How to Quantify OLED Pixel Efficiency in Varying Conditions
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
OLED Efficiency Quantification Background and Objectives
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology has revolutionized display and lighting industries since its commercial introduction in the late 1990s. The evolution of OLED technology represents a significant advancement over traditional LCD displays, offering superior contrast ratios, wider viewing angles, and the ability to create flexible and transparent displays. The quantification of OLED pixel efficiency has become increasingly critical as applications expand across consumer electronics, automotive displays, and emerging wearable technologies.
The fundamental principle of OLED operation involves the electroluminescence of organic compounds when an electric current passes through them. However, the efficiency of this process varies significantly under different operating conditions, creating challenges for consistent performance measurement and optimization. Historical approaches to efficiency quantification have evolved from simple luminance measurements to sophisticated multi-parameter analyses that account for various environmental and operational factors.
Current industry standards primarily focus on measuring efficiency under controlled laboratory conditions, which often fail to represent real-world usage scenarios. This disconnect has led to discrepancies between advertised specifications and actual device performance, highlighting the need for more comprehensive quantification methodologies that account for varying conditions such as ambient temperature, humidity, driving voltage fluctuations, and aging effects.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop robust methodologies for quantifying OLED pixel efficiency across a spectrum of operating conditions that accurately reflect real-world usage scenarios. This includes establishing standardized testing protocols that can reliably measure efficiency parameters under variable environmental conditions, different driving schemes, and throughout the device lifetime.
Additionally, we aim to identify key factors affecting OLED efficiency degradation over time and under stress conditions, enabling more accurate prediction of long-term performance. This understanding is crucial for developing compensation algorithms that can maintain consistent visual quality throughout a device's operational lifespan.
From a technological perspective, we seek to explore novel measurement techniques that can provide real-time efficiency data without disrupting normal device operation. This includes investigating non-invasive optical and electrical characterization methods that could potentially be integrated into commercial OLED displays for continuous monitoring and adaptive optimization.
The ultimate goal is to bridge the gap between laboratory measurements and real-world performance by creating a comprehensive efficiency quantification framework that accounts for the dynamic nature of OLED operation. Such a framework would not only benefit manufacturers in quality control and product development but also enable more accurate comparisons between different OLED technologies and implementations, driving industry-wide innovation and standardization.
The fundamental principle of OLED operation involves the electroluminescence of organic compounds when an electric current passes through them. However, the efficiency of this process varies significantly under different operating conditions, creating challenges for consistent performance measurement and optimization. Historical approaches to efficiency quantification have evolved from simple luminance measurements to sophisticated multi-parameter analyses that account for various environmental and operational factors.
Current industry standards primarily focus on measuring efficiency under controlled laboratory conditions, which often fail to represent real-world usage scenarios. This disconnect has led to discrepancies between advertised specifications and actual device performance, highlighting the need for more comprehensive quantification methodologies that account for varying conditions such as ambient temperature, humidity, driving voltage fluctuations, and aging effects.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop robust methodologies for quantifying OLED pixel efficiency across a spectrum of operating conditions that accurately reflect real-world usage scenarios. This includes establishing standardized testing protocols that can reliably measure efficiency parameters under variable environmental conditions, different driving schemes, and throughout the device lifetime.
Additionally, we aim to identify key factors affecting OLED efficiency degradation over time and under stress conditions, enabling more accurate prediction of long-term performance. This understanding is crucial for developing compensation algorithms that can maintain consistent visual quality throughout a device's operational lifespan.
From a technological perspective, we seek to explore novel measurement techniques that can provide real-time efficiency data without disrupting normal device operation. This includes investigating non-invasive optical and electrical characterization methods that could potentially be integrated into commercial OLED displays for continuous monitoring and adaptive optimization.
The ultimate goal is to bridge the gap between laboratory measurements and real-world performance by creating a comprehensive efficiency quantification framework that accounts for the dynamic nature of OLED operation. Such a framework would not only benefit manufacturers in quality control and product development but also enable more accurate comparisons between different OLED technologies and implementations, driving industry-wide innovation and standardization.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Efficiency OLED Displays
The OLED display market has witnessed substantial growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing adoption in smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices. Current market analysis indicates that the global OLED display market is valued at approximately 48 billion USD in 2023, with projections suggesting growth to reach 72 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 10.7%.
High-efficiency OLED displays have become particularly crucial as consumer electronics manufacturers face mounting pressure to extend battery life while maintaining or improving display quality. Market research reveals that devices featuring energy-efficient displays command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay up to 15% more for smartphones that offer extended battery life without compromising visual performance.
The automotive sector represents an emerging high-potential market for efficient OLED technology. Luxury vehicle manufacturers are increasingly incorporating OLED displays in dashboard systems and entertainment consoles, with the automotive OLED market segment growing at 22% annually—significantly outpacing the broader OLED market.
Healthcare applications present another expanding market opportunity, particularly for medical imaging devices where precise color reproduction and energy efficiency are critical. The medical display market segment is expected to grow at 14% annually through 2028, with OLED technology capturing an increasing share from traditional LCD displays.
Consumer demand trends clearly indicate a preference for displays that maintain high brightness and color accuracy while consuming less power. A recent industry survey found that 78% of smartphone users identified battery life as a "very important" purchasing consideration, directly connecting to display efficiency as screens typically account for 40-60% of mobile device power consumption.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific dominating OLED production, with South Korea and China leading manufacturing capacity. However, consumption markets are more distributed, with North America and Europe showing strong demand for premium OLED products with enhanced efficiency metrics.
The enterprise and professional markets demonstrate increasing requirements for displays that can maintain consistent efficiency across varying ambient lighting conditions—particularly important for remote work applications where professionals operate in diverse environments. This segment values displays that can automatically optimize power consumption while maintaining visual performance regardless of environmental factors.
Industry forecasts suggest that manufacturers who can demonstrate quantifiable improvements in OLED efficiency across varying operational conditions will capture significant market share, particularly as energy consumption becomes an increasingly important differentiator in saturated consumer electronics markets.
High-efficiency OLED displays have become particularly crucial as consumer electronics manufacturers face mounting pressure to extend battery life while maintaining or improving display quality. Market research reveals that devices featuring energy-efficient displays command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay up to 15% more for smartphones that offer extended battery life without compromising visual performance.
The automotive sector represents an emerging high-potential market for efficient OLED technology. Luxury vehicle manufacturers are increasingly incorporating OLED displays in dashboard systems and entertainment consoles, with the automotive OLED market segment growing at 22% annually—significantly outpacing the broader OLED market.
Healthcare applications present another expanding market opportunity, particularly for medical imaging devices where precise color reproduction and energy efficiency are critical. The medical display market segment is expected to grow at 14% annually through 2028, with OLED technology capturing an increasing share from traditional LCD displays.
Consumer demand trends clearly indicate a preference for displays that maintain high brightness and color accuracy while consuming less power. A recent industry survey found that 78% of smartphone users identified battery life as a "very important" purchasing consideration, directly connecting to display efficiency as screens typically account for 40-60% of mobile device power consumption.
Regional analysis shows Asia-Pacific dominating OLED production, with South Korea and China leading manufacturing capacity. However, consumption markets are more distributed, with North America and Europe showing strong demand for premium OLED products with enhanced efficiency metrics.
The enterprise and professional markets demonstrate increasing requirements for displays that can maintain consistent efficiency across varying ambient lighting conditions—particularly important for remote work applications where professionals operate in diverse environments. This segment values displays that can automatically optimize power consumption while maintaining visual performance regardless of environmental factors.
Industry forecasts suggest that manufacturers who can demonstrate quantifiable improvements in OLED efficiency across varying operational conditions will capture significant market share, particularly as energy consumption becomes an increasingly important differentiator in saturated consumer electronics markets.
Current OLED Efficiency Measurement Challenges
The quantification of OLED pixel efficiency presents significant measurement challenges that have become increasingly complex as display technology advances. Current methodologies struggle to accurately capture efficiency metrics across varying operational conditions, creating a substantial gap between laboratory measurements and real-world performance.
One primary challenge is the environmental sensitivity of OLED materials. Temperature fluctuations can cause significant variations in quantum efficiency, with some OLED materials showing up to 30% efficiency reduction when operating temperatures increase from room temperature to 40°C. Humidity exposure similarly degrades performance, making standardized measurement protocols difficult to establish across different testing environments.
Light measurement inconsistency represents another major obstacle. The angular emission characteristics of OLEDs create discrepancies between on-axis and off-axis measurements, with efficiency values potentially varying by 15-25% depending on viewing angle. This directional dependency complicates the creation of comprehensive efficiency profiles that accurately represent real-world usage scenarios.
Temporal degradation factors further complicate measurement efforts. OLED efficiency naturally decreases over time through mechanisms like molecular decomposition and electrode oxidation. Current measurement techniques often fail to account for these temporal changes, providing only static efficiency snapshots rather than dynamic performance models that predict efficiency throughout the device lifecycle.
The industry also faces challenges with color-dependent efficiency variations. Different colored OLED subpixels (red, green, blue) exhibit vastly different efficiency profiles, with blue pixels typically showing 3-4 times lower efficiency than green counterparts. Standard measurement approaches often fail to adequately characterize these differences or account for their combined effect in full-color displays.
Measurement equipment limitations present additional barriers. High-precision spectroradiometers and integrating spheres required for accurate measurements are expensive and require specialized expertise, limiting widespread adoption of standardized testing protocols. Equipment calibration drift can introduce measurement errors of 5-10% even in professional testing environments.
The lack of universally accepted testing standards compounds these issues. Different manufacturers employ varied testing methodologies, making cross-product comparisons nearly impossible. While organizations like VESA and SID have proposed standardization frameworks, industry-wide adoption remains limited, resulting in efficiency claims that cannot be objectively verified or compared across different display technologies and manufacturers.
One primary challenge is the environmental sensitivity of OLED materials. Temperature fluctuations can cause significant variations in quantum efficiency, with some OLED materials showing up to 30% efficiency reduction when operating temperatures increase from room temperature to 40°C. Humidity exposure similarly degrades performance, making standardized measurement protocols difficult to establish across different testing environments.
Light measurement inconsistency represents another major obstacle. The angular emission characteristics of OLEDs create discrepancies between on-axis and off-axis measurements, with efficiency values potentially varying by 15-25% depending on viewing angle. This directional dependency complicates the creation of comprehensive efficiency profiles that accurately represent real-world usage scenarios.
Temporal degradation factors further complicate measurement efforts. OLED efficiency naturally decreases over time through mechanisms like molecular decomposition and electrode oxidation. Current measurement techniques often fail to account for these temporal changes, providing only static efficiency snapshots rather than dynamic performance models that predict efficiency throughout the device lifecycle.
The industry also faces challenges with color-dependent efficiency variations. Different colored OLED subpixels (red, green, blue) exhibit vastly different efficiency profiles, with blue pixels typically showing 3-4 times lower efficiency than green counterparts. Standard measurement approaches often fail to adequately characterize these differences or account for their combined effect in full-color displays.
Measurement equipment limitations present additional barriers. High-precision spectroradiometers and integrating spheres required for accurate measurements are expensive and require specialized expertise, limiting widespread adoption of standardized testing protocols. Equipment calibration drift can introduce measurement errors of 5-10% even in professional testing environments.
The lack of universally accepted testing standards compounds these issues. Different manufacturers employ varied testing methodologies, making cross-product comparisons nearly impossible. While organizations like VESA and SID have proposed standardization frameworks, industry-wide adoption remains limited, resulting in efficiency claims that cannot be objectively verified or compared across different display technologies and manufacturers.
Current Methodologies for OLED Efficiency Quantification
01 Pixel circuit design for improved efficiency
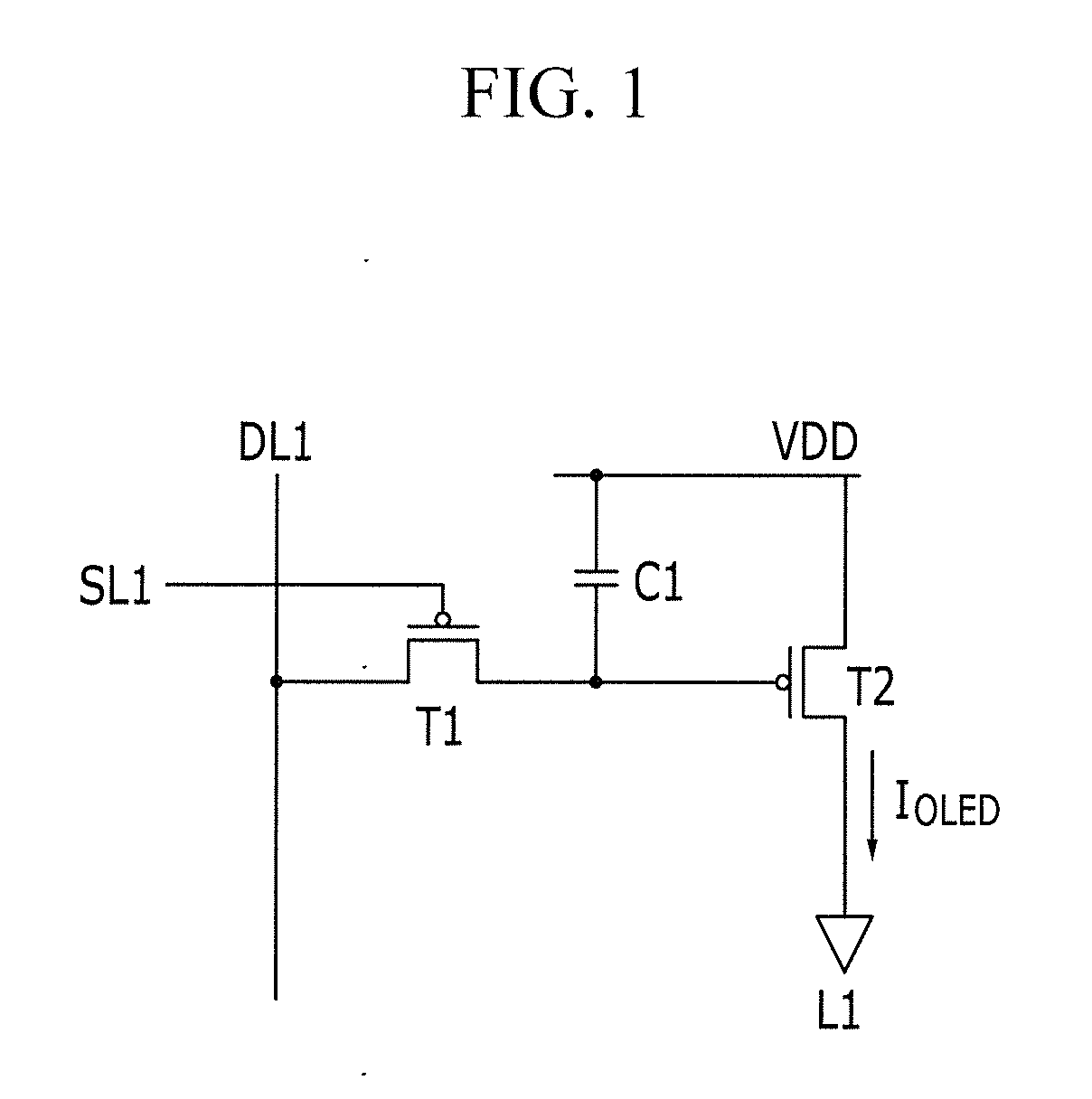
Advanced pixel circuit designs can significantly enhance OLED efficiency by optimizing current flow and reducing power consumption. These designs include compensation circuits that address threshold voltage variations and mobility degradation in thin-film transistors. By implementing specialized driving schemes and transistor arrangements, these circuits ensure uniform brightness across the display while minimizing energy loss, resulting in higher luminous efficiency and extended device lifetime.- Pixel circuit design for improved efficiency: Various pixel circuit designs can enhance OLED efficiency by optimizing current flow and reducing power consumption. These designs include compensation circuits that address threshold voltage variations, specialized driving transistor arrangements, and improved signal processing methods. Advanced pixel architectures enable more precise control of the light emission process, resulting in higher luminous efficiency and extended display lifetime.
- Material composition and structure optimization: The efficiency of OLED pixels can be significantly improved through optimization of material compositions and layer structures. This includes developing advanced emissive materials, optimizing the electron transport layer, hole transport layer, and employing novel dopants. Structural modifications such as microcavity effects and light extraction techniques can enhance both internal and external quantum efficiency of the OLED pixels.
- Driving method and compensation techniques: Specialized driving methods and compensation techniques can improve OLED pixel efficiency by addressing non-uniformities and degradation issues. These include adaptive driving schemes that adjust based on pixel aging, temperature compensation algorithms, and real-time adjustment of driving currents. Advanced compensation techniques can correct for threshold voltage shifts and mobility variations in the driving transistors, ensuring consistent brightness and efficiency over the display lifetime.
- Pixel structure and layout optimization: The physical structure and layout of OLED pixels significantly impact efficiency. Innovations include sub-pixel arrangements that maximize light emission area, minimized non-emissive regions, and optimized aperture ratios. Advanced pixel structures may incorporate micro-lenses, reflective structures, or specialized electrode configurations to enhance light extraction and reduce optical losses, resulting in higher overall pixel efficiency.
- Integration of sensing and feedback mechanisms: Incorporating sensing and feedback mechanisms within OLED displays enables real-time monitoring and adjustment of pixel performance. These systems can detect changes in pixel efficiency due to aging or environmental factors and apply appropriate compensation. Technologies include integrated photosensors, temperature sensors, and sophisticated feedback algorithms that continuously optimize driving parameters to maintain peak efficiency throughout the display's operational life.
02 OLED material and structure optimization
The efficiency of OLED pixels can be improved through optimization of materials and device structures. This includes using high-efficiency emitting materials, optimizing layer thicknesses, and implementing advanced stacking architectures such as tandem OLEDs. Incorporating phosphorescent or thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials can significantly increase internal quantum efficiency. Additionally, optimized electron and hole transport layers ensure balanced charge injection and recombination within the emission layer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Light extraction techniques
Various light extraction techniques can be employed to improve OLED pixel efficiency by reducing internal light loss. These include microlens arrays, photonic crystals, and nanostructured substrates that reduce total internal reflection and waveguide effects. By incorporating optical outcoupling structures, more generated light can be extracted from the device, significantly enhancing external quantum efficiency without increasing power consumption. These techniques can effectively double the light output of conventional OLED structures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Driving method and compensation algorithms
Advanced driving methods and compensation algorithms can significantly improve OLED pixel efficiency. These include adaptive brightness control, dynamic voltage scaling, and real-time compensation for aging effects. By implementing sophisticated driving schemes that adjust current levels based on image content and display conditions, power consumption can be reduced while maintaining optimal visual quality. Additionally, feedback mechanisms can monitor and adjust pixel performance over time to maintain consistent efficiency throughout the display's lifetime.Expand Specific Solutions05 Pixel arrangement and subpixel sharing
Innovative pixel arrangements and subpixel sharing techniques can enhance overall OLED display efficiency. These include pentile matrix arrangements, RGBW pixel structures, and shared electrode configurations that optimize the active area ratio. By strategically designing pixel layouts to maximize light-emitting area while minimizing non-emissive regions, the aperture ratio can be increased, resulting in higher brightness for the same power input. Additionally, subpixel rendering algorithms can further improve perceived resolution and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in OLED Display Technology
The OLED pixel efficiency quantification market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for accurate measurement technologies across varying conditions. The global OLED display market is projected to reach approximately $50 billion by 2025, driven by adoption in smartphones, TVs, and emerging applications. Leading players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology are advancing proprietary efficiency measurement systems, while specialized companies such as IGNIS Innovation and Global OLED Technology focus on compensation algorithms to address efficiency variations. Research institutions like Commissariat à l'énergie atomique and equipment manufacturers including Applied Materials are developing standardized measurement protocols. The competitive landscape shows a mix of established display manufacturers and specialized technology providers working to solve efficiency degradation challenges under different operating conditions.
IGNIS Innovation, Inc.
Technical Solution: IGNIS Innovation has developed a specialized approach to OLED pixel efficiency quantification through their MaxLife™ technology platform. Their methodology centers on in-pixel sensing circuits that continuously monitor electrical characteristics of each OLED pixel during normal display operation. These embedded sensors measure current-voltage relationships and threshold voltage shifts that indicate efficiency changes without requiring external measurement equipment. IGNIS's system captures real-time data on pixel degradation by measuring minute changes in electrical characteristics that correlate with luminous efficiency losses. Their proprietary algorithms translate these electrical measurements into accurate predictions of optical performance changes, enabling precise compensation without interrupting normal display operation. The company's Advanced Measurement Unit (AMU) technology integrates with the display's TFT backplane to provide temporal resolution of efficiency changes as short as 1 millisecond, capturing transient effects that impact perceived image quality[5]. IGNIS has also pioneered stress-dependent measurement protocols that quantify how pixel efficiency varies not just with temperature and brightness, but also with the specific image content history, accounting for image sticking and burn-in effects that conventional measurement systems often miss. Their latest innovation includes machine learning models that predict efficiency changes based on historical pixel usage patterns, enabling preemptive compensation before visible degradation occurs[6].
Strengths: Their in-pixel sensing approach provides continuous real-time efficiency data without external measurement equipment. The system can detect and compensate for efficiency variations at the individual pixel level with minimal computational overhead. Weaknesses: The additional sensing circuitry increases manufacturing complexity and potentially reduces aperture ratio. Their approach focuses primarily on electrical characteristics as proxies for optical efficiency rather than direct optical measurements.
Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Display has developed a comprehensive approach to quantify OLED pixel efficiency across varying conditions using their proprietary Mura compensation technology. Their method employs real-time measurement systems that capture pixel-level luminance and color variations under different temperatures, driving currents, and aging conditions. Samsung's Advanced Pixel Compensation (APC) algorithm continuously monitors individual pixel performance using integrated thin-film transistor (TFT) sensors that detect electrical characteristics changes. This data is processed through machine learning algorithms to create compensation maps that adjust driving voltages for each pixel, ensuring uniform brightness and color accuracy across the display. Samsung also utilizes accelerated aging tests where displays are subjected to controlled degradation while efficiency measurements are taken at regular intervals, creating predictive models for long-term performance[1]. Their latest M12 production line incorporates automated optical measurement systems that can detect sub-pixel efficiency variations as small as 1% across the entire luminance range (0.01-1000 nits)[2].
Strengths: Industry-leading production scale allows for extensive statistical data collection across millions of panels, enabling highly accurate compensation algorithms. Their vertical integration from materials to finished displays provides complete control over the measurement ecosystem. Weaknesses: Their proprietary measurement systems and algorithms are closed-source, limiting academic validation. The compensation approach focuses more on correcting efficiency variations rather than fundamental material improvements.
Critical Technologies for Variable Condition Measurements
Organic light emitting diode display pixel array
PatentInactiveUS20200279517A1
Innovation
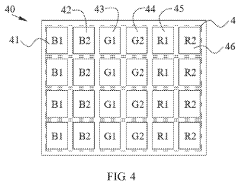
- The OLED display pixel array is designed with multiple sub-pixels of different colors, specifically configured to optimize chromaticity coordinates, and connected to an array control circuit to ensure precise control and uniformity, allowing for various sub-pixel arrangements such as one red, one green, and two blue, or two red and two green sub-pixels, with specific coordinate ranges in the CIE 1931 system.
Organic light emitting diode display
PatentActiveUS20120256218A1
Innovation
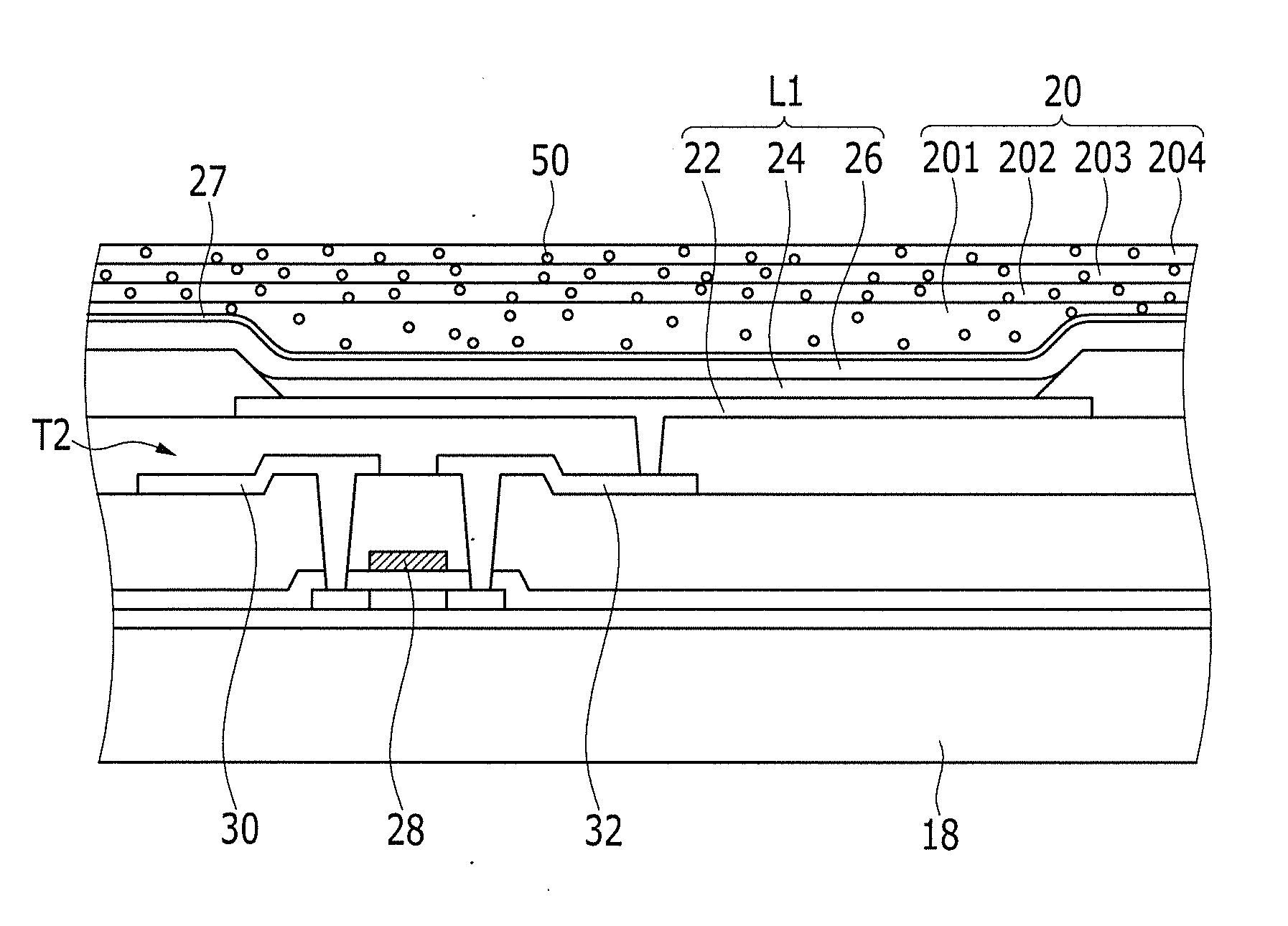
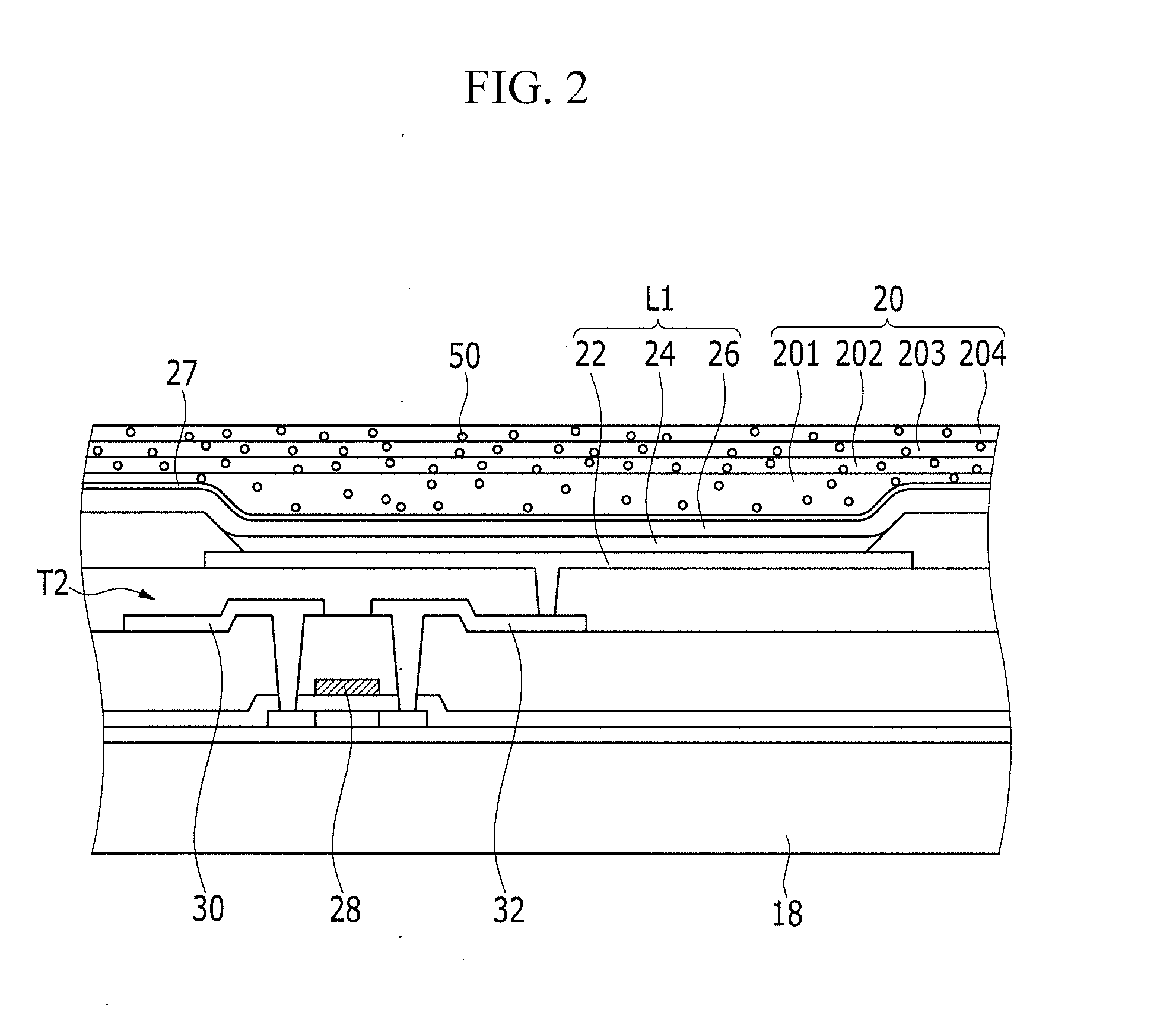
- Incorporating scattering materials with diameters larger than 1/8 of the emitted light wavelength and refractive indices between 1.5 and 3.0 into the thin film encapsulation layer, specifically in organic and inorganic layers, to scatter light and improve transmission.
Environmental Impact of OLED Efficiency Improvements
The environmental implications of OLED efficiency improvements extend far beyond mere energy savings. As OLED technology continues to evolve, enhanced pixel efficiency directly translates to reduced power consumption across billions of devices worldwide. Current estimates suggest that improving OLED efficiency by just 10% could result in annual energy savings equivalent to powering over 1 million households, representing a significant reduction in carbon emissions from electricity generation.
Manufacturing processes for more efficient OLED panels typically require fewer raw materials and energy inputs. Research indicates that high-efficiency OLED production can reduce manufacturing-related carbon emissions by up to 15% compared to standard efficiency panels. Additionally, the reduction in heat generation from more efficient pixels extends device lifespan, potentially decreasing electronic waste by an estimated 20-30% over a five-year product cycle.
The environmental benefits multiply when considering the full lifecycle assessment. More efficient OLEDs require less frequent charging for mobile devices, reducing the cumulative energy demand throughout product lifespans. For large-format displays and lighting applications, efficiency improvements directly impact grid energy requirements, with potential energy savings scaling exponentially with display size and brightness requirements.
Water conservation represents another critical environmental benefit. Advanced OLED manufacturing processes focused on efficiency improvements typically implement closed-loop water systems, reducing freshwater consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional manufacturing methods. This aspect becomes increasingly important as electronics production faces growing scrutiny regarding water resource management.
Chemical usage in OLED production presents both challenges and opportunities for environmental improvement. Efficiency-focused manufacturing often employs more precise deposition techniques, reducing chemical waste by approximately 25%. However, some high-efficiency OLED formulations may incorporate rare earth elements, presenting new recycling challenges that require innovative recovery solutions to prevent environmental contamination.
The quantification of these environmental benefits depends heavily on accurate efficiency measurements across varying conditions. As measurement methodologies improve, manufacturers can more precisely target efficiency improvements with the greatest environmental return on investment, creating a positive feedback loop between technological advancement and sustainability goals.
Manufacturing processes for more efficient OLED panels typically require fewer raw materials and energy inputs. Research indicates that high-efficiency OLED production can reduce manufacturing-related carbon emissions by up to 15% compared to standard efficiency panels. Additionally, the reduction in heat generation from more efficient pixels extends device lifespan, potentially decreasing electronic waste by an estimated 20-30% over a five-year product cycle.
The environmental benefits multiply when considering the full lifecycle assessment. More efficient OLEDs require less frequent charging for mobile devices, reducing the cumulative energy demand throughout product lifespans. For large-format displays and lighting applications, efficiency improvements directly impact grid energy requirements, with potential energy savings scaling exponentially with display size and brightness requirements.
Water conservation represents another critical environmental benefit. Advanced OLED manufacturing processes focused on efficiency improvements typically implement closed-loop water systems, reducing freshwater consumption by up to 40% compared to conventional manufacturing methods. This aspect becomes increasingly important as electronics production faces growing scrutiny regarding water resource management.
Chemical usage in OLED production presents both challenges and opportunities for environmental improvement. Efficiency-focused manufacturing often employs more precise deposition techniques, reducing chemical waste by approximately 25%. However, some high-efficiency OLED formulations may incorporate rare earth elements, presenting new recycling challenges that require innovative recovery solutions to prevent environmental contamination.
The quantification of these environmental benefits depends heavily on accurate efficiency measurements across varying conditions. As measurement methodologies improve, manufacturers can more precisely target efficiency improvements with the greatest environmental return on investment, creating a positive feedback loop between technological advancement and sustainability goals.
Standardization Efforts in OLED Measurement Protocols
The standardization of OLED measurement protocols represents a critical foundation for consistent quantification of pixel efficiency across varying conditions. Currently, several international organizations are actively developing comprehensive standards to address the unique challenges posed by OLED technology's sensitivity to environmental factors and operational parameters.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established the IEC 62341 series specifically for OLED displays, with sections dedicated to measurement methods for optical and electrical performance. These standards provide guidelines for consistent testing environments, including temperature control (23°C ± 2°C) and humidity parameters (55% ± 5% RH), which significantly impact OLED efficiency measurements.
The Society for Information Display (SID) has contributed substantially through its Metrology Committee, which focuses on developing standardized measurement techniques for emerging display technologies. Their recent work includes protocols for measuring OLED efficiency under variable ambient lighting conditions, addressing one of the most challenging aspects of comparative analysis.
VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) has introduced the DisplayHDR True Black standard, which includes specific testing methodologies for OLED displays that account for their unique black level capabilities and efficiency characteristics. This standard provides valuable frameworks for measuring power efficiency across varying brightness levels.
The International Commission on Illumination (CIE) has developed spectroradiometric measurement standards that are increasingly being adapted for OLED-specific applications. Their guidelines for color measurement are particularly relevant for assessing the efficiency of different color subpixels within OLED displays.
Industry consortia have also emerged to address standardization gaps. The OLED Association has established working groups focused on harmonizing test methods across manufacturers, while the UHD Alliance has incorporated OLED-specific measurement protocols into their performance certification programs.
These standardization efforts face several ongoing challenges, including the need to account for OLED aging effects in measurement protocols, establishing consistent methods for measuring efficiency under dynamic content conditions, and developing accelerated testing procedures that can reliably predict long-term efficiency behavior. Cross-calibration between different measurement equipment remains problematic, with inter-laboratory studies showing variations of up to 15% in efficiency measurements using identical samples.
Recent progress includes the development of reference OLED panels with certified performance characteristics, which serve as calibration standards for measurement equipment. Additionally, round-robin testing programs involving multiple laboratories are helping to identify and resolve systematic measurement discrepancies across different facilities and equipment setups.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established the IEC 62341 series specifically for OLED displays, with sections dedicated to measurement methods for optical and electrical performance. These standards provide guidelines for consistent testing environments, including temperature control (23°C ± 2°C) and humidity parameters (55% ± 5% RH), which significantly impact OLED efficiency measurements.
The Society for Information Display (SID) has contributed substantially through its Metrology Committee, which focuses on developing standardized measurement techniques for emerging display technologies. Their recent work includes protocols for measuring OLED efficiency under variable ambient lighting conditions, addressing one of the most challenging aspects of comparative analysis.
VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) has introduced the DisplayHDR True Black standard, which includes specific testing methodologies for OLED displays that account for their unique black level capabilities and efficiency characteristics. This standard provides valuable frameworks for measuring power efficiency across varying brightness levels.
The International Commission on Illumination (CIE) has developed spectroradiometric measurement standards that are increasingly being adapted for OLED-specific applications. Their guidelines for color measurement are particularly relevant for assessing the efficiency of different color subpixels within OLED displays.
Industry consortia have also emerged to address standardization gaps. The OLED Association has established working groups focused on harmonizing test methods across manufacturers, while the UHD Alliance has incorporated OLED-specific measurement protocols into their performance certification programs.
These standardization efforts face several ongoing challenges, including the need to account for OLED aging effects in measurement protocols, establishing consistent methods for measuring efficiency under dynamic content conditions, and developing accelerated testing procedures that can reliably predict long-term efficiency behavior. Cross-calibration between different measurement equipment remains problematic, with inter-laboratory studies showing variations of up to 15% in efficiency measurements using identical samples.
Recent progress includes the development of reference OLED panels with certified performance characteristics, which serve as calibration standards for measurement equipment. Additionally, round-robin testing programs involving multiple laboratories are helping to identify and resolve systematic measurement discrepancies across different facilities and equipment setups.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!