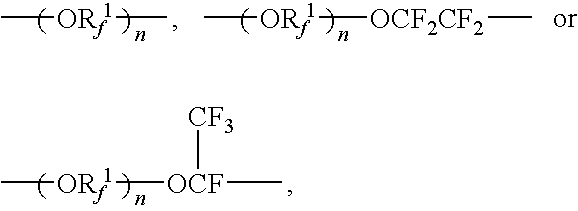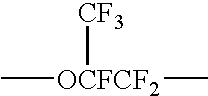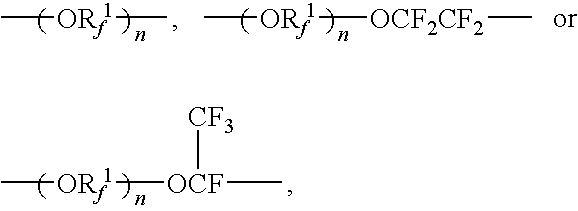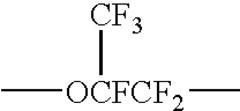How to Improve Synthesis Efficiency with Fluoroantimonic Acid?
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoroantimonic Acid Synthesis Background and Objectives
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, has been a subject of intense research and development in the field of chemistry for decades. Its exceptional acidity, with a Hammett acidity function estimated at -21.6, surpasses that of pure sulfuric acid by far. This remarkable property has positioned fluoroantimonic acid as a potential game-changer in various industrial processes, particularly in the synthesis of complex organic compounds.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the concept of superacids was first introduced. Since then, significant advancements have been made in understanding its chemical properties and potential applications. The primary goal in improving the synthesis efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid is to develop more cost-effective, safer, and environmentally friendly production methods while maintaining or enhancing its potent acidic properties.
Current synthesis methods typically involve the combination of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) in specific ratios. However, these processes often face challenges related to safety, scalability, and environmental concerns. The highly corrosive nature of the components and the resulting acid necessitates specialized handling and storage procedures, which contribute to the overall complexity and cost of production.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for improving fluoroantimonic acid synthesis efficiency are multifaceted. Researchers aim to optimize reaction conditions to increase yield and purity while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation. There is also a strong focus on developing novel catalysts or reaction intermediates that could potentially streamline the synthesis process, reducing the reliance on highly hazardous precursors.
Another critical objective is to enhance the stability and shelf-life of fluoroantimonic acid, which would significantly improve its practicality in industrial applications. This includes exploring new stabilization techniques and storage solutions that can maintain the acid's potency over extended periods without compromising safety or environmental standards.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in exploring alternative synthesis routes that could potentially bypass some of the more dangerous intermediates or utilize more readily available starting materials. This approach not only aims to improve efficiency but also to make the production process more sustainable and accessible to a broader range of industries.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis, it becomes clear that achieving these objectives will require a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in chemical engineering, materials science, and process optimization. The potential impact of these improvements extends far beyond the realm of academic research, promising to revolutionize various industrial processes and open up new possibilities in fields such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and advanced materials manufacturing.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the concept of superacids was first introduced. Since then, significant advancements have been made in understanding its chemical properties and potential applications. The primary goal in improving the synthesis efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid is to develop more cost-effective, safer, and environmentally friendly production methods while maintaining or enhancing its potent acidic properties.
Current synthesis methods typically involve the combination of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) in specific ratios. However, these processes often face challenges related to safety, scalability, and environmental concerns. The highly corrosive nature of the components and the resulting acid necessitates specialized handling and storage procedures, which contribute to the overall complexity and cost of production.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for improving fluoroantimonic acid synthesis efficiency are multifaceted. Researchers aim to optimize reaction conditions to increase yield and purity while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation. There is also a strong focus on developing novel catalysts or reaction intermediates that could potentially streamline the synthesis process, reducing the reliance on highly hazardous precursors.
Another critical objective is to enhance the stability and shelf-life of fluoroantimonic acid, which would significantly improve its practicality in industrial applications. This includes exploring new stabilization techniques and storage solutions that can maintain the acid's potency over extended periods without compromising safety or environmental standards.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in exploring alternative synthesis routes that could potentially bypass some of the more dangerous intermediates or utilize more readily available starting materials. This approach not only aims to improve efficiency but also to make the production process more sustainable and accessible to a broader range of industries.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis, it becomes clear that achieving these objectives will require a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in chemical engineering, materials science, and process optimization. The potential impact of these improvements extends far beyond the realm of academic research, promising to revolutionize various industrial processes and open up new possibilities in fields such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Industrial Demand for Efficient Superacid Synthesis
The industrial demand for efficient superacid synthesis, particularly focusing on fluoroantimonic acid, has been steadily increasing due to its critical role in various high-value applications. Fluoroantimonic acid, known as one of the strongest superacids, finds extensive use in petrochemical processes, especially in the production of high-octane gasoline components. The petroleum industry relies heavily on this superacid for alkylation reactions, which are crucial for improving fuel quality and meeting stringent environmental regulations.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for fluoroantimonic acid has been growing due to its ability to catalyze complex organic reactions. Drug manufacturers are increasingly exploring its potential in synthesizing novel compounds and improving the efficiency of existing production processes. The fine chemicals industry also benefits from the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid, utilizing it in the production of specialty chemicals and advanced materials.
The electronics industry represents another significant market for fluoroantimonic acid. Its use in etching and cleaning processes for semiconductor manufacturing has become indispensable as the demand for smaller, more powerful electronic devices continues to surge. The push towards miniaturization in electronics has intensified the need for highly efficient and precise etching agents, further driving the demand for fluoroantimonic acid.
Moreover, the growing focus on sustainable and green chemistry has paradoxically increased interest in superacid synthesis. While fluoroantimonic acid itself is highly corrosive and environmentally challenging, its ability to catalyze reactions under milder conditions and with higher selectivity can lead to more environmentally friendly processes in the long run. This has prompted research into developing safer handling methods and more efficient synthesis techniques for fluoroantimonic acid.
The global market for superacids, including fluoroantimonic acid, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is driven by increasing industrial applications, technological advancements, and the continuous quest for more efficient chemical processes. As industries strive to optimize their production methods and reduce environmental impact, the demand for highly efficient superacid synthesis methods is expected to rise, making improvements in fluoroantimonic acid synthesis a key area of focus for chemical manufacturers and researchers alike.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for fluoroantimonic acid has been growing due to its ability to catalyze complex organic reactions. Drug manufacturers are increasingly exploring its potential in synthesizing novel compounds and improving the efficiency of existing production processes. The fine chemicals industry also benefits from the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid, utilizing it in the production of specialty chemicals and advanced materials.
The electronics industry represents another significant market for fluoroantimonic acid. Its use in etching and cleaning processes for semiconductor manufacturing has become indispensable as the demand for smaller, more powerful electronic devices continues to surge. The push towards miniaturization in electronics has intensified the need for highly efficient and precise etching agents, further driving the demand for fluoroantimonic acid.
Moreover, the growing focus on sustainable and green chemistry has paradoxically increased interest in superacid synthesis. While fluoroantimonic acid itself is highly corrosive and environmentally challenging, its ability to catalyze reactions under milder conditions and with higher selectivity can lead to more environmentally friendly processes in the long run. This has prompted research into developing safer handling methods and more efficient synthesis techniques for fluoroantimonic acid.
The global market for superacids, including fluoroantimonic acid, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is driven by increasing industrial applications, technological advancements, and the continuous quest for more efficient chemical processes. As industries strive to optimize their production methods and reduce environmental impact, the demand for highly efficient superacid synthesis methods is expected to rise, making improvements in fluoroantimonic acid synthesis a key area of focus for chemical manufacturers and researchers alike.
Current Challenges in Fluoroantimonic Acid Production
The production of fluoroantimonic acid faces several significant challenges that hinder its synthesis efficiency and large-scale application. One of the primary obstacles is the extreme reactivity and corrosiveness of the acid, which necessitates specialized handling and containment measures. This reactivity not only poses safety risks but also complicates the selection of suitable materials for reaction vessels and storage containers.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of reaction conditions. Fluoroantimonic acid is formed by combining hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) in specific ratios. Maintaining the optimal stoichiometry and temperature during the synthesis process is crucial for maximizing yield and purity. Even slight deviations can significantly impact the acid's strength and properties.
The sourcing and handling of precursor materials present additional difficulties. Both HF and SbF5 are hazardous substances that require careful management throughout the supply chain. The availability and cost of high-purity antimony pentafluoride, in particular, can be a limiting factor in large-scale production.
Environmental concerns and regulatory compliance pose further challenges. The production process generates potentially harmful byproducts and emissions, necessitating robust waste management and air treatment systems. Stringent regulations surrounding the use and transport of such highly corrosive materials add complexity to the manufacturing and distribution processes.
Scale-up issues also persist in fluoroantimonic acid production. Translating laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial-scale manufacturing while maintaining efficiency and product quality is a significant hurdle. Heat management, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics can behave differently at larger scales, requiring careful engineering and process optimization.
The instability of fluoroantimonic acid in the presence of moisture presents another challenge. Even trace amounts of water can lead to rapid decomposition, releasing dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas. This necessitates stringent moisture control throughout the production, storage, and application processes, adding to the overall complexity and cost.
Lastly, the limited commercial applications of fluoroantimonic acid, despite its superacidity, contribute to the challenges in its production. The lack of widespread demand makes it difficult to justify large investments in research and development for improving synthesis efficiency. This creates a cycle where limited production capabilities hinder potential new applications, further constraining market growth.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of reaction conditions. Fluoroantimonic acid is formed by combining hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5) in specific ratios. Maintaining the optimal stoichiometry and temperature during the synthesis process is crucial for maximizing yield and purity. Even slight deviations can significantly impact the acid's strength and properties.
The sourcing and handling of precursor materials present additional difficulties. Both HF and SbF5 are hazardous substances that require careful management throughout the supply chain. The availability and cost of high-purity antimony pentafluoride, in particular, can be a limiting factor in large-scale production.
Environmental concerns and regulatory compliance pose further challenges. The production process generates potentially harmful byproducts and emissions, necessitating robust waste management and air treatment systems. Stringent regulations surrounding the use and transport of such highly corrosive materials add complexity to the manufacturing and distribution processes.
Scale-up issues also persist in fluoroantimonic acid production. Translating laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial-scale manufacturing while maintaining efficiency and product quality is a significant hurdle. Heat management, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics can behave differently at larger scales, requiring careful engineering and process optimization.
The instability of fluoroantimonic acid in the presence of moisture presents another challenge. Even trace amounts of water can lead to rapid decomposition, releasing dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas. This necessitates stringent moisture control throughout the production, storage, and application processes, adding to the overall complexity and cost.
Lastly, the limited commercial applications of fluoroantimonic acid, despite its superacidity, contribute to the challenges in its production. The lack of widespread demand makes it difficult to justify large investments in research and development for improving synthesis efficiency. This creates a cycle where limited production capabilities hinder potential new applications, further constraining market growth.
Existing Methods for Fluoroantimonic Acid Synthesis
01 Optimizing reaction conditions for fluoroantimonic acid synthesis
Improving the efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis can be achieved by optimizing reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios. This approach focuses on finding the ideal parameters to maximize yield and purity while minimizing side reactions and waste products.- Optimization of reaction conditions: Improving the synthesis efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid involves optimizing reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios. Careful control of these parameters can lead to higher yields and purity of the final product. Advanced monitoring and control systems may be employed to maintain optimal conditions throughout the synthesis process.
- Novel catalytic systems: Developing new catalytic systems can significantly enhance the efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis. These may include heterogeneous catalysts, supported metal complexes, or enzyme-inspired catalysts. Such systems can lower activation energies, increase reaction rates, and improve selectivity, leading to more efficient production processes.
- Continuous flow synthesis: Implementing continuous flow synthesis techniques can improve the efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid production. This approach allows for better control of reaction parameters, enhanced heat and mass transfer, and the potential for process intensification. Continuous flow reactors can also facilitate safer handling of highly reactive intermediates and products.
- Purification and separation methods: Developing advanced purification and separation methods is crucial for improving the overall efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis. This may include novel distillation techniques, membrane separation processes, or chromatographic methods tailored for highly corrosive and reactive compounds. Efficient purification can lead to higher-quality products and reduced waste.
- Green chemistry approaches: Incorporating green chemistry principles can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis. This may involve using less hazardous reagents, developing atom-economical reactions, or implementing solvent-free processes. These approaches can lead to reduced environmental impact, improved safety, and potentially lower production costs.
02 Use of catalysts in fluoroantimonic acid production
Incorporating specific catalysts in the synthesis process can enhance the efficiency of fluoroantimonic acid production. These catalysts may help to lower activation energy, increase reaction rates, or improve selectivity, leading to higher yields and purer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Continuous flow synthesis methods
Implementing continuous flow synthesis techniques for fluoroantimonic acid production can significantly improve efficiency compared to batch processes. This approach allows for better control of reaction parameters, reduced reaction times, and improved safety in handling highly reactive intermediates.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and handling techniques
Developing advanced purification and handling techniques specific to fluoroantimonic acid can enhance overall synthesis efficiency. This includes methods for removing impurities, storing the highly reactive acid, and minimizing degradation during processing and storage.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alternative precursor materials and synthesis routes
Exploring alternative precursor materials and novel synthesis routes for fluoroantimonic acid production can lead to improved efficiency. This may involve using different starting materials or developing new reaction pathways that offer advantages in terms of yield, purity, or ease of synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Superacid Manufacturing Industry
The competitive landscape for improving synthesis efficiency with fluoroantimonic acid is in a nascent stage, with the market still developing and relatively small. The technology is in its early phases, with research institutions like Central South University, Jiangnan University, and Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH leading academic efforts. Industry players such as DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd., Honeywell International Technologies Ltd., and Evonik Operations GmbH are exploring commercial applications. The technology's maturity is low, with companies like Shiny Materials Science & Technology, Inc. and Nihon Medi-Physics Co., Ltd. focusing on R&D to overcome challenges in handling and application of this super acid. As the potential for improved synthesis efficiency becomes clearer, more players are expected to enter the market, driving innovation and competition.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto has developed a novel synthesis method using fluoroantimonic acid as a super acid catalyst. This approach involves a two-step process: first, the activation of the substrate using fluoroantimonic acid, followed by a controlled addition of reactants. The company has optimized reaction conditions, including temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios, to maximize yield and minimize side products. Additionally, they have implemented a proprietary purification technique to separate the desired product from the highly corrosive reaction mixture.
Strengths: High yield, improved selectivity, and reduced reaction time. Weaknesses: Requires specialized equipment due to the corrosive nature of fluoroantimonic acid, and potential safety concerns in handling.
DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd.
Technical Solution: DAIKIN has engineered a fluoroantimonic acid-based synthesis system that utilizes a unique containment vessel made of fluoropolymer materials. This setup allows for the safe handling of the highly corrosive acid while maintaining its potent catalytic properties. The company has also developed a computer-controlled reaction monitoring system that precisely regulates the addition of reactants and manages reaction parameters in real-time. This approach enables fine-tuning of the synthesis process, resulting in improved efficiency and product quality.
Strengths: Enhanced safety measures, precise control over reaction conditions, and potential for automation. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and limited scalability for certain reactions.
Innovative Approaches in Superacid Catalysis
Process for preparing fluoroamide and fluoronitrile
PatentInactiveUS20100185007A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of a fluoroester with ammonia or ammonium hydroxide in a solvent with a hydroxyl group, followed by dehydration of the fluoroamide in a solvent with an ether bond, ester bond, ketone group, or cyano group, using amines and acid anhydrides as dehydrating agents, to enhance yield and simplify the production process.
Fluorophosphonocinnamic compounds, synthesis and uses for treating disorders caused by oxidative stress
PatentInactiveEP1802642A2
Innovation
- A process using a complex formed between a tertiary amine and hydrogen fluoride to fluorinate phosphonocinnamic compounds at ambient temperature, achieving high yield and selectivity with easily accessible and safe reagents, allowing for the production of fluorophosphonocinnamic compounds with improved antioxidant activity.
Safety Protocols in Superacid Handling and Production
Handling fluoroantimonic acid, one of the strongest known superacids, requires stringent safety protocols to protect personnel and maintain the integrity of the synthesis process. The extreme corrosiveness and reactivity of this superacid necessitate specialized equipment and procedures. All handling must occur in a controlled environment, typically a fume hood with excellent ventilation, to prevent exposure to toxic fumes.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes chemical-resistant suits, gloves made of materials such as fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and a full-face respirator with appropriate acid gas cartridges. Double gloving is recommended, with frequent changes to ensure continued protection.
Storage and containment of fluoroantimonic acid require specially designed vessels made of materials resistant to its corrosive nature, such as PTFE or perfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA). These containers must be sealed tightly and stored in a cool, dry area away from incompatible substances. Regular inspections of storage areas and containers are essential to detect any signs of degradation or leakage.
Emergency response protocols must be well-established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment kits designed for superacids. Neutralization agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate, should be available in large quantities to address potential spills.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling or working near fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be refreshed periodically and updated as new safety information becomes available.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization followed by proper disposal through licensed chemical waste handlers is typically necessary. Strict documentation and tracking of all waste materials are essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
Implementing these safety protocols is crucial for improving synthesis efficiency with fluoroantimonic acid. By ensuring a safe working environment, researchers can focus on optimizing reaction conditions and exploring new synthetic pathways without compromising safety or risking accidents that could disrupt research progress.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes chemical-resistant suits, gloves made of materials such as fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and a full-face respirator with appropriate acid gas cartridges. Double gloving is recommended, with frequent changes to ensure continued protection.
Storage and containment of fluoroantimonic acid require specially designed vessels made of materials resistant to its corrosive nature, such as PTFE or perfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA). These containers must be sealed tightly and stored in a cool, dry area away from incompatible substances. Regular inspections of storage areas and containers are essential to detect any signs of degradation or leakage.
Emergency response protocols must be well-established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment kits designed for superacids. Neutralization agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate, should be available in large quantities to address potential spills.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling or working near fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be refreshed periodically and updated as new safety information becomes available.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization followed by proper disposal through licensed chemical waste handlers is typically necessary. Strict documentation and tracking of all waste materials are essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
Implementing these safety protocols is crucial for improving synthesis efficiency with fluoroantimonic acid. By ensuring a safe working environment, researchers can focus on optimizing reaction conditions and exploring new synthetic pathways without compromising safety or risking accidents that could disrupt research progress.
Environmental Impact of Fluoroantimonic Acid Synthesis
The synthesis of fluoroantimonic acid, while a powerful tool in organic chemistry, poses significant environmental concerns that must be carefully considered. The production process involves highly reactive and corrosive materials, which can have severe impacts on ecosystems if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with fluoroantimonic acid synthesis is the potential for air pollution. The volatile nature of the precursor chemicals and the acid itself can lead to the release of harmful fluorine and antimony compounds into the atmosphere. These emissions can contribute to air quality degradation, potentially affecting both human health and surrounding ecosystems.
Water contamination is another critical environmental issue. Fluoroantimonic acid is extremely water-reactive, and any accidental release into aquatic systems could have catastrophic effects. The acid can rapidly lower pH levels, causing immediate harm to aquatic life and disrupting entire ecosystems. Furthermore, the breakdown products of the acid can persist in water bodies, leading to long-term environmental damage.
Soil contamination is also a significant concern in the synthesis process. Spills or improper disposal of fluoroantimonic acid or its precursors can render soil infertile and toxic. The high acidity can destroy soil structure, kill beneficial microorganisms, and make the area uninhabitable for plants and animals for extended periods.
The production of fluoroantimonic acid also raises concerns about resource depletion. The synthesis requires antimony trifluoride and hydrogen fluoride, both of which are derived from finite mineral resources. The extraction and processing of these raw materials can lead to habitat destruction and further environmental degradation at mining sites.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis. The process generates hazardous waste that requires specialized handling and disposal methods. Improper management of these wastes can lead to long-term environmental contamination and pose risks to human health.
To address these environmental concerns, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in facilities producing fluoroantimonic acid. Advanced air filtration systems, robust containment vessels, and comprehensive waste treatment processes must be implemented to minimize the risk of environmental contamination. Additionally, ongoing research into greener synthesis methods and alternative compounds could help reduce the overall environmental footprint of this powerful acid's production and use.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with fluoroantimonic acid synthesis is the potential for air pollution. The volatile nature of the precursor chemicals and the acid itself can lead to the release of harmful fluorine and antimony compounds into the atmosphere. These emissions can contribute to air quality degradation, potentially affecting both human health and surrounding ecosystems.
Water contamination is another critical environmental issue. Fluoroantimonic acid is extremely water-reactive, and any accidental release into aquatic systems could have catastrophic effects. The acid can rapidly lower pH levels, causing immediate harm to aquatic life and disrupting entire ecosystems. Furthermore, the breakdown products of the acid can persist in water bodies, leading to long-term environmental damage.
Soil contamination is also a significant concern in the synthesis process. Spills or improper disposal of fluoroantimonic acid or its precursors can render soil infertile and toxic. The high acidity can destroy soil structure, kill beneficial microorganisms, and make the area uninhabitable for plants and animals for extended periods.
The production of fluoroantimonic acid also raises concerns about resource depletion. The synthesis requires antimony trifluoride and hydrogen fluoride, both of which are derived from finite mineral resources. The extraction and processing of these raw materials can lead to habitat destruction and further environmental degradation at mining sites.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid synthesis. The process generates hazardous waste that requires specialized handling and disposal methods. Improper management of these wastes can lead to long-term environmental contamination and pose risks to human health.
To address these environmental concerns, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in facilities producing fluoroantimonic acid. Advanced air filtration systems, robust containment vessels, and comprehensive waste treatment processes must be implemented to minimize the risk of environmental contamination. Additionally, ongoing research into greener synthesis methods and alternative compounds could help reduce the overall environmental footprint of this powerful acid's production and use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!