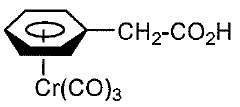
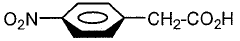
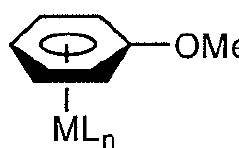
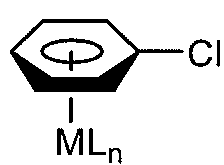
How to Innovate Reaction Techniques with Fluoroantimonic Acid?
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoroantimonic Acid Background and Objectives
Fluoroantimonic acid, a superacid composed of a mixture of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5), has been a subject of intense scientific interest since its discovery in the 1960s. This powerful chemical compound has revolutionized our understanding of acid-base chemistry and opened new avenues for research in various fields, including organic synthesis, catalysis, and materials science.
The development of fluoroantimonic acid can be traced back to the pioneering work of George A. Olah, who explored the potential of superacids in carbocation chemistry. His groundbreaking research led to the creation of increasingly acidic systems, culminating in the synthesis of fluoroantimonic acid, which is considered the strongest known superacid to date.
Over the years, the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid have attracted significant attention from both academia and industry. Its exceptional proton-donating ability and extreme acidity have made it an invaluable tool for studying reaction mechanisms, activating inert molecules, and facilitating challenging chemical transformations that were previously thought impossible.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid technology has been driven by the need for more efficient and selective chemical processes in various industries. From petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals, the potential applications of this superacid have expanded considerably, prompting researchers to explore innovative ways to harness its power while addressing the challenges associated with its handling and use.
As we look towards the future, the primary objective in fluoroantimonic acid research is to develop novel reaction techniques that can fully exploit its unique properties while mitigating its inherent limitations. This includes improving its stability, enhancing its selectivity in chemical reactions, and developing safer handling protocols to broaden its applicability in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Key areas of focus for innovation include the design of new reaction systems that can effectively contain and control the highly corrosive nature of fluoroantimonic acid, the development of supported or immobilized forms of the superacid for easier handling and recycling, and the exploration of synergistic effects with other catalysts or reagents to achieve unprecedented reactivity and selectivity in chemical transformations.
Furthermore, researchers aim to expand the scope of fluoroantimonic acid applications beyond traditional organic synthesis. This includes investigating its potential in materials science for the creation of novel polymers and nanostructures, as well as exploring its use in energy-related applications such as fuel cell technology and hydrogen storage materials.
The development of fluoroantimonic acid can be traced back to the pioneering work of George A. Olah, who explored the potential of superacids in carbocation chemistry. His groundbreaking research led to the creation of increasingly acidic systems, culminating in the synthesis of fluoroantimonic acid, which is considered the strongest known superacid to date.
Over the years, the unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid have attracted significant attention from both academia and industry. Its exceptional proton-donating ability and extreme acidity have made it an invaluable tool for studying reaction mechanisms, activating inert molecules, and facilitating challenging chemical transformations that were previously thought impossible.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid technology has been driven by the need for more efficient and selective chemical processes in various industries. From petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals, the potential applications of this superacid have expanded considerably, prompting researchers to explore innovative ways to harness its power while addressing the challenges associated with its handling and use.
As we look towards the future, the primary objective in fluoroantimonic acid research is to develop novel reaction techniques that can fully exploit its unique properties while mitigating its inherent limitations. This includes improving its stability, enhancing its selectivity in chemical reactions, and developing safer handling protocols to broaden its applicability in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Key areas of focus for innovation include the design of new reaction systems that can effectively contain and control the highly corrosive nature of fluoroantimonic acid, the development of supported or immobilized forms of the superacid for easier handling and recycling, and the exploration of synergistic effects with other catalysts or reagents to achieve unprecedented reactivity and selectivity in chemical transformations.
Furthermore, researchers aim to expand the scope of fluoroantimonic acid applications beyond traditional organic synthesis. This includes investigating its potential in materials science for the creation of novel polymers and nanostructures, as well as exploring its use in energy-related applications such as fuel cell technology and hydrogen storage materials.
Industrial Applications and Market Analysis
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, has garnered significant attention in various industrial sectors due to its exceptional proton-donating ability and catalytic properties. The market for fluoroantimonic acid and related reaction techniques is primarily driven by the petrochemical industry, where it finds extensive use in hydrocarbon cracking and isomerization processes.
In the oil and gas sector, fluoroantimonic acid-based catalysts have shown remarkable potential in enhancing the efficiency of refining processes. These catalysts enable the production of high-octane gasoline components and other value-added products from lower-grade hydrocarbons. The growing demand for cleaner fuels and stricter environmental regulations have further boosted the adoption of advanced catalytic systems, including those based on fluoroantimonic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry has also recognized the potential of fluoroantimonic acid in organic synthesis. Its ability to catalyze challenging reactions, such as C-C bond formations and rearrangements, has opened new avenues for drug discovery and development. This application has led to increased research and development activities, driving the demand for innovative reaction techniques involving fluoroantimonic acid.
In the field of materials science, fluoroantimonic acid has found applications in the synthesis of novel polymers and advanced materials. Its strong acidic properties enable the modification of surface characteristics and the creation of unique molecular structures. This has sparked interest from industries such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive, where high-performance materials are crucial.
The global market for superacids, including fluoroantimonic acid, is expected to grow steadily in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing demand for high-octane fuels, the expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, and the continuous innovation in materials science. However, the market faces challenges related to the handling and storage of fluoroantimonic acid due to its highly corrosive nature and sensitivity to moisture.
To address these challenges and capitalize on the potential of fluoroantimonic acid, there is a growing focus on developing safer handling techniques and more stable formulations. This has led to collaborations between academic institutions and industrial partners to innovate reaction techniques that maximize the acid's catalytic efficiency while minimizing associated risks.
The market landscape for fluoroantimonic acid-based technologies is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized catalyst manufacturers. These players are investing in research and development to expand the application scope of fluoroantimonic acid and improve its overall performance in various industrial processes.
In the oil and gas sector, fluoroantimonic acid-based catalysts have shown remarkable potential in enhancing the efficiency of refining processes. These catalysts enable the production of high-octane gasoline components and other value-added products from lower-grade hydrocarbons. The growing demand for cleaner fuels and stricter environmental regulations have further boosted the adoption of advanced catalytic systems, including those based on fluoroantimonic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry has also recognized the potential of fluoroantimonic acid in organic synthesis. Its ability to catalyze challenging reactions, such as C-C bond formations and rearrangements, has opened new avenues for drug discovery and development. This application has led to increased research and development activities, driving the demand for innovative reaction techniques involving fluoroantimonic acid.
In the field of materials science, fluoroantimonic acid has found applications in the synthesis of novel polymers and advanced materials. Its strong acidic properties enable the modification of surface characteristics and the creation of unique molecular structures. This has sparked interest from industries such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive, where high-performance materials are crucial.
The global market for superacids, including fluoroantimonic acid, is expected to grow steadily in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include the increasing demand for high-octane fuels, the expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, and the continuous innovation in materials science. However, the market faces challenges related to the handling and storage of fluoroantimonic acid due to its highly corrosive nature and sensitivity to moisture.
To address these challenges and capitalize on the potential of fluoroantimonic acid, there is a growing focus on developing safer handling techniques and more stable formulations. This has led to collaborations between academic institutions and industrial partners to innovate reaction techniques that maximize the acid's catalytic efficiency while minimizing associated risks.
The market landscape for fluoroantimonic acid-based technologies is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized catalyst manufacturers. These players are investing in research and development to expand the application scope of fluoroantimonic acid and improve its overall performance in various industrial processes.
Current Challenges in Fluoroantimonic Acid Reactions
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, presents significant challenges in its application for innovative reaction techniques. The primary obstacle lies in its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity, which severely limits the range of materials that can safely contain and handle it. Traditional laboratory equipment and reaction vessels are often inadequate, necessitating specialized materials such as fluoropolymers or certain alloys.
The high reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also poses difficulties in controlling reaction rates and selectivity. Many organic compounds are instantly protonated or decomposed upon contact, making it challenging to achieve desired transformations without unwanted side reactions. This unpredictability complicates the development of new synthetic methodologies and limits the scope of potential applications.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of fluoroantimonic acid to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can lead to rapid decomposition and the generation of highly toxic hydrogen fluoride gas. This necessitates stringent anhydrous conditions and specialized handling techniques, which can be difficult to maintain in large-scale or industrial settings.
The extreme acidity of fluoroantimonic acid also presents analytical challenges. Many conventional characterization techniques are incompatible with such strongly acidic conditions, making it difficult to monitor reactions in real-time or analyze intermediates and products. This limitation hinders the understanding of reaction mechanisms and the optimization of reaction conditions.
Safety concerns represent a significant hurdle in expanding the use of fluoroantimonic acid in reaction techniques. The acid's corrosive nature and potential to generate toxic fumes require extensive safety protocols and specialized equipment, which can be prohibitively expensive for many research laboratories and industrial facilities.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges. The disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and its reaction products requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination. This aspect adds complexity and cost to any process involving the acid, potentially limiting its adoption in large-scale applications.
Scaling up reactions involving fluoroantimonic acid from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. The need for specialized materials and equipment, coupled with safety and environmental concerns, makes it difficult to design and implement economically viable large-scale processes.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining expertise in materials science, chemical engineering, and safety protocols. Innovations in containment materials, reaction vessel design, and handling techniques are crucial for expanding the practical applications of fluoroantimonic acid in synthetic chemistry and industrial processes.
The high reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also poses difficulties in controlling reaction rates and selectivity. Many organic compounds are instantly protonated or decomposed upon contact, making it challenging to achieve desired transformations without unwanted side reactions. This unpredictability complicates the development of new synthetic methodologies and limits the scope of potential applications.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of fluoroantimonic acid to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can lead to rapid decomposition and the generation of highly toxic hydrogen fluoride gas. This necessitates stringent anhydrous conditions and specialized handling techniques, which can be difficult to maintain in large-scale or industrial settings.
The extreme acidity of fluoroantimonic acid also presents analytical challenges. Many conventional characterization techniques are incompatible with such strongly acidic conditions, making it difficult to monitor reactions in real-time or analyze intermediates and products. This limitation hinders the understanding of reaction mechanisms and the optimization of reaction conditions.
Safety concerns represent a significant hurdle in expanding the use of fluoroantimonic acid in reaction techniques. The acid's corrosive nature and potential to generate toxic fumes require extensive safety protocols and specialized equipment, which can be prohibitively expensive for many research laboratories and industrial facilities.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges. The disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and its reaction products requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination. This aspect adds complexity and cost to any process involving the acid, potentially limiting its adoption in large-scale applications.
Scaling up reactions involving fluoroantimonic acid from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. The need for specialized materials and equipment, coupled with safety and environmental concerns, makes it difficult to design and implement economically viable large-scale processes.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining expertise in materials science, chemical engineering, and safety protocols. Innovations in containment materials, reaction vessel design, and handling techniques are crucial for expanding the practical applications of fluoroantimonic acid in synthetic chemistry and industrial processes.
Existing Reaction Techniques with Fluoroantimonic Acid
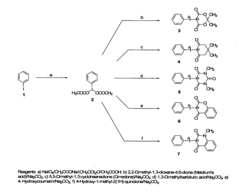
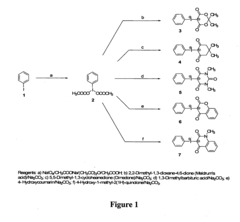
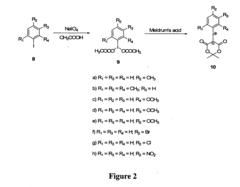
01 Synthesis and preparation methods
Various techniques for synthesizing and preparing fluoroantimonic acid, including methods for controlling reaction conditions, purification processes, and handling procedures for this highly reactive superacid. These methods often involve the combination of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride under specific conditions.- Synthesis and preparation methods: Various techniques for synthesizing and preparing fluoroantimonic acid, including optimized reaction conditions, precursor materials, and purification processes. These methods aim to produce high-quality fluoroantimonic acid for use in different applications.
- Analytical and detection techniques: Development of analytical methods and detection techniques for fluoroantimonic acid, including spectroscopic analysis, chromatography, and other advanced instrumental methods. These techniques are crucial for quality control and research purposes.
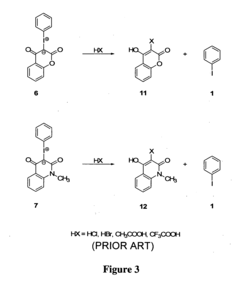
- Applications in organic synthesis: Utilization of fluoroantimonic acid as a powerful superacid catalyst in various organic synthesis reactions, including alkylation, acylation, and isomerization processes. The acid's extreme acidity enables unique transformations in organic chemistry.
- Safety and handling procedures: Development of safety protocols and handling procedures for working with fluoroantimonic acid, including specialized equipment, containment methods, and neutralization techniques. These procedures are essential due to the highly corrosive and reactive nature of the acid.
- Industrial applications and processes: Implementation of fluoroantimonic acid in various industrial processes, such as petrochemical refining, materials processing, and specialty chemical production. The acid's unique properties make it valuable in specific industrial applications.
02 Applications in organic synthesis
Utilization of fluoroantimonic acid as a catalyst or reagent in organic synthesis reactions. This superacid can facilitate various transformations, including alkylations, acylations, and isomerizations, often under milder conditions compared to traditional acid catalysts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Analytical and detection methods
Development of analytical techniques for detecting and quantifying fluoroantimonic acid or its reaction products. These methods may include spectroscopic approaches, chromatographic techniques, or specialized sensors designed to handle highly acidic and corrosive substances.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling protocols
Specialized techniques and equipment for safely handling and storing fluoroantimonic acid, given its extreme reactivity and corrosiveness. This includes the development of containment systems, protective gear, and emergency response procedures for working with this superacid.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications and processes
Implementation of fluoroantimonic acid in various industrial processes, such as petrochemical refining, materials processing, or specialty chemical production. This includes the design of reaction systems, process optimization, and integration of fluoroantimonic acid-based steps into larger manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Superacid Research and Industry
The innovation of reaction techniques with fluoroantimonic acid is in a nascent stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is relatively small but expanding as researchers explore new applications. Technologically, it's still in the early development phase, with varying levels of maturity across companies. DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd. and Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc. are leading in industrial applications, while academic institutions like The Regents of the University of California and Harvard College are pushing fundamental research boundaries. Pharmaceutical companies such as Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. and Eli Lilly & Co. are exploring its potential in drug synthesis. The competitive landscape is diverse, with collaborations between industry and academia driving innovation in this challenging but promising field.
Solvay Specialty Polymers Italy SpA
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed an innovative approach to fluoroantimonic acid reactions through their "Polymer-Supported Super Acid" technology. This technique involves immobilizing the acid on specially designed polymer beads, which allows for easier handling and recovery of the catalyst. They have also created a unique flow chemistry setup optimized for super acid reactions, enabling continuous processing and improved heat management. Additionally, Solvay has implemented advanced in situ spectroscopic techniques for real-time monitoring of reaction kinetics and product formation in fluoroantimonic acid-catalyzed processes.
Strengths: Easier catalyst handling and recovery, continuous processing capabilities, and detailed reaction monitoring. Weaknesses: Potential reduction in acid strength due to immobilization and possible diffusion limitations in polymer support.
Central Glass Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Central Glass Co., Ltd. has innovated fluoroantimonic acid reaction techniques through the development of a unique "Acid-Tolerant Membrane Reactor" system. This technology allows for the controlled addition of reactants through a selectively permeable membrane, which helps to modulate the reaction rate and selectivity. They have also created a novel acid stabilization method using ionic liquids, which extends the usable life of the acid and reduces its volatility. Furthermore, Central Glass has implemented advanced safety protocols and containment systems specifically designed for super acid chemistry.
Strengths: Enhanced reaction control, improved acid stability, and advanced safety measures. Weaknesses: Potential mass transfer limitations due to membrane use and higher operational complexity.
Breakthrough Innovations in Superacid Chemistry
Catalytic radiofluorination
PatentWO2008022319A2
Innovation
- A catalytic radiofluorination method using anhydrous potassium fluoride and crown ethers, such as Kryptofix, which allows for the substitution of leaving groups in alkyl, cycloalkyl, and aryl compounds without the need for activating groups, enabling the production of fluorine-18 labeled compounds like piperazine and phosphonium salts for improved imaging agents.
No-Carrier-Added Nucleophilic [F-18] Fluorination of Aromatic Compounds
PatentInactiveUS20120123120A1
Innovation
- A novel aromatic nucleophilic halogenation reaction is developed without the addition of an ion carrier, using no-carrier-added [F-18] fluoride ion reacted with phenyliodonium ylide derivatives, which are synthesized through specific procedures, to achieve regiospecific F-18 labeled aromatic compounds suitable for PET.
Safety and Handling Protocols for Superacids
Handling fluoroantimonic acid, one of the strongest known superacids, requires stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment. The extreme corrosiveness and reactivity of this compound necessitate rigorous precautions to protect personnel and prevent environmental contamination. All operations involving fluoroantimonic acid must be conducted in a dedicated fume hood with a robust ventilation system to contain and neutralize any vapors or spills.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with superacids. Operators must wear fully encapsulating chemical-resistant suits, including acid-resistant gloves, boots, and face shields. Respiratory protection with supplied air or self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) is mandatory due to the potential for toxic fume generation. Regular inspection and maintenance of PPE are essential to ensure its integrity.
Storage and transportation of fluoroantimonic acid require specially designed containers made of materials resistant to extreme corrosion, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or certain fluoropolymers. These containers must be sealed and stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials. Secondary containment systems are necessary to prevent accidental releases.
Emergency response procedures must be established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill control kits designed for superacid containment. Neutralization agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate, should be available in large quantities for immediate use in case of spills.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain preparedness.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization followed by proper disposal through licensed hazardous waste management facilities is essential. Strict adherence to local, state, and federal regulations regarding hazardous waste disposal is mandatory.
Monitoring and detection systems play a vital role in maintaining safety. Installation of acid vapor detectors and pH monitors in work areas can provide early warning of potential leaks or exposure. Regular environmental monitoring should be conducted to ensure the effectiveness of containment measures.
Documentation and record-keeping are crucial aspects of safety protocols. Detailed logs of all handling procedures, including quantities used, storage conditions, and any incidents or near-misses, must be maintained. These records are essential for continuous improvement of safety measures and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with superacids. Operators must wear fully encapsulating chemical-resistant suits, including acid-resistant gloves, boots, and face shields. Respiratory protection with supplied air or self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) is mandatory due to the potential for toxic fume generation. Regular inspection and maintenance of PPE are essential to ensure its integrity.
Storage and transportation of fluoroantimonic acid require specially designed containers made of materials resistant to extreme corrosion, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or certain fluoropolymers. These containers must be sealed and stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials. Secondary containment systems are necessary to prevent accidental releases.
Emergency response procedures must be established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill control kits designed for superacid containment. Neutralization agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate, should be available in large quantities for immediate use in case of spills.
Training is a critical component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain preparedness.
Waste disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related materials requires specialized procedures. Neutralization followed by proper disposal through licensed hazardous waste management facilities is essential. Strict adherence to local, state, and federal regulations regarding hazardous waste disposal is mandatory.
Monitoring and detection systems play a vital role in maintaining safety. Installation of acid vapor detectors and pH monitors in work areas can provide early warning of potential leaks or exposure. Regular environmental monitoring should be conducted to ensure the effectiveness of containment measures.
Documentation and record-keeping are crucial aspects of safety protocols. Detailed logs of all handling procedures, including quantities used, storage conditions, and any incidents or near-misses, must be maintained. These records are essential for continuous improvement of safety measures and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The use of fluoroantimonic acid in innovative reaction techniques raises significant environmental and sustainability concerns that must be carefully addressed. As one of the strongest known superacids, fluoroantimonic acid poses severe risks to ecosystems and human health if not properly managed. Its highly corrosive and reactive nature can lead to devastating environmental impacts if released into soil or water systems.
Proper containment and handling protocols are critical to prevent accidental spills or emissions. Any industrial processes utilizing fluoroantimonic acid must implement robust safety measures and containment systems to mitigate environmental risks. This includes corrosion-resistant materials for storage and reaction vessels, as well as comprehensive spill response plans.
The production and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid also present sustainability challenges. Its synthesis requires energy-intensive processes and hazardous precursor chemicals. End-of-life management is complex, as the acid cannot be simply neutralized or disposed of through conventional waste treatment methods. Specialized facilities are needed to safely decompose and neutralize spent acid.
From a lifecycle perspective, reactions employing fluoroantimonic acid may have a high environmental footprint compared to alternative approaches. While the acid's superacidity enables novel transformations, the environmental costs must be weighed against potential benefits. Researchers should explore whether comparable results can be achieved through greener chemistry routes with lower hazard profiles.
Efforts to improve the sustainability of fluoroantimonic acid reactions could focus on several areas. Developing more efficient synthetic routes and optimizing reaction conditions could reduce the quantity of acid required. Investigating methods to recycle and regenerate the acid would minimize waste. Exploring ways to immobilize or contain the acid, such as supported acid catalysts, may also enhance safety and reduce environmental risks.
Given growing emphasis on green chemistry principles, any innovations in fluoroantimonic acid reactions should prioritize sustainability. This includes designing processes with reduced waste, improved energy efficiency, and safer alternatives where possible. While fluoroantimonic acid enables unique chemistry, its use must be carefully evaluated against environmental impacts across the entire lifecycle of processes employing it.
Proper containment and handling protocols are critical to prevent accidental spills or emissions. Any industrial processes utilizing fluoroantimonic acid must implement robust safety measures and containment systems to mitigate environmental risks. This includes corrosion-resistant materials for storage and reaction vessels, as well as comprehensive spill response plans.
The production and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid also present sustainability challenges. Its synthesis requires energy-intensive processes and hazardous precursor chemicals. End-of-life management is complex, as the acid cannot be simply neutralized or disposed of through conventional waste treatment methods. Specialized facilities are needed to safely decompose and neutralize spent acid.
From a lifecycle perspective, reactions employing fluoroantimonic acid may have a high environmental footprint compared to alternative approaches. While the acid's superacidity enables novel transformations, the environmental costs must be weighed against potential benefits. Researchers should explore whether comparable results can be achieved through greener chemistry routes with lower hazard profiles.
Efforts to improve the sustainability of fluoroantimonic acid reactions could focus on several areas. Developing more efficient synthetic routes and optimizing reaction conditions could reduce the quantity of acid required. Investigating methods to recycle and regenerate the acid would minimize waste. Exploring ways to immobilize or contain the acid, such as supported acid catalysts, may also enhance safety and reduce environmental risks.
Given growing emphasis on green chemistry principles, any innovations in fluoroantimonic acid reactions should prioritize sustainability. This includes designing processes with reduced waste, improved energy efficiency, and safer alternatives where possible. While fluoroantimonic acid enables unique chemistry, its use must be carefully evaluated against environmental impacts across the entire lifecycle of processes employing it.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!