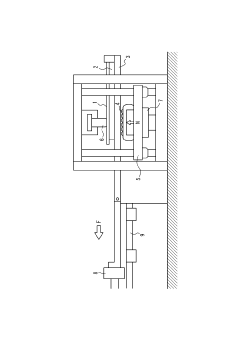
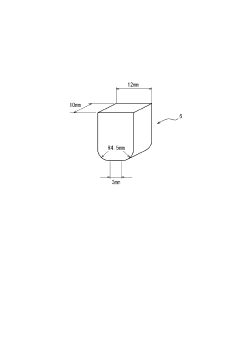
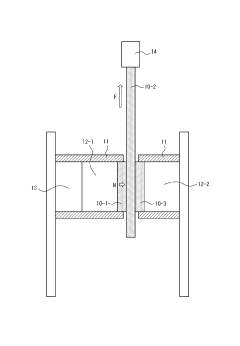
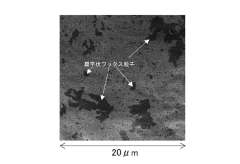
How to Treat Galvanized Steel for Enhanced Aesthetic Finish
SEP 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Galvanized Steel Surface Treatment Background and Objectives
Galvanized steel has been a cornerstone material in various industries for over 150 years, providing exceptional corrosion resistance through its zinc coating. The process of galvanization, first patented in 1837, has evolved significantly from its initial hot-dip method to include electrogalvanizing and other advanced techniques. While the primary function of galvanization remains corrosion protection, modern applications increasingly demand superior aesthetic qualities alongside functional performance.
The evolution of galvanized steel treatment technologies has accelerated in recent decades, driven by expanding applications in architectural facades, automotive components, consumer appliances, and designer furniture. This shift has transformed galvanized steel from a purely utilitarian material to one that must satisfy both engineering requirements and aesthetic expectations. The distinctive spangle pattern and matte gray appearance of traditional galvanized steel, once considered merely acceptable, now represents either a design feature to be enhanced or a limitation to be overcome.
Current market trends indicate growing demand for galvanized steel with customized finishes that maintain or exceed the corrosion resistance of traditional galvanization. The architectural sector particularly seeks galvanized surfaces that can be integrated into contemporary design languages while maintaining long-term durability in various environmental conditions. Similarly, consumer product manufacturers require finishes that convey quality and sophistication while withstanding daily use.
The technical objective of enhanced aesthetic finish treatments for galvanized steel encompasses several specific goals. First, developing surface treatment methodologies that preserve or improve the inherent corrosion resistance of the zinc coating. Second, creating reproducible processes that enable consistent color application, texture development, and surface appearance across production batches. Third, establishing treatments that maintain adhesion and appearance integrity throughout the product lifecycle despite exposure to environmental stressors.
Additionally, modern sustainability requirements necessitate that these aesthetic treatments minimize environmental impact through reduced VOC emissions, elimination of heavy metals and other hazardous substances, and compatibility with end-of-life recycling processes. The ideal solution must balance these technical requirements with commercial viability, offering scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation at reasonable cost points.
This technical research aims to comprehensively evaluate existing approaches to galvanized steel aesthetic enhancement, identify emerging technologies with potential application in this field, and outline promising research directions for developing next-generation surface treatments that satisfy both functional and aesthetic requirements.
The evolution of galvanized steel treatment technologies has accelerated in recent decades, driven by expanding applications in architectural facades, automotive components, consumer appliances, and designer furniture. This shift has transformed galvanized steel from a purely utilitarian material to one that must satisfy both engineering requirements and aesthetic expectations. The distinctive spangle pattern and matte gray appearance of traditional galvanized steel, once considered merely acceptable, now represents either a design feature to be enhanced or a limitation to be overcome.
Current market trends indicate growing demand for galvanized steel with customized finishes that maintain or exceed the corrosion resistance of traditional galvanization. The architectural sector particularly seeks galvanized surfaces that can be integrated into contemporary design languages while maintaining long-term durability in various environmental conditions. Similarly, consumer product manufacturers require finishes that convey quality and sophistication while withstanding daily use.
The technical objective of enhanced aesthetic finish treatments for galvanized steel encompasses several specific goals. First, developing surface treatment methodologies that preserve or improve the inherent corrosion resistance of the zinc coating. Second, creating reproducible processes that enable consistent color application, texture development, and surface appearance across production batches. Third, establishing treatments that maintain adhesion and appearance integrity throughout the product lifecycle despite exposure to environmental stressors.
Additionally, modern sustainability requirements necessitate that these aesthetic treatments minimize environmental impact through reduced VOC emissions, elimination of heavy metals and other hazardous substances, and compatibility with end-of-life recycling processes. The ideal solution must balance these technical requirements with commercial viability, offering scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation at reasonable cost points.
This technical research aims to comprehensively evaluate existing approaches to galvanized steel aesthetic enhancement, identify emerging technologies with potential application in this field, and outline promising research directions for developing next-generation surface treatments that satisfy both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Market Analysis for Decorative Galvanized Steel Applications
The global market for decorative galvanized steel applications has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand in construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors. The aesthetic enhancement of galvanized steel represents a high-value segment within the broader steel coating market, which was valued at approximately $18.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $25.7 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%.
Architectural applications constitute the largest market segment for decorative galvanized steel, accounting for nearly 40% of total demand. This includes façade panels, roofing materials, decorative screens, and interior design elements. The construction industry's shift toward sustainable yet visually appealing materials has created substantial opportunities for enhanced galvanized steel finishes that combine corrosion resistance with aesthetic appeal.
The automotive industry represents the second-largest market segment, with increasing utilization of decoratively treated galvanized steel in both exterior and interior components. Luxury vehicle manufacturers particularly value specialized finishes that offer distinctive visual characteristics while maintaining the durability advantages of galvanized protection.
Consumer goods and home appliance manufacturers have also embraced aesthetically enhanced galvanized steel, particularly for premium product lines where visual differentiation drives consumer purchasing decisions. This segment has shown the fastest growth rate at 7.2% annually, reflecting consumers' willingness to pay premium prices for visually distinctive products.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for decorative galvanized steel applications, collectively accounting for approximately 58% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is experiencing the most rapid growth, with annual market expansion exceeding 9% as urbanization and rising disposable incomes drive demand for aesthetically sophisticated building materials and consumer products.
Market research indicates that customers are increasingly willing to pay a premium of 15-30% for galvanized steel products with enhanced aesthetic finishes compared to standard galvanized options. This price premium represents significant value-creation potential for manufacturers who can develop cost-effective treatment processes that deliver superior visual characteristics.
Industry analysts project that the market for decoratively treated galvanized steel will continue to expand at rates exceeding those of the broader steel market, driven by architectural trends favoring exposed metal finishes, automotive design evolution, and consumer preference for distinctive visual textures in everyday products. Companies that develop proprietary treatment technologies delivering unique aesthetic properties while maintaining or enhancing corrosion protection stand to capture significant market share in this growing segment.
Architectural applications constitute the largest market segment for decorative galvanized steel, accounting for nearly 40% of total demand. This includes façade panels, roofing materials, decorative screens, and interior design elements. The construction industry's shift toward sustainable yet visually appealing materials has created substantial opportunities for enhanced galvanized steel finishes that combine corrosion resistance with aesthetic appeal.
The automotive industry represents the second-largest market segment, with increasing utilization of decoratively treated galvanized steel in both exterior and interior components. Luxury vehicle manufacturers particularly value specialized finishes that offer distinctive visual characteristics while maintaining the durability advantages of galvanized protection.
Consumer goods and home appliance manufacturers have also embraced aesthetically enhanced galvanized steel, particularly for premium product lines where visual differentiation drives consumer purchasing decisions. This segment has shown the fastest growth rate at 7.2% annually, reflecting consumers' willingness to pay premium prices for visually distinctive products.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for decorative galvanized steel applications, collectively accounting for approximately 58% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is experiencing the most rapid growth, with annual market expansion exceeding 9% as urbanization and rising disposable incomes drive demand for aesthetically sophisticated building materials and consumer products.
Market research indicates that customers are increasingly willing to pay a premium of 15-30% for galvanized steel products with enhanced aesthetic finishes compared to standard galvanized options. This price premium represents significant value-creation potential for manufacturers who can develop cost-effective treatment processes that deliver superior visual characteristics.
Industry analysts project that the market for decoratively treated galvanized steel will continue to expand at rates exceeding those of the broader steel market, driven by architectural trends favoring exposed metal finishes, automotive design evolution, and consumer preference for distinctive visual textures in everyday products. Companies that develop proprietary treatment technologies delivering unique aesthetic properties while maintaining or enhancing corrosion protection stand to capture significant market share in this growing segment.
Current Challenges in Galvanized Steel Aesthetic Finishing
Despite the numerous advantages of galvanized steel, achieving high-quality aesthetic finishes remains a significant challenge for manufacturers across various industries. The primary obstacle stems from the inherent surface characteristics of zinc coatings, which often exhibit spangle patterns, surface irregularities, and non-uniform appearance. These visual inconsistencies become particularly problematic in architectural applications, automotive components, and consumer products where aesthetic appeal directly impacts market acceptance.
Surface preparation issues constitute a major challenge in the finishing process. The zinc coating's reactive nature leads to rapid oxidation upon exposure to air, forming zinc oxide and zinc hydroxide layers that can compromise paint adhesion. Additionally, residual processing oils, fingerprints, and contaminants from the galvanizing process frequently interfere with coating adhesion, necessitating thorough cleaning protocols that add complexity and cost to production processes.
Compatibility between finishing systems and galvanized substrates presents another significant hurdle. Conventional solvent-based paints often react adversely with zinc surfaces, causing peeling, blistering, or delamination over time. This chemical incompatibility has forced manufacturers to develop specialized coating systems specifically formulated for galvanized surfaces, increasing production costs and limiting color and texture options.
Environmental regulations have further complicated finishing processes, as traditional surface preparation methods involving chromate conversion coatings face increasing restrictions due to their environmental impact. The industry continues to struggle with finding equally effective yet environmentally compliant alternatives that provide comparable corrosion resistance and adhesion promotion properties.
Durability concerns persist even when aesthetic finishes are successfully applied. The differential thermal expansion between zinc coatings and applied finishes can lead to cracking and adhesion failure during temperature fluctuations. Additionally, moisture penetration through microscopic pores in the finish can initiate underfilm corrosion, causing unsightly bubbling and eventual coating failure.
Quality consistency across large production volumes remains elusive, particularly for complex geometries where uniform coating application becomes technically challenging. Edges, corners, and recessed areas often receive inadequate coverage, creating weak points in both aesthetic appearance and corrosion protection. This inconsistency is especially problematic for architectural panels and automotive components where visual uniformity is paramount.
The cost-effectiveness of enhanced finishing processes presents a final significant challenge. While premium finishing techniques can achieve superior aesthetics, their implementation often involves substantial capital investment in specialized equipment, increased processing time, and higher material costs. Manufacturers must carefully balance these additional expenses against market demands and competitive pricing pressures.
Surface preparation issues constitute a major challenge in the finishing process. The zinc coating's reactive nature leads to rapid oxidation upon exposure to air, forming zinc oxide and zinc hydroxide layers that can compromise paint adhesion. Additionally, residual processing oils, fingerprints, and contaminants from the galvanizing process frequently interfere with coating adhesion, necessitating thorough cleaning protocols that add complexity and cost to production processes.
Compatibility between finishing systems and galvanized substrates presents another significant hurdle. Conventional solvent-based paints often react adversely with zinc surfaces, causing peeling, blistering, or delamination over time. This chemical incompatibility has forced manufacturers to develop specialized coating systems specifically formulated for galvanized surfaces, increasing production costs and limiting color and texture options.
Environmental regulations have further complicated finishing processes, as traditional surface preparation methods involving chromate conversion coatings face increasing restrictions due to their environmental impact. The industry continues to struggle with finding equally effective yet environmentally compliant alternatives that provide comparable corrosion resistance and adhesion promotion properties.
Durability concerns persist even when aesthetic finishes are successfully applied. The differential thermal expansion between zinc coatings and applied finishes can lead to cracking and adhesion failure during temperature fluctuations. Additionally, moisture penetration through microscopic pores in the finish can initiate underfilm corrosion, causing unsightly bubbling and eventual coating failure.
Quality consistency across large production volumes remains elusive, particularly for complex geometries where uniform coating application becomes technically challenging. Edges, corners, and recessed areas often receive inadequate coverage, creating weak points in both aesthetic appearance and corrosion protection. This inconsistency is especially problematic for architectural panels and automotive components where visual uniformity is paramount.
The cost-effectiveness of enhanced finishing processes presents a final significant challenge. While premium finishing techniques can achieve superior aesthetics, their implementation often involves substantial capital investment in specialized equipment, increased processing time, and higher material costs. Manufacturers must carefully balance these additional expenses against market demands and competitive pricing pressures.
Contemporary Surface Treatment Solutions for Galvanized Steel
01 Surface treatment methods for enhanced aesthetics
Various surface treatment methods can be applied to galvanized steel to enhance its aesthetic appearance. These include chemical treatments, mechanical finishing processes, and application of specialized coatings that preserve the corrosion resistance while improving visual appeal. These treatments can create different textures, colors, and finishes that make galvanized steel suitable for architectural and decorative applications.- Surface treatment methods for aesthetic galvanized finishes: Various surface treatment methods can be applied to galvanized steel to enhance its aesthetic appearance. These include chemical treatments, mechanical finishing, and coating applications that modify the surface characteristics while maintaining corrosion protection. These treatments can create different textures, colors, and visual effects on the galvanized surface, making it more suitable for architectural and decorative applications.
- Colored and patterned galvanized coatings: Techniques for creating colored and patterned finishes on galvanized steel involve the application of pigments, dyes, or chemical treatments that react with the zinc coating. These methods can produce a wide range of colors and visual patterns while maintaining the corrosion resistance properties of the galvanized layer. The coloring can be achieved through direct application or through controlled oxidation processes that create stable aesthetic finishes.
- Advanced coating systems for decorative galvanized steel: Multi-layer coating systems can be applied to galvanized steel to achieve superior aesthetic finishes. These systems typically include primers, intermediate layers, and topcoats that provide both decorative appearance and enhanced protection. The coatings can incorporate special additives for texture, gloss control, and visual effects, making the galvanized steel suitable for premium architectural applications and consumer products.
- Environmentally friendly finishing processes for galvanized steel: Sustainable and environmentally friendly processes for finishing galvanized steel have been developed to reduce environmental impact while achieving attractive appearances. These include water-based coatings, VOC-free treatments, and processes that eliminate hazardous chemicals. These methods provide aesthetic finishes that comply with modern environmental regulations while maintaining the desired visual characteristics and performance properties.
- Weathering and aging effects for natural aesthetic finishes: Controlled weathering and aging processes can be applied to galvanized steel to create natural-looking aesthetic finishes. These techniques accelerate or direct the natural patination of zinc to achieve specific visual effects. The resulting finishes can range from matte gray to textured patinas that evolve over time, providing a living finish that changes with environmental exposure while maintaining protective properties.
02 Decorative coating systems for galvanized steel
Specialized coating systems can be applied to galvanized steel to achieve decorative finishes while maintaining corrosion protection. These coating systems may include primers, intermediate layers, and topcoats that provide both functional and aesthetic benefits. The coatings can be formulated to create various appearances such as metallic, matte, glossy, or textured finishes, expanding the design possibilities for galvanized steel products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Color treatment processes for galvanized steel
Color treatment processes allow galvanized steel to be finished in a wide range of colors while maintaining its protective zinc coating. These processes include chemical coloring, pigmented sealers, and specialized painting systems designed specifically for galvanized surfaces. The coloring techniques can produce consistent, durable finishes that resist fading and weathering while providing the desired aesthetic appearance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Texture and pattern creation techniques
Various techniques can be employed to create textures and patterns on galvanized steel surfaces, enhancing their visual appeal. These include embossing, etching, laser treatment, and specialized rolling processes that impart distinctive surface characteristics. The textured finishes can mimic natural materials, create geometric patterns, or provide unique tactile qualities while maintaining the corrosion resistance of the galvanized coating.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmentally friendly finishing methods
Environmentally friendly methods for finishing galvanized steel have been developed to reduce environmental impact while achieving attractive appearances. These include water-based coating systems, VOC-free treatments, and sustainable processing techniques that minimize waste and harmful emissions. These eco-friendly approaches provide aesthetically pleasing finishes while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in Decorative Metal Finishing
The galvanized steel aesthetic finishing market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for visually appealing protective coatings across construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors. The global market size is estimated to exceed $25 billion, driven by urbanization and infrastructure development. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of technical maturity: Henkel AG and Nippon Paint Surf Chemicals focus on advanced chemical treatments; JFE Steel, Nippon Steel, and Tata Steel emphasize integrated production solutions; while Nihon Parkerizing specializes in surface treatment chemicals with proprietary formulations. European companies like voestalpine Stahl and HUECK Engraving are pioneering decorative finishes, while Asian manufacturers including Baoshan Iron & Steel and JSW Steel are rapidly advancing their capabilities through university collaborations and R&D investments.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed advanced pretreatment solutions specifically for galvanized steel surfaces that enhance aesthetic finish while maintaining corrosion protection. Their Bonderite thin-film technology creates nanoscale conversion coatings that promote paint adhesion and improve surface appearance. This process involves a multi-stage treatment including cleaning, activation, phosphating or zirconium-based conversion coating, and final sealing. Henkel's system is particularly effective at creating uniform surfaces on hot-dip galvanized steel, eliminating the typical spangle pattern and surface irregularities. Their eco-friendly formulations reduce heavy metals and phosphates while maintaining performance standards. The company has also developed specialized post-treatments that enhance the metallic luster of galvanized surfaces without requiring painting, creating decorative finishes with controlled reflectivity and texture.
Strengths: Environmentally compliant formulations with reduced phosphates and heavy metals; excellent paint adhesion promotion; compatible with various coating systems. Weaknesses: Some solutions require multi-step application processes; may require specialized equipment for optimal results; premium pricing compared to conventional treatments.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL has pioneered advanced galvannealed steel treatment technologies that significantly enhance aesthetic finish while maintaining structural integrity. Their proprietary ZAM® coating system combines zinc, aluminum, and magnesium to create surfaces with superior corrosion resistance and exceptional appearance. The company employs precise temperature control during the galvanizing process to create ultra-smooth surfaces with minimal spangle patterns. Their post-galvanizing treatment includes specialized chromium-free passivation systems that enhance surface uniformity and provide an ideal substrate for painting or decorative finishes. NIPPON STEEL has also developed innovative surface texturing techniques that can create customized appearances ranging from matte to high-gloss finishes on galvanized steel. Their VIEWKOTE® technology specifically addresses aesthetic requirements by controlling zinc crystal formation during solidification, resulting in visually appealing surfaces suitable for exposed architectural applications.
Strengths: Superior corrosion resistance combined with excellent aesthetic properties; innovative alloy compositions that enhance appearance; extensive experience in architectural applications. Weaknesses: Premium pricing compared to standard galvanized products; some specialized treatments require specific handling and processing parameters; limited availability in certain global markets.
Key Patents and Innovations in Aesthetic Metal Finishing
Galvanized steel with brushed gloss finish and process to form the steel.
PatentPendingMXNL05000081A
Innovation
- Development of a brushed galvanic coating with uniform appearance and not-remarked Zinc Micro crystals, creating an enhanced aesthetic finish on galvanized steel.
- A multi-step process that includes developing Zinc Micro crystals, hardening with gloss finish, brushing without damaging crystal edges, and applying clear organic coating to achieve superior aesthetic results.
- Combination of functional galvanic protection with decorative brushed finish, bridging industrial durability with aesthetic appeal for architectural and consumer applications.
Galvanized steel sheet having surface treatment film and method for manufacturing the same
PatentActiveJP2022158349A
Innovation
- A surface treatment film comprising an elastomer component with butadiene rubber particles, a silicon compound, a phosphorus compound, a vanadium compound, and a titanium compound, along with a wax component, is applied to the zinc-based plated steel sheet, ensuring specific area ratios and dispersion to enhance corrosion resistance, lubricity, and conductivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The treatment of galvanized steel for enhanced aesthetic finishes carries significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered in modern manufacturing processes. Traditional surface treatment methods often involve chemicals that can be harmful to ecosystems when improperly managed. VOC emissions from solvent-based coatings and chromium-containing pretreatments represent particular concerns, with regulatory frameworks increasingly restricting their use across global markets.
Recent advancements have focused on developing more environmentally responsible alternatives. Water-based coating systems have emerged as viable substitutes for solvent-based options, reducing VOC emissions by up to 80% while maintaining comparable aesthetic and protective qualities. Similarly, chromium-free pretreatment technologies utilizing silane-based or phosphate-free formulations have demonstrated promising results in both performance and environmental safety profiles.
Energy consumption represents another critical sustainability factor in galvanized steel finishing. Conventional heat-curing processes for coatings can consume substantial energy resources, contributing to carbon emissions. UV-curable and ambient-temperature curing systems offer significant energy savings, with some manufacturers reporting reductions of 30-45% in energy usage compared to traditional thermal curing methods.
Waste management practices have also evolved considerably. Closed-loop water systems that recycle process water can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 90% in finishing operations. Advanced filtration technologies enable the recovery of valuable metals from treatment baths, minimizing waste generation while recapturing resources that would otherwise be lost.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that environmentally optimized galvanized steel finishing processes can reduce the overall carbon footprint by 15-25% compared to conventional methods. This improvement becomes particularly significant when considering the extended service life that quality finishes provide to galvanized steel products, effectively amortizing environmental impacts over longer periods.
Consumer and regulatory pressures continue to drive innovation in this space. Certification systems such as LEED, BREEAM, and various eco-labels increasingly recognize and reward products manufactured with environmentally responsible finishing processes. Forward-thinking manufacturers are leveraging these sustainability credentials as competitive advantages in markets where environmental considerations influence purchasing decisions.
Recent advancements have focused on developing more environmentally responsible alternatives. Water-based coating systems have emerged as viable substitutes for solvent-based options, reducing VOC emissions by up to 80% while maintaining comparable aesthetic and protective qualities. Similarly, chromium-free pretreatment technologies utilizing silane-based or phosphate-free formulations have demonstrated promising results in both performance and environmental safety profiles.
Energy consumption represents another critical sustainability factor in galvanized steel finishing. Conventional heat-curing processes for coatings can consume substantial energy resources, contributing to carbon emissions. UV-curable and ambient-temperature curing systems offer significant energy savings, with some manufacturers reporting reductions of 30-45% in energy usage compared to traditional thermal curing methods.
Waste management practices have also evolved considerably. Closed-loop water systems that recycle process water can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 90% in finishing operations. Advanced filtration technologies enable the recovery of valuable metals from treatment baths, minimizing waste generation while recapturing resources that would otherwise be lost.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that environmentally optimized galvanized steel finishing processes can reduce the overall carbon footprint by 15-25% compared to conventional methods. This improvement becomes particularly significant when considering the extended service life that quality finishes provide to galvanized steel products, effectively amortizing environmental impacts over longer periods.
Consumer and regulatory pressures continue to drive innovation in this space. Certification systems such as LEED, BREEAM, and various eco-labels increasingly recognize and reward products manufactured with environmentally responsible finishing processes. Forward-thinking manufacturers are leveraging these sustainability credentials as competitive advantages in markets where environmental considerations influence purchasing decisions.
Quality Control and Testing Methodologies for Finished Surfaces
Quality control and testing methodologies are critical components in ensuring that galvanized steel surfaces meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. Systematic inspection protocols must be established at various stages of the treatment process to maintain consistency and identify defects early.
Visual inspection remains the first line of quality assessment, where trained personnel evaluate the surface for uniformity, color consistency, and absence of visible defects such as orange peel, runs, or sags. This inspection should be conducted under standardized lighting conditions that simulate the final installation environment to accurately assess aesthetic qualities.
Instrumental analysis provides quantitative measurements that complement visual assessments. Gloss meters measure surface reflectivity at standardized angles (typically 20°, 60°, and 85°), providing objective data on the finish's appearance. Color spectrophotometers ensure color consistency across batches using CIE L*a*b* color space measurements, with acceptable delta E values typically below 1.0 for premium aesthetic applications.
Adhesion testing is paramount for ensuring the durability of aesthetic finishes. Cross-hatch testing (ASTM D3359) and pull-off adhesion testing (ASTM D4541) provide quantitative measures of coating adhesion strength. For galvanized steel specifically, the coating should achieve a minimum adhesion rating of 4B or higher on the ASTM scale to ensure long-term aesthetic performance.
Corrosion resistance testing, including salt spray testing (ASTM B117) and cyclic corrosion testing, evaluates the protective qualities of the finish. Premium aesthetic finishes should withstand a minimum of 1,000 hours in salt spray conditions without significant deterioration or red rust formation.
Chemical resistance testing using standardized solutions that simulate cleaning agents and environmental contaminants helps predict the finish's ability to maintain its appearance over time. Exposure periods typically range from 24 to 72 hours, with post-exposure evaluation of gloss retention, color stability, and surface integrity.
Accelerated weathering tests using QUV or xenon arc chambers (ASTM G154 or ASTM G155) simulate years of outdoor exposure in weeks or months. These tests evaluate UV resistance, color stability, and gloss retention, with premium finishes expected to maintain at least 80% of original gloss after 2,000 hours of exposure.
Documentation and traceability systems must be implemented to track each batch of treated galvanized steel, recording process parameters, test results, and any corrective actions taken. This information provides valuable feedback for continuous process improvement and serves as reference data for troubleshooting aesthetic inconsistencies that may arise in future production runs.
Visual inspection remains the first line of quality assessment, where trained personnel evaluate the surface for uniformity, color consistency, and absence of visible defects such as orange peel, runs, or sags. This inspection should be conducted under standardized lighting conditions that simulate the final installation environment to accurately assess aesthetic qualities.
Instrumental analysis provides quantitative measurements that complement visual assessments. Gloss meters measure surface reflectivity at standardized angles (typically 20°, 60°, and 85°), providing objective data on the finish's appearance. Color spectrophotometers ensure color consistency across batches using CIE L*a*b* color space measurements, with acceptable delta E values typically below 1.0 for premium aesthetic applications.
Adhesion testing is paramount for ensuring the durability of aesthetic finishes. Cross-hatch testing (ASTM D3359) and pull-off adhesion testing (ASTM D4541) provide quantitative measures of coating adhesion strength. For galvanized steel specifically, the coating should achieve a minimum adhesion rating of 4B or higher on the ASTM scale to ensure long-term aesthetic performance.
Corrosion resistance testing, including salt spray testing (ASTM B117) and cyclic corrosion testing, evaluates the protective qualities of the finish. Premium aesthetic finishes should withstand a minimum of 1,000 hours in salt spray conditions without significant deterioration or red rust formation.
Chemical resistance testing using standardized solutions that simulate cleaning agents and environmental contaminants helps predict the finish's ability to maintain its appearance over time. Exposure periods typically range from 24 to 72 hours, with post-exposure evaluation of gloss retention, color stability, and surface integrity.
Accelerated weathering tests using QUV or xenon arc chambers (ASTM G154 or ASTM G155) simulate years of outdoor exposure in weeks or months. These tests evaluate UV resistance, color stability, and gloss retention, with premium finishes expected to maintain at least 80% of original gloss after 2,000 hours of exposure.
Documentation and traceability systems must be implemented to track each batch of treated galvanized steel, recording process parameters, test results, and any corrective actions taken. This information provides valuable feedback for continuous process improvement and serves as reference data for troubleshooting aesthetic inconsistencies that may arise in future production runs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!