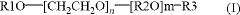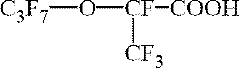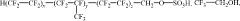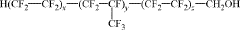How to Lead Chemical Innovations with Fluoroantimonic Acid?
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoroantimonic Acid: Background and Objectives
Fluoroantimonic acid, a superacid with extraordinary chemical properties, has been a subject of intense scientific interest since its discovery in the mid-20th century. This compound, formed by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, exhibits unprecedented acidity levels, surpassing even the strongest mineral acids known to chemistry. Its extreme proton-donating ability has positioned it at the forefront of chemical research, offering potential breakthroughs in various industrial and scientific applications.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid research traces back to the pioneering work of George A. Olah in the 1960s, who explored superacid chemistry and its implications. Over the decades, the understanding of this superacid's behavior and potential applications has grown significantly, driven by advancements in analytical techniques and theoretical chemistry. The trajectory of research has moved from fundamental characterization to exploring practical applications in catalysis, organic synthesis, and materials science.
Current technological trends in fluoroantimonic acid research focus on harnessing its unique properties for innovative chemical processes. Scientists are exploring its potential in activating inert compounds, facilitating novel reaction pathways, and enabling the synthesis of previously unattainable molecules. The extreme acidity of fluoroantimonic acid opens up possibilities for transforming unreactive hydrocarbons, which could revolutionize fuel processing and petrochemical industries.
The primary objective of ongoing research is to unlock the full potential of fluoroantimonic acid while addressing the challenges associated with its handling and application. This includes developing safer methodologies for its use, exploring its role in green chemistry processes, and investigating its potential in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials synthesis. Researchers aim to bridge the gap between laboratory-scale experiments and industrial-scale applications, focusing on scalability, safety, and economic viability.
Another critical goal is to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms underlying fluoroantimonic acid's extreme acidity and its interactions with various substrates. This knowledge is essential for predicting and controlling its reactivity, thereby expanding its applicability across different chemical processes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing novel superacid systems inspired by fluoroantimonic acid, aiming to tailor acidity levels for specific applications while mitigating some of the handling challenges associated with this powerful compound.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid research traces back to the pioneering work of George A. Olah in the 1960s, who explored superacid chemistry and its implications. Over the decades, the understanding of this superacid's behavior and potential applications has grown significantly, driven by advancements in analytical techniques and theoretical chemistry. The trajectory of research has moved from fundamental characterization to exploring practical applications in catalysis, organic synthesis, and materials science.
Current technological trends in fluoroantimonic acid research focus on harnessing its unique properties for innovative chemical processes. Scientists are exploring its potential in activating inert compounds, facilitating novel reaction pathways, and enabling the synthesis of previously unattainable molecules. The extreme acidity of fluoroantimonic acid opens up possibilities for transforming unreactive hydrocarbons, which could revolutionize fuel processing and petrochemical industries.
The primary objective of ongoing research is to unlock the full potential of fluoroantimonic acid while addressing the challenges associated with its handling and application. This includes developing safer methodologies for its use, exploring its role in green chemistry processes, and investigating its potential in emerging fields such as nanotechnology and advanced materials synthesis. Researchers aim to bridge the gap between laboratory-scale experiments and industrial-scale applications, focusing on scalability, safety, and economic viability.
Another critical goal is to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms underlying fluoroantimonic acid's extreme acidity and its interactions with various substrates. This knowledge is essential for predicting and controlling its reactivity, thereby expanding its applicability across different chemical processes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing novel superacid systems inspired by fluoroantimonic acid, aiming to tailor acidity levels for specific applications while mitigating some of the handling challenges associated with this powerful compound.
Market Analysis for Superacid Applications
The market for superacid applications, particularly those involving fluoroantimonic acid, has shown significant growth potential in recent years. This powerful superacid, known for its extreme acidity and unique chemical properties, has found increasing use across various industrial sectors. The global superacid market, which includes fluoroantimonic acid, is experiencing steady expansion driven by rising demand in petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
In the petrochemical industry, fluoroantimonic acid plays a crucial role in catalyzing reactions for the production of high-octane gasoline and other fuel additives. This application has seen substantial growth due to the increasing global demand for cleaner and more efficient fuels. The automotive sector's shift towards higher performance and lower emission standards has further bolstered this market segment.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another key growth area for fluoroantimonic acid applications. Its use in the synthesis of complex organic compounds has made it invaluable in drug discovery and development processes. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to invest heavily in research and development, the demand for superacids like fluoroantimonic acid is expected to rise correspondingly.
Materials science and nanotechnology have emerged as promising new frontiers for superacid applications. Fluoroantimonic acid's ability to manipulate molecular structures at the nanoscale level has opened up possibilities in developing advanced materials with unique properties. This includes applications in electronics, where superacids are used in the production of high-performance semiconductors and display technologies.
The market for superacid applications also extends to the chemical manufacturing sector, where fluoroantimonic acid is used in the production of specialty chemicals and advanced polymers. Its strong acidic properties make it an effective catalyst in various industrial processes, leading to improved efficiency and product quality.
Despite its growth potential, the market for fluoroantimonic acid faces challenges related to handling and safety concerns. The extreme corrosiveness of the acid requires specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols, which can limit its adoption in certain industries. However, ongoing research into safer handling methods and the development of more stable superacid formulations are expected to address these concerns and further expand market opportunities.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in superacid applications, driven by their advanced chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing industrialization and investment in research and development activities.
In the petrochemical industry, fluoroantimonic acid plays a crucial role in catalyzing reactions for the production of high-octane gasoline and other fuel additives. This application has seen substantial growth due to the increasing global demand for cleaner and more efficient fuels. The automotive sector's shift towards higher performance and lower emission standards has further bolstered this market segment.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another key growth area for fluoroantimonic acid applications. Its use in the synthesis of complex organic compounds has made it invaluable in drug discovery and development processes. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to invest heavily in research and development, the demand for superacids like fluoroantimonic acid is expected to rise correspondingly.
Materials science and nanotechnology have emerged as promising new frontiers for superacid applications. Fluoroantimonic acid's ability to manipulate molecular structures at the nanoscale level has opened up possibilities in developing advanced materials with unique properties. This includes applications in electronics, where superacids are used in the production of high-performance semiconductors and display technologies.
The market for superacid applications also extends to the chemical manufacturing sector, where fluoroantimonic acid is used in the production of specialty chemicals and advanced polymers. Its strong acidic properties make it an effective catalyst in various industrial processes, leading to improved efficiency and product quality.
Despite its growth potential, the market for fluoroantimonic acid faces challenges related to handling and safety concerns. The extreme corrosiveness of the acid requires specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols, which can limit its adoption in certain industries. However, ongoing research into safer handling methods and the development of more stable superacid formulations are expected to address these concerns and further expand market opportunities.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in superacid applications, driven by their advanced chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing industrialization and investment in research and development activities.
Current Challenges in Fluoroantimonic Acid Research
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, presents significant challenges in research and application due to its extreme reactivity and corrosive nature. One of the primary obstacles is the development of suitable containment materials that can withstand its highly acidic properties. Traditional laboratory glassware and most metals are rapidly degraded by fluoroantimonic acid, necessitating the use of specialized materials such as Teflon or certain fluoropolymers.
The synthesis and handling of fluoroantimonic acid pose considerable safety risks, requiring advanced protective equipment and stringent safety protocols. Researchers must navigate the complexities of working with a substance that reacts violently with water and most organic compounds, making even routine laboratory procedures potentially hazardous.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control and measurement of fluoroantimonic acid's acidity. Its Hammett acidity function exceeds the conventional pH scale, making accurate quantification difficult. This limitation hampers the standardization of experiments and the reproducibility of results across different research groups.
The extreme reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also complicates its potential industrial applications. While its superacidic properties make it a powerful catalyst for various chemical reactions, harnessing this potential in large-scale processes remains a formidable task. Engineers must devise innovative reactor designs and process control systems to safely and efficiently utilize fluoroantimonic acid in industrial settings.
Environmental concerns present another hurdle in fluoroantimonic acid research. The acid's potential for environmental damage if released, coupled with the difficulties in its neutralization and disposal, necessitates the development of robust containment and waste management strategies. This aspect of research is crucial for ensuring the sustainable use of fluoroantimonic acid in both laboratory and industrial contexts.
Furthermore, the limited availability and high cost of fluoroantimonic acid and its precursors restrict widespread research efforts. This scarcity not only impacts academic studies but also hinders the exploration of potential commercial applications, creating a bottleneck in innovation.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of fluoroantimonic acid research demands collaboration between chemists, materials scientists, and chemical engineers. Bridging the gap between fundamental research and practical applications requires a concerted effort to overcome these multifaceted challenges, driving the need for innovative approaches in superacid chemistry.
The synthesis and handling of fluoroantimonic acid pose considerable safety risks, requiring advanced protective equipment and stringent safety protocols. Researchers must navigate the complexities of working with a substance that reacts violently with water and most organic compounds, making even routine laboratory procedures potentially hazardous.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control and measurement of fluoroantimonic acid's acidity. Its Hammett acidity function exceeds the conventional pH scale, making accurate quantification difficult. This limitation hampers the standardization of experiments and the reproducibility of results across different research groups.
The extreme reactivity of fluoroantimonic acid also complicates its potential industrial applications. While its superacidic properties make it a powerful catalyst for various chemical reactions, harnessing this potential in large-scale processes remains a formidable task. Engineers must devise innovative reactor designs and process control systems to safely and efficiently utilize fluoroantimonic acid in industrial settings.
Environmental concerns present another hurdle in fluoroantimonic acid research. The acid's potential for environmental damage if released, coupled with the difficulties in its neutralization and disposal, necessitates the development of robust containment and waste management strategies. This aspect of research is crucial for ensuring the sustainable use of fluoroantimonic acid in both laboratory and industrial contexts.
Furthermore, the limited availability and high cost of fluoroantimonic acid and its precursors restrict widespread research efforts. This scarcity not only impacts academic studies but also hinders the exploration of potential commercial applications, creating a bottleneck in innovation.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of fluoroantimonic acid research demands collaboration between chemists, materials scientists, and chemical engineers. Bridging the gap between fundamental research and practical applications requires a concerted effort to overcome these multifaceted challenges, driving the need for innovative approaches in superacid chemistry.
Existing Fluoroantimonic Acid Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis and production of fluoroantimonic acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is synthesized by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride. The production process involves careful handling of these highly reactive compounds under controlled conditions to create one of the strongest known superacids.- Synthesis and preparation methods: Various methods for synthesizing and preparing fluoroantimonic acid are described. These methods may involve the use of specific reactants, catalysts, or reaction conditions to produce the acid efficiently and with high purity. The processes often require careful handling due to the highly corrosive nature of the acid.
- Applications in chemical reactions: Fluoroantimonic acid is utilized as a powerful superacid catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can facilitate organic transformations, polymerization processes, and other industrial applications where strong acid catalysis is required. Its extreme acidity allows for reactions that are difficult or impossible with conventional acids.
- Material compatibility and handling: Due to its highly corrosive nature, special considerations are necessary for the handling and storage of fluoroantimonic acid. Research focuses on developing materials and containers that can withstand its extreme acidity. Safety protocols and specialized equipment are essential for working with this superacid.
- Analytical and characterization techniques: Specific analytical methods and characterization techniques are developed for fluoroantimonic acid. These may include spectroscopic methods, electrochemical analyses, or other specialized techniques to determine its properties, purity, and behavior in various chemical environments.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research addresses the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes studies on its reactivity with various substances, potential hazards, proper disposal methods, and the development of safety measures for its use in industrial and laboratory settings.
02 Applications in chemical reactions and catalysis
Fluoroantimonic acid is used as a powerful catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in the petrochemical industry. It can catalyze reactions such as isomerization, alkylation, and polymerization of hydrocarbons, enabling more efficient industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety and handling precautions
Due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity, fluoroantimonic acid requires specialized handling and storage procedures. Safety measures include the use of specialized containment materials, personal protective equipment, and strict protocols for transportation and disposal.Expand Specific Solutions04 Material compatibility and containment
Fluoroantimonic acid is highly corrosive to most materials. Research focuses on developing and identifying materials that can withstand its corrosive nature, such as certain fluoropolymers and specially treated metals, for use in containment vessels and reaction chambers.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and health impacts
The use of fluoroantimonic acid raises environmental and health concerns due to its extreme reactivity and potential for harmful emissions. Research is ongoing to assess its long-term effects and develop safer alternatives or improved handling methods to mitigate risks associated with its use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Superacid Industry
The chemical innovations landscape involving fluoroantimonic acid is characterized by a mature yet specialized market. The industry is in a consolidation phase, with established players like DuPont de Nemours, Inc. and 3M Innovative Properties Co. leading research and development efforts. The market size remains niche due to the acid's extreme corrosiveness and limited applications. Technologically, fluoroantimonic acid research is advanced, with companies like DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd. and Mitsubishi Materials Corp. focusing on improving synthesis methods and exploring novel applications. Academic institutions such as Central South University and Hunan University are also contributing to the field, indicating ongoing efforts to expand the acid's potential uses in various industries.
DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd.
Technical Solution: Daikin has innovated in the field of fluoroantimonic acid by developing a novel fluorination process that utilizes the superacid as a catalyst. Their method involves a continuous flow reactor system that allows for precise control of reaction conditions and minimizes exposure risks. Daikin's approach also includes a recovery and recycling system for the acid, enhancing the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of the process. Additionally, they have engineered specialized fluoropolymer coatings for equipment used in handling the superacid.
Strengths: Advanced reactor design, efficient acid recycling, and expertise in fluoropolymer applications. Weaknesses: Limited to specific applications, potentially high initial investment costs.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a proprietary process for the synthesis and handling of fluoroantimonic acid, utilizing specialized containment systems made from fluoropolymers. Their approach involves a controlled reaction between hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride under precise temperature and pressure conditions. DuPont's method also incorporates advanced purification techniques to ensure the highest purity of the resulting superacid, which is crucial for its effectiveness in various chemical processes.
Strengths: Extensive experience in fluorine chemistry, robust safety protocols, and advanced materials for containment. Weaknesses: High production costs and limited scalability due to the extreme corrosiveness of the acid.
Breakthrough Patents in Fluoroantimonic Acid Technology
Process to reduce the concentration of fluoroorganic acidic compounds in aqueous dispersions
PatentPendingUS20230312776A1
Innovation
- A process involving the formation of a mixture with a pH value of less than 6, using a dispersion of fluoroorganic polymer particles and a protic solvent, reacting the fluoroorganic acidic compounds with an alkylamine to form a hydrophobic ionic compound, and separating this compound from the mixture into distinct phases for efficient removal.
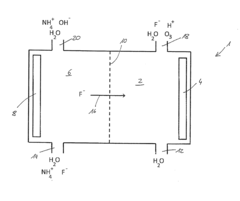
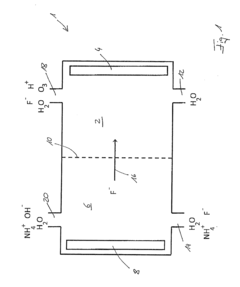
Method for producing diluted hydrofluoric acid
PatentActiveUS20180148332A1
Innovation
- A method using an electrode arrangement with an anode and cathode chambers separated by an anion exchange membrane, where pure water and an electrolyte solution containing fluoride ions are electrolyzed to produce dilute hydrofluoric acid with precise concentration control, and ozone can be simultaneously produced, with the ability to adjust concentrations independently using electrical current and electrolyte concentration.
Safety and Handling Protocols
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, demands rigorous safety and handling protocols due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with this substance. This includes chemical-resistant full-body suits, gloves, and face shields. Respiratory protection with supplied air or self-contained breathing apparatus is essential to prevent inhalation of toxic fumes.
Storage and containment of fluoroantimonic acid require specialized materials resistant to its corrosive nature. Teflon (PTFE) or fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) containers are typically used, as they can withstand the acid's aggressive properties. These containers must be sealed tightly and stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials.
Handling procedures must be conducted in a fume hood or glove box to minimize exposure risks. All equipment used in the handling process should be thoroughly cleaned and decontaminated after use. Strict protocols for waste disposal must be followed, involving neutralization with appropriate bases before disposal through authorized chemical waste management systems.
Emergency response plans are crucial when working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes readily available eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment kits. Personnel must be trained in proper spill response procedures, including the use of neutralizing agents and absorbent materials specifically designed for superacids.
Regular safety audits and equipment inspections are necessary to ensure the integrity of containment systems and the effectiveness of safety measures. This includes checking for signs of corrosion or degradation in storage containers and handling equipment.
Transportation of fluoroantimonic acid requires compliance with strict regulations for hazardous materials. It must be packaged in UN-approved containers with appropriate labeling and documentation. Only authorized personnel should be involved in its transport, and emergency response information must accompany the shipment at all times.
Training and education are fundamental aspects of safety protocols. All personnel working with or around fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be regularly updated to reflect the latest safety standards and best practices in the field.
Storage and containment of fluoroantimonic acid require specialized materials resistant to its corrosive nature. Teflon (PTFE) or fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) containers are typically used, as they can withstand the acid's aggressive properties. These containers must be sealed tightly and stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials.
Handling procedures must be conducted in a fume hood or glove box to minimize exposure risks. All equipment used in the handling process should be thoroughly cleaned and decontaminated after use. Strict protocols for waste disposal must be followed, involving neutralization with appropriate bases before disposal through authorized chemical waste management systems.
Emergency response plans are crucial when working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes readily available eyewash stations, safety showers, and spill containment kits. Personnel must be trained in proper spill response procedures, including the use of neutralizing agents and absorbent materials specifically designed for superacids.
Regular safety audits and equipment inspections are necessary to ensure the integrity of containment systems and the effectiveness of safety measures. This includes checking for signs of corrosion or degradation in storage containers and handling equipment.
Transportation of fluoroantimonic acid requires compliance with strict regulations for hazardous materials. It must be packaged in UN-approved containers with appropriate labeling and documentation. Only authorized personnel should be involved in its transport, and emergency response information must accompany the shipment at all times.
Training and education are fundamental aspects of safety protocols. All personnel working with or around fluoroantimonic acid must undergo comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. This training should be regularly updated to reflect the latest safety standards and best practices in the field.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Fluoroantimonic acid, known as the world's strongest superacid, poses significant environmental risks that require careful assessment and management. The production, handling, and disposal of this highly corrosive substance can have severe impacts on ecosystems and human health if not properly controlled.
The primary environmental concern associated with fluoroantimonic acid is its extreme reactivity and corrosiveness. When released into the environment, it can cause rapid and extensive damage to soil, water bodies, and air quality. The acid's ability to react violently with water and organic compounds means that even small spills can lead to widespread contamination and long-lasting ecological effects.
In aquatic environments, fluoroantimonic acid can drastically alter pH levels, leading to the death of fish, plants, and microorganisms. The release of fluoride and antimony ions from the acid can further contribute to water pollution, potentially affecting drinking water sources and aquatic food chains. Soil contamination by fluoroantimonic acid can render large areas infertile and unsuitable for agriculture or natural habitats.
Air pollution is another significant concern, as the acid can release toxic fumes containing hydrogen fluoride and antimony compounds. These emissions can contribute to acid rain formation, ozone depletion, and respiratory problems in both humans and wildlife. The long-range transport of these pollutants through atmospheric processes can extend the environmental impact far beyond the immediate area of release.
The production of fluoroantimonic acid also raises concerns about resource depletion and energy consumption. The extraction and processing of fluorine and antimony, key components of the acid, can lead to habitat destruction and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the high energy requirements for synthesizing and maintaining the acid in its pure form further add to its environmental footprint.
Waste management and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid present significant challenges. Conventional wastewater treatment methods are often inadequate for handling such a potent acid, necessitating specialized neutralization and disposal techniques. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination and long-term environmental degradation.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in facilities working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes robust storage systems, advanced spill response capabilities, and comprehensive employee training programs. Regular environmental monitoring around production and storage sites is crucial to detect and respond to potential leaks or emissions promptly.
Research into safer alternatives and more environmentally friendly production methods is vital for reducing the ecological impact of fluoroantimonic acid use. Developing closed-loop systems for acid recycling and exploring less hazardous substitutes for specific applications can significantly decrease the environmental risks associated with this superacid.
The primary environmental concern associated with fluoroantimonic acid is its extreme reactivity and corrosiveness. When released into the environment, it can cause rapid and extensive damage to soil, water bodies, and air quality. The acid's ability to react violently with water and organic compounds means that even small spills can lead to widespread contamination and long-lasting ecological effects.
In aquatic environments, fluoroantimonic acid can drastically alter pH levels, leading to the death of fish, plants, and microorganisms. The release of fluoride and antimony ions from the acid can further contribute to water pollution, potentially affecting drinking water sources and aquatic food chains. Soil contamination by fluoroantimonic acid can render large areas infertile and unsuitable for agriculture or natural habitats.
Air pollution is another significant concern, as the acid can release toxic fumes containing hydrogen fluoride and antimony compounds. These emissions can contribute to acid rain formation, ozone depletion, and respiratory problems in both humans and wildlife. The long-range transport of these pollutants through atmospheric processes can extend the environmental impact far beyond the immediate area of release.
The production of fluoroantimonic acid also raises concerns about resource depletion and energy consumption. The extraction and processing of fluorine and antimony, key components of the acid, can lead to habitat destruction and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the high energy requirements for synthesizing and maintaining the acid in its pure form further add to its environmental footprint.
Waste management and disposal of fluoroantimonic acid present significant challenges. Conventional wastewater treatment methods are often inadequate for handling such a potent acid, necessitating specialized neutralization and disposal techniques. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination and long-term environmental degradation.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in facilities working with fluoroantimonic acid. This includes robust storage systems, advanced spill response capabilities, and comprehensive employee training programs. Regular environmental monitoring around production and storage sites is crucial to detect and respond to potential leaks or emissions promptly.
Research into safer alternatives and more environmentally friendly production methods is vital for reducing the ecological impact of fluoroantimonic acid use. Developing closed-loop systems for acid recycling and exploring less hazardous substitutes for specific applications can significantly decrease the environmental risks associated with this superacid.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!