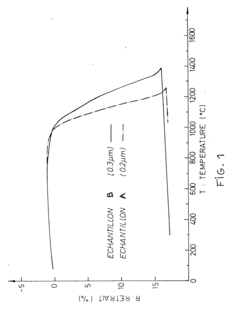
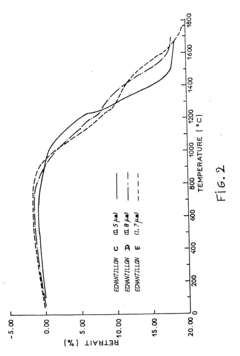
How to Approach Sustainable Zirconia Manufacturing?
Zirconia Manufacturing Evolution and Objectives
Zirconia manufacturing has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for refractory applications, zirconia has expanded its reach into various industries, including ceramics, electronics, and medical devices. The manufacturing process has continuously adapted to meet growing demands for higher quality, increased efficiency, and improved sustainability.
The early stages of zirconia production primarily focused on extracting zirconium from mineral sources such as zircon sand. Traditional methods involved high-temperature chlorination processes, which were energy-intensive and environmentally challenging. As environmental concerns grew, the industry began exploring alternative production methods to reduce energy consumption and minimize harmful emissions.
In recent decades, the zirconia manufacturing landscape has witnessed a shift towards more sustainable practices. Advanced extraction techniques, such as alkaline fusion and hydrothermal processes, have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional methods. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint of zirconia production while maintaining or improving product quality.
The current objectives in sustainable zirconia manufacturing revolve around several key areas. Firstly, there is a strong focus on developing energy-efficient production processes that minimize resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This includes optimizing furnace designs, implementing heat recovery systems, and exploring low-temperature synthesis routes.
Secondly, the industry is actively pursuing the use of renewable energy sources in zirconia production. Solar, wind, and biomass energy are being integrated into manufacturing facilities to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease overall environmental impact. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing closed-loop systems that maximize material recycling and minimize waste generation throughout the production cycle.
Another critical objective is the improvement of raw material utilization. Research efforts are directed towards enhancing extraction efficiencies from zirconium-bearing ores and exploring alternative feedstocks, including recycled materials and industrial by-products. This approach not only conserves natural resources but also contributes to the circular economy principles increasingly adopted by the industry.
Furthermore, the development of advanced process control and monitoring systems is a key focus area. These technologies enable real-time optimization of manufacturing parameters, leading to improved product consistency, reduced energy consumption, and minimized material waste. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is expected to play a crucial role in achieving these goals.
As the zirconia industry continues to evolve, the overarching objective remains clear: to establish a sustainable manufacturing paradigm that balances economic viability with environmental stewardship. This involves not only technological advancements but also the implementation of comprehensive life cycle assessments and the adoption of green chemistry principles throughout the entire production chain.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Zirconia Products
The market for sustainable zirconia products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations across various industries. Zirconia, a versatile ceramic material known for its exceptional mechanical properties and biocompatibility, has traditionally been manufactured through energy-intensive processes with considerable environmental impact. However, the shift towards sustainable manufacturing practices has opened up new opportunities in the market.
The demand for sustainable zirconia products is particularly strong in sectors such as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and electronics. In the healthcare industry, there is a growing preference for eco-friendly dental implants and prosthetics made from sustainably produced zirconia. The aerospace and automotive sectors are seeking lightweight, durable materials that can contribute to fuel efficiency while meeting sustainability goals. Similarly, the electronics industry is exploring sustainable zirconia components for various applications, including sensors and insulators.
Market research indicates that the global sustainable zirconia market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to factors such as increasing adoption of green technologies, rising consumer awareness about environmental issues, and government initiatives promoting sustainable manufacturing practices. Additionally, the market is benefiting from advancements in production technologies that enable more efficient and environmentally friendly zirconia manufacturing processes.
Key market players are investing heavily in research and development to innovate sustainable zirconia production methods. These efforts focus on reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and exploring alternative raw materials. Some companies are developing closed-loop manufacturing systems that recycle and reuse materials, significantly reducing the environmental footprint of zirconia production.
The market for sustainable zirconia products is also witnessing a trend towards vertical integration, with manufacturers seeking to control the entire supply chain to ensure sustainability at every stage. This approach allows companies to implement comprehensive sustainability measures, from raw material sourcing to final product distribution, thereby enhancing their market position and meeting the growing demand for truly sustainable products.
Geographically, Europe and North America are currently leading the sustainable zirconia market, driven by stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to emerge as a significant market in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of sustainable practices in countries like China and Japan.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as higher production costs associated with sustainable manufacturing processes and the need for substantial initial investments in new technologies. However, these challenges are gradually being offset by long-term cost savings, improved brand reputation, and access to environmentally conscious market segments.
Current Challenges in Sustainable Zirconia Production
The sustainable production of zirconia faces several significant challenges in the current manufacturing landscape. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption associated with traditional zirconia production methods. The process typically requires temperatures exceeding 1500°C, resulting in substantial energy expenditure and associated carbon emissions. This energy-intensive nature of zirconia manufacturing poses a considerable obstacle to achieving sustainability goals and reducing the industry's carbon footprint.
Another critical challenge is the limited availability and environmental impact of raw materials used in zirconia production. Zircon, the primary source of zirconium, is a finite resource, and its extraction often involves environmentally disruptive mining practices. The depletion of high-grade zircon deposits has led to increased reliance on lower-grade sources, necessitating more intensive processing and further exacerbating environmental concerns.
Water usage and management present additional sustainability challenges in zirconia production. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of water for various stages, including raw material preparation, wet milling, and post-processing. Ensuring efficient water use and implementing effective water treatment and recycling systems are crucial for minimizing environmental impact and conserving this vital resource.
The generation and management of waste materials also pose substantial challenges. Zirconia production often results in the creation of by-products and residues that require proper handling and disposal. Some of these waste materials may contain hazardous substances, necessitating specialized treatment processes to prevent environmental contamination and ensure regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, the use of chemical additives and stabilizers in zirconia manufacturing raises concerns about potential environmental and health impacts. Many of these additives are synthetic compounds that may have long-term effects on ecosystems if not properly managed. Developing eco-friendly alternatives or optimizing the use of existing additives without compromising product quality remains a significant challenge for the industry.
Lastly, the lack of standardized sustainability metrics and reporting frameworks specific to zirconia production hinders progress towards more sustainable practices. Without clear benchmarks and industry-wide standards, it becomes difficult to assess and compare the environmental performance of different manufacturing processes and products. This absence of standardization also complicates efforts to implement and validate sustainable innovations across the zirconia supply chain.
Existing Sustainable Zirconia Manufacturing Methods
01 Sustainable production methods for zirconia
Developing eco-friendly processes for zirconia production, focusing on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. This includes optimizing synthesis techniques, exploring alternative precursors, and implementing closed-loop systems to recycle materials and reduce environmental impact.- Sustainable production methods for zirconia: Developing eco-friendly processes for zirconia production, focusing on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. This includes optimizing synthesis techniques, exploring alternative precursors, and implementing closed-loop systems for resource recovery.
- Recycling and reuse of zirconia materials: Implementing strategies for recycling and reusing zirconia-based products and waste materials. This involves developing efficient separation techniques, refining processes for reclaimed zirconia, and creating new applications for recycled zirconia to promote circular economy principles.
- Energy-efficient applications of zirconia: Exploring and developing energy-efficient applications of zirconia in various industries. This includes using zirconia in fuel cells, thermal barrier coatings, and other applications that can contribute to overall energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Life cycle assessment of zirconia products: Conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments of zirconia products to identify areas for sustainability improvements. This involves analyzing the environmental impact from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, and using the results to guide more sustainable product design and manufacturing processes.
- Sustainable alternatives and substitutes for zirconia: Researching and developing sustainable alternatives or substitutes for zirconia in various applications. This includes exploring bio-based materials, composite materials, or other innovative solutions that can provide similar properties to zirconia while offering improved sustainability profiles.
02 Zirconia in sustainable energy applications
Utilizing zirconia in renewable energy technologies, such as solid oxide fuel cells and solar cells. The material's unique properties, including high thermal stability and ionic conductivity, make it valuable for improving the efficiency and durability of sustainable energy systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and reuse of zirconia materials
Developing methods for recycling and reusing zirconia-based products, particularly in industries such as dentistry and advanced ceramics. This includes techniques for recovering zirconia from end-of-life products and reprocessing it for new applications, reducing the demand for raw materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Zirconia in sustainable construction materials
Incorporating zirconia into eco-friendly construction materials to enhance their durability, strength, and thermal insulation properties. This application aims to reduce the environmental impact of buildings by improving energy efficiency and extending the lifespan of structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Life cycle assessment of zirconia products
Conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments of zirconia-based products to evaluate their environmental impact from production to disposal. This analysis helps identify areas for improvement in sustainability and guides the development of more eco-friendly zirconia applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Zirconia Industry
The sustainable zirconia manufacturing landscape is evolving rapidly, with the market currently in a growth phase. The global zirconia market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by increasing demand in various industries. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Tosoh Corp., Saint-Gobain, and 3M Innovative Properties Co. leading in innovation. These firms are investing heavily in research and development to improve production efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Emerging players such as Aidite Technology and Kceracell Co. Ltd. are also making strides in sustainable manufacturing processes. The industry is witnessing a shift towards more eco-friendly production methods, with a focus on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste, as exemplified by efforts from Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. and AGC, Inc.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
Tosoh Corp.
Innovative Approaches in Green Zirconia Synthesis
- A method involving pulverization, acid dissolution, dilution, and calcination of zirconia sintered bodies to produce recycled zirconia powder with controlled particle size and specific surface area, followed by molding and firing to create high-quality zirconia sintered bodies, particularly sheets, for use in solid oxide fuel cells.
- A process involving the heat treatment of an aerosol containing a mixture of inorganic zirconium and stabilizing compounds, such as yttrium, calcium, or cerium, without the need for organic precursors or solvents, using a temperature range of 400° to 500°C for short durations and calcination between 650° and 1250°C, produces highly reactive and homogeneous fine zirconia powders.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Zirconia Manufacturing
The environmental impact assessment of zirconia manufacturing is a critical aspect of sustainable production practices. This assessment encompasses various factors that contribute to the overall ecological footprint of the manufacturing process.
One of the primary concerns is energy consumption. Zirconia production typically requires high temperatures for sintering, which leads to significant energy usage. This energy-intensive process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. Manufacturers are increasingly exploring alternative energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to mitigate these impacts.
Water usage is another crucial factor in the environmental assessment. The production process often involves water-intensive steps, including washing and cooling. Proper water management strategies, such as closed-loop systems and water recycling, are essential to reduce consumption and minimize wastewater discharge.
Raw material extraction also plays a significant role in the environmental impact. Mining zircon, the primary source of zirconia, can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and potential water pollution if not managed responsibly. Sustainable mining practices and the exploration of alternative sources, such as recycled materials, are becoming increasingly important.
Air quality is affected by particulate matter emissions during various stages of production. Dust from raw material handling, grinding, and finishing processes can pose health risks to workers and nearby communities. Advanced filtration systems and dust suppression techniques are necessary to mitigate these impacts.
Waste management is a critical component of the assessment. The production process generates both solid and liquid waste, which requires proper handling and disposal. Implementing waste reduction strategies, such as recycling and reuse of materials, can significantly decrease the environmental burden.
Chemical usage in zirconia manufacturing, particularly during the purification and stabilization processes, can have potential environmental impacts. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals are essential to prevent soil and water contamination.
The lifecycle assessment of zirconia products is also considered, including the environmental impacts of transportation, use, and end-of-life disposal. Developing more durable and recyclable zirconia products can help reduce the overall environmental footprint.
Biodiversity impacts, particularly in areas where raw materials are sourced, must be carefully evaluated. Responsible land use practices and habitat restoration efforts are crucial for minimizing negative effects on local ecosystems.
By comprehensively assessing these environmental factors, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and implement sustainable practices throughout the zirconia production process. This holistic approach is essential for developing environmentally responsible manufacturing methods that align with global sustainability goals.
Circular Economy Strategies for Zirconia Industry
The circular economy approach offers significant potential for enhancing sustainability in the zirconia manufacturing industry. By implementing closed-loop systems and resource efficiency strategies, manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize environmental impact, and improve overall economic performance.
One key circular economy strategy for the zirconia industry is the implementation of recycling and recovery processes. This involves collecting and reprocessing zirconia waste materials from various stages of production and end-of-life products. Advanced separation techniques can be employed to recover high-purity zirconia from mixed waste streams, allowing for its reintegration into the manufacturing process. This not only reduces the demand for raw materials but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with mining and processing activities.
Another important aspect of circular economy in zirconia manufacturing is the optimization of production processes to minimize waste generation. This can be achieved through the adoption of lean manufacturing principles, which focus on eliminating inefficiencies and reducing material losses. Additionally, the implementation of advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring can help identify and address sources of waste, leading to improved resource utilization and reduced environmental impact.
The development of innovative product designs that facilitate easier disassembly and material recovery is another crucial circular economy strategy. By incorporating principles of design for recyclability, manufacturers can create zirconia products that are more easily recycled or repurposed at the end of their lifecycle. This approach not only extends the useful life of zirconia materials but also creates new value streams through the recovery and reuse of components.
Collaboration across the value chain is essential for implementing effective circular economy strategies in the zirconia industry. This includes partnerships between manufacturers, suppliers, and waste management companies to establish efficient reverse logistics systems and develop innovative recycling technologies. Furthermore, engaging with customers and end-users to promote responsible consumption and proper disposal practices can significantly enhance the effectiveness of circular economy initiatives.
Lastly, the adoption of digital technologies and data analytics can play a crucial role in enabling circular economy strategies. By leveraging the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, manufacturers can gain deeper insights into material flows, energy consumption, and waste generation throughout the production process. This data-driven approach allows for more precise optimization of resource use and the identification of new opportunities for circularity in the zirconia manufacturing industry.