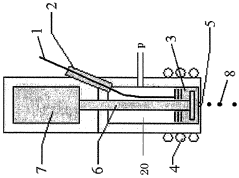
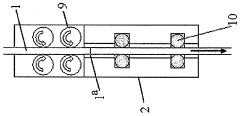
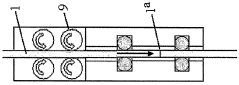
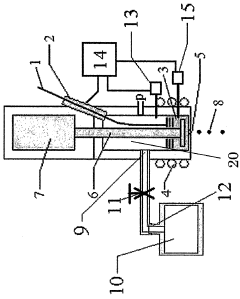
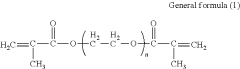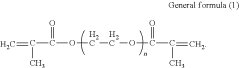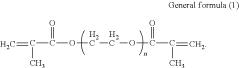Material Jetting QA Documentation: Lot Traceability, Certificates And Audit Readiness
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Material Jetting Technology Background and Objectives
Material Jetting technology has evolved significantly over the past two decades as a prominent additive manufacturing process. Initially developed in the late 1990s, this technology has progressed from basic prototype creation to advanced manufacturing capabilities for functional parts. Material Jetting operates on principles similar to traditional inkjet printing, where droplets of build material are selectively deposited layer by layer to create three-dimensional objects with high precision and surface finish quality.
The evolution of Material Jetting has been marked by several key milestones, including the introduction of multi-material capabilities, enhanced resolution parameters, and expanded material portfolios. From early systems limited to wax-like materials, the technology now accommodates photopolymers, ceramics, and even certain metal-infused resins, significantly broadening its application scope across industries including aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and consumer electronics.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving process stability, material property consistency, and production scalability. These developments have positioned Material Jetting as a viable solution for end-use part production rather than merely prototyping applications. The technology's inherent advantages in producing parts with smooth surfaces, fine details, and homogeneous mechanical properties have driven its adoption in precision-critical applications.
Quality assurance documentation represents a critical frontier in Material Jetting's maturation toward mainstream manufacturing adoption. As the technology transitions from research and development environments to regulated production settings, robust QA frameworks become essential. Lot traceability systems, material and process certificates, and audit-ready documentation structures are increasingly recognized as necessary components of the Material Jetting ecosystem.
The primary technical objectives in this domain include establishing standardized protocols for material batch validation, process parameter verification, and comprehensive part qualification. These objectives align with broader industry trends toward digital manufacturing integration, where complete digital threads connect design intent through production execution to quality verification. Developing systems that can track material properties from raw material to finished part represents a significant technical challenge that must be addressed.
Furthermore, the technology aims to achieve regulatory compliance across multiple industries with varying requirements. This necessitates flexible yet robust documentation frameworks that can adapt to different certification standards while maintaining internal consistency. The ultimate goal is to establish Material Jetting as a trusted manufacturing process with quality assurance mechanisms comparable to traditional manufacturing methods, thereby enabling its adoption in highly regulated industries such as medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive applications.
The evolution of Material Jetting has been marked by several key milestones, including the introduction of multi-material capabilities, enhanced resolution parameters, and expanded material portfolios. From early systems limited to wax-like materials, the technology now accommodates photopolymers, ceramics, and even certain metal-infused resins, significantly broadening its application scope across industries including aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and consumer electronics.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving process stability, material property consistency, and production scalability. These developments have positioned Material Jetting as a viable solution for end-use part production rather than merely prototyping applications. The technology's inherent advantages in producing parts with smooth surfaces, fine details, and homogeneous mechanical properties have driven its adoption in precision-critical applications.
Quality assurance documentation represents a critical frontier in Material Jetting's maturation toward mainstream manufacturing adoption. As the technology transitions from research and development environments to regulated production settings, robust QA frameworks become essential. Lot traceability systems, material and process certificates, and audit-ready documentation structures are increasingly recognized as necessary components of the Material Jetting ecosystem.
The primary technical objectives in this domain include establishing standardized protocols for material batch validation, process parameter verification, and comprehensive part qualification. These objectives align with broader industry trends toward digital manufacturing integration, where complete digital threads connect design intent through production execution to quality verification. Developing systems that can track material properties from raw material to finished part represents a significant technical challenge that must be addressed.
Furthermore, the technology aims to achieve regulatory compliance across multiple industries with varying requirements. This necessitates flexible yet robust documentation frameworks that can adapt to different certification standards while maintaining internal consistency. The ultimate goal is to establish Material Jetting as a trusted manufacturing process with quality assurance mechanisms comparable to traditional manufacturing methods, thereby enabling its adoption in highly regulated industries such as medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive applications.
Market Demand for Material Jetting QA Documentation
The market for Material Jetting QA documentation, particularly focusing on lot traceability, certificates, and audit readiness, has experienced significant growth in recent years. This expansion is primarily driven by increasing regulatory requirements across industries utilizing additive manufacturing technologies, especially in highly regulated sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing.
Healthcare and medical device manufacturers represent the largest market segment demanding robust QA documentation for material jetting processes. With the FDA and other global regulatory bodies implementing stricter requirements for medical device production, comprehensive lot traceability has become non-negotiable. The market value in this segment alone reached $2.3 billion in 2022, with projected annual growth rates of 18-20% through 2028.
Aerospace and defense industries form the second-largest market segment, where material jetting is increasingly used for producing complex components. These industries require extensive documentation to meet stringent safety standards and certification requirements. The documentation needs in this sector are particularly focused on material property verification and process consistency validation.
Automotive manufacturing represents an emerging but rapidly growing market for material jetting QA documentation. As vehicle manufacturers incorporate more 3D-printed components into production vehicles, the demand for standardized quality assurance protocols has intensified. This segment is expected to grow at 22% annually over the next five years.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows North America leading with approximately 42% of global market share, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). The remaining 6% is distributed across other regions. This distribution closely follows the adoption patterns of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key market drivers include increasing regulatory scrutiny, growing adoption of material jetting in critical applications, and the shift toward digital manufacturing ecosystems that require comprehensive data trails. The trend toward Industry 4.0 integration has further accelerated demand for sophisticated documentation systems that can interface with broader manufacturing execution systems.
Customer pain points in this market include the complexity of implementing compliant documentation systems, challenges in standardizing processes across global operations, and difficulties in maintaining real-time traceability throughout complex supply chains. These challenges represent significant opportunities for solution providers who can offer integrated, user-friendly documentation platforms.
Healthcare and medical device manufacturers represent the largest market segment demanding robust QA documentation for material jetting processes. With the FDA and other global regulatory bodies implementing stricter requirements for medical device production, comprehensive lot traceability has become non-negotiable. The market value in this segment alone reached $2.3 billion in 2022, with projected annual growth rates of 18-20% through 2028.
Aerospace and defense industries form the second-largest market segment, where material jetting is increasingly used for producing complex components. These industries require extensive documentation to meet stringent safety standards and certification requirements. The documentation needs in this sector are particularly focused on material property verification and process consistency validation.
Automotive manufacturing represents an emerging but rapidly growing market for material jetting QA documentation. As vehicle manufacturers incorporate more 3D-printed components into production vehicles, the demand for standardized quality assurance protocols has intensified. This segment is expected to grow at 22% annually over the next five years.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows North America leading with approximately 42% of global market share, followed by Europe (31%) and Asia-Pacific (21%). The remaining 6% is distributed across other regions. This distribution closely follows the adoption patterns of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key market drivers include increasing regulatory scrutiny, growing adoption of material jetting in critical applications, and the shift toward digital manufacturing ecosystems that require comprehensive data trails. The trend toward Industry 4.0 integration has further accelerated demand for sophisticated documentation systems that can interface with broader manufacturing execution systems.
Customer pain points in this market include the complexity of implementing compliant documentation systems, challenges in standardizing processes across global operations, and difficulties in maintaining real-time traceability throughout complex supply chains. These challenges represent significant opportunities for solution providers who can offer integrated, user-friendly documentation platforms.
Current State and Challenges in Material Jetting QA
Material Jetting technology has evolved significantly in the additive manufacturing landscape, yet its quality assurance frameworks remain fragmented across the industry. Current QA practices for Material Jetting vary widely between manufacturers, with no universally adopted standard for lot traceability or certification. Leading companies like Stratasys, HP, and 3D Systems have developed proprietary systems for tracking material batches, but these solutions lack interoperability, creating significant challenges for supply chain integration.
The absence of standardized documentation protocols presents a major obstacle for Material Jetting adoption in regulated industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing. Organizations in these sectors require comprehensive audit trails that can demonstrate material provenance from raw material to finished part - a capability that remains inconsistent across current Material Jetting implementations.
Technical limitations further complicate QA processes in Material Jetting operations. The multi-material capabilities that make this technology attractive also create complex material interaction scenarios that are difficult to document and trace. Current systems struggle to adequately track and document cross-contamination risks, material aging effects, and process parameter variations that may impact final part quality.
Regulatory compliance represents another significant challenge. While traditional manufacturing methods have well-established quality frameworks (ISO 9001, AS9100, etc.), Material Jetting lacks specific regulatory guidance. This regulatory gap creates uncertainty for manufacturers implementing lot traceability systems, as they cannot be certain their documentation will satisfy future audit requirements or certification standards.
Data management infrastructure supporting Material Jetting QA remains underdeveloped. Most traceability systems rely on manual documentation or disconnected digital tools rather than integrated platforms capable of automatically capturing material data throughout the production process. This fragmentation increases the risk of documentation errors and creates inefficiencies during quality audits.
The international landscape further complicates standardization efforts. Different regions have developed divergent approaches to Material Jetting QA documentation, with European manufacturers generally implementing more rigorous traceability systems than their North American or Asian counterparts. These geographic disparities create additional challenges for global supply chains and international certification efforts.
Recent industry initiatives have begun addressing these challenges through collaborative working groups focused on developing common standards for Material Jetting QA documentation. Organizations like ASTM International and the Additive Manufacturing Users Group have established committees specifically targeting lot traceability and certification standardization, though consensus solutions remain in early development stages.
The absence of standardized documentation protocols presents a major obstacle for Material Jetting adoption in regulated industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing. Organizations in these sectors require comprehensive audit trails that can demonstrate material provenance from raw material to finished part - a capability that remains inconsistent across current Material Jetting implementations.
Technical limitations further complicate QA processes in Material Jetting operations. The multi-material capabilities that make this technology attractive also create complex material interaction scenarios that are difficult to document and trace. Current systems struggle to adequately track and document cross-contamination risks, material aging effects, and process parameter variations that may impact final part quality.
Regulatory compliance represents another significant challenge. While traditional manufacturing methods have well-established quality frameworks (ISO 9001, AS9100, etc.), Material Jetting lacks specific regulatory guidance. This regulatory gap creates uncertainty for manufacturers implementing lot traceability systems, as they cannot be certain their documentation will satisfy future audit requirements or certification standards.
Data management infrastructure supporting Material Jetting QA remains underdeveloped. Most traceability systems rely on manual documentation or disconnected digital tools rather than integrated platforms capable of automatically capturing material data throughout the production process. This fragmentation increases the risk of documentation errors and creates inefficiencies during quality audits.
The international landscape further complicates standardization efforts. Different regions have developed divergent approaches to Material Jetting QA documentation, with European manufacturers generally implementing more rigorous traceability systems than their North American or Asian counterparts. These geographic disparities create additional challenges for global supply chains and international certification efforts.
Recent industry initiatives have begun addressing these challenges through collaborative working groups focused on developing common standards for Material Jetting QA documentation. Organizations like ASTM International and the Additive Manufacturing Users Group have established committees specifically targeting lot traceability and certification standardization, though consensus solutions remain in early development stages.
Existing Lot Traceability and Certification Methods
01 Quality Assurance Systems for Material Jetting
Quality assurance systems specifically designed for material jetting processes that ensure consistent product quality through automated monitoring and documentation. These systems integrate with manufacturing equipment to collect real-time data on process parameters, material properties, and production conditions. The QA systems generate comprehensive documentation that supports traceability requirements and facilitates audit readiness by maintaining digital records of all production activities.- Quality Assurance Systems for Material Jetting: Quality assurance systems specifically designed for material jetting processes that ensure consistent product quality through automated monitoring and documentation. These systems integrate with manufacturing equipment to collect real-time data on process parameters, material properties, and production conditions. The QA systems generate comprehensive documentation that supports traceability requirements and facilitates audit readiness by maintaining digital records of all production activities.
- Lot Traceability and Material Tracking Solutions: Advanced tracking solutions that enable complete lot traceability throughout the material jetting manufacturing process. These systems assign unique identifiers to material batches and track them from receipt through processing and final product distribution. The solutions incorporate barcode or RFID technology to automatically capture material movement data and maintain chain of custody documentation, allowing manufacturers to quickly trace any quality issues back to specific material lots.
- Digital Certificate Management for Compliance: Digital platforms for managing certificates and compliance documentation related to material jetting processes. These systems automate the generation, storage, and retrieval of certificates of analysis, conformance, and compliance. They ensure that all necessary documentation is properly maintained and readily accessible during audits or customer inquiries. The platforms often include validation features to verify the authenticity of certificates and maintain secure audit trails of document access and modifications.
- Audit Readiness and Compliance Monitoring: Comprehensive systems designed to maintain continuous audit readiness for material jetting operations. These solutions provide real-time monitoring of compliance status against industry standards and regulatory requirements. They include automated gap analysis tools that identify documentation deficiencies before audits occur. The systems also feature customizable dashboards that display compliance metrics and alert management to potential issues requiring attention, ensuring organizations can quickly respond to audit requests with complete and accurate documentation.
- Blockchain-Based Documentation and Traceability: Innovative blockchain technology applications for securing and validating material jetting documentation and traceability records. These systems create immutable records of all quality data, material movements, and production parameters. The blockchain architecture ensures that documentation cannot be altered retroactively, providing auditors with verifiable proof of data integrity. These solutions enable secure sharing of quality documentation across supply chain partners while maintaining controlled access and protecting proprietary information.
02 Lot Traceability in Additive Manufacturing
Systems and methods for implementing lot traceability in material jetting and other additive manufacturing processes. These solutions enable tracking of materials from receipt through production and delivery, creating a complete chain of custody. The traceability systems assign unique identifiers to material batches and maintain records of their usage in specific production runs, allowing manufacturers to quickly identify affected products in case of quality issues and demonstrate compliance during audits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Digital Certificate Management for Manufacturing
Digital platforms for managing certificates and compliance documentation in manufacturing environments, including material jetting operations. These systems automate the creation, storage, and retrieval of certificates of analysis, conformance, and compliance. The platforms implement secure authentication mechanisms to ensure document integrity and provide controlled access to authorized personnel, supporting both internal quality processes and external audit requirements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Audit Readiness and Compliance Management
Comprehensive solutions for maintaining continuous audit readiness in manufacturing operations that use material jetting technologies. These systems implement automated compliance monitoring against industry standards and regulatory requirements. They include features for scheduling internal audits, tracking corrective actions, and maintaining evidence of compliance. The solutions also provide dashboards and reporting tools that give management visibility into compliance status and potential risk areas.Expand Specific Solutions05 Blockchain-Based Documentation Systems
Innovative documentation systems that leverage blockchain technology to create immutable records for material jetting manufacturing processes. These systems provide tamper-proof documentation of material sourcing, production parameters, quality testing, and product delivery. By distributing the verification process across multiple nodes, blockchain ensures that documentation cannot be altered retroactively, creating a trusted source of truth for quality assurance, lot traceability, and audit purposes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Material Jetting QA Solutions
Material Jetting technology is currently in a growth phase within the additive manufacturing industry, with an expanding market driven by increasing applications in prototyping, medical, and industrial sectors. The technology maturity varies across applications, with companies demonstrating different levels of advancement. Leading players like FUJIFILM Dimatix and Ricoh have established strong positions in industrial printhead technology, while Seiko Epson and Canon leverage their expertise from traditional printing to advance material jetting capabilities. Emerging specialists such as Zhuhai Sailner Technology are developing proprietary technologies like WJP white ink filling for multi-material printing. EOS GmbH contributes significant innovations in industrial applications, while companies like Thales and Oracle are focusing on documentation and traceability systems essential for quality assurance and regulatory compliance in advanced manufacturing environments.
Seiko Epson Corp.
Technical Solution: Seiko Epson has developed a comprehensive Material Jetting QA documentation system that integrates lot traceability throughout their production workflow. Their solution employs a centralized database that tracks materials from receipt through processing and final product delivery. Each material batch receives a unique identifier linked to digital certificates of analysis and compliance. Their PrecisionCore technology enables micro-tracking of material properties during jetting processes, with real-time monitoring systems that capture process parameters for each production lot[1]. Epson's system includes automated documentation generation that compiles material property data, process parameters, and quality test results into standardized certificates that meet ISO 9001 and industry-specific requirements. Their audit-ready documentation platform maintains records for the required retention period with secure, tamper-evident storage and retrieval capabilities[3].
Strengths: Seamless integration with existing manufacturing systems, real-time monitoring capabilities, and automated certificate generation reduce manual documentation efforts. Weaknesses: The system requires significant initial investment in infrastructure and training, and may be overly complex for smaller manufacturing operations.
Canon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Canon has implemented a Material Jetting QA documentation framework centered on their proprietary FINE (Full-photolithography Inkjet Nozzle Engineering) technology. Their system incorporates comprehensive lot traceability through a blockchain-based ledger that records material sourcing, processing parameters, and quality control data. Each production batch is assigned a unique digital signature that links to material certificates and processing history. Canon's approach includes automated inspection systems that capture high-resolution images of jetted materials for dimensional and quality verification, with results automatically appended to lot documentation[2]. Their QA system features a hierarchical documentation structure that maintains relationships between raw materials, processing parameters, and finished products, enabling bidirectional traceability. For audit readiness, Canon employs a digital documentation vault with role-based access controls and automated compliance checking against industry standards including ISO 13485 for medical applications and aerospace requirements[4].
Strengths: Advanced integration of visual inspection data with material certificates provides comprehensive quality documentation. Their blockchain approach ensures immutable record-keeping. Weaknesses: The system's complexity may create challenges for integration with third-party manufacturing systems, and the proprietary nature of some components may limit flexibility.
Core Technical Innovations in Material Jetting Documentation
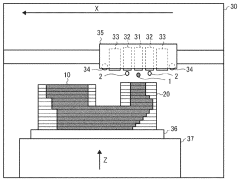
Material jet system
PatentWO2007075084A1
Innovation
- A material jet system that supplies solid metal materials in the form of wires or tapes, using a container with heating means and jetting mechanisms to form droplets, while minimizing molten material quantity through a sealed environment and pressure control with a heat-insulating fluid, allowing for continuous operation and reduced heat load on the printer head.
Inkjet active-energy-ray-curable composition, three-dimensional object producing method, and three-dimensional object producing apparatus
PatentActiveUS11905425B2
Innovation
- An inkjet active-energy-ray-curable composition comprising bisphenol-type methacrylate, a low-viscosity monomer, and an inorganic filler, with a balanced monomer component ratio and polymerization initiator, ensuring low viscosity and effective curing, even with high inorganic filler concentrations.
Regulatory Compliance Framework for Material Jetting
The regulatory landscape for Material Jetting technology operates within a complex framework of standards and compliance requirements across multiple industries. Material Jetting processes must adhere to industry-specific regulations such as FDA requirements for medical applications, aerospace standards like AS9100, and automotive quality management systems such as IATF 16949. These regulatory frameworks establish the foundation for quality assurance documentation practices, particularly regarding lot traceability, certification, and audit preparedness.
For Material Jetting operations, regulatory compliance begins with material qualification and validation protocols. Each jurisdiction may impose different requirements for material safety data sheets (MSDS), chemical composition disclosures, and environmental impact assessments. The European Union's REACH regulations and RoHS directives, for instance, significantly impact material selection and documentation requirements for manufacturers utilizing Material Jetting technologies within EU markets.
Documentation systems for Material Jetting must incorporate comprehensive lot traceability mechanisms that satisfy regulatory expectations. This includes unique identification systems for raw materials, process parameters, and finished products. The FDA's 21 CFR Part 820 for medical devices and ISO 13485 standards outline specific requirements for maintaining traceability throughout the production lifecycle, necessitating robust documentation practices that connect raw material batches to specific production runs and end products.
Certificate management represents another critical component of the regulatory compliance framework. Material Jetting operations must maintain certificates of analysis (CoA), certificates of conformance (CoC), and where applicable, certificates of compliance with specific industry standards. These documents serve as formal attestations that materials and processes meet predetermined specifications and regulatory requirements, forming essential elements of the quality assurance documentation system.
Audit readiness within the regulatory framework requires establishing documented procedures for internal quality audits, management reviews, and corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). ISO 9001:2015 provides general guidelines for quality management systems that support audit preparedness, while industry-specific standards may impose additional requirements. Material Jetting operations must maintain records of process validation, equipment calibration, and operator training to demonstrate compliance during regulatory inspections.
Digital compliance tools are increasingly becoming integral to regulatory frameworks for advanced manufacturing technologies like Material Jetting. Electronic quality management systems (eQMS) that incorporate electronic signatures compliant with 21 CFR Part 11 or equivalent standards enable more efficient documentation management while satisfying regulatory requirements for data integrity, security, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle.
For Material Jetting operations, regulatory compliance begins with material qualification and validation protocols. Each jurisdiction may impose different requirements for material safety data sheets (MSDS), chemical composition disclosures, and environmental impact assessments. The European Union's REACH regulations and RoHS directives, for instance, significantly impact material selection and documentation requirements for manufacturers utilizing Material Jetting technologies within EU markets.
Documentation systems for Material Jetting must incorporate comprehensive lot traceability mechanisms that satisfy regulatory expectations. This includes unique identification systems for raw materials, process parameters, and finished products. The FDA's 21 CFR Part 820 for medical devices and ISO 13485 standards outline specific requirements for maintaining traceability throughout the production lifecycle, necessitating robust documentation practices that connect raw material batches to specific production runs and end products.
Certificate management represents another critical component of the regulatory compliance framework. Material Jetting operations must maintain certificates of analysis (CoA), certificates of conformance (CoC), and where applicable, certificates of compliance with specific industry standards. These documents serve as formal attestations that materials and processes meet predetermined specifications and regulatory requirements, forming essential elements of the quality assurance documentation system.
Audit readiness within the regulatory framework requires establishing documented procedures for internal quality audits, management reviews, and corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). ISO 9001:2015 provides general guidelines for quality management systems that support audit preparedness, while industry-specific standards may impose additional requirements. Material Jetting operations must maintain records of process validation, equipment calibration, and operator training to demonstrate compliance during regulatory inspections.
Digital compliance tools are increasingly becoming integral to regulatory frameworks for advanced manufacturing technologies like Material Jetting. Electronic quality management systems (eQMS) that incorporate electronic signatures compliant with 21 CFR Part 11 or equivalent standards enable more efficient documentation management while satisfying regulatory requirements for data integrity, security, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle.
Data Security in Material Jetting Documentation Systems
Data security in Material Jetting documentation systems represents a critical component of modern additive manufacturing quality assurance frameworks. As material jetting technologies advance in precision manufacturing sectors, the documentation systems supporting lot traceability and certification must implement robust security protocols to protect sensitive production data while maintaining regulatory compliance.
The security architecture for these documentation systems typically employs a multi-layered approach, beginning with comprehensive access control mechanisms. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can view, modify, or generate quality documentation, with permissions granularly defined according to job responsibilities and security clearance levels. This prevents unauthorized alterations to critical lot traceability records that could compromise product integrity or audit readiness.
Encryption technologies form the backbone of data protection within these systems, with AES-256 encryption becoming the industry standard for both data at rest and in transit. Material formulation data, process parameters, and quality test results—all essential components of lot traceability—require end-to-end encryption to prevent industrial espionage and protect intellectual property. Leading manufacturers have implemented hardware security modules (HSMs) to manage encryption keys securely, adding an additional layer of protection.
Audit logging capabilities have evolved significantly, with immutable logging systems that record all interactions with documentation. These systems capture user identity, timestamp, action performed, and affected records, creating an unalterable chain of evidence that supports both internal quality investigations and external regulatory audits. Some advanced implementations utilize blockchain technology to further enhance the immutability of these audit trails.
Secure integration with external systems presents ongoing challenges, particularly as material jetting operations increasingly connect with broader enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). API security protocols, including OAuth 2.0 and API keys with limited scopes, help maintain security boundaries while enabling necessary data flows between systems. This integration security is essential for maintaining continuous lot traceability across the production ecosystem.
Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific frameworks like HIPAA (for medical applications) or ITAR (for defense applications) adds complexity to security implementations. Documentation systems must incorporate privacy-by-design principles, including data minimization and purpose limitation, while still maintaining complete traceability records required for quality assurance and regulatory purposes.
The security architecture for these documentation systems typically employs a multi-layered approach, beginning with comprehensive access control mechanisms. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can view, modify, or generate quality documentation, with permissions granularly defined according to job responsibilities and security clearance levels. This prevents unauthorized alterations to critical lot traceability records that could compromise product integrity or audit readiness.
Encryption technologies form the backbone of data protection within these systems, with AES-256 encryption becoming the industry standard for both data at rest and in transit. Material formulation data, process parameters, and quality test results—all essential components of lot traceability—require end-to-end encryption to prevent industrial espionage and protect intellectual property. Leading manufacturers have implemented hardware security modules (HSMs) to manage encryption keys securely, adding an additional layer of protection.
Audit logging capabilities have evolved significantly, with immutable logging systems that record all interactions with documentation. These systems capture user identity, timestamp, action performed, and affected records, creating an unalterable chain of evidence that supports both internal quality investigations and external regulatory audits. Some advanced implementations utilize blockchain technology to further enhance the immutability of these audit trails.
Secure integration with external systems presents ongoing challenges, particularly as material jetting operations increasingly connect with broader enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). API security protocols, including OAuth 2.0 and API keys with limited scopes, help maintain security boundaries while enabling necessary data flows between systems. This integration security is essential for maintaining continuous lot traceability across the production ecosystem.
Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific frameworks like HIPAA (for medical applications) or ITAR (for defense applications) adds complexity to security implementations. Documentation systems must incorporate privacy-by-design principles, including data minimization and purpose limitation, while still maintaining complete traceability records required for quality assurance and regulatory purposes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!