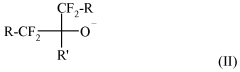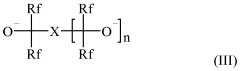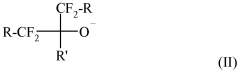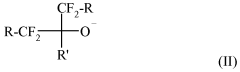How to Enhance Catalytic Efficiency Using Fluoroantimonic Acid?
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoroantimonic Acid Catalysis Background and Objectives
Fluoroantimonic acid, a superacid formed by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, has emerged as a powerful catalyst in various chemical processes. Its exceptional acidity, surpassing that of conventional acids, has attracted significant attention in the field of catalysis. The development of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with pioneering work by George A. Olah and his colleagues.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and selective chemical transformations in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. As global competition intensifies and environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing need for catalysts that can operate under milder conditions, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation.
The primary objective of enhancing catalytic efficiency using fluoroantimonic acid is to overcome the limitations of traditional acid catalysts. These limitations include low activity, poor selectivity, and rapid deactivation. By harnessing the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid, researchers aim to develop catalytic systems that can achieve higher conversion rates, improved product yields, and enhanced selectivity towards desired products.
Another crucial goal is to expand the scope of reactions that can be catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. This includes exploring its potential in challenging transformations such as C-H bond activation, isomerization of hydrocarbons, and polymerization reactions. By broadening the range of applications, fluoroantimonic acid catalysis could revolutionize various industrial processes and enable the synthesis of novel materials and compounds.
Furthermore, understanding the fundamental mechanisms of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis is essential for rational catalyst design and optimization. Researchers are focusing on elucidating the nature of active sites, the role of counter-ions, and the influence of reaction conditions on catalytic performance. This knowledge will facilitate the development of tailored catalytic systems for specific applications and guide the search for even more potent superacid catalysts.
Addressing the challenges associated with handling and containment of fluoroantimonic acid is also a key objective. Due to its extreme corrosiveness and moisture sensitivity, developing safer and more practical methods for its application in industrial settings is crucial. This includes exploring supported catalysts, ionic liquids, and other innovative approaches to harness the power of fluoroantimonic acid while mitigating its inherent risks.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and selective chemical transformations in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. As global competition intensifies and environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing need for catalysts that can operate under milder conditions, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation.
The primary objective of enhancing catalytic efficiency using fluoroantimonic acid is to overcome the limitations of traditional acid catalysts. These limitations include low activity, poor selectivity, and rapid deactivation. By harnessing the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid, researchers aim to develop catalytic systems that can achieve higher conversion rates, improved product yields, and enhanced selectivity towards desired products.
Another crucial goal is to expand the scope of reactions that can be catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. This includes exploring its potential in challenging transformations such as C-H bond activation, isomerization of hydrocarbons, and polymerization reactions. By broadening the range of applications, fluoroantimonic acid catalysis could revolutionize various industrial processes and enable the synthesis of novel materials and compounds.
Furthermore, understanding the fundamental mechanisms of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis is essential for rational catalyst design and optimization. Researchers are focusing on elucidating the nature of active sites, the role of counter-ions, and the influence of reaction conditions on catalytic performance. This knowledge will facilitate the development of tailored catalytic systems for specific applications and guide the search for even more potent superacid catalysts.
Addressing the challenges associated with handling and containment of fluoroantimonic acid is also a key objective. Due to its extreme corrosiveness and moisture sensitivity, developing safer and more practical methods for its application in industrial settings is crucial. This includes exploring supported catalysts, ionic liquids, and other innovative approaches to harness the power of fluoroantimonic acid while mitigating its inherent risks.
Industrial Demand for Enhanced Catalytic Efficiency
The industrial demand for enhanced catalytic efficiency using fluoroantimonic acid is driven by several key factors in the chemical and petrochemical sectors. As one of the strongest known superacids, fluoroantimonic acid has garnered significant attention for its potential to revolutionize catalytic processes across various industries.
In the petrochemical industry, there is a growing need for more efficient catalysts to improve the conversion rates of hydrocarbons and reduce energy consumption in refining processes. Fluoroantimonic acid's exceptional acidity offers the potential to catalyze reactions at lower temperatures and pressures, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This aligns with the industry's push towards more sustainable and economically viable production methods.
The pharmaceutical sector also shows increasing interest in enhanced catalytic efficiency. Drug synthesis often involves complex multi-step processes, where improved catalysts can significantly reduce production time and costs. Fluoroantimonic acid's ability to catalyze challenging reactions, such as C-C bond formations and isomerizations, makes it an attractive option for developing more efficient synthetic routes for active pharmaceutical ingredients.
In the polymer industry, there is a constant demand for catalysts that can improve the production of high-performance materials. Fluoroantimonic acid's potential to catalyze polymerization reactions more efficiently could lead to the development of novel materials with enhanced properties, meeting the growing demand for advanced polymers in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
The fine chemicals industry is another sector where the demand for enhanced catalytic efficiency is prominent. Manufacturers are seeking ways to improve yields and selectivity in the production of specialty chemicals. Fluoroantimonic acid's strong acidic properties could potentially catalyze reactions that are currently challenging or impossible with conventional catalysts, opening up new possibilities for product development and process optimization.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also driving the demand for more efficient catalytic processes. Industries are looking for ways to reduce waste generation and minimize the use of hazardous substances. While fluoroantimonic acid itself is highly corrosive and requires careful handling, its potential to enable more efficient reactions could lead to overall reductions in chemical waste and energy consumption in industrial processes.
The electronics industry is another sector showing interest in enhanced catalytic efficiency. In semiconductor manufacturing, precise control of chemical reactions is crucial. Fluoroantimonic acid's strong acidic properties could potentially be harnessed to improve etching processes or catalyze the deposition of thin films, contributing to the development of more advanced and efficient electronic components.
In the petrochemical industry, there is a growing need for more efficient catalysts to improve the conversion rates of hydrocarbons and reduce energy consumption in refining processes. Fluoroantimonic acid's exceptional acidity offers the potential to catalyze reactions at lower temperatures and pressures, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This aligns with the industry's push towards more sustainable and economically viable production methods.
The pharmaceutical sector also shows increasing interest in enhanced catalytic efficiency. Drug synthesis often involves complex multi-step processes, where improved catalysts can significantly reduce production time and costs. Fluoroantimonic acid's ability to catalyze challenging reactions, such as C-C bond formations and isomerizations, makes it an attractive option for developing more efficient synthetic routes for active pharmaceutical ingredients.
In the polymer industry, there is a constant demand for catalysts that can improve the production of high-performance materials. Fluoroantimonic acid's potential to catalyze polymerization reactions more efficiently could lead to the development of novel materials with enhanced properties, meeting the growing demand for advanced polymers in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
The fine chemicals industry is another sector where the demand for enhanced catalytic efficiency is prominent. Manufacturers are seeking ways to improve yields and selectivity in the production of specialty chemicals. Fluoroantimonic acid's strong acidic properties could potentially catalyze reactions that are currently challenging or impossible with conventional catalysts, opening up new possibilities for product development and process optimization.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also driving the demand for more efficient catalytic processes. Industries are looking for ways to reduce waste generation and minimize the use of hazardous substances. While fluoroantimonic acid itself is highly corrosive and requires careful handling, its potential to enable more efficient reactions could lead to overall reductions in chemical waste and energy consumption in industrial processes.
The electronics industry is another sector showing interest in enhanced catalytic efficiency. In semiconductor manufacturing, precise control of chemical reactions is crucial. Fluoroantimonic acid's strong acidic properties could potentially be harnessed to improve etching processes or catalyze the deposition of thin films, contributing to the development of more advanced and efficient electronic components.
Current State and Challenges in Superacid Catalysis
Superacid catalysis has emerged as a powerful tool in organic synthesis and industrial processes, with fluoroantimonic acid (HSbF6) at the forefront of this field. The current state of superacid catalysis is characterized by significant advancements in reaction efficiency and selectivity, yet it faces several challenges that hinder its widespread application.
Recent developments have shown remarkable progress in the use of fluoroantimonic acid as a catalyst. Its exceptional acidity, surpassing even that of sulfuric acid, enables it to protonate a wide range of substrates, including weakly basic compounds. This property has led to its successful application in various reactions, such as isomerization, alkylation, and polymerization processes.
However, the extreme reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also presents significant challenges. Its corrosive nature necessitates specialized handling and storage equipment, limiting its use in many industrial settings. Moreover, the high sensitivity to moisture requires stringent anhydrous conditions, complicating large-scale applications and increasing operational costs.
Another critical challenge lies in controlling the selectivity of reactions catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. While its strong acidity can activate numerous substrates, it can also lead to undesired side reactions and product degradation. Researchers are actively working on developing methods to fine-tune the acid's reactivity and improve reaction selectivity.
The environmental impact of superacid catalysis remains a concern. The production and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related compounds pose potential risks to ecosystems. Efforts are underway to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives or to implement effective recycling and waste management strategies.
In terms of scalability, the transition from laboratory-scale reactions to industrial processes presents significant hurdles. The need for specialized equipment and the challenges associated with maintaining anhydrous conditions on a large scale have limited the industrial adoption of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research is focused on overcoming these limitations. Scientists are exploring novel catalyst designs, such as supported superacids and ionic liquid-based systems, which aim to combine the high activity of fluoroantimonic acid with improved stability and ease of handling.
The development of in situ characterization techniques has also advanced our understanding of superacid catalysis mechanisms. These insights are crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and designing more efficient catalytic systems.
In conclusion, while superacid catalysis using fluoroantimonic acid offers tremendous potential for enhancing catalytic efficiency, significant challenges remain in terms of handling, selectivity, environmental impact, and scalability. Addressing these issues is critical for the broader adoption of this powerful catalytic approach in both academic and industrial settings.
Recent developments have shown remarkable progress in the use of fluoroantimonic acid as a catalyst. Its exceptional acidity, surpassing even that of sulfuric acid, enables it to protonate a wide range of substrates, including weakly basic compounds. This property has led to its successful application in various reactions, such as isomerization, alkylation, and polymerization processes.
However, the extreme reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also presents significant challenges. Its corrosive nature necessitates specialized handling and storage equipment, limiting its use in many industrial settings. Moreover, the high sensitivity to moisture requires stringent anhydrous conditions, complicating large-scale applications and increasing operational costs.
Another critical challenge lies in controlling the selectivity of reactions catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. While its strong acidity can activate numerous substrates, it can also lead to undesired side reactions and product degradation. Researchers are actively working on developing methods to fine-tune the acid's reactivity and improve reaction selectivity.
The environmental impact of superacid catalysis remains a concern. The production and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related compounds pose potential risks to ecosystems. Efforts are underway to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives or to implement effective recycling and waste management strategies.
In terms of scalability, the transition from laboratory-scale reactions to industrial processes presents significant hurdles. The need for specialized equipment and the challenges associated with maintaining anhydrous conditions on a large scale have limited the industrial adoption of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research is focused on overcoming these limitations. Scientists are exploring novel catalyst designs, such as supported superacids and ionic liquid-based systems, which aim to combine the high activity of fluoroantimonic acid with improved stability and ease of handling.
The development of in situ characterization techniques has also advanced our understanding of superacid catalysis mechanisms. These insights are crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and designing more efficient catalytic systems.
In conclusion, while superacid catalysis using fluoroantimonic acid offers tremendous potential for enhancing catalytic efficiency, significant challenges remain in terms of handling, selectivity, environmental impact, and scalability. Addressing these issues is critical for the broader adoption of this powerful catalytic approach in both academic and industrial settings.
Existing Methods for Improving Catalytic Efficiency
01 Catalytic efficiency in chemical reactions
Fluoroantimonic acid demonstrates high catalytic efficiency in various chemical reactions due to its extreme acidity. It is particularly effective in promoting reactions such as isomerization, alkylation, and polymerization. The acid's strong proton-donating ability enhances reaction rates and yields, making it valuable in industrial processes and organic synthesis.- Catalytic applications in chemical processes: Fluoroantimonic acid demonstrates high catalytic efficiency in various chemical processes, particularly in hydrocarbon transformations. Its strong acidity enables it to catalyze reactions such as isomerization, alkylation, and cracking of hydrocarbons. The acid's unique properties allow for enhanced reaction rates and selectivity in these processes.
- Synthesis and preparation methods: The synthesis and preparation of fluoroantimonic acid involve careful handling due to its highly corrosive nature. Methods for producing this superacid often include the combination of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride under controlled conditions. Optimizing the synthesis process can lead to improved purity and catalytic efficiency of the resulting acid.
- Catalytic efficiency in petroleum refining: Fluoroantimonic acid exhibits exceptional catalytic efficiency in petroleum refining processes. Its use in isomerization and alkylation reactions can lead to improved octane ratings in gasoline production. The acid's strong protonating ability allows for more efficient conversion of low-value hydrocarbons into higher-value products.
- Enhancing catalytic performance: Researchers have explored various methods to enhance the catalytic performance of fluoroantimonic acid. These include the use of support materials, the addition of co-catalysts, and the development of novel reaction systems. Such enhancements aim to improve the acid's stability, recyclability, and overall catalytic efficiency in industrial applications.
- Safety and handling considerations: Due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity, the use of fluoroantimonic acid requires stringent safety measures and specialized handling techniques. Researchers and industry professionals have developed protocols for safe storage, transport, and application of this superacid to maximize its catalytic efficiency while minimizing risks associated with its use.
02 Application in hydrocarbon processing
Fluoroantimonic acid is utilized in hydrocarbon processing, particularly in the petroleum industry. Its catalytic properties are exploited for cracking, isomerization, and alkylation of hydrocarbons. The acid's efficiency in these processes contributes to the production of high-octane fuels and other valuable petrochemical products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synthesis and preparation methods
Various methods for synthesizing and preparing fluoroantimonic acid have been developed to optimize its catalytic efficiency. These methods focus on controlling the concentration and purity of the acid, as well as developing stable forms for easier handling and application in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic systems and supports
Research has been conducted on developing catalytic systems and supports for fluoroantimonic acid to enhance its efficiency and recyclability. These systems aim to immobilize the acid on various supports, allowing for easier separation and recovery while maintaining its catalytic activity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling considerations
Due to the extreme reactivity and corrosiveness of fluoroantimonic acid, special safety and handling procedures are necessary to ensure its efficient and safe use as a catalyst. This includes the development of specialized equipment, containment systems, and protocols for storage, transport, and application in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Superacid Catalyst Industry
The catalytic efficiency enhancement using fluoroantimonic acid is in a nascent stage of development, with a growing market potential due to its applications in various industries. The technology is still evolving, with a moderate level of maturity. Key players like BASF Corp., Honeywell International Technologies Ltd., and 3M Innovative Properties Co. are leading the research and development efforts. Academic institutions such as Central South University and Monash University are contributing to fundamental research. The market is characterized by collaborations between industry and academia, with companies like PetroChina Co., Ltd. and Evonik Operations GmbH focusing on practical applications. As the technology advances, we can expect increased competition and innovation from both established chemical companies and emerging specialized firms.
DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd.
Technical Solution: DAIKIN has developed a novel approach to enhance catalytic efficiency using fluoroantimonic acid in fluoropolymer synthesis. Their method involves using fluoroantimonic acid as a super-acid catalyst in a specially designed fluorinated solvent system. This unique combination allows for the polymerization of fluorinated monomers under milder conditions than traditional methods. The fluorinated solvent helps to stabilize the reactive intermediates and control the reaction kinetics, resulting in improved polymer properties and higher yields. Additionally, DAIKIN has developed a proprietary reactor design that allows for safe handling of the fluoroantimonic acid catalyst and efficient heat transfer during the polymerization process.
Strengths: Improved polymer properties, higher yields, and milder reaction conditions. Weaknesses: Specialized equipment requirements and potential environmental concerns related to fluorinated compounds.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has developed an advanced process for enhancing catalytic efficiency using fluoroantimonic acid in conjunction with their UOP (Universal Oil Products) technology. Their approach involves using fluoroantimonic acid as a promoter in a multi-component catalyst system for hydrocarbon processing. The fluoroantimonic acid is carefully integrated into a zeolite-based catalyst matrix, which provides both high acidity and shape selectivity. This combination allows for enhanced catalytic activity in processes such as alkylation and isomerization of hydrocarbons, while also improving the catalyst's resistance to deactivation.
Strengths: High catalytic activity, improved selectivity, and enhanced catalyst lifetime. Weaknesses: Complexity of the catalyst system and potential corrosion issues in processing equipment.
Core Innovations in Fluoroantimonic Acid Catalysis
Curing compositions for fluoropolymers
PatentInactiveUS20120065321A1
Innovation
- Development of a catalyst composition comprising a cation and anion, specifically an organo onium, that is essentially free of hydrocarbon-containing alcohol, allowing for improved rheology control and reduced scorch in fluoroelastomers, particularly through the use of anions like tetra-alkylammonium 2-phenyl-1,1,1,3,3,3 hexafluoroisopropanoate, which effectively generates triazine crosslinks in perfluoroelastomers.
Curing compositions for fluoropolymers
PatentWO2010151610A2
Innovation
- A catalyst composition comprising a cation and anion, specifically an organo onium compound, is developed, which is essentially free of hydrocarbon-containing alcohol, allowing for improved rheology control and reduced scorch in fluoroelastomers, thereby enhancing their high-temperature performance and reducing metal residue issues.
Safety and Handling Protocols for Superacids
Fluoroantimonic acid, being one of the strongest known superacids, requires stringent safety measures and handling protocols. The extreme corrosiveness and reactivity of this compound necessitate specialized equipment and procedures to ensure the safety of personnel and the integrity of research facilities.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with fluoroantimonic acid. Operators must wear fully encapsulating chemical-resistant suits, including gloves, boots, and face shields. The suit material should be specifically rated for resistance to hydrofluoric acid and antimony pentafluoride. Respiratory protection in the form of self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) is essential due to the potential for toxic fume generation.
Containment systems for fluoroantimonic acid must be constructed from materials that can withstand its corrosive nature. Teflon (PTFE) and certain fluoropolymers are among the few materials capable of resisting attack. All storage and reaction vessels should be sealed and kept under an inert atmosphere, typically dry nitrogen or argon, to prevent moisture contamination which can lead to violent reactions.
Workplace design plays a crucial role in safety. Dedicated fume hoods with specialized scrubber systems are required for all operations involving fluoroantimonic acid. The work area should be equipped with emergency showers, eyewash stations, and spill containment kits specifically designed for superacid incidents. Proper ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the accumulation of potentially hazardous fumes.
Training and emergency response protocols are critical components of safe handling. All personnel working with or around fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. Emergency response teams should be trained and equipped to deal with superacid spills and exposures. Clear, well-rehearsed evacuation procedures must be established and regularly practiced.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization should only be attempted by trained professionals using appropriate equipment. Disposal must comply with all relevant environmental regulations and should typically involve specialized chemical waste management services.
Monitoring and maintenance of safety systems are ongoing requirements. Regular inspections of containment systems, PPE, and emergency equipment are necessary to ensure their effectiveness. Environmental monitoring for potential acid vapors or leaks should be conducted routinely using appropriate detection equipment.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with fluoroantimonic acid. Operators must wear fully encapsulating chemical-resistant suits, including gloves, boots, and face shields. The suit material should be specifically rated for resistance to hydrofluoric acid and antimony pentafluoride. Respiratory protection in the form of self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) is essential due to the potential for toxic fume generation.
Containment systems for fluoroantimonic acid must be constructed from materials that can withstand its corrosive nature. Teflon (PTFE) and certain fluoropolymers are among the few materials capable of resisting attack. All storage and reaction vessels should be sealed and kept under an inert atmosphere, typically dry nitrogen or argon, to prevent moisture contamination which can lead to violent reactions.
Workplace design plays a crucial role in safety. Dedicated fume hoods with specialized scrubber systems are required for all operations involving fluoroantimonic acid. The work area should be equipped with emergency showers, eyewash stations, and spill containment kits specifically designed for superacid incidents. Proper ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the accumulation of potentially hazardous fumes.
Training and emergency response protocols are critical components of safe handling. All personnel working with or around fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. Emergency response teams should be trained and equipped to deal with superacid spills and exposures. Clear, well-rehearsed evacuation procedures must be established and regularly practiced.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization should only be attempted by trained professionals using appropriate equipment. Disposal must comply with all relevant environmental regulations and should typically involve specialized chemical waste management services.
Monitoring and maintenance of safety systems are ongoing requirements. Regular inspections of containment systems, PPE, and emergency equipment are necessary to ensure their effectiveness. Environmental monitoring for potential acid vapors or leaks should be conducted routinely using appropriate detection equipment.
Environmental Impact of Fluoroantimonic Acid Use
The use of fluoroantimonic acid in catalytic processes presents significant environmental challenges due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity. As one of the strongest known superacids, its potential impact on ecosystems and human health is a major concern for researchers and environmental agencies.
When released into the environment, fluoroantimonic acid can cause severe damage to soil and water systems. Its high acidity can lead to the rapid degradation of organic matter, disrupting natural biogeochemical cycles and potentially causing long-term ecological imbalances. The acid's ability to dissolve many materials, including glass and metals, poses risks to infrastructure and wildlife habitats.
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to fluoroantimonic acid contamination. Even small amounts can dramatically alter water pH levels, leading to the death of fish, amphibians, and aquatic plants. The acid's fluorine content may also contribute to the bioaccumulation of fluoride in aquatic organisms, potentially affecting entire food chains.
Air pollution is another significant concern. Vapors from fluoroantimonic acid can form toxic aerosols, contributing to acid rain and smog formation. These emissions can have far-reaching effects on air quality, potentially impacting human respiratory health and vegetation in affected areas.
The production and handling of fluoroantimonic acid also present occupational hazards. Strict safety protocols are essential to prevent accidental releases and protect workers from exposure. Personal protective equipment and specialized containment systems are necessary, adding to the overall environmental footprint of its use.
Waste management is a critical aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid. Neutralization and proper disposal techniques must be employed to prevent contamination of soil and water resources. However, these processes themselves can generate hazardous by-products, requiring additional treatment and disposal considerations.
Given these environmental concerns, there is growing interest in developing alternative catalysts that offer similar efficiency without the associated risks. Green chemistry initiatives are exploring more environmentally benign options, such as ionic liquids and solid acid catalysts, which could potentially replace fluoroantimonic acid in certain applications.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the use of fluoroantimonic acid, implementing stricter guidelines for its handling, storage, and disposal. Environmental impact assessments are becoming mandatory for industries utilizing this superacid, driving the development of more sustainable practices and technologies.
When released into the environment, fluoroantimonic acid can cause severe damage to soil and water systems. Its high acidity can lead to the rapid degradation of organic matter, disrupting natural biogeochemical cycles and potentially causing long-term ecological imbalances. The acid's ability to dissolve many materials, including glass and metals, poses risks to infrastructure and wildlife habitats.
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to fluoroantimonic acid contamination. Even small amounts can dramatically alter water pH levels, leading to the death of fish, amphibians, and aquatic plants. The acid's fluorine content may also contribute to the bioaccumulation of fluoride in aquatic organisms, potentially affecting entire food chains.
Air pollution is another significant concern. Vapors from fluoroantimonic acid can form toxic aerosols, contributing to acid rain and smog formation. These emissions can have far-reaching effects on air quality, potentially impacting human respiratory health and vegetation in affected areas.
The production and handling of fluoroantimonic acid also present occupational hazards. Strict safety protocols are essential to prevent accidental releases and protect workers from exposure. Personal protective equipment and specialized containment systems are necessary, adding to the overall environmental footprint of its use.
Waste management is a critical aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid. Neutralization and proper disposal techniques must be employed to prevent contamination of soil and water resources. However, these processes themselves can generate hazardous by-products, requiring additional treatment and disposal considerations.
Given these environmental concerns, there is growing interest in developing alternative catalysts that offer similar efficiency without the associated risks. Green chemistry initiatives are exploring more environmentally benign options, such as ionic liquids and solid acid catalysts, which could potentially replace fluoroantimonic acid in certain applications.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the use of fluoroantimonic acid, implementing stricter guidelines for its handling, storage, and disposal. Environmental impact assessments are becoming mandatory for industries utilizing this superacid, driving the development of more sustainable practices and technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!