlined. These may include distillation, absorption, adsorption, and membrane separation processes to obtain high-purity propyne.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of propyne in chemical synthesis
Propyne is used as a versatile building block in various chemical syntheses, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its triple bond reactivity is exploited in cycloaddition reactions and other transformations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Propyne as a fuel or fuel additive
Research into the use of propyne as a fuel or fuel additive is presented. This includes studies on combustion properties, engine performance, and emissions reduction when propyne is incorporated into fuel blends.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of propyne
Methods and equipment for the safe handling, storage, and transportation of propyne are described. This includes specialized containers, pressure regulation systems, and safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with this flammable gas.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propyne-Based Green Chemistry
The green chemistry initiatives involving propyne are in an early development stage, with a growing market driven by sustainability demands. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Genomatica, Braskem, and Evonik are leading research efforts, while academic institutions such as Zhejiang University of Technology and the University of Campinas contribute to fundamental studies. The involvement of major chemical companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Sumitomo Chemical indicates increasing industry interest. However, the field remains relatively niche, with potential for significant growth as propyne-based green chemistry solutions mature and find broader commercial applications.
Genomatica, Inc.
Technical Solution: Genomatica has pioneered a bio-based approach to propyne production as part of their green chemistry initiatives. Their innovative process utilizes genetically engineered microorganisms to produce propyne from renewable feedstocks such as sugar or agricultural waste[4]. This biotechnology platform significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to traditional petrochemical routes. Genomatica's process operates under mild conditions, requiring less energy and producing fewer byproducts[5]. The company has also developed a proprietary purification method that ensures high-quality propyne suitable for various downstream applications in the green chemistry sector. Their technology enables the production of bio-based materials and chemicals, contributing to the circular economy and reducing reliance on fossil resources[6].
Strengths: Renewable feedstock utilization, reduced carbon footprint, and potential for scalable bio-based production. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to petrochemical routes, and challenges in achieving high yields at industrial scales.
Braskem SA
Technical Solution: Braskem SA has incorporated propyne into its green chemistry initiatives through innovative polymer production techniques. The company has developed a proprietary process that utilizes propyne as a comonomer in the production of high-performance, eco-friendly plastics[7]. This approach results in materials with enhanced properties while reducing the overall carbon footprint. Braskem's method involves the copolymerization of propyne with bio-based ethylene, derived from sugarcane ethanol, to create novel sustainable polymers[8]. These materials find applications in various industries, including packaging and automotive, offering improved recyclability and biodegradability. Additionally, Braskem has implemented a closed-loop system for propyne recovery and reuse within their production facilities, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency[9].
Strengths: Integration of bio-based feedstocks with propyne, creating novel sustainable materials. Established market presence for eco-friendly plastics. Weaknesses: Limited by the availability of bio-based ethylene and potential scalability challenges.
Innovative Propyne-Based Green Chemistry Techniques
Microorganisms for producing propylene and methods related thereto
PatentActiveUS20120329119A1
Innovation
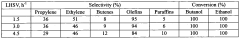
- Development of non-naturally occurring microbial organisms engineered with propylene biosynthetic pathways, using nucleic acids encoding propylene pathway enzymes to produce propylene through fermentation from renewable feedstocks like sugars and syngas, eliminating the need for dehydration steps and reducing waste and emissions.
Method of producing alkenes by dehydration of a mixture of alcohols
PatentWO2011162717A1
Innovation
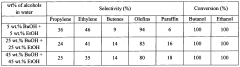
- A method involving a metal-modified zeolite catalyst, specifically Zr-modified ZSM-5, is used to dehydrate a mixture of alcohols at temperatures between 350 to 500 °C, allowing for a single-step production of alkenes with high propylene and C3+ olefins selectivity, overcoming deactivation issues and improving stability.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Propyne Use
The environmental impact assessment of propyne use is a critical aspect of evaluating its contribution to green chemistry initiatives. Propyne, also known as methylacetylene, is a hydrocarbon with potential applications in various industrial processes. Its environmental footprint must be thoroughly examined to determine its viability as a green chemistry alternative.
One of the primary considerations in assessing propyne's environmental impact is its greenhouse gas potential. Compared to other hydrocarbons, propyne has a relatively low global warming potential, making it a promising candidate for reducing carbon emissions in certain applications. However, its production process must be carefully evaluated to ensure that the overall lifecycle emissions are indeed lower than conventional alternatives.
The ozone depletion potential of propyne is another crucial factor to consider. Studies have shown that propyne has a negligible impact on stratospheric ozone, which is a significant advantage over many chlorinated and brominated compounds traditionally used in industrial processes. This characteristic aligns well with the principles of green chemistry, which emphasize the importance of preserving atmospheric integrity.
Water pollution is a concern with many chemical processes, and propyne's impact on aquatic ecosystems must be assessed. Initial research suggests that propyne has low water solubility and does not persist in aquatic environments, reducing the risk of long-term contamination. However, more comprehensive studies are needed to fully understand its behavior in different water bodies and its potential effects on aquatic life.
The biodegradability of propyne is an essential aspect of its environmental profile. As a simple hydrocarbon, propyne is generally more biodegradable than complex synthetic compounds. This property suggests that it may have a lower environmental persistence and reduced long-term ecological impact compared to some traditional chemical alternatives.
Air quality impacts are also a significant consideration in the environmental assessment of propyne. While it is less reactive than many other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), its potential contribution to smog formation and local air pollution must be carefully evaluated. Emission control strategies and proper handling procedures are crucial to minimize any adverse effects on air quality.
Land use and ecosystem impacts associated with propyne production and use should not be overlooked. The sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and disposal methods all play a role in determining the overall environmental footprint. Sustainable production practices and efficient resource utilization are essential to ensure that propyne truly contributes to green chemistry goals.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propyne use reveals several promising aspects that align with green chemistry principles. Its low greenhouse gas potential, minimal ozone depletion impact, and biodegradability are significant advantages. However, comprehensive lifecycle analyses and further research into its long-term ecological effects are necessary to fully validate its status as a green chemistry solution. Balancing its benefits against potential risks will be crucial in determining propyne's role in sustainable industrial processes.
One of the primary considerations in assessing propyne's environmental impact is its greenhouse gas potential. Compared to other hydrocarbons, propyne has a relatively low global warming potential, making it a promising candidate for reducing carbon emissions in certain applications. However, its production process must be carefully evaluated to ensure that the overall lifecycle emissions are indeed lower than conventional alternatives.
The ozone depletion potential of propyne is another crucial factor to consider. Studies have shown that propyne has a negligible impact on stratospheric ozone, which is a significant advantage over many chlorinated and brominated compounds traditionally used in industrial processes. This characteristic aligns well with the principles of green chemistry, which emphasize the importance of preserving atmospheric integrity.
Water pollution is a concern with many chemical processes, and propyne's impact on aquatic ecosystems must be assessed. Initial research suggests that propyne has low water solubility and does not persist in aquatic environments, reducing the risk of long-term contamination. However, more comprehensive studies are needed to fully understand its behavior in different water bodies and its potential effects on aquatic life.
The biodegradability of propyne is an essential aspect of its environmental profile. As a simple hydrocarbon, propyne is generally more biodegradable than complex synthetic compounds. This property suggests that it may have a lower environmental persistence and reduced long-term ecological impact compared to some traditional chemical alternatives.
Air quality impacts are also a significant consideration in the environmental assessment of propyne. While it is less reactive than many other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), its potential contribution to smog formation and local air pollution must be carefully evaluated. Emission control strategies and proper handling procedures are crucial to minimize any adverse effects on air quality.
Land use and ecosystem impacts associated with propyne production and use should not be overlooked. The sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and disposal methods all play a role in determining the overall environmental footprint. Sustainable production practices and efficient resource utilization are essential to ensure that propyne truly contributes to green chemistry goals.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of propyne use reveals several promising aspects that align with green chemistry principles. Its low greenhouse gas potential, minimal ozone depletion impact, and biodegradability are significant advantages. However, comprehensive lifecycle analyses and further research into its long-term ecological effects are necessary to fully validate its status as a green chemistry solution. Balancing its benefits against potential risks will be crucial in determining propyne's role in sustainable industrial processes.
Regulatory Framework for Green Chemistry Initiatives
The regulatory framework for green chemistry initiatives plays a crucial role in shaping the adoption and implementation of sustainable practices in the chemical industry. As propyne contributes to green chemistry initiatives, understanding the regulatory landscape is essential for its effective utilization.
At the international level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM), which provides a policy framework to promote chemical safety around the world. This framework encourages the development and use of safer alternatives, including propyne-based solutions, in various industrial processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Green Chemistry Program, which promotes the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. The program offers incentives and recognition for innovations in green chemistry, potentially benefiting propyne-based applications.
The European Union has introduced the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from the risks posed by chemicals. REACH encourages the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, creating opportunities for propyne-based green chemistry solutions.
Many countries have also established their own regulatory frameworks to promote green chemistry. For instance, Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances both incorporate elements of green chemistry principles, influencing the development and use of sustainable chemical processes.
Regulatory bodies often provide guidelines and standards for assessing the environmental impact of chemical processes. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed guidelines for testing chemicals, which can be applied to evaluate the environmental performance of propyne-based solutions.
Industry-specific regulations also play a role in shaping the adoption of green chemistry practices. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) encourages the use of green chemistry principles in drug development and manufacturing processes, potentially opening avenues for propyne applications.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, it is likely that more stringent requirements for sustainable chemical processes will be implemented. This trend is expected to drive further innovation in green chemistry, including the exploration of propyne's potential in various applications.
At the international level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM), which provides a policy framework to promote chemical safety around the world. This framework encourages the development and use of safer alternatives, including propyne-based solutions, in various industrial processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Green Chemistry Program, which promotes the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. The program offers incentives and recognition for innovations in green chemistry, potentially benefiting propyne-based applications.
The European Union has introduced the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from the risks posed by chemicals. REACH encourages the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, creating opportunities for propyne-based green chemistry solutions.
Many countries have also established their own regulatory frameworks to promote green chemistry. For instance, Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances both incorporate elements of green chemistry principles, influencing the development and use of sustainable chemical processes.
Regulatory bodies often provide guidelines and standards for assessing the environmental impact of chemical processes. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed guidelines for testing chemicals, which can be applied to evaluate the environmental performance of propyne-based solutions.
Industry-specific regulations also play a role in shaping the adoption of green chemistry practices. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) encourages the use of green chemistry principles in drug development and manufacturing processes, potentially opening avenues for propyne applications.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, it is likely that more stringent requirements for sustainable chemical processes will be implemented. This trend is expected to drive further innovation in green chemistry, including the exploration of propyne's potential in various applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!