How to Revolutionize Production Techniques with Cellulose Acetate?
Cellulose Acetate Evolution and Objectives
Cellulose acetate has a rich history dating back to its discovery in the late 19th century. Initially developed as a substitute for celluloid, it quickly gained prominence in various industries due to its versatility and unique properties. The evolution of cellulose acetate production techniques has been marked by continuous improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
In the early stages, cellulose acetate was primarily produced through the acetylation of cellulose using acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This process, known as the acetic acid process, remained the dominant method for decades. However, it faced challenges in terms of environmental impact and production costs.
The mid-20th century saw significant advancements in cellulose acetate production. The introduction of the methylene chloride process offered a more efficient alternative, reducing production time and improving product quality. This method allowed for better control over the degree of substitution, resulting in cellulose acetate with tailored properties for specific applications.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards more sustainable production techniques. The development of bio-based acetylation processes, utilizing enzymes and green solvents, has gained traction. These methods aim to reduce the environmental footprint of cellulose acetate production while maintaining or enhancing product performance.
The current objectives in cellulose acetate production revolve around several key areas. Firstly, there is a strong focus on improving energy efficiency throughout the production process. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, enhancing heat recovery systems, and implementing advanced process control technologies.
Secondly, there is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable feedstocks. Research is underway to explore alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste and fast-growing crops, to reduce reliance on traditional wood pulp.
Thirdly, the industry is striving to enhance the material properties of cellulose acetate. This includes improving its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and barrier properties to expand its applications in high-performance materials and packaging.
Lastly, there is a concerted effort to revolutionize the end-of-life management of cellulose acetate products. The development of biodegradable variants and efficient recycling technologies are key objectives to address environmental concerns and promote a circular economy approach.
As we look to the future, the evolution of cellulose acetate production techniques will likely continue to focus on sustainability, efficiency, and versatility. The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and process intensification, holds promise for further optimizing production processes and expanding the material's potential applications.
Market Demand Analysis for Cellulose Acetate Products
The market demand for cellulose acetate products has been steadily growing, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. In the textile sector, cellulose acetate fibers are increasingly sought after for their silk-like texture, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. This has led to a surge in demand for cellulose acetate-based fabrics in high-end clothing, sportswear, and home textiles.
The packaging industry represents another significant market for cellulose acetate products. With the global push towards sustainable packaging solutions, cellulose acetate films are gaining traction as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic packaging. Their biodegradability and transparency make them ideal for food packaging, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products, contributing to the overall market growth.
In the consumer goods sector, cellulose acetate's durability and aesthetic appeal have made it a popular choice for eyeglass frames, handles for tools and utensils, and various decorative items. The material's ability to mimic the appearance of natural materials like tortoiseshell and ivory, without the associated ethical concerns, has further boosted its demand in this segment.
The automotive industry has also shown increasing interest in cellulose acetate products. As manufacturers strive to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, cellulose acetate composites are being explored as potential replacements for certain metal and plastic components. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for market expansion in the coming years.
In the electronics sector, cellulose acetate films are finding applications in flexible displays and touch screens, owing to their optical clarity and flexibility. As the demand for foldable and rollable electronic devices grows, this application is projected to become a significant driver of market growth.
The global cellulose acetate market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with Asia-Pacific emerging as the fastest-growing region. This growth is attributed to rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and the expanding textile and packaging industries in countries like China and India.
However, the market faces challenges from the availability of alternative materials and environmental concerns related to the acetylation process. To address these issues, industry players are investing in research and development to improve production techniques and enhance the sustainability profile of cellulose acetate products.
Current Challenges in Cellulose Acetate Production
The production of cellulose acetate faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes. The use of acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid in the acetylation process generates substantial amounts of waste and potentially harmful byproducts, raising concerns about sustainability and ecological footprint.
Another major challenge lies in the energy-intensive nature of cellulose acetate production. The process requires high temperatures and prolonged reaction times, leading to considerable energy consumption and increased production costs. This energy inefficiency not only affects the economic viability of cellulose acetate but also contributes to its carbon footprint, making it less attractive in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
The quality control of cellulose acetate production presents additional hurdles. Achieving consistent product properties, such as degree of substitution and molecular weight distribution, can be difficult due to the heterogeneous nature of cellulose raw materials. This variability can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, affecting its performance in various applications and potentially limiting its market acceptance.
Furthermore, the sourcing of raw materials poses a challenge for cellulose acetate manufacturers. The demand for high-quality cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, competes with other industries, potentially leading to supply chain issues and price fluctuations. This competition for raw materials can impact the stability and scalability of cellulose acetate production.
The limited solubility of cellulose in common solvents also presents a significant technical challenge. This characteristic complicates the processing and modification of cellulose, necessitating the use of specialized solvents or complex chemical treatments. Overcoming this solubility issue is crucial for expanding the range of cellulose acetate applications and improving its processability.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in developing more efficient and eco-friendly production methods. While research into alternative acetylation processes and greener solvents is ongoing, scaling these innovations to industrial levels remains a significant hurdle. The transition from laboratory-scale discoveries to commercially viable production techniques requires substantial investment and technological advancements.
Existing Cellulose Acetate Production Methods
01 Production methods for cellulose acetate
Various methods for producing cellulose acetate are described, including improvements in acetylation processes, solvent systems, and reaction conditions. These methods aim to enhance the efficiency and quality of cellulose acetate production, potentially leading to better material properties for diverse applications.- Cellulose acetate production methods: Various methods for producing cellulose acetate are described, including improvements in acetylation processes, solvent systems, and reaction conditions. These methods aim to enhance the efficiency and quality of cellulose acetate production for different applications.
- Cellulose acetate fiber applications: Cellulose acetate fibers are utilized in diverse applications, such as textiles, filters, and packaging materials. The properties of these fibers can be tailored through modifications in the production process or by incorporating additives to enhance performance characteristics.
- Cellulose acetate film and membrane technology: Advancements in cellulose acetate film and membrane technology focus on improving properties such as permeability, selectivity, and durability. These developments are particularly relevant for applications in separation processes, water treatment, and gas purification.
- Cellulose acetate composites and blends: Research on cellulose acetate composites and blends explores the combination of cellulose acetate with other materials to create products with enhanced properties. This includes the development of biodegradable composites and materials with improved mechanical or thermal characteristics.
- Cellulose acetate modification and functionalization: Techniques for modifying and functionalizing cellulose acetate are investigated to impart specific properties or functionalities. This includes chemical modifications, surface treatments, and the incorporation of reactive groups to expand the material's potential applications.
02 Cellulose acetate fibers and films
Innovations in the production and properties of cellulose acetate fibers and films are presented. These developments focus on improving the mechanical strength, flexibility, and other physical characteristics of cellulose acetate-based materials for use in textiles, packaging, and other industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cellulose acetate composites and blends
Research on cellulose acetate composites and blends with other materials is discussed. These combinations aim to enhance the properties of cellulose acetate, such as biodegradability, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, for applications in various fields including packaging and biomedical materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of cellulose acetate
Techniques for modifying and functionalizing cellulose acetate are explored. These methods involve chemical treatments or the incorporation of additives to impart new properties to cellulose acetate, such as improved water resistance, flame retardancy, or specific reactive groups for further applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of cellulose acetate in various industries
The diverse applications of cellulose acetate across different industries are highlighted. These include its use in textiles, packaging materials, filters, membranes, and biomedical devices. The focus is on leveraging the unique properties of cellulose acetate to meet specific industry requirements and develop innovative products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellulose Acetate Industry
The cellulose acetate production techniques market is in a mature stage, with established players like Daicel Corp., Eastman Chemical Co., and BASF Corp. leading the industry. However, there's ongoing innovation driven by sustainability demands and new applications. The global market size is substantial, with steady growth projected. Technologically, the field is well-developed but evolving, as evidenced by research from institutions like the Chinese Academy of Sciences and universities worldwide. Companies such as Nantong Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd. and Zhuhai Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd. are pushing for advancements in production efficiency and product quality. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical corporations and specialized manufacturers, with increasing focus on eco-friendly processes and novel applications in various industries.
Daicel Corp.
BASF Corp.
Innovative Cellulose Acetate Technologies
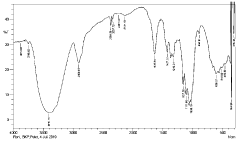
- A method involving the reaction of cellulose with acetic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst and acetic acid solvent, followed by hydrolysis to adjust the acetylation degree to 52-59%, precipitation in water, and dispersion in a mixed solvent with specific solubility parameters to form cellulose acetate flakes, reducing low-molecular-weight components and enhancing transparency.
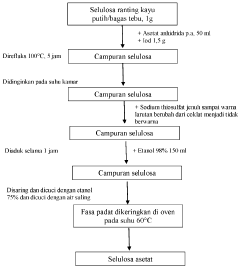
- Utilization of agro-industrial waste (eucalyptus and sugarcane bagasse) as raw materials for cellulose acetate production, promoting sustainability and waste reduction.
- Two-stage process involving cellulose extraction followed by acetylation, allowing for optimization of each stage separately.
- Use of iodine (I2) as a catalyst in the acetylation reaction, potentially improving reaction efficiency and product quality.
Environmental Impact of Cellulose Acetate Manufacturing
The environmental impact of cellulose acetate manufacturing is a critical consideration in the quest to revolutionize production techniques. The process of producing cellulose acetate involves several stages that can have significant environmental implications. Initially, the raw material sourcing, primarily wood pulp or cotton linters, raises concerns about deforestation and land use changes. The cultivation and harvesting of these materials can lead to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss if not managed sustainably.
During the manufacturing process, the use of acetic anhydride and acetic acid as key reagents presents potential environmental hazards. These chemicals, if not properly handled and contained, can contribute to air and water pollution. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during production can lead to smog formation and negatively impact air quality in surrounding areas. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of cellulose acetate production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change concerns.
Water usage in cellulose acetate manufacturing is another significant environmental factor. The process requires substantial amounts of water for various stages, including washing and purification. This high water demand can strain local water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions. Moreover, the wastewater generated during production often contains chemical residues and requires thorough treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of the environmental impact assessment. The production of cellulose acetate generates solid waste, including off-spec materials and by-products. Proper disposal or recycling of these wastes is essential to minimize landfill usage and reduce the overall environmental footprint of the manufacturing process. Furthermore, the end-of-life considerations for cellulose acetate products, such as their biodegradability and potential for recycling, play a significant role in the long-term environmental impact of this material.
To address these environmental challenges, innovative approaches in cellulose acetate production are being explored. These include the development of more efficient manufacturing processes that reduce energy consumption and minimize chemical usage. Closed-loop systems for water and solvent recycling are being implemented to decrease water demand and minimize waste generation. Additionally, research into bio-based alternatives for acetic anhydride and other chemicals used in the process aims to reduce the reliance on petrochemical-derived inputs.
Advancements in green chemistry principles are driving the search for more environmentally friendly catalysts and reaction conditions. These efforts seek to lower the environmental impact of cellulose acetate production while maintaining or improving product quality. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities is being pursued to reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy consumption.
Regulatory Framework for Cellulose Acetate Production
The regulatory framework for cellulose acetate production plays a crucial role in shaping the industry's practices and ensuring environmental and safety standards. At the international level, organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidelines that influence national regulations. These standards often focus on quality control, environmental impact, and worker safety in the production process.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cellulose acetate when used in food packaging and medical applications. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees environmental aspects of production, including emissions and waste management. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for worker safety in manufacturing facilities.
European Union regulations are particularly stringent, with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requiring manufacturers to register chemicals and provide safety data. The EU's Waste Framework Directive also impacts cellulose acetate production, promoting recycling and proper disposal of waste materials.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory bodies. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment sets environmental standards, while Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cellulose acetate in food contact materials.
Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in technology and processes. Companies must implement robust quality management systems, conduct regular environmental impact assessments, and ensure proper handling and disposal of chemicals used in production.
The regulatory landscape is dynamic, with increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles. This is driving innovation in production techniques, pushing manufacturers to develop more environmentally friendly processes and explore bio-based alternatives to traditional cellulose acetate production.
Emerging regulations are also addressing the end-of-life management of cellulose acetate products, particularly in the context of single-use plastics. This is prompting manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products and explore biodegradable formulations.
As the industry seeks to revolutionize production techniques, navigating this complex regulatory environment is crucial. Companies must stay abreast of evolving regulations across different markets and proactively adapt their production methods to ensure compliance while driving innovation.