How Vacuum Pumps Facilitate Advanced Hydrocarbon Processing
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Vacuum Pump Evolution
The evolution of vacuum pumps in the context of advanced hydrocarbon processing has been marked by significant technological advancements and innovations. Initially, simple mechanical pumps were used to create low-pressure environments for basic distillation processes. These early pumps, while effective for their time, had limitations in terms of achievable vacuum levels and efficiency.
As the petrochemical industry expanded and demanded more sophisticated processing techniques, vacuum pump technology underwent rapid development. The introduction of rotary vane pumps in the mid-20th century marked a significant milestone. These pumps offered improved vacuum levels and reliability, enabling more efficient separation of hydrocarbon fractions.
The 1960s and 1970s saw the emergence of liquid ring vacuum pumps, which became widely adopted in the hydrocarbon processing industry. These pumps excelled in handling condensable vapors and were particularly suited for applications involving high vapor loads, such as in vacuum distillation units.
The late 20th century witnessed the advent of dry screw vacuum pumps, which revolutionized the field by eliminating the need for sealing fluids. This innovation not only improved pump efficiency but also reduced contamination risks in sensitive processes. Dry screw pumps quickly became the preferred choice for many advanced hydrocarbon processing applications due to their ability to handle corrosive gases and maintain high vacuum levels.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Modern vacuum pumps incorporate advanced materials and designs to minimize power consumption while maximizing performance. Variable speed drives and intelligent control systems have been integrated to optimize pump operation based on process demands.
The latest generation of vacuum pumps for hydrocarbon processing includes hybrid systems that combine different pump technologies to achieve optimal performance across a wide range of operating conditions. These systems often integrate dry screw pumps with booster pumps or ejector stages to handle high gas loads efficiently.
Advancements in sealing technology have also played a crucial role in vacuum pump evolution. The development of magnetic couplings and advanced shaft seals has significantly improved pump reliability and reduced the risk of hydrocarbon leaks, addressing both safety and environmental concerns.
As the hydrocarbon processing industry continues to evolve, vacuum pump technology is expected to advance further. Current research focuses on developing pumps with even higher efficiency, improved corrosion resistance, and enhanced capabilities for handling complex gas mixtures. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT sensors and predictive maintenance algorithms, is also shaping the future of vacuum pumps in advanced hydrocarbon processing.
As the petrochemical industry expanded and demanded more sophisticated processing techniques, vacuum pump technology underwent rapid development. The introduction of rotary vane pumps in the mid-20th century marked a significant milestone. These pumps offered improved vacuum levels and reliability, enabling more efficient separation of hydrocarbon fractions.
The 1960s and 1970s saw the emergence of liquid ring vacuum pumps, which became widely adopted in the hydrocarbon processing industry. These pumps excelled in handling condensable vapors and were particularly suited for applications involving high vapor loads, such as in vacuum distillation units.
The late 20th century witnessed the advent of dry screw vacuum pumps, which revolutionized the field by eliminating the need for sealing fluids. This innovation not only improved pump efficiency but also reduced contamination risks in sensitive processes. Dry screw pumps quickly became the preferred choice for many advanced hydrocarbon processing applications due to their ability to handle corrosive gases and maintain high vacuum levels.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Modern vacuum pumps incorporate advanced materials and designs to minimize power consumption while maximizing performance. Variable speed drives and intelligent control systems have been integrated to optimize pump operation based on process demands.
The latest generation of vacuum pumps for hydrocarbon processing includes hybrid systems that combine different pump technologies to achieve optimal performance across a wide range of operating conditions. These systems often integrate dry screw pumps with booster pumps or ejector stages to handle high gas loads efficiently.
Advancements in sealing technology have also played a crucial role in vacuum pump evolution. The development of magnetic couplings and advanced shaft seals has significantly improved pump reliability and reduced the risk of hydrocarbon leaks, addressing both safety and environmental concerns.
As the hydrocarbon processing industry continues to evolve, vacuum pump technology is expected to advance further. Current research focuses on developing pumps with even higher efficiency, improved corrosion resistance, and enhanced capabilities for handling complex gas mixtures. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT sensors and predictive maintenance algorithms, is also shaping the future of vacuum pumps in advanced hydrocarbon processing.
Hydrocarbon Market Needs
The hydrocarbon processing industry is experiencing a significant shift driven by increasing global energy demands, environmental regulations, and the need for more efficient production methods. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in meeting these market needs by enabling advanced processing techniques that improve product quality, increase yield, and reduce environmental impact.
The global demand for refined petroleum products continues to grow, with projections indicating a steady increase in consumption over the next decade. This growth is particularly pronounced in emerging economies, where rapid industrialization and urbanization are fueling the need for transportation fuels, petrochemicals, and other hydrocarbon-based products. To meet this demand, refineries and petrochemical plants are under pressure to maximize their production capacity and efficiency.
Environmental concerns have also become a major driver in the hydrocarbon processing market. Stringent regulations on emissions and product specifications require refineries to produce cleaner fuels with lower sulfur content and reduced aromatic compounds. This has led to a growing demand for advanced desulfurization and hydrotreatment processes, where vacuum pumps play a critical role in maintaining the low-pressure environments necessary for these reactions.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards the processing of heavier crude oils and unconventional feedstocks, such as oil sands and shale oil. These feedstocks often require more intensive processing and specialized techniques to convert them into valuable products. Vacuum distillation units, which rely heavily on vacuum pumps, are essential for processing these challenging feedstocks and extracting maximum value from each barrel of oil.
Energy efficiency has become a key focus for hydrocarbon processors as they seek to reduce operating costs and minimize their carbon footprint. Vacuum pumps contribute significantly to this goal by enabling lower-temperature operations, which reduce energy consumption and extend the life of processing equipment. The market is increasingly demanding more efficient and reliable vacuum pump technologies that can maintain stable low-pressure environments while consuming less power.
The petrochemical sector, a major segment of the hydrocarbon processing industry, is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing demand for plastics, synthetic fibers, and other chemical products. Vacuum pumps are essential in many petrochemical processes, including polymerization reactions and the production of high-purity chemicals. The market needs vacuum systems that can handle corrosive gases and maintain ultra-high vacuum levels for these specialized applications.
As the hydrocarbon processing industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on process intensification and modular plant designs. These approaches aim to increase productivity while reducing the physical footprint of processing facilities. Vacuum pumps that are compact, easy to integrate, and capable of handling multiple process streams are in high demand to support these new plant designs and retrofitting projects.
The global demand for refined petroleum products continues to grow, with projections indicating a steady increase in consumption over the next decade. This growth is particularly pronounced in emerging economies, where rapid industrialization and urbanization are fueling the need for transportation fuels, petrochemicals, and other hydrocarbon-based products. To meet this demand, refineries and petrochemical plants are under pressure to maximize their production capacity and efficiency.
Environmental concerns have also become a major driver in the hydrocarbon processing market. Stringent regulations on emissions and product specifications require refineries to produce cleaner fuels with lower sulfur content and reduced aromatic compounds. This has led to a growing demand for advanced desulfurization and hydrotreatment processes, where vacuum pumps play a critical role in maintaining the low-pressure environments necessary for these reactions.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards the processing of heavier crude oils and unconventional feedstocks, such as oil sands and shale oil. These feedstocks often require more intensive processing and specialized techniques to convert them into valuable products. Vacuum distillation units, which rely heavily on vacuum pumps, are essential for processing these challenging feedstocks and extracting maximum value from each barrel of oil.
Energy efficiency has become a key focus for hydrocarbon processors as they seek to reduce operating costs and minimize their carbon footprint. Vacuum pumps contribute significantly to this goal by enabling lower-temperature operations, which reduce energy consumption and extend the life of processing equipment. The market is increasingly demanding more efficient and reliable vacuum pump technologies that can maintain stable low-pressure environments while consuming less power.
The petrochemical sector, a major segment of the hydrocarbon processing industry, is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing demand for plastics, synthetic fibers, and other chemical products. Vacuum pumps are essential in many petrochemical processes, including polymerization reactions and the production of high-purity chemicals. The market needs vacuum systems that can handle corrosive gases and maintain ultra-high vacuum levels for these specialized applications.
As the hydrocarbon processing industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on process intensification and modular plant designs. These approaches aim to increase productivity while reducing the physical footprint of processing facilities. Vacuum pumps that are compact, easy to integrate, and capable of handling multiple process streams are in high demand to support these new plant designs and retrofitting projects.
Vacuum Tech Challenges
Vacuum technology plays a crucial role in advanced hydrocarbon processing, yet it faces several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the maintenance of high vacuum levels in large-scale industrial processes. As hydrocarbons are processed, various contaminants and byproducts can accumulate within the vacuum system, potentially compromising its efficiency and effectiveness. This necessitates the development of robust filtration and purification systems that can operate under extreme conditions without impeding the vacuum pumps' performance.
Another major challenge lies in the energy efficiency of vacuum pumps used in hydrocarbon processing. These pumps often consume substantial amounts of power, particularly when maintaining high vacuum levels over extended periods. The industry is constantly seeking ways to improve the energy efficiency of these systems without sacrificing their performance or reliability. This challenge is further compounded by the need to scale up operations to meet growing demand, which can lead to exponential increases in energy consumption if not addressed effectively.
Corrosion and wear present ongoing challenges in vacuum technology for hydrocarbon processing. The aggressive nature of many hydrocarbons and their byproducts can cause significant damage to pump components over time. This necessitates the use of specialized materials and coatings that can withstand these harsh environments while maintaining their structural integrity and performance characteristics. However, the development and implementation of such materials often come with increased costs and complexity in manufacturing and maintenance processes.
The control and monitoring of vacuum systems in hydrocarbon processing environments pose another set of challenges. Precise regulation of pressure levels is critical for optimal process efficiency and product quality. However, achieving this level of control in large-scale industrial settings can be complex, requiring sophisticated sensors, actuators, and control algorithms. The integration of these systems with existing process control infrastructure presents both technical and operational challenges that must be overcome to ensure seamless operation.
Environmental concerns also factor into the challenges faced by vacuum technology in hydrocarbon processing. The potential for emissions and leaks from vacuum systems must be carefully managed to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This requires the development of advanced sealing technologies and leak detection systems, as well as the implementation of comprehensive maintenance and monitoring protocols to minimize environmental impact.
Lastly, the adaptation of vacuum technology to emerging hydrocarbon processing techniques presents ongoing challenges. As new methods for refining and processing hydrocarbons are developed, vacuum systems must evolve to meet these changing requirements. This often involves redesigning pump configurations, optimizing flow dynamics, and developing new materials and coatings to handle novel process conditions. The rapid pace of innovation in the hydrocarbon processing industry demands continuous research and development efforts in vacuum technology to keep pace with these advancements.
Another major challenge lies in the energy efficiency of vacuum pumps used in hydrocarbon processing. These pumps often consume substantial amounts of power, particularly when maintaining high vacuum levels over extended periods. The industry is constantly seeking ways to improve the energy efficiency of these systems without sacrificing their performance or reliability. This challenge is further compounded by the need to scale up operations to meet growing demand, which can lead to exponential increases in energy consumption if not addressed effectively.
Corrosion and wear present ongoing challenges in vacuum technology for hydrocarbon processing. The aggressive nature of many hydrocarbons and their byproducts can cause significant damage to pump components over time. This necessitates the use of specialized materials and coatings that can withstand these harsh environments while maintaining their structural integrity and performance characteristics. However, the development and implementation of such materials often come with increased costs and complexity in manufacturing and maintenance processes.
The control and monitoring of vacuum systems in hydrocarbon processing environments pose another set of challenges. Precise regulation of pressure levels is critical for optimal process efficiency and product quality. However, achieving this level of control in large-scale industrial settings can be complex, requiring sophisticated sensors, actuators, and control algorithms. The integration of these systems with existing process control infrastructure presents both technical and operational challenges that must be overcome to ensure seamless operation.
Environmental concerns also factor into the challenges faced by vacuum technology in hydrocarbon processing. The potential for emissions and leaks from vacuum systems must be carefully managed to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This requires the development of advanced sealing technologies and leak detection systems, as well as the implementation of comprehensive maintenance and monitoring protocols to minimize environmental impact.
Lastly, the adaptation of vacuum technology to emerging hydrocarbon processing techniques presents ongoing challenges. As new methods for refining and processing hydrocarbons are developed, vacuum systems must evolve to meet these changing requirements. This often involves redesigning pump configurations, optimizing flow dynamics, and developing new materials and coatings to handle novel process conditions. The rapid pace of innovation in the hydrocarbon processing industry demands continuous research and development efforts in vacuum technology to keep pace with these advancements.
Current Vacuum Solutions
01 Improvements in vacuum pump design
Various advancements in vacuum pump design have been made to enhance efficiency and performance. These improvements include modifications to pump components, optimized fluid flow paths, and innovative sealing mechanisms. Such enhancements contribute to increased pumping capacity, reduced power consumption, and improved reliability in vacuum systems.- Improvements in vacuum pump design: Various advancements in vacuum pump design have been made to enhance efficiency and performance. These improvements include modifications to pump components, optimized fluid flow paths, and innovative sealing mechanisms. Such enhancements contribute to increased pumping capacity, reduced energy consumption, and improved reliability in vacuum systems.
- Vacuum pumps for semiconductor manufacturing: Specialized vacuum pumps have been developed for use in semiconductor manufacturing processes. These pumps are designed to handle specific gases and maintain ultra-high vacuum levels required for various fabrication steps. Features may include corrosion-resistant materials, contamination control mechanisms, and precise pressure regulation capabilities.
- Multi-stage vacuum pump systems: Multi-stage vacuum pump systems have been developed to achieve higher vacuum levels and improved pumping efficiency. These systems typically combine different types of pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, diffusion pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, in series or parallel configurations. This approach allows for a wider operating range and better overall system performance.
- Vacuum pumps for automotive applications: Vacuum pumps have been adapted for use in automotive systems, particularly for brake boosters and other pneumatic components. These pumps are designed to be compact, durable, and efficient, often integrating with existing engine systems. Innovations in this area focus on reducing noise, improving fuel efficiency, and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
- Historical developments in vacuum pump technology: The evolution of vacuum pump technology spans several decades, with numerous innovations and improvements. Early designs focused on mechanical pumps, while later developments introduced new principles such as diffusion pumps and cryogenic pumps. These historical advancements have laid the foundation for modern vacuum pump technology and continue to influence current designs.
02 Specialized vacuum pumps for semiconductor manufacturing
Vacuum pumps tailored for semiconductor manufacturing processes have been developed to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. These pumps are designed to handle corrosive gases, maintain high vacuum levels, and operate with minimal contamination. Features may include corrosion-resistant materials, advanced filtration systems, and precise control mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of vacuum pumps in automotive systems
Vacuum pumps have been incorporated into various automotive systems to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. Applications include brake boosters, engine management systems, and emissions control devices. These integrated vacuum pump solutions are designed to be compact, energy-efficient, and compatible with modern vehicle architectures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advancements in oil-free vacuum pump technology
Oil-free vacuum pump designs have been developed to address the need for clean, contamination-free vacuum environments. These pumps utilize alternative technologies such as scroll mechanisms, diaphragm systems, or magnetic levitation to eliminate the need for oil lubrication. Benefits include reduced maintenance, improved vacuum quality, and suitability for sensitive applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Vacuum pump control and monitoring systems
Advanced control and monitoring systems have been implemented to optimize vacuum pump performance and efficiency. These systems may include sensors for real-time monitoring of pump parameters, intelligent control algorithms for adaptive operation, and remote monitoring capabilities. Such features enable predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and improved process control in vacuum applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The vacuum pump industry for advanced hydrocarbon processing is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to be in the billions of dollars. The technology has reached a high level of sophistication, with key players like Pfeiffer Vacuum GmbH, Edwards Ltd., and Tokyo Electron Ltd. leading innovation. These companies are focusing on developing more efficient and specialized vacuum pumps for the petrochemical sector. The competitive landscape is characterized by established firms with strong R&D capabilities, such as Canon Anelva Corp. and Oerlikon Leybold Vacuum, continuously improving pump performance and reliability. Emerging players like LOT VACUUM Co., Ltd. are also making strides in the market, particularly in Asia, where demand for advanced hydrocarbon processing equipment is growing rapidly.
Pfeiffer Vacuum GmbH
Technical Solution: Pfeiffer Vacuum specializes in advanced vacuum solutions for hydrocarbon processing. Their HiPace turbopumps utilize innovative five-axis magnetic bearing technology, enabling oil-free operation and reducing maintenance needs in petrochemical applications[1]. The company's multi-stage Roots pumps offer high pumping speeds and ultimate pressures, crucial for efficient hydrocarbon distillation and separation processes[2]. Pfeiffer's vacuum systems incorporate smart sensors and IoT connectivity, allowing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which significantly enhances the reliability and uptime of hydrocarbon processing equipment[3].
Strengths: High-performance, oil-free pumps; advanced monitoring capabilities; wide range of specialized solutions. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment compared to conventional pumps; may require specialized training for operation and maintenance.
Edwards Ltd.
Technical Solution: Edwards Ltd. has developed cutting-edge vacuum technologies tailored for hydrocarbon processing. Their GXS dry screw vacuum pumps feature a unique tapered screw design, optimizing performance in harsh chemical environments common in refineries[4]. The company's innovative heat management system in these pumps allows for efficient handling of condensable hydrocarbons, reducing the risk of process contamination[5]. Edwards' vacuum systems also incorporate advanced control algorithms that adjust pump speed based on process demands, resulting in energy savings of up to 50% compared to traditional fixed-speed pumps in hydrocarbon applications[6].
Strengths: Robust design for harsh chemical environments; energy-efficient operation; advanced process control integration. Weaknesses: May have higher upfront costs; potential complexity in maintenance for advanced features.
Core Vacuum Innovations
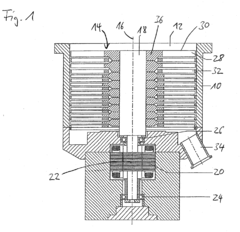
Vacuum pump
PatentActiveEP2740943A3
Innovation
- Incorporating nanoparticles, such as carbon nanotubes, into metal components like rotor disks to enhance mechanical and thermal resistance, maintaining metallic properties while increasing strength and heat resistance, allowing for reliable operation with high gas loads and flow rates.
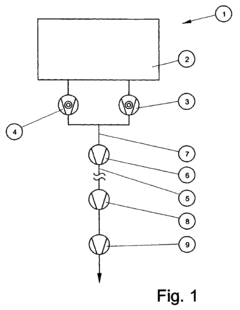
Vacuum pump system
PatentInactiveEP1441128A3
Innovation
- Incorporating an intermediate pump between the high-vacuum pump discharge and the fore-vacuum system, which can be a molecular or turbomolecular pump, connected directly to minimize conductance losses and enhance compression, allowing for series or parallel configurations to increase pumping speed and throughput.
Energy Efficiency Impact
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency within advanced hydrocarbon processing systems. By creating and maintaining low-pressure environments, these pumps significantly reduce the energy requirements for various processes, leading to substantial cost savings and environmental benefits.
One of the primary ways vacuum pumps contribute to energy efficiency is through lowering the boiling points of hydrocarbons. This reduction in boiling temperature allows for separation and distillation processes to occur at lower temperatures, thereby decreasing the overall energy input needed. For instance, in vacuum distillation units, the energy savings can be as high as 30-40% compared to atmospheric distillation processes.
Furthermore, vacuum pumps enable more efficient heat transfer in processing equipment. The lower pressure environment reduces the thermal resistance between fluids and heat exchange surfaces, resulting in improved heat transfer coefficients. This enhancement allows for smaller heat exchangers and reduced pumping power, both of which contribute to energy savings.
In catalytic cracking units, vacuum pumps help maintain optimal reaction conditions while minimizing energy consumption. By precisely controlling the pressure, these pumps ensure that reactions occur at the most favorable thermodynamic states, maximizing yield and selectivity while minimizing energy input.
Vacuum pumps also play a vital role in reducing energy losses associated with product recovery. In processes such as solvent recovery or light ends separation, vacuum systems allow for more complete extraction of valuable components at lower temperatures, reducing the energy required for subsequent processing steps.
The implementation of advanced vacuum pump technologies, such as dry screw pumps or liquid ring pumps with variable frequency drives, further enhances energy efficiency. These modern systems offer improved performance characteristics and can be precisely controlled to match process demands, minimizing unnecessary energy consumption during periods of reduced load.
Moreover, vacuum pumps contribute to energy efficiency by enabling the use of lower-grade heat sources in certain processes. This capability allows for better integration of waste heat recovery systems and the utilization of low-temperature heat sources that would otherwise be discarded, thereby improving overall plant energy efficiency.
One of the primary ways vacuum pumps contribute to energy efficiency is through lowering the boiling points of hydrocarbons. This reduction in boiling temperature allows for separation and distillation processes to occur at lower temperatures, thereby decreasing the overall energy input needed. For instance, in vacuum distillation units, the energy savings can be as high as 30-40% compared to atmospheric distillation processes.
Furthermore, vacuum pumps enable more efficient heat transfer in processing equipment. The lower pressure environment reduces the thermal resistance between fluids and heat exchange surfaces, resulting in improved heat transfer coefficients. This enhancement allows for smaller heat exchangers and reduced pumping power, both of which contribute to energy savings.
In catalytic cracking units, vacuum pumps help maintain optimal reaction conditions while minimizing energy consumption. By precisely controlling the pressure, these pumps ensure that reactions occur at the most favorable thermodynamic states, maximizing yield and selectivity while minimizing energy input.
Vacuum pumps also play a vital role in reducing energy losses associated with product recovery. In processes such as solvent recovery or light ends separation, vacuum systems allow for more complete extraction of valuable components at lower temperatures, reducing the energy required for subsequent processing steps.
The implementation of advanced vacuum pump technologies, such as dry screw pumps or liquid ring pumps with variable frequency drives, further enhances energy efficiency. These modern systems offer improved performance characteristics and can be precisely controlled to match process demands, minimizing unnecessary energy consumption during periods of reduced load.
Moreover, vacuum pumps contribute to energy efficiency by enabling the use of lower-grade heat sources in certain processes. This capability allows for better integration of waste heat recovery systems and the utilization of low-temperature heat sources that would otherwise be discarded, thereby improving overall plant energy efficiency.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of advanced hydrocarbon processing, particularly in the context of vacuum pump applications. These regulations are designed to mitigate the environmental impact of industrial processes and promote sustainable practices within the oil and gas sector.
One of the primary focuses of environmental regulations in this field is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Vacuum pumps, being integral to many hydrocarbon processing operations, are subject to stringent emission control standards. Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) have established limits on the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful gases during processing activities.
To comply with these regulations, industries are increasingly adopting advanced vacuum pump technologies that offer improved sealing mechanisms and enhanced efficiency. These innovations not only reduce the risk of fugitive emissions but also contribute to overall energy conservation, aligning with broader environmental goals.
Water conservation and wastewater management are other key areas addressed by environmental regulations in hydrocarbon processing. Vacuum pumps are often utilized in processes that involve the separation of water from hydrocarbons, and regulations mandate the proper treatment and disposal of wastewater generated during these operations. This has led to the development of more efficient vacuum pump systems that minimize water consumption and facilitate better wastewater handling.
The concept of Best Available Techniques (BAT) has been incorporated into many environmental regulations, encouraging industries to adopt the most effective and advanced practices to prevent or minimize environmental impact. For vacuum pump applications in hydrocarbon processing, this translates to the implementation of state-of-the-art technologies that offer superior performance while meeting or exceeding regulatory requirements.
Noise pollution is another aspect regulated in industrial settings, including those involving vacuum pumps. Environmental regulations often specify maximum noise levels for industrial equipment, prompting manufacturers to design quieter vacuum pump systems. This not only ensures compliance but also improves working conditions for personnel in processing facilities.
As global environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. This trend is driving innovation in vacuum pump technology, pushing manufacturers to develop more environmentally friendly solutions. The focus is shifting towards pumps that are not only more efficient and less polluting but also made from sustainable materials and designed for easier recycling at the end of their lifecycle.
One of the primary focuses of environmental regulations in this field is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Vacuum pumps, being integral to many hydrocarbon processing operations, are subject to stringent emission control standards. Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) have established limits on the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful gases during processing activities.
To comply with these regulations, industries are increasingly adopting advanced vacuum pump technologies that offer improved sealing mechanisms and enhanced efficiency. These innovations not only reduce the risk of fugitive emissions but also contribute to overall energy conservation, aligning with broader environmental goals.
Water conservation and wastewater management are other key areas addressed by environmental regulations in hydrocarbon processing. Vacuum pumps are often utilized in processes that involve the separation of water from hydrocarbons, and regulations mandate the proper treatment and disposal of wastewater generated during these operations. This has led to the development of more efficient vacuum pump systems that minimize water consumption and facilitate better wastewater handling.
The concept of Best Available Techniques (BAT) has been incorporated into many environmental regulations, encouraging industries to adopt the most effective and advanced practices to prevent or minimize environmental impact. For vacuum pump applications in hydrocarbon processing, this translates to the implementation of state-of-the-art technologies that offer superior performance while meeting or exceeding regulatory requirements.
Noise pollution is another aspect regulated in industrial settings, including those involving vacuum pumps. Environmental regulations often specify maximum noise levels for industrial equipment, prompting manufacturers to design quieter vacuum pump systems. This not only ensures compliance but also improves working conditions for personnel in processing facilities.
As global environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. This trend is driving innovation in vacuum pump technology, pushing manufacturers to develop more environmentally friendly solutions. The focus is shifting towards pumps that are not only more efficient and less polluting but also made from sustainable materials and designed for easier recycling at the end of their lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!