How to Improve Polyurethane Adhesives for Better Bonding?
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PU Adhesive Evolution
Polyurethane (PU) adhesives have undergone significant evolution since their introduction in the 1940s. Initially developed as a byproduct of World War II research, these versatile adhesives quickly gained traction in various industries due to their exceptional bonding properties and durability.
The early stages of PU adhesive development focused primarily on improving their basic formulations and understanding the chemistry behind their curing mechanisms. Scientists worked on optimizing the ratio of isocyanates to polyols, which forms the backbone of PU adhesives, to achieve better bonding strength and flexibility.
In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers made substantial progress in enhancing the moisture resistance of PU adhesives. This breakthrough expanded their application range, particularly in outdoor and marine environments. During this period, the introduction of two-component PU adhesives also marked a significant milestone, offering improved control over curing times and bond strength.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards environmentally friendly formulations. Manufacturers began developing water-based PU adhesives and reducing the volatile organic compound (VOC) content in their products. This era also witnessed advancements in UV-curable PU adhesives, which provided faster curing times and improved energy efficiency in manufacturing processes.
At the turn of the millennium, nanotechnology started influencing PU adhesive development. The incorporation of nanoparticles, such as carbon nanotubes and nanoclays, into PU formulations led to significant improvements in mechanical properties and thermal stability. This innovation opened up new possibilities for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
Recent years have seen a focus on bio-based PU adhesives, addressing growing environmental concerns and sustainability requirements. Researchers are exploring renewable raw materials, such as plant-based polyols, to replace petroleum-derived components. This shift not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the overall eco-friendliness of PU adhesives.
The ongoing evolution of PU adhesives continues to push the boundaries of bonding technology. Current research efforts are concentrated on developing smart PU adhesives with self-healing properties, improving their resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals, and enhancing their compatibility with a wider range of substrates. These advancements aim to further expand the application scope of PU adhesives and meet the ever-increasing demands of modern industries for stronger, more versatile, and sustainable bonding solutions.
The early stages of PU adhesive development focused primarily on improving their basic formulations and understanding the chemistry behind their curing mechanisms. Scientists worked on optimizing the ratio of isocyanates to polyols, which forms the backbone of PU adhesives, to achieve better bonding strength and flexibility.
In the 1960s and 1970s, researchers made substantial progress in enhancing the moisture resistance of PU adhesives. This breakthrough expanded their application range, particularly in outdoor and marine environments. During this period, the introduction of two-component PU adhesives also marked a significant milestone, offering improved control over curing times and bond strength.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards environmentally friendly formulations. Manufacturers began developing water-based PU adhesives and reducing the volatile organic compound (VOC) content in their products. This era also witnessed advancements in UV-curable PU adhesives, which provided faster curing times and improved energy efficiency in manufacturing processes.
At the turn of the millennium, nanotechnology started influencing PU adhesive development. The incorporation of nanoparticles, such as carbon nanotubes and nanoclays, into PU formulations led to significant improvements in mechanical properties and thermal stability. This innovation opened up new possibilities for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
Recent years have seen a focus on bio-based PU adhesives, addressing growing environmental concerns and sustainability requirements. Researchers are exploring renewable raw materials, such as plant-based polyols, to replace petroleum-derived components. This shift not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the overall eco-friendliness of PU adhesives.
The ongoing evolution of PU adhesives continues to push the boundaries of bonding technology. Current research efforts are concentrated on developing smart PU adhesives with self-healing properties, improving their resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals, and enhancing their compatibility with a wider range of substrates. These advancements aim to further expand the application scope of PU adhesives and meet the ever-increasing demands of modern industries for stronger, more versatile, and sustainable bonding solutions.
Market Demand Analysis
The global market for polyurethane adhesives has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics. This growth is primarily attributed to the superior bonding properties, versatility, and durability of polyurethane adhesives compared to traditional adhesive solutions.
In the construction sector, there is a rising need for high-performance adhesives that can withstand extreme weather conditions and provide long-lasting bonds for structural applications. Polyurethane adhesives are increasingly preferred for their excellent moisture resistance and ability to bond dissimilar materials, making them ideal for both interior and exterior construction projects.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for improved polyurethane adhesives. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and enhance fuel efficiency, there is a growing demand for adhesives that can effectively bond lightweight materials such as composites and plastics to metal substrates. Polyurethane adhesives with enhanced bonding strength and durability are crucial for meeting these requirements.
In the furniture industry, manufacturers are seeking adhesives that offer fast curing times, high initial tack, and strong bonds for various materials including wood, metal, and plastics. Improved polyurethane adhesives that address these needs while maintaining flexibility and resistance to temperature fluctuations are highly sought after.
The electronics sector presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for polyurethane adhesive development. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing use of flexible substrates, there is a growing demand for adhesives that can provide reliable bonds in compact spaces while maintaining electrical insulation properties.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping market demand. There is an increasing focus on developing eco-friendly polyurethane adhesives with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and improved recyclability. Manufacturers are actively seeking solutions that maintain high performance while meeting stringent environmental standards.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for polyurethane adhesives, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing automotive production. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialized adhesive solutions.
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for improved polyurethane adhesives is expected to grow. Key areas of focus include enhancing bond strength, reducing curing times, improving chemical and environmental resistance, and developing adhesives tailored for specific applications and substrates. The market is poised for innovation, with opportunities for manufacturers to differentiate themselves through advanced formulations and application-specific solutions.
In the construction sector, there is a rising need for high-performance adhesives that can withstand extreme weather conditions and provide long-lasting bonds for structural applications. Polyurethane adhesives are increasingly preferred for their excellent moisture resistance and ability to bond dissimilar materials, making them ideal for both interior and exterior construction projects.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for improved polyurethane adhesives. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and enhance fuel efficiency, there is a growing demand for adhesives that can effectively bond lightweight materials such as composites and plastics to metal substrates. Polyurethane adhesives with enhanced bonding strength and durability are crucial for meeting these requirements.
In the furniture industry, manufacturers are seeking adhesives that offer fast curing times, high initial tack, and strong bonds for various materials including wood, metal, and plastics. Improved polyurethane adhesives that address these needs while maintaining flexibility and resistance to temperature fluctuations are highly sought after.
The electronics sector presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for polyurethane adhesive development. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing use of flexible substrates, there is a growing demand for adhesives that can provide reliable bonds in compact spaces while maintaining electrical insulation properties.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping market demand. There is an increasing focus on developing eco-friendly polyurethane adhesives with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and improved recyclability. Manufacturers are actively seeking solutions that maintain high performance while meeting stringent environmental standards.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for polyurethane adhesives, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing automotive production. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialized adhesive solutions.
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for improved polyurethane adhesives is expected to grow. Key areas of focus include enhancing bond strength, reducing curing times, improving chemical and environmental resistance, and developing adhesives tailored for specific applications and substrates. The market is poised for innovation, with opportunities for manufacturers to differentiate themselves through advanced formulations and application-specific solutions.
Technical Challenges
Polyurethane adhesives face several technical challenges that hinder their performance and limit their applications. One of the primary issues is their sensitivity to moisture during curing. This can lead to inconsistent bonding strength and reduced durability, especially in high-humidity environments. The presence of moisture can interfere with the chemical reactions necessary for proper adhesive curing, resulting in weakened bonds and potential failure over time.
Another significant challenge is the limited temperature resistance of many polyurethane adhesives. While they perform well at room temperature, their bonding strength can deteriorate significantly at elevated temperatures. This thermal instability restricts their use in applications that involve exposure to high temperatures or frequent temperature fluctuations, such as automotive or aerospace industries.
The curing time of polyurethane adhesives also presents a challenge in certain applications. Some formulations require extended periods to achieve full bond strength, which can slow down production processes and limit their use in time-sensitive applications. Balancing the need for a reasonable working time with a faster curing rate remains a complex issue for adhesive manufacturers.
Adhesion to certain substrates, particularly low surface energy materials like polyethylene or polypropylene, poses another technical hurdle. Polyurethane adhesives often struggle to form strong, durable bonds with these materials without additional surface treatments or primers, limiting their versatility in multi-material bonding applications.
The environmental impact of polyurethane adhesives is also a growing concern. Many formulations contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or isocyanates, which can be harmful to human health and the environment. Developing eco-friendly alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of polyurethane adhesives while reducing their environmental footprint is a significant challenge facing the industry.
Lastly, the long-term durability of polyurethane adhesives under various environmental conditions remains an area of concern. Factors such as UV exposure, chemical resistance, and fatigue strength can affect the longevity of the bond. Improving the overall durability and resistance to degradation factors is crucial for expanding the use of polyurethane adhesives in demanding applications.
Another significant challenge is the limited temperature resistance of many polyurethane adhesives. While they perform well at room temperature, their bonding strength can deteriorate significantly at elevated temperatures. This thermal instability restricts their use in applications that involve exposure to high temperatures or frequent temperature fluctuations, such as automotive or aerospace industries.
The curing time of polyurethane adhesives also presents a challenge in certain applications. Some formulations require extended periods to achieve full bond strength, which can slow down production processes and limit their use in time-sensitive applications. Balancing the need for a reasonable working time with a faster curing rate remains a complex issue for adhesive manufacturers.
Adhesion to certain substrates, particularly low surface energy materials like polyethylene or polypropylene, poses another technical hurdle. Polyurethane adhesives often struggle to form strong, durable bonds with these materials without additional surface treatments or primers, limiting their versatility in multi-material bonding applications.
The environmental impact of polyurethane adhesives is also a growing concern. Many formulations contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or isocyanates, which can be harmful to human health and the environment. Developing eco-friendly alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of polyurethane adhesives while reducing their environmental footprint is a significant challenge facing the industry.
Lastly, the long-term durability of polyurethane adhesives under various environmental conditions remains an area of concern. Factors such as UV exposure, chemical resistance, and fatigue strength can affect the longevity of the bond. Improving the overall durability and resistance to degradation factors is crucial for expanding the use of polyurethane adhesives in demanding applications.
Current PU Solutions
01 Composition of polyurethane adhesives
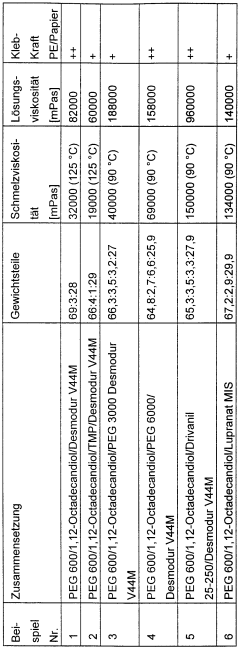
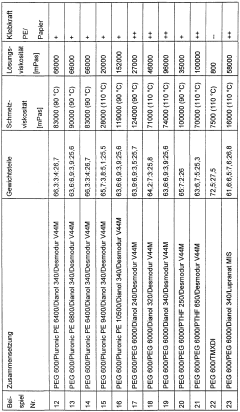
Polyurethane adhesives are formulated with specific components to enhance bonding properties. These may include isocyanates, polyols, catalysts, and additives. The composition is tailored to achieve desired characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and durability in various bonding applications.- Composition of polyurethane adhesives: Polyurethane adhesives are formulated with specific components to enhance bonding properties. These may include isocyanates, polyols, catalysts, and additives. The composition is tailored to achieve desired characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and curing time.
- Surface preparation techniques: Proper surface preparation is crucial for effective polyurethane adhesive bonding. This may involve cleaning, degreasing, or applying primers to improve adhesion. Techniques such as plasma treatment or mechanical abrasion can also enhance the bonding surface.
- Curing methods and conditions: Various curing methods are employed for polyurethane adhesives, including heat curing, moisture curing, and UV curing. Controlling temperature, humidity, and curing time is essential for optimal bond strength and performance.
- Adhesive application techniques: Effective application of polyurethane adhesives involves selecting appropriate methods such as spraying, rolling, or dispensing. Factors like viscosity, open time, and substrate compatibility influence the choice of application technique to ensure uniform coverage and optimal bonding.
- Performance enhancement additives: Additives are incorporated into polyurethane adhesives to enhance specific properties. These may include reinforcing agents for improved strength, plasticizers for flexibility, or UV stabilizers for outdoor applications. Careful selection of additives can significantly improve bonding performance and durability.
02 Surface preparation techniques
Proper surface preparation is crucial for effective polyurethane adhesive bonding. This may involve cleaning, degreasing, or applying primers to enhance adhesion. Techniques such as plasma treatment or corona discharge can be used to modify surface properties and improve bonding strength.Expand Specific Solutions03 Curing methods for polyurethane adhesives
Various curing methods are employed to optimize the bonding process of polyurethane adhesives. These may include heat curing, moisture curing, or UV curing. The choice of curing method depends on the specific adhesive formulation and the requirements of the bonding application.Expand Specific Solutions04 Specialized polyurethane adhesives for specific substrates
Polyurethane adhesives can be tailored for bonding specific substrates such as metals, plastics, composites, or wood. These specialized formulations may incorporate additional components or undergo specific treatments to enhance adhesion to particular materials, improving overall bonding performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Development of polyurethane adhesives focuses on improving environmental friendliness and safety. This includes formulations with reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs), non-toxic components, and improved recyclability. Adhesives may also be designed to meet specific industry standards or regulations regarding emissions and health hazards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polyurethane adhesives market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach $10.5 billion by 2025. The technology is well-established but continues to evolve, driven by demands for improved performance and sustainability. Key players like Henkel, Sika, BASF, and Bayer are investing heavily in R&D to enhance bonding strength, durability, and environmental friendliness. Emerging companies such as Wanhua Chemical and PPG Coatings are also making significant strides in innovation. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized regional players, with a focus on developing advanced formulations for specific applications and industries.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a range of innovative polyurethane adhesives focusing on improving bonding strength and durability. Their technology involves the use of silane-terminated polyurethanes (STPUs) which combine the strength of polyurethanes with the flexibility of silicones. These adhesives feature a unique cross-linking mechanism that allows for better adhesion to a wide variety of substrates, including metals, plastics, and composites. Henkel's formulation also incorporates nano-sized fillers to enhance mechanical properties and thermal stability.
Strengths: Excellent adhesion to multiple substrates, improved durability, and enhanced mechanical properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized ingredients and more complex manufacturing process.
Sika Technology AG
Technical Solution: Sika has developed a novel polyurethane adhesive system that utilizes a two-component approach for improved bonding. Their technology involves a base polyurethane component combined with a specially formulated hardener that contains reactive silane groups. This combination results in a hybrid adhesive that offers both the strength of polyurethanes and the weathering resistance of silicones. The adhesive also incorporates proprietary additives that enhance its elongation properties, allowing for better stress distribution across bonded joints.
Strengths: High strength, excellent weathering resistance, and improved flexibility. Weaknesses: May require precise mixing ratios and specialized application equipment.
Core PU Innovations
Use of Polyurethane-based compositions as adhesive
PatentInactiveEP0335182A3
Innovation
- The use of polyurethane mixtures containing phenol B1 and/or acid amide B2, optionally with polyisocyanate C, dissolved in a solvent, which provides improved contact tack both with and without heat activation, and can include specific phenols and amides to enhance peel strength and bonding capabilities.
Polyurethane adhesive
PatentWO1999015573A1
Innovation
- A polyurethane adhesive is developed using a combination of at least one diisocyanate and low molecular weight polyethylene glycol with a degree of crystallization less than 20%, resulting in a product that remains permanently tacky and exhibits high viscosity, allowing instant bonding to almost any substrate with light pressure without activation.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of polyurethane adhesives is a critical consideration in their development and application. These adhesives, while effective for bonding, can pose significant challenges to sustainability and ecological balance. The production process of polyurethane adhesives often involves the use of isocyanates, which are derived from fossil fuels and can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the manufacturing of these adhesives may require substantial energy consumption, further increasing their carbon footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polyurethane adhesives is their end-of-life disposal. Many traditional polyurethane adhesives are not biodegradable, leading to long-term accumulation in landfills or potential contamination of ecosystems if improperly disposed of. The presence of harmful chemicals in some formulations can leach into soil and water systems, potentially affecting wildlife and human health.
To address these environmental challenges, researchers and manufacturers are exploring various strategies to improve the ecological profile of polyurethane adhesives. One approach involves the development of bio-based polyurethanes, which utilize renewable resources such as plant-derived polyols instead of petroleum-based components. This shift towards bio-based materials can significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the overall carbon footprint of the adhesive production.
Another area of focus is the enhancement of recyclability and biodegradability of polyurethane adhesives. Efforts are being made to design adhesive formulations that can be more easily separated from bonded materials at the end of their lifecycle, facilitating recycling processes. Additionally, research is ongoing to develop polyurethane adhesives that can degrade under specific environmental conditions, reducing their long-term impact on ecosystems.
The reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in polyurethane adhesives is also a key environmental consideration. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health. Manufacturers are working on low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations to minimize these emissions during application and curing processes, improving both environmental and occupational safety.
Water-based polyurethane adhesives are gaining traction as a more environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based systems. These formulations reduce the release of harmful solvents into the atmosphere and decrease the risk of fire hazards associated with traditional solvent-based adhesives. The transition to water-based systems aligns with global efforts to reduce industrial emissions and improve air quality.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, the adhesive industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments to evaluate and minimize the environmental impact of polyurethane adhesives throughout their entire lifecycle. This holistic approach considers factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, application methods, and end-of-life scenarios to identify areas for improvement and innovation in creating more sustainable adhesive solutions.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polyurethane adhesives is their end-of-life disposal. Many traditional polyurethane adhesives are not biodegradable, leading to long-term accumulation in landfills or potential contamination of ecosystems if improperly disposed of. The presence of harmful chemicals in some formulations can leach into soil and water systems, potentially affecting wildlife and human health.
To address these environmental challenges, researchers and manufacturers are exploring various strategies to improve the ecological profile of polyurethane adhesives. One approach involves the development of bio-based polyurethanes, which utilize renewable resources such as plant-derived polyols instead of petroleum-based components. This shift towards bio-based materials can significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the overall carbon footprint of the adhesive production.
Another area of focus is the enhancement of recyclability and biodegradability of polyurethane adhesives. Efforts are being made to design adhesive formulations that can be more easily separated from bonded materials at the end of their lifecycle, facilitating recycling processes. Additionally, research is ongoing to develop polyurethane adhesives that can degrade under specific environmental conditions, reducing their long-term impact on ecosystems.
The reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in polyurethane adhesives is also a key environmental consideration. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health. Manufacturers are working on low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations to minimize these emissions during application and curing processes, improving both environmental and occupational safety.
Water-based polyurethane adhesives are gaining traction as a more environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based systems. These formulations reduce the release of harmful solvents into the atmosphere and decrease the risk of fire hazards associated with traditional solvent-based adhesives. The transition to water-based systems aligns with global efforts to reduce industrial emissions and improve air quality.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, the adhesive industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments to evaluate and minimize the environmental impact of polyurethane adhesives throughout their entire lifecycle. This holistic approach considers factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, application methods, and end-of-life scenarios to identify areas for improvement and innovation in creating more sustainable adhesive solutions.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the development and application of polyurethane adhesives for improved bonding. As these adhesives are widely used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and consumer goods, manufacturers must adhere to strict regulations to ensure product safety and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in adhesives under the Clean Air Act. Polyurethane adhesives must comply with VOC emission limits, which vary depending on the specific application and region. Manufacturers are required to develop low-VOC formulations or water-based alternatives to meet these standards while maintaining optimal bonding performance.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes stringent requirements on the use of chemicals in adhesives. Manufacturers must register their substances with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed safety information. This regulation has led to the development of more environmentally friendly polyurethane adhesives, with reduced use of harmful substances and improved overall safety profiles.
Food contact applications of polyurethane adhesives are subject to regulations by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These agencies set specific requirements for adhesives used in food packaging and processing equipment to prevent contamination and ensure consumer safety. Compliance with these regulations often necessitates the use of specialized formulations and rigorous testing protocols.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, mandate proper handling and application procedures for polyurethane adhesives in workplace settings. This includes providing adequate ventilation, personal protective equipment, and training for workers involved in the manufacturing and application processes.
To improve polyurethane adhesives for better bonding while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must focus on developing innovative formulations that meet performance requirements without compromising safety or environmental standards. This may involve exploring new raw materials, optimizing curing processes, or incorporating advanced additives that enhance bonding strength while reducing harmful emissions.
Compliance with global regulations also requires manufacturers to invest in comprehensive testing and documentation processes. This includes conducting thorough chemical analyses, performance evaluations, and safety assessments to ensure that their products meet or exceed regulatory standards across different markets and applications.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed about upcoming changes and proactively adapting formulations and manufacturing processes is essential for maintaining compliance and market competitiveness. This may involve collaborating with regulatory bodies, participating in industry associations, and engaging in ongoing research and development efforts to anticipate and address future regulatory challenges in the polyurethane adhesive industry.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in adhesives under the Clean Air Act. Polyurethane adhesives must comply with VOC emission limits, which vary depending on the specific application and region. Manufacturers are required to develop low-VOC formulations or water-based alternatives to meet these standards while maintaining optimal bonding performance.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes stringent requirements on the use of chemicals in adhesives. Manufacturers must register their substances with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed safety information. This regulation has led to the development of more environmentally friendly polyurethane adhesives, with reduced use of harmful substances and improved overall safety profiles.
Food contact applications of polyurethane adhesives are subject to regulations by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). These agencies set specific requirements for adhesives used in food packaging and processing equipment to prevent contamination and ensure consumer safety. Compliance with these regulations often necessitates the use of specialized formulations and rigorous testing protocols.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, mandate proper handling and application procedures for polyurethane adhesives in workplace settings. This includes providing adequate ventilation, personal protective equipment, and training for workers involved in the manufacturing and application processes.
To improve polyurethane adhesives for better bonding while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must focus on developing innovative formulations that meet performance requirements without compromising safety or environmental standards. This may involve exploring new raw materials, optimizing curing processes, or incorporating advanced additives that enhance bonding strength while reducing harmful emissions.
Compliance with global regulations also requires manufacturers to invest in comprehensive testing and documentation processes. This includes conducting thorough chemical analyses, performance evaluations, and safety assessments to ensure that their products meet or exceed regulatory standards across different markets and applications.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed about upcoming changes and proactively adapting formulations and manufacturing processes is essential for maintaining compliance and market competitiveness. This may involve collaborating with regulatory bodies, participating in industry associations, and engaging in ongoing research and development efforts to anticipate and address future regulatory challenges in the polyurethane adhesive industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!