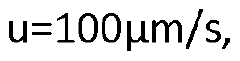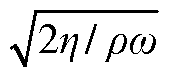How to Develop Methods for HPLC Problematic Compounds
SEP 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HPLC Method Development Background and Objectives
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 1960s, becoming an indispensable analytical technique in pharmaceutical, environmental, food, and clinical laboratories worldwide. The development of HPLC methods has progressed from simple isocratic separations to complex gradient elutions, accommodating an increasingly diverse range of analytes. However, certain compounds continue to present substantial challenges for conventional HPLC approaches, necessitating specialized method development strategies.
Problematic compounds in HPLC typically include those with extreme polarity characteristics (either highly polar or highly non-polar), structurally similar compounds, stereoisomers, compounds prone to on-column degradation, and those with poor UV absorption properties. The historical approach to these challenges has evolved from trial-and-error methodologies to more systematic, science-based strategies incorporating computer modeling and quality-by-design principles.
Recent technological advancements have expanded the HPLC toolkit, with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), and supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) offering alternative approaches for difficult separations. Additionally, the development of new stationary phases, including core-shell particles, monolithic columns, and mixed-mode phases, has provided analysts with more options for addressing challenging separations.
The primary objective of modern HPLC method development for problematic compounds is to establish robust, reproducible, and efficient analytical procedures that can reliably quantify target analytes in complex matrices. This includes achieving adequate resolution, sensitivity, and selectivity while minimizing analysis time and resource consumption. Furthermore, methods must be suitable for validation according to regulatory guidelines and transferable across different laboratory settings and instrument platforms.
Current trends in HPLC method development emphasize automation, high-throughput screening approaches, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to predict chromatographic behavior and optimize separation conditions. These advancements aim to reduce the time and resources required for method development while improving the quality and robustness of the resulting methods.
The evolution of green analytical chemistry principles has also influenced HPLC method development, driving efforts to reduce solvent consumption, minimize waste generation, and utilize more environmentally friendly mobile phases. This trend aligns with broader sustainability initiatives within the analytical chemistry community and represents an important consideration in modern method development strategies.
Looking forward, the field continues to move toward more integrated, knowledge-based approaches that combine fundamental understanding of chromatographic principles with advanced computational tools and innovative hardware solutions to address the persistent challenges posed by problematic compounds in HPLC analysis.
Problematic compounds in HPLC typically include those with extreme polarity characteristics (either highly polar or highly non-polar), structurally similar compounds, stereoisomers, compounds prone to on-column degradation, and those with poor UV absorption properties. The historical approach to these challenges has evolved from trial-and-error methodologies to more systematic, science-based strategies incorporating computer modeling and quality-by-design principles.
Recent technological advancements have expanded the HPLC toolkit, with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), and supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) offering alternative approaches for difficult separations. Additionally, the development of new stationary phases, including core-shell particles, monolithic columns, and mixed-mode phases, has provided analysts with more options for addressing challenging separations.
The primary objective of modern HPLC method development for problematic compounds is to establish robust, reproducible, and efficient analytical procedures that can reliably quantify target analytes in complex matrices. This includes achieving adequate resolution, sensitivity, and selectivity while minimizing analysis time and resource consumption. Furthermore, methods must be suitable for validation according to regulatory guidelines and transferable across different laboratory settings and instrument platforms.
Current trends in HPLC method development emphasize automation, high-throughput screening approaches, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to predict chromatographic behavior and optimize separation conditions. These advancements aim to reduce the time and resources required for method development while improving the quality and robustness of the resulting methods.
The evolution of green analytical chemistry principles has also influenced HPLC method development, driving efforts to reduce solvent consumption, minimize waste generation, and utilize more environmentally friendly mobile phases. This trend aligns with broader sustainability initiatives within the analytical chemistry community and represents an important consideration in modern method development strategies.
Looking forward, the field continues to move toward more integrated, knowledge-based approaches that combine fundamental understanding of chromatographic principles with advanced computational tools and innovative hardware solutions to address the persistent challenges posed by problematic compounds in HPLC analysis.
Market Analysis for Advanced HPLC Solutions
The global HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) market continues to expand rapidly, driven by increasing demand across pharmaceutical, biotechnology, food safety, and environmental monitoring sectors. Current market valuations place the advanced HPLC solutions segment at approximately 5.7 billion USD in 2023, with projections indicating growth to reach 8.2 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 7.5%.
Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries remain the dominant consumers of advanced HPLC technologies, accounting for nearly 65% of the total market share. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements for drug development and quality control processes, particularly for problematic compounds that present separation challenges.
The market for specialized HPLC solutions addressing problematic compounds is experiencing particularly robust growth, estimated at 9.3% annually, outpacing the broader HPLC market. This accelerated growth reflects the increasing complexity of drug molecules being developed and the expanding requirements for analyzing challenging biological samples.
Regional analysis reveals North America maintains market leadership with approximately 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth trajectory at 10.2% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities in China and India, coupled with increasing regulatory standards in these regions.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of biologics and biosimilars development, which frequently involve complex molecules requiring sophisticated separation techniques. Additionally, the growing focus on personalized medicine has increased demand for highly sensitive analytical methods capable of detecting and quantifying low-abundance biomarkers and metabolites in complex matrices.
Customer demand trends indicate growing preference for integrated HPLC systems offering enhanced capabilities for problematic compounds, including improved resolution for closely related substances, better peak symmetry for basic compounds, reduced carryover for sticky molecules, and higher sensitivity for low-concentration analytes. End-users increasingly prioritize method robustness and transferability across different laboratory settings.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by market segment, with academic and small research institutions demonstrating higher price sensitivity compared to large pharmaceutical companies and contract research organizations. The latter group demonstrates willingness to invest in premium solutions that address specific analytical challenges posed by problematic compounds, particularly when these solutions can accelerate drug development timelines or ensure regulatory compliance.
Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries remain the dominant consumers of advanced HPLC technologies, accounting for nearly 65% of the total market share. This dominance stems from stringent regulatory requirements for drug development and quality control processes, particularly for problematic compounds that present separation challenges.
The market for specialized HPLC solutions addressing problematic compounds is experiencing particularly robust growth, estimated at 9.3% annually, outpacing the broader HPLC market. This accelerated growth reflects the increasing complexity of drug molecules being developed and the expanding requirements for analyzing challenging biological samples.
Regional analysis reveals North America maintains market leadership with approximately 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth trajectory at 10.2% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities in China and India, coupled with increasing regulatory standards in these regions.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of biologics and biosimilars development, which frequently involve complex molecules requiring sophisticated separation techniques. Additionally, the growing focus on personalized medicine has increased demand for highly sensitive analytical methods capable of detecting and quantifying low-abundance biomarkers and metabolites in complex matrices.
Customer demand trends indicate growing preference for integrated HPLC systems offering enhanced capabilities for problematic compounds, including improved resolution for closely related substances, better peak symmetry for basic compounds, reduced carryover for sticky molecules, and higher sensitivity for low-concentration analytes. End-users increasingly prioritize method robustness and transferability across different laboratory settings.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by market segment, with academic and small research institutions demonstrating higher price sensitivity compared to large pharmaceutical companies and contract research organizations. The latter group demonstrates willingness to invest in premium solutions that address specific analytical challenges posed by problematic compounds, particularly when these solutions can accelerate drug development timelines or ensure regulatory compliance.
Current Challenges in HPLC Analysis of Problematic Compounds
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) faces significant challenges when analyzing problematic compounds, which often exhibit characteristics that interfere with standard analytical procedures. These compounds may demonstrate poor solubility in common mobile phases, instability under typical HPLC conditions, strong retention on columns, or complex matrix effects that obscure detection and quantification.
Polar compounds present particular difficulties due to their limited retention on conventional reversed-phase columns, often eluting near the void volume where matrix components and other interferences are concentrated. This results in poor resolution and quantification challenges. Conversely, highly hydrophobic compounds may exhibit excessive retention, leading to broad peaks, long analysis times, and potential carryover issues between injections.
Ionizable compounds introduce additional complexities as their retention behavior varies significantly with mobile phase pH. Achieving consistent results requires precise pH control, which becomes especially challenging when dealing with compounds having multiple ionizable groups or those with pKa values near the working pH range of common HPLC columns.
Thermally labile compounds may degrade during analysis, particularly when exposed to elevated temperatures in HPLC systems. This degradation can lead to multiple peaks, reduced sensitivity, and inaccurate quantification. Similarly, light-sensitive compounds require special handling throughout the analytical workflow to prevent photodegradation.
Matrix effects represent another significant challenge, particularly in biological, environmental, and food samples. Complex matrices can cause ion suppression or enhancement in LC-MS applications, protein binding issues, and co-elution of interfering compounds that complicate accurate analysis.
Chiral compounds present unique separation challenges, often requiring specialized chiral stationary phases or derivatization strategies to achieve enantiomeric resolution. The selection of appropriate chiral selectors and optimization of separation conditions frequently involves extensive method development efforts.
Technical limitations of conventional HPLC systems also contribute to analytical challenges. Detector sensitivity may be insufficient for trace analysis of certain compounds, while pressure limitations can restrict the use of smaller particle size columns that might otherwise improve resolution for difficult separations.
The increasing regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical and environmental analysis have raised the bar for method robustness and validation. Methods must now demonstrate reliability across different laboratories, instruments, and operators, which is particularly challenging for problematic compounds that operate at the boundaries of conventional HPLC capabilities.
These multifaceted challenges necessitate innovative approaches to HPLC method development, including the exploration of alternative separation modes, novel stationary phases, and advanced detection techniques to overcome the inherent limitations of traditional methodologies.
Polar compounds present particular difficulties due to their limited retention on conventional reversed-phase columns, often eluting near the void volume where matrix components and other interferences are concentrated. This results in poor resolution and quantification challenges. Conversely, highly hydrophobic compounds may exhibit excessive retention, leading to broad peaks, long analysis times, and potential carryover issues between injections.
Ionizable compounds introduce additional complexities as their retention behavior varies significantly with mobile phase pH. Achieving consistent results requires precise pH control, which becomes especially challenging when dealing with compounds having multiple ionizable groups or those with pKa values near the working pH range of common HPLC columns.
Thermally labile compounds may degrade during analysis, particularly when exposed to elevated temperatures in HPLC systems. This degradation can lead to multiple peaks, reduced sensitivity, and inaccurate quantification. Similarly, light-sensitive compounds require special handling throughout the analytical workflow to prevent photodegradation.
Matrix effects represent another significant challenge, particularly in biological, environmental, and food samples. Complex matrices can cause ion suppression or enhancement in LC-MS applications, protein binding issues, and co-elution of interfering compounds that complicate accurate analysis.
Chiral compounds present unique separation challenges, often requiring specialized chiral stationary phases or derivatization strategies to achieve enantiomeric resolution. The selection of appropriate chiral selectors and optimization of separation conditions frequently involves extensive method development efforts.
Technical limitations of conventional HPLC systems also contribute to analytical challenges. Detector sensitivity may be insufficient for trace analysis of certain compounds, while pressure limitations can restrict the use of smaller particle size columns that might otherwise improve resolution for difficult separations.
The increasing regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical and environmental analysis have raised the bar for method robustness and validation. Methods must now demonstrate reliability across different laboratories, instruments, and operators, which is particularly challenging for problematic compounds that operate at the boundaries of conventional HPLC capabilities.
These multifaceted challenges necessitate innovative approaches to HPLC method development, including the exploration of alternative separation modes, novel stationary phases, and advanced detection techniques to overcome the inherent limitations of traditional methodologies.
Current Approaches for Problematic Compound Analysis
01 HPLC method optimization for pharmaceutical analysis
Development of optimized HPLC methods for pharmaceutical compounds, focusing on parameters such as mobile phase composition, column selection, and detection techniques. These methods are designed to achieve better separation, resolution, and quantification of active pharmaceutical ingredients and their impurities, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while reducing analysis time and solvent consumption.- HPLC method optimization for pharmaceutical analysis: Development of optimized HPLC methods for pharmaceutical compounds, focusing on parameters such as mobile phase composition, column selection, and detection techniques. These methods are designed to achieve better separation, resolution, and sensitivity for drug substances and their impurities. The optimization process typically involves systematic adjustment of chromatographic conditions to enhance method robustness and reproducibility for quality control applications.
- Green HPLC method development approaches: Development of environmentally friendly HPLC methods that reduce the use of toxic organic solvents and minimize waste generation. These approaches focus on using water-based mobile phases, shorter columns, reduced flow rates, and alternative green solvents. The methods aim to maintain analytical performance while decreasing environmental impact and operational costs, aligning with sustainable laboratory practices and regulatory requirements for green chemistry.
- HPLC method validation techniques: Comprehensive validation strategies for HPLC methods according to international guidelines such as ICH, USP, and FDA requirements. These techniques involve systematic evaluation of method parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, robustness, and stability-indicating capabilities. The validation process ensures that developed methods are reliable, reproducible, and suitable for their intended analytical purpose across different laboratory settings.
- Advanced detection systems for HPLC methods: Integration of sophisticated detection technologies with HPLC systems to enhance sensitivity, selectivity, and compound identification capabilities. These include mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), diode array detection (DAD), fluorescence, electrochemical detection, and evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD). The advanced detection systems enable analysis of complex matrices, identification of unknown compounds, and quantification at lower concentration levels than conventional UV detection methods.
- HPLC method transfer and standardization: Techniques for successful transfer of developed HPLC methods between different laboratories, instruments, and column technologies. This includes strategies for method standardization, robustness testing, and equivalency assessment to ensure consistent analytical performance across various platforms. The approach addresses challenges in method transfer such as differences in instrument configurations, column variations, and laboratory environments to maintain method integrity and comparability of results.
02 Green HPLC method development approaches
Implementation of environmentally friendly HPLC techniques that reduce the use of toxic organic solvents and minimize waste generation. These approaches include using water-based mobile phases, shorter columns, reduced flow rates, and alternative detection methods. Green HPLC methods aim to maintain analytical performance while decreasing environmental impact and operational costs in analytical laboratories.Expand Specific Solutions03 HPLC method validation strategies
Comprehensive validation protocols for HPLC methods to ensure reliability, reproducibility, and robustness. These strategies involve systematic evaluation of analytical parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limits, and stability. Method validation is critical for regulatory compliance and ensures that analytical methods consistently produce accurate results across different laboratory conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced HPLC technologies for complex samples
Implementation of sophisticated HPLC techniques for analyzing complex matrices and challenging compounds. These technologies include ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), multi-dimensional chromatography, and specialized detection systems. Advanced HPLC methods enable improved separation efficiency, higher sensitivity, and faster analysis of complex biological samples, natural products, and formulations with multiple components.Expand Specific Solutions05 HPLC method transfer and standardization
Strategies for successful transfer of HPLC methods between different instruments, laboratories, and analytical platforms. This includes systematic approaches to address variations in equipment specifications, column properties, and detection systems. Method transfer protocols ensure consistent analytical performance across different settings, facilitating global harmonization of analytical procedures and enabling reliable data comparison between laboratories.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in HPLC
The HPLC problematic compounds market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing pharmaceutical R&D demands. Major players include Waters Technology Corp., which leads with advanced chromatography solutions, alongside pharmaceutical giants F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Boehringer Ingelheim that integrate HPLC technologies into their drug development processes. Specialized companies like S-Matrix Corp. offer innovative experimental design approaches, while academic institutions such as University College Cork contribute research advancements. The technology maturity varies across applications, with established methodologies for common compounds but ongoing innovation needed for challenging analytes. Asian players including Sunshine Lake Pharma and Tidetron Bioworks are expanding capabilities, indicating the global nature of this approximately $4-5 billion market segment within analytical instrumentation.
Waters Technology Corp.
Technical Solution: Waters Technology Corp. has developed comprehensive solutions for HPLC problematic compounds through their patented ACQUITY UPLC and ACQUITY Premier systems. Their technology incorporates hybrid particle chemistry with MaxPeak High Performance Surface (HPS) technology that minimizes non-specific adsorption of metal-sensitive compounds[1]. The system utilizes sub-2-μm particle columns that provide enhanced resolution and sensitivity for challenging analytes. Waters' method development approach includes their Columns Manager software that enables automated screening of multiple column chemistries and mobile phase combinations to quickly identify optimal separation conditions[2]. Their ACQUITY Premier columns feature a hybrid organic/inorganic surface technology that reduces peak tailing and improves recovery for basic compounds and metal-chelating molecules like phosphorylated peptides and oligonucleotides[3]. Additionally, their Arc Premier system extends this technology to conventional HPLC applications, providing a seamless transition path for laboratories working with problematic compounds.
Strengths: Industry-leading surface technology that specifically addresses metal sensitivity issues; comprehensive software tools for automated method development; broad range of column chemistries optimized for different compound classes. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment compared to standard HPLC systems; proprietary consumables may increase operational costs; requires specialized training to fully utilize advanced features.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed a comprehensive strategy for handling problematic compounds in HPLC analysis through their Analytical Method Innovation platform. Their approach combines traditional reversed-phase chromatography with alternative separation modes including HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) for highly polar compounds and SFC (Supercritical Fluid Chromatography) for compounds with solubility challenges[1]. For thermally labile compounds, Roche employs low-temperature chromatography systems with precise column temperature control. Their method development workflow incorporates automated column screening with parallel analysis capabilities, allowing simultaneous evaluation of multiple stationary phases and mobile phase compositions. For compounds prone to ionic interactions or metal chelation, Roche utilizes mobile phase additives including ion-pairing reagents, chelating agents, and pH modifiers to improve peak shape and resolution[2]. Their platform includes specialized detection techniques such as charged aerosol detection (CAD) for compounds lacking chromophores and high-resolution mass spectrometry for complex mixtures. Roche has also implemented machine learning algorithms that predict chromatographic behavior based on molecular structure, accelerating method development for novel compounds[3]. For biologics and large molecules, they employ size-exclusion chromatography with advanced light scattering detection to characterize aggregation and higher-order structure.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach covering multiple separation modes; integration with drug development pipeline ensures methods are suitable for regulatory submission; advanced predictive tools reduce development time. Weaknesses: Complex methods may be challenging to transfer to manufacturing or quality control environments; specialized equipment requirements increase implementation costs; requires high level of analytical expertise.
Key Innovations in HPLC Column and Mobile Phase Technology
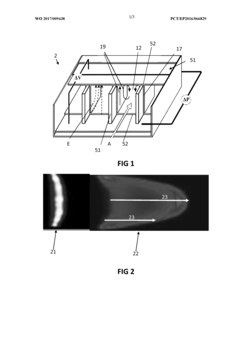
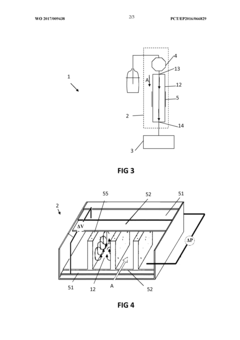
High-performance liquid chromatography with a controllable transverse flow inducer
PatentWO2017009438A1
Innovation
- The use of a controllable transverse flow inducer, such as an array of electrodes generating an alternating current electrokinetic field, to create micro-scale vortices that reduce dispersion and enhance mass transfer between support structures in the chromatography column, allowing for efficient separation without permanent surface charges and minimizing direct contact with electrodes.
Method and apparatus for high performance separation by sample displacement chromatography
PatentInactiveCA2059114A1
Innovation
- A multi-segment HPLC apparatus and method where a solution of compounds is added to a chromatography bed with connected upstream, intermediate, and downstream segments, each containing stationary phase material, allowing saturation and subsequent elution of segments to isolate a selected compound in pure form without solvent gradients, using valved connectors to manage pressure and fluid communication.
Regulatory Compliance in Analytical Method Validation
Regulatory compliance represents a critical aspect of analytical method validation for HPLC techniques, particularly when dealing with problematic compounds. The pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries operate under stringent regulatory frameworks established by authorities such as the FDA, EMA, ICH, and USP, which mandate comprehensive validation of analytical methods to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy.
For HPLC method development targeting problematic compounds, compliance with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines is paramount. These guidelines specify validation parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, range, robustness, and system suitability. When handling challenging analytes with poor UV absorption, stability issues, or complex matrices, additional validation considerations become necessary to demonstrate method reliability.
FDA's Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics guidance further emphasizes the importance of method lifecycle management, particularly for problematic compounds where traditional approaches may prove insufficient. This framework encompasses method design, development, qualification, and continued verification phases, ensuring ongoing method performance even under challenging analytical conditions.
The implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) principles in HPLC method development has gained regulatory acceptance as an effective approach for problematic compounds. This systematic approach involves defining analytical target profiles, identifying critical method attributes, and establishing a design space where method parameters can be adjusted while maintaining compliance and performance standards.
Documentation requirements for regulatory submission present another significant compliance consideration. For problematic compounds, comprehensive method development reports must include detailed justification for non-standard approaches, robustness studies demonstrating method reliability under varying conditions, and complete validation data addressing specific challenges posed by the analyte properties.
Transfer of validated methods between laboratories requires adherence to USP <1224> guidelines, with particular attention to problematic compounds that may exhibit different behaviors across various analytical systems or environments. Successful method transfer protocols must account for these variations while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Ongoing compliance monitoring through periodic revalidation and system suitability testing is essential, especially for methods analyzing unstable or complex compounds. Regulatory bodies increasingly expect continuous verification data demonstrating sustained method performance throughout the product lifecycle, with appropriate control strategies for managing method variability.
For HPLC method development targeting problematic compounds, compliance with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines is paramount. These guidelines specify validation parameters including specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, detection limit, quantitation limit, range, robustness, and system suitability. When handling challenging analytes with poor UV absorption, stability issues, or complex matrices, additional validation considerations become necessary to demonstrate method reliability.
FDA's Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics guidance further emphasizes the importance of method lifecycle management, particularly for problematic compounds where traditional approaches may prove insufficient. This framework encompasses method design, development, qualification, and continued verification phases, ensuring ongoing method performance even under challenging analytical conditions.
The implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) principles in HPLC method development has gained regulatory acceptance as an effective approach for problematic compounds. This systematic approach involves defining analytical target profiles, identifying critical method attributes, and establishing a design space where method parameters can be adjusted while maintaining compliance and performance standards.
Documentation requirements for regulatory submission present another significant compliance consideration. For problematic compounds, comprehensive method development reports must include detailed justification for non-standard approaches, robustness studies demonstrating method reliability under varying conditions, and complete validation data addressing specific challenges posed by the analyte properties.
Transfer of validated methods between laboratories requires adherence to USP <1224> guidelines, with particular attention to problematic compounds that may exhibit different behaviors across various analytical systems or environments. Successful method transfer protocols must account for these variations while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Ongoing compliance monitoring through periodic revalidation and system suitability testing is essential, especially for methods analyzing unstable or complex compounds. Regulatory bodies increasingly expect continuous verification data demonstrating sustained method performance throughout the product lifecycle, with appropriate control strategies for managing method variability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Advanced HPLC Methods
When evaluating the implementation of advanced HPLC methods for problematic compounds, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is essential for making informed decisions. The initial investment in advanced HPLC technologies can be substantial, with high-end systems ranging from $50,000 to $150,000, depending on the level of automation, detection capabilities, and column technology required for challenging analytes.
Operational costs must also be considered, including specialized columns ($500-$2,000 each) that may have shorter lifespans when used with problematic compounds, high-purity solvents, and maintenance requirements. Personnel training represents another significant investment, as analysts require specialized knowledge to develop and optimize methods for difficult compounds.
However, these costs must be weighed against the considerable benefits. Advanced HPLC methods significantly improve analytical precision and accuracy, with detection limits often 10-100 times lower than conventional approaches. This enhanced sensitivity directly translates to better quality control and regulatory compliance, potentially avoiding costly product recalls or regulatory penalties that can exceed millions of dollars.
Time efficiency represents another major benefit, as optimized methods can reduce analysis time by 30-70% compared to traditional approaches. For pharmaceutical companies, this acceleration can substantially impact time-to-market for new drugs, where each day of delay can represent $1-3 million in lost revenue opportunities.
The return on investment timeline typically shows that while advanced HPLC methods require higher initial expenditure, the break-even point often occurs within 12-24 months through improved operational efficiency, reduced method development time, and enhanced analytical capabilities. Organizations handling large sample volumes or high-value products tend to realize ROI more quickly.
Risk mitigation represents an often-overlooked benefit in the analysis. Advanced HPLC methods provide more robust and reliable results for problematic compounds, reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives that could lead to significant downstream costs. This improved reliability can be particularly valuable when analyzing compounds in complex matrices or those with challenging physicochemical properties.
For organizations considering implementation, a phased approach often provides the optimal balance between cost management and capability enhancement, allowing for strategic investment in the specific technologies most relevant to their problematic compounds while building institutional expertise progressively.
Operational costs must also be considered, including specialized columns ($500-$2,000 each) that may have shorter lifespans when used with problematic compounds, high-purity solvents, and maintenance requirements. Personnel training represents another significant investment, as analysts require specialized knowledge to develop and optimize methods for difficult compounds.
However, these costs must be weighed against the considerable benefits. Advanced HPLC methods significantly improve analytical precision and accuracy, with detection limits often 10-100 times lower than conventional approaches. This enhanced sensitivity directly translates to better quality control and regulatory compliance, potentially avoiding costly product recalls or regulatory penalties that can exceed millions of dollars.
Time efficiency represents another major benefit, as optimized methods can reduce analysis time by 30-70% compared to traditional approaches. For pharmaceutical companies, this acceleration can substantially impact time-to-market for new drugs, where each day of delay can represent $1-3 million in lost revenue opportunities.
The return on investment timeline typically shows that while advanced HPLC methods require higher initial expenditure, the break-even point often occurs within 12-24 months through improved operational efficiency, reduced method development time, and enhanced analytical capabilities. Organizations handling large sample volumes or high-value products tend to realize ROI more quickly.
Risk mitigation represents an often-overlooked benefit in the analysis. Advanced HPLC methods provide more robust and reliable results for problematic compounds, reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives that could lead to significant downstream costs. This improved reliability can be particularly valuable when analyzing compounds in complex matrices or those with challenging physicochemical properties.
For organizations considering implementation, a phased approach often provides the optimal balance between cost management and capability enhancement, allowing for strategic investment in the specific technologies most relevant to their problematic compounds while building institutional expertise progressively.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!